Submitted:
29 April 2025
Posted:
30 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
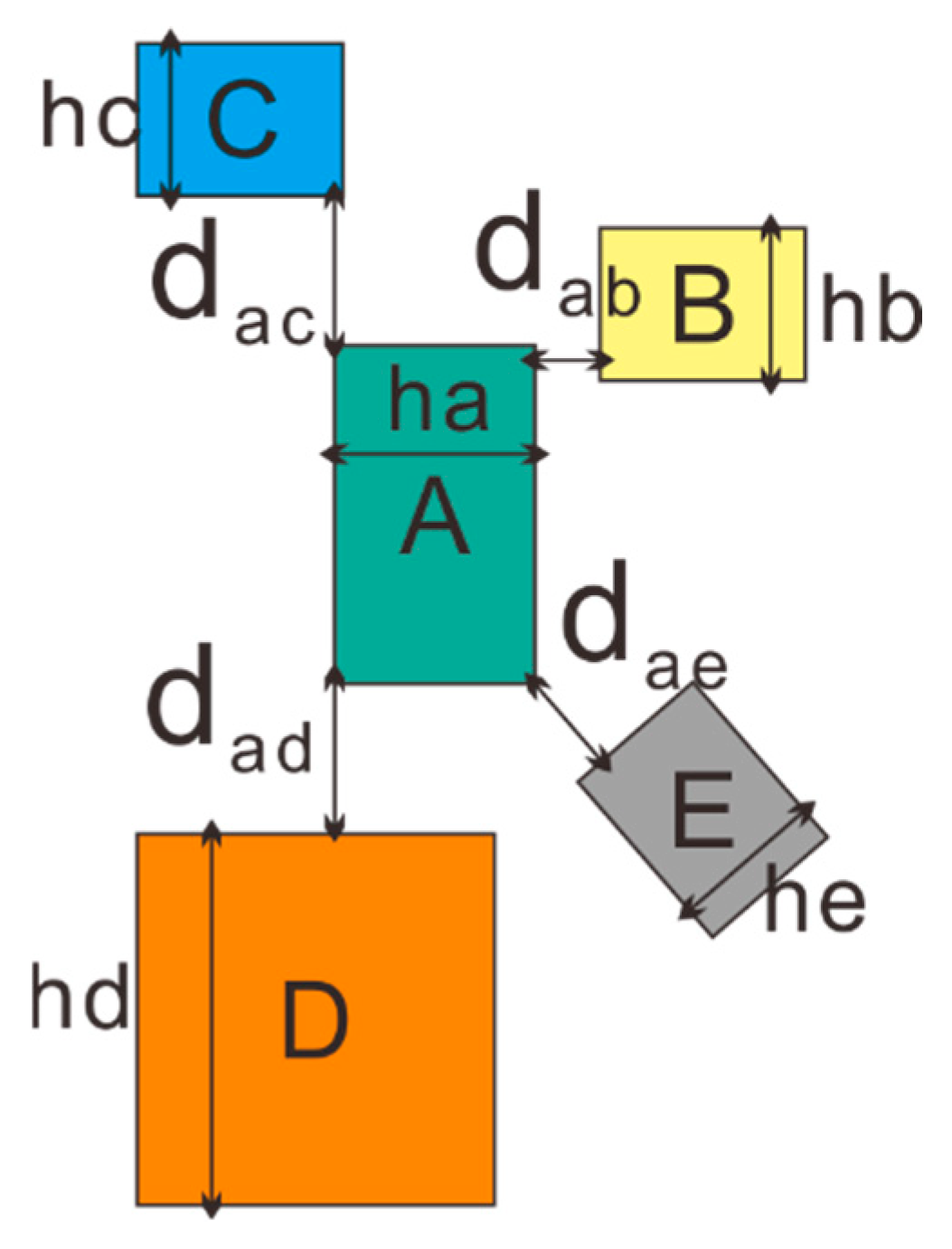
2.1. Descriptive Methods for Edge State Building Features
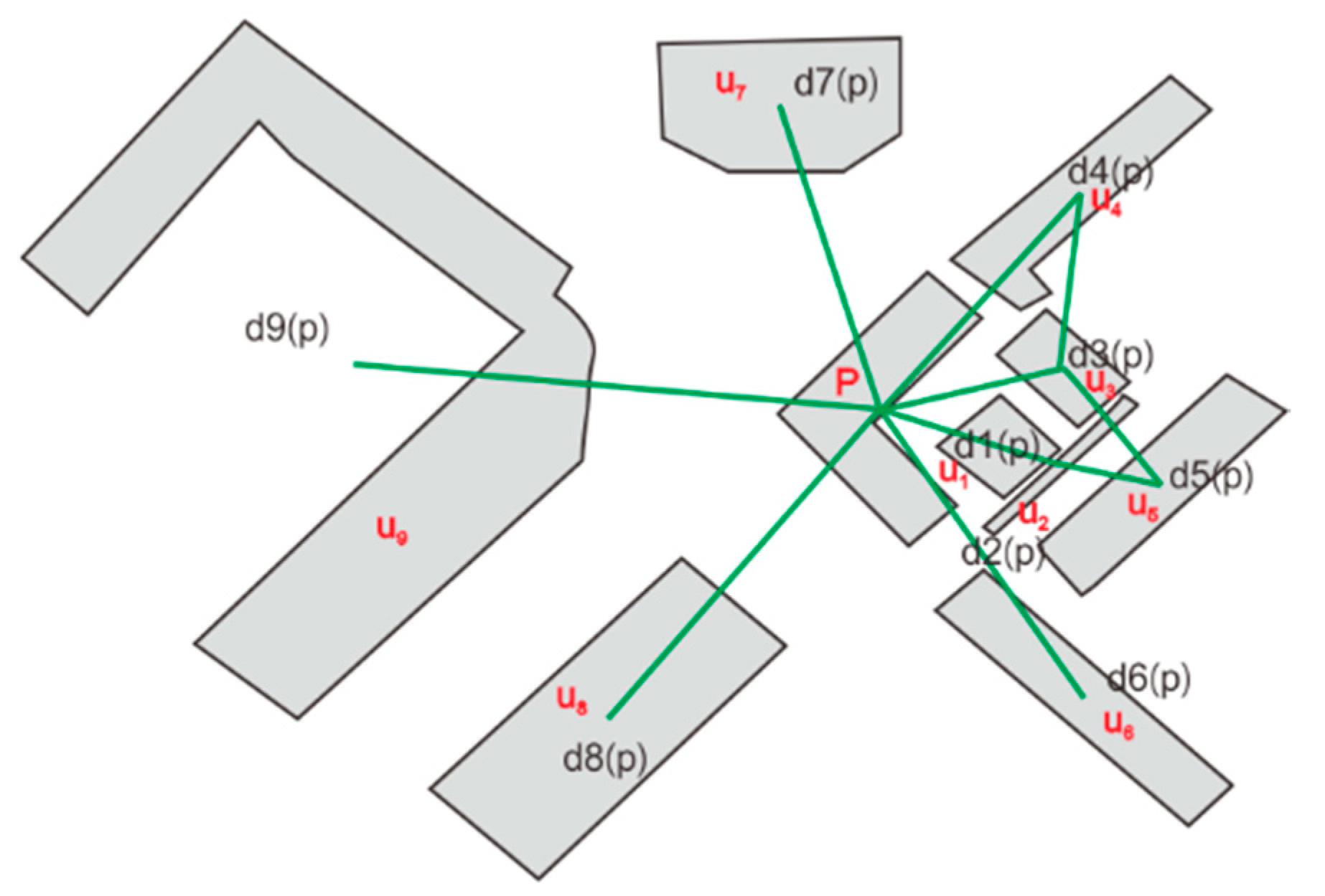
2.1.1. Expand the K-NN Neighborhoods in Graph
2.1.2. The LOF Characteristic of the Building [21]
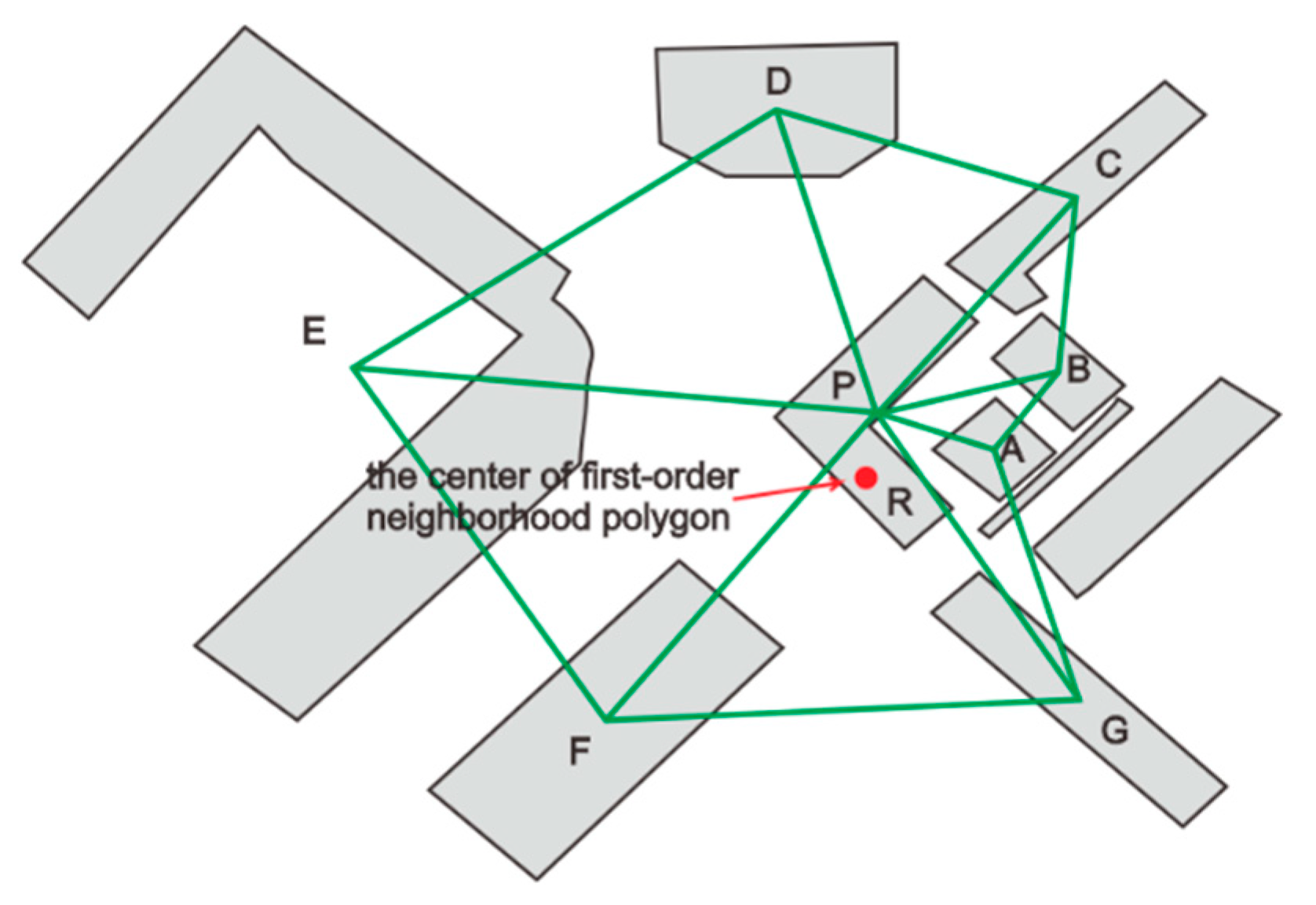
2.1.3. The Center_Devia and First_Neighbor_avg_r Features of Buildings
2.1.4. The Density and vo_to_b_Length Characters of the Building

2.1.5. The m_dis of Two Adjacent Buildings and the m_dis_cv Character of a Building
