3. Research Method
The longitudinal study is conducted to estimate and compare the sustainable finance issues in Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan, which countries have similar political, economic, social, and cultural backgrounds to conduct the research in terms of sustainable finance to respond to the UN 17 SDGs. The research uses the longitudinal approach to analyze the quantitative data along with a literature review to identify the ESG challenges in the period of 2019 – 2022, when THE was first using the impact ranking to evaluate the sustainable factors in 2019. The study organizes and classifies the secondary data from four partners measuring the sustainable impacts of universities, THE, QS, STARS, and GRI, which are the leading prestigious ranking systems for higher education institutions worldwide. Through the theoretical framework of sustainable finance namely the H2ESD framework, the secondary data will interpret whether its components are challenging sustainable finance in the entire higher education system or not. Then, the study propose the solutions based on the literature review to mitigate the dominant challenges to promote the development of sustainable finance in higher education institutions in East Asian countries.
3.1. Data Collection
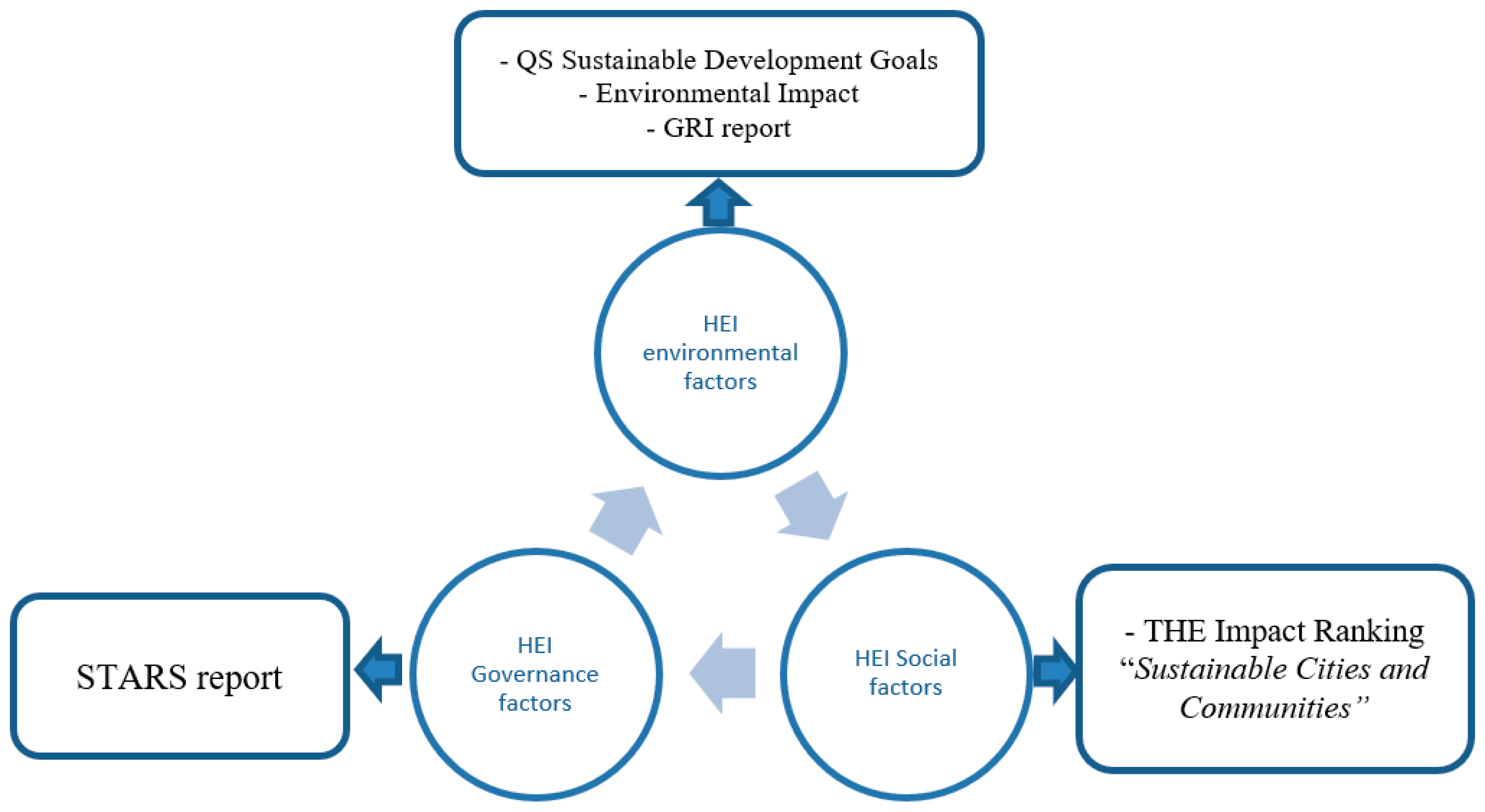
The research utilized secondary data from various sources including the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), THE (Times Higher Education) impact ranking, QS World University Rankings - Sustainable Development Goals, and the Sustainability Tracking, Assessment and Ranking System (STARS) to determine the challenging elements based on the theoretical framework of HE. Furthermore, the data collected from these three databases were categorized into three groups of factors, including the HEI environment factor, the HEI social factor, and the HEI governance factor (see
