Submitted:
16 April 2025
Posted:
17 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
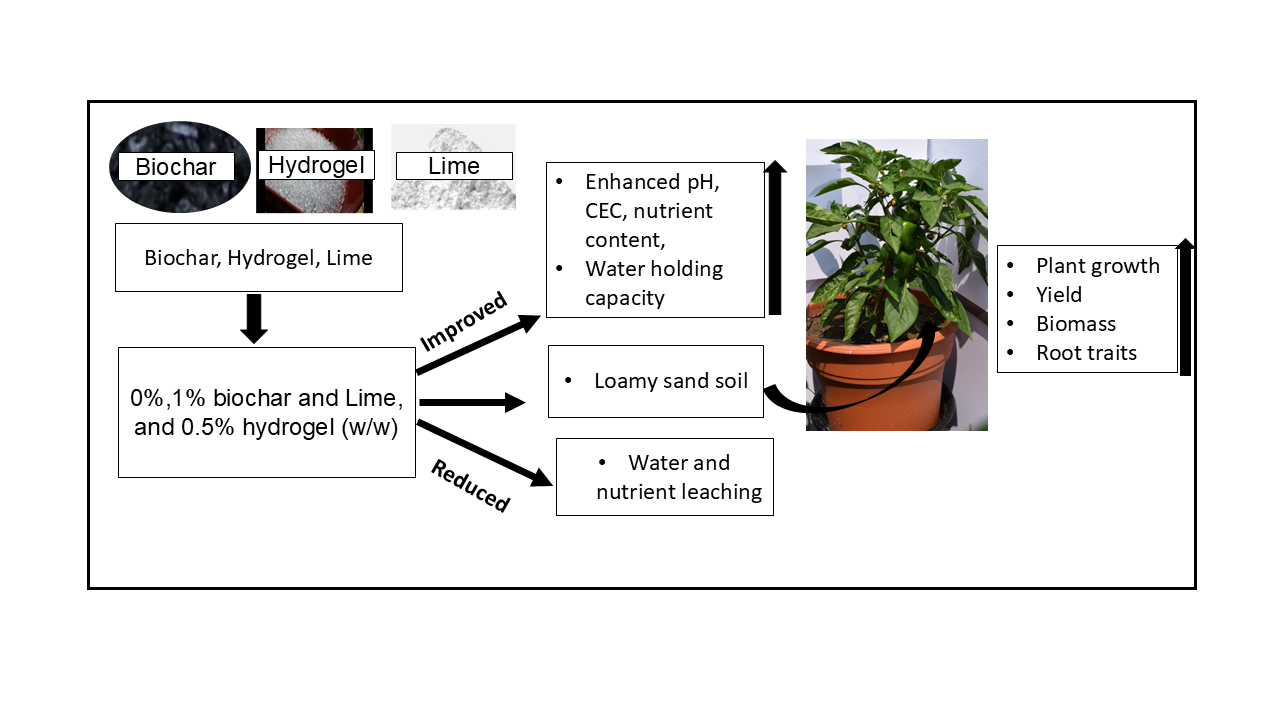
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Collection and Characterization
2.2. Soil Amendments and Their Characterization
2.3. Experimental Site and Design
2.4. Data Collection and Measurements
2.4.1. Plant Growth Parameters Measurement
2.4.2. Green Pepper Harvest and Biomass Analysis
2.4.3. Leachate Collection and Analysis
2.4.4. Soil Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Amendments Affected the Physio-Chemical Properties of the Soil
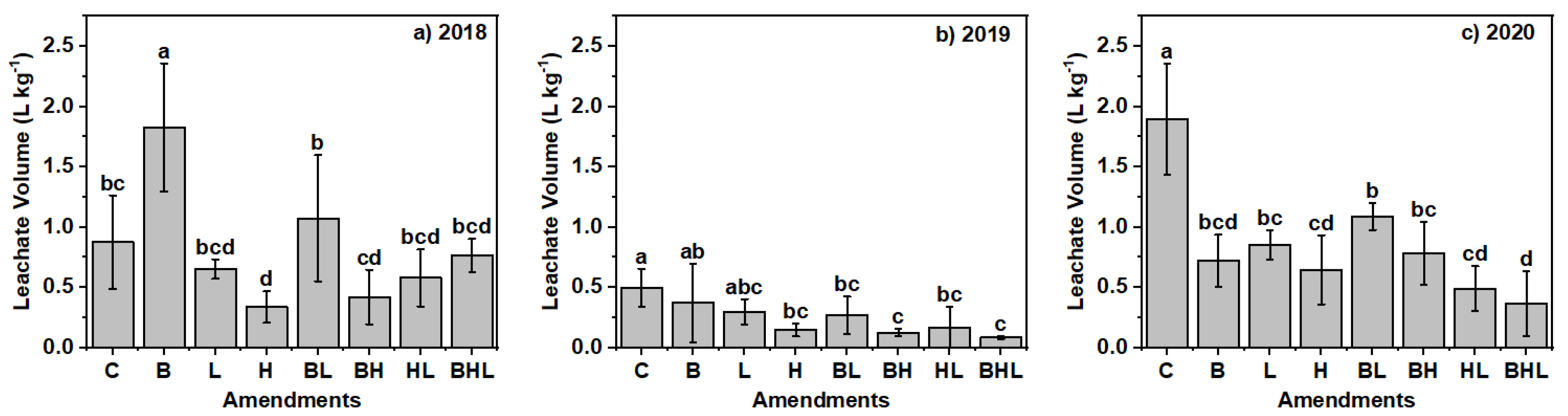
3.2. Soil Amendments Impacted Leachate Volume
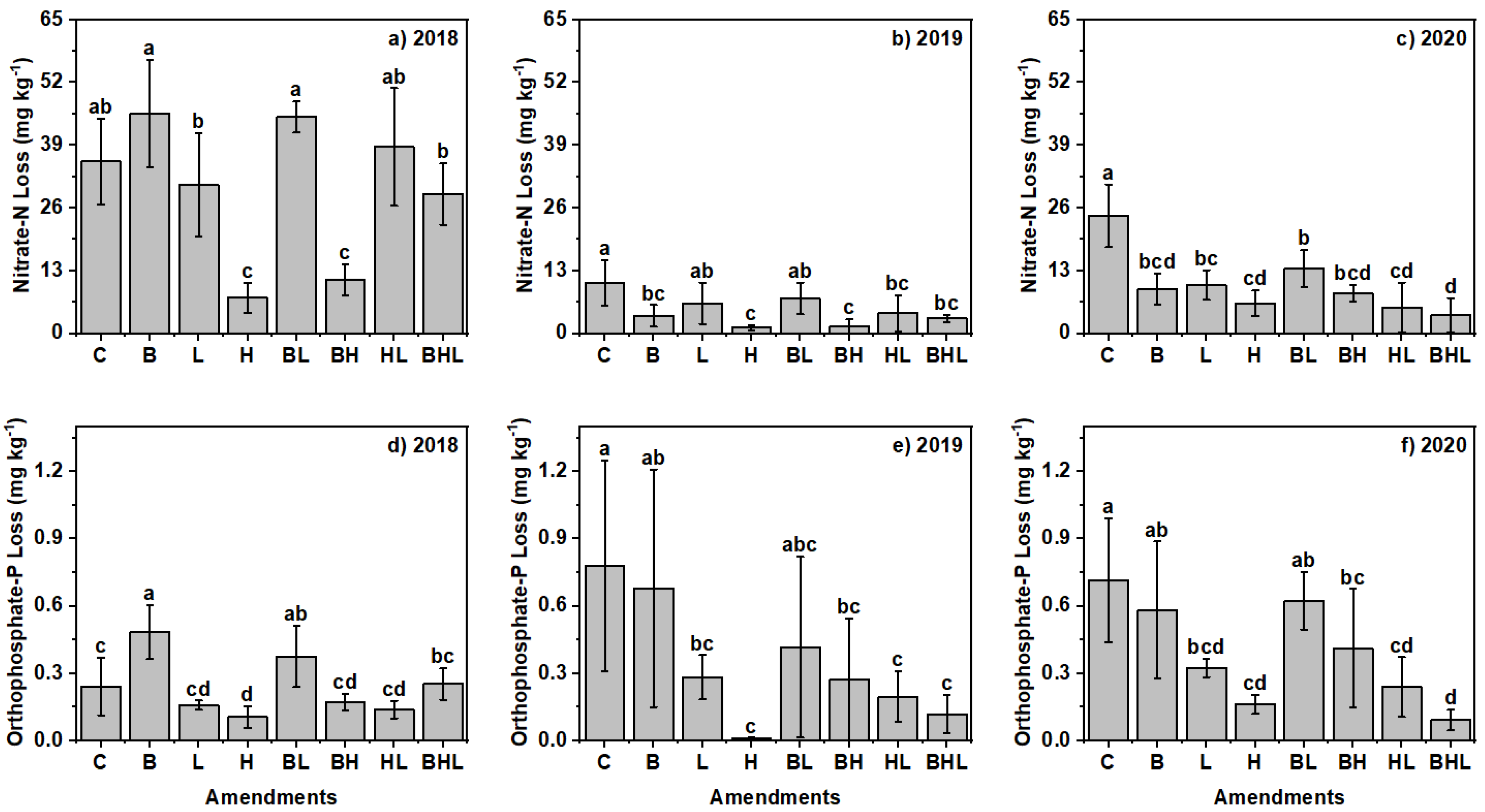
3.3. Effects of Soil Amendments on Nutrient Leaching
3.3.1. Nutrient Leaching Concentration
3.3.2. Nutrient Losses:
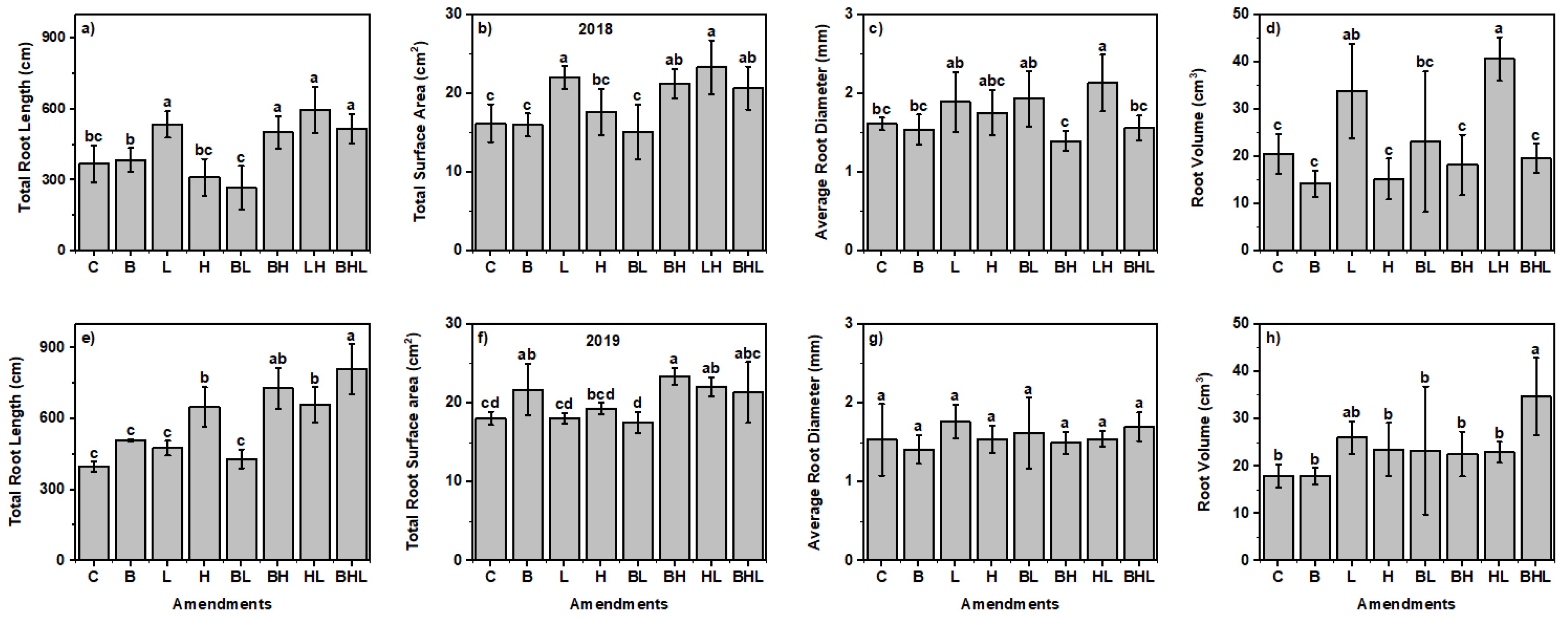
3.4. Soil Amendments Affected Plant Growth Parameters Based on Growth Stages
3.4.1. Plant Greenness (SPAD)
3.4.2. NDVI
3.4.3. Photosynthesis Rate
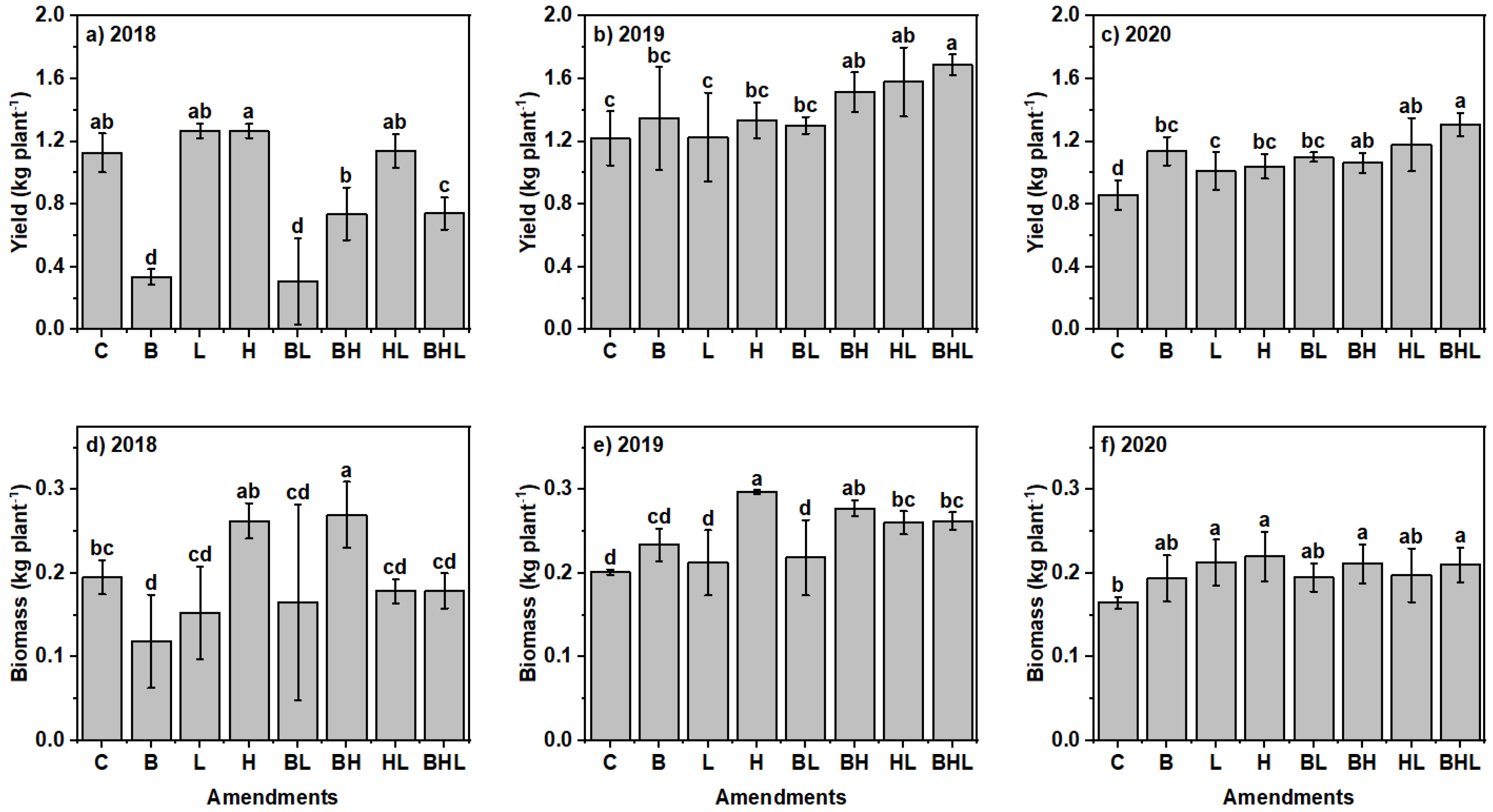
3.5. Soil Amendments Affected Plant Yield and Biomass
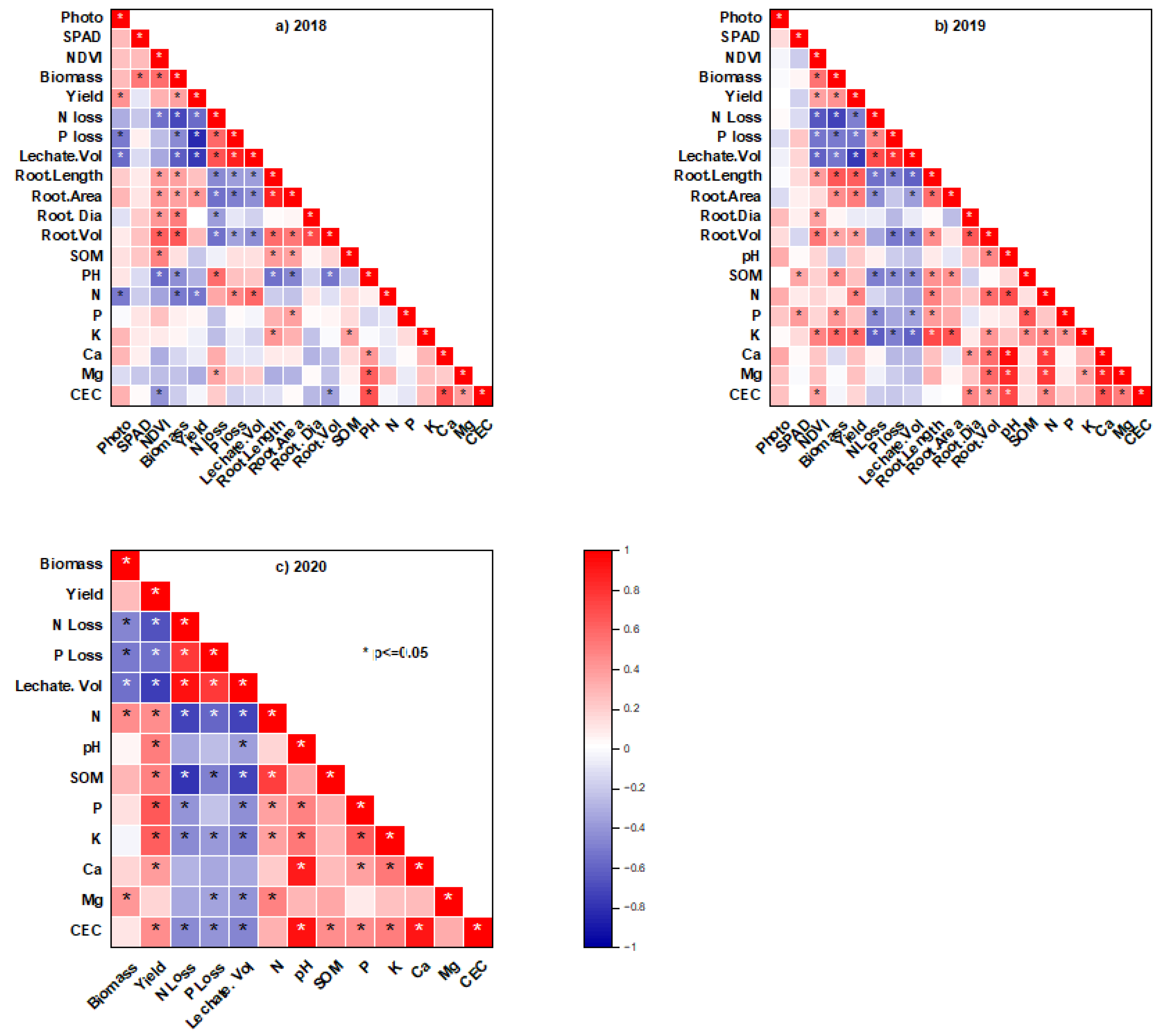
3.6. Correlation Between Leachate Properties, Soil and Plant Parameters
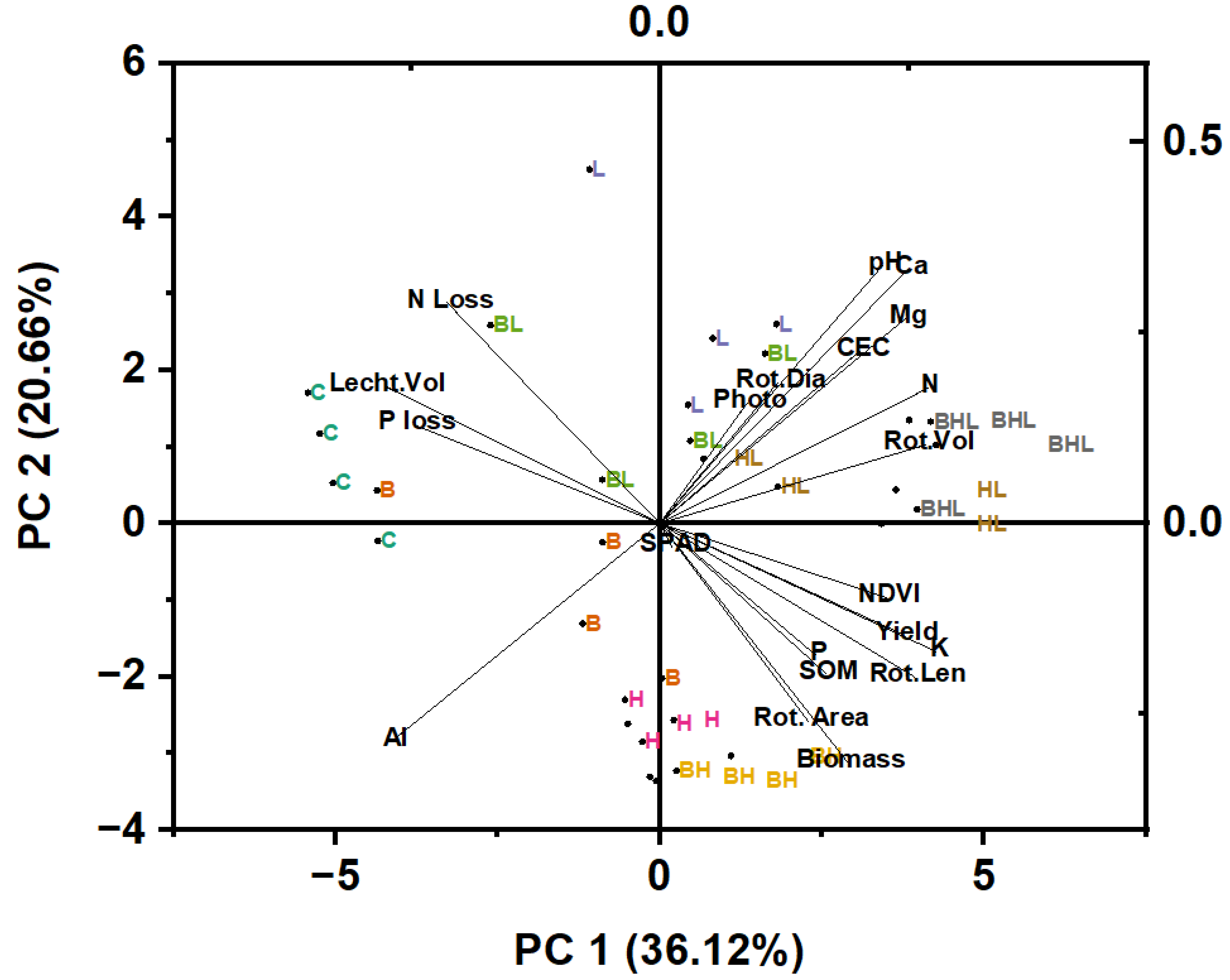
3.7. Principal Component Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Environmental and Economic Implications
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
References
- Kaur, S., & Chauhan, B. S. (2023). Challenges and opportunities to sustainable crop production. Plant Small RNA in Food Crops, 25-43. [CrossRef]
- Grassini, P., Bussel, v. L. G. J., Wart, v. J., Wolf, J., Claessens, L., Yang, H., Cassman, K. G. (2015). How good is good enough? Data requirements for reliable crop yield simulations and yield-gap analysis. Field Crops Research, 177, 49-63. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y., Feng, K., & Hubacek, K. (2013). Tele-connecting local consumption to global land use. Global Environmental Change, 23(5), 1178-1186. [CrossRef]
- El Idrissi, A., Dardari, O., Metomo, F. N. N. N., Essamlali, Y., Akil, A., Amadine, O., Zahouily, M. (2023). Effect of sodium alginate-based superabsorbent hydrogel on tomato growth under different water deficit conditions. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 253, 127229. [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J., Pereira da Silva, J., Steiner, C., Nehls, T., Zech, W., & Glaser, B. (2003). Nutrient availability and leaching in an archaeological Anthrosol and a Ferralsol of the Central Amazon basin: fertilizer, manure and charcoal amendments. Plant Soil, 249(2), 343-357. [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J., Kuzyakov, Y., Pan, G., & Ok, Y. S. (2015). Biochars and the plant-soil interface. Plant and Soil, 395, 1-5. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, E., Curaqueo, G., Cea, M., Vera, L., & Navia, R. (2017). Environmental hotspots in the life cycle of a biochar-soil system. Journal of Cleaner Production, 158, 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Singh Mavi, M., Singh, G., Singh, B. P., Singh Sekhon, B., Choudhary, O. P., Sagi, S., & Berry, R. (2018). Interactive effects of rice-residue biochar and N-fertilizer on soil functions and crop biomass in contrasting soils. Journal of Soil Science Plant Nutrition, 18(1), 41-59. [CrossRef]
