1. Introduction
Mental health challenges affect millions worldwide, highlighting the need for accessible and effective support systems. In response to this growing concern, our team has undertaken the task of improving an existing mental wellness software system to better serve users in need. Our vision is to create a comprehensive platform that not only provides valuable information and guidance but also fosters a supportive community for individuals struggling with mental health issues [
1].
The mission of our project is to refine the software to enhance user convenience, engagement, and accessibility. By implementing a user-centric design, optimizing system performance, and integrating features that promote mental well-being, we aim to bridge the gap between mental health care and technology. This paper discusses our development process, the challenges encountered, and the key enhancements introduced to ensure a more effective and inclusive mental wellness platform [
2,
3,
4].
Now, people are in an increasingly salient state of sub-health. Sub-health state commonly depicts the individual in the body, psychology, or society adaptation of the existence of discomfort or deterioration of function but without a definitive standard for disease yet. On the psychological level, subhealth states manifest themselves as mood changes, anxiety, depression, feeling of stress, sleep disorders, etc. These problems have a considerable effect on people's quality of life and feelings of well-being. Specifically, 30 per cent of the world's population is currently in a sub-healthy mental condition, and the figure keeps growing [
5,
6,
7,
8].
Conversely, the fast-paced and stressful lifestyle of modern society is an important cause of being in a sub-healthy mental condition. Work pressure, study pressure, and relationship pressure make people stay in a state of ongoing stress, and they have no time for leisure and relaxation. The issue is also aggravated by the neglect of people's mental health and poor coping styles. The majority of people lack appropriate knowledge regarding psychological discomfort and the management of such, and therefore tend to repress or console themselves, with the cumulative result being gradual and eventual formation of problems which, in due course, tend to develop into chronic psychological illnesses [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14].
Therefore, the sub-health problems of mental status that people are currently facing need to be dealt with urgently and resolved. The App that we created is to solve the psychological problems that people in the world are currently facing. Our research application is titled " BetterMood". The project is well aligned with the team vision and mission. We aim to build a world where mental health comes first and where every person has access to mental health assistance and support [
15,
16,
17,
18].
This research work was started with the aim to bring this vision into reality by providing people with easy and effective mental health services through technology to help them cope more effectively with the psychological problems in their lives. And we care about people's mental health and committed to providing personalized mental health care and promoting mutual support among the community to work together to promote people's mental and emotional well-being [
19,
20]. Besides providing information and guidance, the app enables users to offer support and share experiences with one another through the community mutual support function, creating a warm psychological community. It is in strict accordance with our mission of empowering community mutual support and working together to improve people's mental health. The public release of this app project is also in line with our core values as a team: transparency of information, mutual support in the community, and continuous improvement. We hope that through this app, more people will learn about mental health, understand how to cope with which is suited to them, and support each other and develop together as a community [
21,
22].
2. Proposed Methodology
To enhance the existing mental well-being software platform, our team employed a rigorous and iterative development methodology that focused on user experience, performance optimization, and feature enrichment [
21]. The project started with a thorough evaluation of the in-place system to identify areas of usability limitation, functionality, and accessibility. Best practices and user feedback were studied to identify areas of high-priority improvement [
22,
23,
24].
The development process was conducted with an agile methodology, allowing continuous testing and iteration. Our team divided the work into several stages, starting with requirements gathering, where user needs and technical limitations were analyzed [
25]. This was succeeded by the design stage, where intuitive user interfaces and better navigation structures were developed to provide a good user experience. Accessibility was the priority, ensuring that the software would be accessible to individuals with different mental health needs.
During the rollout phase, features like customized mental well-being content, community features for interactive support, and AI-driven recommendations to help users depending on their concerns were added. Additionally, performance optimization initiatives like database restructuring and code efficiency optimizations were made to provide a seamless and responsive user interface [
26,
27].
Testing also played a key role in our strategy. Unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing (UAT) were used to validate the enhancements. User feedback was continuously incorporated to further improve the system. Lastly, deployment plans were properly made to reduce disruptions in transitioning to the upgraded platform, with post-deployment monitoring conducted to detect and address issues as well as maintain the system stable [
28].
With this methodical process, our team endeavored to create a robust and accessible mental wellness platform that enhances availability, interaction, and overall effectiveness in treating mental health.
2.1. Discuss the Impact of Solution/Competitive Solutions
BetterMood app has the potential to make a significant social and economic impact. Socially, BetterMood contributes to the improvement of society's overall mental health indicator. Since the application offers professionally designed mental health tests, it can accurately diagnose users' psychological conditions and offer effective treatment recommendations. This kind of availability of mental health support can lead to a healthier and emotionally stable society with reduced instances of untreated mental illnesses.
Economically, BetterMood can drive growth in two significant ways. First, the app drives consumer activity, generating revenue and contributing to government tax revenue as more and more people invest in its services. Second, the platform encourages the generation of employment as mental health professionals must be employed to develop assessment tools and treatment strategies, as well as qualified educators and technical personnel to monitor system operation and user support. This development drives employment in mental health, education, and technology sectors.
2.2. Impact of the BetterMood App on People
BetterMood has a positive influence on individuals to a large degree through the global extent of a mental well-being platform. With just an internet-connected smartphone, an individual from diverse geographical and demographic bases is able to seek the advantages. The fact that the app has the potential to connect individuals at a mass scale implies there are greater avenues for access to mental health care in the event of traditional therapy or sessions not being available to them.
2.3. BetterMood App Effectiveness in Handling Mental Health Conditions
BetterMood effectively addresses mental illnesses by delivering personalized solutions to suit the unique requirements of each user. With advanced mental health assessments and AI-powered recommendations, the app delivers targeted interventions that help users cope with or overcome mental illnesses. With evidence-based interventions, BetterMood is capable of reducing symptoms significantly or completely eliminating mental illness in most users, thus making it a very effective tool in preventing mental illness.
2.4. Competitor Analysis of the Market
To ascertain the market position of BetterMood, three potential competitors, SeekMed, BookDoc, and MaNaDr, were put through a SWOT analysis. A SWOT analysis of BetterMood too was conducted with the aim of ascertaining its strength, weakness, opportunity, and threat. This helps a great deal in bringing to light BetterMood's competitive advantage and where it can strategically evolve for the future in the evolving mental health technology market.
Table 1.
First Competitor: SeekMed.
Table 1.
First Competitor: SeekMed.
| STRENGTHS + |
WEAKNESSES – |
-Establishment as a well-known brand.
-Wide spectrum of mental health professionals. |
-Restricted geographic reach.
-Insufficiently tailored services.
-Dependency on conventional models for appointments. |
| OPPORTUNITIES + |
THREATS – |
-Entering new markets.
-Including services related to telemedicine. |
-Emerging competition.
-Regulatory changes. |
Table 2.
Second Competitor: BookDoc.
Table 2.
Second Competitor: BookDoc.
| STRENGTHS + |
WEAKNESSES – |
-Cutting-edge telemedicine systems.
-User friendly interface.
-Affordable pricing model. |
-Restricted mental healthcare professional system.
-Dependance on internet connectivity. |
| OPPORTUNITIES + |
THREATS – |
| -Working together with healthcare providers. |
-Technological disruptions.