Table 1) for analyzing and comparing among countries. The data set was structured by longitudinal data on sustainable finance and sustainable finance in the higher education field at the national level. For example, the study used the THEIR database, particularly the dimension of Sustainable Cities and Communities, to collect the research data for analyzing the HEI Social factor of sustainable finance. For analyzing the environmental factor of sustainable finance, the study exported the environmental impact dimension of the GRI database and the environment impact dimension of the QSDSG database. Regarding the HEI governance factors, the authors collected the governance dimension of the STARTS database for the data analysis. Additionally, the study collected data in 2019 and beyond because the QS ranking database about Sustainability launched later than the other three partners in 2019.
3.2. Data Analysis
The secondary data from various four sources are systematically collected, classified, refined, and analyzed according to the three components of ESG sustainable finance in the context of higher education industry. The descriptive data analysis is addressed comparably and related to the previous literature review to explore the similar challenges and the propose the adoptive policies based on the development context of higher education system in East Asian region.
The research uses GRI database to estimate the environmental impacts in universities. Furthermore, the study addresses data from THE Impact Ranking with the category of sustainable cities and communities to evaluate and compare the social impacts of universities, from QS World University Rankings - Sustainable Development Goals with the group of environmental impact to explore and compare the social impact factors. For the sustainable governance, the research uses the Sustainability Tracking, Assessment and Ranking System (STARS) database to analyze and interpret because this metric mainly focuses on the elements of governance containing the academics, operation, planning and administration, innovation, and leadership.
5. Discussion
The higher education sustainable finance covers the financial activities in the university with the operation of three dimensions consisting of environmental, social and governance factors. The study aimed to discover the challenges of sustainable financing in higher education in East Asian countries as well as recommend the solutions to improve the sustainable financing in HEIs in the region.
