Submitted:
05 April 2025
Posted:
08 April 2025
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Prediction Models
- Model 1:
- is a three dimensional vector represents the prices of Bitcoin in US dollars, fear and greed index (FGI), and exchange trading volume (USD) of Bitcoin at time . Thus, model (1) can be rewritten as follows:where , , and are the prices (USD) of Bitcoin, fear and greed index, and exchange trading volume of Bitcoin (USD) at time , respectively.
- Model 2:
- is a four dimensional vector represents the prices of Ethereum, Bitcoin in US dollars, fear and greed index (FGI), and exchange trading volume of Ethereum (USD) at time .where is price of Ethereum at time .
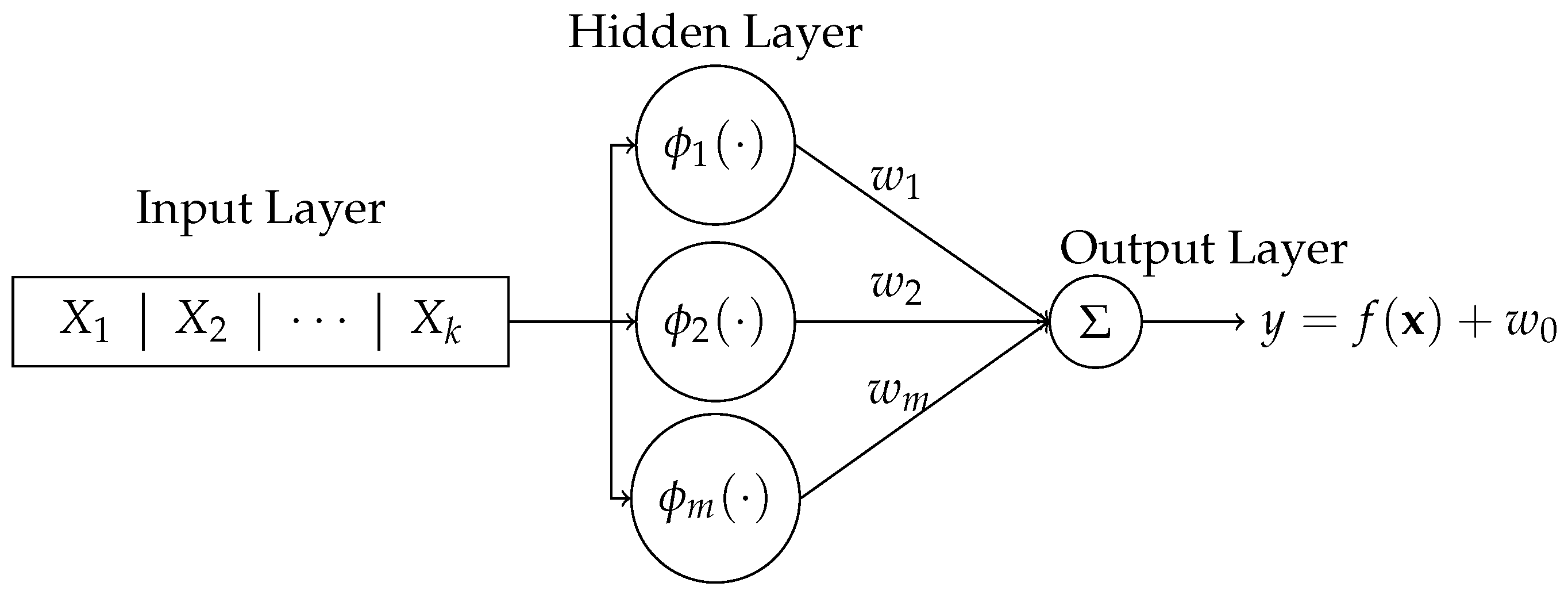
2.1. Radial Basis Function Network (RBFN)
2.2. General Regression Neural Network (GRNN) Model
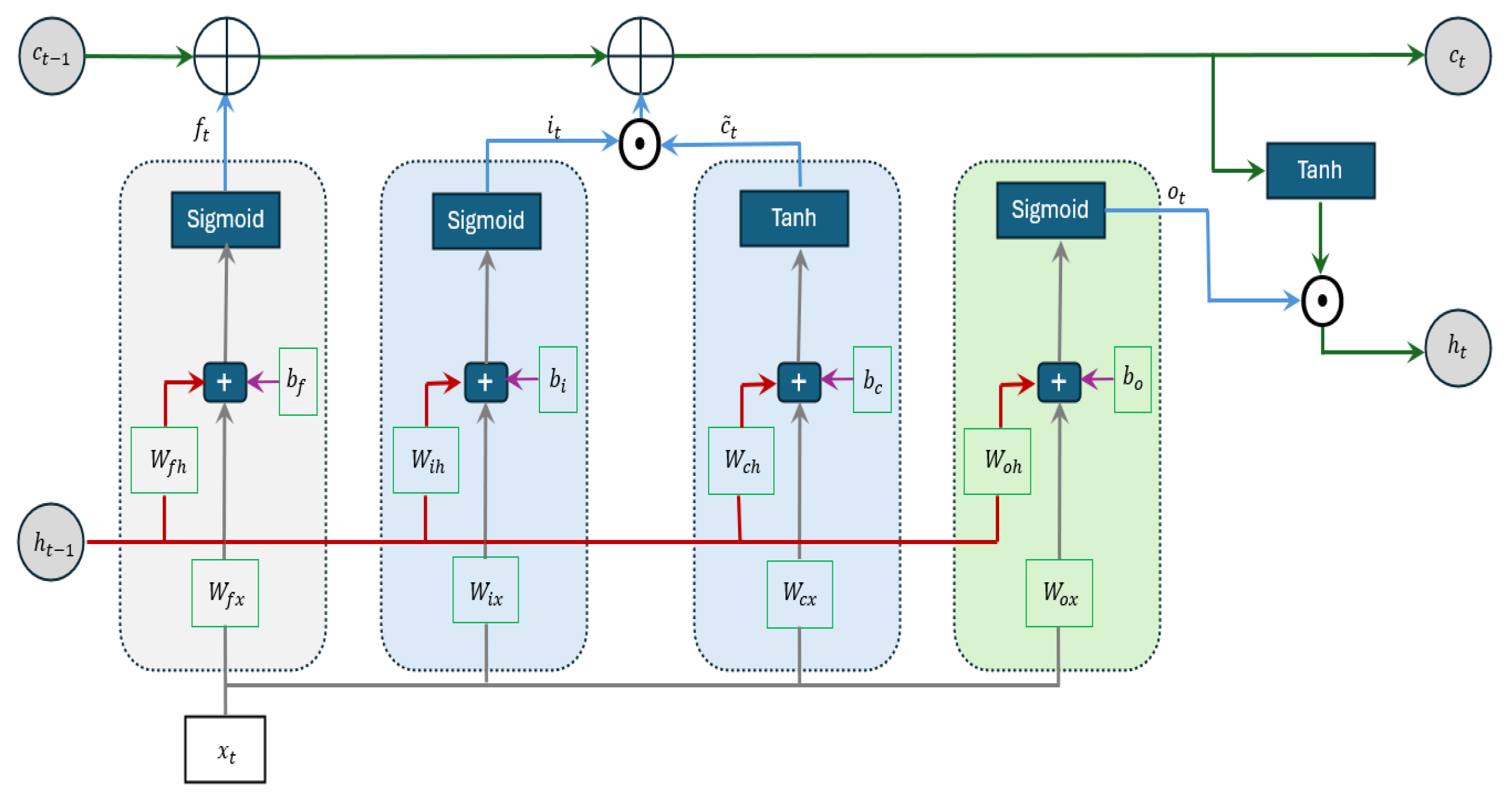
2.3. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Model
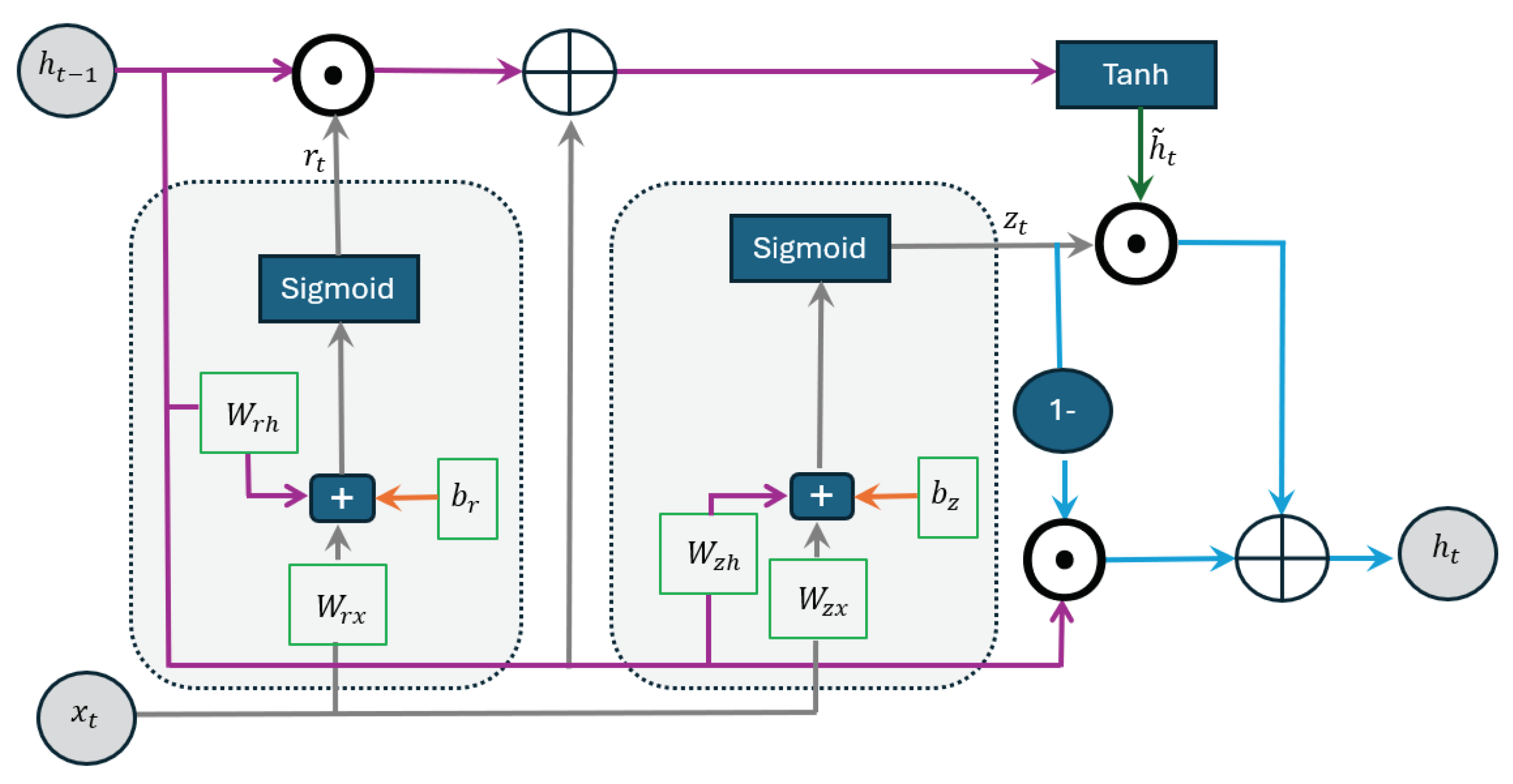
