1. Introduction
In today’s digital world, businesses use Artificial Intelligence (AI) to improve customer experience. Emotion AI, a branch of AI, helps recognize and respond to human emotions, making customer interactions more personalized and engaging [
1]. However, while it enhances customer service, it also raises serious concerns about data privacy and security [
2].
Emotion AI analyzes emotions through text, speech, and facial expressions, allowing businesses to offer better responses [
3]. In industries like banking and customer service, AI-powered personalization builds customer trust and improves service quality. Studies show that emotion-aware AI can increase customer satisfaction, engagement, and sales by making interactions feel more natural [
4].
However, recent fraud trends highlight the risks of AI-driven personalization. Cybercriminals increasingly exploit AI-generated synthetic voices and deepfake facial expressions to manipulate biometric authentication systems, leading to unauthorized access and financial fraud. Such incidents emphasize the need for robust security mechanisms in AI-driven customer interactions.
Despite its benefits, Emotion AI relies on personal and biometric data, raising concerns about privacy and misuse [
5]. Techniques like differential privacy and federated learning help protect user data. Businesses must also follow strict regulations to ensure ethical AI use.
To address these challenges, we propose emoAIsec, a system that combines Emotion AI with strong data protection. It uses encryption, privacy-focused analytics, and legal compliance to ensure safe and ethical AI-powered customer experiences. This approach allows businesses to balance innovation with security, making AI-driven interactions more trustworthy and effective.
2. Related Work
The integration of advanced technologies, including Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and data protection strategies, has profoundly altered the optimization of customer experience. This section examines relevant research [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11] that underscores the combination of AI, emotion recognition, and data security to improve customer engagement and loyalty.
Rane et al. (2023) [
6] explored the revolutionary possibilities of the Metaverse, driven by technologies such as Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Artificial Intelligence (AI). The study highlighted that immersive virtual environments, along with gamified experiences and real-time customer care, can enhance emotional ties and elevate customer engagement and satisfaction. Customized avatars and interactive components inside the Metaverse cultivate a sense of community, rendering it an effective instrument for augmenting client loyalty.
Baddam (2022) [
7] examined the use of augmented reality and virtual reality technologies in developing immersive brand experiences. The research indicated that these technologies profoundly captivate viewers and create enduring impressions, hence augmenting brand engagement and loyalty. Baddam emphasized the need for voice search optimization for businesses to address the growing prevalence of speech-enabled devices. The incorporation of multichannel experiences, user-generated content (UGC), and influencer marketing was emphasized as crucial techniques to improve digital visibility and cultivate consumer trust.
Fatin Aqilah et al. (2023) [
8] examined the influence of AI-driven voice assistants on contemporary customer service models. These assistants offer round-the-clock availability, instantaneous responses, and exceptional customization. The research emphasized their capacity to meet modern consumer needs for immediacy, precision, and seamless device integration while effectively handling privacy concerns.
Rane (2023) [
9] analyzed how the combination of AI, IoT, and Big Data technologies might enhance consumer loyalty through real-time data collection and predictive analytics. The study highlighted Blockchain’s importance in facilitating safe transactions and data transparency, hence enhancing trust and reinforcing customer connections. This strategy improves customer satisfaction by providing customized solutions and anticipatory assistance. Finally, Rane et al. also investigated the capacity of Blockchain and decentralized networks to improve customer data security. The research illustrated how these technologies enable users to manage their data, promoting transparency in business-consumer relations. Through the integration of decentralized systems, enterprises may establish trust and provide strong data protection.
H. Vijaykumar (2023) [
10] investigated the link between revenue growth rate and AI-powered customer experience by examining the impact of organizations’ annual subscriptions (
$ value). Companies can take steps to maximize AI deployment for long-term company performance and customer experience by evaluating revenue growth and the value of customer experience. Companies that have adopted AI technology have been able to increase customer happiness and loyalty while also providing more tailored and efficient services.
