Submitted:
09 April 2025
Posted:
10 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Preparation of Zr MOFs and Zr MOFs-PEI Composite
2.2. Preparation of Luminol-Apt
2.3. Preparation of ECL Aptamer Sensors
3. Results and Discussion
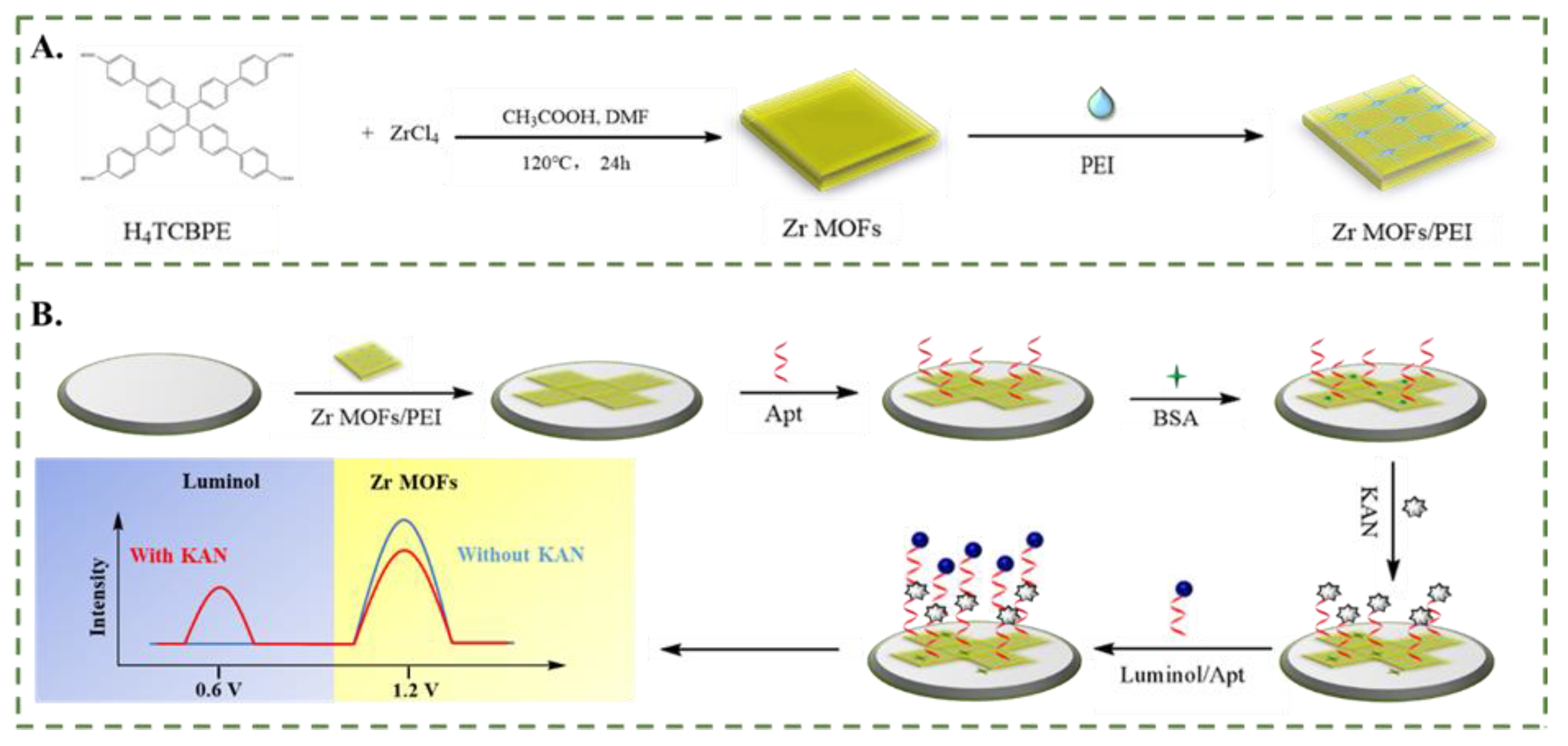
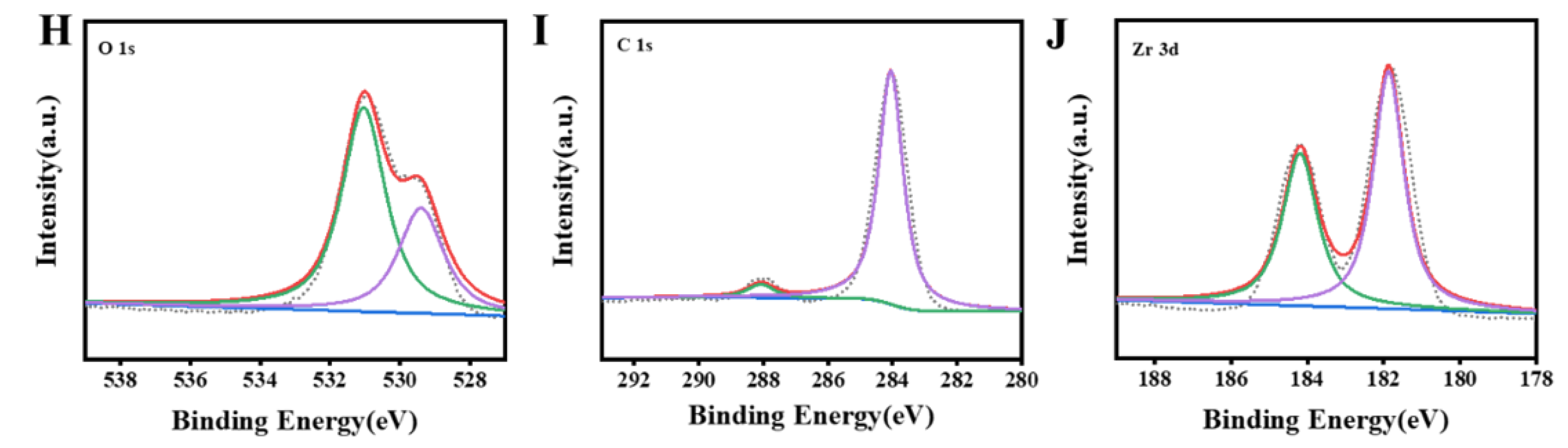
3.1. Characterization of Zr MOFs and Zr MOFs-PEI
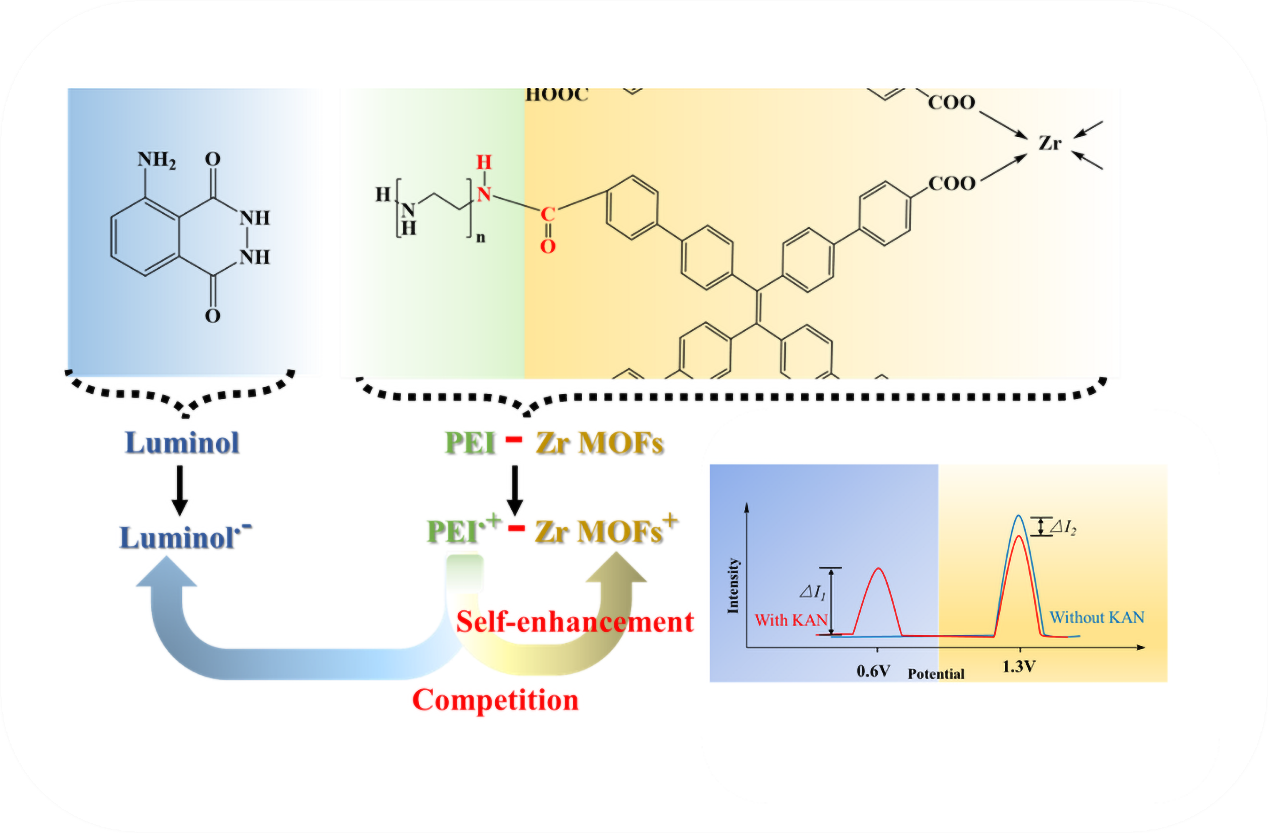
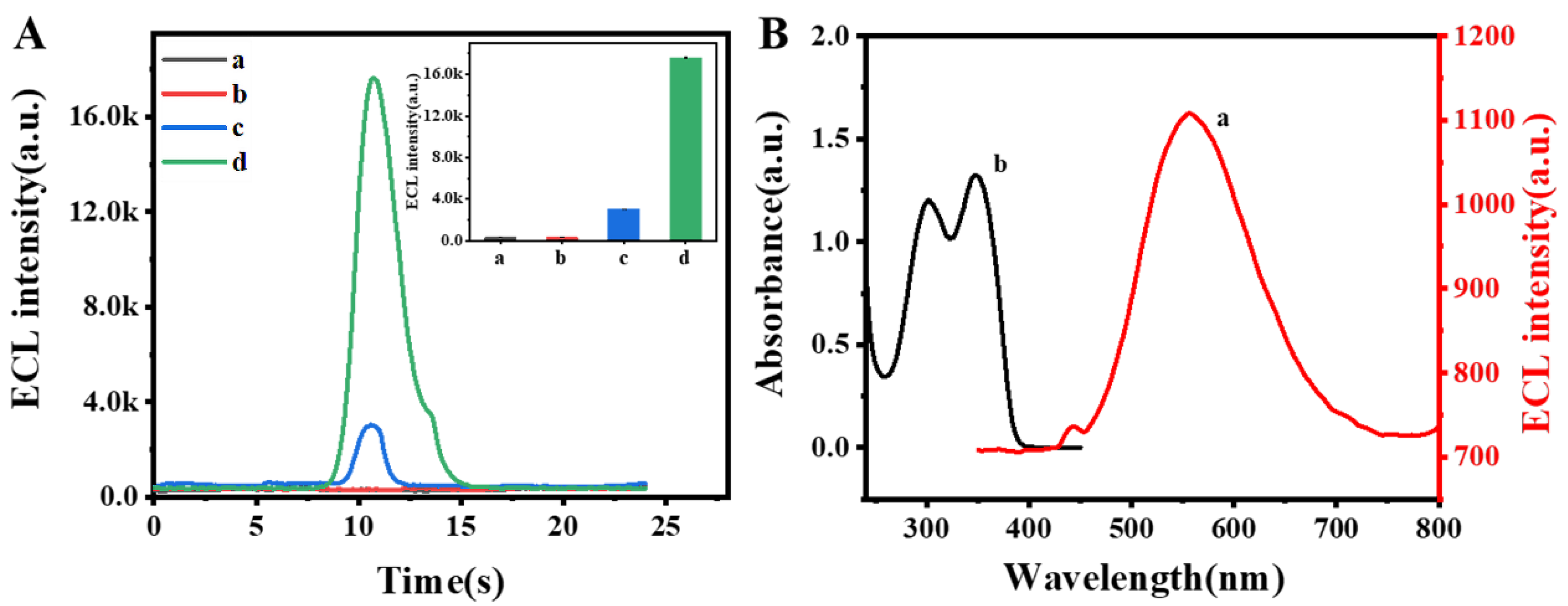
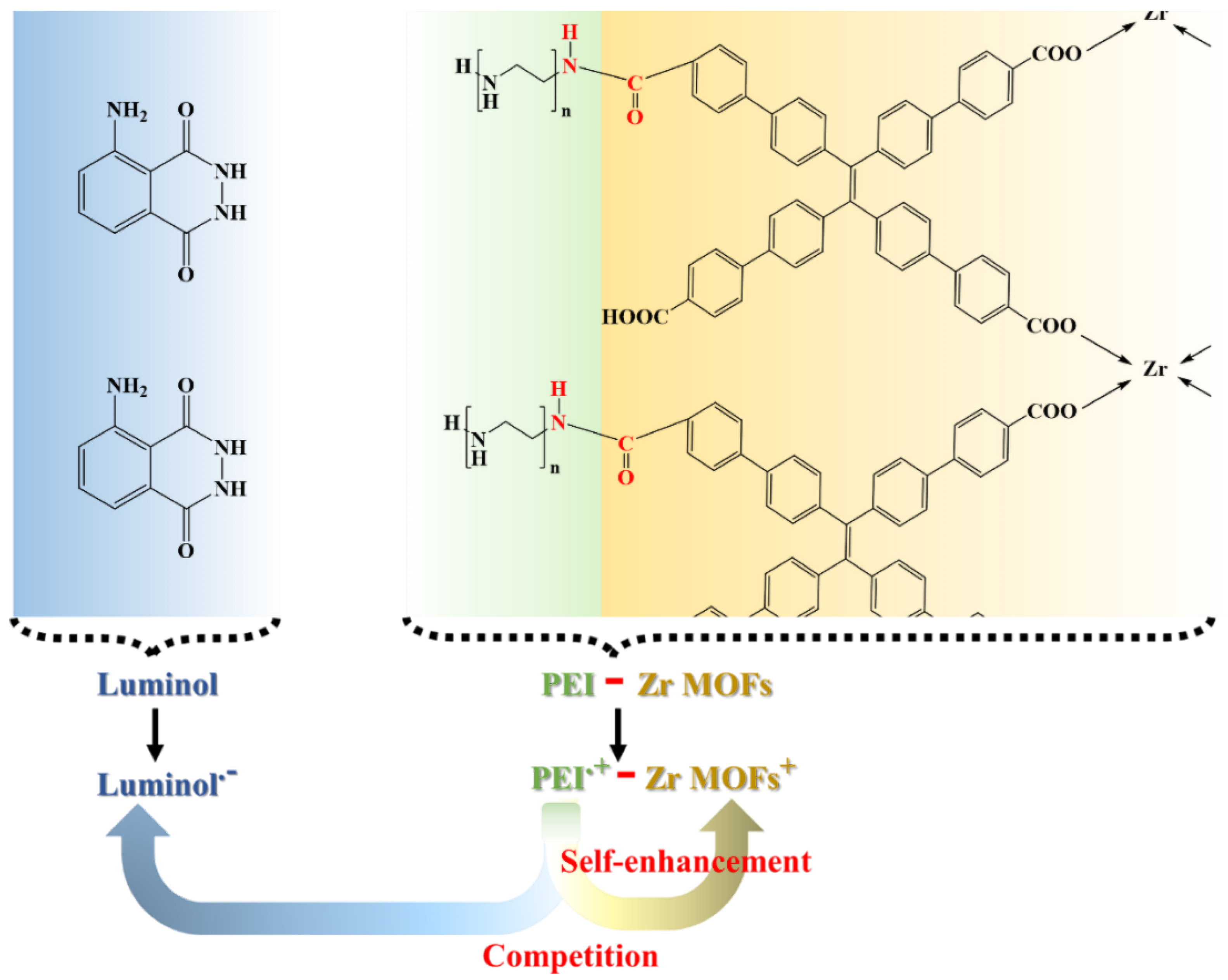
3.2. Performance of the ECL Self-Enhancement and Competition Mechanism




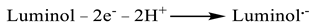


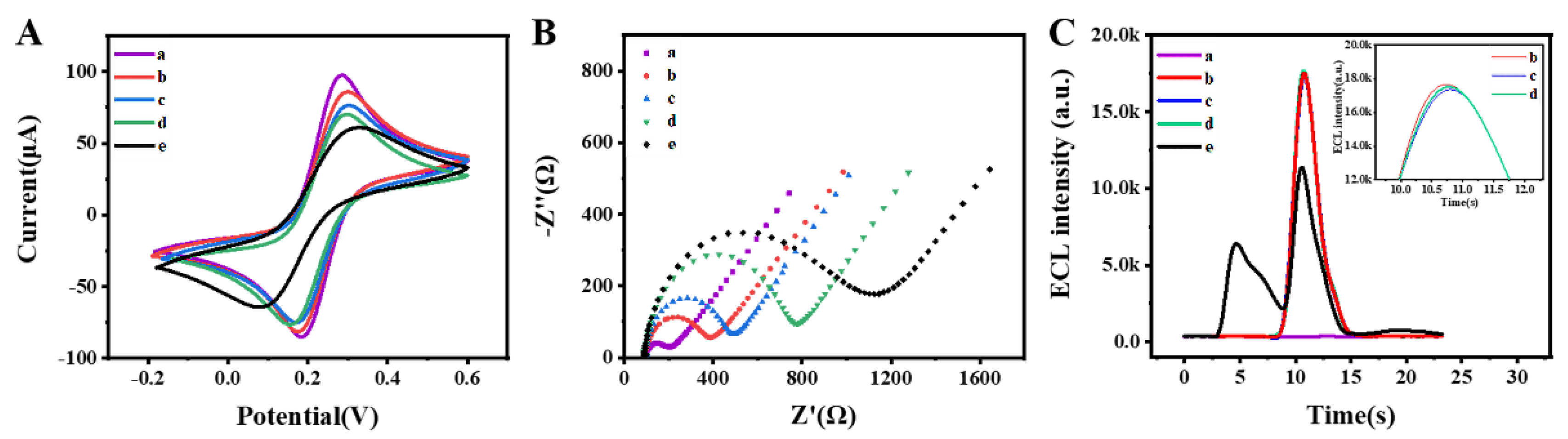
3.3. Electrochemical Characterization and ECL Behavior
3.4. Optimization of the Detection Conditions
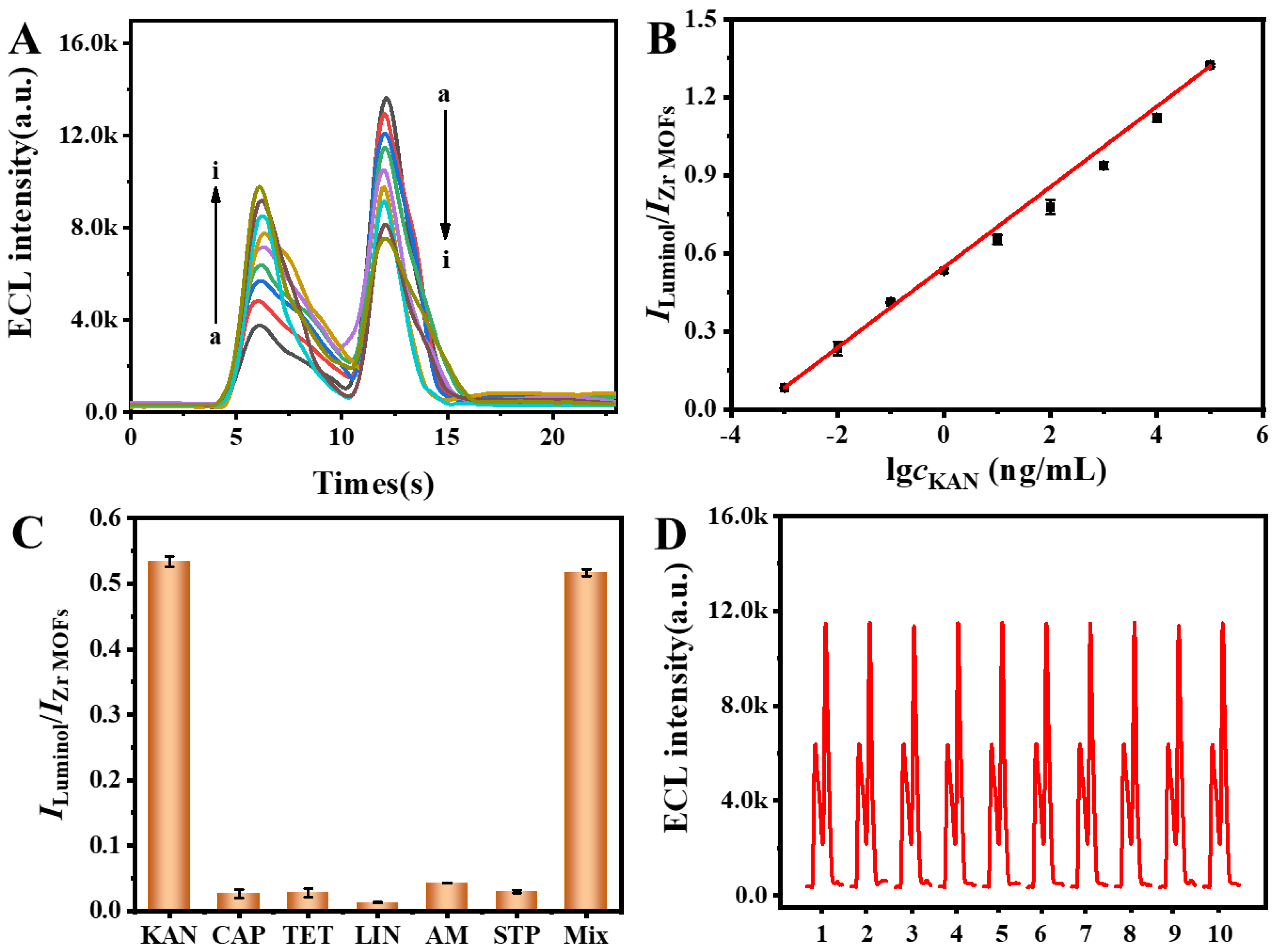
3.5. Analytical Performance
3.6. Real Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heysell, SK.; Ahmed, S.; Rahman, MT. Hearing loss with kanamycin treatment for multidrug−resistant tuberculosis in Bangladesh. Eur. Respir. J 2018, 51, 1701778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezden, A.; Mohamed, M.F.; Nepal, M.; Harwood, J.S.; Kuriakose, J.; Seleem, M.N.; Chmielewski, J. Correction to “dual targeting of intracellular pathogenic bacteria with a cleavable conjugate of kanamycin and an antibacterial cell-penetrating peptide”. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2016, 138, 10945–10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.J.; Zhu, Y.B.; Zhou, X.H.; Lin, Q.; He, M. High−κ solid-gate transistor configured graphene biosensor with fully integrated structure and enhanced sensitivity. Adv. Funct. Mater 2016, 26, 7668–7678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeeb Rahman, A.P.; Pranjal; Behera, S.K.; Mishra, A.; Lundborg, C.S.; Tripathy, S.K. Transcriptomic regulation of Salmonella Typhimurium during sonophotocatalysis and the effect of stress adaptation on the antibiotic resistance and tolerance post−treatment. Chem. Eng. J 2022, 446, 137442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.W.; Han, Y.; Shen, Y.M.; Chen, B.L.; Wang, M.Z. Deglycosylation inactivation initiated by a novel periplasmic dehydrogenase complex provides a novel strategy for eliminating the recalcitrant antibiotic kanamycin. Environ. Sci. Technol 2023, 57, 4298–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; He, J.X.; Mahadevegowda, S.H.; Kho, S.H.; Chan-Park, M.B.; Liu, X.W. Multifunctional glyco−nanosheets to eradicate drug-resistant bacteria on wounds. Adv. Healthc. Mater 2020, 9, 2000265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.; Liu, C.; Luo, J.B.; Tian, Y.P.; Zhou, N.D. Direct electrochemical detection of kanamycin based on peroxidase-like activity of gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 936, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Z.; Gunasekaran, S. Oxygen-terminated