Submitted:
10 February 2025
Posted:
11 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Innovative drug delivery systems are revolutionizing contemporary pharmacotherapy with better bioavailability, controlled delivery, and better patient compliance. This review covers some advances in nanoparticle-based drug delivery against the background of liposomal and vesicular systems for precision therapeutics. This review further checks the oral formulation, including chewable, effervescent, and film-based delivery, against the advantageous ease of administration and the rapid onset of the drug's action. In addition, strategies of naso-pulmonary and antibiotic drug delivery are further described in terms of respiratory health and infection management in relation to nanocarrier-based formulations. Moreover, herbal therapeutics are incorporated as demonstrated with Tribulus terrestris in urolithiasis treatment, which in turn, actually merges traditional medicine delivery with modern drug delivery platforms. Based on clinical applications, advantages, and disadvantages, comparative analysis of nanocarriers including liposomes, polymeric nanoparticles, niosomes, and dendrimers has been presented. In the future, it will be all about the biodegradable AI-driven stimuli responsive nanocarrier supporting the precision of medicine and personalized care. This review provides insight into recent developments, challenges, and future directions in advanced drug delivery systems for developing more effective and patient-friendly therapeutic solutions.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Targeted and Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery
2.1. Nanotechnology in Targeted Drug Delivery
3. Liposomal and Vesicular Drug Delivery Systems
| S. No. | Application | Details | Advantages | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Oncology | Liposomal formulations like doxorubicin and paclitaxel-loaded nanoparticles improve chemotherapy efficacy. | Reduces cardiotoxicity and enhances drug accumulation in tumors [7]. | Liposomal Doxorubicin, Paclitaxel [7] |
| 2 | Antibiotic Therapy | Nanoparticle-based drug delivery enhances penetration into bacterial biofilms, reducing resistance. | Overcomes bacterial resistance by improving drug delivery to infection sites [9]. | Nanoparticle-mediated antibiotics [9] |
| 3 | Future Advancements | Development of stimuli-responsive nanoparticles that release drugs based on pH, temperature, or enzyme activity. | Enables controlled, site-specific drug release, minimizing side effects [6]. | pH-responsive nanoparticles [6] |
