1. Introduction
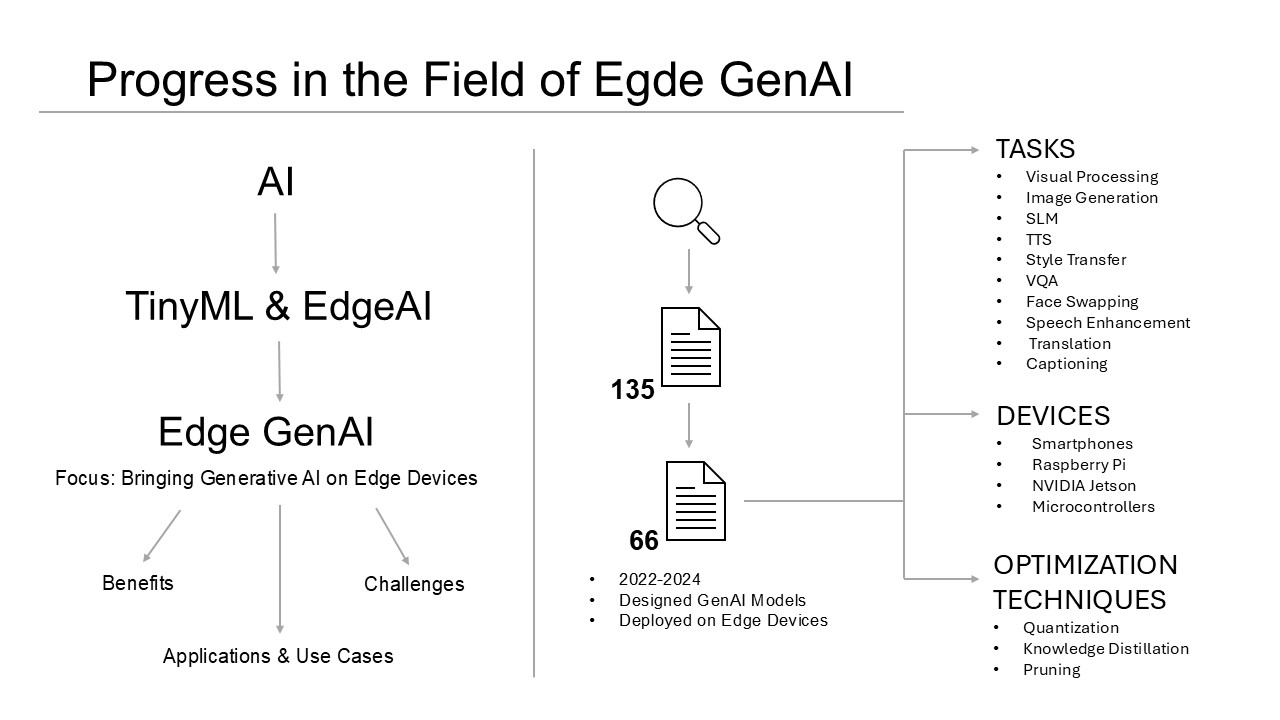
With the machine learning (ML) technology advancements over the past few years, the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has witnessed increasing efforts in designing light-weighted AI models that can be deployed on edge devices. For a long time, the majority of these models have operated primarily on powerful compute servers, benefiting from virtually unlimited resources that hide constraints on computational power, memory, and energy consumption. However, not all AI-based applications can rely on these assets, particularly when real-time data analysis and scalability at the edge are required. For instance, AI-driven solutions for monitoring personal health conditions or detecting faults in manufacturing processes demand rapid responses to act promptly and mitigate any potential undesirable consequences. In such scenarios, the latency introduced by transmitting data to a remote compute server could lead to harmful delays, undermining the effectiveness of these solutions. The need for AI solutions that don’t rely on these servers has led to the emergence of the EdgeAI community. This community focuses on the deployment of AI models on embedded, resource-constrained devices, where data are generated and processed by AI workloads. Similarly, TinyML has also gained importance as a field dedicated to the deployment of ML algorithms on low-cost, resource- and power-constrained, such as tiny microcontrollers (MCUs). Since the potential of EdgeAI was largely understood and developed in the last seven years by the community, the next step forward was to explore the deployment of Generative AI (GenAI) models on edge devices. Edge GenAI is rapidly emerging as a key area of interest for EdgeAI researchers, as it unlocks new research opportunities and innovative use cases.
