Submitted:
17 February 2025
Posted:
18 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
This study explores, the multifaceted aspects of sushi rice preparation is explored, including washing, soaking and cooking processes, and their impact on the texture and sensory properties of rice. Selenio rice, a premium short-grain rice, was analysed for variations in amylose content and viscosity profiles. The study allows to highlight how the rice's compositional characteristics, particularly the amylose-to-amylopectin ratio, influence gelatinisation and cooling behaviour. The effects of soaking duration, vinegar mix composition, and water-to-rice ratio on texture profile analysis (TPA) are also examined, as well as overall sensory quality. Rice reaches maximum water absorption within three minutes of soaking, independent of water temperature (10-50°C). Vinegar mix addition effectively lowered rice pH to below 4.5, contributing to improved shelf stability. Additionally, the TPA of sushi rice was evaluated over a 10-day storage period, with findings suggesting that optimised preparation techniques can improve rice quality, extending its freshness and acceptability. The importance is underscored of precise preparation methods in optimising the quality of sushi rice, contributing to the broader field of rice research and culinary science.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Initial Characterisation of Sushi Rice
2.2. Investigating the Sushi Rice Production Process
2.2.1. Washing and soaking Sushi Rice
2.2.2. Cooking, Seasoning and Rice Formation
2.3. Shelf-Life Examination of Cooked Sushi Rice
2.3.1. TPA
2.3.2. Sensory Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
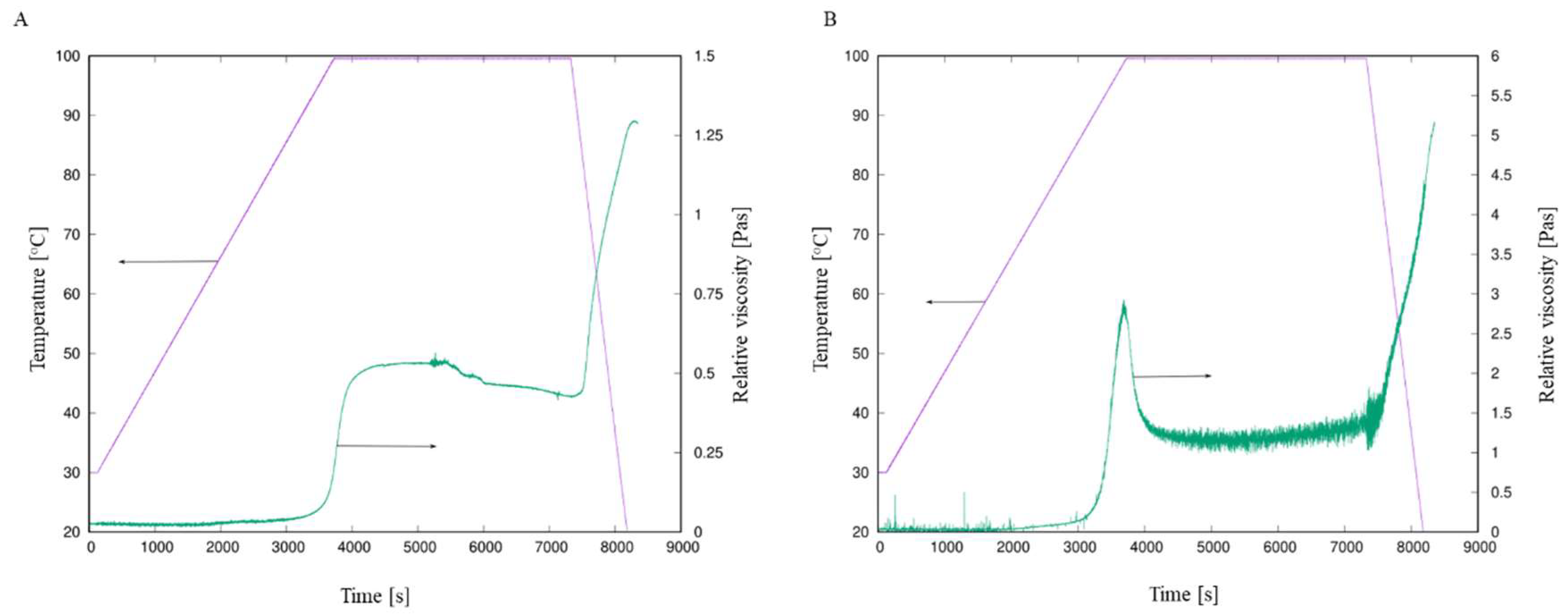
