Submitted:
27 February 2025
Posted:
28 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
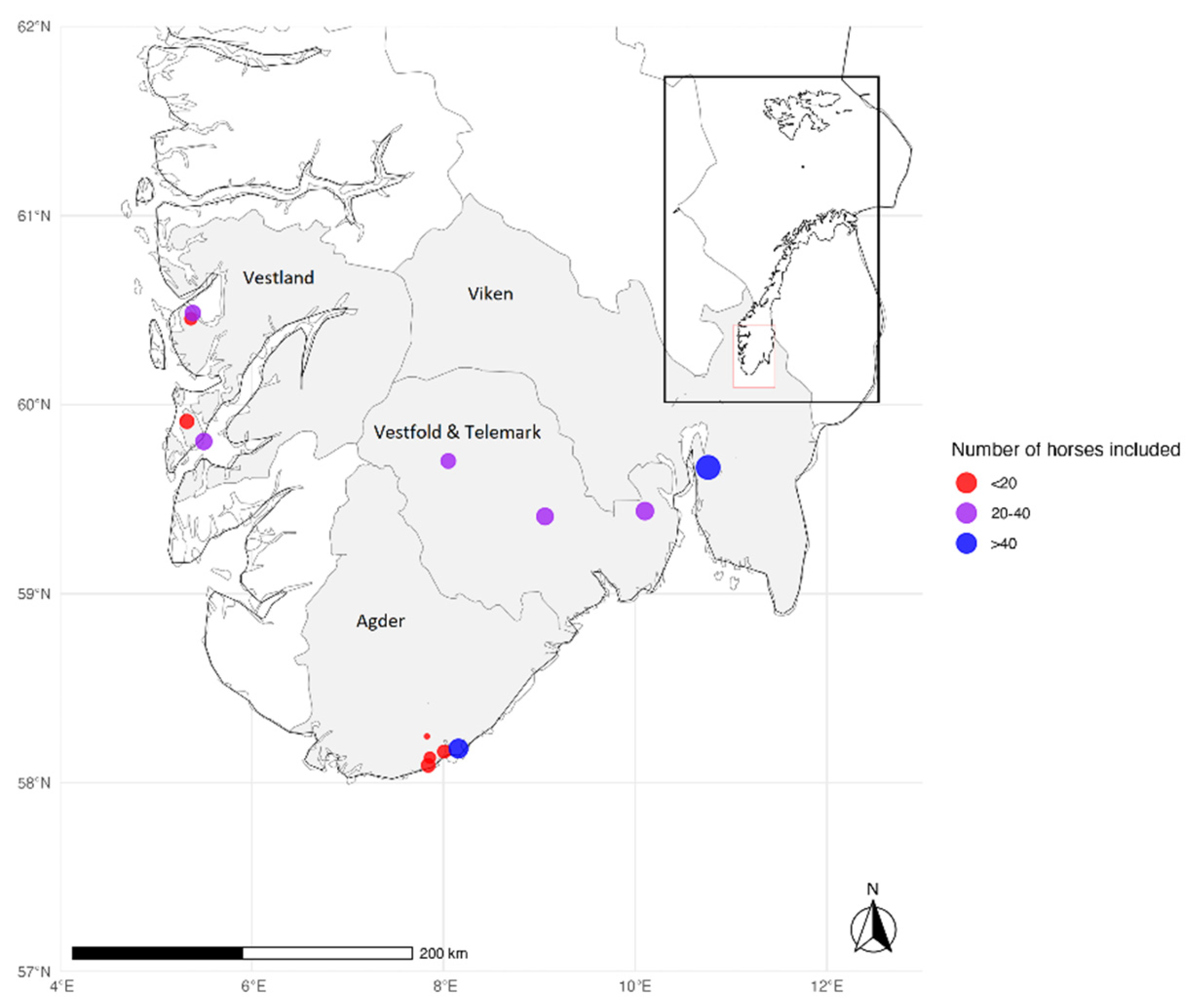
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. IgG-Antibody Testing
2.3. Statistics
2.4. Spatial Visualization
2.5. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Seroprevalence of Tick-Borne Pathogens in Horses in Southern Norway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | In January 2024, Vestfold & Telemark County was split into two counties; Vestfold and Telemark, whereas Viken County was split into three counties; Østfold, Akershus, and Buskerud. |
References
- Kjaer, L.J.; Soleng, A.; Edgar, K.S.; Lindstedt, H.E.H.; Paulsen, K.M.; Andreassen, A.K.; Korslund, L.; Kjelland, V.; Slettan, A.; Stuen, S.; et al. A large-scale screening for the taiga tick, Ixodes persulcatus, and the meadow tick, Dermacentor reticulatus, in southern Scandinavia, 2016. Parasit Vectors 2019, 12, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleng, A.; Edgar, K.S.; Paulsen, K.M.; Pedersen, B.N.; Okbaldet, Y.B.; Skjetne, I.E.B.; Gurung, D.; Vikse, R.; Andreassen, A.K. Distribution of Ixodes ricinus ticks and prevalence of tick-borne encephalitis virus among questing ticks in the Arctic Circle region of northern Norway. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2018, 9, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, R. The distribution and host relations of Norwegian ticks (Acari, Ixodides). 1983.
- Hvidsten, D.; Stuen, S.; Jenkins, A.; Dienus, O.; Olsen, R.S.; Kristiansen, B.E.; Mehl, R.; Matussek, A. Ixodes ricinus and Borrelia prevalence at the Arctic Circle in Norway. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2014, 5, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jore, S.; Vanwambeke, S.O.; Viljugrein, H.; Isaksen, K.; Kristoffersen, A.B.; Woldehiwet, Z.; Johansen, B.; Brun, E.; Brun-Hansen, H.; Westermann, S.; et al. Climate and environmental change drives Ixodes ricinus geographical expansion at the northern range margin. Parasit Vectors 2014, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otranto, D.; Wall, R. New strategies for the control of arthropod vectors of disease in dogs and cats. Med Vet Entomol 2008, 22, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjelland, V.; Stuen, S.; Skarpaas, T.; Slettan, A. Prevalence and genotypes of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato infection in Ixodes ricinus ticks in southern Norway. Scand J Infect Dis 2010, 42, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjelland, V.; Ytrehus, B.; Vikorren, T.; Stuen, S.; Skarpaas, T.; Slettan, A. Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato detected in skin of Norwegian mountain hares (Lepus timidus) without signs of dissemination. J Wildl Dis 2011, 47, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaer, L.J.; Klitgaard, K.; Soleng, A.; Edgar, K.S.; Lindstedt, H.E.H.; Paulsen, K.M.; Andreassen, A.K.; Korslund, L.; Kjelland, V.; Slettan, A.; et al. Spatial patterns of pathogen prevalence in questing Ixodes ricinus nymphs in southern Scandinavia, 2016. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 19376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosef, O.; Radzijevskaja, J.; Paulauskas, A.; Haslekas, C. The prevalence of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in host-seeking Ixodes ricinus ticks in Norway. Clin Microbiol Infect 2009, 15 Suppl 2, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreassen, A.; Jore, S.; Cuber, P.; Dudman, S.; Tengs, T.; Isaksen, K.; Hygen, H.O.; Viljugrein, H.; Ånestad, G.; Ottesen, P. Prevalence of tick borne encephalitis virus in tick nymphs in relation to climatic factors on the southern coast of Norway. Parasites & vectors 2012, 5, 177. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, A.; Raasok, C.; Pedersen, B.N.; Jensen, K.; Andreassen, A.; Soleng, A.; Edgar, K.S.; Lindstedt, H.H.; Kjelland, V.; Stuen, S.; et al. Detection of Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis in Norway up to the northern limit of Ixodes ricinus distribution using a novel real time PCR test targeting the groEL gene. BMC Microbiol 2019, 19, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarsten, H.; Skarpaas, T.; Fajs, L.; Noraas, S.; Kjelland, V. Tick-borne bacteria in Ixodes ricinus collected in southern Norway evaluated by a commercial kit and established real-time PCR protocols. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2015, 6, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjelland, V.; Rollum, R.; Korslund, L.; Slettan, A.; Tveitnes, D. Borrelia miyamotoi is widespread in Ixodes ricinus ticks in southern Norway. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2015, 6, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oines, O.; Radzijevskaja, J.; Paulauskas, A.; Rosef, O. Prevalence and diversity of Babesia spp. in questing Ixodes ricinus ticks from Norway. Parasit Vectors 2012, 5, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacristan, C.; das Neves, C.G.; Suhel, F.; Sacristan, I.; Tengs, T.; Hamnes, I.S.; Madslien, K. Bartonella spp. detection in ticks, Culicoides biting midges and wild cervids from Norway. Transbound Emerg Dis 2021, 68, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thortveit, E.T.; Aase, A.; Petersen, L.B.; Lorentzen, A.R.; Mygland, A.; Ljostad, U. Human seroprevalence of antibodies to tick-borne microbes in southern Norway. