Submitted:
15 February 2025
Posted:
18 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a global health concern with limited treatment options. Radix Astragali and Panax notoginseng, widely used in Chinese herbal medicine, have shown nephroprotective potential. This study evaluated their impact on AKI recovery.Methods: A retrospective study was conducted at our Hospital(2012–2022). Univariate and multifactor logistic regression analyses assessed the effects of Radix Astragali and Panax notoginseng on short-term AKI outcomes.Results: Radix Astragali (RR=0.33, P=0.01, 95%CI:[0.13, 0.53]) and its combination with Panax notoginseng (RR=0.31, P=0.01, 95%CI:[0.11, 0.50]) significantly improved AKI recovery. Other positive factors included albumin levels (RR=0.02, P=0.03), ICU admission (RR=0.43, P=0.01), hemoglobin levels (RR=0.01, P=0.01), and diabetes mellitus (RR=0.22, P=0.04).Conclusion: Radix Astragali and Panax notoginseng enhance AKI recovery, particularly at peak serum creatinine levels, suggesting their potential as therapeutic options for AKI management.
Keywords:
Introduction
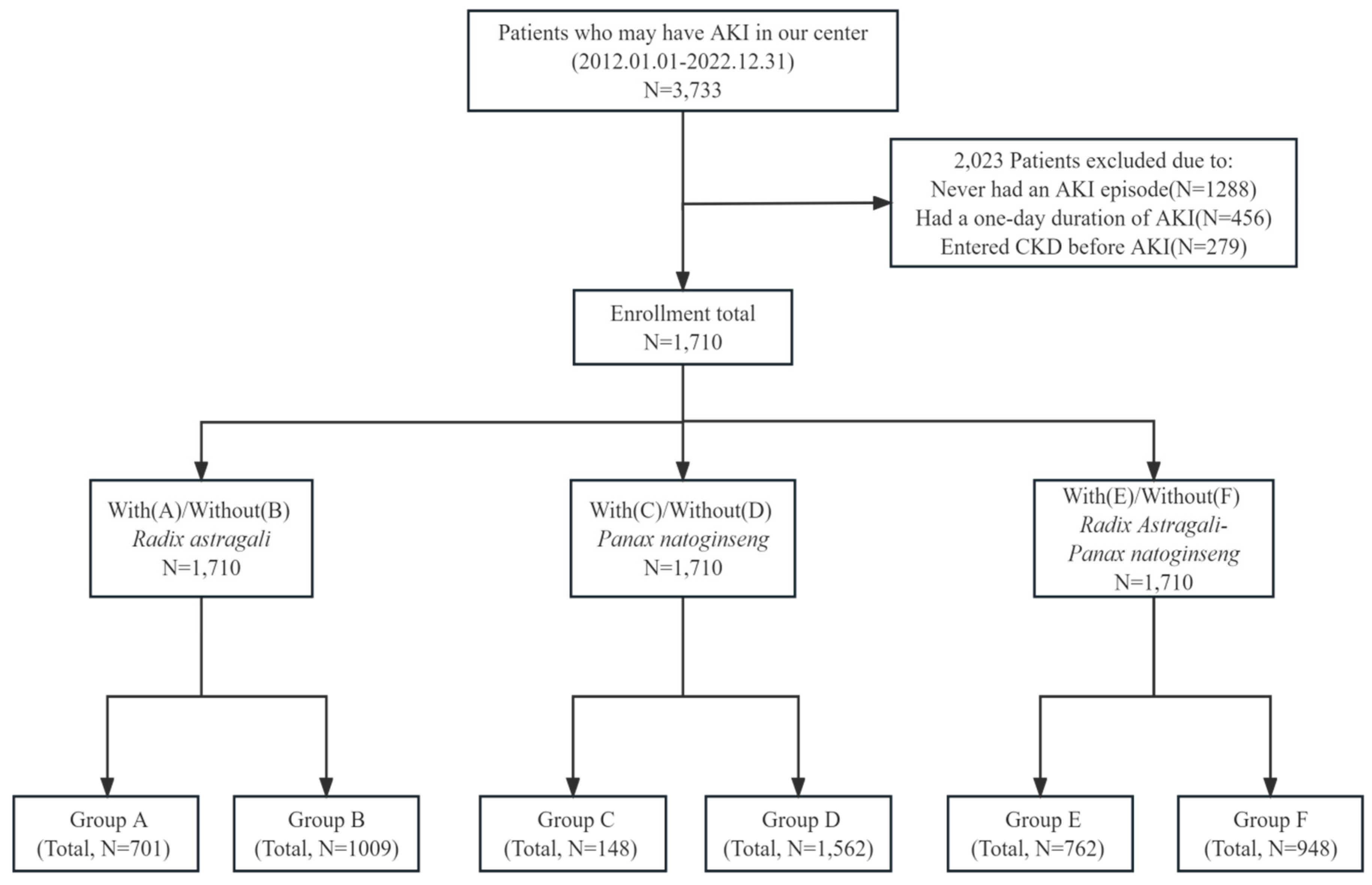
Materials and Methods
Study Population
Covariates
Events
Statistical Methods
Results
The Baseline Characteristics of the AKI Patients
Logistic Regression Analyses
Discussion Principal Findings
Review of Relevant Molecular Mechanisms
Limitation of the Study
References
- Ostermann M, Bellomo R, Burdmann EA, Doi K, Endre ZH, Goldstein SL, Kane-Gill SL, Liu KD, Prowle JR, Shaw AD et al: Controversies in acute kidney injury: conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Conference. Kidney Int 2020, 98(2):294-309. [CrossRef]
- Mehta RL, Cerdá J, Burdmann EA, Tonelli M, García-García G, Jha V, Susantitaphong P, Rocco M, Vanholder R, Sever MS et al: International Society of Nephrology's 0by25 initiative for acute kidney injury (zero preventable deaths by 2025): a human rights case for nephrology. Lancet 2015, 385(9987):2616-2643. [CrossRef]
- Yang Y, Song M, Liu Y, Liu H, Sun L, Peng Y, Liu F, Venkatachalam MA, Dong Z: Renoprotective approaches and strategies in acute kidney injury. Pharmacol Ther 2016, 163:58-73. [CrossRef]
- Li HD, Meng XM, Huang C, Zhang L, Lv XW, Li J: Application of Herbal Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of Acute Kidney Injury. Front Pharmacol 2019, 10:376. [CrossRef]