3.1. Initial Characterisation of Sushi Rice
3.2. Investigating the Sushi Rice Production Process
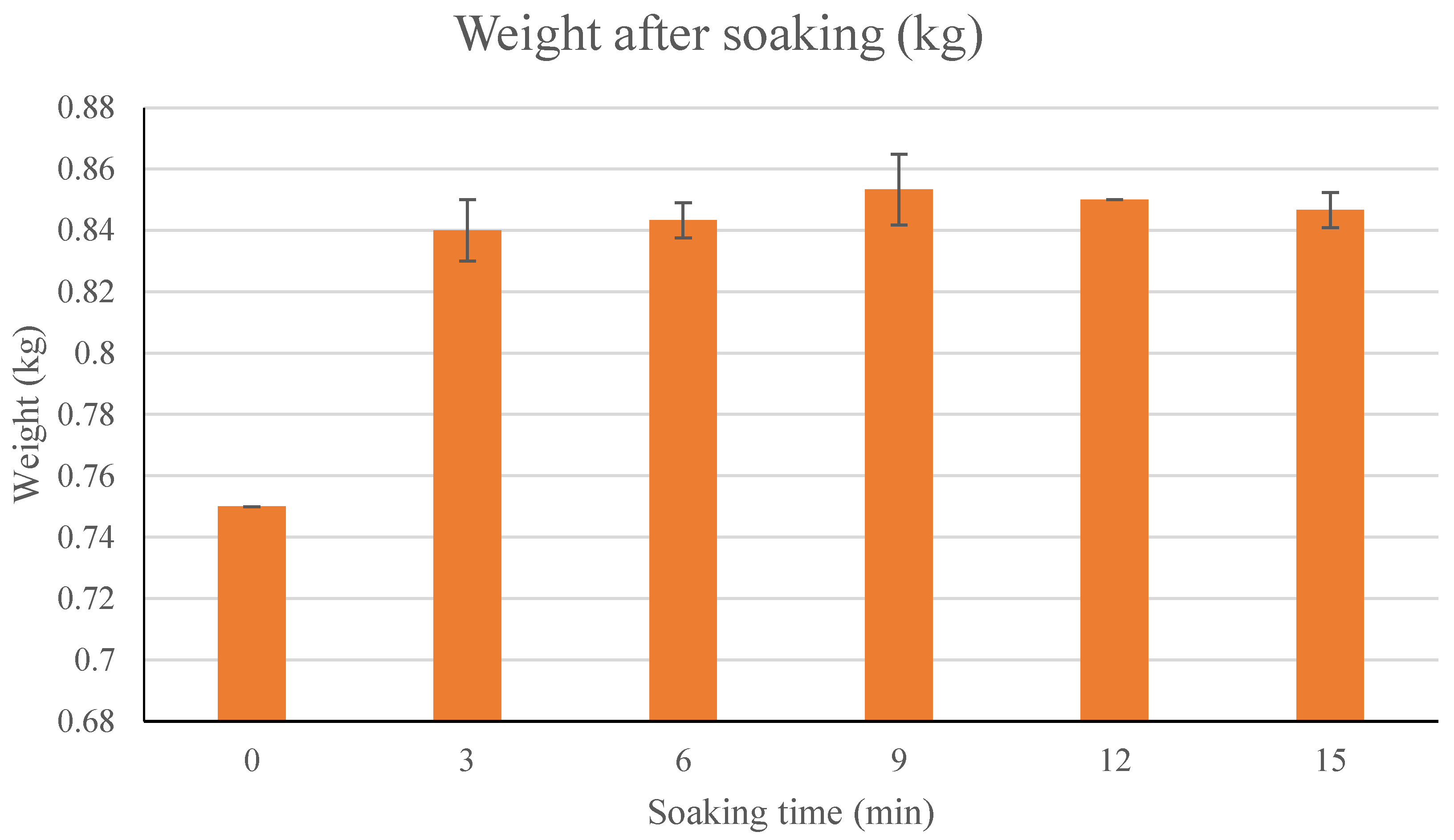
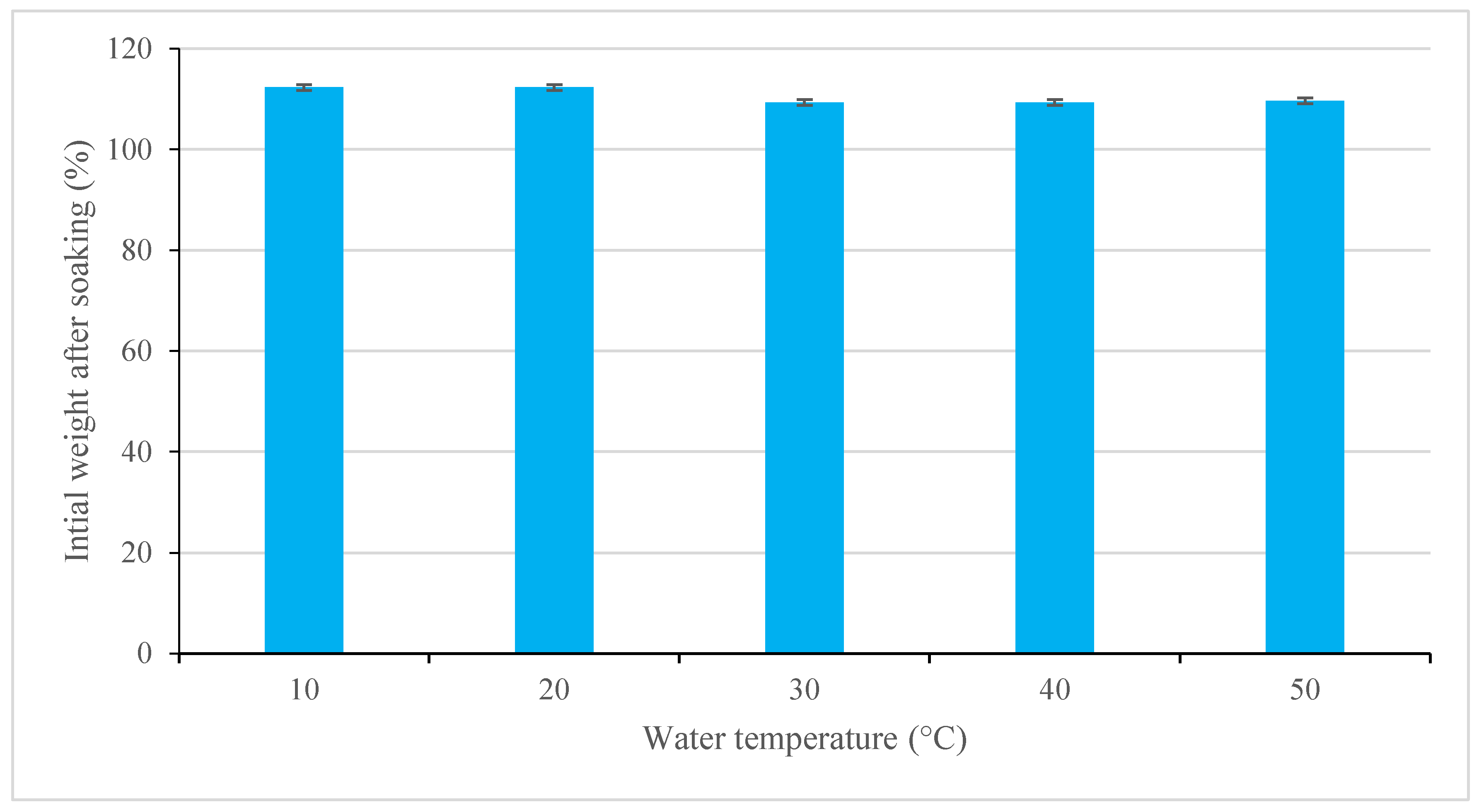
3.2.1. Washing and soaking Sushi Rice
3.2.2. Seasoning
| Amount | Seasoned Rice 1 | Seasoned Rice 2 | Seasoned Rice 3 | Seasoned Rice 4 |
| 120 g/kg | 4.28 ± 0.01 | 4.22 ± 0.01 | 4.18 ± 0.01 | 4.46 ± 0.10 |
| 180 g/kg | 4.16 ± 0.02 | 4.09 ± 0.01 | 4.08 ± 0.01 | 4.33 ± 0.02 |
| Group | WashingDuration [s] | Initial Weight After Soaking (%) | ||||
| 15 min | 30 min | 45 min | 60 min | 75 min | ||
| W1 | 200 | 112.50a ± 0.71 | 112.50a ± 0.71 | 113a ± 0 | 112.50a ± 0.71 | 112a ± 0 |
| W2 | 230 | 112.50a ± 0.71 | 113a ± 0 | 112.5a ± 0.71 | 112.50a ± 0.71 | 110.50a ± 2.12 |
| W3 | 260 | 114b ± 1.41 | 116c ± 0 | 115.5c ± 0.71 | 115bc ± 1.41 | 113b ± 0 |
| W4 | 290 | 113.50b ± 0.71 | 116c ± 0 | 116.5c ± 2.12 | 114.50b ± 0.71 | 113.50b ± 0.71 |
| W5 | 320 | 114b ± 1.41 | 114.50bc ± 2.12 | 114b ± 1.41 | 114.50b ± 2.12 | 112.50a ± 0.71 |
| W6 | 350 | 114.50b ± 2.12 | 116c ± 0 | 116c ± 0 | 114.50b ± 2.12 | 113.50b ± 0.71 |
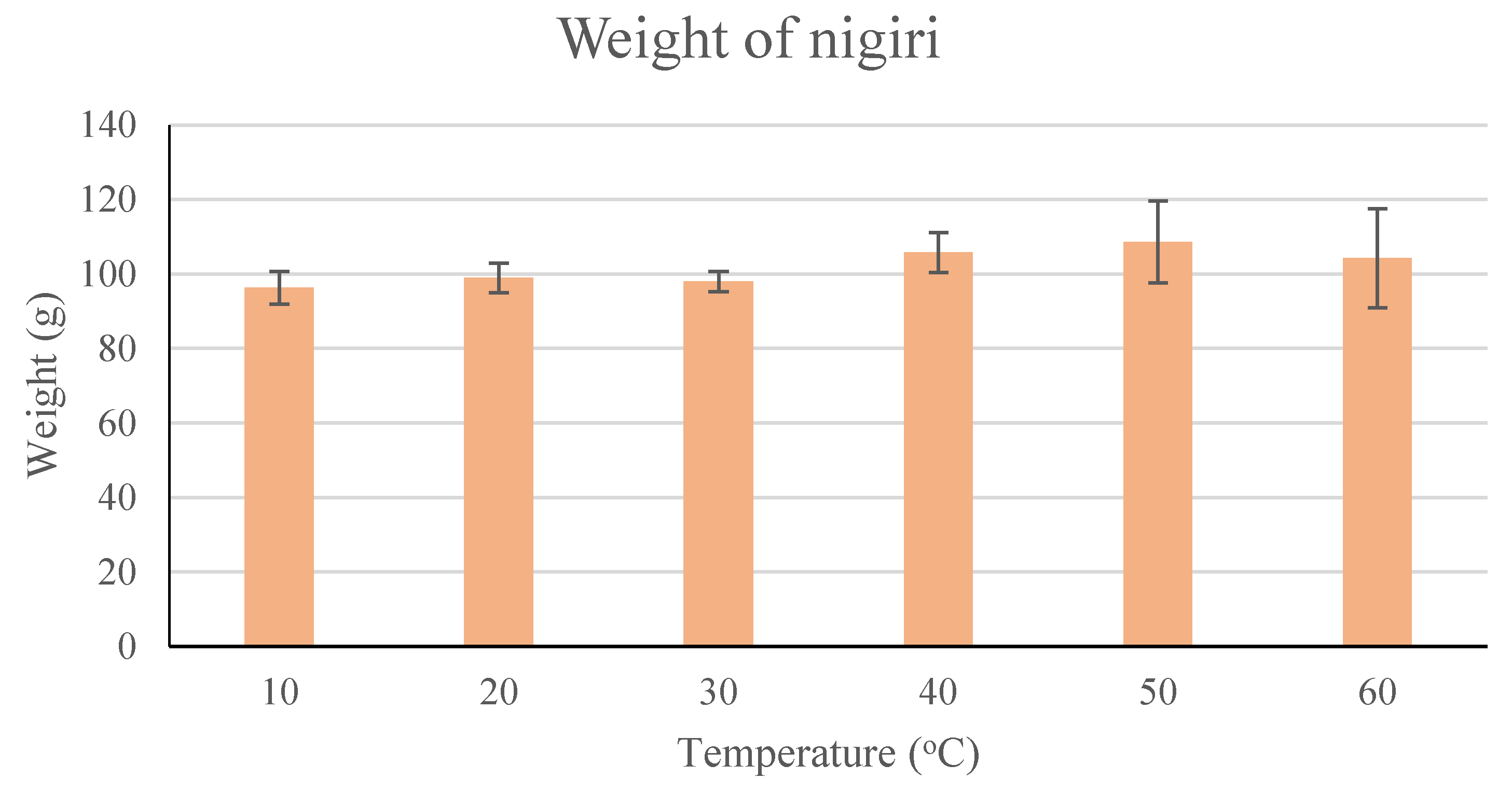
3.2.3. Nigiri Ball Weight at Different Temperatures
3.3. Shelf-Life Study of Cooked Sushi Rice
3.3.1. TPA
3.3.1.1. Different Washing Time on TPA
3.3.1.2. Different Water to Rice Ratio on TPA
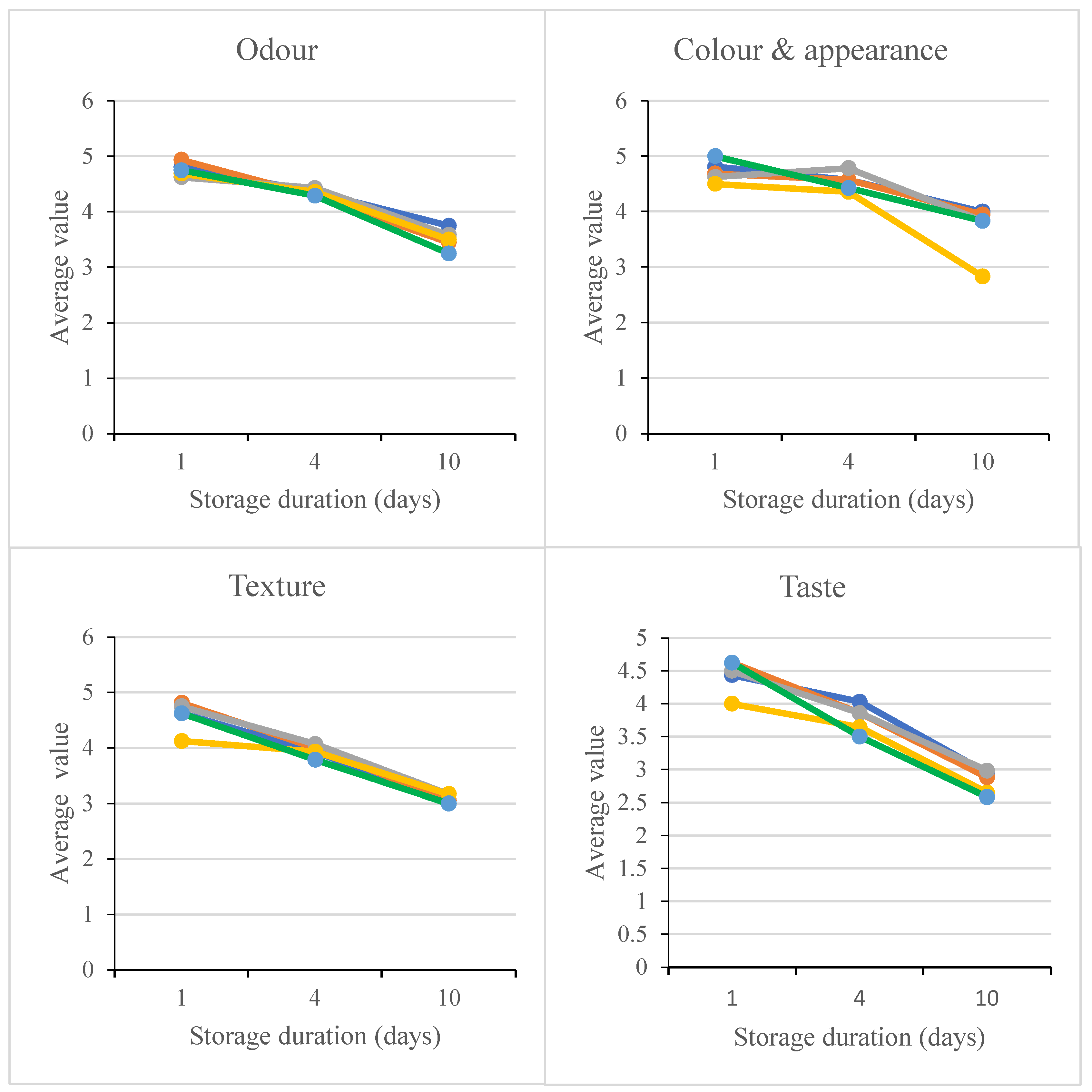
3.2.2. Sensory Evaluation
4. Conclusions
References
- P. Kulawik and D. Dordević, "Sushi processing: microbiological hazards and the use of emerging technologies," Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, vol. 62, no. 5, pp. 1270-1283, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. Hong et al., "Quality characteristics of rice varieties suitable for sushi," Korean Journal of Crop Science/Hanguk Jakmul Hakhoe Chi, vol. 57, no. 4, pp. 436-440, 2012. [CrossRef]
