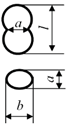
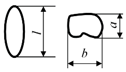
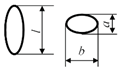
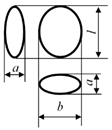
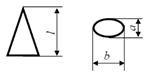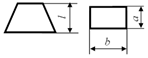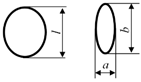The quality of planting onions seeds with planting machine depends on the probability of how many seeds fall into the cells of the wheel. The fact that the seeds fall into the wheel cells can be considered a coincidence. Therefore, we are investigating how many onion seeds are likely to fall into the disc slots.
The fact that how many seeds fall into the wheel slots of the planting machine and their position depends on their shape. According to ([
1] p.7-8), [
2,
3], seeds can be in the following forms: spherical, elliptical, pyramidal, truncated pyramidal, oval, and bean-shaped (
Table 1).
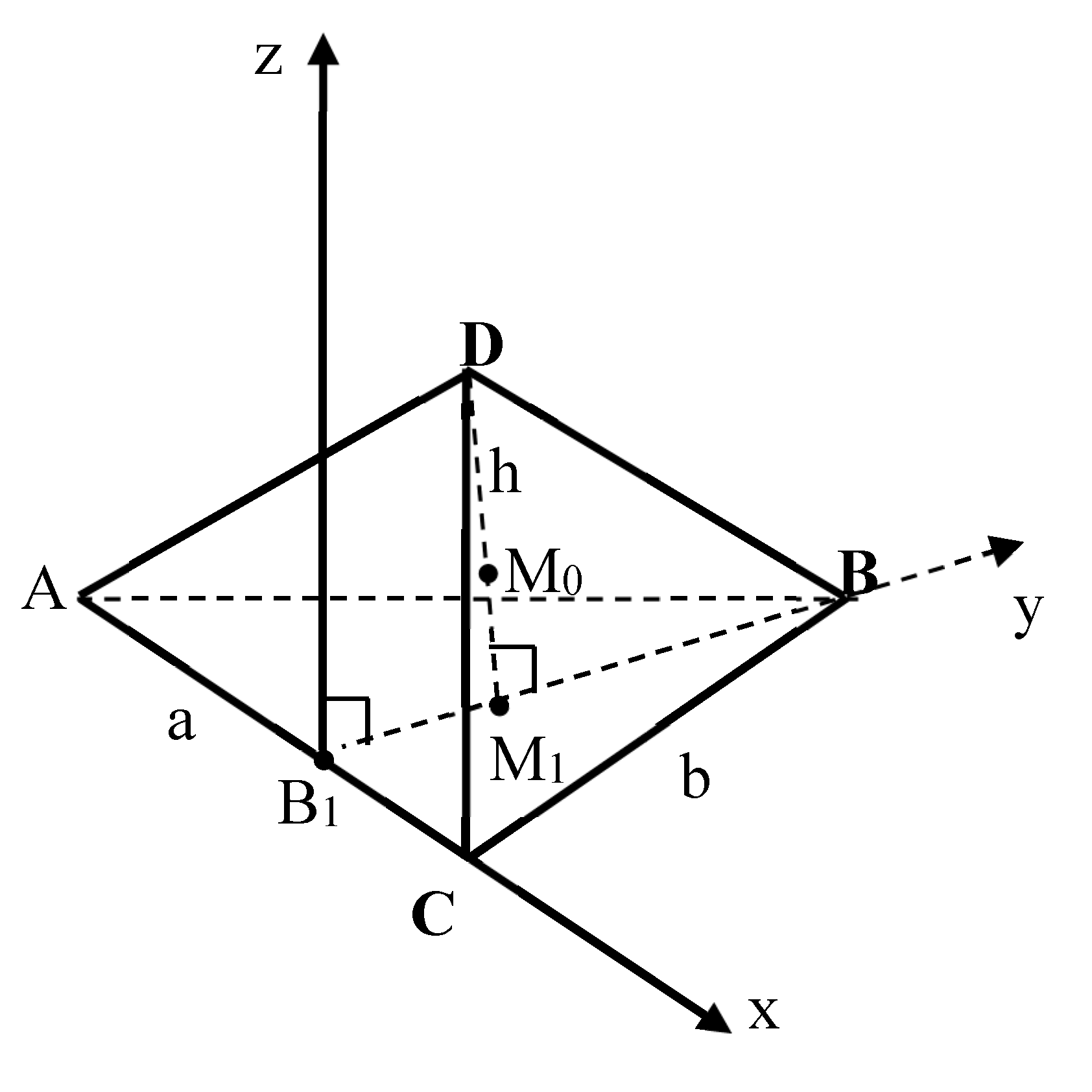
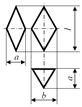
Based on the above information, based on the above, we can assume that the shape of the onion seed will be a ABCD pyramid whose base consists of an equilateral ABS triangle. Here, let
,
, be the center of gravity of the base M
0 (the point of intersection of the medians). For convenience, let the AC side lie on the x axis and have point B
1 in its center. Assuming point B
1 as the coordinate head, we align the positive direction of that axis with the light B
1B (
Figure 1). In this case, the coordinates of points A, B and C are as follows
The coordinate of point
М0 is the arithmetic mean of the coordinates of A, B, C points, i.e.
