1. Introduction
In today’s interconnected world, security applications play a critical role in mitigating risks to personal and property safety. With the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), there is a growing opportunity to develop sophisticated security solutions that offer real-time monitoring, anomaly detec- tion, and incident management. This paper introduces a security-focused mobile appli- cation that leverages IoT and AI technologies to deliver enhanced situational awareness and incident response capabilities.
The proposed application is designed to address a wide range of security challenges, from personal safety concerns such as emergency alerts and location tracking to prop- erty security features like motion detection and remote access control. By integrating AI-powered anomaly detection and facial recognition, the application provides a robust security solution that can adapt to various user needs and environments.
2. System Design and Architecture
2.1. Core Features
The application’s core features are categorized into three main use cases: personal secu- rity, property security, and AI integration.
Table 1 provides an overview of these features.
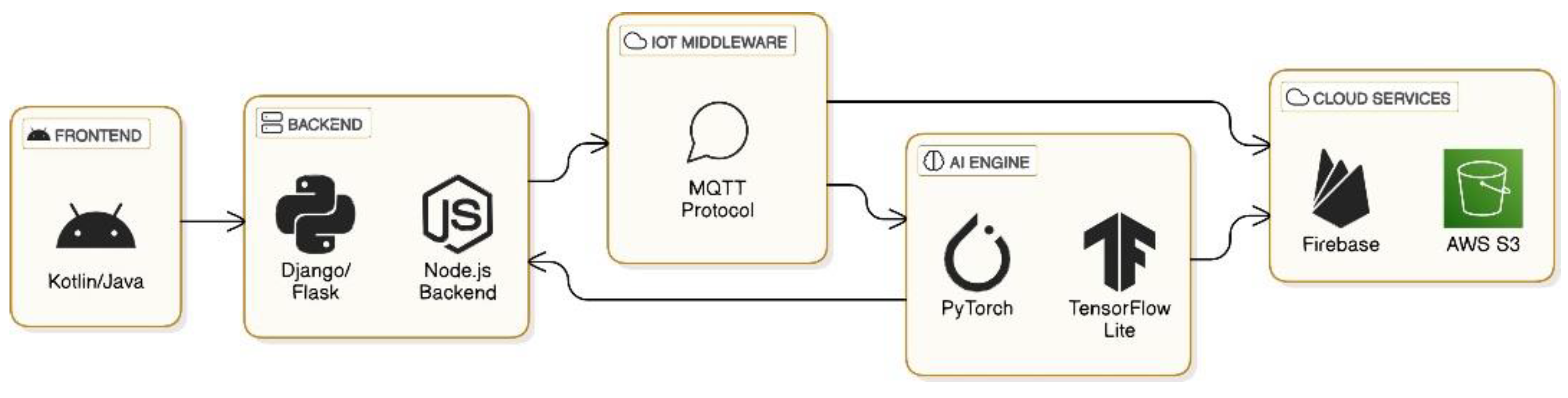
2.2. Technology Stack
The technology stack for the application includes a combination of modern tools and frameworks to ensure scalability, security, and performance.
Figure 1 illustrates the technology stack, which includes cloud services, IoT protocols, and AI libraries such as TensorFlow and PyTorch.