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2020, 11, 101410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, A.; Glass, A.; Topp, A.K.; Strube, C. Zoonotic Tick-Borne Pathogens in Temperate and Cold Regions of Europe-A Review on the Prevalence in Domestic Animals. Front Vet Sci 2020, 7, 604910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, C.; Nijhof, A.; Jongejan, F.; Van der Kolk, J. Anaplasma phagocytophilum infection in horses in the Netherlands. Veterinary record 2008, 162, 216–217. [Google Scholar]
- M’Ghirbi, Y.; Yaich, H.; Ghorbel, A.; Bouattour, A. Anaplasma phagocytophilum in horses and ticks in Tunisia. Parasit Vectors 2012, 5, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passamonti, F.; Veronesi, F.; Cappelli, K.; Capomaccio, S.; Coppola, G.; Marenzoni, M.L.; Piergili, F.D.; Verini, S.A.; Coletti, M. Anaplasma phagocytophilum in horses and ticks: a preliminary survey of Central Italy. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 2010, 33, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conze, T.M.; Bagó, Z.; Revilla-Fernández, S.; Schlegel, J.; Goehring, L.S.; Matiasek, K. Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) infection in two horses. Viruses 2021, 13, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divers, T.J. Equine lyme disease. Journal of equine veterinary science 2013, 33, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Heus, P.; Bagó, Z.; Weidinger, P.; Lale, D.; Trachsel, D.S.; Revilla-Fernández, S.; Matiasek, K.; Nowotny, N. Severe neurologic disease in a horse caused by tick-borne encephalitis virus, Austria, 2021. Viruses 2023, 15, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C. R: A language and environment for statistical computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Henry, L.; Pedersen, T.L.; Takahashi, K.; Wilke, C.; Woo, K.; Yutani, H.; Dunnington, D.; Brand, T.v.d. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer-Verlag New York: 2016.
- Pebesma, E. Simple Features for R: Standardized Support for Spatial Vector Data. R Journal 2018, 10, 439–446. [Google Scholar]
- Kjaer, L.J.; Soleng, A.; Edgar, K.S.; Lindstedt, H.E.H.; Paulsen, K.M.; Andreassen, A.K.; Korslund, L.; Kjelland, V.; Slettan, A.; Stuen, S.; et al. Predicting and mapping human risk of exposure to Ixodes ricinus nymphs using climatic and environmental data, Denmark, Norway and Sweden, 2016. Euro Surveill 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyngholt, M.C. Anaplasma phagocytophilum hos hest: En seroprevalensstudie hos islandshest i Grimstad kommune. Available online: https://www.ddd.dk/media/2090/mari-c-lyngholt.pdf (accessed on 20.10).