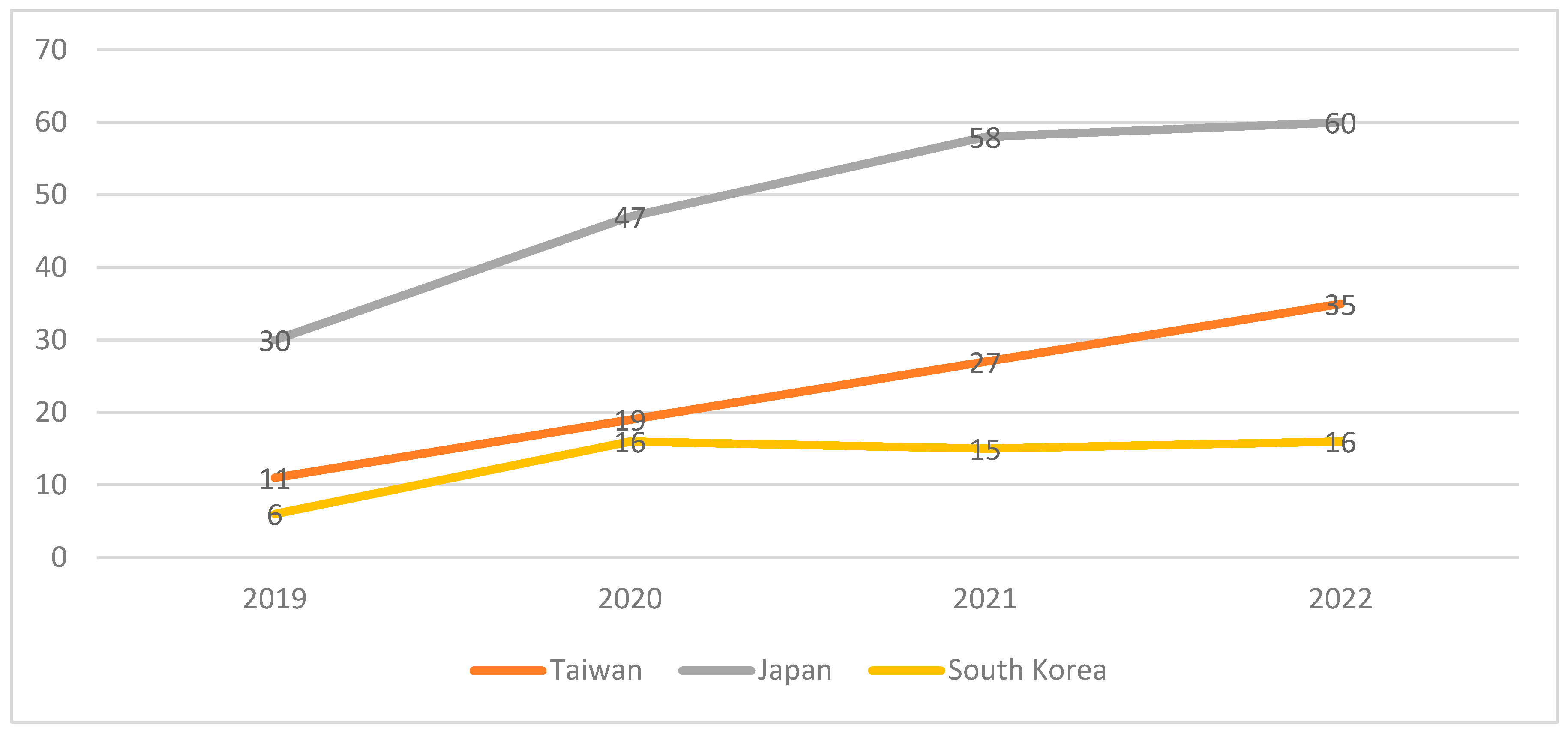
In East Asia, Taiwan is emerging the leading country which achieves the best performance in terms of sustainable finance in higher education in all the dimensions. It is the fact that the country has the relevant policies and practices in higher education to overcome the challenges in the sustainable finance. Because the university finance is always the challenging issue for all the institutions, which is the most key factor deciding the health and development of the higher education organization. In three dimensions, although a third of Taiwanese universities achieve the world universities impact by the THE ranking, the number of universities with the sustainable governance was existing the challenges. Therefore, the leadership commitments in HEIs needs to reinforce for forcing the entire universities moving award in the journey of increasing the competency of the organizational sustainable finance. The top management actions to increase the governance capacities must concentrate on uplifting the obstacles and challenges in legalization, operations, controls, and measurement of universities. As a results, the university will reinforce the leadership and management in the sustainable factors in terms of education and research, operations, planning, administration and engagement, and innovation. Furthermore, the universities should enhance the responsible financial investments in order to transfer the sustainable finance elements into the university's academic activities for improving the in-dept awareness and actions of staff and students. This policy priority could contribute to improve the academic leadership of the universities towards the sustainability, so the public investment will be more effective and dominant with higher public trust and competitiveness for higher education [
13]. It’s the fact that these actions were launched by the leading universities according to the NTU Social Responsibility and Sustainability Report [
18] in Taiwan and necessary spill over the whole higher education systems in the East Asian region especially the universities in Japan and South Korea. Furthermore, the impact of the leading universities in Taiwan and other leading universities with specifically sustainable finance schemes in Asia Pacific region like MU, NTU, NUS [
9,
10,
11] could have a benchmark and belief of adapting sustainable development in higher education finance for other universities with the similar geopolitical contexts in Asia Pacific region. It will later become a positive movement in higher education for sustainable development to respond to the climate change and global warning issues in the vulnerable Asia Pacific and worldwide.