R. Panditharathna (2024) et al. [
11] explored the function of robotic service quality as a moderator of the link between customer retention, commitment, and latent trust components. The study’s findings include cybersecurity policy and cybersecurity awareness into the implementation of marketing strategies, benefiting marketers outside of the Latin American region. The authors analyze 231 valid replies from Brazil utilizing a survey-based study with the PLS-SEM technique, emphasizing the importance of marketing plan implementation.
Table 1.
Summary of technology integrated along with objective and insights of the study from related work [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11].
Table 1.
Summary of technology integrated along with objective and insights of the study from related work [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11].
| Ref |
Technology |
Objective of Study |
Insight(s) of Study |
| [6] |
Metaverse, VR, AR, AI |
Enhance customer loyalty in virtual environments |
Interactive connections, gamification, and real-time assistance enhance engagement and enjoyment. |
| [7] |
AR, VR, Multichannel Marketing |
Enhance brand engagement and visibility |
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality generate immersive experiences; multichannel strategies guarantee consistent client journeys. |
| [8] |
AI-powered Voice Assistants |
Transform customer service paradigms |
Customer expectations are redefined by real-time responses, 24/7 availability, and personalization. |
| [9] |
AI, IoT, Big Data |
Improve loyalty through data-driven personalization |
Real-time data acquisition and Blockchain technology ensure secure, tailored consumer engagements. |
| [10] |
Customer Experience with AI |
Increase revenue growth rate revolutionizing customer exp |
Deliver exceptional customer experience (not just in product terms), support, service, execution, and commitment |
| [11] |
Cybersecurity for trust |
Help marketers achieve their aim of providing high level of service |
Trust and commitment have positive impact on customer retention, robotic service quality has a partial effect |
3. emoAIsec Framework
The emoAIsec framework is a comprehensive system designed to enhance real-time customer experience optimization by integrating multimodal Emotion AI techniques with advanced data security measures. This framework ensures ethical and secure handling of emotional data while delivering highly personalized customer interactions. By combining emotion recognition technologies with robust privacy safeguards, the system addresses both technical and ethical challenges in leveraging emotional data for customer engagement.
The emoAIsec Framework is structured around three core modules: Emotion Recognition, Customer Experience Optimization, and Data Security. These modules work collaboratively to deliver personalized, real-time customer interactions while maintaining stringent data protection standards. The Emotion Recognition Module employs multimodal Emotion AI techniques to detect emotions through facial expressions, vocal tones, and textual sentiment. Advanced deep learning models such as CNN-LSTM for voice and Inception-ResNet-v2 for facial expressions are utilized for feature extraction and emotion classification [
13]. Additionally, a fusion layer integrates features from multiple modalities using attention mechanisms to achieve high accuracy in emotion detection [
12].
The Customer Experience Optimization Module dynamically adjusts responses based on detected emotional states using adaptive algorithms. For example, if frustration is detected, the system escalates the case to a human agent or modifies chatbot interactions for empathy. Predictive analytics models anticipate customer needs, providing proactive solutions that enhance satisfaction and reduce churn [
14].
The Data Security Module addresses privacy concerns associated with emotional data collection by incorporating encryption protocols and federated learning models to process data locally without exposing sensitive information [
15]. Differential privacy techniques ensure that aggregated data remains anonymous while retaining utility for analytics (Hutson et al., 2023) [S6-R4].
Table 2.
Core Modules of the emoAIsec Framework and Their Key Techniques [
13,
14,
15], [S6-R4].
Table 2.