- E. Hebishy, D. Buchanan, J. Rice, and S. Oyeyinka, "Variation in amylose content in three rice variants predominantly influences sushi rice," 2024. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization (2024) 18:4545–4557. [CrossRef]
- M.-Y. Kang, C. W. Rico, and S.-C. Lee, "Physicochemical properties of eight popular glutinous rice varieties in Korea," Plant Production Science, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 177-184, 2010. [CrossRef]
- W. Tadele, P. Kulawik, A. Szymkowiak, A. R. Jambrak, Y. Ozogul, and F. Ozogul, "Cold-Storage Preservation of Cooked Rice Quality: Exploring Challenges and Strategies, Featuring Insights on Sushi Rice," Food Bioscience, p. 104553, 2024. [CrossRef]
- C. J. Bergman, "Rice end-use quality analysis," Chemistry and Technology 2019, pp. 273-337. [CrossRef]
- H. Li, S. Prakash, T. M. Nicholson, M. A. Fitzgerald, and R. G. Gilbert, "The importance of amylose and amylopectin fine structure for textural properties of cooked rice grains," Food Chemistry, vol. 196, pp. 702-711, 2016. [CrossRef]
- E. T. Champagne et al., "Important sensory properties differentiating premium rice varieties," Rice, vol. 3, pp. 270-281, 2010. [CrossRef]
- G. P. Yadav, D. Kumar, C. G. Dalbhagat, and H. N. Mishra, "A Comprehensive Review on Instant rice: Preparation Methodology, Characterization, and Quality Attributes," Food Chemistry Advances, p. 100581, 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. Yu, M. Turner, M. Fitzgerald, J. Stokes, and T. Witt, "Review of the effects of different processing technologies on cooked and convenience rice quality," Trends in Food Science & Technology, vol. 59, pp. 124-138, 2017. [CrossRef]