- Egenvall, A.; Franzén, P.; Gunnarsson, A.; Engvall, E.O.; Vågsholm, I.; Wikström, U.-B.; Artursson, K. Cross-sectional study of the seroprevalence to Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato and granulocytic Ehrlichia spp. and demographic, clinical and tick-exposure factors in Swedish horses. Preventive veterinary medicine 2001, 49, 191–208. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M.G.; Christoffersen, M.; Thuesen, L.R.; Petersen, M.R.; Bojesen, A.M. Seroprevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Danish horses. Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica 2010, 52, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Traversa, D.; Milillo, P.; Maggi, R.; Simonato, G.; Di Cesare, A.; Pezzuto, C.; Grillini, M.; Morelli, S.; Colombo, M.; Passarelli, A.; et al. Seroexposure to Zoonotic Anaplasma and Borrelia in Dogs and Horses That Are in Contact with Vulnerable People in Italy. Pathogens 2023, 12, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanasiou, L.V.; Katsogiannou, E.G.; Tyrnenopoulou, P.; Gougoulis, D.; Apostolidis, K.N.; Papadakis, S.M.; Kokkinaki, K.C.G.; Papatsiros, V.G.; Tsokana, C.N. Evidence of Horse Exposure to Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Borrelia burgdorferi, and Leishmania infantum in Greece through the Detection of IgG Antibodies in Serum and in an Alternative Diagnostic Sample—The Saliva. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, I.; Silaghi, C.; Fischer, S.; Marsboom, C.; Hendrickx, G.; Gehlen, H.; Muller, E. Detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in horses from Germany by molecular and serological testing (2008-2021). Vet Parasitol 2022, 312, 109840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehlen, H.; Inerle, K.; Bartel, A.; Stöckle, S.D.; Ulrich, S.; Briese, B.; Straubinger, R.K. Seroprevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato and Anaplasma phagocytophilum Infections in German Horses. Animals 2023, 13, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjelland, V.; Paulsen, K.M.; Rollum, R.; Jenkins, A.; Stuen, S.; Soleng, A.; Edgar, K.S.; Lindstedt, H.H.; Vaino, K.; Gibory, M.; et al. Tick-borne encephalitis virus, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, Borrelia miyamotoi, Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis in Ixodes ricinus ticks collected from recreational islands in southern Norway. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2018, 9, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, A.; Kristiansen, B.E.; Allum, A.G.; Aakre, R.K.; Strand, L.; Kleveland, E.J.; van de Pol, I.; Schouls, L. Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato and Ehrlichia spp. in Ixodes ticks from southern Norway. J Clin Microbiol 2001, 39, 3666–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stigum, V.M.; Jaarsma, R.I.; Sprong, H.; Rolandsen, C.M.; Mysterud, A. Infection prevalence and ecotypes of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in moose Alces alces, red deer Cervus elaphus, roe deer Capreolus capreolus and Ixodes ricinus ticks from Norway. Parasit Vectors 2019, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mysterud, A.; Easterday, W.R.; Qviller, L.; Viljugrein, H.; Ytrehus, B. Spatial and seasonal variation in the prevalence of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in questing Ixodes ricinus ticks in Norway. Parasit Vectors 2013, 6, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuen, S.; Pettersen, K.S.; Granquist, E.G.; Bergstrom, K.; Bown, K.J.; Birtles, R.J. Anaplasma phagocytophilum variants in sympatric red deer (Cervus elaphus) and sheep in southern Norway. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2013, 4, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatat, S.E.H.; Kachani, M.; Duchateau, L.; Elhachimi, L.; Sahibi, H.; Daminet, S. Anaplasma spp in dogs: Is there a danger for humans? Revue Vétérinaire Clinique 2022, 57, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wass, L.; Grankvist, A.; Mattsson, M.; Gustafsson, H.; Krogfelt, K.; Olsen, B.; Nilsson, K.; Martensson, A.; Quarsten, H.; Henningsson, A.J.; et al. Serological reactivity to Anaplasma phagocytophilum in neoehrlichiosis patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2018, 37, 1673–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, A.; Raasok, C.; Pedersen, B.N.; Jensen, K.; Andreassen, A.; Soleng, A.; Edgar, K.S.; Lindstedt, H.H.; Kjelland, V.; Stuen, S.; et al. Correction to: Detection of Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis in Norway up to the northern limit of Ixodes ricinus distribution using a novel real time PCR test targeting the groEL gene. BMC Microbiol 2020, 20, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefančíková, A.; Štepánová, G.; Pet’ko, B.; Nadzamová, D.; Szestáková, E.; Škardová, I.; Leinstein, R. Prevalence of antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in horses of East Slovakia. Veterinarni Medicina 2000, 45, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Ebani, V.V.; Bertelloni, F.; Pinzauti, P.; Cerri, D. Seroprevalence of Leptospira spp. and Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in Italian horses. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine 2012, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Kiss, T.; Cadar, D.; Krupaci, A.F.; Bordeanu, A.; Brudasca, G.F.; Mihalca, A.D.; Mircean, V.; Gliga, L.; Dumitrache, M.O.; Spinu, M. Serological reactivity to Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in dogs and horses from distinct areas in Romania. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2011, 11, 1259–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strnad, M.; Honig, V.; Ruzek, D.; Grubhoffer, L.; Rego, R.O.M. Europe-Wide Meta-Analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato Prevalence in Questing Ixodes ricinus Ticks. Appl Environ Microbiol 2017, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, A.K.; Springer, A.; Mischke, R.; Rieder, J.; Feige, K.; Ganter, M.; Nagel-Kohl, U.; Nordhoff, M.; Boelke, M.; Becker, S.; et al. Seroprevalence of tick-borne encephalitis virus in wild and domestic animals in northern Germany. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2023, 14, 102220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikutova, S.; Hornok, S.; Hubalek, Z.; Dolezalkova, I.; Juricova, Z.; Rudolf, I. Serological survey of domestic animals for tick-borne encephalitis and Bhanja viruses in northeastern Hungary. Vet Microbiol 2009, 135, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, J.O.; Lecollinet, S.; Hubalek, Z.; Svobodova, P.; Lussy, H.; Nowotny, N. Tick-borne encephalitis virus in horses, Austria, 2011. Emerg Infect Dis 2013, 19, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csank, T.; Drzewnioková, P.; Korytár, Ľ.; Major, P.; Gyuranecz, M.; Pistl, J.; Bakonyi, T. A serosurvey of flavivirus infection in horses and birds in Slovakia. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases 2018, 18, 206–213. [Google Scholar]
- Vilibic-Cavlek, T.; Krcmar, S.; Bogdanic, M.; Tomljenovic, M.; Barbic, L.; Roncevic, D.; Sabadi, D.; Vucelja, M.; Santini, M.; Hunjak, B.; et al. An Overview of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Epidemiology in Endemic Regions of Continental Croatia, 2017-2023. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautienius, A.; Armonaite, A.; Simkute, E.; Zagrabskaite, R.; Buitkuviene, J.; Alpizar-Jara, R.; Grigas, J.; Zakiene, I.; Zienius, D.; Salomskas, A.; et al. Cross-Sectional Study on the Prevalence and Factors Influencing Occurrence of Tick-Borne Encephalitis in Horses in Lithuania. Pathogens 2021, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gothe, L.M.; Ganzenberg, S.; Ziegler, U.; Obiegala, A.; Lohmann, K.L.; Sieg, M.; Vahlenkamp, T.W.; Groschup, M.H.; Hörügel, U.; Pfeffer, M. Horses as Sentinels for the Circulation of Flaviviruses in Eastern–Central Germany. Viruses 2023, 15, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, K.M.; Stuen, S.; das Neves, C.G.; Suhel, F.; Gurung, D.; Soleng, A.; Stiasny, K.; Vikse, R.; Andreassen, A.K.; Granquist, E.G. Tick-borne encephalitis virus in cows and unpasteurized cow milk from Norway. Zoonoses Public Health 2019, 66, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, K.M.; Das Neves, C.G.; Granquist, E.G.; Madslien, K.; Stuen, S.; Pedersen, B.N.; Vikse, R.; Rocchi, M.; Laming, E.; Stiasny, K. Cervids as sentinel-species for tick-borne encephalitis virus in Norway-A serological study. Zoonoses and Public Health 2020, 67, 342–351. [Google Scholar]