GenAI models are those models designed to produce realistic data, such as written text, images, or speech. A more precise definition, and the one adopted for this article, is the following:
"Generative Artificial Intelligence is a family of machine learning algorithms that convert a representation of observable data into a target, being capable of creating all possible observable-target pairs of said representations. For both, the conversion involves the syntax and semantics of the observable and target information, even if not presented explicitly in the learning phase. Learning occurs through the available distribution of information. The information is traced back to the distribution of the learned information and generates the target information".
This definition follows the one proposed in [
1] and is included in this manuscript to ensure that this review is comprehensive and self-contained.
Compared to traditional AI (e.g. classifiers, detectors, fixed function ML workloads), GenAI requires higher computational and memory footprint. This makes its deployment on edge devices very challenging due to their limited computational, memory and energy resources. The biggest challenge of Edge GenAI is therefore ensuring that models deliver optimal performance while requiring minimized resources. This is not an issue when running GenAI models on remote servers, in which the computational resources that the model can use are virtually unlimited. On the other hand, the benefits of running GenAI models on embedded devices are many, as already proven by EdgeAI and TinyML. They are: the independence from internet connectivity, enabling the use of these models in remote areas where compromised or no infrastructure exist, the possibility of keeping data stored and processed on the device, thereby enhancing privacy and data security and etc. Additional advantages include low latency and reduced costs, as no billion dollars compute server is required, as well as improved scalability of the enabled services.
Several enterprises at worldwide level are starting to invest in the potential of running GenAI models on edge devices, with the EDGE AI FOUNDATION leading the way [
2]. The foundation was established in 2018 under the name TinyML Foundation. In November 2024, as its field of interest expanded beyond tiny devices, it was renamed to reflect its broader interest in edge AI technologies as a whole. This community strongly believes that running GenAI models on edge devices has the future potential to revolutionize the entire industry, enabling devices to act as problem solvers rather than merely performing data processing. Furthermore, it could enable devices to interact with end users in a natural manner, for example through natural interaction and language. The goal of the foundation is to play a central role in shaping the future of AI on the edge, acting as a bridge between the minds that are working on EdgeAI and the companies that would benefit from it [
3].
1.1. Contributions
This paper aims to review and evaluate the progress achieved to date in the field of Edge GenAI. It focuses on identifying and analyzing GenAI models designed for deployment on edge devices, highlighting their use cases and performance. Additionally, this review aims to provide valuable insights to the AI research community on this emerging and largely under-explored field, as it provides a quick overview of the efforts already made, what else needs to be done, which approaches are more promising, and what requires further improvements. Several papers published between 2022 and 2024 are described and analyzed. Specifically, papers that addressed the deployment of the developed GenAI models on physical devices and that also described in detail the models’ performance on the chosen devices, as well as the overall effectiveness of the models. The papers collected will be categorized according to the tasks they addressed, in order to facilitate the comparison of the different approaches adopted for similar tasks and the results achieved.
1.2. Organization
The paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 briefly describes the methodology used to select and collect papers reviewed in this work.
Section 3 showcases different use cases where running GenAI models on edge devices aimed to offer significant benefits over a cloud server approach. In
Section 4, the collected papers are divided into categories and the propose models are described, along with their performance.
Section 5 gathers and describes the most frequently adopted optimization techniques used in the collected papers to reduce the resource usage of models before deployment.
Section 6 provides a high-level discussion of the publications collected and reviewed, along with potential future research directions.
Section 7 summarizes the review and concludes the paper.
2. Methodology
For the purpose of this review, several papers released between the years 2022 and 2024 that addressed the design of GenAI models and their deployment on embedded devices were considered. Commonly referred edge devices include smartphones, Raspberry Pi, STM32 MCUs, and NVIDIA Jetson boards, all characterized by different degrees of limited resources in terms of memory, computational power, and power consumption. Additionally, only papers that also provided an analysis of the model’s performance on the selected device were considered, including information such as latency, number of parameters, model size, or energy consumption.