- Jo SK, Rosner MH, Okusa MD: Pharmacologic treatment of acute kidney injury: why drugs haven't worked and what is on the horizon. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2007, 2(2):356-365. [CrossRef]
- Hapca S, Siddiqui MK, Kwan RSY, Lim M, Matthew S, Doney ASF, Pearson ER, Palmer CNA, Bell S: The Relationship between AKI and CKD in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: An Observational Cohort Study. J Am Soc Nephrol 2021, 32(1):138-150. [CrossRef]
- Lu H: Clinical study of Erhuang Decoction in the treatment of non-dialysis patients withacute kidney injury and the mechanism of Erhuang Decoction in the treatment ofacute kidney injury based on network pharmacology. phD. Chengdu University of TCM; 2022.
- Lei S: Clinical Study on the Treatment of Huaxiancapsule 3 in Sepsis Acute Kidney Injury(Stasis Resistance Type). M.A.: Heilongjiang University Of Chinese Medicine; 2021.
- Tang JL, Xin M, Zhang LC: Protective effect of Astragalus membranaceus and Astragaloside IV in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Aging (Albany NY) 2022, 14(14):5855-5877. [CrossRef]
- Sun J, Wei S, Zhang Y, Li J: Protective Effects of Astragalus Polysaccharide on Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst) 2021, 2021:7178253. [CrossRef]
- Hao Y, Miao J, Liu W, Peng L, Chen Y, Zhong Q: Formononetin protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through activation of the PPARα/Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 pathway. Int J Mol Med 2021, 47(2):511-522. [CrossRef]
- Yan W, Xu Y, Yuan Y, Tian L, Wang Q, Xie Y, Shao X, Zhang M, Ni Z, Mou S: Renoprotective mechanisms of Astragaloside IV in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Free Radic Res 2017, 51(7-8):669-683. [CrossRef]
- Song Y, Hu T, Gao H, Zhai J, Gong J, Zhang Y, Tao L, Sun J, Li Z, Qu X: Altered metabolic profiles and biomarkers associated with astragaloside IV-mediated protection against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in rats: An HPLC-TOF/MS-based untargeted metabolomics study. Biochem Pharmacol 2021, 183:114299. [CrossRef]
- Liu X, Huang Z, Zou X, Yang Y, Qiu Y, Wen Y: Panax notoginseng saponins attenuates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via inhibiting the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014, 7(12):8391-8400.