М1. If we consider the coordinates of A, B, C points, the coordinates of point
М0 will be
Using
Figure 1, we write the coordinates of point D through the height
h drawn from that point as follows
here
h is the height from point D to the center of gravity
We write the coordinate
М0 of the center of gravity of the onion seed, considering the point D, as in the following
Given the coordinates of points A, B, C, D, the coordinates
М1, the center of gravity of the onion seed as in the following
Whichever side the center of gravity of the onion seed is closer, the more likely it is to fall with that side. It follows that onion seeds are more likely to fall with the side where their center of gravity is. We therefore calculate the distances from the center of gravity to all sides.
Considering the ADC and BCD edges of the onion seed as a triangular flatness, we form the equation of plane of these triangles in accordance with ([
4] p.43-44), [
5,
6,
7].
The following is the equation of plane for ADC side of an onion seed:
Simplifying the determinant, we obtain the following expression for the ADC side of an onion seed:
The following is the equation of plane for the BCD side of an onion seed:
If we simplify the determinant, the following expression is formed for the BCD side of an onion seed:
Considering the distances between the sides of an onion seed and the center of gravity
М1 as plane, we determine the distance from the point to the plane. According to ([
4] p. 47-48), [
9], the distance from the point to the plane is expressed in the following:
Using expression (10), we determine the distances between the sides of an onion seed and the center of gravity
М1
The longer the distance is from the center of gravity to the side, the smaller the probability of falling with this side. If we consider that the ratios of the distances from the point to the sides are equal to the inverse of the probabilities of falling with that point:
here,
d1 is the distance from the center of gravity to the side ABC, mm;
d2 is the distance from the center of gravity to the side ACD, mm;
d3 is the distance from the center of gravity to the side ABD, mm; and
d4 is the distance from the center of gravity to the side BCD, mm.
What can be concluded from the above equations is that since the onion seed is considered to be pyramidal, the sum of the probabilities of falling into the slot with each side is equal to one, i.e. [
9,
10,
11,
12].
Given the expressions (14) and (15), we obtain the following:
Based on the expression (13), we obtain the following
In order to simplify the operations on expressions, we introduce the following notation:
Using expressions (17), (18) and (19), we obtain the following results:
To determine the probability of the side that the onion seed is likely to fall, we perform a numerical solution of the system of equations (20).
We perform the numerical solution of the system of equations (20) in the following dimensions of the onion seed: a=2,54, мм; b=3,54, мм; h=2,17, мм.
According to the results of numerical solutions of the system of equations (20), the probability of onion seeds falling into the wheel slot with a large surface side is 65%, the probability of falling with a medium surface side is 18% and the probability of falling with a small surface side is 17%.
Conclusions
Studies on how many onion seeds are placed in the wheel slot of the planting machine were carried out taking into account the center of gravity. The result is a system of equations that allows you to determine the probable number of placements in a slot. Based on the numerical solution, it was found that onion seeds are more likely to fall with a large surface area.
References
- N.P. Kryuchin. Seeding machines. Design features and development trends: Textbook. - Samara: RIC SGSKhA 2009, p.175.
- Ya. Narmanov. Analyst geometry. - T .: National society of Uzbekistan Philosophers Press, 2008. – p.176.
- V.E. Gmurman. Probability Theory and a Handbook for solving problems from mathematical statistics. - T .: O’qituvchi, 1980. – p. 322.
- Umurzakov, A.K., Turdaliev, V.M. & Khakimov, U.A. Low-Power Hydraulic Motor for Mobile Micropower Stations and Pumps. Russ. Engin. Res. 42, 791–793 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Makhkamov, G.U., Khakimov, U.A. Experimental Study of Micro-Hydropower Plants. Calculation of Water Wheel Efficiency. Russ. Engin. Res. 43, 1524–1527 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Khakimov, U. A. (2025). Issues of Creation of Water Engines for Mobile Micro-HPP and Pumps.
- Hakimov, UA (2025). Mobil mikro GES va nasoslar uchun suv dvigatellarini yaratish masalalari. Oldindan chop etish. [CrossRef]
- Khakimovich, U. A.; Akramovich, K. U. Creation of Water Engines for Mobile Micro Hydropower. Preprints 2025, 2025031277. [CrossRef]
- A X Umurzakov; M X Imomov; F R Maxmudov; S X Mamasoliyeva. The influence of the front section teeth lengths on the agrotechnical and energy performance of a two-stage vibratory gear hardware for land. 2023, 1284, 012025 . [CrossRef]
- A X Umurzakov; A A Qosimov; M X Imomov; K A Xamidov. Theoretical study of the formation of relaxation autovibration in the working organs of a toothed harrow. 2022, 1112 . [CrossRef]
- Khakimov, U.; Kosimov, A. Justification of the Modes of Movement of the Seeding Apparatus. Preprints 2025, 2025031425. [CrossRef]
- Khakimovich, U. A.; Akramovich, K. U. Creation of Water Engines for Mobile Micro Hydropower. Preprints 2025, 2025031277. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).