-Data privacy concerns. |
Table 3.
Third Competitor: MaNaDr.
Table 3.
Third Competitor: MaNaDr.
| STRENGTHS + |
WEAKNESSES – |
-Expertise in a particular area of mental health.
-Better treatment plans. |
-Restricted accessibility in rural regions.
-High-cost services.
-Longer wait times for appointments.  |
| OPPORTUNITIES + |
THREATS – |
-Increasing the reach of the network.
-Develop the features of mobile app.
-Combining forces with insurers. |
-Regulatory restrictions.
-Economic downturns.
-Competition from traditional healthcare models. |
Table 4.
Better Mood.
| STRENGTHS + |
WEAKNESSES – |
-Innovative Approach.
-Strong Team.
-Technological Viability.
-Clear Vision and Mission. |
-Dependency on User Feedback.
-Limited Market Reach.
-Competitor Dominance. |
| OPPORTUNITIES + |
THREATS – |
-Global Expansion.
-Strategic Partnership. |
-Economic Factors.
-Regulatory Changes.
-Emerging Competition. |
This SWOT analysis sheds light on the advantages, disadvantages, possibilities, and dangers posed by three possible rivals in the market for mental health apps. BetterMood may find ways to separate out from the competition and take advantage of market possibilities by having a thorough understanding of these variables.
3. Commercial Feasibility of the BetterMood App
High commercial feasibility is the indication of the BetterMood app, in alignment with Adam Smith's economic principle in The Wealth of Nations: "Where there is demand, there is a market." With the rising prevalence of mental illnesses, BetterMood meets a significant social requirement very effectively through affordability and personalized mental well-being assistance. This guarantees a consistent market presence along with profitability.
3.1. Technical and Economic Feasibility Analysis
Technical Feasibility
The use of BetterMood employs state-of-the-art and popular technologies to ensure a seamless and efficient user interface. For the purpose of cross-platform compatibility, frameworks such as React Native and Flutter are considered, enabling seamless performance on both iOS and Android platforms.
For its core functionalities, BetterMood utilizes machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) technology to provide authentic mental health diagnoses and customized recommendations. Therapeutic sound exercises and guided meditation features also use high-fidelity audio processing technologies to create an immersive environment.
Security is of high importance, with industry-grade encryption and secure data storage practices implemented to protect user data. While these technologies are mature and widely employed, integrating and tuning them to deliver the best user experience requires knowledge of AI model training, audio processing, and system performance tuning. With a capable development team and ideal resource allocation, the technical rollout of BetterMood is fully feasible.
3.2. Economic Viability
There is a greater demand for mental health care, and with society more and more attentive to emotional health, many are willing to pay for a solution that can better their mental health. While creation, maintenance, and operational expenses at first cost money, the reality that the app has access to so many individuals at a less expensive rate than normal therapy makes it an inexpensive solution.
BetterMood competes in a competitive market, yet its tailored advice and expert meditation exercises set it apart from the rest of the mental health apps. The potential for generating revenue is high, considering the scalability of the app and the potential for user adoption. Nevertheless, market risks such as changing user tastes, rising competition, and the pace of technological change must be closely tracked. Keeping pace with industry trends and continually enhancing features will be crucial to long-term economic prosperity.
3.3. Business Model and Revenue Strategies
There are multiple business models through which BetterMood can generate revenue streams and expand its market base:
Subscription-Based Model – Customers have the option to choose different subscription plans such as a basic plan, an advanced plan, and a premium plan with varying levels of features and customized support. Payments can be done in the form of monthly or annual subscriptions.
Advertising Partnerships – The app may collaborate with mental health brands, wellness organizations, and comparable products to display ads or promotional messages. This would generate advertising revenue as well as app exposure.
Paid Content – Users may pay for premium content, including professionally authored mental health articles, audio therapy sessions, and guided meditation exercises, which enhance their well-being experience as well as provide a source of additional revenue.
Community Value-Added Services – Special features such as webinars through the internet, specialist advice, and unique community functions can be offered as premium services, allowing for in-depth participation along with revenues generation.
E-Commerce Partnerships – The app can partner with mental well-being product vendors such as self-help book publishers, audio therapy equipment manufacturers, and counseling websites. Purchase links and advertisement content could be made available for users via direct integration within the app.
Corporate Wellness Programs – Corporates can sign up for BetterMood services to guarantee mental wellness of their employees. Special corporate packages may include mental health checkups, training modules, and consultancy services on a B2B basis.
Personalized Consultation Services – BetterMood may offer personalized counseling sessions, where the user pays for fee-based individual psychological counseling specifically directed toward the individual's own mental health needs.
Since BetterMood is still in beta, there will be in-app purchases included in an initial revenue model with a low-scale test launch. This first step will allow the team to understand user feedback, tweak the price strategy, and be aware of the best monetization strategy to achieve future growth.
By embracing these diverse revenue models and having the power of adapting in its business model, BetterMood can attain long-term sustainability and become a leading mental health support website.
4. System Requirements
4.1. Documentation of Requirements Gathering Elicitation
We interviewed to know the drawback system of an application and how we can improve this drawback to a better system. The application is called Headspace. Headspace is an application of mental disorder that helps in managing stress by providing mindfulness exercises and give information on how to manage their stress. This application is widely used in Europe because it is simple to use and gives short video options to fit our day.
During our interview with Ms. Marry, Ms. Marry mentioned that the drawback of Headspace is there is no test to reach the level of the user's mental illness. In our application, BetterMood, we use a function called test function so that we will know how deep of the level of the user's mental illness problem.
Our second interview was held in the Counselling Services Centre, Block, Level 2. During our interview, Ms. Ng Shan Na and Ms. Tong Yung Shin mentioned that the drawback of Headspace is no tests too, just like the first interview. By having such features included, it becomes more precise with the results provided to the users.
In Jerry's interview with his mother, Jerry's mom explained that the drawback of Headspace is no language choice, and tests. Including the language features makes it help users choose their own language and become more accessible.
From our all-interview responses and suggestions, we can conclude that language options and tests are very crucial aspects to introduce in the apps. Including such features will assist us to improve our software system in order to facilitate the user and make the user more accessible easily.
The BetterMood system offers an array of features intended to facilitate treatment for mental illness as accessible, effective, and personalized as possible. They include:
Language Setting: Users have the option to select the system language to their preferred language of choice when logging in.
Assessment: Users undertake a mental health assessment to determine their present state of well-being.
Personalized Recommendation: Following the unique design of this APP's system and the depiction of the exclusive customization of personal users, we will integrate meditation exercises, audio guidance, sleep sound, breathing exercises and other functions into the personalized recommendation function, after the user has been tested through the psychological test, the professional psychological practitioners and big data analysis will recommend to the user's present most pressing need for the function according to the test result.
Life Skills: Apart from meditation, BetterMood also provides various life skills and advice like emotional control and relationship enhancement to help users enhance quality of life overall.
Community Support: Users can interact with other members of the BetterMood community, sharing experiences, providing support, and encouragement.