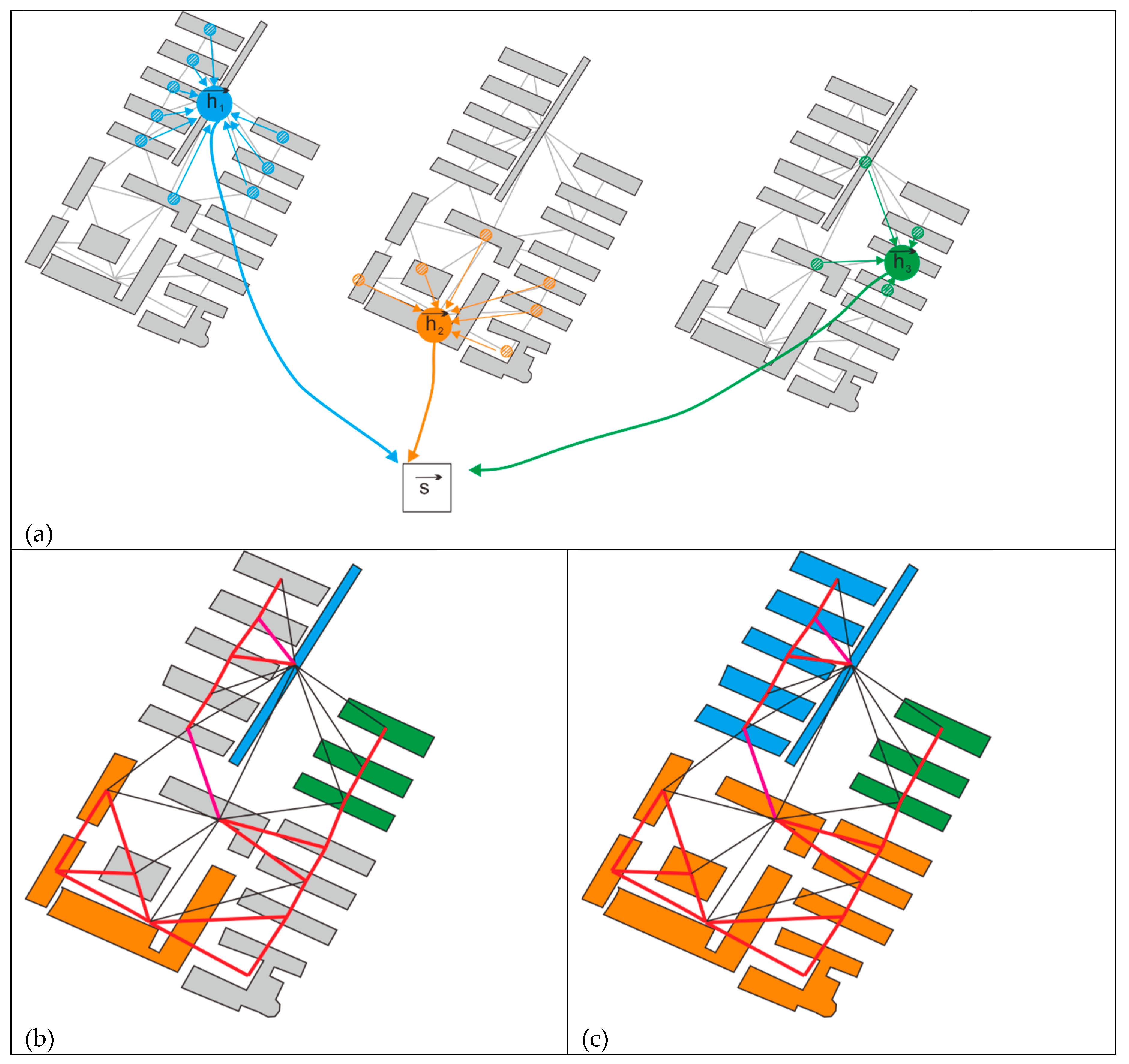
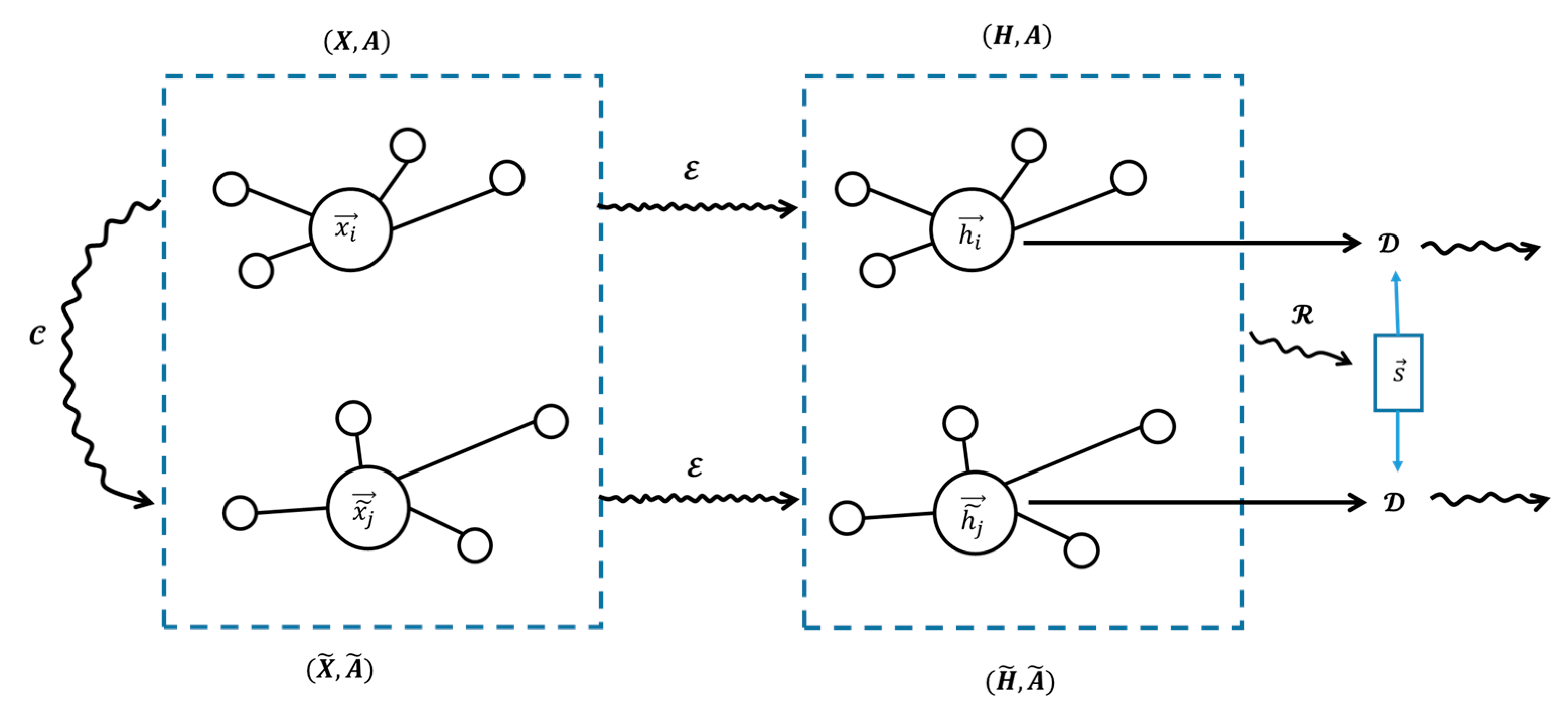
2.2. The Node Representation Learning Based on DGI Model
2.3. The Traverse of Building Graph
| Algorithm BFS with KY Value Limit for Graph Traversal | |
| 1 | Input: Graph G=(V,E) (where V represents buildings and E represents edges), starting building Vstart , threshold m_dis_limit |
| 2 | Initialize: visited: an empty set to store visited buildings. queue: a list initialized withVstart. traversal_result: an empty list to store the result of BFS traversal. |
| 3 | While queue is not empty do: |