- Tian, X., Li, C., Zhang, M., Wan, Y., Xie, Z., Chen, B., & Li, W. (2018). Biochar derived from corn straw affected availability and distribution of soil nutrients and cotton yield. PLoS ONE, 13(1), e0189924. [CrossRef]
- Purkaystha, J., Prasher, S., Afzal, M. T., Nzediegwu, C., & Dhiman, J. (2022). Wheat straw biochar amendment significantly reduces nutrient leaching and increases green pepper yield in a less fertile soil. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 28, 102655. [CrossRef]
- Arif, M., Ali, K., Jan, M. T., Shah, Z., Jones, D. L., & Quilliam, R. S. (2016). Integration of biochar with animal manure and nitrogen for improving maize yields and soil properties in calcareous semi-arid agroecosystems. Field Crops Research, 195, 28-35. [CrossRef]
- Agegnehu, G., Nelson, P. N., & Bird, M. I. (2016). Crop yield, plant nutrient uptake and soil physicochemical properties under organic soil amendments and nitrogen fertilization on Nitisols. Soil Tillage Research, 160, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y., Deng, C., Meng, F., Shi, Q., Feijen, J., & Zhong, Z. (2011). Novel injectable biodegradable glycol chitosan-based hydrogels crosslinked by Michael-type addition reaction with oligo (acryloyl carbonate)-b-poly (ethylene glycol)-b-oligo (acryloyl carbonate) copolymers. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 99(2), 316-326. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E. M. (2015). Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review. Journal of Advanced Research, 6(2), 105-121. [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z., Tian, X., Zhai, S., Liu, Z., Chu, P., Li, C., ... & Li, T. (2022). Co-application of controlled-release urea and a superabsorbent polymer to improve nitrogen and water use in maize. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 68(7), 914-928. [CrossRef]
- Rezashateri, M., Khajeddin, S. J., Abedi-Koupai, J., Majidi, M. M., & Matinkhah, S. H. (2017). Growth characteristics of Artemisia sieberi influenced by super absorbent polymers in texturally different soils under water stress condition. Archives of Agronomy Soil Science, 63(7), 984-997. [CrossRef]
- Elbarbary, A. M., & Ghobashy, M. M. (2017). Controlled release fertilizers using superabsorbent hydrogel prepared by gamma radiation. Radiochimica Acta 105(10), 865-876. [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, J., Prasher, S. O., ElSayed, E., Patel, R. M., Nzediegwu, C., & Mawof, A. (2021). Effect of hydrogel based soil amendments on heavy metal uptake by spinach grown with wastewater irrigation. Journal of Cleaner Production, 311, 127644. [CrossRef]