Core Modules of the emoAIsec Framework and Their Key Techniques [
13,
14,
15], [S6-R4].
| Module |
Key Techniques |
Purpose |
| Emotion Recognition |
Multimodal analysis (facial expressions, voice, text), CNN-LSTM, Inception-ResNet-v2 |
Accurate detection of user emotions from multiple data sources |
| Customer Experience Optimization |
Adaptive algorithms, predictive analytics |
Real-time personalization and dynamic adjustment of responses |
| Data Security |
Federated learning, differential privacy, encryption |
Ensures ethical data handling and compliance with privacy regulations |
3.1. Integration of Multimodal Emotion AI Techniques
The integration of multimodal inputs allows the framework to capture a comprehensive emotional profile. Facial expressions are analyzed using advanced neural networks like GhostNet that ensure robust feature extraction while mitigating overfitting risks. Voice analysis detects micro-variations in pitch and tone using CNN-LSTM networks [
13], while textual sentiment analysis leverages NLP models like GPT-4 for contextual understanding and detecting complex emotions such as sarcasm or hesitation [
14].
3.2. Real-Time Optimization Techniques
Machine learning algorithms enable continuous feedback loops, which allow for real-time optimization. The technology tracks client emotions across touchpoints, allowing for dynamic modifications in service delivery. Emotion-driven personalization tailors’ recommendations and support to users’ real-time emotional states, increasing engagement and loyalty.
3.3. Algorithm for Real-Time Emotion Recognition
The following pseudocode illustrates the process of multimodal emotion recognition within the emoAIsec Framework:

3.4. Ethical Considerations
To ensure ethical implementation of the framework:
This framework establishes a robust foundation for businesses seeking to balance innovation in customer experience optimization with the imperative of data security.
4. Emotion Recognition and Sentiment Analysis
Emotion recognition and sentiment analysis are critical components of the emoAIsec system, enabling businesses to understand and respond to customer emotions in real time. These capabilities enhance customer satisfaction by delivering personalized interactions while addressing challenges related to privacy and security [
13,
17]. This section explores advanced techniques for multimodal emotion recognition, introduces a novel adaptive sentiment analysis algorithm with contextual feedback, and highlights the integration of emotion data to deliver personalized customer interactions.
4.1. Techniques for Multimodal Emotion Recognition
Multimodal emotion recognition combines inputs from text, voice, and facial expressions to create a comprehensive emotional profile. This approach addresses the limitations of single-modal systems by leveraging complementary information from multiple modalities. Text-based emotion recognition uses advanced natural language processing (NLP) models such as Transformer-based architectures (e.g., GPT-4). These models excel at capturing contextual nuances, sarcasm, and ambiguous emotional cues in textual data [
13,
17]. Voice-based emotion recognition relies on acoustic features like pitch, tone, and energy levels. Techniques such as CNN-LSTM architectures process these features effectively, mapping raw audio signals to emotional states with high precision [
19]. Facial expression analysis employs neural networks like Inception-ResNet-v2 to extract micro-expressions and subtle facial cues indicative of emotions [
13]. Fusion techniques are essential for integrating these modalities. Feature-level fusion combines feature vectors from different modalities into a unified representation, while decision-level fusion aggregates predictions from individual modalities. Attention mechanisms further enhance performance by prioritizing the most relevant features for emotion recognition tasks [
16].
4.2. Adaptive Sentiment Analysis with Contextual Feedback
To complement multimodal emotion recognition, we propose an adaptive sentiment analysis algorithm that incorporates contextual feedback loops for dynamic refinement of sentiment predictions. This algorithm addresses real-time sentiment classification challenges by employing hierarchical sentiment classification and reinforcement learning to optimize responses over time. The adaptive sentiment analysis algorithm begins with input preprocessing. Text data is tokenized and embedded using domain-specific NLP models like GPT-4, which excel at understanding complex emotional expressions such as sarcasm or hesitation [
14]. Voice data is processed using lightweight convolutional neural networks (LFCNNs) that extract acoustic features efficiently while maintaining high accuracy [
13]. Contextual data from historical interactions is integrated into the model to provide additional insights into customer behavior. Features from text, voice, and context are fused into a unified representation using attention mechanisms that prioritize relevant features for sentiment classification. The hierarchical classification process begins by categorizing sentiments broadly into positive, negative, or neutral categories before refining them into fine-grained levels such as “very positive” or “slightly negative” [
18]. A contextual feedback loop continuously refines predictions based on new interaction data. For example, if a customer’s tone shifts from neutral to frustrated during a call center interaction, the system dynamically updates its sentiment prediction and adjusts its responses accordingly. Reinforcement learning further optimizes this process by learning from past interactions to improve future predictions. Below is the pseudocode for the proposed adaptive sentiment analysis algorithm shown above. This adaptive algorithm enables businesses to anticipate customer needs based on emotional trends while providing personalized responses in real-time. By integrating predictive analytics with continuous monitoring, it allows businesses to proactively address potential issues before they escalate.