- Li Q, Zhang Y, Yang Y, Huang S, Zou X, Wei C, Liang T, Zhong X: Panax notoginseng saponins reduces the cisplatin-induced acute renal injury by increasing HIF-1α/BNIP3 to inhibit mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 2021, 142:111965. [CrossRef]
- Wei M, Gao Y, Cheng D, Zhang H, Zhang W, Shen Y, Huang Q, An X, Wang B, Yu Z et al: Notoginsenoside Fc ameliorates renal tubular injury and mitochondrial damage in acetaminophen-induced acute kidney injury partly by regulating SIRT3/SOD2 pathway. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022, 9:1055252. [CrossRef]
- Liu WJ, Tang HT, Jia YT, Ma B, Fu JF, Wang Y, Lv KY, Xia ZF: Notoginsenoside R1 attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Shock 2010, 34(3):314-320. [CrossRef]
- Shou DW, Yu ZL, Meng JB, Lai ZZ, Pang LS, Dai MH, Yang X, Tu YX: Panax notoginseng Alleviates Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Reducing Inflammation in Rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2022, 2022:9742169. [CrossRef]
- Hui D, Rui-Zhi T, Jian-Chun L, Xia Z, Dan W, Jun-Ming F, Li W: Astragalus propinquus Schischkin and Panax notoginseng (A&P) compound relieved cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through inhibiting the mincle maintained macrophage inflammation. J Ethnopharmacol 2020, 252:112637. [CrossRef]
| name | Radix Astragali using group (Group A) | Non-Radix Astragali using group (Group B) | P | |
| 0 | Demographic data | |||
| 1 | Total(n) | 701(100.00%) | 1009(100.00%) | 1.00 |
| 2 | Male(n) | 418(59.63%) | 645(63.92%) | 0.08 |
| 3 | The mean ages when AKI first develops (years) | 58.74±19.97 | 60.21±22.08 | 0.15 |
| 4 | Operation before AKI | 36(5.14%) | 76(7.53%) | 0.06 |
| 5 | Admission to the ICU when AKI occurs | 202(28.82%) | 322(31.91%) | 0.19 |
| 6 | Highest Cr during AKI periods(μmol/L) | 483.44±373.22 | 414.97±348.91 | <0.05 |
| 7 | Recover from AKI in 28 Days(n) | 364(51.93%) | 441(43.71%) | <0.05 |
| 8 | Use renal replace treatment during AKI period(n) | 115(16.41%) | 123(12.19%) | <0.05 |
| 9 | Use herbal decoction during AKI period(n) | 701(100.00%) | 802(79.48%) | <0.05 |
| 10 | Diabetes(n) | 228(32.52%) | 337(33.40%) | 0.74 |
| 11 | Hypertension(n) | 444(63.34%) | 622(61.65%) | 0.51 |
| 12 | Laboratory tests | |||
| 13 | Plasma albumin(g/L) | 33.71±8.86 | 33.55±8.12 | 0.71 |
| 14 | Hemoglobin(g/L) | 113.68±28.63 | 114.15±28.85 | 0.74 |
| 15 | Hemoglobin A1c (%) | 6.89±2.28 | 6.74±2.02 | 0.28 |
| 16 | Serum Potassium(mmol/L) | 4.42±0.94 | 4.30±0.87 | <0.05 |
| 17 | Serum Sodium(mmol/L) | 137.81±7.41 | 137.54±7.56 | 0.47 |
| name | Panax natoginseng using group (Group C) | Non- Panax natoginseng using group (Group D) | P | |
| 0 | Demographic data | |||
| 1 | Total(n) | 148(100.00%) | 1562(100.00%) | 1.00 |
| 2 | Male(n) | 96(64.86%) | 967(61.91%) | 0.54 |