- Del Campo, M. M., Esteller, M., Morell, I., Expósito, J., Bandenay, G., & Díaz-Delgado, C. (2019). A lysimeter study under field conditions of nitrogen and phosphorus leaching in a turf grass crop amended with peat and hydrogel. Science of the Total Environment, 648, 530-541. [CrossRef]
- Omogbohu Anetor, M., & Akinkunmi Akinrinde, E. (2007). Lime effectiveness of some fertilizers in a tropical acid alfisol. Journal of Central European Agriculture, 8(1), 17-24.
- Ayalew, A. (2011). The influence of applying lime and NPK fertilizers on yield of maize and soil properties on acid soil of Areka, southern region of Ethiopia. Innovative Systems Design and Engineering, 2(7), 33-42.
- Fageria, N. K., & Nascente, A. S. (2014). Management of soil acidity of South American soils for sustainable crop production. Advances in Agronomy, 128, 221-275. [CrossRef]
- Raboin, L.-M., Razafimahafaly, A. H. D., Rabenjarisoa, M. B., Rabary, B., Dusserre, J., & Becquer, T. (2016). Improving the fertility of tropical acid soils: Liming versus biochar application? A long-term comparison in the highlands of Madagascar. Field Crops Research, 199, 99-108. [CrossRef]
- Ulén, B., & Etana, A. (2014). Phosphorus leaching from clay soils can be counteracted by structure liming. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B—Soil Plant Science, 64(5), 425-433. [CrossRef]
- Eslamian, F., Qi, Z., Tate, M. J., & Romaniuk, N. (2020). Lime application to reduce phosphorus release in different textured intact and small repacked soil columns. Journal of Soils Sediments, 20, 2053-2066. [CrossRef]
- Olsson, Å., Persson, L., & Olsson, S. (2019). Influence of soil characteristics on yield response to lime in sugar beet. Geoderma, 337, 1208-1217. [CrossRef]
- Holland, J. E., Bennett, A., Newton, A., White, P., McKenzie, B., George, T., Hayes, R. (2018). Liming impacts on soils, crops and biodiversity in the UK: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 610, 316-332. [CrossRef]
- Blomquist, J., Simonsson, M., Etana, A., & Berglund, K. (2018). Structure liming enhances aggregate stability and gives varying crop responses on clayey soils. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B—Soil & Plant Science, 68(4), 311-322. [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, J., Prasher, S. O., ElSayed, E., Patel, R. M., Nzediegwu, C., & Mawof, A. (2020). Heavy metal uptake by wastewater irrigated potato plants grown on contaminated soil treated with hydrogel based amendments. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 19, 100952. [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, J., Prasher, S. O., ElSayed, E., Patel, R., Nzediegwu, C., & Mawof, A. (2020). Use of polyacrylamide superabsorbent polymers and plantain peel biochar to reduce heavy metal mobility and uptake by wastewater-irrigated potato plants. Transactions of the ASABE, 63(1), 11-28. [CrossRef]