| 4 | Pop the first building Vcurrent from queue. |
| 5 | If Vcurrent ∉ visited and G[Vcurrent].we=1: |
| 6 | Add Vcurrent to visited. |
| 7 | Append Vcurrent to traversal_result. |
| 8 | For each neighbor Vneighbor of Vcurrent: |
| 9 | If Vneighbor∉ visited: |
| 10 | Retrieve edge_data for (Vcurrent,Vneighbor). |
| 11 | If edge_data exists and edge_data.m_dis ≤ m_dis_limit |
| 12 | Append Vneighbor to queue |
| 13 | Return: traversal_result. |
3. Results
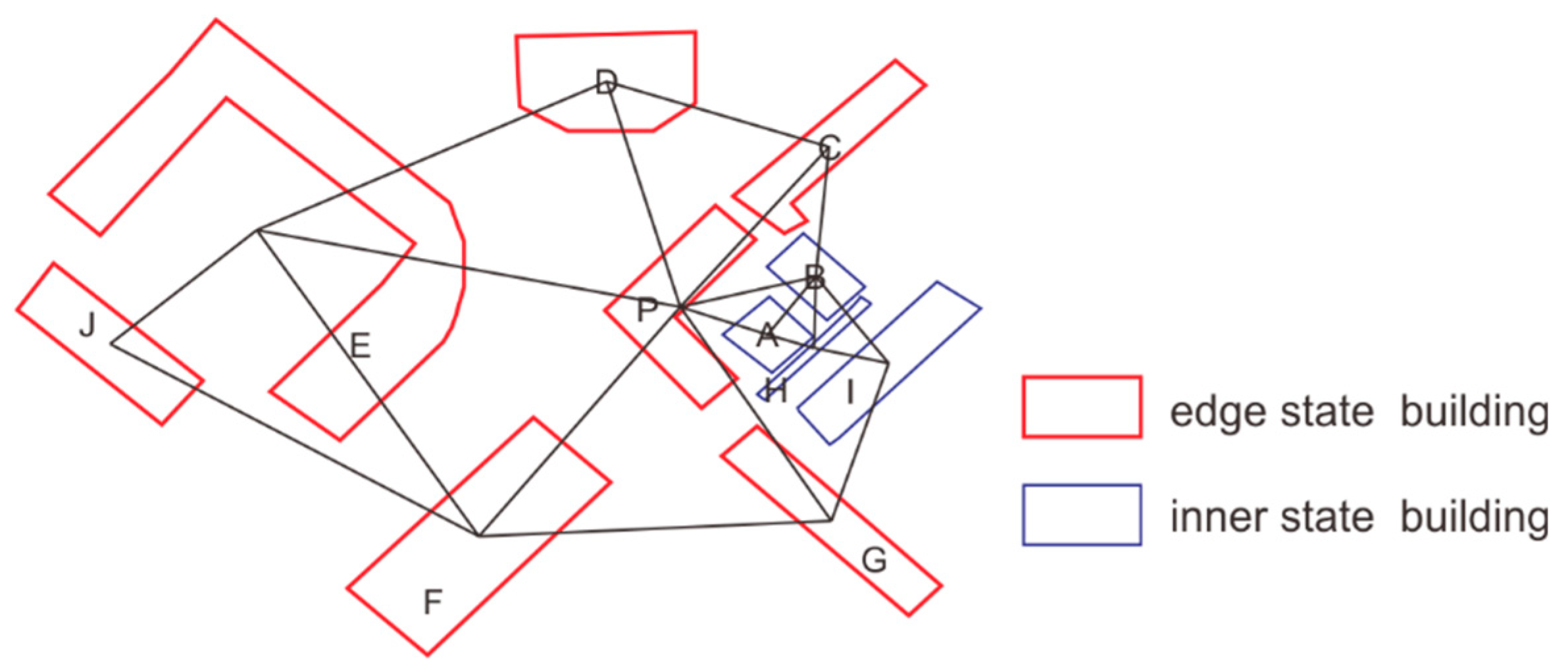
3.1. Experiment for Semi-Automatically Labeling Edge State Buildings
3.1.1. Attribute Definition and Grading