4.3. Integration of Emotion Data for Personalized Customer Interactions
The integration of multimodal emotion data with adaptive sentiment analysis enables businesses to tailor interactions based on individual customer emotions. By combining real-time sentiment analysis with multimodal recognition techniques, the emoAIsec system delivers empathetic and personalized responses that dynamically adjust service delivery based on detected emotional states. For instance, if frustration is detected during a chatbot interaction, the system can escalate the issue to a human agent or modify its tone for greater empathy [
19].
This holistic approach fosters deeper emotional connections between businesses and customers by providing seamless experiences across multiple touchpoints. The ability to adapt interactions in real time not only improves engagement but also strengthens brand loyalty [
14].
5. Emotion Recognition and Sentiment Analysis
Multimodal emotion identification has developed into an efficient method for comprehending human emotions by integrating input from several sources, including text, vocal intonations, and facial expressions [
20]. This technique facilitates a nuanced understanding of emotional states, acknowledging the intricate nature of human emotional expression in dialogue. The amalgamation of diverse modalities is accomplished by multiple fusion approaches that improve the precision of emotional detection and the profundity of emotional reasoning. The execution of these methodologies frequently entails deep learning frameworks capable of efficiently processing multimodal data.
Advanced natural language processing techniques are utilized in text-based emotion recognition. Convolutional Neural Network-Long Short-Term Memory (CNN-LSTM) architectures have demonstrated efficacy in capturing both local and long-range dependencies in textual input [
21]. These models can efficiently interpret sequential information, rendering them especially apt for examining the emotional content of textual communications. Voice-based emotion recognition depends on the examination of acoustic characteristics. The utilization of MELD spectrogram characteristics through convolutional neural networks integrated with a fully connected layer has shown improved precision in connecting raw voice to emotional subtleties [
20]. Moreover, sophisticated models have been utilized as audio encoders to derive extensive auditory representations from input audio signals, demonstrating exceptional efficacy in emotion recognition tasks. Deep learning architectures have been employed for face expression analysis to extract feature data from video inputs [
20]. The amalgamation of different modalities is accomplished via diverse fusion processes. Feature-level fusion, using the concatenation of feature vectors from many modalities, has demonstrated encouraging outcomes [
21]. Attention methods have been utilized to selectively concentrate on pertinent segments of input data, especially advantageous when various modalities contribute unequally to the emotion recognition task [
22]. Innovative techniques, such as contextualized graph neural networks, have been proposed to boost the performance of multi-modal emotion recognition systems. These models effortlessly combine auditory, visual, and textual inputs, markedly improving the precision of emotional recognition and the profundity of emotional reasoning [
23]. The execution of these strategies often requires the use of deep learning frameworks. An example of a PyTorch implementation of a multi-modal emotion recognition model may appear like follows:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class MultiModalEmotionRecognizer (nn.Module):
def __init__(self, text_model, audio_model, visual_model):
super().__init__()
self.text_model = text_model
self.audio_model = audio_model
self.visual_model = visual_model
self.fusion_layer = nn.Linear(text_dim + audio_dim + visual_dim, num_emotions)
def forward(self, text_input, audio_input, visual_input):
text_features = self.text_model(text_input)
audio_features = self.audio_model(audio_input)
visual_features = self.visual_model(visual_input)
fused_features = torch.cat([text_features, audio_features, visual_features], dim=1)
emotion_output = self.fusion_layer(fused_features)
return emotion_output
This code snippet illustrates a fundamental framework for a multi-modal emotion identification model, integrating information from textual, auditory, and visual inputs. The unification of causal thinking and the advancement of intricate attention mechanisms represent prospective avenues for future inquiry, likely resulting in enhanced accuracy and interpretability of emotion detection systems [
24]. Utilizing these sophisticated methods for multi-modal emotion recognition, emoAIsec establishes a strong basis for real-time enhancement of customer experience, delivering detailed insights into consumer emotions across diverse contacts.