4.2. Functional and Non-Functional Requirements of The System
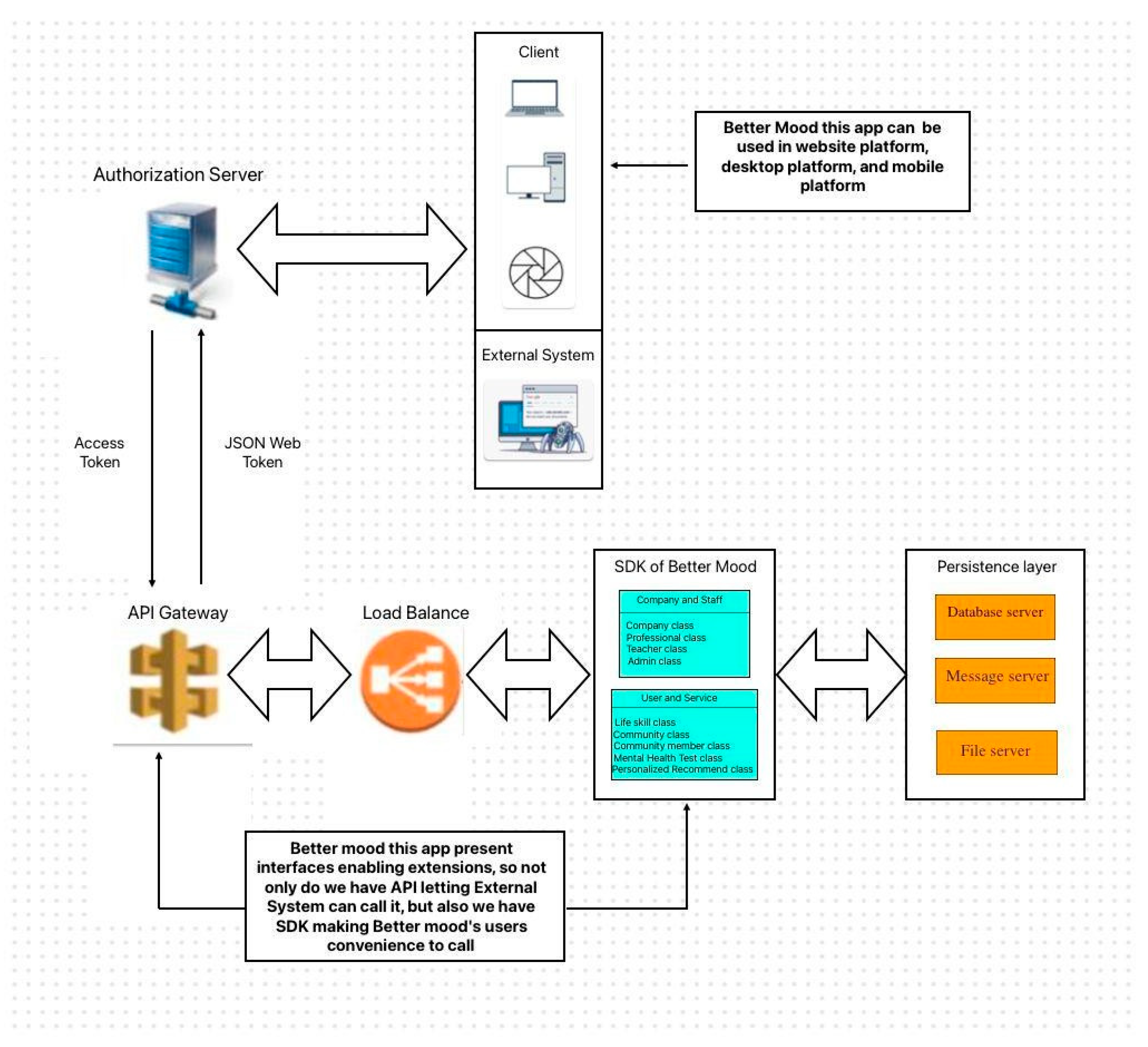
The user takes the registration information to access the system, and the Authorization server will be doing the login and permission verification. After that, the Authorization server takes the token to access API Gateway and accesses the function of BetterMood through the Load Balance. The final data of all operations in the system will be stored in the Persistence Layer.
Table 5.
Table for Functional and Non-Functional Requirements.
Table 5.
Table for Functional and Non-Functional Requirements.
| Category |
Requirements |
| Functional Requirements |
| 1. Language Setting |
-Upon logging in, users can set the system
language to their preferred language. |
| 2. Assessment |
-Users undergo a mental health assessment/test
to determine their current well-being. |
| 3. Personalized Recommendations |
-Based on the assessment results, users receive
personalized recommendations. |
| 4. Life-Skills |
-In addition to mediation, BetterMood also provides various Life Skills and advice such as emotional management and relationship improvement to help users learn meditation
techniques and apply them to daily life. |
| 5. Community Support |
-Users can interact with other members of the |
| |
BetterMood community, sharing experiences,
offering support, and encouragement. |
| Category |
Requirements |
| Non-Functional Requirements |
| 1. Usability |
-The system should be user friendly, user interface that is clear and made to be simple to use and traverse, allowing users easily locate
and access the features. |
| 2. Reliability |
-The system should be reliable, with minimal downtime to guarantee that the program continues to function even in the case of
unforeseen circumstances. |
| 3. Security |
-The system must securely handle by the admin. Using safe login procedures to confirm user identities.
-Ensuring safe protocols between software and
application. |
| 4. Performance |
-The system should be responsive to how
quickly the app reacts to user events, such as login or sign-in to minimize delay. |
| 5. Scalability |
-The system should be scalable to adapt to demand by scaling resources through
monitoring. |
| 6. Maintainability |
-The system should be easy to maintain and update, allowing quick adjustment to the
feature system with significant downtime. |
Figure 1.
Architectural Design.
Figure 1.
Architectural Design.