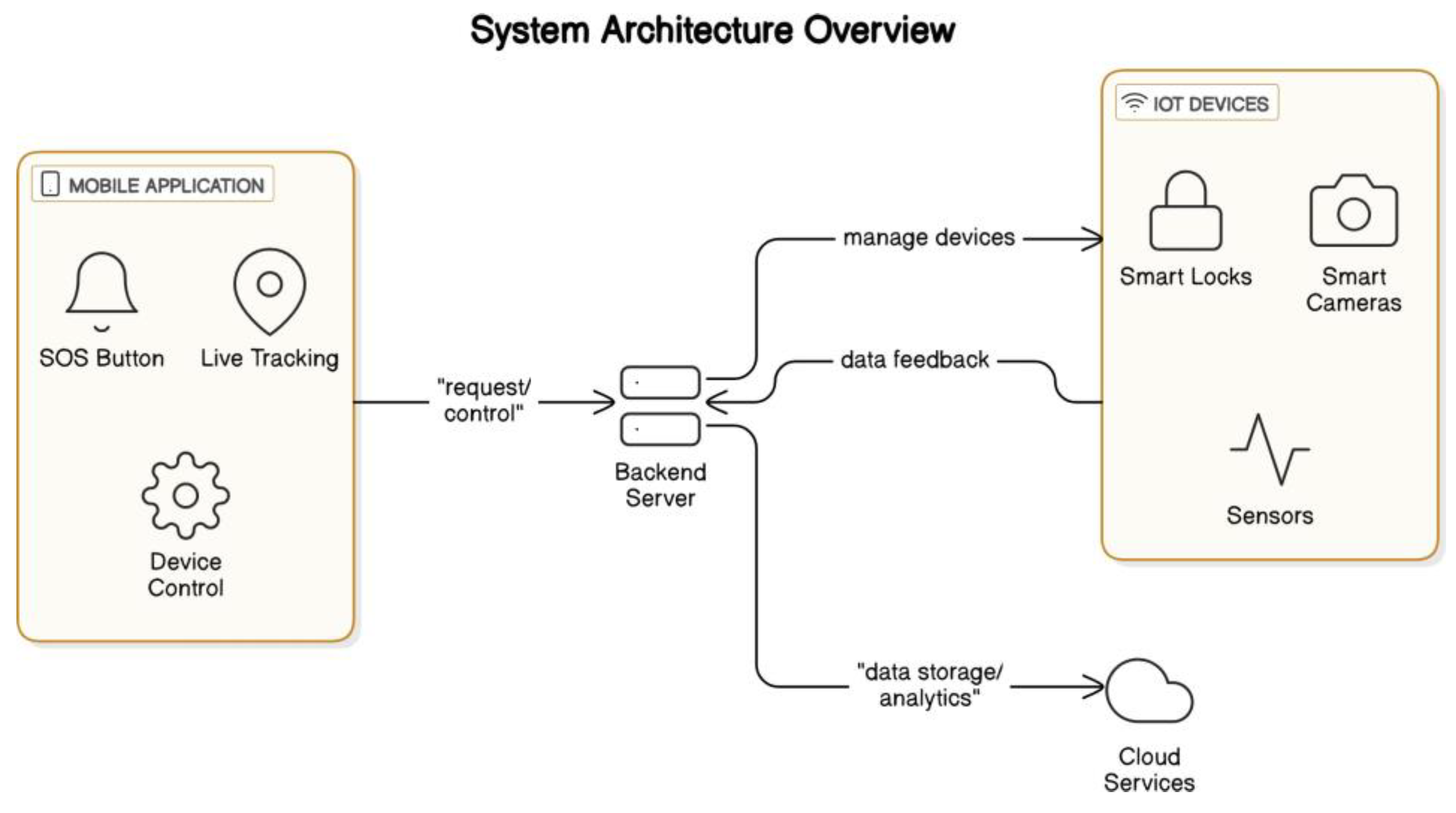
2.3. System Architecture
The system architecture is modular, allowing for flexibility and scalability.
Figure 2 provides an overview of the architecture, which includes user authentication, IoT device integration, AI-powered analytics, and cloud-based data storage.