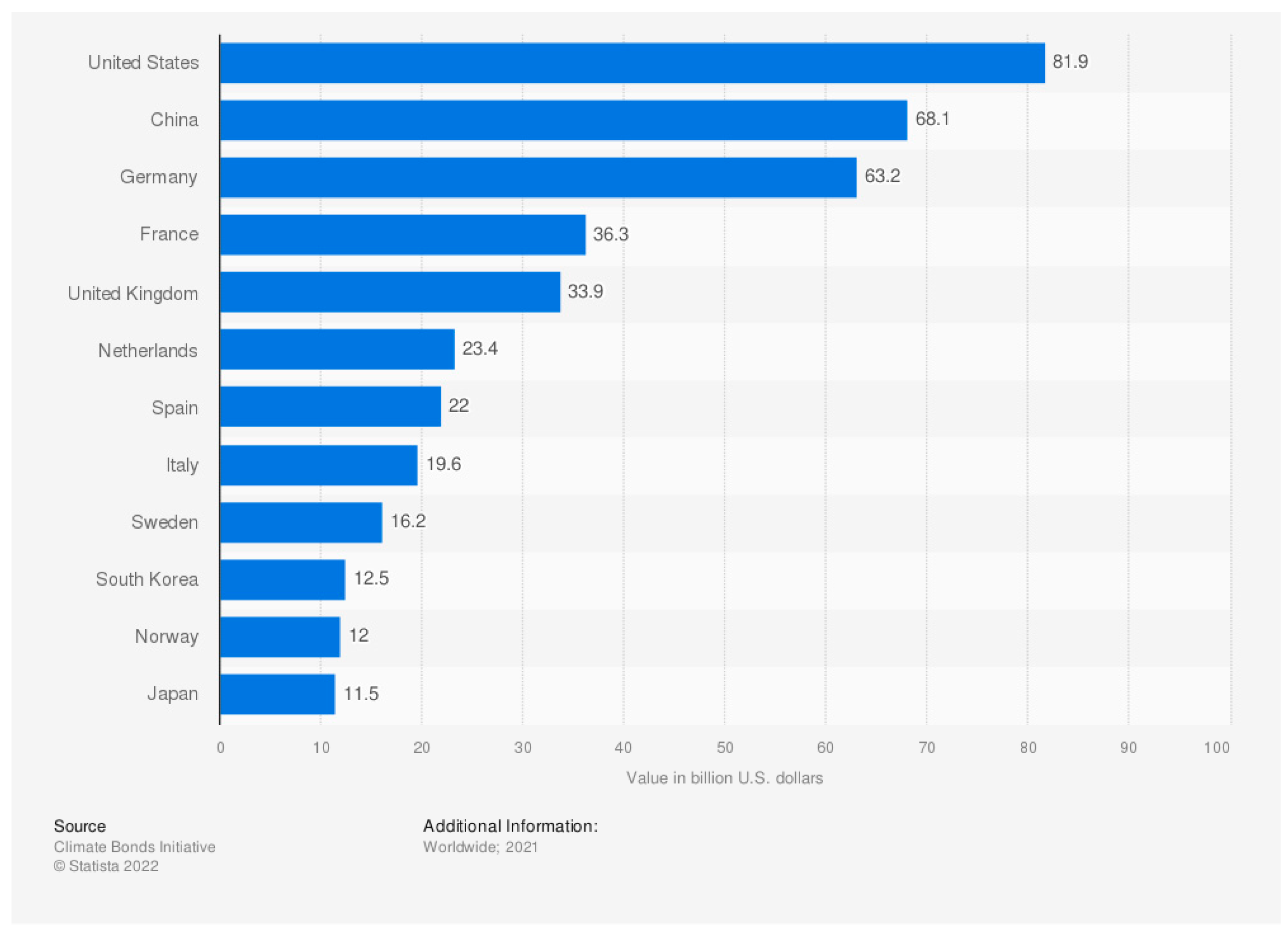
The impact of environment and social factors in East Asian higher education systems attained better scenarios than the governance. However, the higher education system in Japan faced the most serious challenges in the environmental impact factors and following by South Korean higher education system. It considers that the study explored the issues which can be enrich the statements in terms of awareness of green growth by universities stakeholders’ perspectives. The lack of understanding the entities and nature of sustainable finance and economy exist and limit the financing of universities, which were affirmed by the lack of the interest in the green growth in South Korean context [
20]. In addition, the development perspectives [
21] of green finance network in the public and private area will strengthen the organization financial capacity toward enhance the environmental impact in Japan context. However, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan along with other Asian financial centers like Singapore and Hong Kong SAR are in the advantage of the leading countries in the investment of sustainable finance worldwide. It is foundation to improve the investment of sustainable development for higher education finance if the public and private partner investment is more priority to the higher education with top management commitments and long-term visions. It seems that the macro level of higher education systems in the region need to navigate the policy making, practices, and research and development in ESG factors and sustainable finance in order to create more spaces for uncovering and developing in the ESG global context. Consequently, it will decrease the challenges in the sustainable finance of the higher education systems in East Asia. The positive signal of the impact of environment and social factors in East Asian universities would be the convincing evidence to help other higher educational systems in Asia Pacific understand the strategic