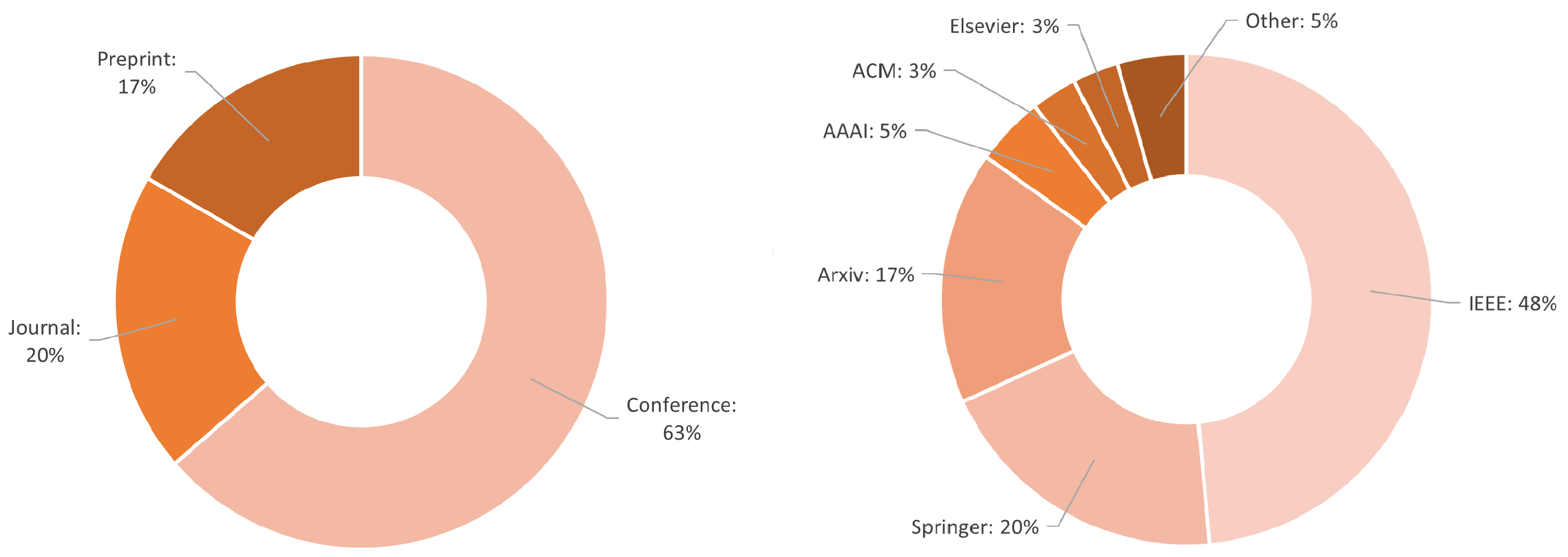
Various data sources were considered, including IEEE, Springer, and arXiv. Publications were gathered using the Google search engine with the keyword querying method. Publications of interest for the review were collected, while irrelevant ones were excluded. Examples of excluded publications include those that claimed the developed model could be deployed on an edge or tiny device and, unfortunately, did not actually perform such deployment, those that provided insufficient details about the device used for deployment, and those in which the model’s performance on the selected device was not reported. The total number of revised papers, including the excluded ones, was 135, while the short list of considered papers was 66.
Figure 1 shows the statistics of the 66 collected papers, including their sources (e.g. IEEE, Springer, ArXiv, ACM, etc.) and the type of publication (preprint, journal article, and conference paper).