5. System Analysis and Design
5.1. UML Use Case Diagram (Before)
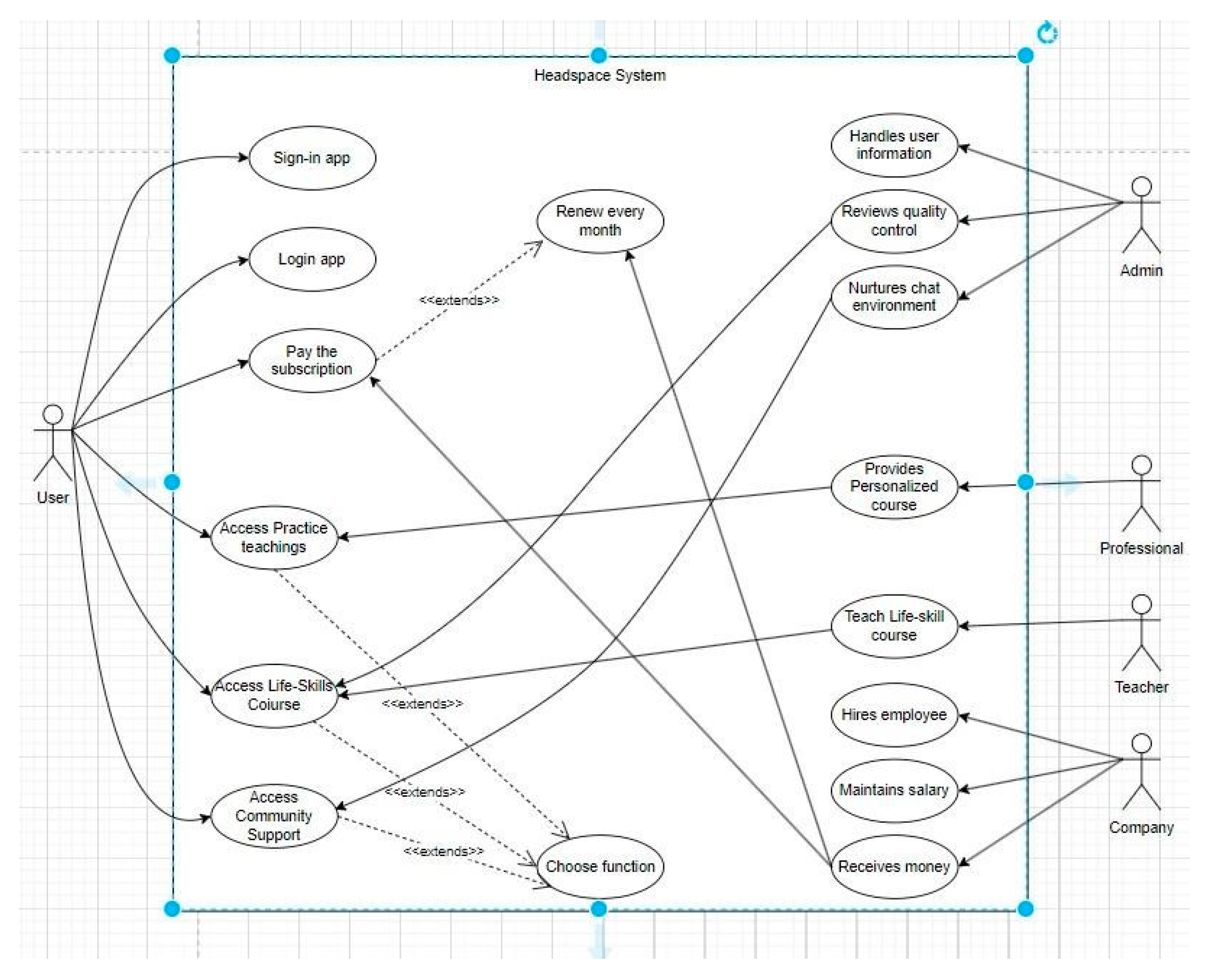
Headspace is a mental wellness application. New users need to register and pay before they can use it for the first time, and they need to pay a monthly fee thereafter to continue using the app. Upon logging in, users can choose from four types of exercise courses according to their preferences: meditation, music, sleep, and breathing exercises. The content of these four exercise courses is prepared in advance by professionals at Headspace and made available to users via videos. Additionally, there is a course on life happiness skills, which is taught by teachers online, and administrators also review the quality of this course during classes. Finally, users can interact with other users facing similar situations in the community support section, where administrators also maintain the chat environment.
Figure 2.
UML Use Case Diagram of Headspace system.
Figure 2.
UML Use Case Diagram of Headspace system.
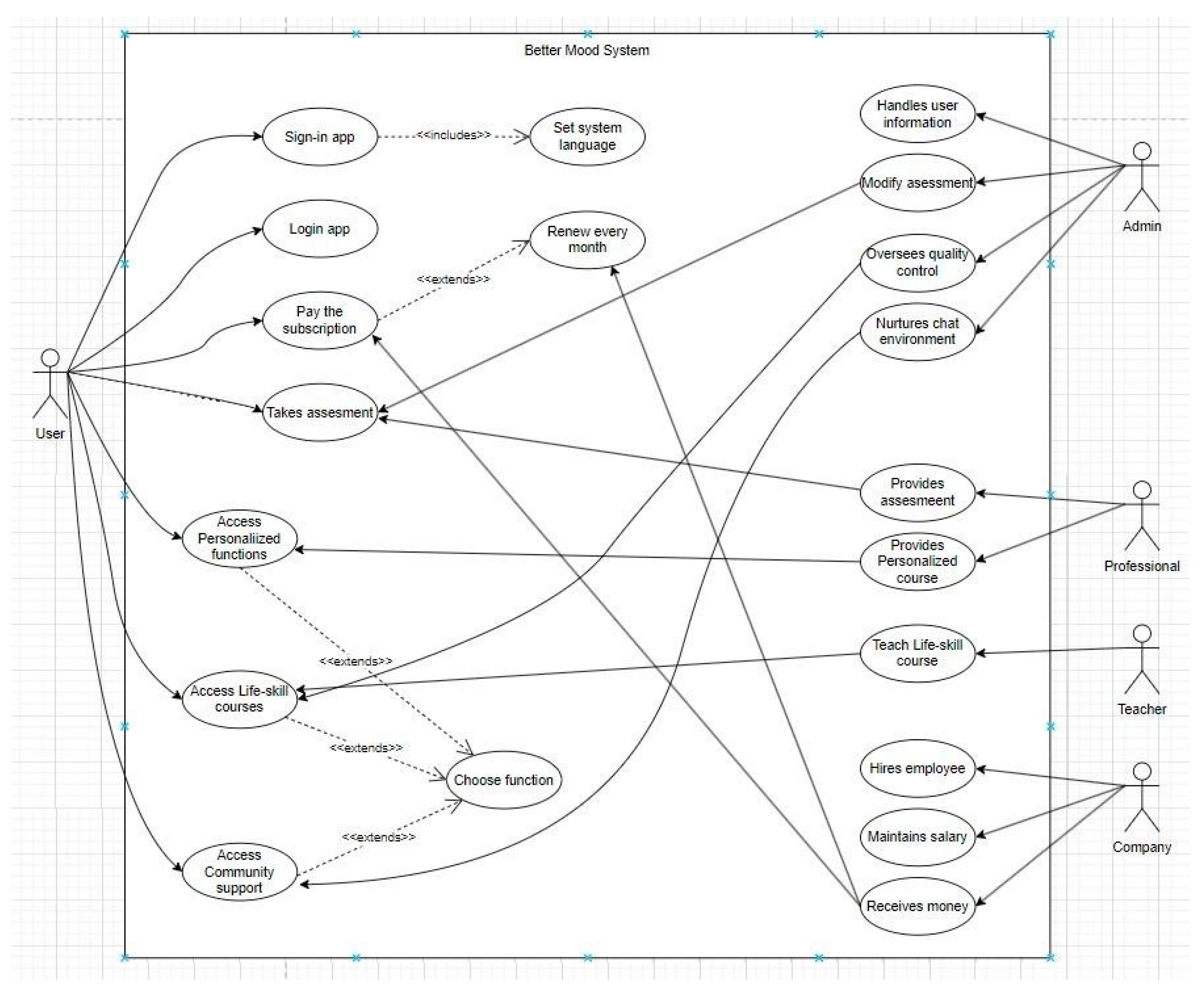
Figure 3.
UML Use Case Diagram of BetterMood system.
Figure 3.
UML Use Case Diagram of BetterMood system.