- L. Yu, M. S. Turner, M. Fitzgerald, J. R. Stokes, and T. Witt, "Review of the effects of different processing technologies on cooked and convenience rice quality," Trends in Food Science & Technology, vol. 59, pp. 124-138, Jan 2017. [CrossRef]
- L. Zhu et al., "Effect of soaking and cooking on structure formation of cooked rice through thermal properties, dynamic viscoelasticity, and enzyme activity," Food Chemistry, vol. 289, pp. 616-624, Aug 15 2019. [CrossRef]
- Y. Tian, J. Zhao, Z. Xie, J. Wang, X. Xu, and Z. Jin, "Effect of different pressure-soaking treatments on color, texture, morphology and retrogradation properties of cooked rice," LWT-Food Science and Technology, vol. 55, no. 1, pp. 368-373, 2014. [CrossRef]
- D. Mohapatra and S. Bal, "Cooking quality and instrumental textural attributes of cooked rice for different milling fractions," Journal of Food Engineering, vol. 73, no. 3, pp. 253-259, 2006. [CrossRef]
- M. Altheide, R. Morawicki, and T. Hager, "Impact of milling and water-to-rice ratio on cooked rice and wastewater properties," Food Science and Technology International, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 291-298, 2012. [CrossRef]
- M. Peleg, "Quantitative instrumental assessment of cooked rice stickiness," Food Engineering Reviews, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 452-459, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y. Yamaguchi, Y. OkAWA, K. Ninomiya, H. Kumagai, and H. Kumagai, "Evaluation and suppression of retrogradation of gelatinized rice starch," Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology, vol. 65, no. Supplement, pp. S134-S138, 2019. [CrossRef]