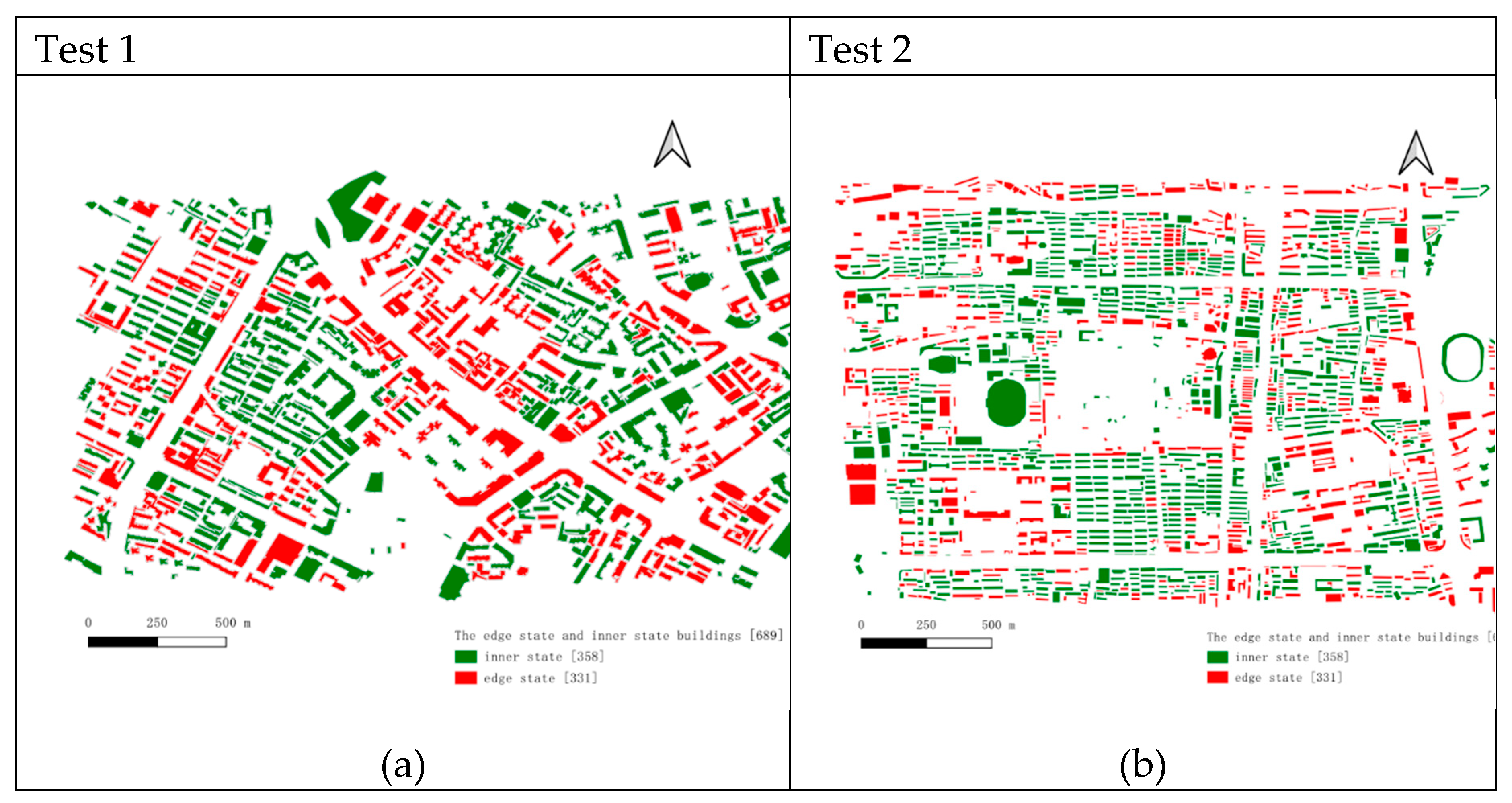
3.1.2. The Semi-automated Labeling of Edge State Buildings
- When a building's vo_to_b_length value falls within the high-value range (>8.690), it receives the label of an edge state building (whether_edge=1).
- If the vo_to_b_length value falls within the medium-value range (3.236–8.690) and the corresponding LOF value falls within the high-value range (>1.055), it is also labeled as an edge state building (whether_edge=1).
- Buildings that do not satisfy the above conditions are labeled as inner state buildings (whether_edge=0).