| 3 | The mean ages when AKI first develops (years) | 63.95±17.97 | 59.20±21.49 | <0.05 |
| 4 | Operation before AKI | 14(9.46%) | 98(6.27%) | 0.19 |
| 5 | Admission to the ICU when AKI occurs | 43(29.05%) | 481(30.79%) | 0.73 |
| 6 | Highest Cr during AKI periods(μmol/L) | 452.73±465.04 | 442.12±349.20 | 0.73 |
| 7 | Recover from AKI in 28 Days(n) | 67(45.27%) | 738(47.25%) | 0.71 |
| 8 | Use renal replace treatment during AKI period(n) | 24(16.22%) | 214(13.70%) | 0.47 |
| 9 | Use herbal decoction during AKI period(n) | 148(100.00%) | 1355(86.75%) | <0.05 |
| 10 | Diabetes(n) | 57(38.51%) | 508(32.52%) | 0.16 |
| 11 | Hypertension(n) | 95(64.19%) | 971(62.16%) | 0.69 |
| 12 | Laboratory tests | |||
| 13 | Plasma albumin(g/L) | 33.38±7.86 | 33.64±8.48 | 0.73 |
| 14 | Hemoglobin(g/L) | 110.05±29.14 | 114.33±28.69 | 0.08 |
| 15 | Hemoglobin A1c (%) | 7.01±2.61 | 6.78±2.08 | 0.33 |
| 16 | Serum Potassium(mmol/L) | 4.40±0.91 | 4.35±0.90 | 0.49 |
| 17 | Serum Sodium(mmol/L) | 139.10±8.16 | 137.51±7.42 | <0.05 |
| name | Radix Astragali- Panax natoginseng using group (Group E) | Non- Radix Astragali- Panax natoginseng using group (Group F) | P | |
| 0 | Demographic data | |||
| 1 | Total(n) | 762(100.00%) | 948(100.00%) | 1.00 |
| 2 | Male(n) | 463(60.76%) | 600(63.29%) | 0.31 |
| 3 | The mean ages when AKI first develops (years) | 59.19±19.97 | 59.94±22.22 | 0.46 |
| 4 | Operation before AKI | 44(5.77%) | 68(7.17%) | 0.29 |
| 5 | Admission to the ICU when AKI occurs | 222(29.13%) | 302(31.86%) | 0.25 |
| 6 | Highest Cr during AKI periods(μmol/L) | 478.10±379.97 | 414.86±341.74 | <0.05 |
| 7 | Recover from AKI in 28 Days(n) | 390(51.18%) | 415(43.78%) | <0.05 |
| 8 | Use renal replace treatment during AKI period(n) | 125(16.40%) | 113(11.92%) | <0.05 |
| 9 | Use herbal decoction during AKI period(n) | 762(100.00%) | 741(78.16%) | <0.05 |
| 10 | Diabetes(n) | 253(33.20%) | 312(32.91%) | 0.94 |
| 11 | Hypertension(n) | 487(63.91%) | 579(61.08%) | 0.25 |
| 12 | Laboratory tests | |||
| 13 | Plasma albumin(g/L) | 33.67±8.74 | 33.57±8.18 | 0.82 |
| 14 | Hemoglobin(g/L) | 113.70±28.68 | 114.16±28.82 | 0.74 |
| 15 | Hemoglobin A1c (%) | 6.96±2.37 | 6.67±1.90 | 0.05 |
| 16 | Serum Potassium(mmol/L) | 4.40±0.93 | 4.31±0.87 | <0.05 |
| 17 | Serum Sodium(mmol/L) | 137.96±7.52 | 137.40±7.47 | 0.13 |
| RR | Std err | z | P>|z| | [0.025 | 0.975] | |
|
Use Radix Astragali |
0.42 | 0.12 | 3.53 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 0.65 |
| Intercept | -0.37 | 0.08 | -4.71 | 0.00 | -0.53 | -0.22 |
| Multivariable logistic regression analyses of Radix Astragali | ||||||
| RR | Std err | z | P>|z| | [0.025 | 0.975] | |
| The mean ages when AKI first develops | -0.01 | 0.01 | -1.46 | 0.14 | -0.01 | 0.01 |
| Gender | 0.17 | 0.13 | 1.29 | 0.20 | -0.09 | 0.43 |
|
Use Radix Astragali |
0.47 | 0.12 | 3.87 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 0.72 |