priority in terms of the sustain finance, which weights directly on the environment issues inside and outside of universities and their missions on social and community development in long-term period. Nevertheless, the shortage of the sustainable governance factor from the research result reminds the top management to promote the commitment and long-term vision of leadership in order to enhance the sustainable governances in the entire university leadership and administration across the Asia Pacific context.
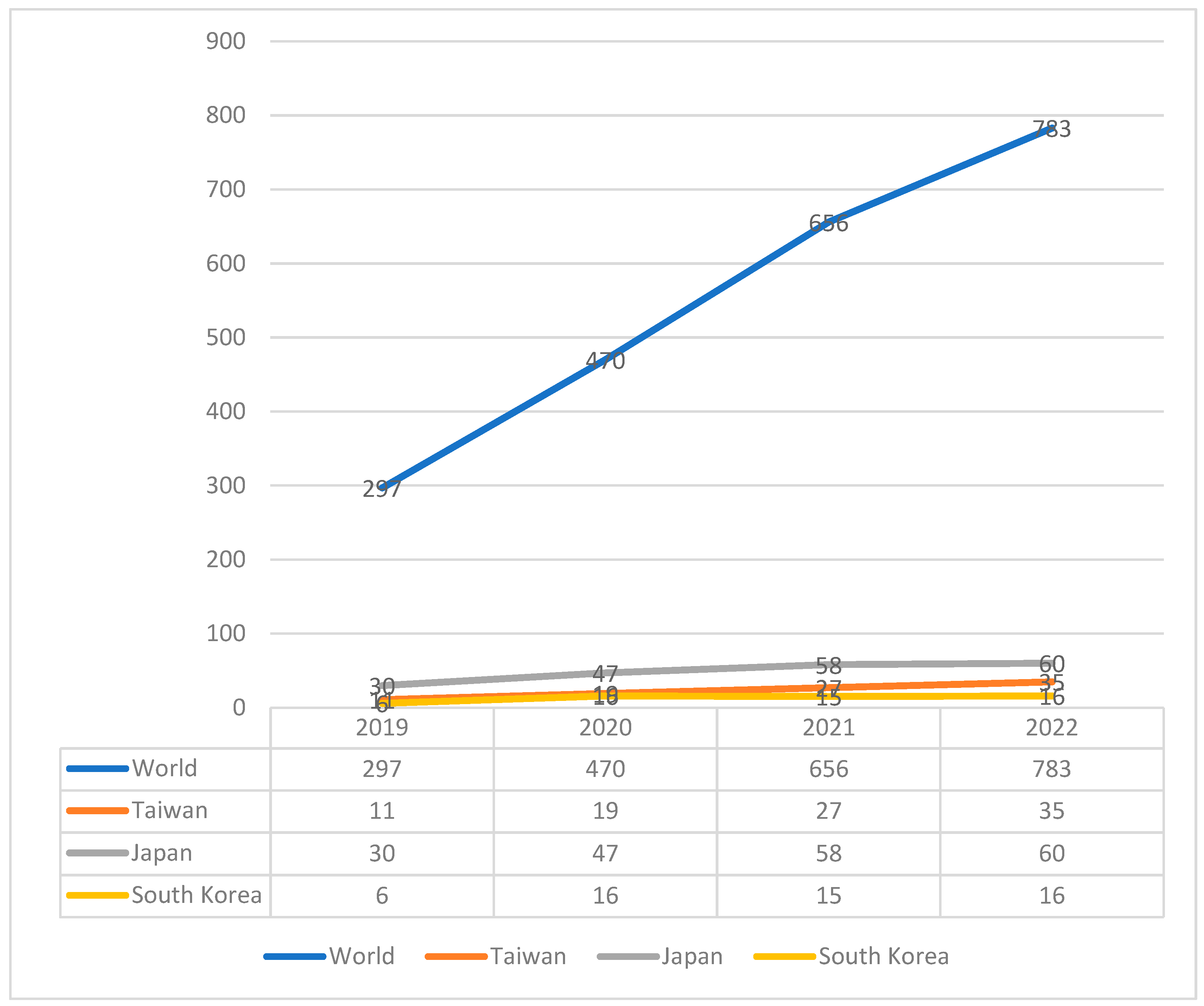
Moreover, the most positive factor in the ESG dimensions in East Asian region is the social impact. Higher education systems were progressive steps to enhance their social and community influence. The contribution in global impacts were identified by the ranking better annually. Nearly a third of Taiwanese universities, and a number of Japanese and South Korean universities achieved the THE global achievement in the influence factor of sustainable cities and communities in 2022. As a result, the universities gradually had the effective sustainable finance investment to achieve global influences in the factor of social impact. It is the fact that the universities in the region reinforced the advantages of available resources, especially the academic size of the leading global higher education systems with the world class universities in research field to support the sustainable finance development. It is not difficult to see the top world ranking map of Taiwanese, Japanese, and South Korean universities in the world ranking database (e.g., THE and QS database). The research clarified the perspective of Chan and Liu [
19] in terms of impact factors on sustainable finance in higher education such as the size of universities, and the entire higher education system with the student enrollment rate, and limitation of resources in the investment decision in order to improve the environmental impact, support the society and community. With the similar economic, cultural and social context of countries in the Asia Pacific region, the research could enrich the evidences to help the policymakers, researchers and practitioners of higher education towards to the effective social and community impacts with the long-term vision.
The sustainable governance faced the most challenges in the higher education sector. The limitation in investing sustainably on education and research, operations, planning, administration and engagement, and innovation were the rationale for existing the shortage of universities governance in the region. This result affirmed that the sustainable governance was the global challenge for the universities leadership and management as Alshuwaikhat, Adenle [
14] explored the entire universities executives were impacted by the limited competency of sustainable financial management. It is the fact that the internal executive systems need to improve the sustainable governance in terms of the legislation, operations, controls, and measurement by itself to achieve the stakeholders' needs. Moreover, this issue is impacting higher education systems with the low domestic student enrollment rate across the countries in Asia Pacific where the birthrate is low with the decreasing tendency [
16,
17]. The weight of financial affairs at universities focuses on the internal regular expenditure in short-time period from the main revenue of universities which are from the student tuition fee, so the sustainable governance for long-term benefits will be difficult to achieve and impacted in the policy priority of the universities in the region. Consequently, the university governance for the sustainability is necessary integrated into the university vision and long-term strategic plans with the leader commitments in order to create a shared vision and a policy framework of sustainable finance to navigate all the members in the university acting toward sustainable development of the organization and the culture of sustainability across Asia Pacific.