- Zainul, A., Hans-Werner, K., Bernhard, H., Bilquees, G., & Ajmal, K. (2017). Impact of a Biochar or a Compost-Biochar Mixture on Water relation, Nutrient uptake and Photosynthesis of Phragmites karka.. In: Pedosphere.
- Naeem, M. A., Khalid, M., Aon, M., Abbas, G., Amjad, M., Murtaza, B., Ahmad, N. (2018). Combined application of biochar with compost and fertilizer improves soil properties and grain yield of maize. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 41(1), 112-122. [CrossRef]
- Alkhasha, A., Al-Omran, A., & Louki, I. (2019). Impact of deficit irrigation and addition of biochar and polymer on soil salinity and tomato productivity. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 99(4), 380-394. [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M. E.-S., Al-Easily, I., & AS Nawar, D. (2017). Impact of biochar addition on productivity and tubers quality of some potato cultivars under sandy soil conditions. Egyptian Journal of Horticulture, 44(2), 199-217. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A., Elad, Y., Tsechansky, L., Abrol, V., Lew, B., Offenbach, R., & Graber, E. R. (2018). Biochar potential in intensive cultivation of Capsicum annuum L. (sweet pepper): crop yield and plant protection. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 98(2), 495-503. [CrossRef]
- De Lima, W. B., Cavalcante, A. R., Bonifácio, B. F., da Silva, A. A. R., de Oliveira, L. D., de Souza, R. F. A., & Chaves, L. H. G. (2019). Growth and development of bell peppers submitted to fertilization with biochar and nitrogen.
- Wang, G., Govinden, R., Chenia, H. Y., Ma, Y., Guo, D., & Ren, G. (2019). Suppression of Phytophthora blight of pepper by biochar amendment is associated with improved soil bacterial properties. Biology Fertility of Soils, 55, 813-824. [CrossRef]
- Xu, D., Zhao, Y., Zhou, H., & Gao, B. (2016). Effects of biochar amendment on relieving cadmium stress and reducing cadmium accumulation in pepper. Environmental Science Pollution Research, 23, 12323-12331. [CrossRef]
- yan, U., & El-Shimi, N. (2015). Effect of using some treatments on sweet pepper irrigation and its effect on fruit yield and its quality. Arab Universities Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 23(1), 25-36.
- Rasanjali, K.,, De Silva, C., & Priyadarshani, K. (2019). Influence of super absorbent polymers (saps) on irrigation interval and growth of black pepper (Piper nigrum L.) in nursery management. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.,Wang, C., Wang, J., Yang, Y., Han, K., Bakpa, E. P.,... Xie, J. (2023). Comprehensive fruit quality assessment and identification of aroma-active compounds in green pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Frontiers in Nutrition, 9, 1027605. [CrossRef]
- Benson, G., Obadofin, A., & Adesina, J. (2014). Evaluation of plant extracts for controlling insect pests of pepper (Caspicum spp.) in Nigeria humid rainforest. New York Science Journal, 7(1), 39-43.