BetterMood is a software designed to help people address mental health issues, offering a variety of features. New users are required to register upon their initial use and must subscribe to access the platform's services. After that, they must renew every month, otherwise, they cannot use the software. Upon logging in, users can set the system language according to their preferences. Better Mood's medical professionals conduct a mental health assessment for users each time they log in. After they have done the assessment, professionals will depend on the assessment’s result to provide personalized recommended exercise from different categories. Apart from these assessment-based exercises, two features aimed at improving users' mental well-being are managed by administrators. One feature is life skills courses, for which administrators oversee quality control. The other feature is community support, with administrators responsible for maintaining a supportive chat environment within the community.
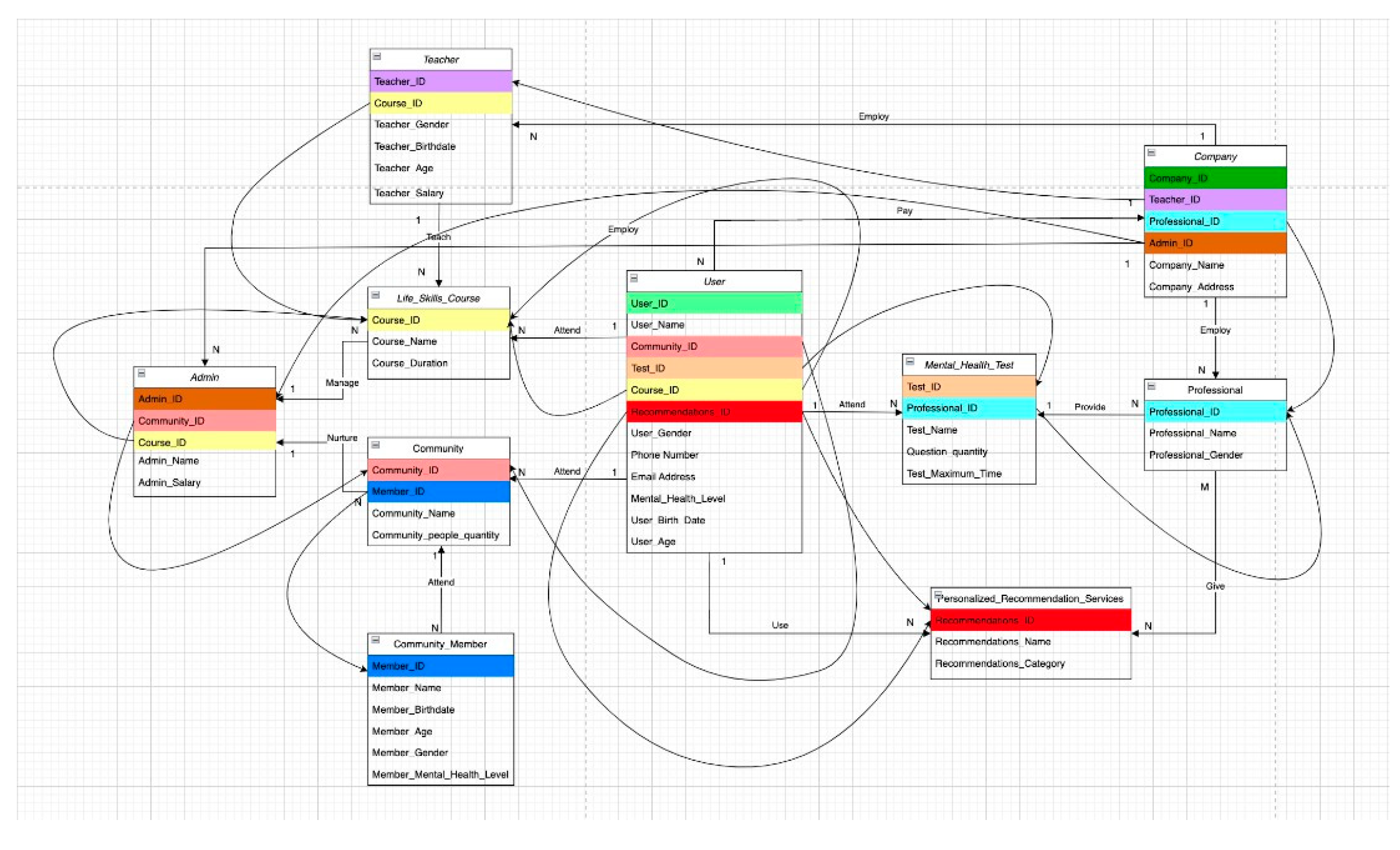
5.2. UML Class Diagram
BetterMood is software designed to help people address mental health issues, offering a variety of features. New users are required to register upon their initial use and must subscribe to access the platform's services. After that, they must renew every month, otherwise, they cannot use the software. Upon logging in, users can set the system language according to their preferences. Better Mood's medical professionals conduct a mental health assessment for users each time they log in. After they have done the assessment, professionals will depend on the assessment’s result to provide personalized recommended exercise from