3. Implementation Details
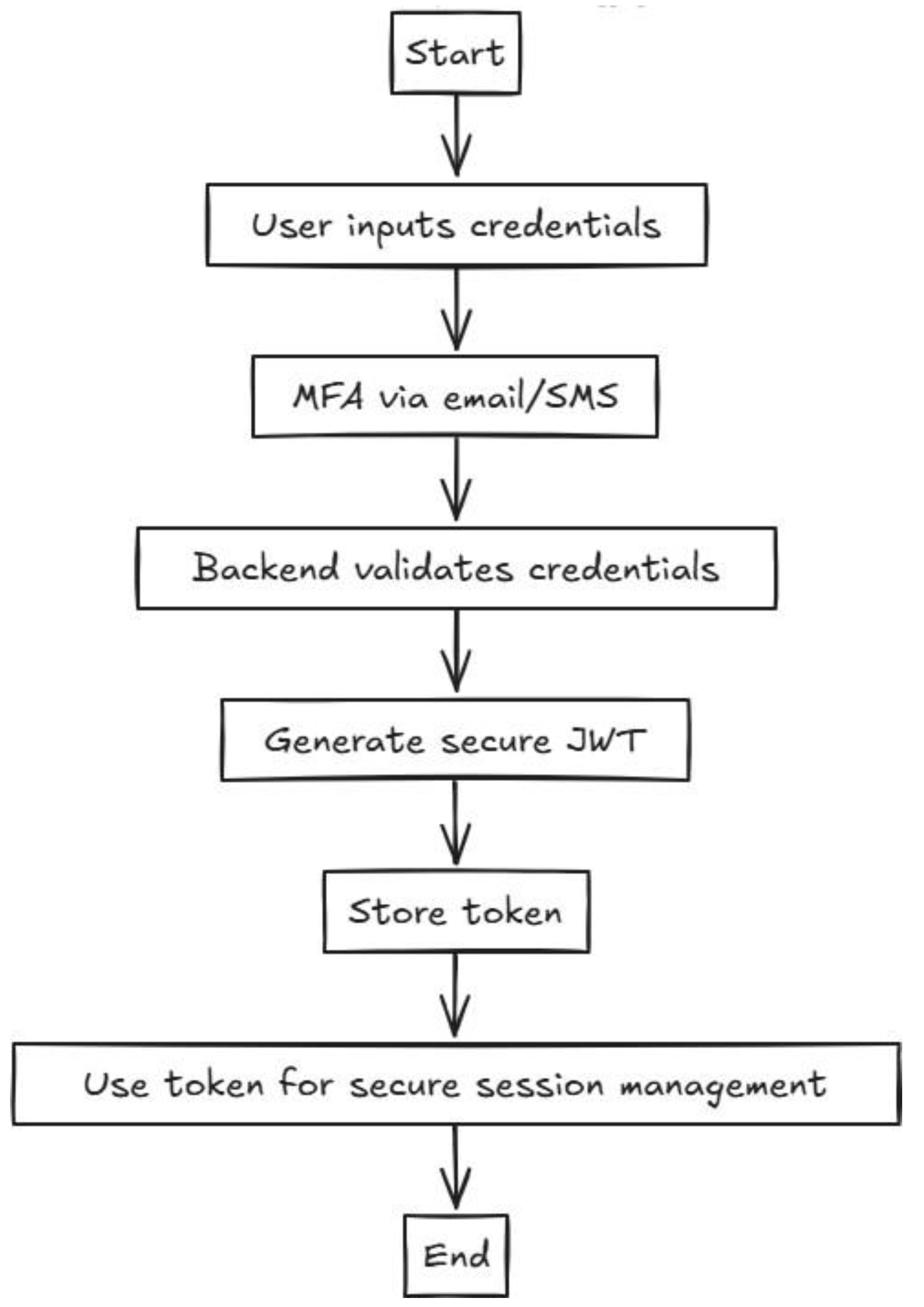
3.1. User Authentication Workflow
User authentication is a critical component of the application, ensuring secure access to sensitive data and features. The authentication workflow, depicted in
Figure 3, utilizes JSON Web Tokens (JWT) for secure session management. The process involves user credential validation, token generation, and secure session management.