2.4. Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) Model
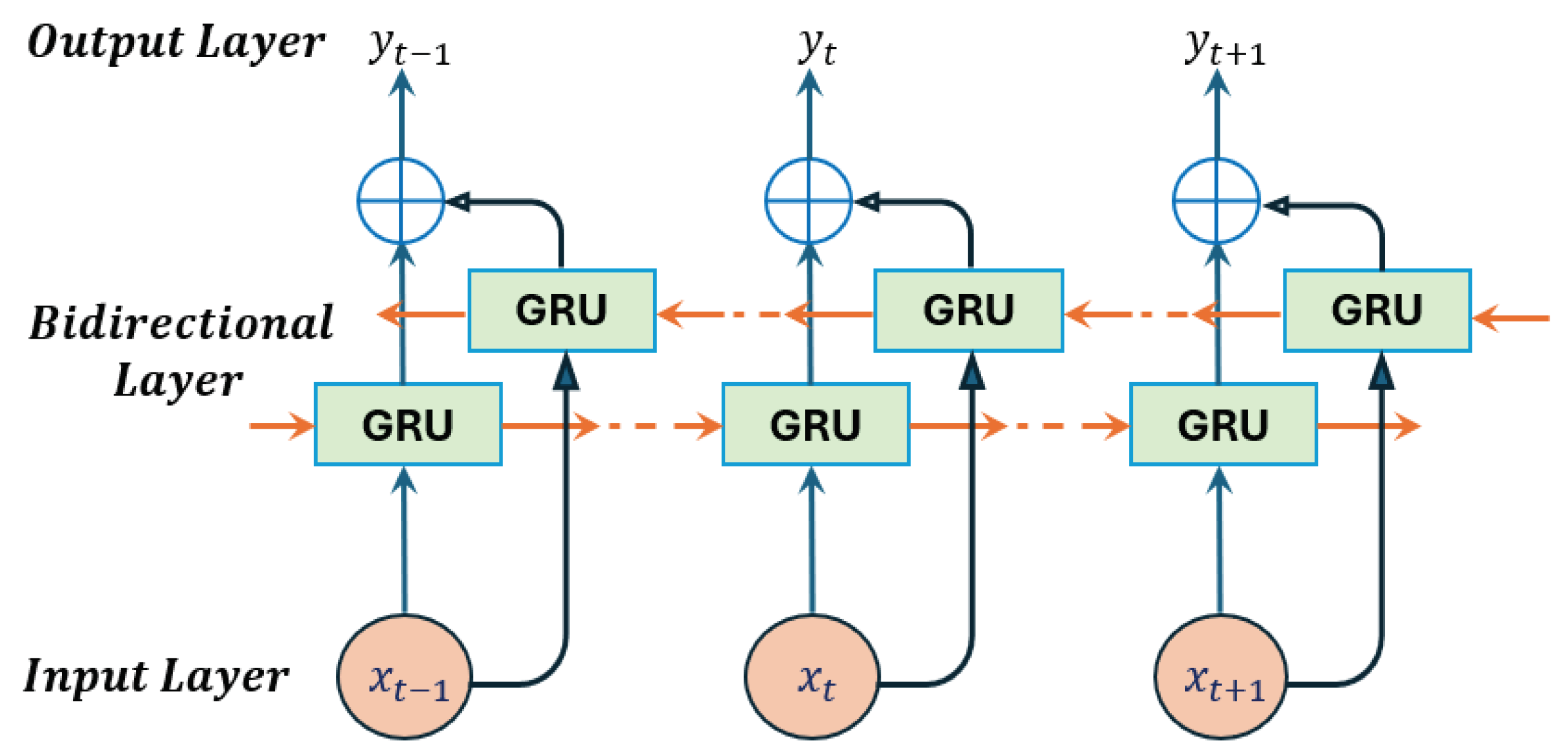
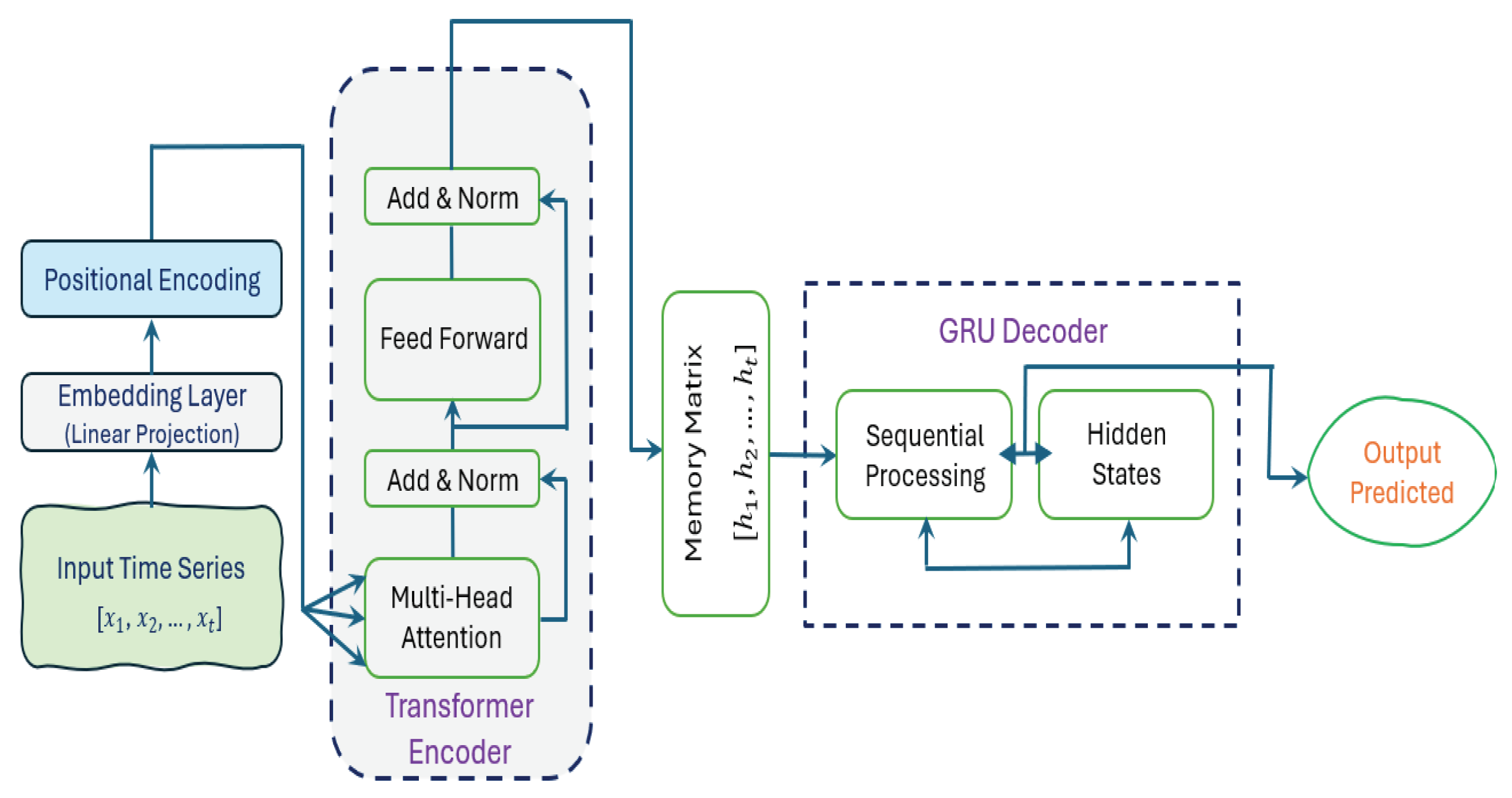
3. Hybrid Transformer + GRU Architecture
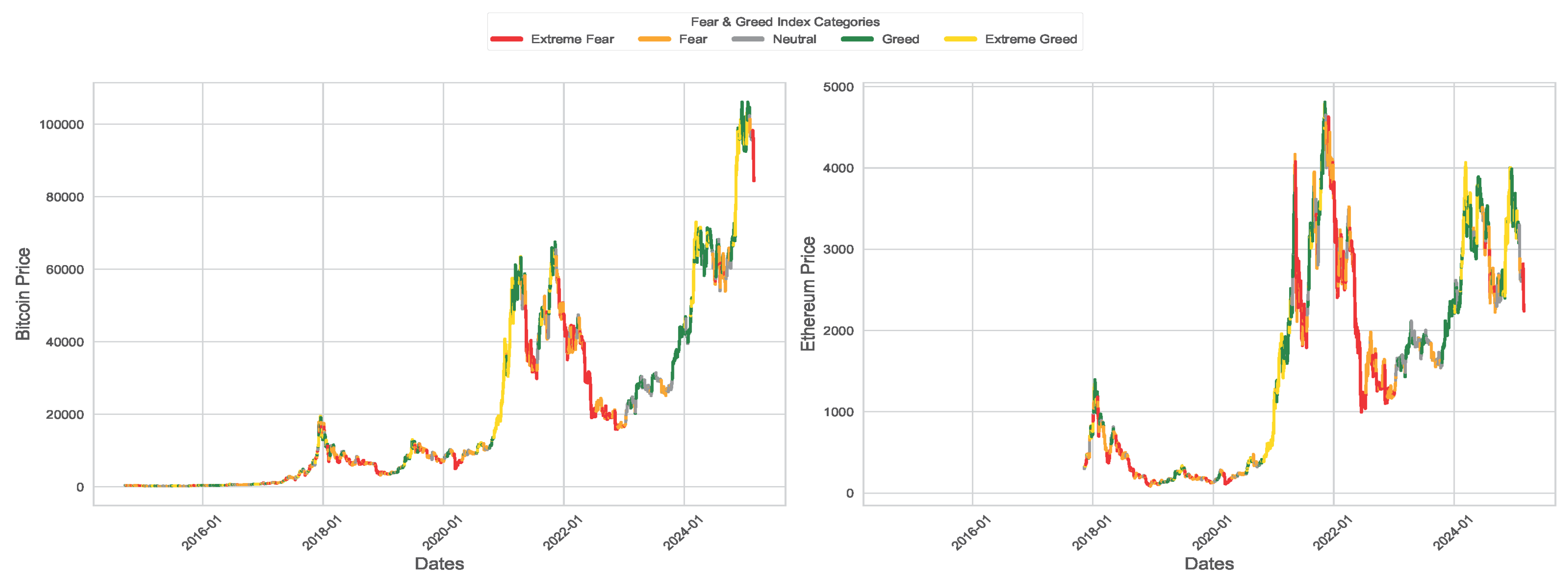
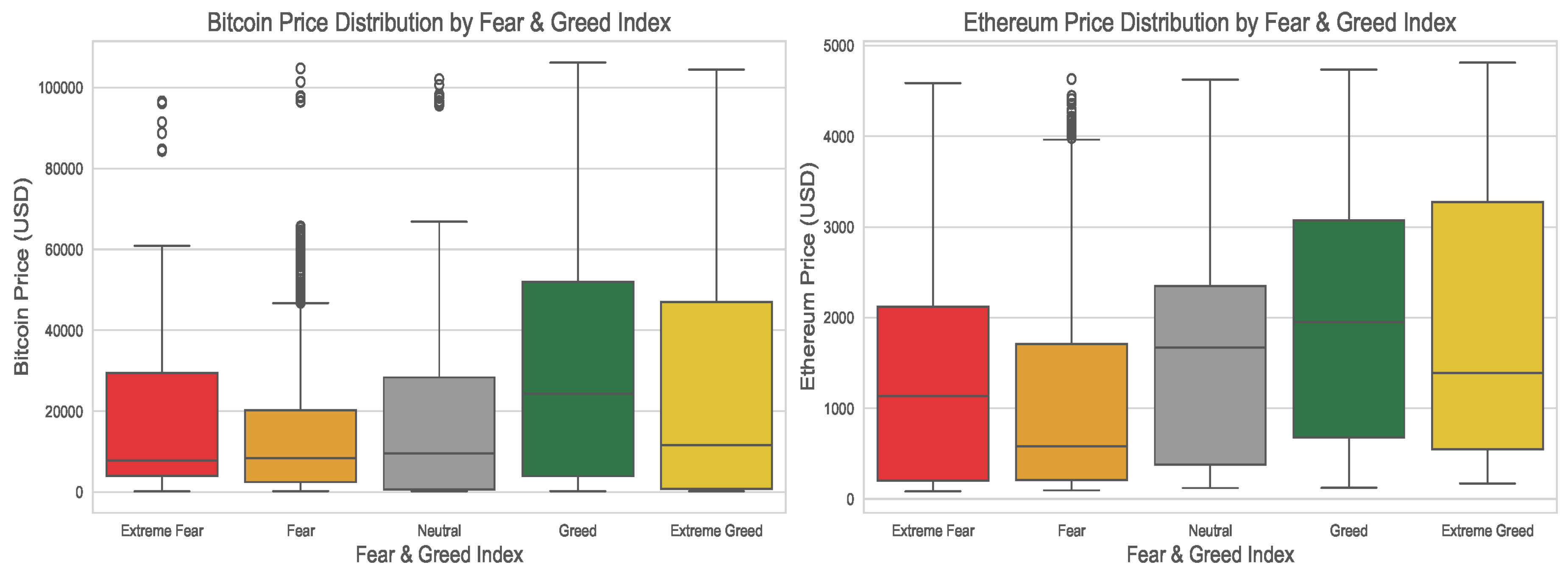
4. Exploratory Data Analysis
5. Conclusions and Recommendation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Razi, M.A., Athappilly, K. (2005). A comparative predictive analysis of neural networks (NNS), nonlinear regression and classification and regression tree (CART) models. Expert Systems with Applications, 29, 65–74.
- Ślepaczuk, R., Zenkova, M. (2018). Robustness of support vector machines in algorithmic trading on cryptocurrency market. Central European Economic Journal, 5, 186–205.
- Chen, Z., Li, C., Sun, W. (2020). Bitcoin price prediction using machine learning: An approach to sample dimension engineering. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 365, 112395.
- Mahdi, E., Leiva, V., Mara’Beh, S., Martin-Barreiro, C. (2021). A New Approach to Predicting Cryptocurrency Returns Based on the Gold Prices with Support Vector Machines during the COVID-19 Pandemic Using Sensor-Related Data. Sensors, 21, 6319. [CrossRef]
- Akyildirim, E., Goncu, A., Sensoy, A. (2021). Prediction of cryptocurrency returns using machine learning. Annals of Operations Research, 297, 3–36. [CrossRef]
- Makala, D., Li, Z. (2021). Prediction of gold price with ARIMA and SVM. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1767, 012022.