different categories. Apart from these assessment-based exercises, two features aimed at improving users' mental well-being are managed by administrators. One feature is life skills courses, for which administrators oversee quality control. The other feature is community support, with administrators responsible for maintaining a supportive chat environment within the community.
Figure 4.
UML Class Diagram of BetterMood system.
Figure 4.
UML Class Diagram of BetterMood system.
5.3. UML Object Diagram
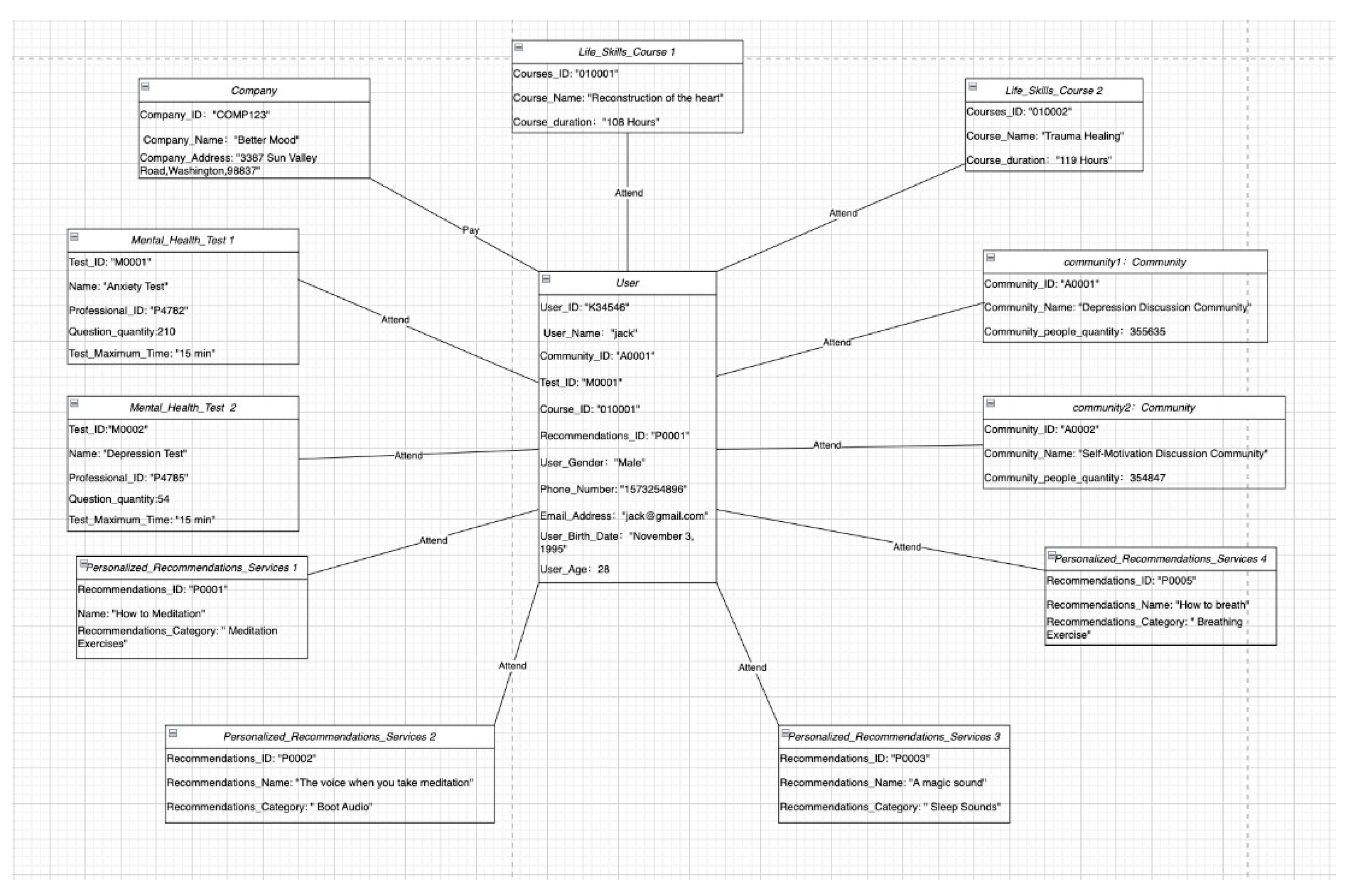
In the BetterMood app, the user first needs to submit a certain amount of funds to the company and complete the corresponding user registration. After the user enters the APP, they will attend various psychological tests. Then, based on the test result, the mental professionals will provide personalized recommendation services to users, such as "meditation exercises", "sleep exercises", "breathing exercises”, etc. In addition to these exercises that must be tested before participating, users can also discuss in different communities, such as "Depression Discussion Community", "Self-prompt Discussion Community", "Anxiety Discussion Community", and so on. At the same time, users can also participate in many life skills courses to improve their quality of life.
Figure 4.
UML Object Diagram of User.
Figure 4.
UML Object Diagram of User.
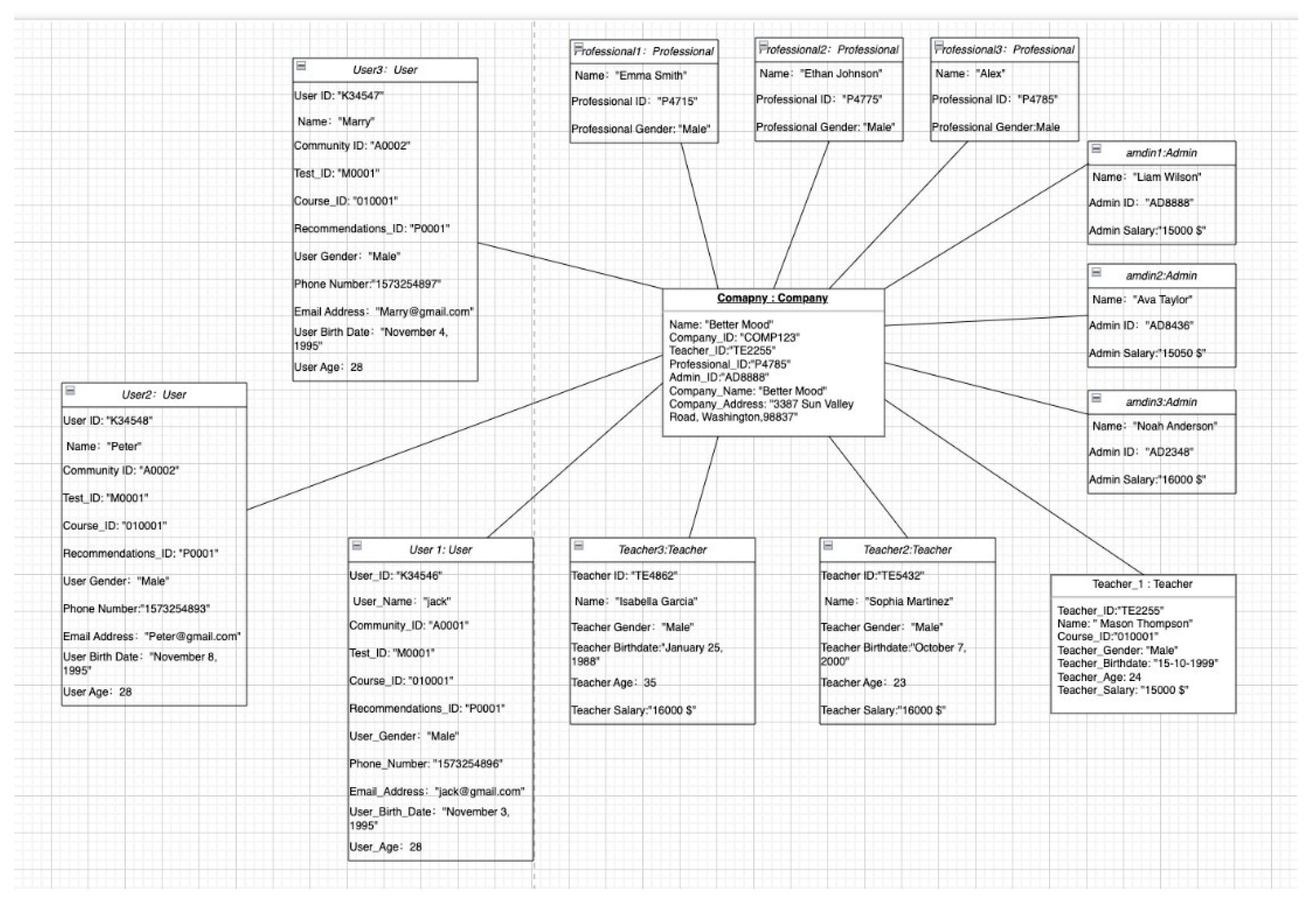
Figure 5.
UML Object Diagram of Company.
Figure 5.
UML Object Diagram of Company.
When we bring the perspective of "BetterMood" company, "BetterMood" company can employ multiple professionals, admins, and teachers. Moreover, all users will need to pay the company to use the APP.