3. Use Cases for Edge GenAI
Perhaps one of the greatest challenges in deploying GenAI models on edge devices is achieving optimal performance while minimizing deployment costs. This raises the following question: why to focus on lightening these models for resource-constrained devices when they could be deployed on powerful remote servers, rich in compute assets, where resource availability is virtually unlimited? Actually, there are multiple use cases where deploying a model on a device is required, as not all AI-based solutions can rely on these servers. For instance, relying on cloud servers is not adequate when real-time low-latency responses are required to close a processing loop, when the application shall continue to operate even without an internet connectivity, when massive edge scalability (e.g. to operate trillion of sensors) is required or when ensuring user privacy is crucial. For such applications, deploying GenAI models at the edge is considered essential. Below, more concrete examples of use cases for Edge GenAI are presented.
3.1. Assisting People with Disabilities
Models for image and video captioning and visual questioning and answering can be extremely helpful in assisting blind or visually impaired individuals in understanding their surroundings and engaging independently with visual information. Ensuring that these models safeguard user privacy and function without requiring an Internet connection is of paramount importance. This can be achieved by deploying these models directly on edge devices.
3.2. Personal Digital Assistants
In the years to come, greater efforts will be dedicated to the development of intelligent personal digital assistants for edge devices. These types of assistants won’t just be required to interact with users in an intelligent way, and also with the other devices themselves. Deploying these assistants directly on edge devices will ensure better situational awareness, faster response times and independence from an internet connection. Integrating a text-to-speech (TTS) (and vice-versa speech-to-text STT) models could further enable natural interaction with them, making engaging interactions like can happen between humans rather than between machines. Other types of assistants or applications could also facilitate real-time translation, all while keeping data localized on the device and ensuring scalability as well as independence from an internet connection.
3.3. Real-Time Image Enhancement and Super-Resolution
A recent trend in edge design is the development of smartphones equipped with under-display cameras. The raw photos captured by these cameras often lack quality, therefore image enhancement methods are required to improve them. The image enhancement can be carried out by GenAI models, which have proven to be capable of producing impressive results. Deploying these models directly on the device is crucial to perform real-time image enhancement without relying on an internet connection and keeping user data localized on the device itself. Indeed, as the imaging technology is evolving, image sensors are tightly coupled with AI processing, through back to back dies hosting embedded RAM and powerful neural processing units (NPUs) devised to accelerated AI workloads.
3.4. Video Surveillance and Health Monitoring
Edge GenAI models can be utilized for video surveillance in private homes, businesses, or public places to intelligently monitor activities, alert users when a suspicious activity is detected, provide explanations of observed events, and suggest the best course of action. Additionally, edge GenAI models could also be applied to health monitoring, enabling interaction with users and supporting medical staff during diagnosis.
3.5. Anonymization
Adopting anonymization techniques directly on devices can further enhance people privacy, and GenAI models can be employed to achieve that. For example, by changing the style of an image or the video accordingly to the style of another given image, neural style transfer models can be used to modify faces and bodies while preserving information about actions or activities [
4]. This ensures that individuals cannot be identified, should they wish to do so, but the context and actions in the image or video remain clearly understandable. Anonymized images, videos, or audio can then be used for further processing while safeguarding people’s identities.
3.6. Autonomicity
Autonomicity is used to presume a local “intelligence” of some degree that can be studied from a very low components level, up to the highest system level. For example, an audio and video home intrusion monitoring system, could be prompted in a such way : “Let me know as soon as it happens if there is an intruder in my house and call immediately 911 service for an prompt intervention, at any time in a day, discussing the best way to deal with that event”. Therefore, an Edge GenAI agent might first leverage usage of natural interaction with the home’ distributed sensors such as the image camera and microphones, aggregate the results of such interactions, reason upon them to generate an executive summary, classify the severity of the event and then decide to calls a 911 notify function that connects to the application programming interface (API) of the police platform. The agent would talk naturally with the 911 agent by entering useful details, upon request, based on the executive summary and reasoning and support 911 during the execution of the intervention. AI agents are defined as advanced artificial intelligence systems that are able to complete a task or make a decision. Humans set the needs, and agents address these on their own, autonomously, and the best course of action. Therefore the agents can interface with external systems to take action in the world. This new field is also known as Agentic AI.
4. Edge Generative AI Approaches
In this section, Edge Generative AI models from the selected papers, published in the years between 2022 and 2024, are described and analyzed, and their performances mentioned. Moreover, the papers are categorized accordingly to the tasks they served to ease the comparison among the tasks them-self and their models.