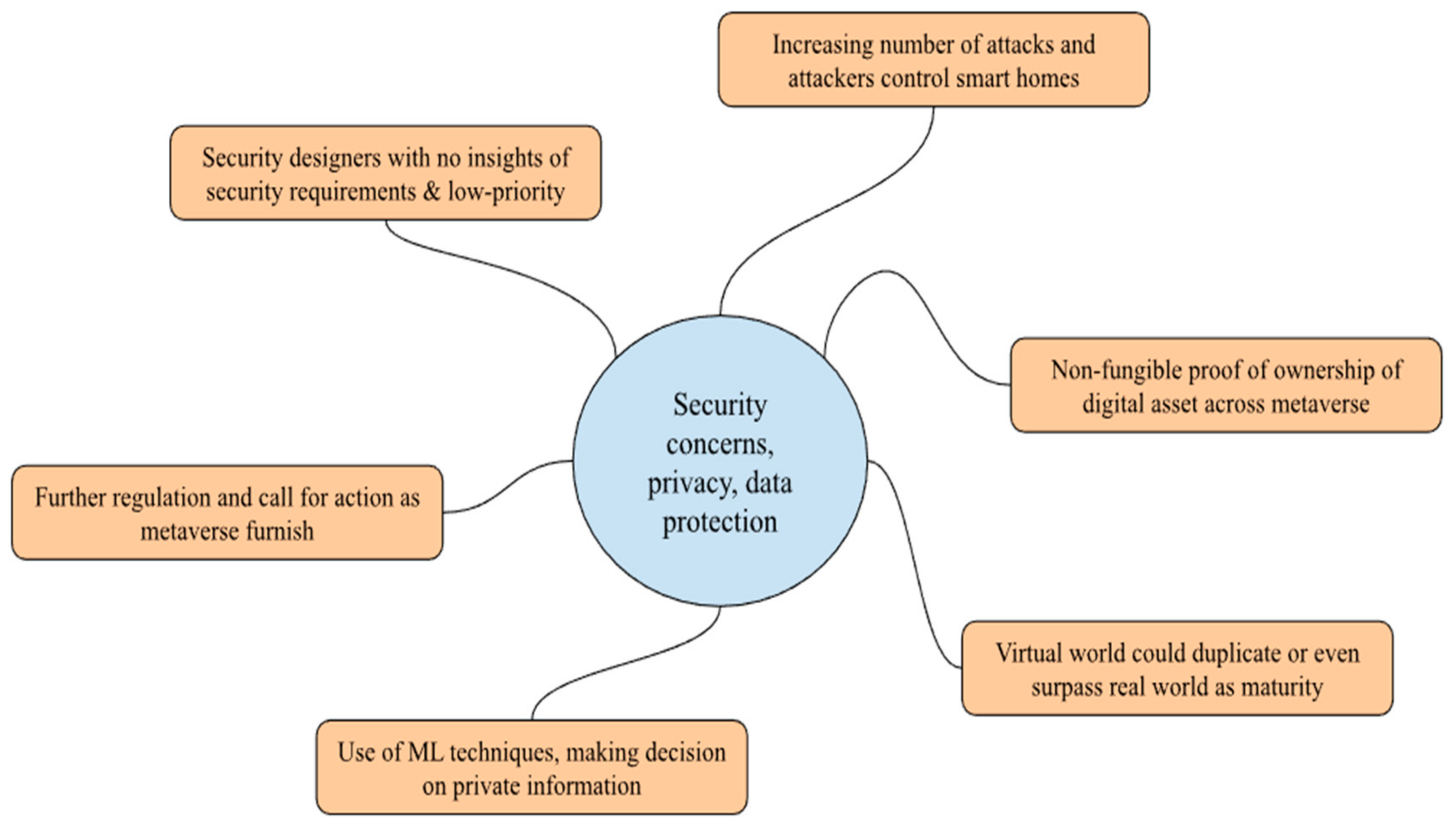
6. Privacy Safeguards and Security Concerns
There are always some unresolved questions about potential metaverse security and privacy, as cyberspace realizes the process of digitizing and virtualizing the real world [
25]. Identify, friends, immersion, low latency, diversity, anytime, anywhere, economic systems, and civilization are eight elements of Metaverse identified by game platform, Roblox. User experience principles to security and privacy, data can be used to spy or create device inferences [
26]. Social communication, aspects of security and privacy design, contextual trust in relation to smart home surveillance i.e., data collection, data sharing, and data use.
Privacy concerns and communication overhead remains as sending data to the remote cloud or edge servers willing to deploy service via edge computing and run machine learning at edge [
27]. ML-based prediction with data as ML techniques are increasingly used and much of that data seems to be sensitive. Legal abuse, the real future state with main challenges for commercial users remains in the regulatory and legal arenas as always there [
28]. The digital currency market of today as first introduced via bitcoin cryptocurrency has the ability to bypass existing legislation resulting in further regulation and call for action.
Figure 1.
Summary of security concerns, privacy safeguards, data protection with respect to customer experience optimization [
25,
26,
27,
28].
Figure 1.
Summary of security concerns, privacy safeguards, data protection with respect to customer experience optimization [
25,
26,
27,
28].
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Emotion AI has shown great potential in improving customer experiences by enabling personalized and emotionally aware interactions. Our proposed emoAIsec framework enhances these capabilities while ensuring robust data security and ethical AI usage. By integrating deep learning models for emotion recognition, adaptive customer response strategies, and advanced privacy safeguards, emoAIsec provides a well-rounded solution to current challenges. Despite these advancements, further research is needed to refine real-time emotion detection and enhance