- Jaquart, P., K¨opke, S., Weinhardt, C. (2022). Machine learning for cryptocurrency market prediction and trading. The Journal of Finance and Data Science, 8: 331–352. [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, E., Al-Abdulla, A. (2022). Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic News on the Cryptocurrency Market and Gold Returns: A Quantile-on-Quantile Regression Analysis. Econometrics, 10, 26. [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, M., Iftikhar, H., Rodrigues, P. C., Rehman, M. Z., Salar, S. A. A. (2024). Statistical Modeling to Improve Time Series Forecasting Using Machine Learning, Time Series, and Hybrid Models: A Case Study of Bitcoin Price Forecasting. Mathematics, 12(23), 3666. [CrossRef]
- Broomhead, D. S., Lowe, D. (1988). Radial basis functions, multi-variable functional interpolation and adaptive networks (Technical report). Royal Signals and Radar Establishment (RSRE), Memorandum 4148.
- Broomhead, D. S.; Lowe, D. (1988). Multivariable functional interpolation and adaptive networks. Complex Systems, 2: 321–355.
- Alahmari, S., A., (2020). Predicting the Price of Cryptocurrency Using Support Vector Regression Methods. Journal of Mechanics of Continua and Mathematical Sciences, 15(4): 313–322. [CrossRef]
- Casillo, M., Lombardi, M., Lorusso, A., Marongiu, F., Santaniello, D., Valentino, C. (2022). Sentiment Analysis and Recurrent Radial Basis Function Network for Bitcoin Price Prediction. IEEE 21st Mediterranean Electrotechnical Conference (MELECON), Palermo, Italy, pp. 1189–1193, 10.1109/MELECON53508.2022.9842889.
- Zhang, Y. (2025). Stock price behavior determination using an optimized radial basis function. Intelligent Decision Technologies, 1–18. doi:10.1177/18724981251315846.
- Specht, D. F. (1991). A general regression neural network. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2(6): 568–576. doi:10.1109/72.97934.
- Martínez, F., Charte, F., Rivera, A.J., Frías, M.P. (2019). Automatic Time Series Forecasting with GRNN: A Comparison with Other Models. In: Rojas, I., Joya, G., Catala, A. (eds) Advances in Computational Intelligence. IWANN 2019, Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), 11506. Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- Martínez, F., Charte, F., Frías, M., P., Martínez-Rodríguez, A. M. (2022). Strategies for time series forecasting with generalized regression neural networks. Neurocomputing, 49: 509-521 . [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term memory. Neural Computation, 9(8): 1735–1780. [CrossRef]
- McNally, S., Roche, J., Caton, S. (2018). Predicting the Price of Bitcoin Using Machine Learning. 26th Euromicro International Conference on Parallel, Distributed and Network-based Processing (PDP), 339–343. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:206505441.
- Liu, Y., Gong, C., Yang, L., Chen, Y. (2020). DSTP-RNN: A dual-stage two-phase attention-based recurrent neural network for long-term and multivariate time series prediction. Expert Systems with Applications, 143, 113082.
- Zoumpekas, T. Houstis, E., Vavalis, M. (2020). ETH analysis and predictions utilizing deep learning. Expert Systems with Applications, 162: 113866. [CrossRef]
- Lahmiri, S., Bekiros, S. (2019). Cryptocurrency forecasting with deep learning chaotic neural networks. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 118, 35–40. [CrossRef]
- Ji, S., Kim, J., Im, H. (2019). A Comparative Study of Bitcoin Price Prediction Using Deep Learning. Mathematics, 7(10), 898. [CrossRef]
- Uras, N., Marchesi, L., Marchesi, M., Tonelli, R. (2020). Forecasting Bitcoin closing price series using linear regression and neural networks models. PeerJ Computer Science, 6: e279. [CrossRef]
- Lahmiri, S., and Bekiros, S. (2021). Deep learning forecasting in cryptocurrency high frequency trading. Cognitive Computation, 13: 485–487.
- Cho, K., Merrienboer, B., Gulcehre, C., Bahdanau, D., Fethi, B., Holger, S., Bengio, Y. (2014). Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder- decoder for statistical machine translation. https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.1078.
- Jianwei, E., Ye, J., Jin, H. (2019). A novel hybrid model on the prediction of time series and its application for the gold price analysis and forecasting. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 527, 121454. [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A., Kumar, S., Basu, M. (2020). A gated recurrent unit approach to bitcoin price prediction. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 13(2): 23. [CrossRef]
- Tanwar, S., Patel, N. P. , Patel, S. N., Patel, J. R., Sharma, G., Davidson, I.E. Deep Learning-Based Cryptocurrency Price Prediction Scheme With Inter-Dependent Relations. IEEE Access, 9: 138633–138646. 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3117848.
- Ye, Z., Wu, Y., Chen, H., Pan, Y., Jiang, Q. (2022). A Stacking Ensemble Deep Learning Model for Bitcoin Price Prediction Using Twitter Comments on Bitcoin. Mathematics, 10(8), 1307. [CrossRef]
- Patra1, G., R., Mohanty, M., N., (2023). Price Prediction of Cryptocurrency Using a Multi-Layer Gated Recurrent Unit Network with Multi Features. Computational Economics, 62: 1525–1544. [CrossRef]
- Hansun, S., Wicaksana, A ., Khaliq, A.Q.M. (2022). Multivariate cryptocurrency prediction: comparative analysis of three recurrent neural networks approaches. Journal of Big Data, 9, 50.
- Ferdiansyah, F., Othman, S. H., Radzi, R. Z., M., Stiawan, D., Sutikno T., (2023). Hybrid gated recurrent unit bidirectional-long short-term memory model to improve cryptocurrency prediction accuracy. IAES International Journal of Artificial Intelligence (IJ-AI), 12 (1). http://doi.org/10.11591/ijai.v12.i1.pp251-261.
- Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A. N., Polosukhin, I. (2017). Attention is all you need. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 30.
- Devlin, J., Chang, M. W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K. (2018). BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), pages 4171–4186, Minneapolis, Minnesota. Association for Computational Linguistics. 10.18653/v1/N19-1423.
- Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn, D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer, M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S., Uszkoreit, J., Houlsby, N. (2020). An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. ArXiv, abs/2010.11929.
- Zhou, H., Zhang, S., Peng, J., Zhang, S., Li, J., Xiong, H., Zhang, W. (2021). Informer: Beyond Efficient Transformer for Long Sequence Time-Series Forecasting. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 35(12), 11106–11115. [CrossRef]
- Grigsby, J., Wang, Z., Qi, Y. (2021). Long-Range Transformers for Dynamic Spatiotemporal Forecasting. computer science bibliography. ArXiv, https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.12218.
- Lezmi, E., Xu, J. (2023). Time Series Forecasting with Transformer Models and Application to Asset Management. Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4375798 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4375798.
- Kristoufek, L. (2013). BitCoin meets Google Trends and Wikipedia: Quantifying the relationship between phenomena of the Internet era. Scientific Reports, 3, 3415. [CrossRef]
- Urquhart, A. (2018). What causes the attention of Bitcoin?. Economics Letters, 166, 40–44, . [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.S., Day, M.Y., Chou, K.H. (2024). A comparison of bitcoin futures return and return volatility based on news sentiment contemporaneously or lead-lag. The North American Journal of Economics and Finance, 72, 102159. [CrossRef]
- Colah Understanding LSTM Networks. (2015). Available online: http://colah.github.io/posts/2015-08-Understanding-LSTMs/ (accessed on March 01, 2024).
| Cryptocurrency | Start Date | End Date | Number of Records |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin | September 17, 2014 | February 28, 2025 | 3818 |
| Ethereum | November 9, 2017 | February 28, 2025 | 2669 |
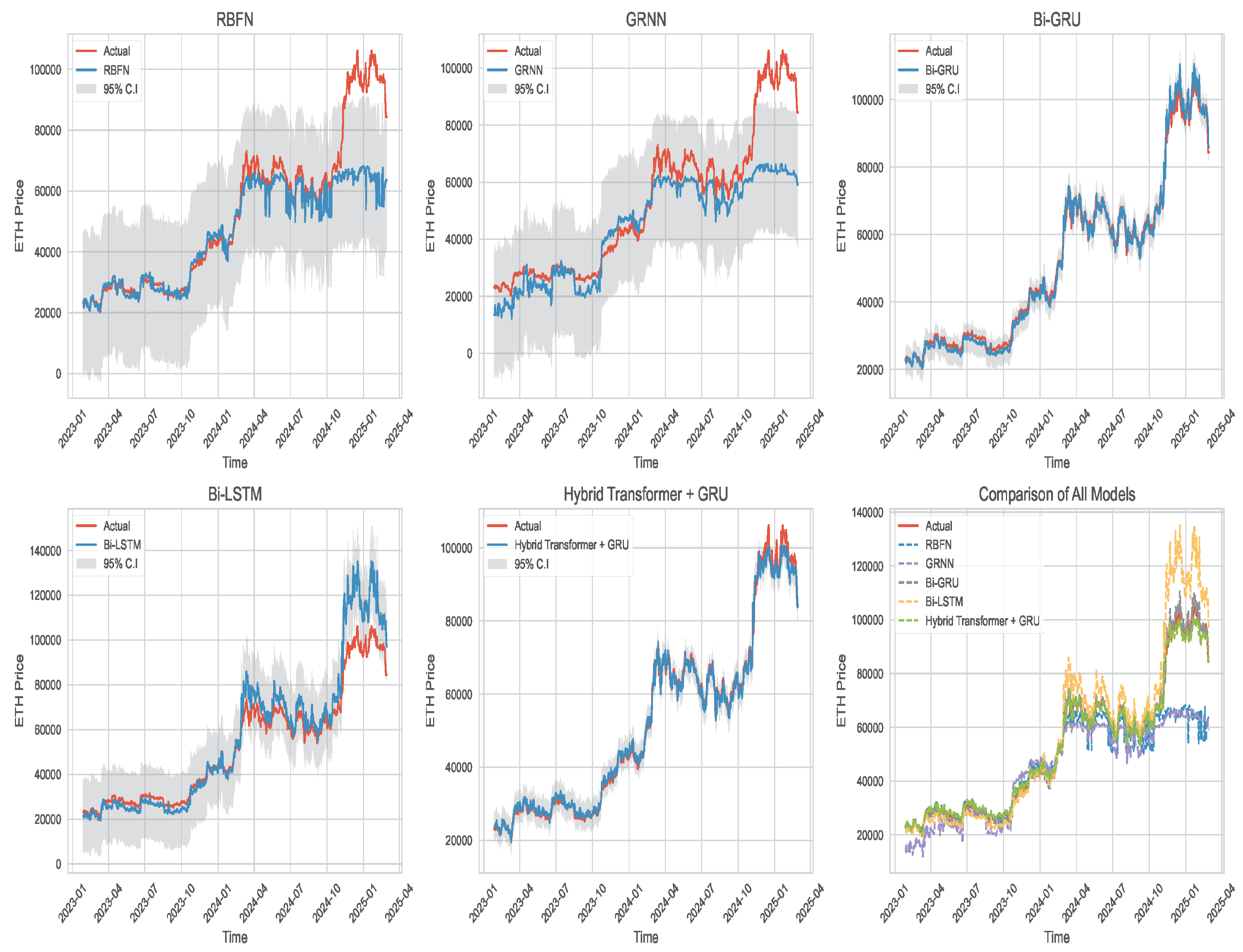
| Model | MSE | RMSE | MAE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBFN | 1.731258e+08 | 13157.727 | 6928.640 | 9.479 |
| GRNN | 1.875502e+08 | 13694.897 | 9179.342 | 15.857 |
| BiGRU | 4.358457e+06 | 2087.692 | 1559.954 | 3.271 |
| BiLSTM | 8.184621e+07 | 9046.889 | 5877.042 | 9.600 |
| Hybrid Transformer + GRU | 3.818128e+06 | 1954.003 | 1419.972 | 2.825 |
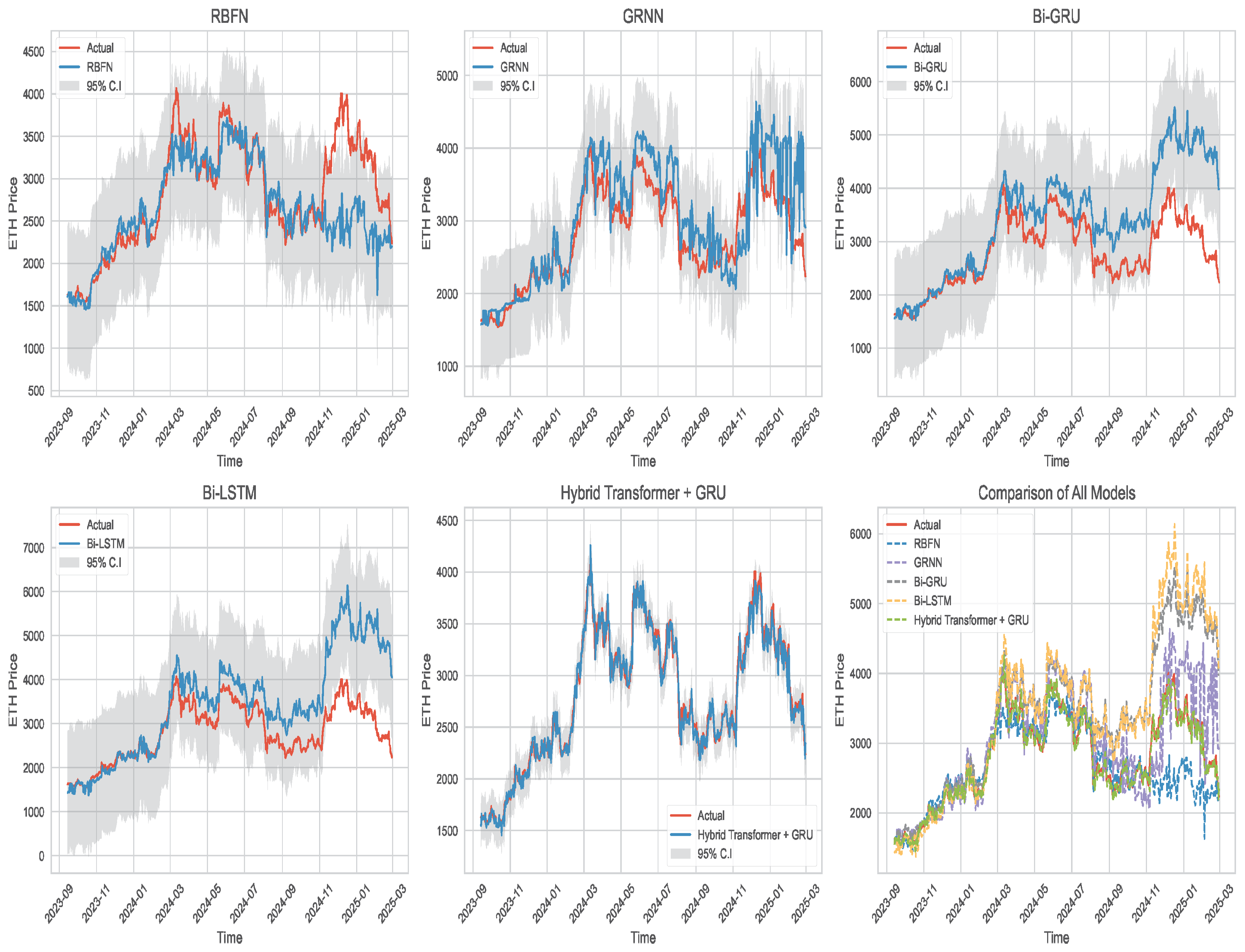
| Model | MSE | RMSE | MAE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBFN | 203541.169 | 451.155 | 288.453 | 9.362 |
| GRNN | 194985.943 | 441.572 | 345.963 | 11.901 |
| BiGRU | 687799.984 | 829.337 | 608.416 | 20.735 |
| BiLSTM | 907844.180 | 952.809 | 675.427 | 22.640 |
| Hybrid Transformer + GRU | 11344.686 | 106.511 | 78.809 | 2.755 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