- Ytrehus, B.; Vainio, K.; Dudman, S.G.; Gilray, J.; Willoughby, K. Tick-borne encephalitis virus and louping-ill virus may co-circulate in Southern Norway. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2013, 13, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvik, A.; Tveten, Y.; Pedersen, A.B.; Stiasny, K.; Andreassen, A.K.; Grude, N. Low prevalence of tick-borne encephalitis virus antibodies in Norwegian blood donors. Infect Dis (Lond) 2021, 53, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikse, R.; Paulsen, K.M.; Edgar, K.S.; J, H.O.P.; Ottesen, P.S.; Okbaldet, Y.B.; Kiran, N.; Lamsal, A.; Lindstedt, H.E.H.; Pedersen, B.N.; et al. Geographical distribution and prevalence of tick-borne encephalitis virus in questing Ixodes ricinus ticks and phylogeographic structure of the Ixodes ricinus vector in Norway. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MSIS. The Norwegian Surveillance System for Communicable Dieases (MSIS). Available online: https://msis.no/ (accessed on 15.01).
- Hjetland, R.; Henningsson, A.J.; Vainio, K.; Dudman, S.G.; Grude, N.; Ulvestad, E. Seroprevalence of antibodies to tick-borne encephalitis virus and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in healthy adults from western Norway. Infect Dis (Lond) 2015, 47, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, K.M.; Vikse, R.; Soleng, A.; Edgar, K.S.; Dudman, S.; Wiklund, B.S.; Andreassen, A. TBE in Norway. TBE-the book 2017.
- Gao, G.F.; Jiang, W.R.; Hussain, M.H.; Venugopal, K.; Gritsun, T.S.; Reid, H.W.; Gould, E.A. Sequencing and antigenic studies of a Norwegian virus isolated from encephalomyelitic sheep confirm the existence of louping ill virus outside Great Britain and Ireland. Journal of General Virology 1993, 74, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Lamsal, A.; Tryland, M.; Paulsen, K.M.; Romano, J.S.; Nymo, I.H.; Stiasny, K.; Soleng, A.; Vikse, R.; Andreassen, A.K. Serological screening for tick-borne encephalitis virus in eight Norwegian herds of semi-domesticated reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus). Zoonoses Public Health 2023, 70, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasparkova, N.; Bartova, E.; Zakovska, A.; Budikova, M.; Sedlak, K. Antibodies against Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato in Clinically Healthy and Sick Horses: First Report from the Czech Republic. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
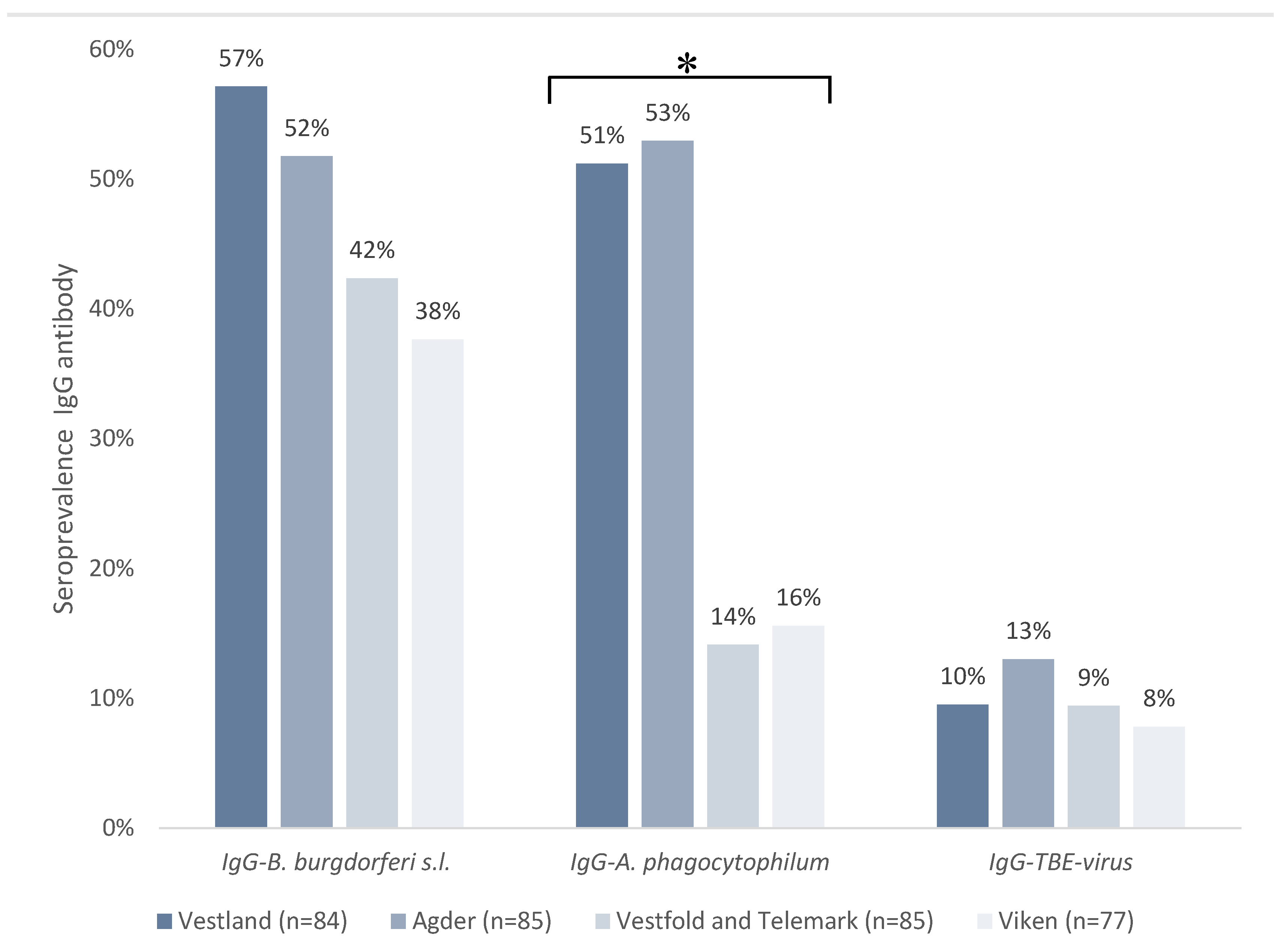
| Total (N = 331) | Agder (N = 85) | Vestfold & Telemark (N = 85) | Vestland (N = 84) | Viken (N = 77) | |
| % (n) | % (n) | % (n) | % (n) | % (n) | |
| Bbsl1 | 26 (85) | 19 (16) | 31 (26) | 24 (20) | 30 (23) |
| Ap2 | 13 (42) | 20 (17) | 5 (4) | 18 (15) | 8 (6) |
| TBEV3 | 2 (8) | 0 | 6 (5) | 1 (1) | 3 (2) |
| Bbsl + Ap | 17 (55) | 24 (20) | 8 (7) | 29 (24) | 5 (4) |
| Bbsl + TBEV | 4 (12) | 6 (5) | 2 (2) | 4 (3) | 3 (2) |
| Ap + TBEV | 2 (8) | 4 (3) | 0 | 4 (3) | 3 (2) |
| Bbsl + Ap + TBEV | 2 (7) | 6 (5) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Total positive | 66 (217) | 78 (66) | 53 (45) | 80 (67) | 51 (39) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