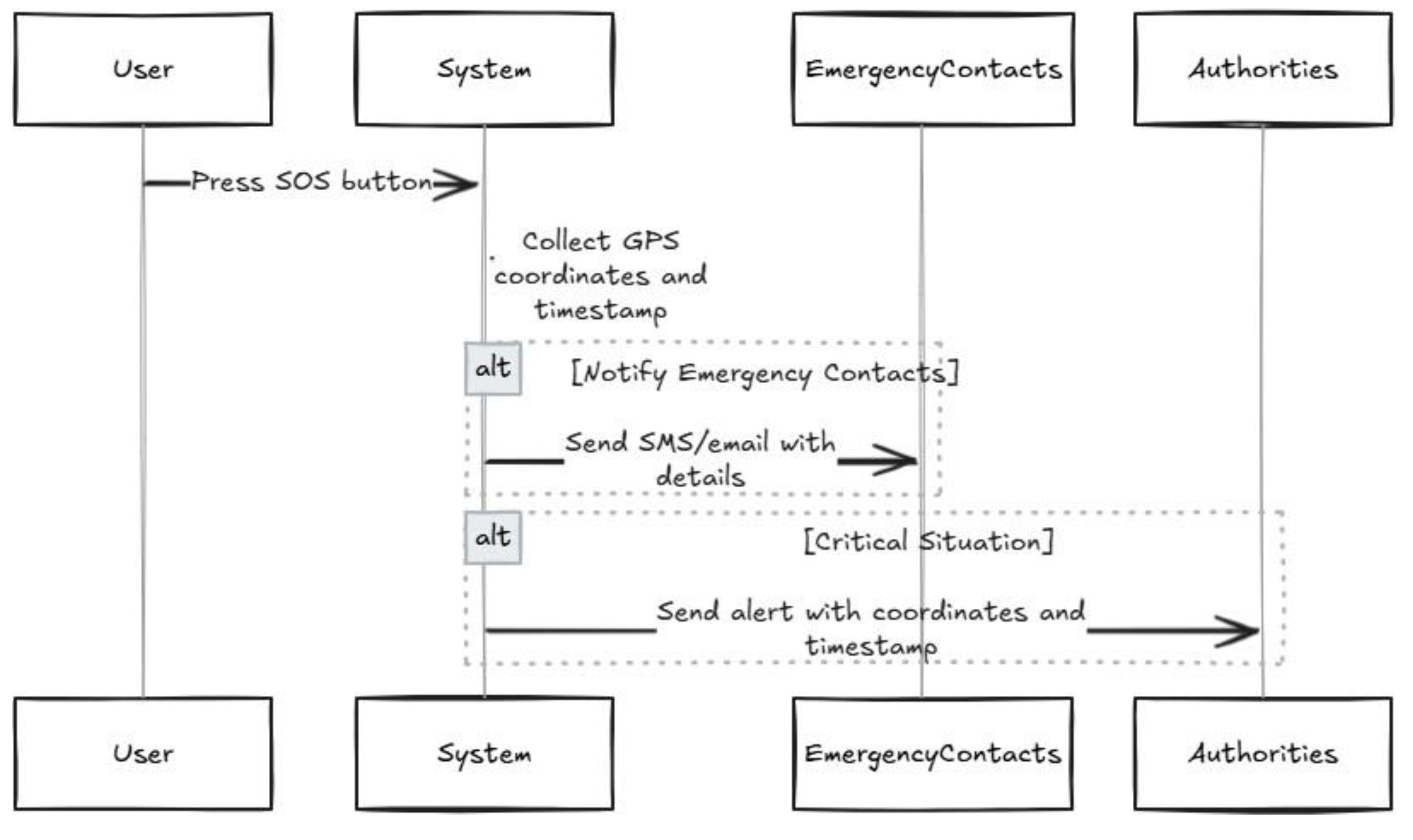
3.2. SOS and Geo-Fencing Logic
The SOS feature allows users to send emergency alerts with their GPS coordinates to predefined contacts or authorities. The geo-fencing feature enables users to set virtual boundaries and receive alerts when these boundaries are breached.
Figure 4 illustrates the workflow for SOS alert generation, which includes GPS coordinate collection, emergency contact verification, and alert dissemination.
3.3. AI-Powered Motion Detection
AI algorithms are employed for motion detection, enabling the application to differentiate between humans, pets, and objects.
Table 2 lists the AI algorithms used, including object detection, activity classification, and anomaly detection. These algorithms are implemented using libraries such as OpenCV, TensorFlow Lite, and PyTorch.