Proposed Solutions for Improving Sustainable Financing in Higher Education in East Asia
Strategy and sustainable financial policy framework. The development of an entire costing and benefiting strategy and sustainable financial policy framework on campus will drive the universities on track of achieving the sustainable development. This solution is relevant to Alshuwaikhat, Adenle [
14] when the challenge of the bias of public delivery due to the unstable economy development and the students’ enrollment ratios that burden on the universities financing towards the sustainability. A sustainable financing framework will be the scaffold to navigate the universities on track of implementing the priorities to make the decision in financial investment in teaching and learning, doing research and addressing the educational service and community activities.
Sustainable evidence-based policy making. Evidence based policy making for sustainable development is the determinant to improve the sustainable financing in the universities [
23]. Thus, the necessity of setting the sustainable finance policy targets for higher education need to be consider by the policy makers as well as practitioner in East Asia. As a result of the sustainable finance policy for all the fields that was stated in Schumacher, Chenet [
21]’s study, the higher education industry will improve the sustainable investments directly in its own knowledge production business and indirectly impact on the other field by providing the new generations of labor force with the knowledge and competencies related to the sustainable development and sustainable finance.
Development of the sustainable educational service business models. Along with the relevant policy framework for driving the universities in the sustainable investment decision covering the ESG factors, the development of the sustainable educational service business models for universities should be focusing to improve the sustainable governance in higher education institutions. The sustainable educational services will improve the sustainable finance development in which education and research, operations, planning, administration and engagement, and innovation in the universities will be the central of all the educational services management. The sustainable investment in the higher education services could be beneficial in legislation, operation, control, and measurement in higher education institutions by themselves to meet the stakeholders' needs.
Limitation. The study was conducted in the context of universities in East Asian regions by analyzing the results of global impact factors from the database in Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), THE (Times Higher Education) impact ranking, QS World University Rankings - Sustainable Development Goals and the Sustainability Tracking, Assessment and Ranking System (STARS). The several databases were published in the short term, for example the QS just launched the ranking for Sustainable Development Goals in 2022. As a result, the longitudinal study could be occurring the bias in the comparative analysis in the study.
The research concentrated on emerging the challenges and proposing systematic solutions of sustainable finance based on the success factors of sustainable finance as the social impact, environmental influence, and sustainable governance in the higher educational systems. The future studies should explore the empirical results in the specific university level from the perspective of stakeholders (e.g., leaders, administrators, faculty members and students) to propose the practical and technical the solutions for improving the sustainable financial cost and benefit at the university level. Other comparative studies in other similar countries context in the Asia Pacific region could explore the impact level of specific ESG factors in various higher educational systems in order to gain a total viewpoint of ESG impact factors in higher education in Asia Pacific region to respond to the UNESCO SDGs.
For the practical implication of the study to policy makers and practitioners in higher education systems with the similar economic, social and cultural context of major Asia Pacific countries, the suggestions of policy making to respond to the East Asian universities with the sustainable finance could be considered as a policy reference framework in order to help the change makers to benchmark by using the policy borrowing approach to solve the similar issues in their own systems and beyond. Further, a network of higher education policy makers in Asia Pacific could establish with the shared vision and collective leadership in dealing with the sustainable development in education. Therefore, it would be a good policy making model for the sustainable development in the entire region, which is one of the most vulnerable areas by the climate change and global warning issues, towards necessary joint consciousness and actions of all the citizens to address the sustainable development in which higher education plays a key and proactive role in the whole sustainable ecosystem.