| Albumin | 0.02 | 0.01 | 2.12 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| Hemoglobin | 0.01 | 0.01 | 3.46 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.26 | 0.14 | 1.79 | 0.07 | -0.02 | 0.53 |
| Hypertension | -0.37 | 0.14 | -2.71 | 0.01 | -0.64 | -0.10 |
| Operation before AKI | -1.18 | 0.30 | -4.00 | 0.00 | -1.77 | -0.60 |
| Admission to the ICU when AKI occurs | 0.43 | 0.14 | 3.08 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.71 |
| Intercept | -1.56 | 0.37 | -4.19 | 0.00 | -2.29 | -0.83 |
| RR | Std err | z | P>|z| | [0.025 | 0.975] | |
|
Use Panax natoginseng |
-0.07 | 0.22 | -0.33 | 0.74 | -0.49 | 0.35 |
| Intercept | -0.18 | 0.06 | -2.97 | 0.01 | -0.30 | -0.06 |
| Multivariable logistic regression analyses of Panax natoginseng | ||||||
| RR | Std err | z | P>|z| | [0.025 | 0.975] | |
| The mean ages when AKI first develops | 0.01 | 0.01 | -1.45 | 0.15 | -0.01 | 0.01 |
| Gender | 0.14 | 0.13 | 1.07 | 0.28 | -0.12 | 0.39 |
|
Use Radix Astragali |
0.04 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.85 | -0.39 | 0.48 |
| Albumin | 0.02 | 0.01 | 2.18 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| Hemoglobin | 0.01 | 0.01 | 3.41 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.23 | 0.14 | 1.61 | 0.11 | -0.05 | 0.50 |
| Hypertension | -0.35 | 0.14 | -2.55 | 0.01 | -0.61 | -0.08 |
| Operation before AKI | -1.21 | 0.29 | -4.12 | 0.00 | -1.79 | -0.64 |
| Admission to the ICU when AKI occurs | 0.40 | 0.14 | 2.83 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.67 |
| Intercept | -1.32 | 0.36 | -3.62 | 0.00 | -2.03 | -0.61 |
| RR | Std err | z | P>|z| | [0.025 | 0.975] | |
| Use the combination of Panax natoginseng- Radix Astragali | 0.37 | 0.12 | 3.16 | 0.00 | 0.14 | 0.60 |
| Intercept | -0.36 | 0.08 | -4.47 | 0.00 | -0.52 | -0.20 |
| Multivariable logistic regression analyses of Panax natoginseng- Radix Astragali | ||||||
| RR | Std err | z | P>|z| | [0.025 | 0.975] | |
| The mean ages when AKI first develops | -0.01 | 0.01 | -1.46 | 0.14 | -0.01 | 0.01 |
| Gender | 0.16 | 0.13 | 1.25 | 0.21 | -0.09 | 0.42 |
| Use the combination of Panax natoginseng- Radix Astragali | 0.43 | 0.12 | 3.54 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 0.67 |
| Albumin | 0.02 | 0.01 | 2.15 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| Hemoglobin | 0.01 | 0.01 | 3.48 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.25 | 0.14 | 1.78 | 0.08 | -0.03 | 0.53 |
| Hypertension | -0.37 | 0.14 | -2.71 | 0.01 | -0.64 | -0.10 |
| Operation before AKI | -1.18 | 0.30 | -4.01 | 0.00 | -1.76 | -0.61 |
| Admission to the ICU when AKI occurs | 0.43 | 0.14 | 3.05 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.71 |
| Intercept | -1.55 | 0.37 | -4.17 | 0.00 | -2.29 | -0.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