4. Global Market Adaptation
To ensure global market adaptability, the application’s features are tailored to meet regional requirements.
Table 3 compares the feature adaptations for the U.S. and Asian markets, including emergency service integration, IoT device compatibility, and language support.
5. Challenges and Solutions
The development of the application presented several challenges, including IoT device compatibility, user trust, and scalability.
Table 4 summarizes these challenges and the proposed solutions, such as using the MQTT protocol for IoT communication, imple- menting strong encryption for data security, and adopting a cloud-based architecture for scalability.
6. Discussion
The proposed security-focused Android application demonstrates the potential of inte- grating IoT, AI, and cloud technologies to address modern security challenges. The mod- ular architecture and use of advanced AI algorithms for motion detection and anomaly detection provide a robust foundation for real-time monitoring and incident response. The application’s adaptability to different regional markets, as highlighted in
Table 3, ensures its relevance and usability across diverse environments.
One of the key strengths of the application is its ability to balance security and usability. Features such as SOS alerts and geo-fencing are designed to be intuitive and easy to use, ensuring that users can quickly respond to emergencies. At the same time, the integration of AI-powered analytics enhances the system’s ability to detect and respond to potential threats proactively.
However, there are limitations to consider. The reliance on IoT devices and cloud services introduces potential vulnerabilities, such as data breaches and device malfunc- tions. While the proposed solutions, such as strong encryption and the MQTT protocol, address some of these concerns, ongoing research and development are needed to ensure the system remains secure as new threats emerge.
Overall, the application represents a significant step forward in the field of security- focused mobile applications. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies, it offers a compre- hensive solution that can be adapted to meet the evolving needs of users worldwide.
7. Future Directions
Future enhancements to the application include the integration of advanced AI-powered capabilities, such as threat prediction and behavior analysis.
Table 5 outlines these future features, which aim to further improve the application’s ability to detect and respond to security threats.
8. Conclusions
This research demonstrates the feasibility of a security-focused mobile application that combines IoT, AI, and cloud technologies to address modern security challenges. By in- tegrating advanced features such as real-time monitoring, anomaly detection, and emer- gency alerts, the proposed system offers a comprehensive solution for personal and prop- erty security. The application’s modular architecture and global market adaptability ensure its scalability and relevance in diverse environments. Future work will focus on enhancing the application’s AI capabilities and expanding its feature set to address emerg- ing security threats.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of their respective institutions and colleagues in the development of this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rawat, D.B.; Bajracharya, C.; Retnasothie, S.R.D. Fusion of AI and IoT for Smart Home Applications: A Review. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8, 3661–3676. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Goyal, R.; Rahman, T. Machine Learning Models for Real- Time Anomaly Detection in IoT Systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 34563–34572. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, R.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J. IoT-Enabled Smart Home Security System with Real-Time Monitoring. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 2020, 156, 102632. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Chen, K.; Hu, X. Location-Based Geo-Fencing in Mobile Applications: Algorithms and Performance Analysis. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 2020, 19, 2437–2448. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, W. Design of MQTT-Based IoT Middleware for Security and Performance Optimization. In Proc. 2022 IEEE Int. Conf. on Com- munications (ICC); May 2022, pp. 3056–3061.
- Sharma, A.; Gupta, P. AI-Driven Anomaly Detection in Surveillance Systems: Challenges and Opportunities. ACM Computing Surveys 2021, 53, 45–78. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.S.; Rahman, A.M. Blockchain-Based Secure Data Management for IoT Applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2021, 17, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Heo, D. Privacy-Preserving Protocols for IoT Devices: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2021, 23, 1515–1535. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Smartphone-Based SOS Alert Systems for Emergency Management. In Proc. 2021 Int. Conf. on Smart Cities and Systems (ICSC); Apr. 2021, pp. 105–112.
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Wei, R. Cloud Integration Techniques for IoT-Enabled Security Systems. IEEE Cloud Computing 2021, 8, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).