- K. Tao, W. Yu, S. Prakash, and R. G. Gilbert, "Investigating cooked rice textural properties by instrumental measurements," Food Science and Human Wellness, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 130-135, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Yu, Y. Ma, and D.-W. Sun, "Impact of amylose content on starch retrogradation and texture of cooked milled rice during storage," Journal of Cereal Science, vol. 50, no. 2, pp. 139-144, 2009. [CrossRef]
- K. L. Bett-Garber, E. T. Champagne, D. A. Ingram, and A. M. McClung, "Influence of water-to-rice ratio on cooked rice flavor and texture," Cereal Chemistry, vol. 84, no. 6, pp. 614-619, 2007. [CrossRef]
- M. R. A. Avaro, Z. Pan, T. Yoshida, and Y. Wada, "Two alternative methods to predict amylose content of rice grain by using tristimulus CIE lab values and developing a specific color board of starch-iodine complex solution," Plant Production Science, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 164-168, 2011. [CrossRef]
- H.-S. Kim, B. Patel, and J. N. BeMiller, "Effects of the amylose–amylopectin ratio on starch–hydrocolloid interactions," Carbohydrate Polymers, vol. 98, no. 2, pp. 1438-1448, 2013. [CrossRef]
- E.-H. Jang et al., "Correlation between physicochemical properties of japonica and indica rice starches," LWT-Food Science and Technology, vol. 66, pp. 530-537, 2016. [CrossRef]
- S. Wang, P. Li, J. Yu, P. Guo, and S. Wang, "Multi-scale structures and functional properties of starches from Indica hybrid, Japonica and waxy rice," International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, vol. 102, pp. 136-143, 2017. [CrossRef]