| 4 | Personalized Medicine | Integrating nanotechnology with patient-specific drug formulations for individualized treatment. | Ensures higher therapeutic precision and better patient outcomes [6-9]. | Personalized nanomedicine approaches [6-9] |
3.1. Structure and Composition [11]
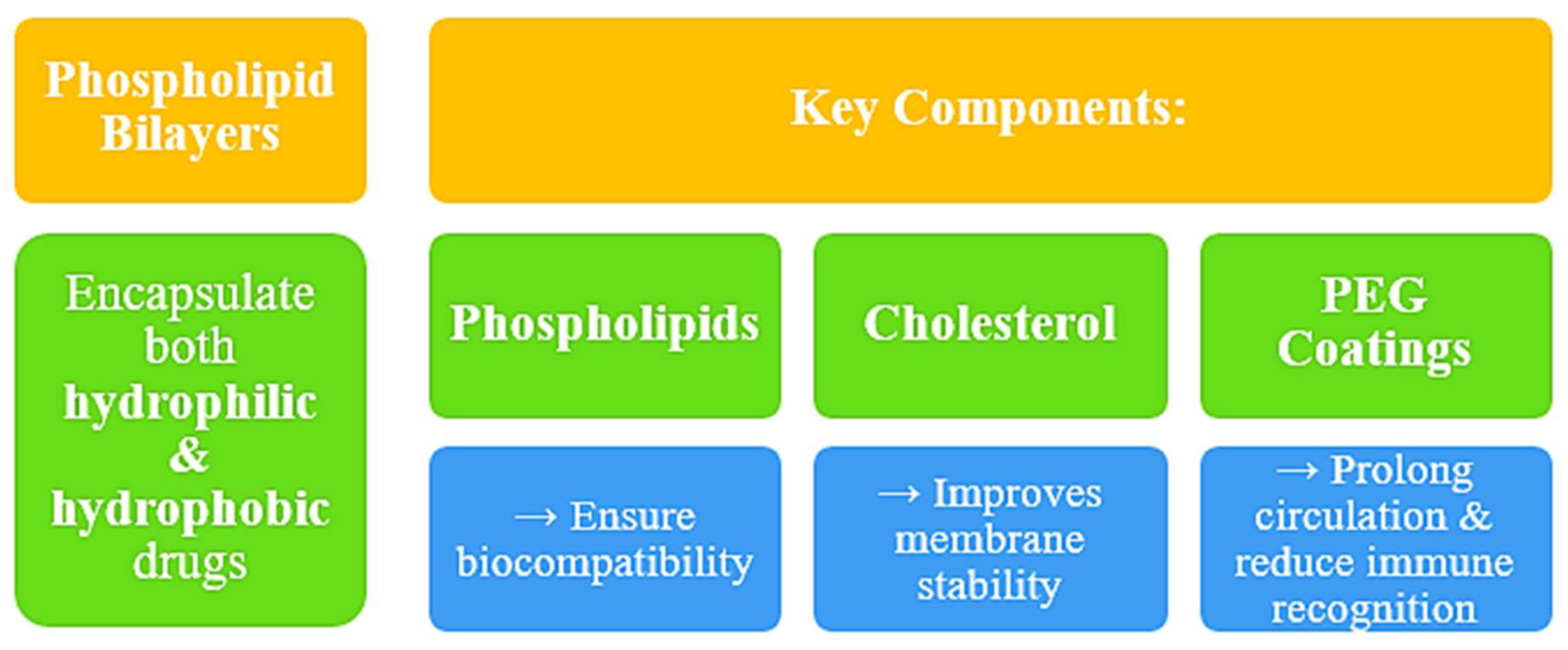
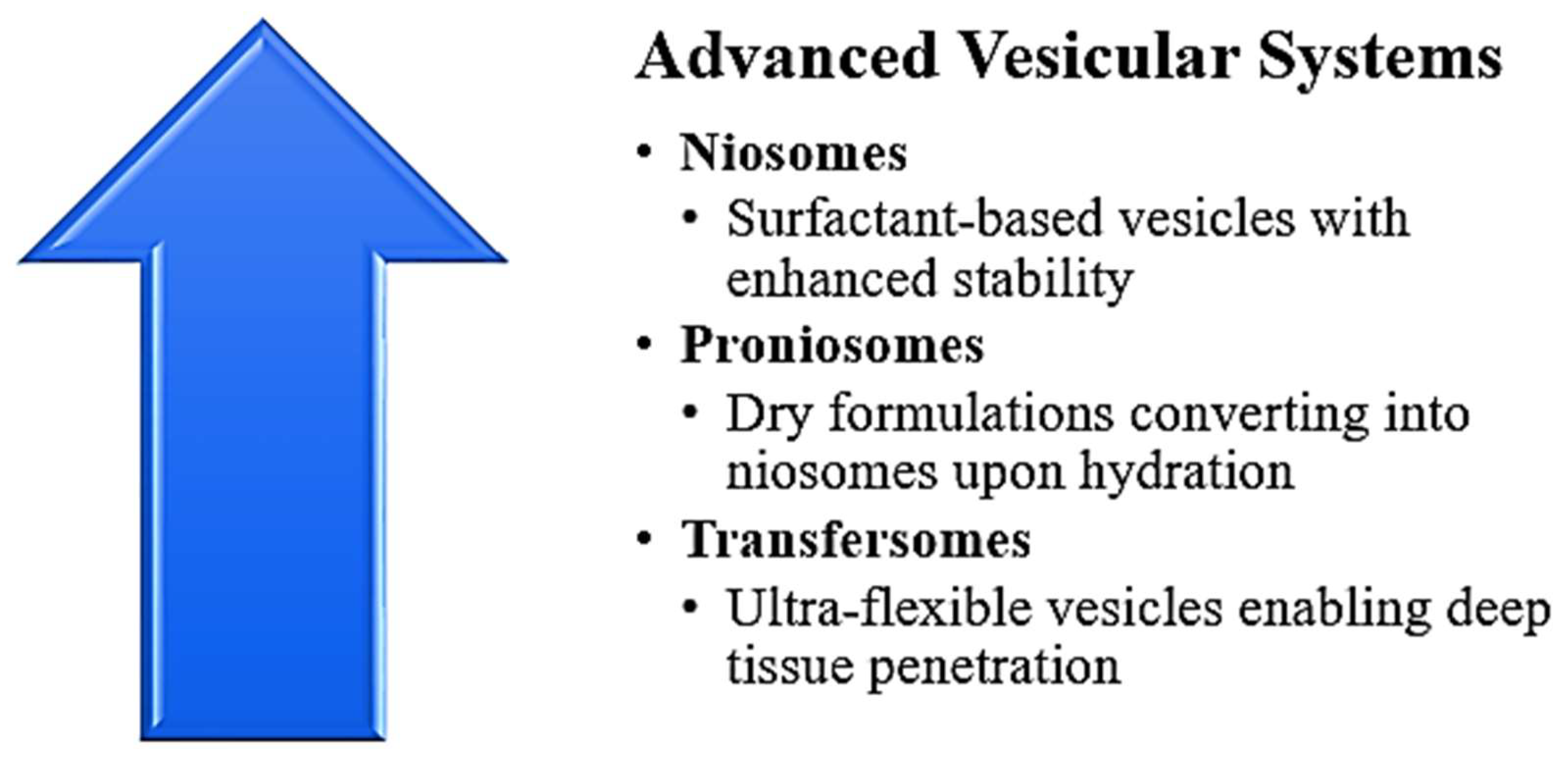
3.2. Advanced Vesicular Systems [12, 13]
4. Oral Drug Delivery Systems: Chewable, Effervescent, and Films
4.1. Chewable Tablets [5]
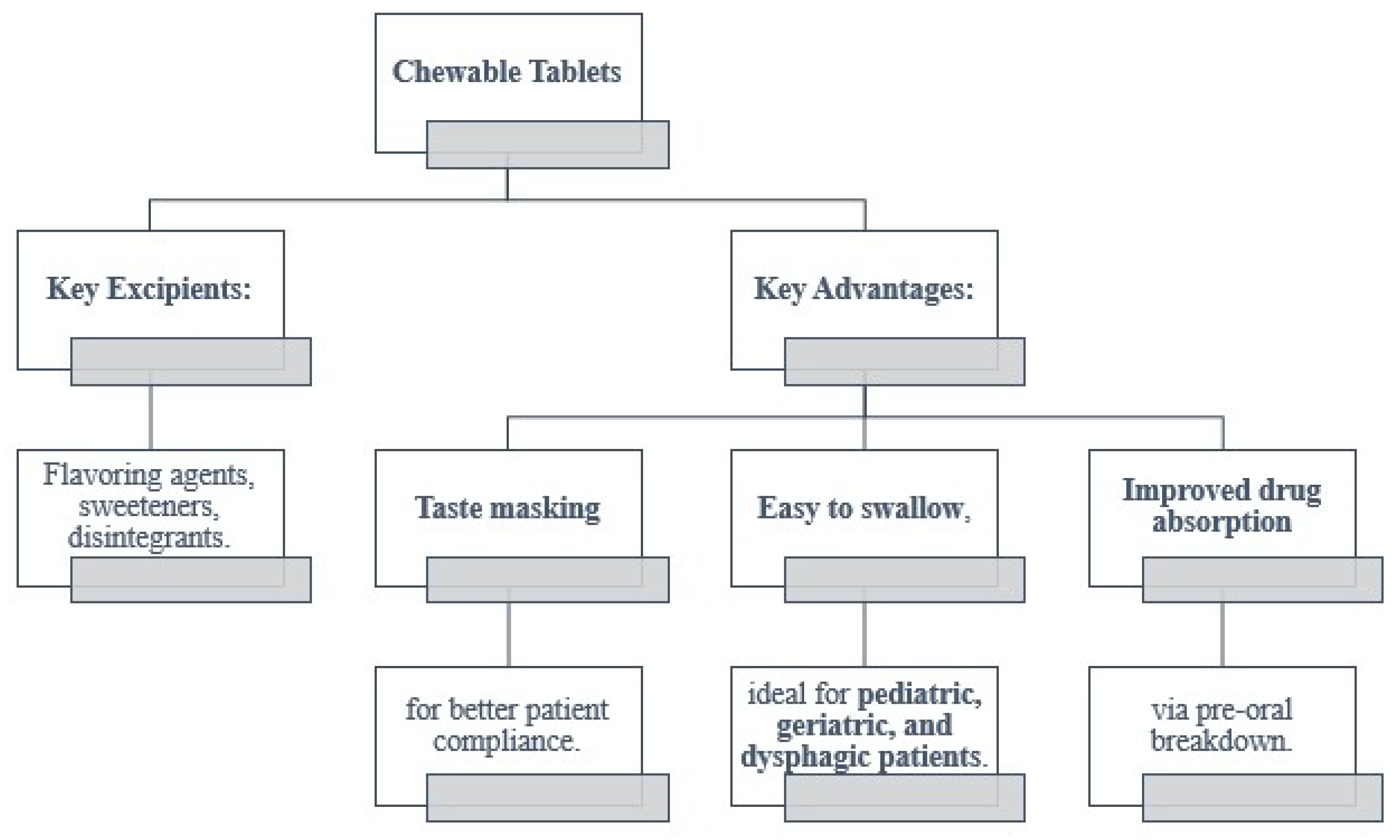
4.2. Effervescent Tablets [14]
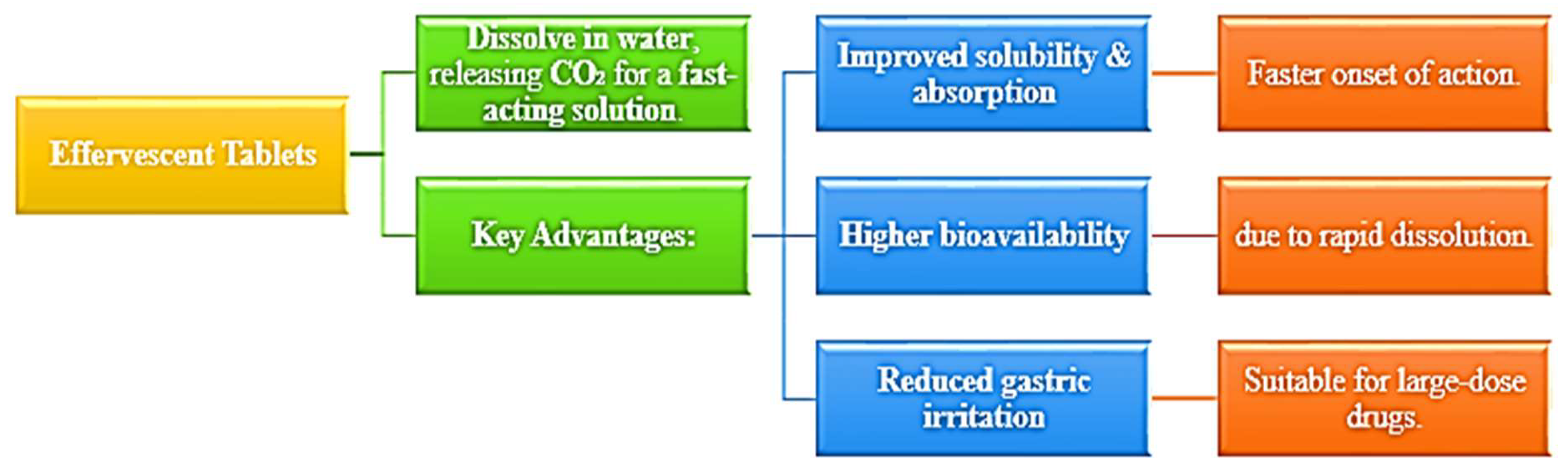
4.3. Mouth-Dissolving Films
5. Advancements in Naso-Pulmonary and Antibiotic Drug Delivery
| S. No. | Category | Innovation | Advantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Naso-Pulmonary Drug Delivery | Nanoparticle-Based Inhalers | Enhances drug retention in the lungs and provides sustained release [17]. | Asthma, COPD [17] |
| 2 | Naso-Pulmonary Drug Delivery | Liposome-Encapsulated Pulmonary Drugs | Improves deep lung penetration, reducing systemic side effects [17]. | Pulmonary infections, lung cancer [17] |
| 3 | Naso-Pulmonary Drug Delivery | Nasal Drug Delivery for CNS Disorders | Utilizes the nose-to-brain pathway for targeted therapy [16]. | Neurodegenerative diseases, migraines [16] |