- Hendershot, W. H., Lalande, H., & Duquette, M. (2008). Soil reaction and exchangeable acidity. Soil sampling and methods of analysis. In C. M.R. & GregorichE.G. (Eds.), Soil sampling and methods of analysis (2nd edition ed., pp. 173-178). Pinawa, Manitoba, Canada: CRC Press. [CrossRef]
- Schulte, E., Kaufmann, C., & Peter, J. (1991). The influence of sample size and heating time on soil weight loss-on-ignition. Communications in Soil Science Plant Analysis, 22(1-2), 159-168. [CrossRef]
- Ziadi, N., & Tran, T. S. (2008). Mehlich 3-extractable elements. Soil sampling and methods of analysis. In M. R. Carter & E. G. Gregorich (Eds.), Soil sampling and methods of analysis (2nd edition ed., pp. 81-88). Pinawa, Manitoba: CRC press. [CrossRef]
- ugdug, A. A., Chang, S. X., Ok, Y. S., Rajapaksha, A. U., & Anyia, A. (2018). Phosphorus sorption capacity of biochars varies with biochar type and salinity level. Environmental science and pollution research international, 25(26), 25799-25812. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C. J. (2005). Chemical facts pertaining to environmental uses for lime. USA: Graymont Inc. Booklet.
- Brunauer, S., Emmett, P. H., & Teller, E. (1938). Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 60(2), 309-319. [CrossRef]
- El-Tohamy, W. A., El-Abagy, H. M., Ahmed, E. M., Aggor, F. S., & Hawash, S. I. (2014). Application of super absorbent hydrogel poly (acrylate/acrylic acid) for water conservation in sandy soil. Transaction of the Egyptian Society of Chemical Engineering, 40(2), 1-8.
- Ahmed, E. M., Aggor, F. S., Nada, S. S., & Hawash, S. J. I. J. S. E. R. (2015). Synthesis and characterization of super absorbent polymers for agricultural purposes. International Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research, 6(3), 282-287.
- Batool, A., Taj, S., Rashid, A., Khalid, A., Qadeer, S., Saleem, A. R., & Ghufran, M. A. (2015). Potential of soil amendments (Biochar and Gypsum) in increasing water use efficiency of Abelmoschus esculentus L. Moench. Frontiers in plant science, 6, 733. [CrossRef]
- Suresh, R., Prasher, S. O., Patel, R. M., Qi, Z., Elsayed, E., Schwinghamer, T., & Ehsan, A. M. (2018). Super absorbent polymer and irrigation regime effects on growth and water use efficiency of container-grown cherry tomatoes. Transactions of the ASABE, 61(2), 523-531. [CrossRef]
- Pellerin, A. (2010). Les grilles de référence. In L. o.-E. t. Parent & G. Gagné (Eds.), Guide de Référence en Fertilisation (2e édition ed., pp. 359-471). Québec, Canada: Centre de Référence en Agriculture et Agroalimentaire du Québec.
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). (2008). Chapter 2: Crop water needs. Retrieved from http://www.fao.org/3/s2022e/s2022e02.
- Smittle, D. A., Dickens, W. L., & Stansell, J. R. (1994). Irrigation regimes affect yield and water use by Bell Pepper. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science., 119(5), 936. [CrossRef]
- Netto, A. T., Campostrini, E., de Oliveira, J. G., & Bressan-Smith, R. E. (2005). Photosynthetic pigments, nitrogen, chlorophyll a fluorescence and SPAD-502 readings in coffee leaves. Scientia Horticulturae, 104(2), 199-209. [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A. K., Chai, L., Singh, R. P., & Kafatos, M. (2006). Crop yield estimation model for Iowa using remote sensing and surface parameters. International Journal of Applied Earth Observations and Geoinformation, 8(1), 26-33. [CrossRef]
- Hui, D., Yu, C.-L., Deng, Q., Saini, P., Collins, K., & Koff, J. (2018). Weak effects of biochar and nitrogen fertilization on Switchgrass photosynthesis, biomass, and soil respiration. Agriculture, 8(9), 143. [CrossRef]
- Sigge, G. O., Hansmann, C. F., & Joubert, E. (1998). Effect of temperature and relative humidity on the drying rates and drying times of green bell peppers (Capsicum annuum L.) Drying Technology, 16(8), 1703-1714. [CrossRef]
- Achalu, C., Heluf, G., Kibebew, K., Abi, T. (2012). Status of selected physicochemical properties of soils under different land use systems of Western Oromia, Ethiopia. Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences, 2(3), 57-71.
- Liang, B., Lehmann, J., Solomon, D., Kinyangi, J., Grossman, J., O’Neill, B., . . . Petersen. (2006). Black carbon increases cation exchange capacity in soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 70(5), 1719-1730. [CrossRef]
- Maru, A., Haruna, A. O., Asap, A., Majid, N. M. A., Maikol, N., & Jeffary, A. V. (2020). Reducing acidity of tropical acid soil to improve phosphorus availability and Zea mays L. Productivity through efficient use of chicken litter biochar and triple superphosphate. Applied Sciences, 10(6), 2127. [CrossRef]
- Suliman, W., Harsh, J. B., Abu-Lail, N. I., Fortuna, A. M., Dallmeyer, I., & Garcia-Pérez, M. (2017). The role of biochar porosity and surface functionality in augmenting hydrologic properties of a sandy soil. Science of the Total Environment, 574, 139-147. [CrossRef]
- Barman, M., Shukla, L. M., Datta, S. P., & Rattan, R. K. (2014). Effect of applied lime and boron on the availability of nutrients in an acid soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 37(3), 357-373. [CrossRef]
- Farina, M. P. W., Channon, P., & Thibaud, G. R. (2000). A Comparison of Strategies for Ameliorating Subsoil Acidity I. Long-Term Growth Effects. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 64(2), 646-651. [CrossRef]
- Conyers, M., Heenan, D., McGhie, W., & Poile, G. (2003). Amelioration of acidity with time by limestone under contrasting tillage. Soil and Tillage Research, 72(1), 85-94. [CrossRef]
- Major, J., Rondon, M., Molina, D., Riha, S. J., & Lehmann, J. (2012). Nutrient Leaching in a colombian savanna oxisol amended with biochar. Journal of Environmental lity, 41(4), 1076-1086. [CrossRef]
- Parvage, M. M., Ulén, B., Eriksson, J., Strock, J., & Kirchmann, H. (2013). Phosphorus availability in soils amended with wheat residue char. J Biology fertility of soils, 49(2), 245-250. [CrossRef]
- Vandecasteele, B., Sinicco, T., D’Hose, T., Nest, T. V., & Mondini, C. (2016). Biochar amendment before or after composting affects compost quality and N losses, but not P plant uptake. Journal of Environmental Management, 168, 200-209. [CrossRef]
- Chintala, R., Schumacher, T. E., McDonald, L. M., Clay, D. E., Malo, D. D., Papiernik, S. K., . . . Julson, J. L. (2014). Phosphorus sorption and availability from biochars and soil/B iochar mixtures. CLEAN–Soil, Air, Water, 42(5), 626-634. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S., Fahmy, A. J. J. o. S. S., & Engineering, A. (2019). Applications of natural polysaccharide polymers to overcome water scarcity on the yield and quality of tomato fruits. Journal of Soil Sciences Agricultural Engineering10(4), 199-208. [CrossRef]
- Costa, M. C. G., Freire, A. G., Lourenço, D. V., Sousa, R. R. d., Feitosa, J. P. d. A., & Mota, J. C. A. (2021). Hydrogel composed of potassium acrylate, acrylamide, and mineral as soil conditioner under saline conditions. Scientia Agricola, 79. [CrossRef]
- Abobatta, W. (2018). Impact of hydrogel polymer in agricultural sector. Adv. Agric. Environ. Sci. Open Access, 1(2), 59-64. [CrossRef]
- Wu, X., Sun, L., Qin, B., Wang, T., Wang, Y., Zhao, J., & Fu, Y. (2024). Novel antimicrobial polysaccharide hydrogel with fertilizer slow-release function for promoting Sesamum indicum L. seeds germination. Polymer, 311, 127491. [CrossRef]
- Tariq, M., & Mott, C. J. B. (2006). Effect of boron supply on the uptake of micronutrients by radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Journal of Agricultural and Biological Science, 1(2), 1-8.