few−layered Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets as peroxidase−mimic nanozyme for colorimetric detection of kanamycin. Biosens. Bioelectron 2022, 218, 114774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.T.; Chen, Q.; Wen, Y.L.; Bian, X.J.; Tao, Q.; Liu, G.; Yan, J. A competitive colorimetric aptasensor for simple and sensitive detection of kanamycin based on terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated signal amplification strategy. Food Chem 2022, 377, 132072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.H.; Wen, X.Y.; Zhang, B.Y.; Fan, Z.F. Novel aptasensor for the ultrasensitive detection of kanamycin based on graphene oxide quantum−dot−linked single−stranded DNA−binding protein. Sens. Actuators B Chem 2018, 265, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, W.Q.; Gao, X.L.; Sun, Z.C.; Sun, X.; Guo, Y.M.; Li, F.L.; Boboriko, N.E. Fluorescent aptasensor based on DNA−AgNCs emitting in the visible red wavelength range for detection of kanamycin in milk. Sens. Actuators B Chem 2022, 360, 131665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.; Liu, J.; Han, X.Y.; Liu, C.; Tian, Y.P.; Zhou, N.D. UV-visible spectroscopic detection of kanamycin based on target−induced growth of gold nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.Z.; Zhang, C.Z.; Yang, Y.; Liang, X.X.; Pang, Q.; Zhou, L.Y.; Chen, P.C. Synergistic effect of photoelectrochemical aptasensor based on staggered gap ZnO/BiFeO3 heterojunction coupled with cDNA−CdS sensitizer enabling ultrasensitive assay of kanamycin. Food Chem 2024, 437, 137877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.T.; Liu, H.M.; Zhang, H.; Chu, G.L.; Guo, Y.M.; Sun, X. Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for kanamycin detection based on silver nanoparticle−catalyzed chemiluminescent reaction between luminol and hydrogen peroxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem 2020, 304, 127367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.L.; Sun, Z.C.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, W.Q.; Xu, D.Y.; Sun, X.; Guo, Y.M.; Xu, S.C.; Li, F.L. Construction of a dual-model aptasensor based on G-quadruplexes generated via rolling circle amplification for visual/sensitive detection of kanamycin. Sci. Total Environ 2022, 839, 156276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Li, Q.; Deng, X.K.; Guo, Q.F.; Liu, D.D.; Nie, G.M.J. A novel electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on Ru(bpy)32+−functionalized MOF composites and cycle amplification technology of DNAzyme walker for ultrasensitive detection of kanamycin. Colloid Interface Sci 2024, 659, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, P.L.; Nie, Y.X.; Ma, Q. Recent development of organic nanoemitter-based ECL sensing application. TrAC 2021, 143, 116410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.H.; Fan, Z.J.; Deng, H.P.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Tan, Q.Q.; Li, B.; Huang, X. Zika virus liquid biopsy: A dendritic Ru(bpy)32+−polymer−amplified ECL diagnosis strategy using a drop of blood. ACS Cent. Sci 2018, 4, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhang, H.X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhuang, T.T.; Wang, Z.H. Boosting the electrochemiluminescence of luminol by high-intensity focused ultrasound pretreatment combined with 1T/2H MoS2 catalysis to construct a sensitive sensing platform. Ultrason. Sonochem 2023, 92, 106264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hu, F. X.; Zhao, J. W.; Yang, G. M.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Chen, S. H.; Yuan, R. Bifunctional moderator-powered ratiometric electrochemiluminescence enzymatic biosensors for detecting organophosphorus pesticides based on dual-signal combined nanoprobes. Anal. Chem 2021, 93, 8783–8790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.Y.; Tan, H.S.; Liu, M.J.; Li, S.S. Electrochemical ratiometric dual−signal immunoassay for accurate detection of carcinoembryonic antigen in clinical serum based on rGO−Pd@Au−Thi and Chi−Fc−Au. Sens. Actuators B Chem 2023, 380, 133340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Li, Y.R.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Xiang, Y.M.; Bai, R.R.