| 4 | Antibiotic Drug Delivery | Liposomal Antibiotics | Enhances stability and enables targeted bacterial eradication [18]. | Bacterial infections, MRSA, resistant strains [18] |
| 5 | Antibiotic Drug Delivery | Inhalable Antibiotics | Improves lung drug delivery for respiratory infections [18]. | Tuberculosis, cystic fibrosis [18] |
| 6 | Antibiotic Drug Delivery | Stimuli-Responsive Antibiotic Systems | Enables site-specific drug release triggered by pH or enzymes [18]. | Targeted infection treatment [18] |
6. Herbal and Alternative Therapeutics in Drug Delivery
7. Comparative Analysis of Nanocarriers
| Nanocarrier Type | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Liposomes | Biocompatible, suitable for hydrophilic & hydrophobic drugs, prolonged circulation | Stability issues, high production costs [20] |
| Polymeric Nanoparticles | Controlled drug release, improved drug solubility | Possible toxicity, complex synthesis [21] |
| Niosomes | Stable, cost-effective alternative to liposomes | Lower entrapment efficiency compared to liposomes [22, 23] |
| Dendrimers | High drug-loading capacity, precise targeting | Potential cytotoxicity, high production costs [21] |
Conclusion
References
- Sengar, A. (2023). Targeting methods: A short review including rationale, goal, causes, strategies for targeting. International Journal of Research Publication and Reviews, 4(8), 1379-1384.