- Yu, J., Shi, J., Ma, X., Dang, P., Yan, Y., Mamedov, A. I., Levy, G. J. (2017). Superabsorbent polymer properties and concentration effects on water retention under drying conditions. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 81(4), 889-901. [CrossRef]
- Mohawesh, O., & Durner, W. (2019). Effects of bentonite, hydrogel and biochar amendments on soil hydraulic properties from saturation to oven dryness. Pedosphere, 29(5), 598-607. [CrossRef]
- Paluszek, J. (2010). Quality of structure and water-air properties of eroded Haplic Luvisol treated with gel-forming polymer. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 19(6), 1287.
- Knowles, O., Robinson, B., Contangelo, A., & Clucas, L. (2011). Biochar for the mitigation of nitrate leaching from soil amended with biosolids. Science of the total Environment, 409(17), 3206-3210. [CrossRef]
- Laird, D., Fleming, P., Wang, B., Horton, R., & Karlen, D. (2010). Biochar impact on nutrient leaching from a Midwestern agricultural soil. Geoderma, 158(3-4), 436-442. [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, S., Meinders, M. B., Stoof, C. R., Bezemer, T. M., van de Voorde, T. F., Mommer, L., & van Groenigen, J. W. (2015). Biochar application does not improve the soil hydrological function of a sandy soil. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 251, 47-54. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y., Brickler, C., Li, S., & Chen, G. (2021). Synthesis of microwave-mediated biochar-hydrogel composites for enhanced water absorbency and nitrogen release. Polymer Testing, 93, 106996. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y., Yang, L., & Xue, L. (2019). Effects of biochar addition on nitrogen leaching loss in the vegetable soil. Journal of Advanced Agricultural Technologies, 6(2). [CrossRef]
- Hardie, M. A., Oliver, G., Clothier, B. E., Bound, S. A., Green, S. A., & Close, D. C. (2015). Effect of biochar on nutrient leaching in a young apple orchard. Journal of Environmental Quality, 44(4), 1273-1282. [CrossRef]
- Bu, X., Xue, J., Zhao, C., Wu, Y., & Han, F. (2017). Nutrient leaching and retention in riparian soils as influenced by rice husk biochar addition. Soil Science, 182(7), 241-247. [CrossRef]
- Silva, I. C. B. d., Basílio, J. J. N., Fernandes, L. A., Colen, F., Sampaio, R. A., & Frazão, L. A. (2017). Biochar from different residues on soil properties and common bean production. Scientia Agricola, 74, 378-382. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B. T., Phan, B. T., Nguyen, T. X., Nguyen, V. N., Van Tran, T., & Bach, Q.-V. (2020). Contrastive nutrient leaching from two differently textured paddy soils as influenced by biochar addition. Journal of Soils Sediments, 20(1), 297-307. [CrossRef]
- yvertsen, J., & Dunlop, J. (2004). Hydrophilic gel amendments to sand soil can increase growth and nitrogen uptake efficiency of citrus seedlings. Horticultural Science, 39, 267-271. [CrossRef]
- Arbona, V., Iglesias, D. J., Jacas, J., Primo-Millo, E., Talon, M., & Gómez-Cadenas, A. (2005). Hydrogel substrate amendment alleviates drought effects on young citrus plants. Plant Soil, 270, 73-82. [CrossRef]
- Rubin, R. L., Anderson, T. R., & Ballantine, K. A. (2020). Biochar simultaneously reduces nutrient leaching and greenhouse gas emissions in restored wetland soils. Wetlands, 40(6), 1981-1991. [CrossRef]
- Kalu, S., Oyekoya, G. N., Ambus, P., Tammeorg, P., Simojoki, A., Pihlatie, M., & Karhu, K. (2021). Effects of two wood-based biochars on the fate of added fertilizer nitrogen—a 15 N tracing study. Biology Fertility of Soils, 57, 457-470. 10.1007/s00374-020-01534-0. [CrossRef]
- Alkharabsheh, H. M., Seleiman, M. F., Battaglia, M. L., Shami, A., Jalal, R. S., Alhammad, B. A., . . . Al-Saif, A. M. (2021). Biochar and its broad impacts in soil quality and fertility, nutrient leaching and crop productivity: A review. Agronomy, 11(5), 993. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y., Silveira, M. L., O’Connor, G. A., Vendramini, J. M., Erickson, J. E., Li, Y. C., & Cavigelli, M. (2020). Biochar impacts on nutrient dynamics in a subtropical grassland soil: 1. Nitrogen and phosphorus leaching (0047-2425). [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, S., & Jayaganesh, S. (2010). Characterisation of magnesium toxicity, its influence on amino acid synthesis pathway and biochemical parameters of tea. Phytochem, 4, 67-77. [CrossRef]
- Haider, G., Steffens, D., Moser, G., Müller, C., & Kammann, C. I. (2016). Biochar reduced nitrate leaching and improved soil moisture content without yield improvements in a four-year field study. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 237, 80-94. [CrossRef]
- Sadaf, J., Shah, G. A., Shahzad, K., Ali, N., Shahid, M., Ali, S., ... & Rashid, M. I. (2017). Improvements in wheat productivity and soil quality can accomplish by co-application of biochars and chemical fertilizers. Science of the Total Environment, 607, 715-724. [CrossRef]
- Sänger, A., Reibe, K., Mumme, J., Kaupenjohann, M., Ellmer, F., Roß, C.-L., & Meyer-Aurich, A. (2017). Biochar application to sandy soil: effects of different biochars and N fertilization on crop yields in a 3-year field experiment. Archives of Agronomy Soil Science, 63(2), 213-229. [CrossRef]
- Kammann, C. I., Schmidt, H. P., Messerschmidt, N., Linsel, S., Steffens, D., Müller, C., ... & Joseph, S. (2015). Plant growth improvement mediated by nitrate capture in co-composted biochar. Scientific Reports, 5(1), 11080. [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y., Gao, B., Zhang, M., Inyang, M., & Zimmerman, A. R. (2012). Effect of biochar amendment on sorption and leaching of nitrate, ammonium, and phosphate in a sandy soil. Chemosphere, 89(11), 1467-1471. [CrossRef]
- Cong, M., Hu, Y., Sun, X., Yan, H., Yu, G., Tang, G., . . . Jia, H. (2023). Long-term effects of biochar application on the growth and physiological characteristics of maize. Frontiers in Plant Science, 14, 1172425. [CrossRef]
- Hou, X., Li, R., He, W., Dai, X., Ma, K., & Liang, Y. (2018). Superabsorbent polymers influence soil physical properties and increase potato tuber yield in a dry-farming region. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 18, 816-826. [CrossRef]
- Blumenschein, T. G., Nelson, K. A., & Motavalli, P. P. (2018). Impact of a new deep vertical lime placement practice on corn and soybean production in conservation tillage systems. Agronomy, 8(7), 104. [CrossRef]
- Godsey, C. B., Pierzynski, G. M., Mengel, D. B., & Lamond, R. E. (2007). Management of soil acidity in no-till production systems through surface application of lime. Agronomy Journal, 99(3), 764-772. [CrossRef]
- Brown, T. T., Koenig, R. T., Huggins, D. R., Harsh, J. B., & Rossi, R. E. (2008). Lime effects on soil acidity, crop yield, and aluminum chemistry in direct-seeded cropping systems. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 72, 634-640.
- Caires, E., Joris, H., & Churka, S. (2011). Long-term effects of lime and gypsum additions on no-till corn and soybean yield and soil chemical properties in southern Brazil. Soil Use and Management, 27(1), 45-53. [CrossRef]
- Wan, H., Liu, X., Shi, Q., Chen, Y., Jiang, M., Zhang, J., . . . Hossain, M. A. (2023). Biochar amendment alters root morphology of maize plant: Its implications in enhancing nutrient uptake and shoot growth under reduced irrigation regimes. Frontiers in Plant Science, 14, 1122742. [CrossRef]
- Mosharrof, M., Uddin, M. K., Sulaiman, M. F., Mia, S., Shamsuzzaman, S. M., & Haque, A. N. A. (2021). Combined Application of Rice Husk Biochar and Lime Increases Phosphorus Availability and Maize Yield in an Acidic Soil. Agriculture, 11(8), 793. [CrossRef]
- Guan, X., Zhou, J., Ma, N., Chen, X., Gao, J., & Zhang, R. (2015). Studies on modified conditions of biochar and the mechanism for fluoride removal. Desalination and ter Treatment, 55(2), 440-447. [CrossRef]
- Palta, J. A., & Yang, J. C. (2014). Crop root system behaviour and yield preface. Field Crops Res 165:1–4. [CrossRef]
- Orikiriza, L. J., Agaba, H., Tweheyo, M., Eilu, G., Kabasa, J. D., & Huettermann, A. (2009). Amending soils with hydrogels increases the biomass of nine tree species under Non-water stress conditions. Clean–Soil, Air, Water, 37(8), 615-620. [CrossRef]
- Najafinezhad, H., Tahmasebi Sarvestani, Z., Modarres Sanavy, S. A. M., & Naghavi, H. (2015). Evaluation of yield and some physiological changes in corn and sorghum under irrigation regimes and application of barley residue, zeolite and superabsorbent polymer. Archives of Agronomy Soil Science, 61(7), 891-906. [CrossRef]
- Liu, R., Gu, M., Huang, L., Yu, F., Jung, S.-K., & Choi, H.-S. (2019). Effect of pine wood biochar mixed with two types of compost on growth of bell pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Horticulture, Environment, and Biotechnology, 60(3), 313-319. [CrossRef]
- Mawof, A., Prasher, S., Bayen, S., & Nzediegwu, C. (2021). Effects of Biochar and Biochar-Compost Mix as Soil Amendments on Soil Quality and Yield of Potatoes Irrigated with Wastewater. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 21(4), 2600-2612. [CrossRef]
- Paulus, A., & Anyi, W. (2011). Pepper production technology in Malaysia,(eds.). In L. K. F. a. S. S. Liang (Ed.), (pp. 3-2). Kuching, Malaysia: Malaysian Pepper Board.