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.L.; Meng, G.R.; Pan, S.L.; Zhang, F.; Mi, L.; Hu, Y.H. Dual−signal ratiometric electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on Au NPs-induced low-potential emission of PFO Pdots and LSPR-ECL mechanism for ultra-sensitive detection of microRNA-141. Biosens. Bioelectron 2024, 261, 116495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Cui, X.M.; Li, F.H.; Yan, W.; Wang, Y.Y.; Shang, L.; Ma, R.N.; Jia, L.P.; Li, C.; Wang, H.S. Perylene diimide and g−C3N4 nanosheet as potential-resolved cathode luminophores for ultrasensitive ratiometric electrochemiluminescence immunosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem 2022, 371, 132492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W. J.; Chen, G. X.; Wang, X. Y.; Zhen, S. J.; Huang, C. Z.; Zhan, L.; Li, Y. F. Facile synthesis of dual-ligand europium-metal organic gels for ratiometric electrochemiluminescence detecting I27L gene. Biosens. Bioelectron 2024, 246, 115863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.X.; Hu, C.Y.; Dai, W.J.; Luo, Z.L.; Zang, H.; Sun, S.Y.; Zhen, S.J.; Zhan, L.; Huang, C.Z.; Li, Y.F. Coreactant-free zirconium metal−organic framework with dual emission for ratiometric electrochemiluminescence detection of HIV DNA. Anal. Chem 2024, 96, 10102–10110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Hou, C.T.; Zhang, F.F.; Xia, J.F.; Wang, Z.H. Highly sensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on novel TiO2−porphyrin organic framework with self−enhanced luminescent property. Sens. Actuators