4.1. Visual Question Answering
Visual Question Answering (VQA) is the task which provides answers to natural language questions by processing a given image. While VQA has been applied to various use cases, the resource-intensive nature of these models presents challenges for deployment on edge devices.
One of the earliest attempts to bring VQA to edge devices was made with MobiVQA [
5]. The goal of the authors was to deploy VQA models on mobile devices to allow users, particularly those with visual impairments, to use them privately and without incurring cloud costs. MobiVQA introduced a set of optimizations focused on early exit and selective processing which can be applied to several existing VQA models, making them suitable for edge devices. The optimizations consisted of:
Attention-based two-stage early exit: the processing was exited for questions that cannot be answered and if further processing won’t improve the accuracy.
Question-aware pruning: only the most salient part of the image to answer a given question was processed, while the remaining part of the image was pruned.
Adapting to grid-based models: region-based models, more accurate but computationally expensive, were converted to grid-based models, less accurate but more efficient.
These optimizations were applied to LXMERT [
6], X-LXMERT [
7], and ViLT [
8], and the optimized models were then compared with original versions in terms of accuracy, latency, and energy consumption. The models were deployed on two platforms: a Nvidia Jetson TX2 board and a Pixel 3XL Android smartphone with a Snapdragon 845 chipset, with the exception of ViLT and its optimized counterpart on the latter device due to unsupported model operations. With only a 1% decrease in accuracy, all optimized models demonstrated lower energy consumption and latency compared to their original counterparts, specifically latency decreased from several seconds to just a few hundred milliseconds. Additionally, the optimized models on mobile devices also exhibited lower latency compared to their cloud-deployed versions.
A subsequent attempt to make VQA models suitable for different resource-limited devices was made by Yu et al. [
9]. The authors observed that transformer-based VQA models needed compression accordingly to the specific efficiency requirements of the device they were intended for. To meet the needs of different platforms, the compressed model architecture had to be redesigned and the model retrained. To this end, this work proposed a general framework called the Bilaterally Slimmable Transformer (BST), which supported training a single transformer-based VQA model and subsequently pruning it to obtain multiple efficient sub-models of different width and depth. These sub-models can fit different platforms with varying requirements depending on the chosen width and depth, and without requiring further fine-tuning. The BST framework can be applied to any VQA model of transformer-based architecture, accordingly the authors tested its performance on three different models: MCAN [
10], UNITER [
11], and CLIP-ViL [
12]. The resulting slimmed sub-models achieved performance comparable to the original models, with a substantial reduction in the number of parameters and overall model size. Naturally, greater reductions in model size led to more significant performance degradation. Three of the sub-models derived from slimmable MCAN were then deployed on various hardware platforms, including three smartphones equipped with Qualcomm Snapdragon 888, MediaTek Dimensity 1100, and Qualcomm Snapdragon 660 chipsets. The tiniest model, with fewer than 10 million parameters, achieved latencies of a few tens of milliseconds on these edge devices.
On the other hand, Rashid et al. [
13] explored deploying VQA models on TinyML hardware. They proposed TinyVQA, a multimodal deep neural network specifically designed to perform VQA tasks on extremely resource-limited hardware. Beyond assisting visually impaired individuals, on-device VQA can be useful for assessing post-disaster conditions in areas where infrastructure may be compromised and cloud services unreachable. TinyVQA was specifically trained and evaluated for this purpose using the FloodNet dataset [
14]. A baseline VQA model was developed based on the prior work of Sakara et al. [
15], then knowledge distillation (KD) was applied to train tinyVQA. To further compress the model, post-training quantization was employed, quantizing both the weights and activations to 8-bit integers. The baseline model achieved 81% accuracy with a footprint of 479 MB, while TinyVQA achieved 79.5% accuracy with a footprint of just 339 KiB, demonstrating a substantial reduction in model size with only a slight drop in accuracy. The TinyVQA model was ultimately deployed on the GAP8 processor equipped on a Crazylie 2.0 drone, achieving a low latency of 56 ms and minimal power consumption, demonstrating its suitability for resource-constrained embedded systems.