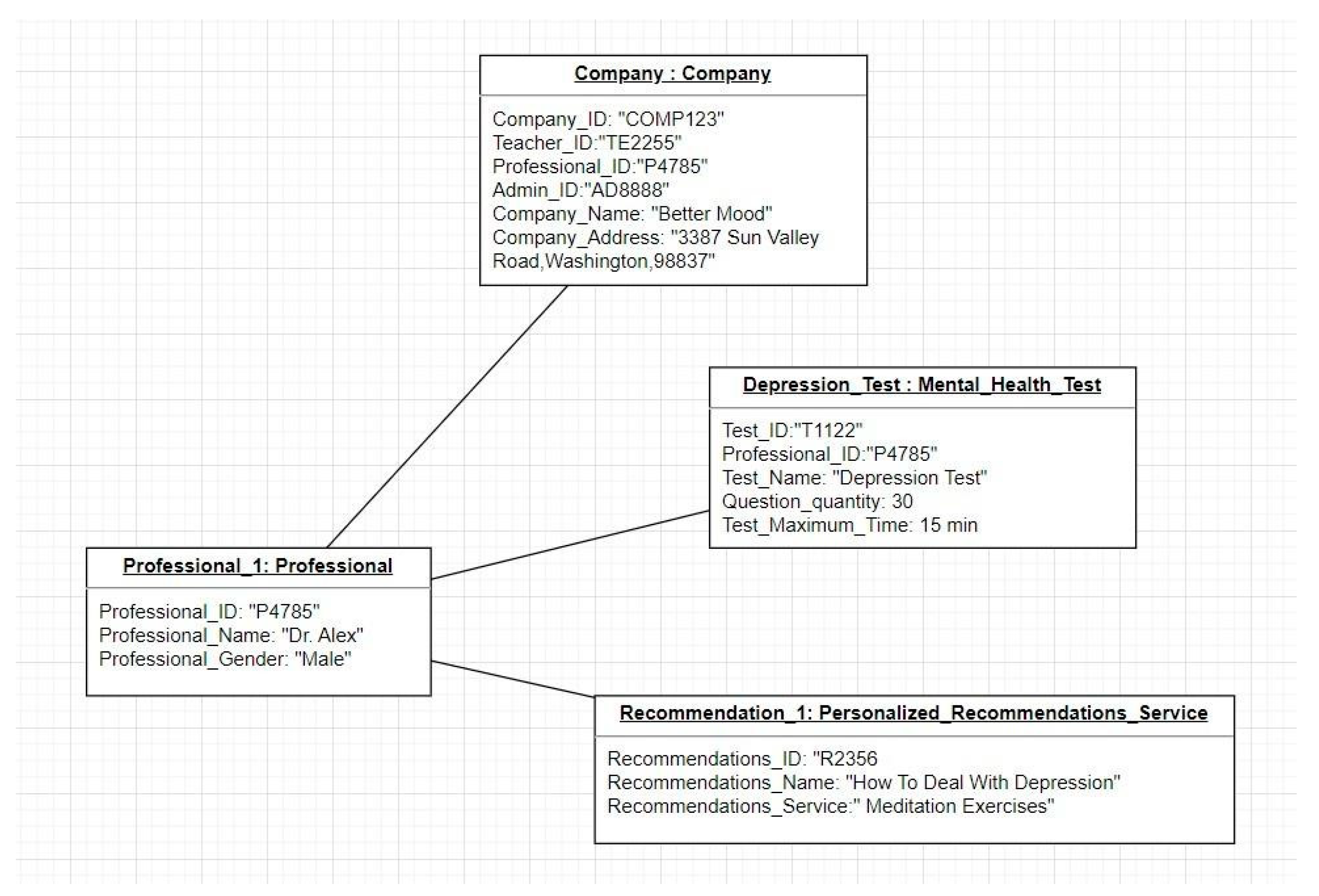
Figure 6.
UML Object Diagram of Professional.
Figure 6.
UML Object Diagram of Professional.
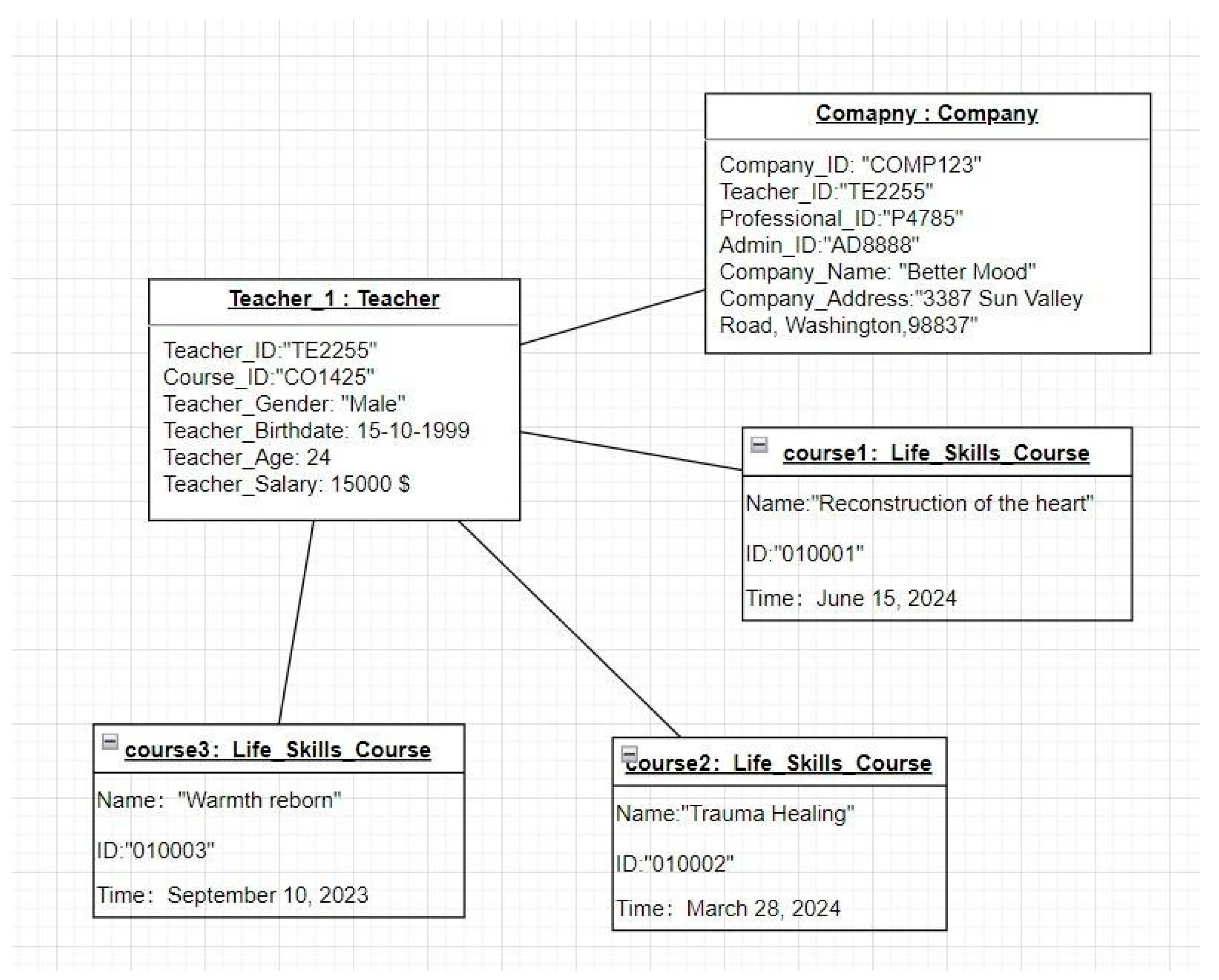
The company employes teachers which they play an important role in guiding the users through personalized content aimed at enhancing emotional well-being. Through assessments and feedback mechanisms, and personalized courses.