- W. Tadele et al., "Effects of multilayer Nano/Mini Furcellaran/Chitosan Emulsions with oregano essential oil and bioactive peptides on sensory, physicochemical properties and retrogradation in Sushi in cold storage conditions," Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, vol. 96, p. 103767, 2024. [CrossRef]
- S. Wang, C. Li, L. Copeland, Q. Niu, and S. Wang, "Starch Retrogradation: A Comprehensive Review," Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, vol. 14, no. 5, pp. 568-585, 2015. [CrossRef]
- R. Sumida, C. Inaguma, and K. Kawai, "Effects of maltotriose syrup, water content, and pH on the retrogradation of cooked rice in chilled storage," Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 2510-2517, 2022. [CrossRef]
- F. Balestra, "Empirical and fundamental mechanical tests in the evaluation of dough and bread rheological properties," 2009. [CrossRef]
- H. Li, J. Yang, M. Gao, J. Wang, and B. Sun, "Washing rice before cooking has no large effect on the texture of cooked rice," Food Chemistry, vol. 271, pp. 388-392, 2019. [CrossRef]
- C. N. Molina, R. Garzón, and C. M. Rosell, "Unraveling seasonings impact on cooked rice quality: Technological and nutritional implications for sushi," Journal of Cereal Science, vol. 104, p. 103442, 2022. [CrossRef]
| Ingredient | Mix 1 | Mix 2 | Mix 3 | Mix 4 |
| Rice vinegar | 52 | 64 | 76 | 40 |
| Sugar | 42 | 31 | 21 | 52 |
| Salt | 6 | 5 | 3 | 8 |
| Storage Duration(Days) | Group | Hardness (N) | Adhesiveness | Springiness | Cohesiveness | Chewiness | Resilience |
| 1 | W1 | 51.39def ± 17.79 | -730.1def ± 8.67 | 0.88a ± 0.13 | 0.54a ± 0.07 | 24.28bcde ± 8.71 | 0.21a ± 0.02 |
| 4 | 110bc ± 12.56 | -164bg ± 21.95 | 0.84a ± 0.02 | 0.43a ± 0.03 | 40.13abcd ± 2.56 | 0.21a ± 0.01 | |
| 6 | 132ab ± 5.37 | -19ab ± 14.28 | 0.67a ± 0.36 | 0.51a ± 0.08 | 50.72ab ± 5.03 | 0.24a ± 0.03 | |