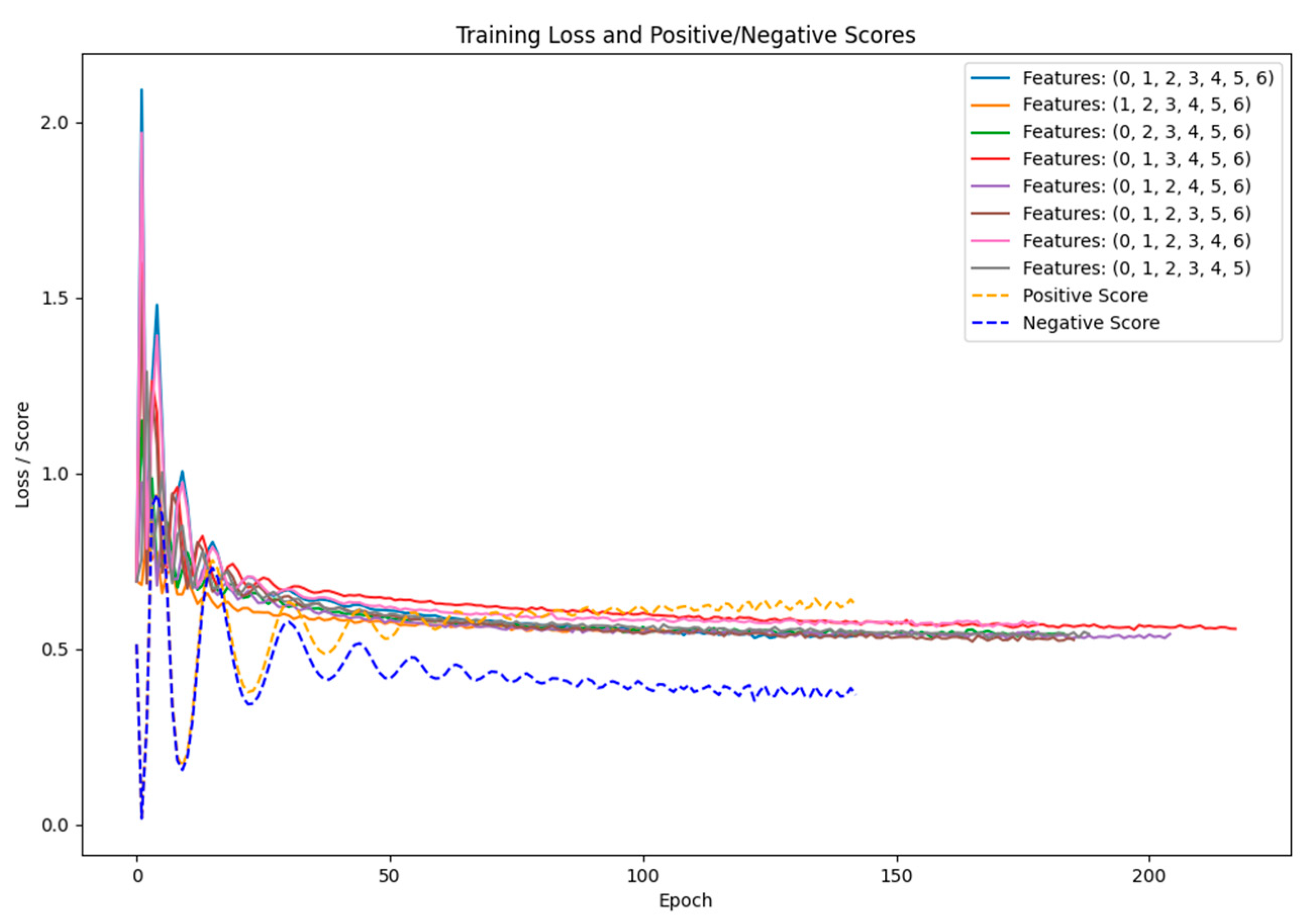
3.2. The DGI Model Training Phase
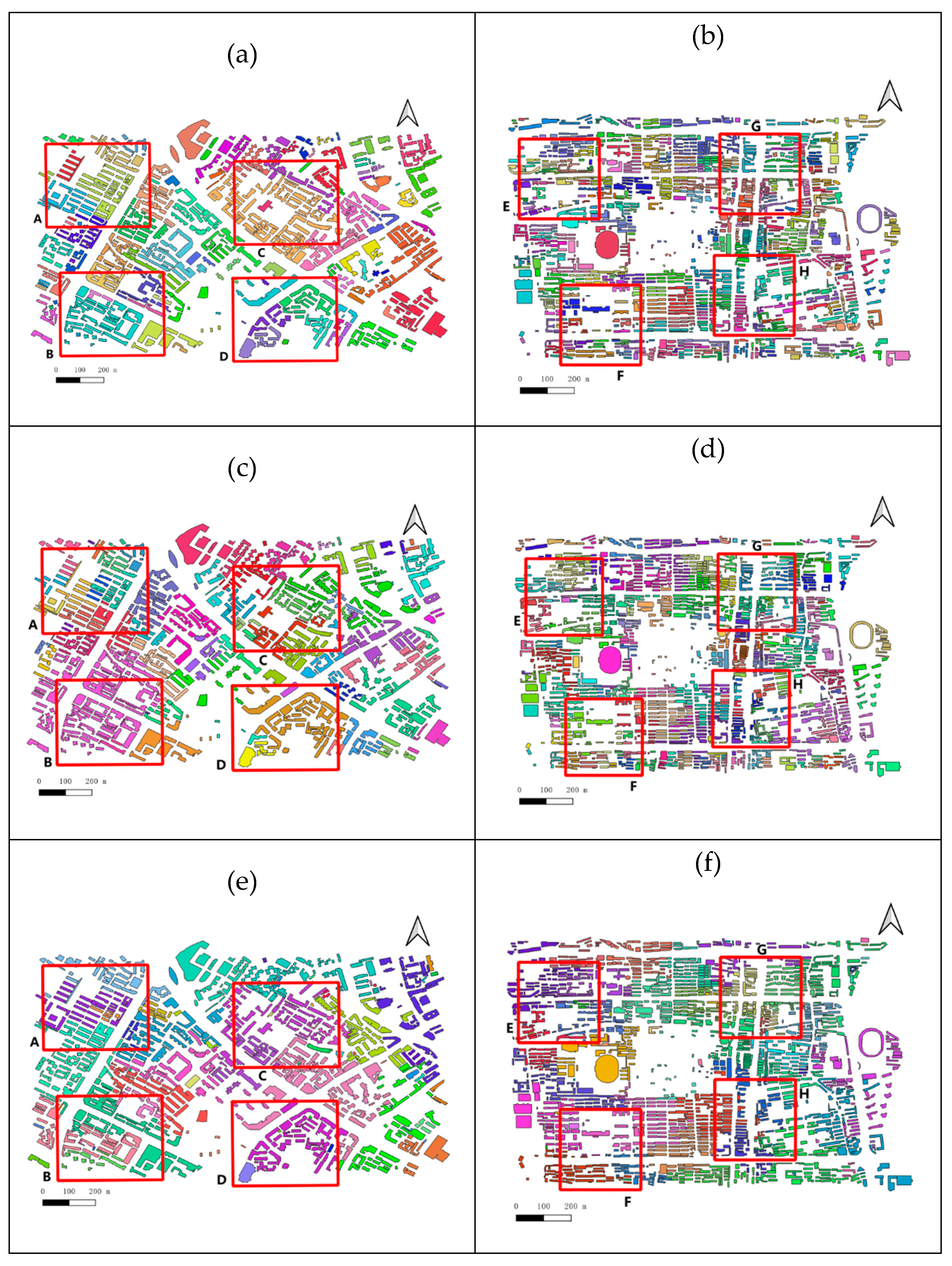
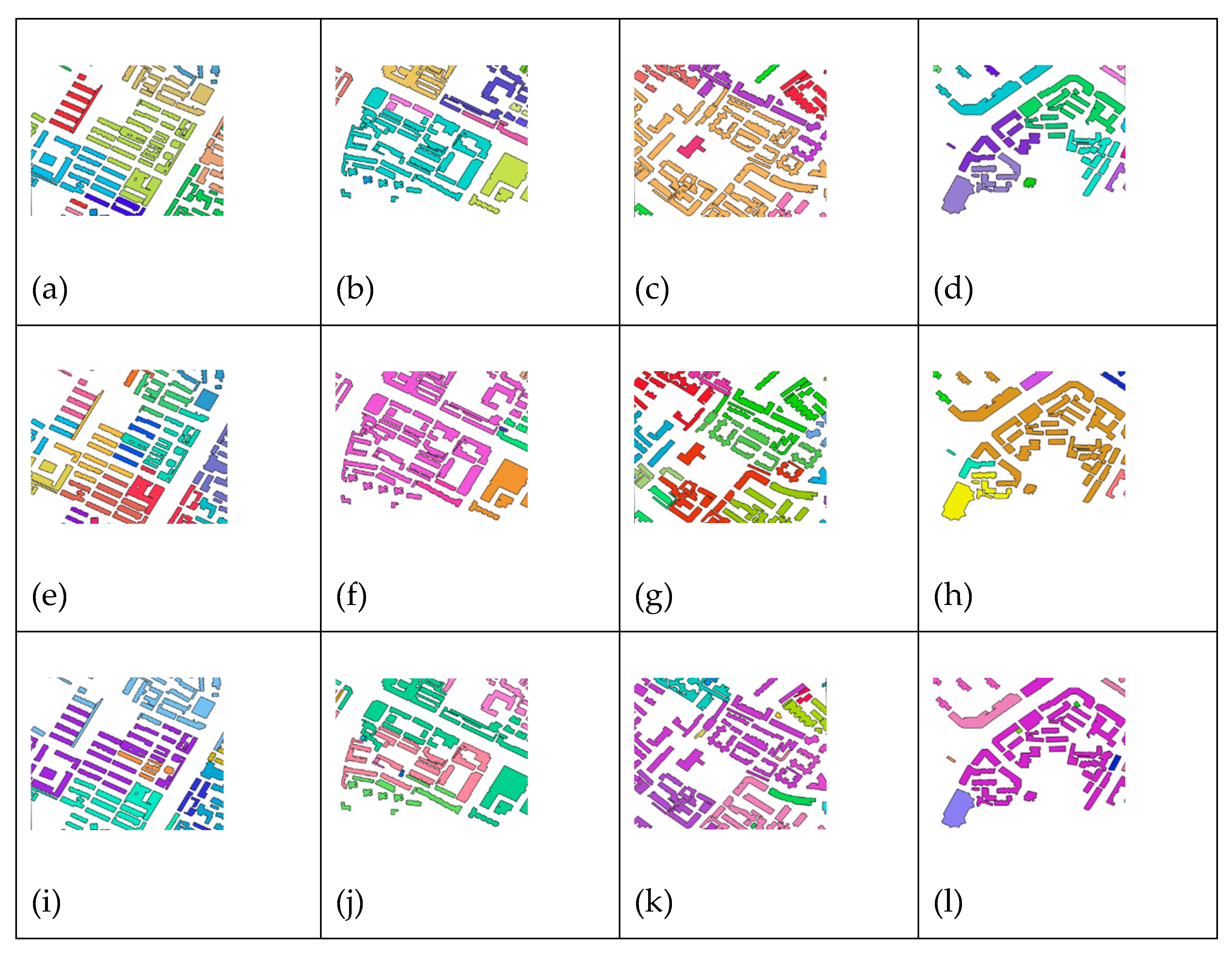
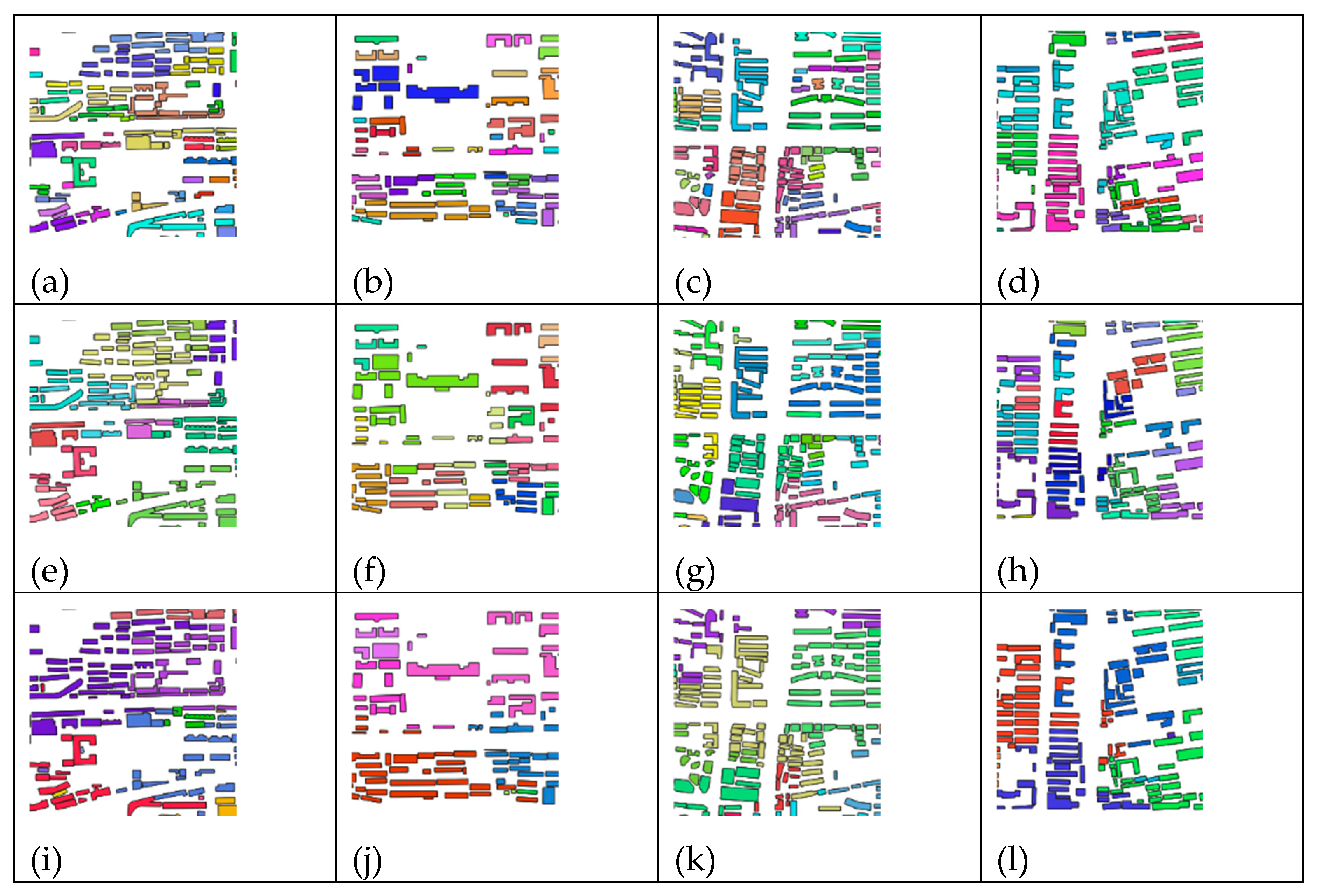
3.3. Clustering Comparison Experiment
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Liu Q.; Tang J. Towards a Scale-driven Theory for Spatial Clustering. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 1534–1548.
- Allouche M K.; Moulin B. Amalgamation in cartographic generalization using Kohonen's feature nets. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2005, 19(8-9): 899-914. [CrossRef]
- Basaraner, M.; Selcuk, M. A structure recognition technique in contextual generalisation of buildings and built-up areas. The Cartographic Journal, 2008, 45(4): 274-285. [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Guo Q.; Sun Y.; et al. Reducing building conflicts in map generalization with an improved PSO algorithm. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2017, 6(5): 127.
- Sahbaz, K.; Basaraner, M. A zonal displacement approach via grid point weighting in building generalization. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2021, 10(2): 105. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yan, H.; Ai, T.; et al. Automated building generalization based on urban morphology and Gestalt theory. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2004, 18(5): 513-534. [CrossRef]
- Qi, H B.; Li, Z L. An approach to building grouping based on hierarchical constraints. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci, 2008: 449-454.
- Yan, H.; Weibel, R.; Yang, B. A multi-parameter approach to automated building grouping and generalization. Geoinformatica, 2008, 12: 73-89. [CrossRef]
- Anders, K H. A hierarchical graph-clustering approach to find groups of objects. Proceedings 5th workshop on progress in automated map generalization. Citeseer, 2003: 1-8.
- Zhang, L.; Deng, H.; Chen, D., et al. A spatial cognition-based urban building clustering approach and its applications. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2013, 27(4): 721-740.