Finally, another effort to bring VQA to mobile devices was made by Mishra et al. [
16] from the Samsung Bangalore Research Institute. The authors proposed a novel transformer-style architecture for VQA, along with a new Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) scheme. The baseline model achieved an accuracy of 66.7% on the VQA-2.0 dataset [
17] with a model footprint of 214 MB. The proposed algorithm for PTQ was then employed to quantize the floating point 32-bits (fp32) model into integer 8-bits (int8) precision. The quantized model achieved 65.4% accuracy and reduced the model footprint to 58 MB, approximately a quarter of the baseline model size. The quantized model was deployed on a Samsung Galaxy S23 smartphone equipped with a Snapdragon sm8550 chipset, achieving a latency of 2.8 ms.
Table 1 offers a comparison of the VQA models described earlier. Three out of four models have been deployed on a smartphone. The model achieving the lowest latency on a smartphone is the one proposed by Mishra et al., although its accuracy is lower than MobiVQA on the same dataset. On the other hand, Rashid et al. achieved comparably low latency by deploying TinyVQA on a device with even more constrained computational capabilities.
4.2. Image and Video Captioning
Image and video captioning involves generating textual descriptions for images or video without human intervention. One of the most important uses is assisting visually impaired and blind people with engaging independently with visual information, but they can also be used to support applications in image and video retrieval or video surveillance. While powerful image and video captioning models are primarily accessible through cloud services, implementing these models on edge devices can provide faster, offline, and privacy-preserving alternatives to users.
Although several efforts aim to bring image captioning [
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24] or video captioning [
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30] models to physical devices, they often omitted critical details about the model’s performance on the target device, such as latency. One of the first studies to thoroughly examine the deployment of an image captioning model on an edge device is that of Wang et al. [
31], which introduced LightCap, a lightweight image captioner for mobile devices. LightCap consists of an image encoder, a concept extractor, and a cross-modal modulator. It also employs a lightweight TinyBERT model to fuse multi-modal representations and an ensemble head module to generate image captions. With merely 40M parameters, 9.8 GFLOPs, and a storage memory of 112.5 MB, LightCap achieved a latency of 188 ms per image when deployed on a Huawei P40 smartphone powered by a Kirin 990 chipset. Additionally, it delivered state-of-the-art performance, comparable to that of heavyweight image captioners.
Another study related to image and video captioning is the one conducted by Fiorenza et al. [
1], whose goal was to generate descriptions of future actions of mice based on a few video frames of their current and short-term past behavior. They proposed two models that employed the Video MAE transformer as an encoder and the Open Pre-Trained Transformer (OPT) as a decoder for generating textual description. Additionally, they utilized KD and Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT), and assessed performance degradation following int8 quantization. The two models achieved comparable task-related performance, with the smallest version, TinyV2A, achieving lower latency. TinyV2A featured 169M parameters and a 1.3 GB memory need, achieving execution times of 811 ms and 271 ms on a Raspberry Pi 4 and 5, respectively.
A model that is also worth mentioning is VILA [
32], a visual language model (VLM) that can be deployed on the NVIDIA Jetson Orin. VLMs are large language models (LLMs) augmented with visual inputs, allowing them to be used for several visual language tasks, such as image and video captioning and VQA. VILA outperformed state-of-the-art models, while the use of 4-bit Action-aware Weight Quatization (AWQ) [
33] enabled its cheap deployment on the edge.
4.3. Text-to-Speech
Text-to-Speech (TTS), also known as speech synthesis, aims to generate natural-sounding voices from a given text. As discussed in
Section 3, TTS can significantly enhance interaction between humans and technology, particularly when combined with speech-to-text. For this reason, the deployment of TTS models on edge devices is essential for Edge GenAI, as it complements the text-generation models already deployed on these devices. TTS models can either be end-to-end systems, which generate waveforms directly from text, or two-stage systems composed of an acoustic model and a vocoder, where the acoustic model generates mel spectrograms and the vocoder converts these spectrograms into corresponding waveforms. Two-stage TTS models generally offer greater training stability and produce higher-quality synthetic voices compared to end-to-end models, but they often result in bigger model footprint [
34].