| 1 | W2 | 11.46g ± 3.19 | -658.5c ± 33.44 | 0.71a ± 0.26 | 0.57a ± 0.10 | 18.74de ± 18.82 | 0.22a ± 0.03 |
| 4 | 36.14efg ± 13.15 | -51.05cde ± 5.10 | 0.39a ± 0.11 | 0.57a ± 0.05 | 8.47e ± 4.46 | 0.26a ± 0.03 | |
| 6 | 129.50ab ± 5.65 | -113ab ± 43.95 | 0.64a ± 0.17 | 0.51a ± 0.10 | 50.23abc ± 1.73 | 0.24a ± 0.04 | |
| 1 | W3 | 29.65fg ± 13.44 | -653.40cd ± 20.91 | 0.73a ± 0.24 | 0.53a ± 0.08 | 11.85e ± 6.61 | 0.20a ± 0.03 |
| 4 | 63.54de ± 9.63 | -134.10ef ± 17.02 | 0.67a ± 0.12 | 0.47a ± 0.02 | 23.29bcde ± 10.33 | 0.22a ± 0.02 | |
| 6 | 166.20a ± 13.56 | -8.32a ± 3.24 | 0.60a ± 0.39 | 0.54a ± 0.14 | 60.96a ± 19.88 | 0.26a ± 0.05 | |
| 1 | W4 | 42.10fg ± 12.60 | -645.30cd ± 30.80 | 0.76a ± 0.21 | 0.54a ± 0.08 | 18.96de ± 13.50 | 0.20a ± 0.02 |
| 4 | 76.60de ± 11.00 | -103.50c ± 16.00 | 0.58a ± 0.12 | 0.50a ± 0.03 | 27.62bcde ± 7.80 | 0.23a ± 0.02 | |
| 6 | 146.10ab ± 8.00 | -10.80a ± 8.20 | 0.60a ± 0.31 | 0.53a ± 0.09 | 55.11ab ± 6.10 | 0.25a ± 0.03 | |
| 1 | W5 | 31.20fg ± 10.20 | -649.8cd ± 25.50 | 0.78a ± 0.23 | 0.56a ± 0.09 | 15.81de ± 12.1 | 0.21a ± 0.02 |
| 4 | 69.50def ± 12.80 | -92.80c ± 12.50 | 0.63a ± 0.10 | 0.49a ± 0.04 | 22.64bcde ± 6.90 | 0.23a ± 0.02 | |
| 6 | 155.30a ± 9.40 | -16.10a ± 9.00 | 0.59a ± 0.28 | 0.52a ± 0.10 | 58.84a ± 7.20 | 0.25a ± 0.03 | |
| 1 | W6 | 77.49cd ± 16.47 | -654.20fg ± 41.48 | 0.82a ± 0.23 | 0.48a ± 0.05 | 22.38cde ± 13.15 | 0.18a ± 0.01 |
| 4 | 27.11fg ± 4.90 | -45.93cd ± 14.20 | 0.55a ± 0.30 | 0.59a ± 0.11 | 13.61e ± 11.67 | 0.24a ± 0.05 | |
| 6 | 139.90ab ± 12.36 | -23.41ab ± 17.43 | 0.55a ± 0.48 | 0.54a ± 0.08 | 57.62a ± 4.01 | 0.24a ± 0.04 |
| Storage Duration(Days) | Group | Hardness (N) | Adhesiveness | Springiness | Cohesiveness | Chewiness | Resilience |