- Wang, W.; Du, S.; Guo, Z.; et al. Polygonal clustering analysis using multilevel graph-partition. Transactions in GIS, 2015, 19(5): 716-736. [CrossRef]
- Zahn, C T. Graph-theoretical methods for detecting and describing gestalt clusters. IEEE Transactions on computers, 1971, 100(1): 68-86. [CrossRef]
- Regnauld, N. Contextual building typification in automated map generalization. Algorithmica, 2001, 30: 312-333. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Miao, D.; Wang, R. A graph-theoretical clustering method based on two rounds of minimum spanning trees. Pattern Recognition, 2010, 43(3): 752-766. [CrossRef]
- Cetinkaya, S.; Basaraner, M.; Burghardt, D. Proximity-based grouping of buildings in urban blocks: a comparison of four algorithms. Geocarto International, 2015, 30(6): 618-632. [CrossRef]
- Pilehforooshha, P; Karimi, M. An integrated framework for linear pattern extraction in the building group generalization process. Geocarto International, 2019, 34(9): 1000-1021. [CrossRef]
- Yan, X; Ai, T; Yang, M; et al. Graph convolutional autoencoder model for the shape coding and cognition of buildings in maps. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2021, 35(3): 490-512. [CrossRef]
- Shuai, Y; Shuai, H; Ni, L. Polygon cluster pattern recognition based on new visual distance. Geoinformatics 2007: Geospatial Information Science. SPIE, 2007, 6753: 411-423.
- Zhan, Q; Deng, S; Zheng, Z. An adaptive sweep-circle spatial clustering algorithm based on gestalt. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2017, 6(9): 272. [CrossRef]
- Sander, J.; Ester, M.; Kriegel, H P.; et al. Density-based clustering in spatial databases: The algorithm gdbscan and its applications. Data mining and knowledge discovery, 1998, 2: 169-194. [CrossRef]
- Breunig, M M.; Kriegel, H P.; Ng, R T.; et al. LOF: identifying density-based local outliers. Proceedings of the 2000 ACM SIGMOD international conference on Management of data. 2000: 93-104.
- Rodriguez, A.; Laio, A. Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks. science, 2014, 344(6191): 1492-1496. [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, C C. Outlier detection in graphs and networks. Outlier analysis. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 369-397.
- Pilehforooshha, P.; Karimi, M. A local adaptive density-based algorithm for clustering polygonal buildings in urban block polygons. Geocarto International, 2020, 35(2): 141-167. [CrossRef]
- Meng, N.; Wang Z.; Gao, C.; et al. A vector building clustering algorithm based on local outlier factor. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2024, 49(4): 562-571.
- Bei, W; Guo, M; Huang, Y. A spatial adaptive algorithm framework for building pattern recognition using graph convolutional networks. Sensors, 2019, 19(24): 5518. [CrossRef]
- Yan, X; Ai, T; Yang, M; et al. A graph deep learning approach for urban building grouping. Geocarto International, 2022, 37(10): 2944-2966. [CrossRef]
- Kipf, T N; Welling, M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.02907, 2016.
- Cover, T; Hart, P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE transactions on information theory, 1967, 13(1): 21-27. [CrossRef]
- Peng, D; Gui, Z; Wang, D; et al. Clustering by measuring local direction centrality for data with heterogeneous density and weak connectivity. Nature communications, 2022, 13(1): 5455. [CrossRef]
- Veličković, P; Fedus, W; Hamilton, W L; et al. Deep Graph Infomax. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.10341, 2018.
- Wu, J; Dai, P; Hu, X; et al. An adaptive approach for generating Voronoi diagrams for residential areas containing adjacent polygons. International Journal of Digital Earth, 2024, 17(1): 2431100. [CrossRef]
- Edsger, W D. A note on two problems in connexion with graphs. Numerische mathematik, 1959, 1(1): 269-271.