Figure 7.
UML Object Diagram of Teacher.
Figure 7.
UML Object Diagram of Teacher.
The company employes teachers which they play an important role in guiding the users through personalized content aimed at enhancing emotional well-being. Through assessments and feedback mechanisms, and personalized courses.
6. Conclusions and Future Enhancement
In summary, BetterMood development and design is a giant leap in the right direction to solve the dismal world mental health challenge. BetterMood seeks to revolutionize seekers of and seekers to mental health help through such innovative features as Life Skills, faster provider access of mental health care providers, language translation, and testing. Through the generation of awareness and the simplification of access to mental health centers, the efforts of our team have generated a comprehensive solution that not only enhances the current needs of individuals afflicted with mental health but also general well-being. With BetterMood, it aims to provide individuals with a platform on which they can take care of their own mental health and access assistance they require. Looking ahead, BetterMood has recognized several areas of major direction for future development and growth to maintain its leadership position in the area of digital mental health. First, BetterMood aims to grow by investigating the addition of other therapy modalities, networking features, and educational content focused on addressing particular mental health issues. To grow reach and accessibility to resources and maintain BetterMood's position at the front of mental wellbeing creativity, strategic partnerships and relationships with healthcare practitioners and mental well-being organizations will also be at the top of the agenda to develop. Together with continuing the improvement of client satisfaction and delight, customer opinions will have to be gathered and acted upon with incremental changes.
Lastly, BetterMood is going to investigate possibilities of expansion on a worldwide scale, projecting future growth past existing boundaries of geography and bringing top-shelf mental health care to people across the globe. BetterMood is dedicated to making good on its goal of significantly improving the lives of those who struggle with mental wellness problems, and because of this, it is implementing these preventative actions.
References
- Babbar, H.; Rani, S.; Masud, M.; Verma, S.; Anand, D.; Jhanjhi, N. Load balancing algorithm for migrating switches in software-defined vehicular networks. Computational Materials and Continua 2021, 67, 67–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgini, P.; Massacci, F.; Zannone, N. (Eds.). (n.d.). International school on foundations of security analysis and design (pp. 237–272). Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
- Hou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, L.; … & Wang, H. Large language models for software engineering: A systematic literature review. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.10620, arXiv.
- Koç, H.; Erdoğan, A.M.; Barjakly, Y.; Peker, S. UML diagrams in software engineering research: A systematic literature review. Proceedings of MDPI 2021, 74, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Laplante, P.A.; Kassab, M. (2022). What every engineer should know about software engineering. CRC Press.
- Munthe, I.R.; Rambe, B.H.; Pane, R.; Irmayani, D.; Nasution, M. UML modeling and black box testing methods in the school payment information system. Jurnal Mantik 2020, 4, 1634–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Ouhbi, S.; Pombo, N. (2020, April). Software engineering education: Challenges and perspectives. In 2020 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON) (pp. 202–209).
- Planas, E.; Cabot, J. How are UML class diagrams built in practice? A usability study of two UML tools: MagicDraw and Papyrus. Computer Standards & Interfaces 2020, 67, 103363. [Google Scholar]
- Ralph, P.; Ali, N.B.; Baltes, S.; Bianculli, D.; Diaz, J.; Dittrich, Y.; … & Vegas, S. Empirical standards for software engineering research. arXiv 2020, arXiv:arXiv:2010.03525, arXiv.
- Saeed, S.; Abdullah, A. Analysis of lung cancer patients for data mining tool. International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security 2019, 19, 90–105. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, S.; Abdullah, A. Combination of brain cancer with hybrid K-NN algorithm using statistical analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) surgery. International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security 2021, 21, 120–130. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, S.; Abdullah, A.; Naqvi, M. Implementation of Fourier transformation with brain cancer and CSF images. Indian Journal of Science & Technology 2019, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, S.; Abdullah, A.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Naqvi, M.; Nayyar, A. New techniques for efficiently k-NN algorithm for brain tumor detection. Multimedia Tools and Applications 2022, 81, 18595–18616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, S.; Khan, H. Global mortality rate and statistical results of Coronavirus. Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicine 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Tsui, F.; Karam, O.; Bernal, B. (2022). Essentials of software engineering. Jones & Bartlett Learning.
- Alkinani, M.H.; Almazroi, A.A.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Khan, N.A. 5G and IoT-based reporting and accident detection (RAD) system to deliver first aid box using unmanned aerial vehicle. Sensors 2021, 21, 6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, A. Investigation of brain cancer with interfacing of 3-dimensional image processing. Indian Journal of Science & Technology 2019, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Dogra, V.; Singh, A.; Verma, S.; Kavita, Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Talib, M.N. (2021). Analyzing DistilBERT for sentiment classification of banking financial news. In S. L. Peng, S.Y. Hsieh, S. Gopalakrishnan, & B. Duraisamy (Eds.), Intelligent computing and innovation on data science (Vol. 248, pp. 665–675). Springer. [CrossRef]
- Ralph, P.; Ali, N.B.; Baltes, S.; Bianculli, D.; Diaz, J.; Dittrich, Y.; Vegas, S. Empirical standards for software engineering research. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.03525. https://arxiv.org/abs/2010, arXiv. [Google Scholar]
- Aldughayfiq, B.; Ashfaq, F.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Humayun, M. Explainable AI for retinoblastoma diagnosis: interpreting deep learning models with LIME and SHAP. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaullah, M.; Ali, M.; Almufareh, M.F.; Ahmad, M.; Hussain, L.; Jhanjhi, N.; Humayun, M. Initial stage COVID-19 detection system based on patients’ symptoms and chest X-ray images. Applied Artificial Intelligence 2022, 36, 2055398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.H.; Razzaq, M.A.; Ahmad, M.; Almansour, F.M.; Haq, I.U.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; ... & Masud, M. Security and privacy aspects of cloud computing: a smart campus case study. Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing 2022, 31, 117–128.
- Alferidah, D.K.; Jhanjhi, N.Z. (2020, October). Cybersecurity impact over bigdata and iot growth. In 2020 International Conference on Computational Intelligence (ICCI) (pp. 103–108). IEEE.
- Babbar, H.; Rani, S.; Masud, M.; Verma, S.; Anand, D.; Jhanjhi, N. Load balancing algorithm for migrating switches in software-defined vehicular networks. Comput. Mater. Contin 2021, 67, 1301–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.S.; Vimal, S.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Dhanabalan, S.S.; Alhumyani, H.A. Blockchain based peer to peer communication in autonomous drone operation. Energy Reports 2021, 7, 7925–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, K.K.; Bhoi, S.K.; Malik, T.K.; Sahoo, K.S.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Bhatia, S.; Amsaad, F. E-learning course recommender system using collaborative filtering models. Electronics 2022, 12, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, I.A.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Laraib, A. (2023). Cybersecurity and blockchain usage in contemporary business. In Handbook of Research on Cybersecurity Issues and Challenges for Business and FinTech Applications (pp. 49–64). IGI Global.
- Muzafar, S.; Jhanjhi, N.Z. (2020). Success stories of ICT implementation in Saudi Arabia. In Employing Recent Technologies for Improved Digital Governance (pp. 151–163). IGI Global.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).