privacy-preserving techniques. Future work should explore more efficient AI models that require less computational power, ensuring broader adoption across industries. Additionally, regulatory frameworks must continue to evolve alongside AI advancements to ensure ethical and responsible use of emotion recognition technologies. By addressing these challenges, emoAIsec can become a key driver of trust and engagement in digital customer interactions, making businesses more adaptive in an increasingly AI-driven world.
Moreover, emoAIsec should focus on increasing real-time emotion recognition with lightweight AI models that boost accuracy while minimizing computing costs, thus making the system scalable across industries [
29]. Improving privacy-preserving approaches, such as homomorphic encryption and federated learning, will assist in preserving sensitive emotional data while retaining AI’s performance [
30]. Integrating Emotion AI into financial security systems can improve fraud detection by analyzing behavioral and emotional cues, lowering cyber risks in banking and online transactions [
31]. Future research should also look into AI’s role in cybersecurity by using machine learning to detect irregularities and prevent emerging cyber threats, as attackers constantly adapt malware to avoid detection [
29]. Implementing blockchain-based security models, such as HNMblock, can improve data integrity by ensuring the safe and tamper-proof storage of important customer interactions. Furthermore, incorporating Emotion AI into healthcare could aid in mental health assessments and personalized treatment by employing AI-powered emotion identification [
32]. As AI rules advance, aligning Emotion AI systems with privacy laws such as GDPR and CCPA is critical to guaranteeing ethical deployment and data protection [
28]. The use of AI-driven cybersecurity models in healthcare, as demonstrated by HealthShieldAI, may also assure secure cloud deployment, protect patient data, and optimize healthcare operations [
33]. Furthermore, Integrating frameworks such as AssessITS can improve AI security by streamlining risk assessment, allowing enterprises to address IT threats autonomously and reduce operational vulnerabilities [
34].