- Yan, X; Ai, T; Yang, M; et al. A graph convolutional neural network for classification of building patterns using spatial vector data. ISPRS journal of photogrammetry and remote sensing, 2019, 150: 259-273. [CrossRef]
- Peura, M., Iivarinen, J., 1997. Efficiency of simple shape descriptors. In: Proceedings of the Third International Workshop on Visual Form, pp. 443–451.
- Basaraner, M; Cetinkaya, S. Performance of shape indices and classification schemes for characterising perceptual shape complexity of building footprints in GIS. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2017, 31(10): 1952-1977. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Ai T, Stoter J. The evalutation of spatial distribution density in map generalization, ISPRS 2008: Proceedings of the XXI congress: Silk road for information from imagery: the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 3-11 July, Beijing, China. Comm. II, WG II/2. Beijing: ISPRS, 2008. pp. 181-187. International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (ISPRS), 2008: 181-187.
- Chen, J; Yang, S T; Li, H W; et al. Research on geographical environment unit division based on the method of natural breaks (Jenks. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2013, 40: 47-50. [CrossRef]
- Openstreetmap. Available online: https://www.openstreetmap.org (accessed on 18, April, 2025).
- Arbelaitz, O.; Gurrutxaga, I.; Muguerza, J.; et al. An extensive comparative study of cluster validity indices. Pattern recognition, 2013, 46(1): 243-256. [CrossRef]
| Number | Name | Notation/equation | Description |
| 1 | concavity | The area ratio of the building to its convex hull [36] | |
| 2 | LOF | Section 2.1.2 | |
| 3 | Density | The area of the building is divided by the area of the Voronoi map unit where it is located [37] | |
| 4 | vo_to_b_length | The vector length of the Voronoi graph unit center pointing to the center of the building it contains | |
| 5 | center_devia | Illustrated in Section 2.1.3 | |
| 6 | first_neighbor_avg_r, | - | Average radius of first-order neighborhood polygons of a building |
| 7 | M_dis_cv | Illustrated in Section 2.1.5 |
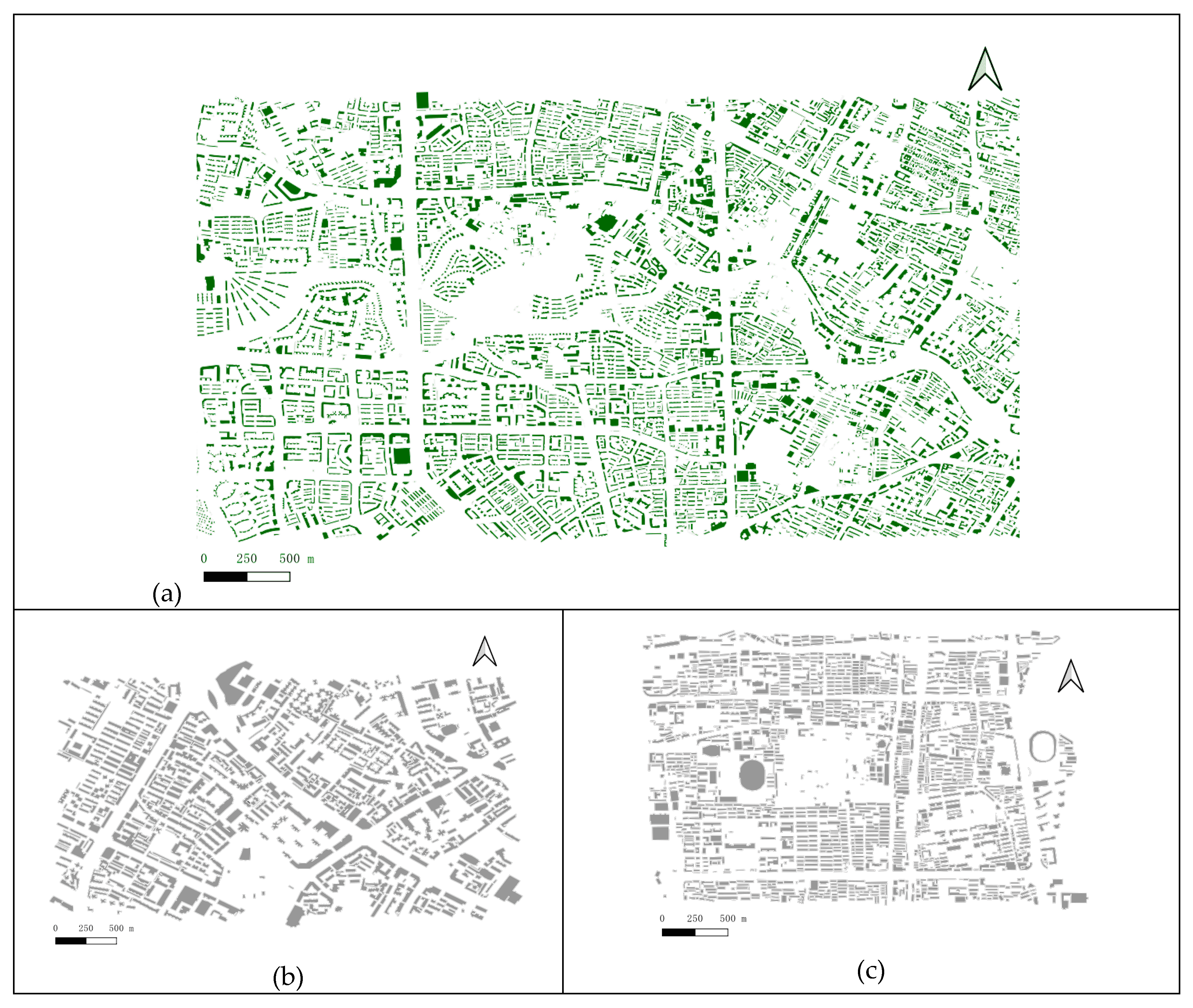
| Dataset | Number of Buildings | Percent of Concave Polygon (%) | Percent of Rectangles (ERI index [36]) (%), | Location |
| Training | 4851 | 91.4 | 17.3 | 104.00E,30.66N |
| Test1 | 689 | 94.0 | 16.5 | 104.05E,30.68N |
| Test2 | 1737 | 19.3 | 82.5 | 117.08.E, 28.68。N |
| Training number | Feature combination used in training | Feature combination description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [concavity,lof,density,vo_to_b_length,center_devia,first_neighbor_avg_r] | Remove m_dis_cv from all seven features |
| 2 | [concavity,lof,density,vo_to_b_length,center_devia , m_dis_cv] | Remove first_neighbor_avg_r from all seven features |
| 3 | [concavity,lof,density,vo_to_b_length ,first_neighbor_avg_r, m_dis_cv] | Remove center_devia from all seven features |
| 4 | [concavity,lof,density ,center_devia,first_neighbor_avg_r, m_dis_cv] | Remove vo_to_b_length from all seven features, |
| 5 | [concavity,lof ,vo_to_b_length,center_devia,first_neighbor_avg_r, m_dis_cv] | Remove density from all seven features, |
| 6 | [concavity ,density,vo_to_b_length,center_devia,first_neighbor_avg_r, m_dis_cv] | Remove lof from all seven features |
| 7 | [lof,density,vo_to_b_length,center_devia,first_neighbor_avg_r, m_dis_cv] | Remove concavity from all seven features |
| 8 | [concavity,lof,density,vo_to_b_length,center_devia,first_neighbor_avg_r, m_dis_cv] | All seven features |
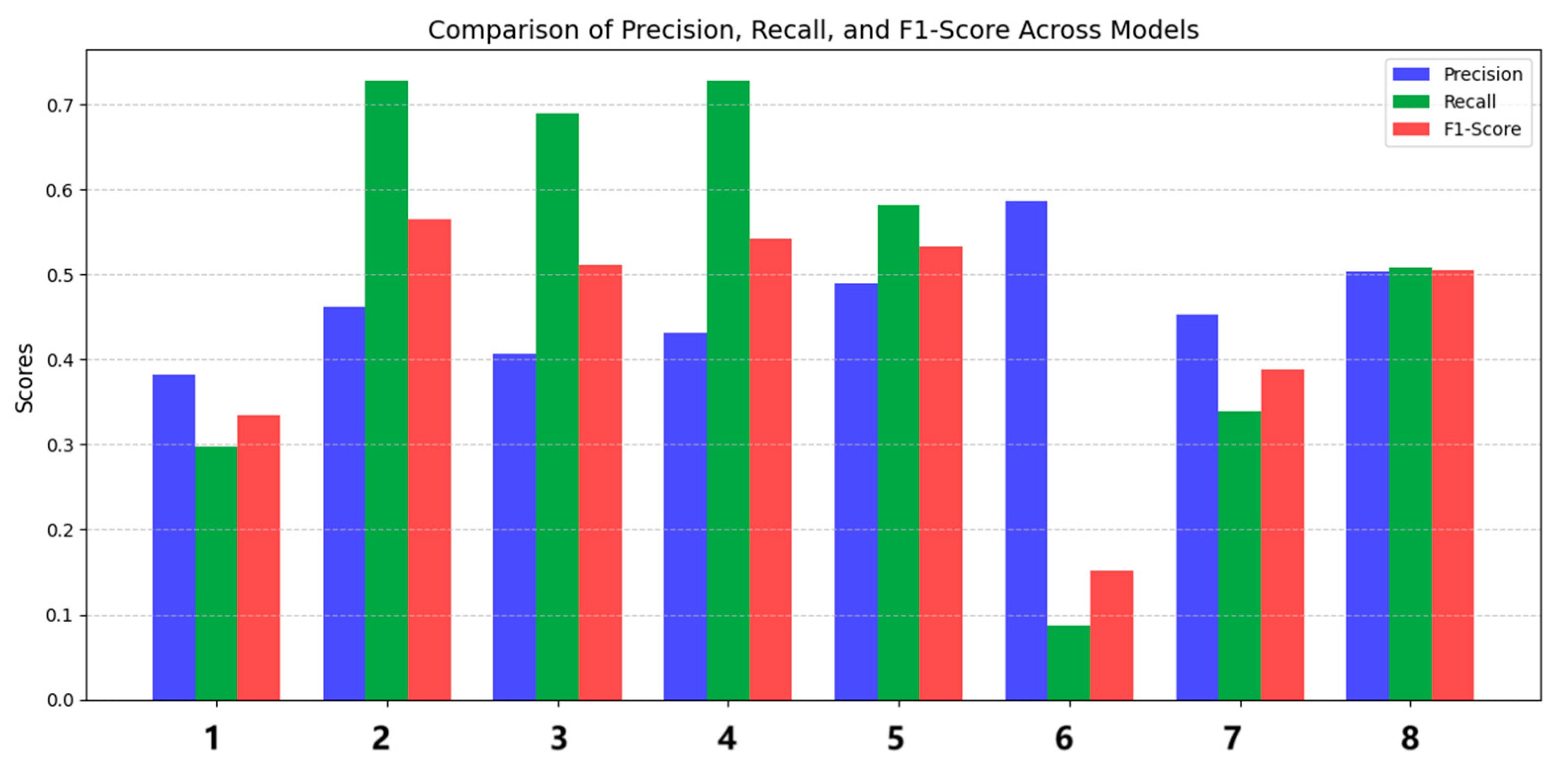
| Experiment data | Method | silhouette coefficient, | davies bouldin index | calinski harabasz index, | ARI |
| Test 1 | DGI-EIC | -0.44 | 4.03 | 5.15 | 0.45 |
| CDC | -0.37 | 4.52 | 5.90 | 0.32 | |
| MGP | -0.46 | 2.26 | 5.70 | 0.37 | |
| Test 2 | DGI-EIC | -0.35 | 3.79 | 5.52 | 0.20 |
| CDC | -0.23 | 3.89 | 10.53 | 0.26 | |
| MGP | -0.35 | 2.12 | 14.93 | 0.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