| 1 | R1 | 406.30cd ± 15.13 | -369.30a ± 70.25 | 0.99a ± 0.02 | 0.27ab ± 0.01 | 109.50b ± 6.56 | 0.14abcd ± 0.01 |
| 4 | 538.90a ± 23.85 | -718.80c ± 14.44 | 0.99a ± 0.02 | 0.30ab ± 0.02 | 155.40a ± 14.19 | 0.16ab ± 0.01 | |
| 10 | 538.10a ± 27.73 | -532.10b ± 73.50 | 0.89a ± 0.26 | 0.44a ± 0.26 | 152.90a ± 13.52 | 0.21a ± 0.15 | |
| 1 | R2 | 411.30c ± 19.49 | -1650j ± 30.44 | 0.88a ± 0.27 | 0.25b ± 0.02 | 100.60bc ± 10.67 | 0.12abcd ± 0.01 |
| 4 | 265.40b ± 19.55 | -913.10d ± 58.51 | 1.00a ± 0.00 | 0.29ab ± 0.00 | 138.10a ± 7.68 | 0.15abc ± 0.01 | |
| 10 | 415.30c ± 11.09 | -948.70de ± 39.37 | 0.99a ± 0.02 | 0.29ab ± 0.02 | 117.20b ± 10.20 | 0.14abcd ± 0.02 | |
| 1 | R3 | 301.20fg ± 11.18 | -1341hi ± 27.12 | 0.99a ± 0.02 | 0.22b ± 0.01 | 63.88ef ± 1.73 | 0.09bcd ± 0.00 |
| 4 | 325.40ef ± 29.41 | -1127fg ± 5.16 | 1.00a ± 0.00 | 0.23b ± 0.00 | 74.76de ± 5.53 | 0.11bcd ± 0.01 | |
| 10 | 365de ± 15.48 | -669.60bc ± 27.26 | 1.00a ± 0.00 | 0.23b ± 0.00 | 85.32cd ± 8.83 | 0.11bcd ± 0.01 | |
| 1 | R4 | 225.60h ± 19.14 | -1292gh ± 39.87 | 1.03a ± 0.06 | 0.22b ± 0.02 | 50.07fg ± 3.79 | 0.09bcd ± 0.01 |
| 4 | 265.40gh ± 15.71 | -1155fg ± 25.10 | 1.00a ± 0.01 | 0.20b ± 0.01 | 51.85f ± 4.21 | 0.08bcd ± 0.00 | |
| 10 | 276g ± 17.29 | -1122f ± 54.31 | 0.88a ± 0.26 | 0.20b ± 0.26 | 48.07fg ± 14.42 | 0.08bcd ± 0.01 | |
| 1 | R5 | 167.30i ± 13.64 | -1474i ± 11.18 | 0.99a ± 0.02 | 0.20b ± 0.01 | 32.36gh ± 3.41 | 0.08bcd ± 0.03 |
| 4 | 169.20i ± 12.20 | -1117ef ± 13.98 | 0.87a ± 0.24 | 0.17b ± 0.24 | 24.53h ± 7.48 | 0.06cd ± 0.01 | |
| 10 | 161.60i ± 12.82 | -1228fgh ± 47.98 | 0.88a ± 0.27 | 0.16b ± 0.27 | 22.15h ± 7.07 | 0.05d ± 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