References
- K. Gopalakrishnan, “Emotion AI: A Catalyst for Enhanced Customer Relations in Banking,” European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, vol. 2024, no. 8, pp. 7–9.
- Y. Kan, Y. Yu, L. Jia, and Y. Tan, “Emotion AI in Disguise Spurs Strategic Behavior in Customer Care,” SSRN 4806616, 2024.
- Melise Peruchini, G. Modena, and Julio Monteiro Teixeira, “Between artificial intelligence and customer experience: a literature review on the intersection,” Discover AI, vol. 4, no. 1, Jan. 2024.
- M. Vyas, “Exploring the Impact of ‘Emotion-Recognition-AI’ on Consumer Trust and Satisfaction,” 2020 IEEE Int Students’ Conf on Elec, Elect and Comp Sci (SCEECS), vol. 5, pp. 1–6, Feb. 2024.
- Y. Yu, L. Jia, and Y. Tan, “Emotion AI Meets Strategic Users,” SSRN Electronic Journal, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Rane, N., Choudhary, S., & Rane, J. (2023). Metaverse for enhancing customer loyalty: effective strategies to improve customer relationship, service, engagement, satisfaction, and experience. Social Science Research Network 4624197.
- Baddam, P.R. (2022). Revolutionizing Customer Experience through Innovative Digital Marketing Approaches. Global Disclosure of Economics and Business, 11(2), 71–86.
- Roslan, F. A. B. M., & Ahmad, N. B. (2023). The Rise of AI-Powered Voice Assistants: Analyzing Their Transformative Impact on Modern Customer Service Paradigms and Consumer Expectations. Quarterly Journal of Emerging Technologies and Innovations, 8(3), 33–64.
- Rane, N. (2023). Enhancing Customer Loyalty through Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and Big Data Technologies: Improving Customer Satisfaction, Engagement, Relationship, and Experience. Social Science Research Network 4616051.
- Vijayakumar, H. (2023, June). Revolutionizing customer experience with AI: a path to increase revenue growth rate. In 2023 15th Int Conf on Electronics, Comp and AI (ECAI) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Panditharathna, R., Liu, Y., de Macedo Bergamo, F. V., Appiah, D., Trim, P. R., & Lee, Y. I. (2024). How Cyber Security Enhances Trust and Commitment to Customer Retention: The Mediating Role of Robotic Service Quality. Big Data and Cog Comp, 8(11), 165.
- Maheen, S. M., Faisal, M. R., & Rahman, R. (2022). Alternative non-BERT model choices for the textual classification in low-resource languages and environments. 192–202. [CrossRef]
- Liu, D., Wang, Z., Wang, L., & Chen, L. (2021). Multi-Modal Fusion Emotion Recognition Method of Speech Expression Based on Deep Learning. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 15.
- Wilder, S.K. (2024, December 18). The Science of Customer Emotions: Advances in Sentiment Analysis. Available online: CMSWire.com.
- Hou, J., Liu, H., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Wan, P.-J., & Li, X.-Y. (2021). Model Protection: Real-Time Privacy-Preserving Inference Service for Model Privacy at the Edge. IEEE Tran on DSC, 19(6), 4270–4284.
- Poria, S., Cambria, E., Bajpai, R., & Hussain, A. (2017). A review of affective computing: From unimodal analysis to multimodal fusion. Information Fusion, 37(37), 98–125.
