Submitted:
28 April 2025
Posted:
30 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
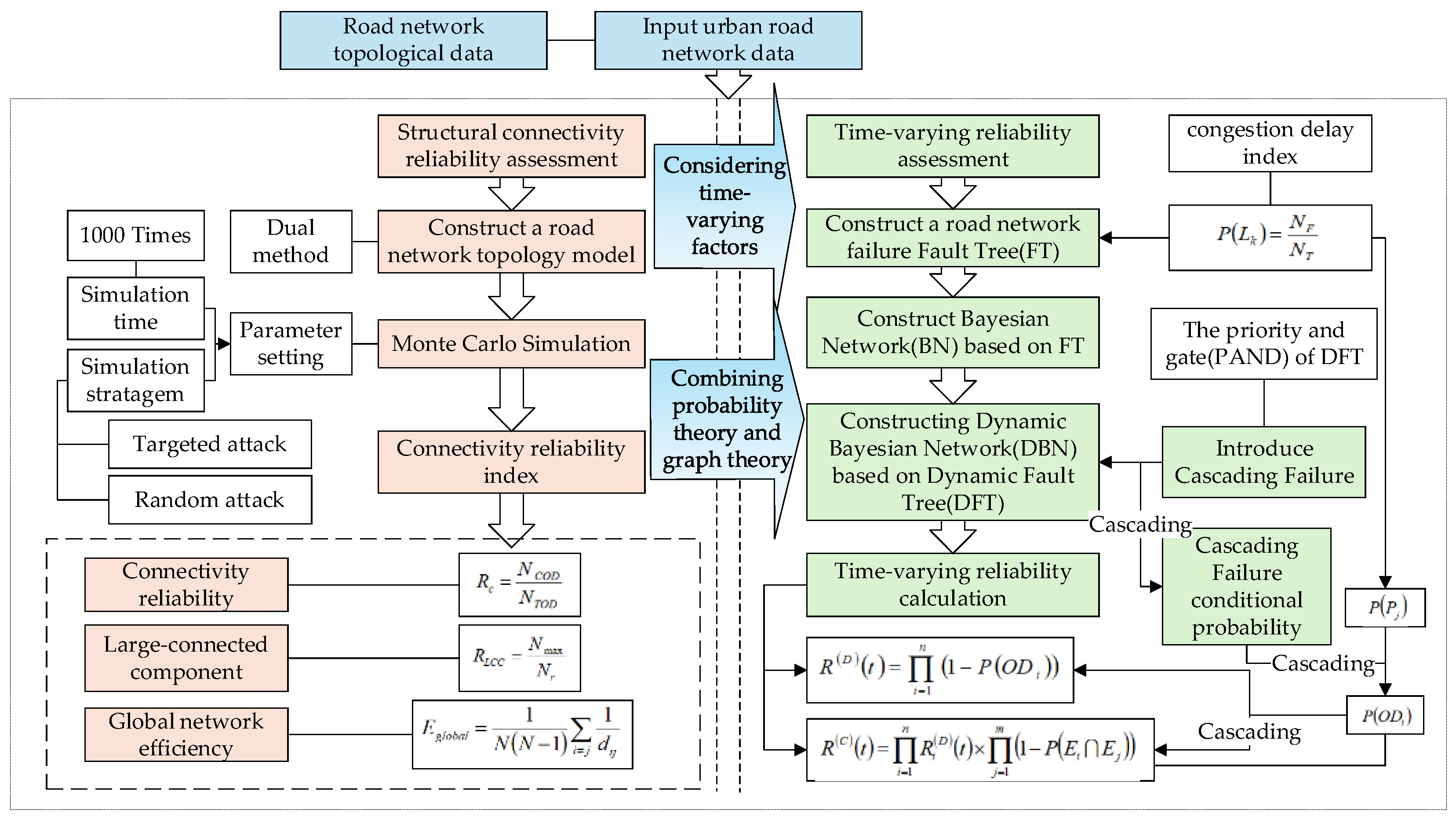
2. Methods and Models
2.1. Structural Connectivity Reliability Modeling and Assessment
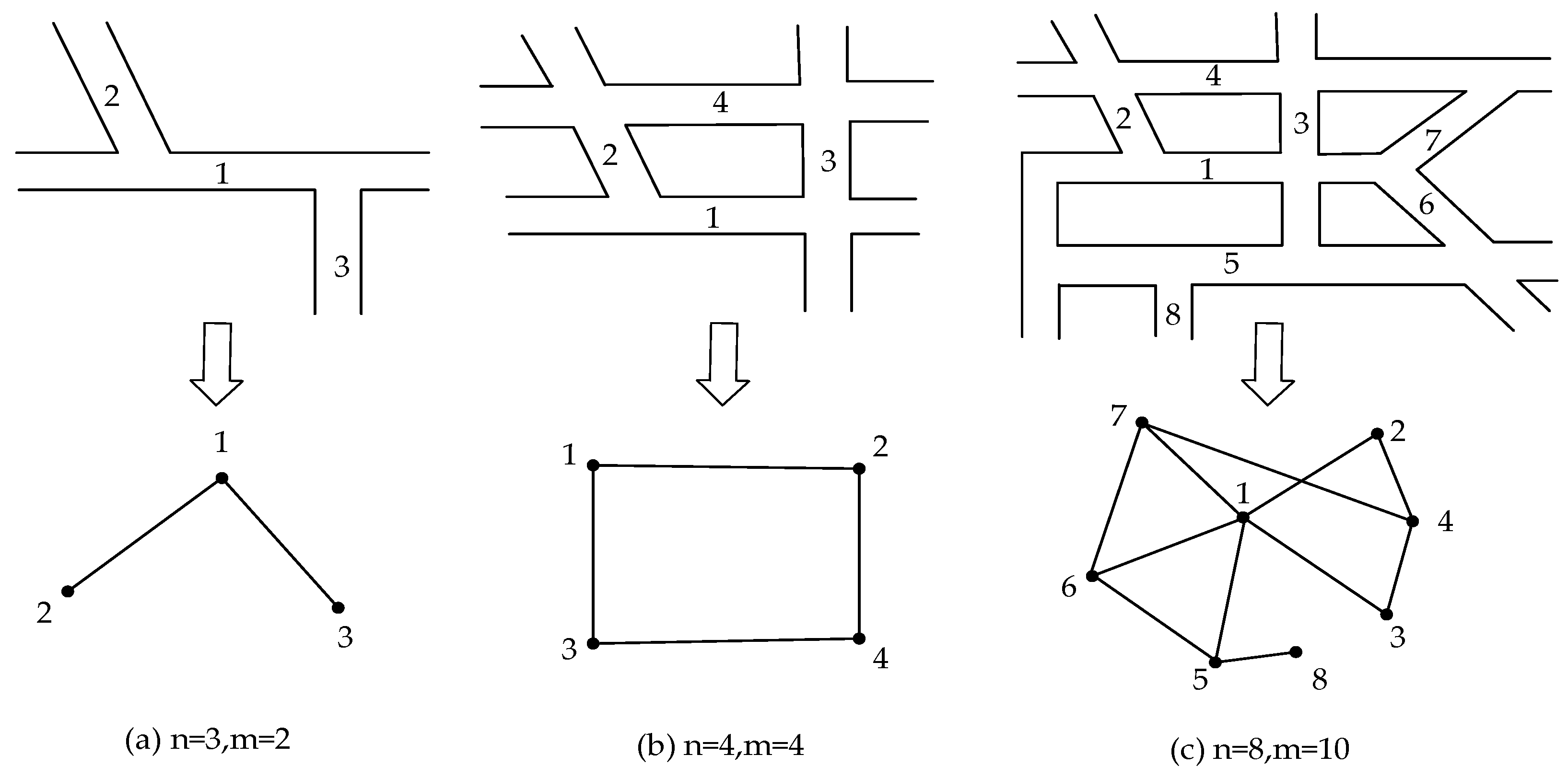
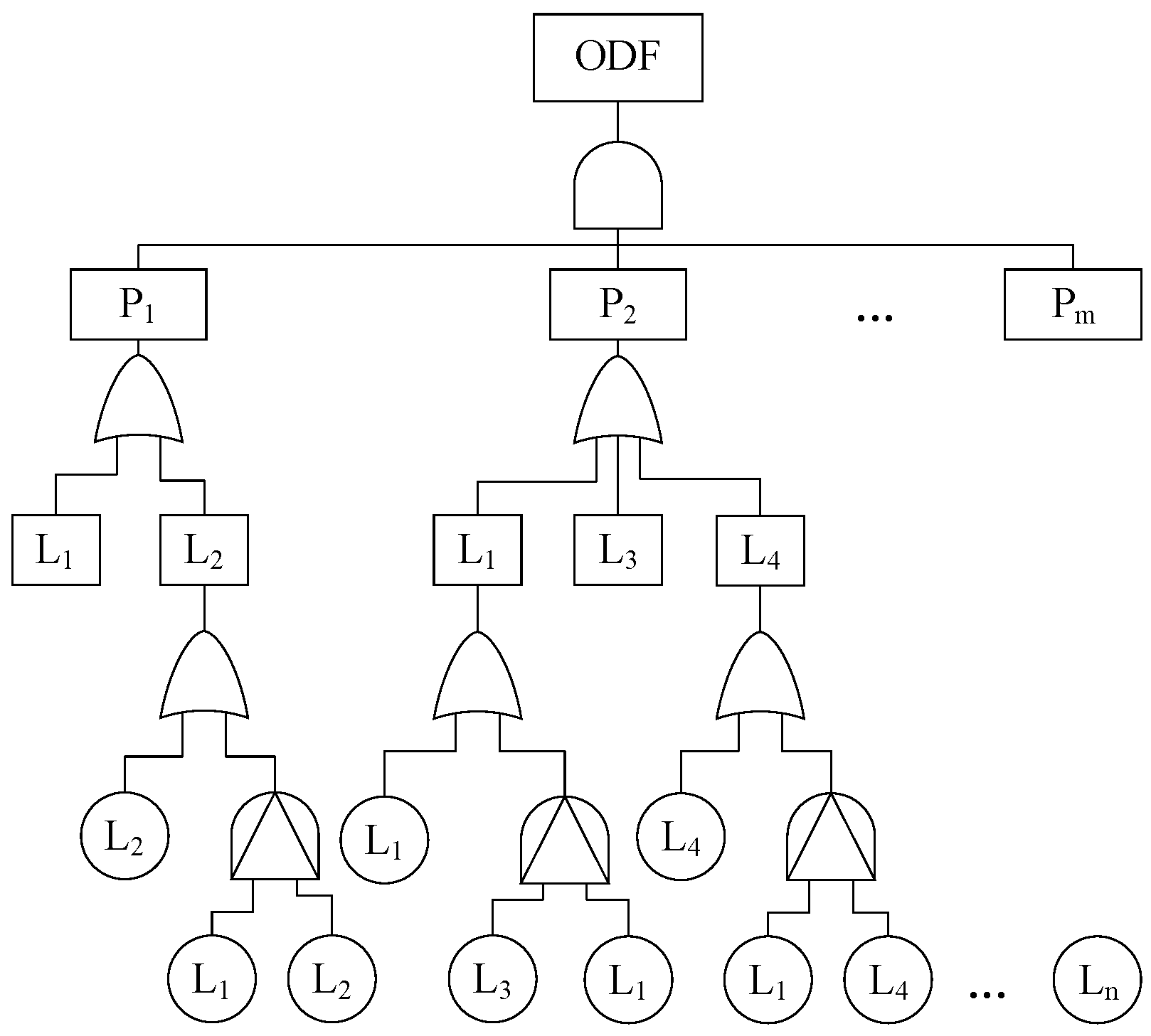
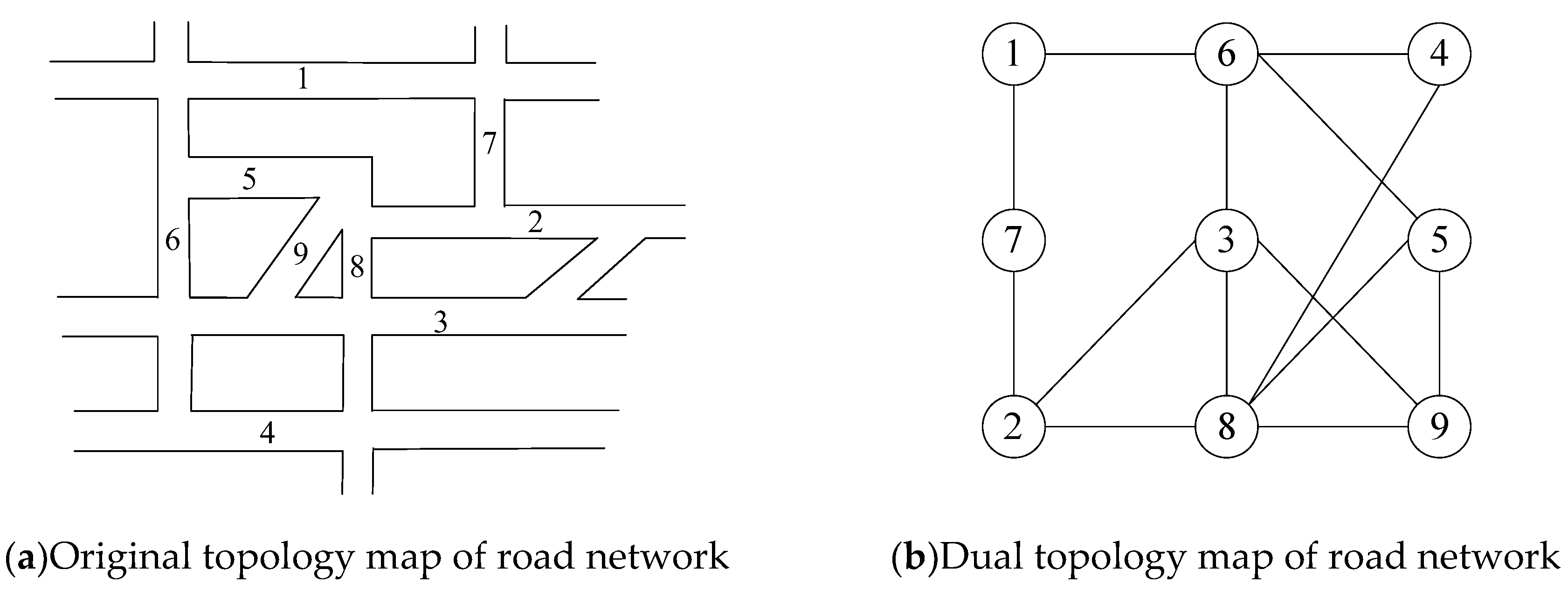
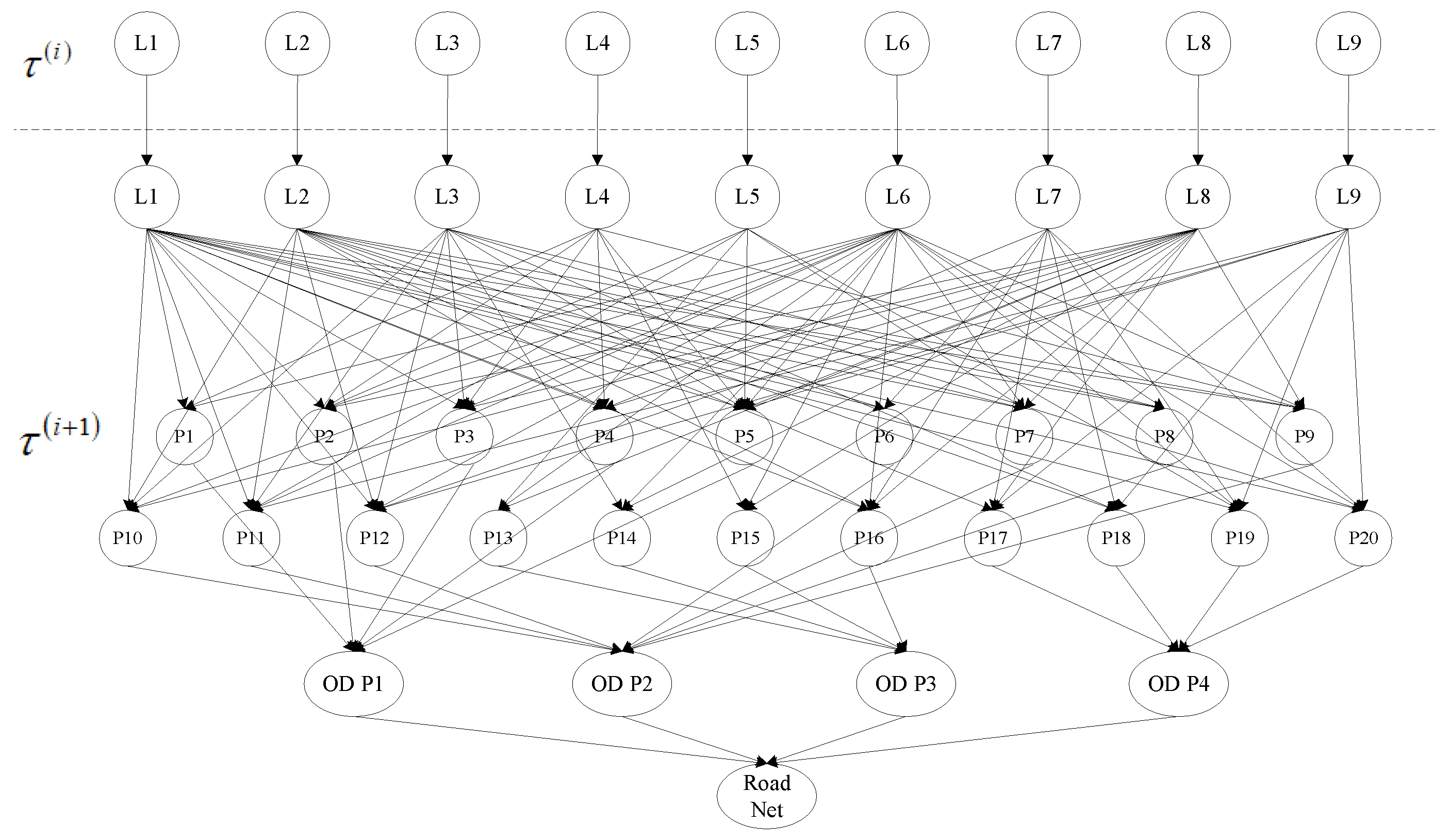
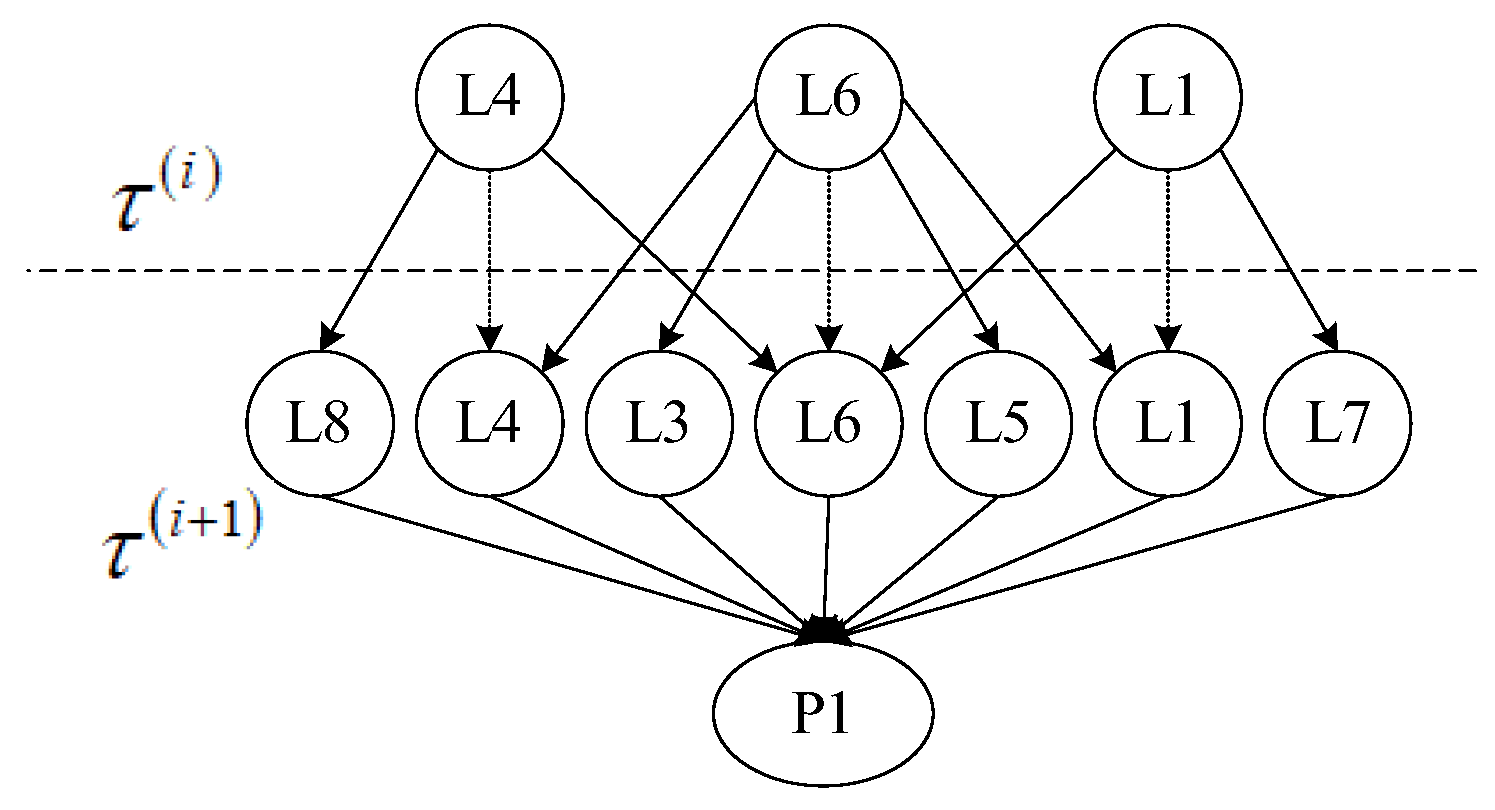
2.1.1. Road Network Connectivity Reliability Modeling
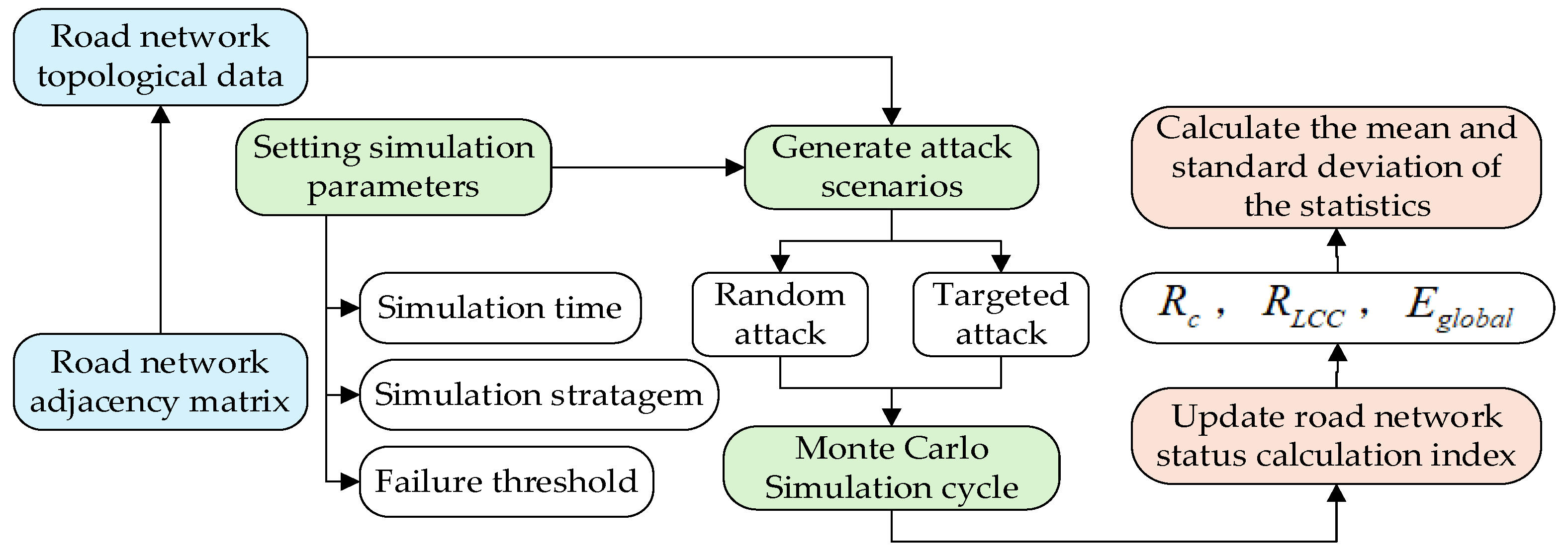
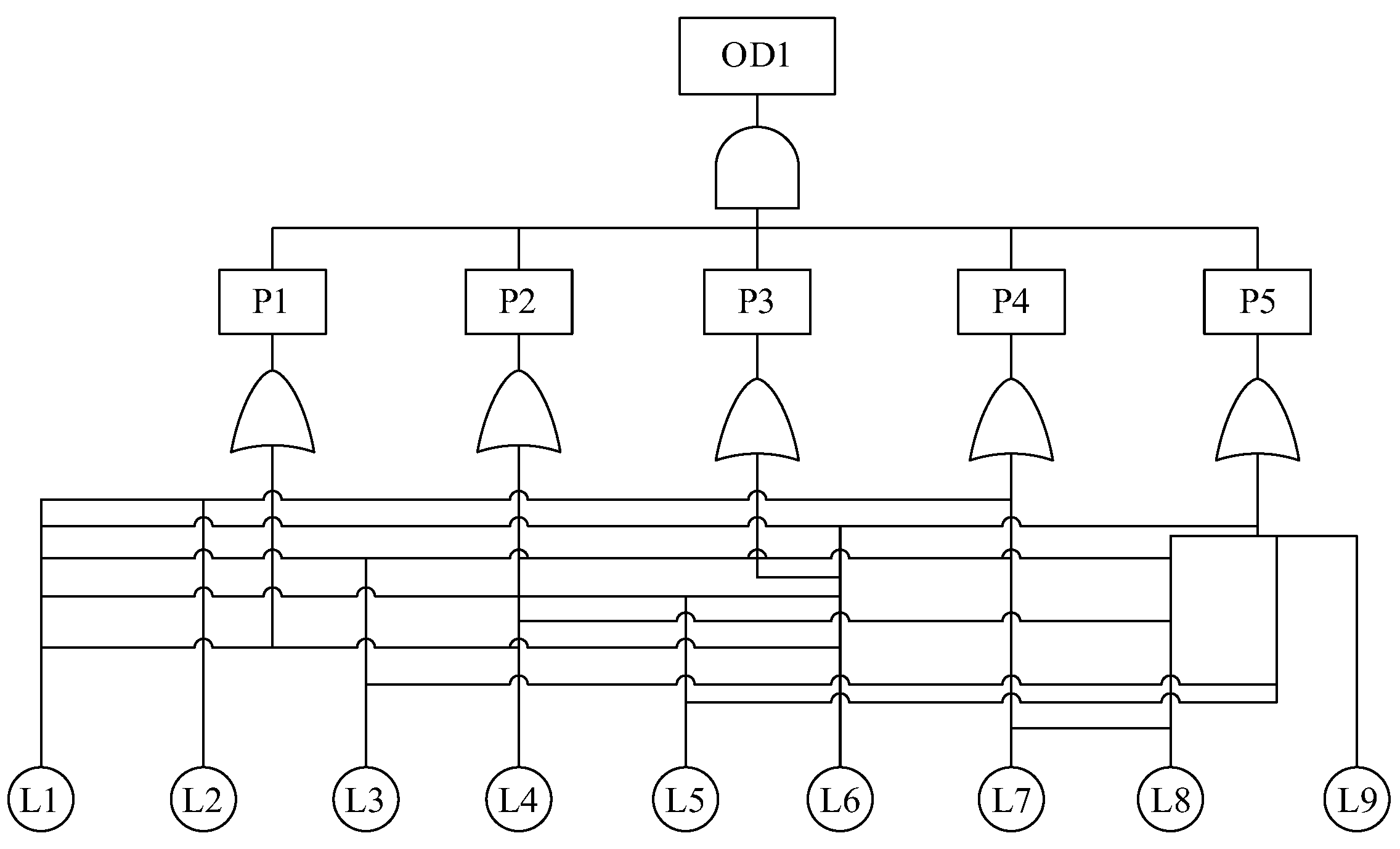
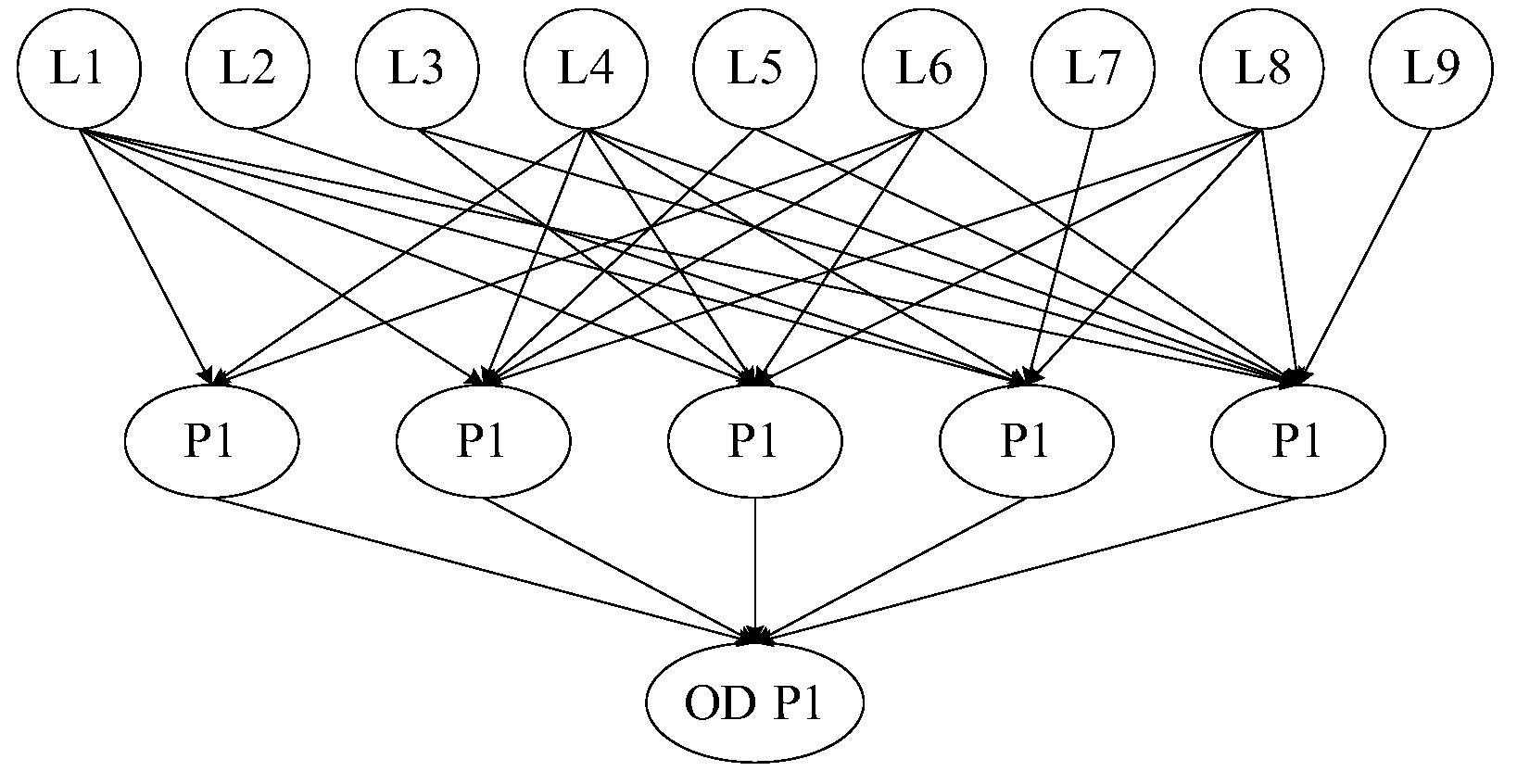
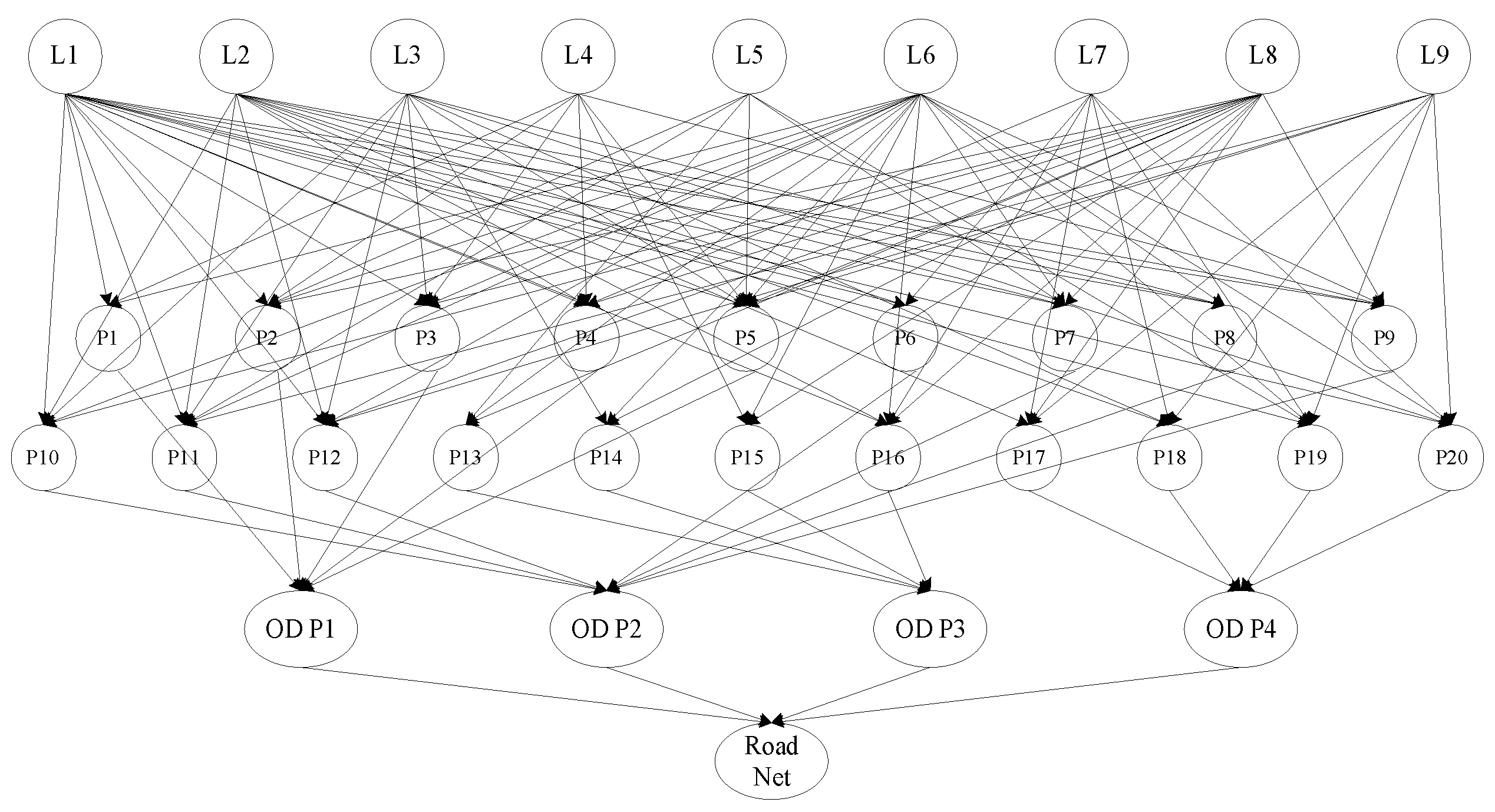
2.1.2. Road Network Reliability Assessment Based on MCS
2.2. Time-Varying Connectivity Reliability Modeling and Assessment
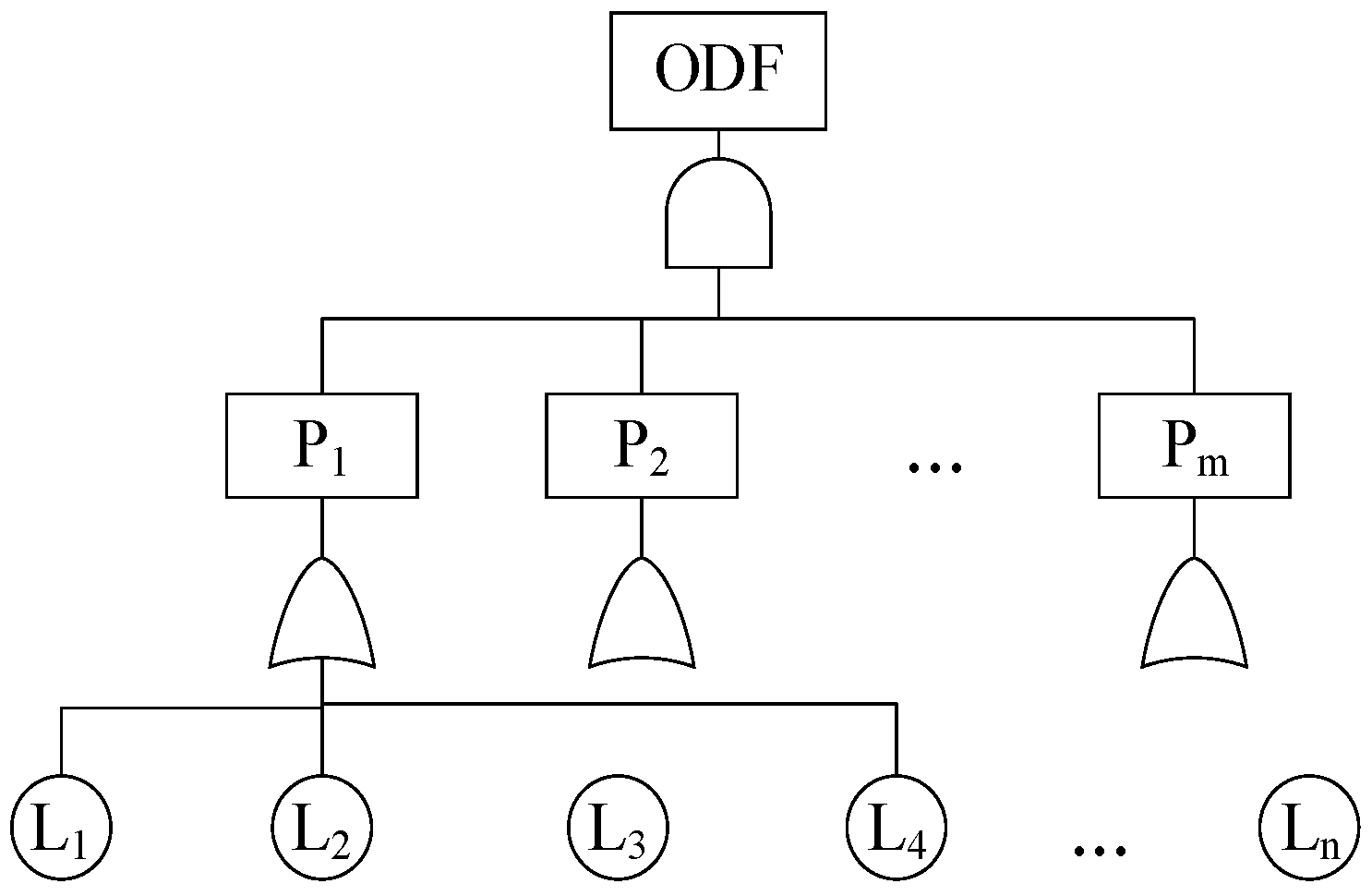
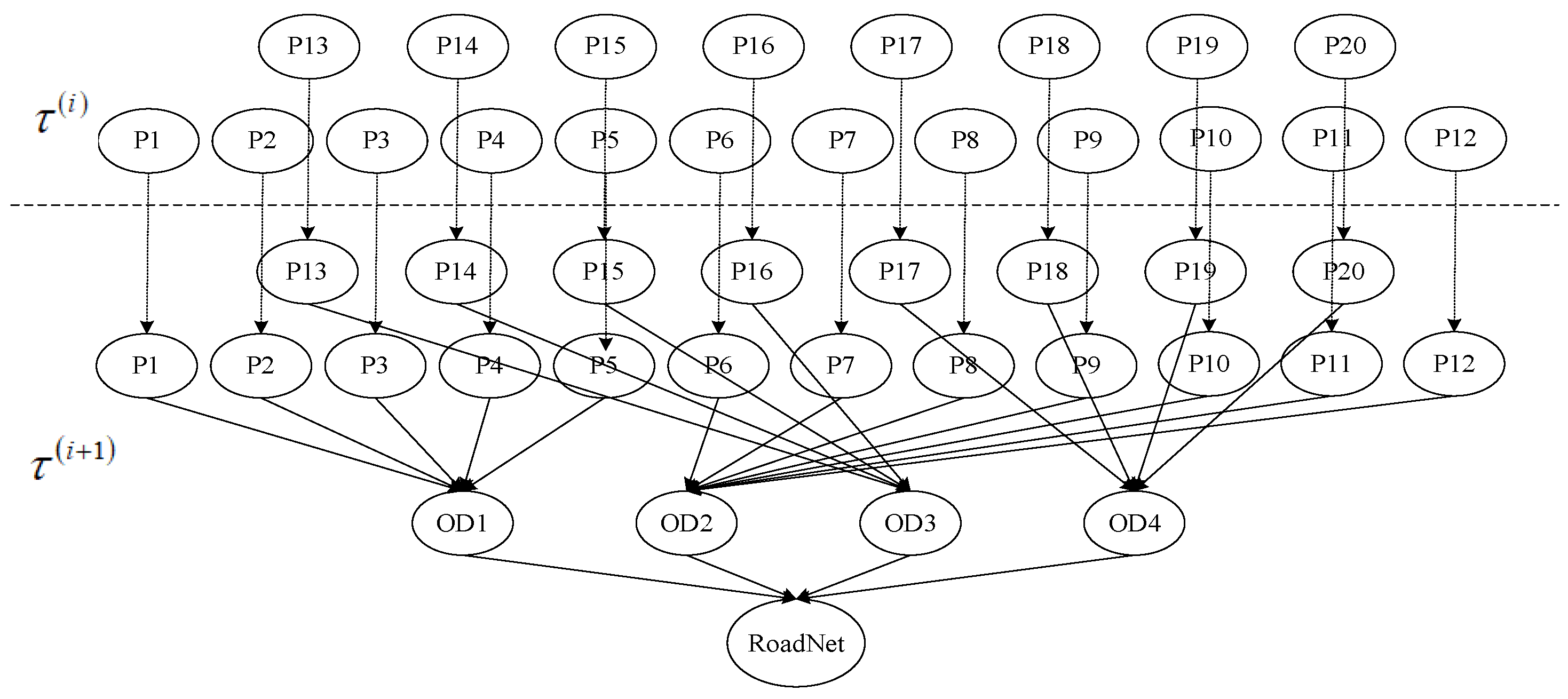
2.2.1. Road Network Time-Varying Reliability Modeling
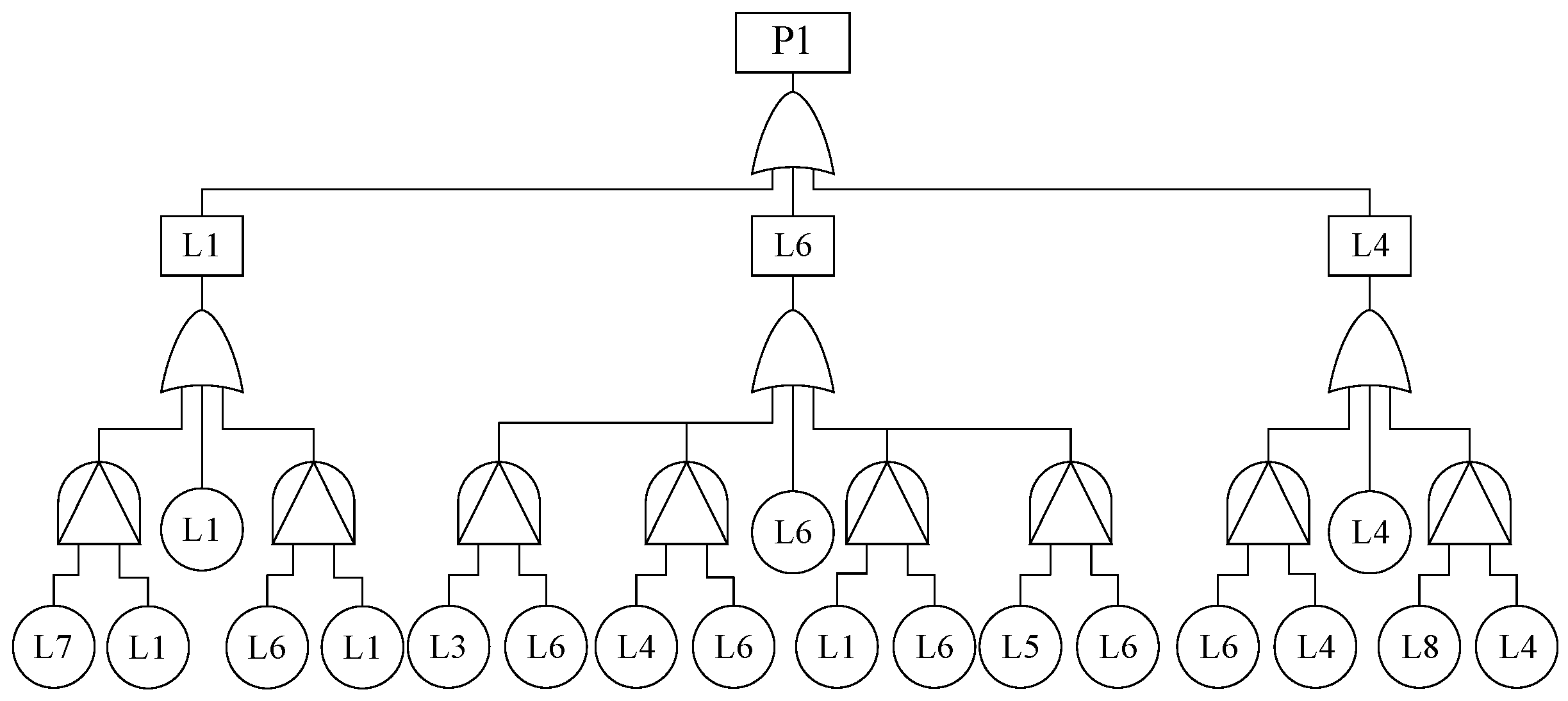
2.2.2. Road Network Reliability Assessment Based on FT-DBN
3. Case Analysis
3.1. Assessment of Road Network Structural Connectivity Reliability
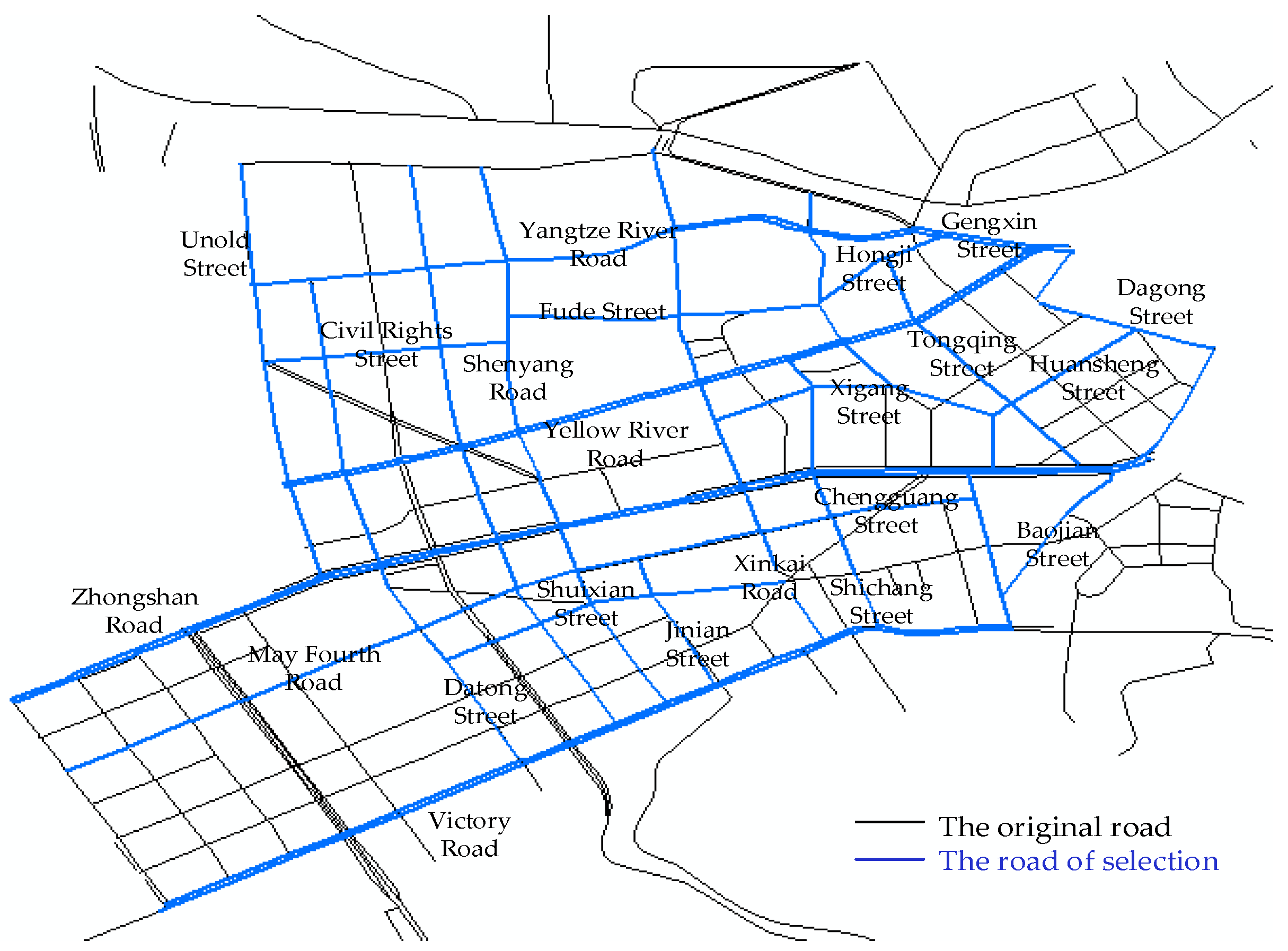
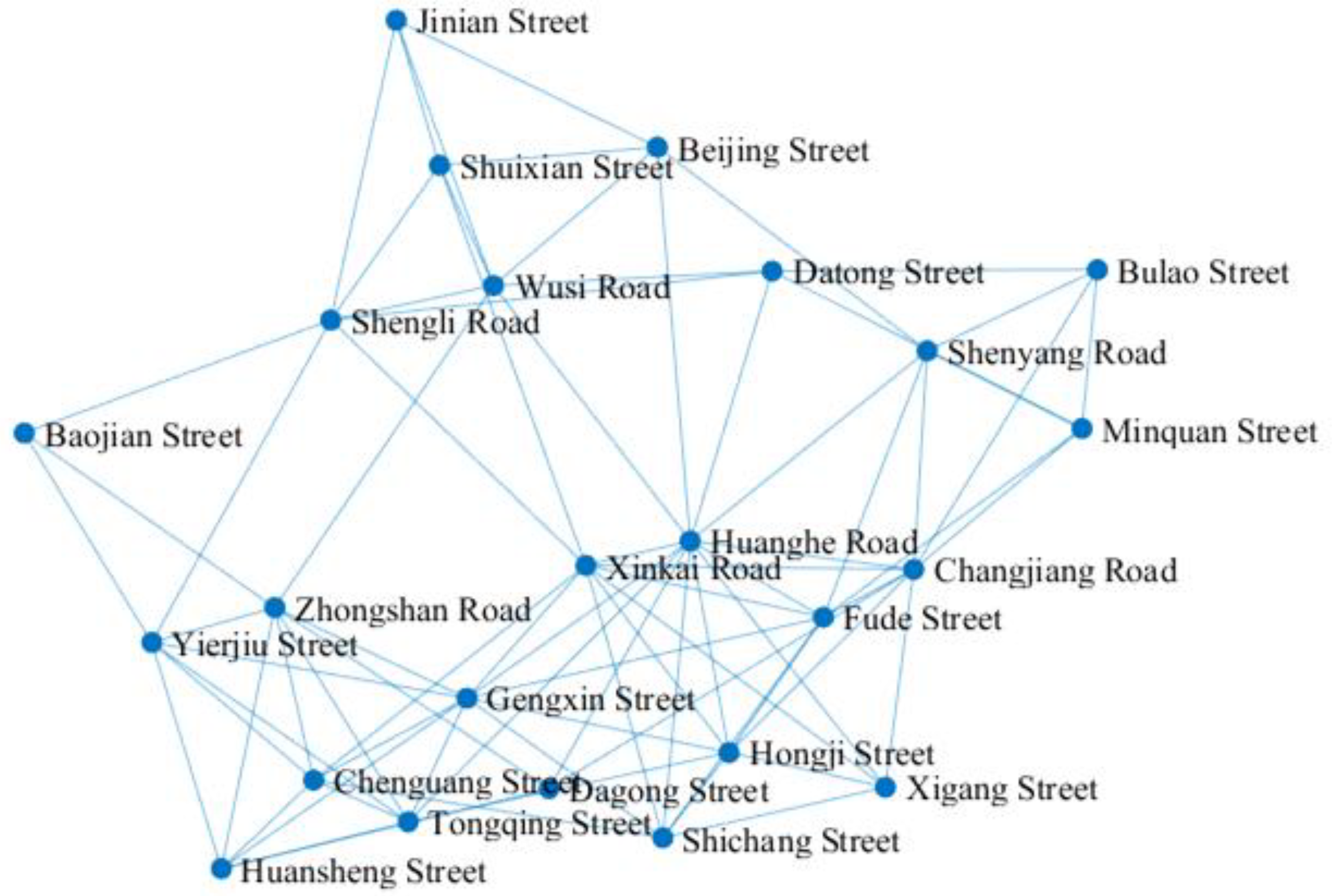
3.1.1. Analysis of Road Network Basic Characteristics
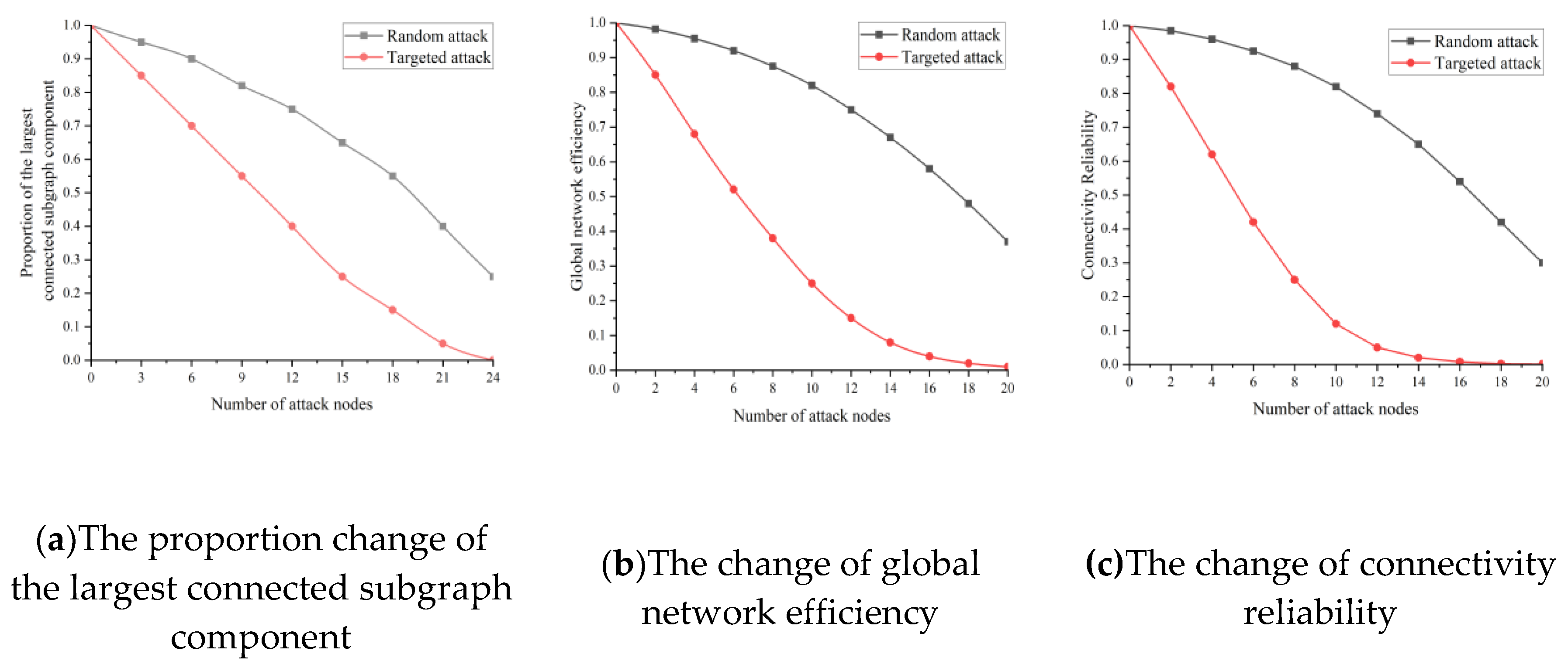
3.1.2. Assessment of Road Network Structural Reliability
3.2. Assessment of Road Network Time-Varying Connectivity Reliability
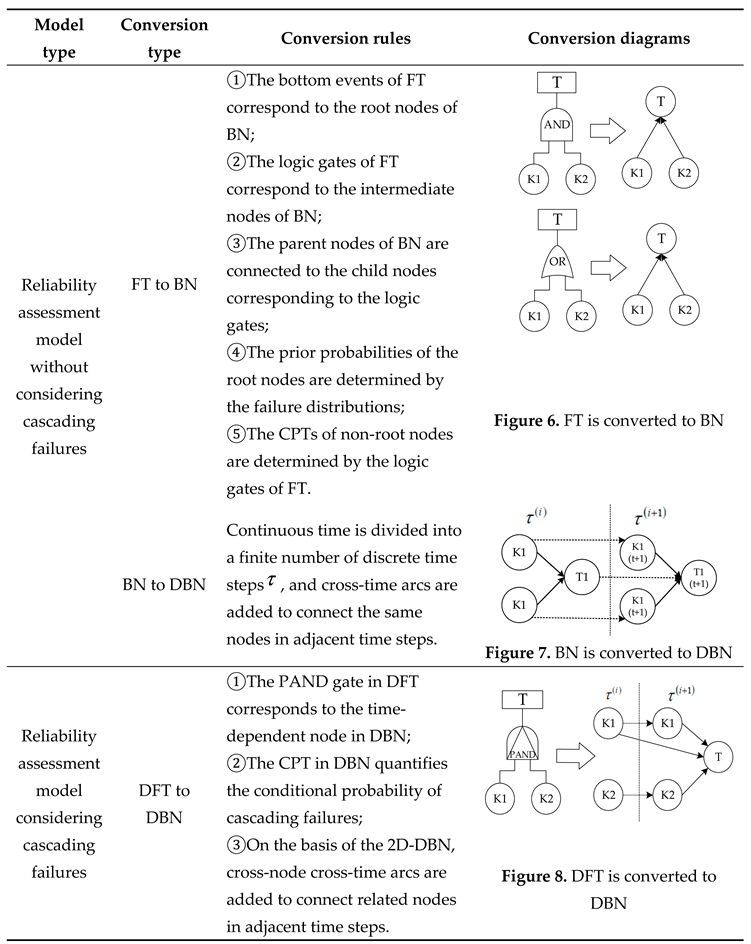
3.2.1. Reliability Assessment Model without Considering Cascading Failures
3.2.2. Reliability Assessment Model Considering Cascading Failures
3.2.3. Assessment of Road Network Time-Varying Reliability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DBN | Dynamic Bayesian Network |