- Sulok, K. M. T., Ahmed, O. H., Khew, C. Y., Zehnder, J. A. M., Lai, P. S., Jalloh, M. B., Abdu, A. (2021). Effects of Organic Amendments Produced from Agro-Wastes on Sandy Soil Properties and Black Pepper Morpho-Physiology and Yield. Agronomy, 11(9), 1738. [CrossRef]
- Heidari, F., Tilaki, G. A. D., & Kooch, Y. (2022). Effects of Drought Stress on Morphological and Physiological Traits of Kochia Prostrata (L.). International Journal of Natural Sciences Research, 10(2), 102-115.
- hang, Y.-s., Tang, G.-m., Long, X.-s., Ge, C.-h., & Xu, W.-l. (2021). Effects of one\| time biochar input on soil properties and corn yield in irrigation sandy soil.
| Properties | Soil | Hardwood Biochar |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size distribution (%) | ||
| Sand | 83 | - |
| Silt | 13 | - |
| Clay | 4 | - |
| Texture | Loamy sand | - |
| Bulk density (Mg m-3) | 1.29 ± 0.05 | |
| pH | 5.57+0.087 | 9.96 ± 0.01 |
| EC (1:5) (dS m−1) | 0.27 ± 0.01 | |
| SOM (%) | 3.28+0.42 | - |
| BET Surface area (m2 g−1) | - | 324.6 |
| Pore volume (cm3 g−1) | 0.02 | |
| Ash content (%) | 35.8 ± 1.4 | |
| Pore size (nm) | 17.44 | |
| Pyrolysis temperature (°C) | 500–550 | |
| Available nutrients (mg kg-1) | ||
| C | - | 892200 |
| H | - | 26700 |
| O | - | 79000 |
| S | - | 100 |
| N | 15.2±7.65 | 2000 |
| NH4+ | 4.59±0.54 | 3130 ± 0.34 |
| P | 125.36±9.71 | 350 |
| K | 121.40±35.68 | 2700 ± 0.24 |
| Ca | 1602.33±99.81 | 1700± 0.23 |
| Mg | 85.73±21.95 | 180± 0.01 |
| Al | 1453.47±12.89 | - |
| Na | 380± 0.06 | |
| CEC (cmol (+) kg-1) | 8.19±0.39 | 18 |
| Base saturation (%) | 99.68±0.32 | - |
| Year | Amendments | pH | SOM (%) | NO3- -N (mg kg-1) | AV P (mg kg-1) | AV K (mg kg-1) | AV Ca (mg kg-1) | AV Mg (mg kg-1) | AV Al (mg kg-1) | CEC (cmol (+) kg-1) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | C | 5.7 ± 0.28 d | 2.04 ± 0.08 bc | 3.77 ± 1.06 c | 132.00 ± 38.14 a | 109.50 ± 35.50 d | 1252.50 ± 316.90 c | 53.22 ± 8.26 c | 1420.00 ± 48.30 a | 6.71 ± 1.33 d |
| B | 6.20 ± 0.12 c | 2.62 ± 0.15 ab | 13.38 ± 4.06 a | 148.50 ± 33.21 a | 174.50 ± 29.35 bcd | 1400.00 ± 153.84 c | 68.50 ± 9.38 ab | 1447.50 ± 12.58 a | 8.94 ± 0.84 c | |
| L | 6.95 ± 0.48 ab | 1.75 ± 0.76 c | 7.66 ± 1.76 b | 145.00 ± 35.29 a | 113.25 ± 25.51 d | 2062.5 ± 241.72 bc | 62.52 ± 4.60 abc | 1237.50 ± 26.30 b | 13.31 ± 1.55 ab | |
| H | 5.35 ± 0.25 d | 2.14 ± 0.45 abc | 4.39 ± 2.27 bc | 176.33 ± 62.22 a | 182.00 ± 45.96 bc | 1070.00 ± 229.20c | 51.20 ± 16.12 c | 1435.00 ± 78.52 a | 9.00 ± 1.94 c | |
| BL | 7.1 ± 0.10 a | 2.044 ± 0.83 bc | 7.32 ± 3.48 bc | 136.00 ± 8.75 a | 140.75 ± 26.45 cd | 2837.50 ± 1000.00 ad | 73.52 ± 4.03 a | 1197.51 ± 49.91 bc | 13.48 ± 1.31 ab | |
| BH | 5.32 ± 0.47 d | 2.78 ± 0.20 ab | 7.89 ± 1.91 b | 149.67 ± 4.76 a | 181.67 ± 11.90 bc | 1827.50 ± 1354.93 bc | 55.93 ± 16.08 bc | 1455.00 ± 90.36 a | 8.79 ± 0.61 c | |
| HL | 6.65 ± 0.23 abc | 2.85 ± 0.13 a | 5.21 ± 1.55 bc | 172.66 ± 27.18 a | 216.75 ± 79.35 ab | 3840.00 ± 179.63 a | 71.25 ± 5.68 a | 1132.49 ± 20.61 c | 14.84 ± 1.31 a | |
| BHL | 6.55 ± 0.40 bc | 2.56 ± 0.21 ab | 5.64 ± 0.71 bc | 178.50 ± 17.60 a | 264.25 ± 72.03 a | 2645.00 ± 1085.56 b | 63.60 ± 7.44 abc | 1185.00 ± 69.52 bc | 12.09 ± 0.85 b | |
| 2019 | C | 5.55 ± 0.51 c | 2.58 ± 0.12 b | 1.37 ± 0.06 de | 227.60 ± 12.78 b | 95.00 ± 11.53 d | 1145.67 ± 371.54 d | 47.00 ± 13.00 e | 1584.00 ± 89.01 a | 7.36 ± 2.72 c |
| B | 6.11 ± 0.20 b | 3.18 ± 0.23 a | 2.67 ± 0.38 c | 338.38 ± 33.16 a | 148.66 ± 31.08 bcd | 1352.33 ± 204.96 d | 55.00 ± 5.00 bcde | 1551.00 ± 44.24 a | 11.82 ± .86 b | |
| L | 7.38 ± 0.09 a | 3.16 ± 0.10 a | 2.78 ± 0.44 c | 287.03 ± 30.87 ab | 138.67 ± 68.06 d | 3459. 35 ± 442.56 ab | 65.68 ± 9.30 ab | 1334 .00 ± 23.34 bc | 16.92 ± 5.26 a | |
| H | 5.73 ± 0.04 c | 3.46 ± 0.15 a | 1.57 ± 0.04 de | 329.27 ± 68.00 a | 145.66 ± 1.15 cd | 1266.68 ± 146.96 d | 50.33 ± 4.93 de | 1524. 34 ± 43.57 a | 8.61 ± 0.94 bc | |
| BL | 7.17 ± 0.08 a | 3.44 ± 0.27 a | 2.24 ± 0.60 cd | 314.17 ± 54.29 a | 131.33 ± 21.47 d | 2869.33 ± 293.68 c | 63.00 ± 4.36 bc | 1377.68 ± 30.02 b | 12.44 ± 2.64 a | |
| BH | 5.82 ± 0.06 bc | 3.52 ± 0.15 a | 1.32 ± 0.34 e | 308.30 ± 32.70 a | 211.00 ± 18.73 a | 1341.33 ± 101.95 d | 51.57 ± 5.85 cde | 1560.00 ± 52.74 a | 9.58 ± 0.41 bc | |
| HL | 7.26 ± 0.11 a | 3.22 ± 0.23 a | 3.98 ± 0.57 b | 309.43 ± 26.91 a | 203.33 ± 28.94 ab | 3148.69 ± 411.63 bc | 62.00 ± 6.08 bcd | 1276.35 ± 56.20 c | 14.23 ± 0.95 a | |