B Chem 2023, 379, 133229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Q.; Zhao, A.J.; Wang, Z.Z.; Xu, Y.H.; Feng, Y.J.; Lan, Y.B.; Han, Z.G.; Lu, X.Q. Enhancing the electrochemiluminescence of porphyrin via crystalline networks of metal−organic frameworks for sensitive detection of cardiac troponin I. Anal. Chem 2023, 95, 11687–11694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L. Y.; Zhao, H. Q.; Shang, L.; Shen, G.D.; Ma, R.N.; Wang, H.S. A robust ECL-enhanced system based on UiO-66-COOH promoting perylene diimide derivative electrochemiluminescence for tumor biomarker detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem 2025, 423, 136824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, X.; Wu, T. T.; Zhang, X. Y.; Ren, X.; Feng, R.; Du, Y.; Lee, J. Y.; Liu, X. T.; Wei, Q. Zirconium based metal–organic frameworks with aggregation-induced electrochemiluminescence for sensitive analysis of aflatoxin B1 by signal dual-amplification strategy. Chem. Eng. J 2024, 500, 157308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushira, F.A.; Hussain, A.; Wang, P.; Li, H.J.; Zheng, L.R.; Gao, Z.Q.; Dong, H.F.; Jin, Y.D. Boosting electrochemiluminescence performance of a dual-active site iron single-atom catalyst-based luminol–dissolved oxygen system via plasmon-induced hot holes. Anal. Chem 2024, 96, 9704–9712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.D.; Xv, H.J.; Li, C.; Kong, L.H.; Li, C.X.; Li, F. Fe-single-atom