| MCS | Monte Carlo Simulation |
| CPT | Conditional Probability Table |
| FT | Fault Tree |
| BN | Bayesian Network |
| DFT | Dynamic Bayesian Network |
References
- Peiravian, F.; Derrible, S. Multi-dimensional geometric complexity in urban transportation systems. arxiv 2015, arXiv:1507.03607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yangyang, M. Vulnerability Comparisons of Various Complex Urban Metro Networks Under Multiple Failure Scenarios. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9603–9603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, T. A complex network approach to quantifying flood resilience in high-density coastal urban areas: A case study of Macau. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction 2025, 119, 105335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumedah, G.; Garsonu, E.K. Characterising the structural pattern of urban road networks in Ghana using geometric and topological measures. Geo: Geography and Environment 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jia, H.; Lin, J.; Hu, H. Seismic Damage Rapid Assessment of Road Networks considering Individual Road Damage State and Reliability of Road Networks in Emergency Conditions. Advances in Civil Engineering 2020, 2020, 9631804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuwen, L. Improve the reliability index of power supply - strengthen reliability management and reduce the average power outage time of customers. Science and Technology Wind 2017, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Tang, M.; Yang, H. The reliability measures model of multilayer urban distribution network. Soft Computing 2018, 22, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Shao, H.; Wang, D.; Lam, W.H. A multi-task spatio-temporal generative adversarial network for prediction of travel time reliability in peak hour periods. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 2024, 638, 129632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Huang, S. Analyzing connectivity reliability and critical units for highway networks in high-intensity seismic region using Bayesian network. Journal of Infrastructure Intelligence and Resilience 2022, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menghan, Q. Dynamic estimation and reliability calculation method of urban arterial travel time. Doctoral dissertation, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chinese, 2020.
- Kato, T.; Uchida, K.; Lam, W. H. , & Sumalee, A. Estimation of the value of travel time and of travel time reliability for heterogeneous drivers in a road network. Transportation 2021, 48, 1639–1670. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.Q.; Hou, Q.H.; Duan, Y.Q. The research of the road network capacity based on the unblocked reliability. BioTechnology: An Indian Journal 2014, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, A.; Tang, Z.; Shan, L. Road network capacity reliability considering travel time reliability. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences 2013, 96, 1818–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Mu, L.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Hou, K. Fault Spread and Recovery Strategy of Urban Rail Transit System Based on Complex Network. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2021, 2037, 012049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Guohua, C.; Hao, W.; Shenghua, C.; Yun, Z. Reliability analysis method of power system based on GT-RBD. Journal of Shenyang University of Technology 2023, 45, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Cui, J.; Ren, G.; Thompson, R.G.; Zhang, L. Cascading failures and resilience evolution in urban road traffic networks with bounded rational route choice. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 2025, 664, 130456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Lu, C. Reliability analysis for continuous degrading systems subject to multi-level failure dependence. Quality Engineering 2025, 37, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Reliability analysis of dynamic fault trees with Priority-AND gates using conditional binary decision diagrams. Reliability Engineering & System Safety 2025, 253, 110495. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, Q.; Lu, D.G.; Zhang, B.Y. Physical resilience assessment of road transportation systems during post-earthquake emergency phase: With a focus on restoration modeling based on dynamic Bayesian networks. Reliability Engineering & System Safety 2025, 257, 110807. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.J.; Guang, S.W.; Xue, J.F.; Tong, Y.; Zhi, Y.L. Study on cascading failure vulnerability of the 21st-century Maritime Silk Road container ship network. Journal of Transport Geography 2024, 117, 103891. [Google Scholar]
- Ziqiang, G. Study on the resilience of dynamic heterogeneous urban road traffic network considering the influence of information conditions. Doctoral dissertation, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chinese, 2021.
- Qingguo, W. Comprehensive analysis of urban road importance evaluation methods. Surveying and mapping bulletin 2018, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, H. Study on the evaluation method of road network failure degree and safety level. Doctoral dissertation, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Chinese, 2010.
- Lei, J. Research on reliability and availability modeling and evaluation methods of high-speed railway signal systems. Doctoral dissertation, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chinese, 2020.
- Meiling, L. Research on the invulnerability of high-speed railway network in China based on complex network theory. Doctoral dissertation, Beijing Jiaotong University, Chinese, 2025.
- Xuliang, G. Research and development of road network traffic operation situation assessment method and system under disaster events. Doctoral dissertation, Chang 'an University, Chinese, 2022.
- Shen, S.; Cheng, J.; Liu, Z.; Tan, J.; Zhang, D. Bayesian inference-assisted reliability analysis framework for robotic motion systems in future factories. Reliability Engineering & System Safety 2025, 110894. [Google Scholar]
- Monfared, M.A.S.; Rezazadeh, M.; Alipour, Z. Road networks reliability estimations and optimizations: A Bi-directional bottom-up, top-down approach. Reliability Engineering & System Safety 2022, 222, 108427. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Song, S. Bayesian network approach for dynamic fault tree with common cause failures and interval uncertainty parameters. Maintenance & Reliability 2024, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Barahimi, A.H.; Eydi, A.; Aghaie, A. Urban transportation network reliability calculation considering correlation among the links comprising a route. Scientia Iranica 2022, 29, 1742–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, D.J. Urban rail transit system network reliability analysis based on a coupled map lattice model. Journal of Advanced Transportation 2021, 2021, 5548956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Number of nodes | The number of nodes in the network |
| Number of edges | The number of edges in the network |
| Average degree | The average value of the degrees of all nodes in the network |
| Average path length | The average distance between any two nodes in the network |
| Average clustering coefficient | The average clustering coefficient of all nodes in the network |
| Global network efficiency | The average of the reciprocals of the shortest path lengths between all pairs of nodes in the network |
| Parameter | Number of nodes | Number of edges | Average degree | Average path length | Average clustering coefficient | Global network efficiency |
| feature value | 24 | 80 | 6.6667 | 1.9094 | 0.55476 | 0.61202 |
| Indicator | Random attack | Targeted attack |
|---|---|---|
| Number of attacks required for collapse | 28.3±4.2 | 9.1±1.5 |
| Decrease rate of the largest connected component per attack | -3.2%(±0.5%)/attack | -10.5%(±1.2%)/attack |
| Decrease rate of global efficiency per attack | -2.1%(±0.3%)/attack | -8.7%(±1.0%)/attack |