- Jagrati, K. M. , & Sengar, A. (2024). Liposomal vesicular delivery system: An innovative nano carrier. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 13(13), 1155-1169.
- Prajapati, R. N. , Jagrati, K., Sengar, A., & Prajapati, S. K. (2024). Nanoparticles: Pioneering the future of drug delivery and beyond. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 13(13), 1243-1262.
- Sengar, A. , Jagrati, K., & Khatri, S. (2024). Enhancing therapeutics: A comprehensive review on naso-pulmonary drug delivery systems for respiratory health management. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 13(13), 1112-1140.
- Sengar, A. , Vashisth, H., Chatekar, V. K., Gupta, B., Thange, A. R., & Jillella, M. S. R. S. N. (2024). From concept to consumption: A comprehensive review of chewable tablets. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 13(16), 176-189.
- Sengar, A. (2024). Precision in Practice: Nanotechnology and Targeted Therapies for Personalized Care. International Journal of Advanced Nano Computing and Analytics, 3(2), 56-67.
- Sengar, A. (2025). Targeting Strategies in Liposomal Drug Delivery. Preprints. [CrossRef]
- Sengar, A. (2025). The Interplay of Drug Delivery Systems: A Comparative Study of Nanocarriers and Vesicular Formulations. Preprints. [CrossRef]
- Sengar, A. (2025). Innovations in Drug Delivery and Advanced Therapeutics. Preprints. [CrossRef]
- Sengar, A. (2025). "Liposomal Drug Delivery Systems: An Intro as a Primer for Advanced Therapeutics." Preprints. [CrossRef]
- Sengar, A. (2025). Innovations and Mechanisms in Liposomal Drug Delivery: A Comprehensive Introduction. Preprints. [CrossRef]
- Sengar, A. (2025). Next-Generation Liposomal Drug Delivery Systems: Core Principles, Innovations, and Targeting Strategies. Preprints. [CrossRef]
- Sengar, A. (2025). Advanced Targeting Strategies and Applications of Liposomal Drug Delivery Systems. Preprints. [CrossRef]
- Sengar, A. , Yadav, S., & Niranjan, S. K. (2024). Formulation and evaluation of mouth-dissolving films of propranolol hydrochloride. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 13(16), 850-861.
- Sengar, A. , Tile, S. A., Sen, A., Malunjkar, S. P., Bhagat, D. T., & Thete, A. K. (2024). Effervescent tablets explored: Dosage form benefits, formulation strategies, and methodological insights. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 13(18), 1424-1435.
- Sengar, A. , Saha, S., Sharma, L., Hemlata, Saindane, P. S., & Sagar, S. D. (2024). Fundamentals of proniosomes: Structure & composition, and core principles. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 13(21), 1063-1071.
- Sengar, A. , Chatekar, V. K., Andhare, S. B., & Sharma, L. (2025). Clinical pharmacology of antibiotics: Mechanisms, therapeutic uses, and resistance patterns. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 14(1), 1531–1545.
- Sengar, A. (2025). Historical Evolution and Modern Advances in Vesicular Nanocarriers. Preprints. [CrossRef]
- Sengar, A.; et al. (2025). Advancing urolithiasis treatment through herbal medicine: A focus on Tribulus terrestris fruits. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 14(2), 91–105.
- Sengar, A. (2024). Liposomes and Beyond: Pioneering Vesicular Systems for Drug Delivery. Preprints. [CrossRef]
- Sengar, A. (2025). Innovations and Mechanisms in Liposomal Drug Delivery: A Comprehensive Introduction. J Emerg Med OA, 3(1), 01-05.
- Sengar, A. (2025). The Interplay of Drug Delivery Systems: A Comparative Study of Nanocarriers and Vesicular Formulations. Preprints. [CrossRef]
- Sengar, A. (2025). Personalized Medicine and Nanotechnology: Transforming Modern Therapeutics. Preprints. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