catalysts boosting electrochemiluminescence via bipolar electrode integrated with its peroxidase-like activity for bioanalysis. Biosens. Bioelectron 2024, 258, 116351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Zou, Y.Q.; Ru, H.J.; Yan, F.; Liu, J.Y. Silica nanochannels as nanoreactors for the confined synthesis of Ag NPs to boost electrochemical stripping chemiluminescence of the luminol-O2 system for the sensitive aptasensor. Anal. Chem 2024, 96, 10264–10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.W.; Gu, Z.Y.; Arvapally, R.K.; Chen, Y.P.; McDougald, R.M., Jr.; Ivy, J.F.; Yakovenko, A.A.; Feng, D.W.; Omary, M.A.; Zhou, H.C. Rigidifying fluorescent linkers by metal−organic framework formation for fluorescence blue shift and quantum yield enhancement. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2014, 136, 8269–8276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample | Spiked (ng/mL) | Found (ng/mL) | Recovery (%) | RSD(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk | 0 | No Found | - | - |
| 0.01 | 0.01 | 100 | 0.4 | |
| 1.00 | 1.00 | 100 | 1.1 | |
| 100.0 | 102.6 | 103 | 1.1 | |
| River water | 0 | No Found | - | - |
| 0.01 | 0.01 | 100 | 2.9 | |
| 1.00 | 1.03 | 103 | 2.2 | |
| 100.0 | 97.11 | 97.1 | 1.0 | |
| Honey | 0 | No Found | - | - |
| 0.01 | 0.01 | 100 | 1.2 | |
| 1.00 | 1.04 | 104 | 1.5 | |
| 100.0 | 98.78 | 98.8 | 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