| Number of attacked nodes | Reliability under random attacks | Reliability under targeted attack |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.988 | 0.752 |
| 5 | 0.985 | 0.403 |
| 10 | 0.961 | 0.211 |
| 20 | 0.856 | 0.032 |
| Number | Road name | Connected road numbers | Failure probability during peak hours | Failure probability during non-peak hours |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | Zhonghua West Road | L6、L7 | 0.1 | 0.0087 |
| L2 | Yangtze Road | L3、L7、L8 | 0.2 | 0.0091 |
| L3 | Yellow River Road | L2、L6、L8、L9 | 0.05 | 0.0032 |
| L4 | Digital Road | L6、L8 | 0.15 | 0.0067 |
| L5 | North China Road | L6、L8、L9 | 0.08 | 0.0043 |
| L6 | Southwest Road | L1、L3、L4、L5 | 0.3 | 0.0098 |
| L7 | Northeast Expressway | L1、L2 | 0.25 | 0.0084 |
| L8 | Xi'an Road | L2、L3、L4、L5、L9 | 0.12 | 0.0072 |
| L9 | Zhongchang Street | L3、L5、L8 | 0.18 | 0.0079 |
| Triggering event | Affected road section | Conditional failure probability | Propagation delay time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Failure of L1 | L6 | 0.4577 | 30 minutes |
| Failure of L1 | L7 | 0.3728 | 15 minutes |
| Failure of L6 | L1 | 0.4278 | 15 minutes |
| Failure of L6 | L3 | 0.3897 | 15 minutes |
| Failure of L6 | L4 | 0.2738 | 30 minutes |
| Failure of L6 | L5 | 0.5637 | 30 minutes |
| Failure of L4 | L6 | 0.4359 | 30 minutes |
| Failure of L4 | L8 | 0.4893 | 45 minutes |
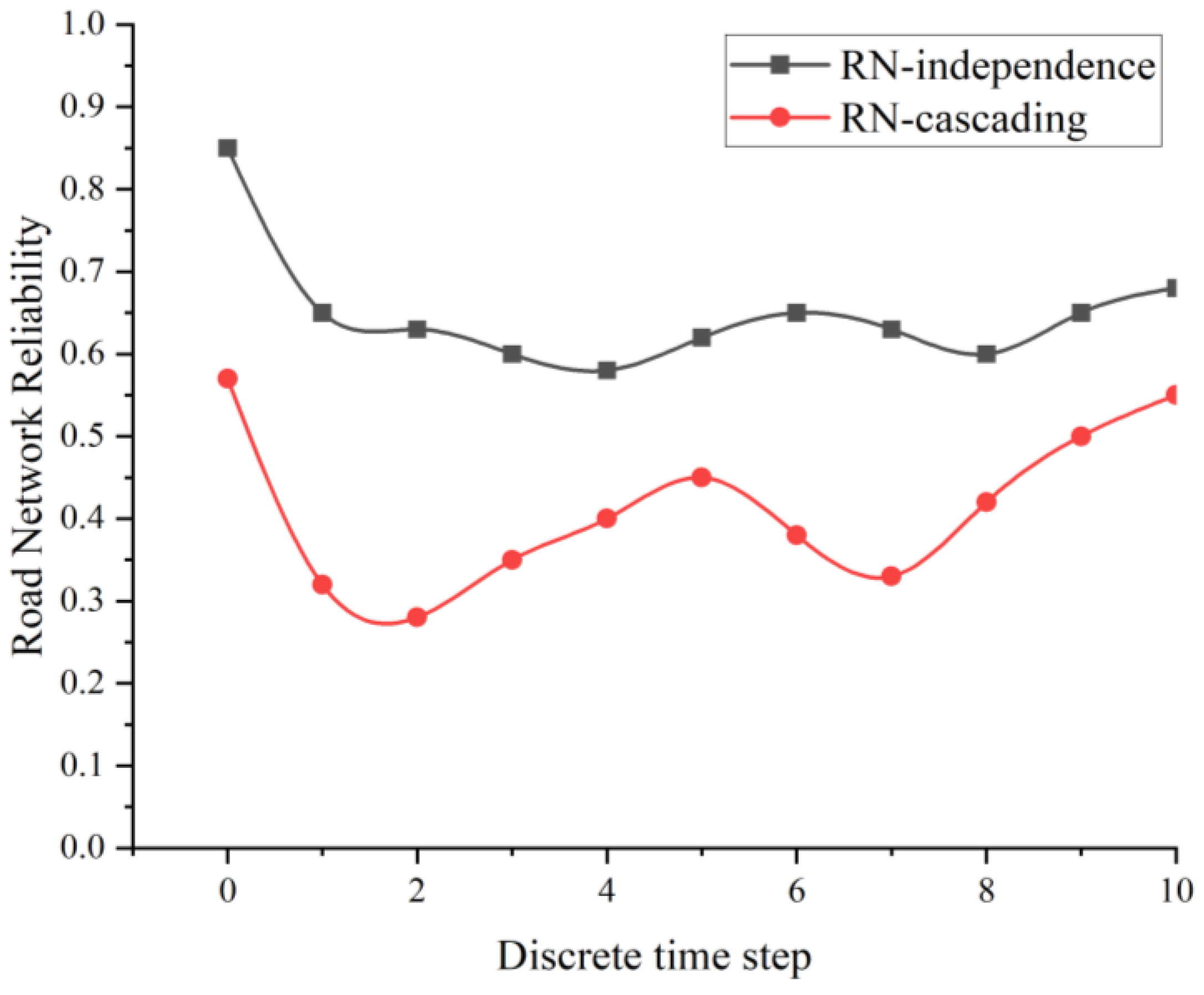
| ) | Time (minutes) | R(D)(t) | R(C)(t) | Key event description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0.85 | 0.57 | Initial state |
| 1 | 15 | 0.65 | 0.32 | Early peak starts, cascading triggered from L1 to L6 |
| 2 | 30 | 0.63 | 0.28 | Cascading spreads to L3 |