| BHL | 7.26 ± 0.2 a | 3.31 ± 0.44 a | 5.67 ± 1.01 a | 318.50 ± 23.52 a | 200.68 ± 13.20 abc | 3811.00 ± 376.26 a | 75.68 ± 2.31 a | 1272.68 ± 16.07 c | 12.54 ± 0.65a | |
| 2020 | C | 5.33 ± 0.21 c | 2.60 ± 0.21 b | 2.78 ± 1.14 b | 283.27 ± 59.25 c | 98.44 ± 3.75 b | 946.47 ± 223.08 b | 31.38 ± 10.72 c | 2617.33 ± 313.46 a | 8.61 ± 0.68 d |
| B | 5.95 ± 0.25 b | 3.41 ± 0.28 a | 5.71 ± 0.51 a | 474.00 ± 181.03 ab | 131.97 ± 38.38 b | 977.13 ± 349.37 b | 48.78 ± 8.53 abc | 2641.21 ± 586.62 a | 10.63 ± 0.58 bc | |
| L | 6.96 ± 0.27 a | 3.37 ± 0.23 a | 4.78 ± 0.75 a | 366.93 ± 97.04 abc | 103.84 ± 27.27 b | 2566.67 ± 310.31 a | 65.98 ± 33.19 a | 1038.67 ± 209.77 b | 14.29 ± 1.10 a | |
| H | 5.16 ± 0.15 c | 3.36 ± 0.17 a | 5.78 ± 0.57 a | 370.07 ± 31.66 abc | 112.61 ± 42.48 b | 821.07 ± 66.81 b | 47.14 ± 9.28 abc | 2242.67 ± 65.86 a | 9.60 ± 0.41 cd | |
| BL | 7.01 ± 0.11 a | 3.21 ± 0.21 a | 4.70 ± 0.65 a | 427.13 ± 62.34 abc | 128.50 ± 16.92 b | 2558.62 ± 256.85 a | 36.64 ± 5.02 bc | 1132.47 ± 156.11 b | 13.72 ± 0.76 bc | |
| BH | 5.33 ± 0.11 c | 3.32 ± 0.21 a | 5.70 ± 0.91 a | 319.80 ± 44.35 bc | 116.74 ± 11.98 b | 953.93 ± 125.31 b | 50.98 ±6.52 abc | 2304.68 ± 234.83 a | 9.75 ± 0.58 cd | |
| HL | 7.00 ± 0.21 a | 3.35 ± 0.21 a | 5.56 ± 1.54 a | 494.53 ± 130.30 a | 199.80 ± 36.13 a | 2682.00 ± 633.75 a | 57.94 ± 6.74 ab | 1192.66 ± 310.72 b | 14.70 ± 1.52 ab | |
| BHL | 6.98 ± 0.15 a | 3.45 ± 0.29 a | 6.09 ± 0.19 a | 464.8 ± 83.66 ab | 204.25 ± 9.88 a | 2800.00 ± 675.56 a | 56.68 ± 9.22 ab | 1418.00 ± 152.00 b | 13.83 ± 1.16 bc |
| Amendments | Plant Growth Parameters and Growing Stages | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GI (SPAD) | NDVI | PS | |||||||
| Growing | Flowering | Fruiting | Growing | Flowering | Fruiting | Growing | Flowering | Fruiting | |
| 2018 | |||||||||
| C | 66.90 ±1.57 | 71.15 ± 1.70 | 70.50 ± 2.07 | 0.76 ± 0.05 | 0.91 ± 0.01 | 0.84 ± 0.01 | 17.3 ± 1.67 | 18.27 ± 4.03 | 16.30 ± 1.18 |
| B | 70.76 ±4.40 | 70.42 ± 3.61 | 66.16 ± 6.30 | 0.73 ± 0.04 | 0.82 ± 0.09 | 0.74 ± 0.05 | 14.20 ± 1.69 | 15.18 ± 4.14 | 16.15 ± 2.58 |
| L | 65.64 ± 2.27 | 71.04 ± 3.63 | 69.59 ± 7.27 | 0.69 ± 0.05 | 0.83 ± 0.04 | 0.69 ± 0.01 | 17.25 ± 2.11 | 19.52 ± 5.82 | 14.37 ± 2.22 |
| H | 69.90 ± 0.72 | 71.93 ± 0.56 | 70.98 ± 2.04 | 0.79 ± 0.04 | 0.90 ± 0.03 | 0.85 ± 0.02 | 13.73 ± 2.98 | 20.27 ± 2.41 | 15.2 ± 2.63 |
| BL | 64.8 ± 10.09 | 63.65 ±15.25 | 65.36 ± 14.43 | 0.69 ± 0.08 | 0.81 ± 0.14 | 0.81 ± 0.13 | 13.73 ± 2.18 | 11.94 ± 10.09 | 15.13 ± 0.90 |
| BH | 68.8 ± 1.45 | 73.52 ± 1.75 | 69.09 ± 4.34 | 0.79 ± 0.6 | 0.89 ± 0.03 | 0.88 ± 0.01 | 15.47 ± 1.68 | 22.72 ± 1.18 | 18.00 ± 0.97 |
| HL | 70.19 ± 2.67 | 70.11 ± 4.53 | 68.58 ± 1.54 | 0.69 ± 0.5 | 0.87 ± 0.03 | 0.83 ± 0.1 | 16.07 ± 1.88 | 20.70 ± 1.83 | 13.03 ± 4.73 |
| BHL | 69.27 ± 2.05 | 70.71 ± 4.96 | 70.77 ± 1.23 | 0.74 ± 0.06 | 0.85 ± 0.05 | 0.83 ± 0.01 | 15.10 ± 3.54 | 21.65 ± 1.04 | 19.85 ± 2.21 |
| 2019 | |||||||||
| C | 64.95 ± 2.84 | 68.98 ± 0.45 | 63.03 ± 2.60 | 0.87 ± 0.1 | 0.92 ± 0.02 | 0.89 ± 0.01 | 17.66 ± 2.80 | 18.10 ± 1.06 | 15.42 ± 1.67 |
| B | 62.06 ± 2.45 | 72.08 ± 2.77 | 68.4 ± 6.67 | 0.88 ± 0.01 | 0.93 ± 0.02 | 0.91 ± 0.01 | 18.10 ± 3.47 | 19.42 ± 1.36 | 14.83 ± 2.13 |
| L | 62.71 ± 2.65 | 68.48 ± 1.22 | 67.27 ± 2.92 | 0.90 ± 0.03 | 0.94 ± 0.01 | 0.93 ± 0.02 | 18.42 ± 1.66 | 19.60 ± 1.71 | 15.79 ± 1.05 |
| H | 63.03 ± 2.57 | 70.45 ± 1.56 | 67.71 ± 1.61 | 0.91 ± 0.01 | 0.94 ± 0.01 | 0.92 ± 0.02 | 17.30 ± 1.52 | 18.10 ± 2.21 | 16.23 ± 1.83 |
| BL | 62.72 ± 1.21 | 70.81 ± 2.53 | 68.23 ±1.89 | 0.88 ± 0.04 | 0.93 ± 0.02 | 0.92 ± 0.03 | 17.15 ± 1.11 | 18.32 ± 0.80 | 17.79 ± 2.50 |
| BH | 62.56 ± 2.18 | 68.81 ± 1.40 | 68.72 ± 1.91 | 0.90 ± 0.01 | 0.94 ± 0.02 | 0.92 ± 0.02 | 15.11 ± 2.39 | 18.57 ± 0.87 | 14.94 ± 1.38 |
| HL | 64.96 ± 1.28 | 68.7 ± 1.69 | 68.26 ± 1.76 | 0.89 ± 0.03 | 0.95 ± 0.02 | 0.91 ± 0.04 | 17.15 ± 1.32 | 18.91 ± 1.75 | 16.32 ± 1.96 |
| BHL | 61.53 ± 2.58 | 70.51 ± 0.66 | 68.05 ± 2.47 | 0.88 ± 0.03 | 0.95 ± 0.01 | 0.92 ± 0.01 | 16.79 ± 1.32 | 19.14 ± 1.20 | 16.84 ± 2.58 |
| Effect/Year | Plant Growth Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GI (SPAD) | NDVI | PS | |
| 2018 | |||
| Amendment | ns | * | * |
| Season | ns | * | * |
| Amendment*season | ns | ns | ns |
| 2019 | |||
| Amendment | ns | * | ns |
| Season | * | * | * |
| Amendment*season | ns | ns | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