- Real-Time AI Customer Sentiment Analysis—Cobbai Blog. (2024). Available online: Cobbai.com.
- Transforming Customer Experience Through Emotion AI. (2024, August 29). New Metrics.
- Mamieva, D., Abdusalomov, A. B., Kutlimuratov, A., Muminov, B., & Whangbo, T. K. (2023). Multimodal Emotion Detection via Attention-Based Fusion of Extracted Facial and Speech Features. Sensors 23(12), 5475. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F., Ding, Z., Xia, R., Li, Z., & Yu, J. (2023). Multimodal Emotion-Cause Pair Extraction in Conversations. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 14(3), 1832–1844.
- Sahu, Gaurav. “Multimodal Speech Emotion Recognition and Ambiguity Resolution.” ArXiv.org, 2019. arXiv:1904.06022.
- Poria, Soujanya, et al. “A Review of Affective Computing: From Unimodal Analysis to Multimodal Fusion.” Information Fusion, vol. 37, no. 37, Sept. 2017, pp. 98–125.
- Joshi, Abhinav, et al. “COGMEN: COntextualized GNN Based Multimodal Emotion RecognitioN.” ACLWeb, ACL, 2022.
- Cheng, Z., Niu, F., Lin, Y., Cheng, Z., Peng, X., & Zhang, B. (2024). MIPS at SemEval-2024 Task 3: Multimodal Emotion-Cause Pair Extraction in Conversations with Multimodal Language Models. Proc of the 16th Int Workshop on Semantic Eval (SemEval-2022), 667–674.
- Chen, Z., Wu, J., Gan, W., & Qi, Z. (2022). Metaverse security and privacy: An overview. In IEEE Big Data (pp. 2950-2959).
- Chalhoub, G., Flechais, I., Nthala, N., & Abu-Salma, R. (2020). Innovation inaction or in action? the role of user experience in the security and privacy design of smart home cameras. In Sixteenth Symp on Usable Privacy and Security (SOUPS 2020) (pp. 185-204).
- Hou, J., Liu, H., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Wan, P. J., & Li, X. Y. (2021). Model protection: Real-time privacy-preserving inference service for model privacy at the edge. IEEE Tran on DSC, 19(6), 4270-4284.
- Hutson, J., Banerjee, G., Kshetri, N., Odenwald, K., & Ratican, J. (2023). Architecting the metaverse: blockchain and the financial and legal regulatory challenges of virtual real estate. JILSA, 15.
- Sultana, I. Sultana, I., Maheen, S. M., Sunna, A. A., & Kshetri, N. (2024, November 19). SmSeLib: Smart & Secure Libraries—Navigating the Intersection of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence. Preprints.org. Available online: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202411.1445/v1.
- Kshetri, N., Sultana, I., Rahman, M. M., & Shah, D. (2024). DefTesPY: Cyber Defense Model with Enhanced Data Modeling and Analysis for Tesla Company via Python Language. IEEE.
- Kshetri N., et al. (2024). cryptoRAN: A Review on Cryptojacking and Ransomware Attacks W.R.T. Banking Industry—Threats, Challenges, Problems. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Naresh Kshetri, Mishra, R., Rahman, M. M., & Steigner, T. (2024). HNMblock: Blockchain Technology Powered Healthcare Network Model for Epidemiological Monitoring, Medical Systems Security, and Wellness. 01–08. [CrossRef]
- Sultana, I., Islam, K., Mensah, R., Shaharier Arafat Sumon, & Syed Mustavi Maheen. (2025, January 29). HealthShieldAI: A Multi-Layered Framework for Secure Cloud Deployment in Healthcare. ResearchGate. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. M., Kshetri, N., Sayeed, S. A., & Rana, M. M. (2024). AssessITS: Integrating Procedural Guidelines and Practical Evaluation Metrics for Organizational IT and Cybersecurity Risk Assessment. Jou of Inf Sec, 15(04), 564–588. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).