| 3 | 45 | 0.60 | 0.35 | Partial effectiveness of repair mechanism |
| 4 | 60 | 0.58 | 0.40 | Peak ends, pressure relieved |
| 5 | 75 | 0.62 | 0.45 | Traffic flow stabilizes |
| 6 | 90 | 0.65 | 0.38 | Evening peak starts, secondary cascading from L6 to L4 |
| 7 | 105 | 0.63 | 0.33 | Cascading impact expands |
| 8 | 120 | 0.60 | 0.42 | Secondary effectiveness of repair mechanism |
| 9 | 135 | 0.65 | 0.50 | System stabilizes |
| 10 | 150 | 0.68 | 0.55 | Low traffic flow period at night |
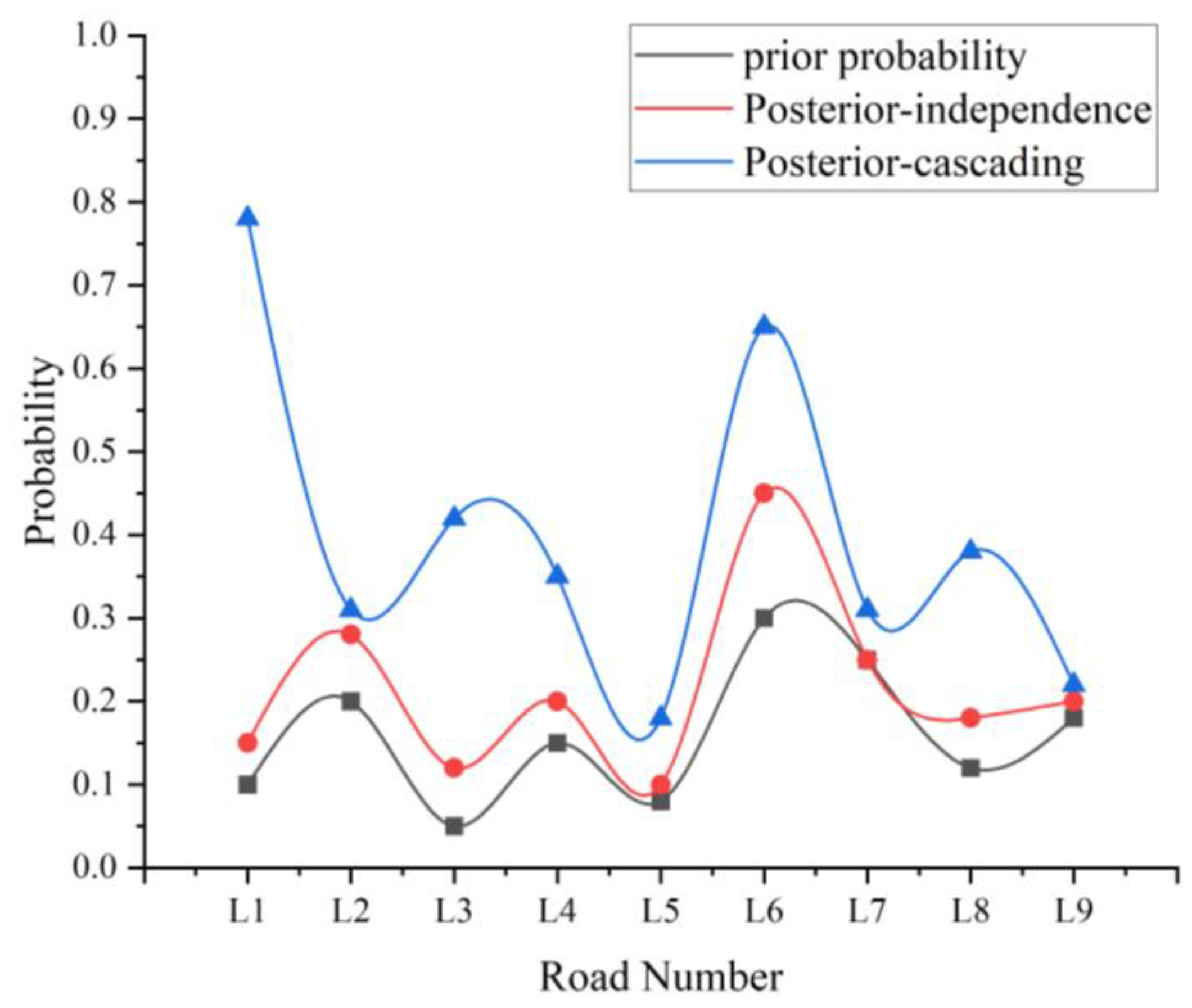
| Road number | Prior probability | Posterior probability (independentfailure) | Posterior probability (cascading failure) | Keyness ranking (independent failure) | Keyness ranking (cascading failure) | Keyness analysis and cascading failure analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.78 | 6 | 1 | Triggering cascading failures of L6 and L7 |
| L2 | 0.20 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 2 | 6 | Secondary impact |
| L3 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.42 | 8 | 3 | Affected by L6 |
| L4 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.35 | 5 | 5 | Affected by L6 and L8 |
| L5 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.18 | 9 | 8 | Connecting L6 and L8 |
| L6 | 0.30 | 0.45 | 0.65 | 1 | 2 | Connecting L3, L4, and L5 |
| L7 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.31 | 3 | 7 | Affected by L1 |
| L8 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.38 | 7 | 4 | Multiple path dependencies |
| L9 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 4 | 9 | Minimal impact |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