With regard to end-to-end TTS models deployed on edge devices, Chevi et al. [
35] introduced Nix-TTS, a non-autoregressive, end-to-end TTS model developed through knowledge distillation from VITS [
36]. The resulting model required only 5.23M parameters and had a footprint of 21.2 MB while exhibiting slightly lower performance than VITS in terms of naturalness and intelligibility. Specifically, it achieved a CMOS of -0.27 when evaluated against VITS and a phoneme error rate (PER) of 2.07 %, while VITS achieved a PER of 1.51 %. Furthermore, the authors evaluated the deployment of Nix-TTS on a Raspberry Pi 3B. The model achieved a real-time factor (RTF) of 1.97, significantly outperforming VITS, which achieved an RTF of 16.50.
Another noteworthy project that adopted an end-to-end approach is Piper [
37] from Michael Hansen. Piper is a neural system optimized for the Raspberry Pi 4 and based on VITS, a Conditional Variational Autoencoder for end-to-end TTS. With a model of 15.7M parameters, Piper enables fast and local TTS synthesis.
On the other hand, Atienza [
34] explored the deployment on a Raspebby Pi 4B of a non-autoregressive, two-stage TTS model. The author proposed EfficientSpeech, which utilizes an encoder-decoder architecture to generate mel spectrograms from phonemes, paired with the compact version of HiFi-GAN [
38] as the vocoder. The resulting model contained 1.2M parameters, including 266k for the acoustic model, and achieved an RTF of 1.7 on a Raspebby Pi 4B. Moreover, the model achieved a CMOS of -0.14 when evaluated against FastSpeech2 [
39], indicating that their performance were comparable.
Similarly, a two-step approach was also adopted in FastStreamSpeech [
40]. It is a non-autoregressive TTS model that used Fastspeech2 [
39] as the acoustic model and Multi-band MelGAN [
41] as the vocoder. Additionally, a streaming mechanism has been incorporated to significantly enhance its speed, particularly on resource-limited devices. FastStreamSpeech delivered performance comparable to the baseline model consisting of Fastspeech2 and Multi-band MelGAN without the streaming mechanism, as it achieved an Mean Opinion Score (MOS) of 4.5. The authors also evaluated its deployment on a device equipped with a MediaTek Helio G35 processor, where it achieved an RTF ranging from 0.01 to 0.1, depending on the length of the generated audio.
Table 2 offers a comparison of the TTS models previously described that perform speech synthesis on physical devices. Nix-TTS and EfficientSpeech achieved similar RTF on two different Raspberry Pi devices, although they used different approaches. On the other hand, FastStreamSpeech demonstrated very fast inference on a smartphone processor, while adopting a two-step approach.
Vocoders are versatile components that can be paired with different models generating mel spectrograms. Designing vocoders optimized for edge devices plays a crucial role in facilitating the deployment of TTS models on such platforms. In this regard, TinyVocos [
42] and Bunched LPCNet [
43] are two vocoders designed to be suitable for edge deployment. Specifically, the performance of TinyVocos has been evaluated on various MCUs, while Bunched LPCNet has been tested on a Raspberry Pi 3B. Despite their reduced model footprint and fast inference times, both of them demonstrated competitive performance.
4.4. Speech Enhancement
Within the domain of speech enhancement, Chen et al. [
44] designed TransFiLm, an audio super-resolution network specifically tailored for deployment on mobile devices. This network incorporated Transformer blocks and Feature-Wise Linear Modulation (FiLM), operating as a one-dimensional U-Net that converted the low-resolution speech signals to full-resolution high-quality signals. The model required only 1M parameters and demonstrated notable performance in terms of the log-spectral distance (LSD) metric. Furthermore, Chen et al. deployed TransFiLM on a Meizu 16S smartphone and achieved an inference time of 181 ms with an input of 8192 samples.
On the other hand, Šljubura et al. [
45] proposed a speech enhancement system suitable for MCUs that could be used in industrial safety helmets to enhance speech and emergency sounds while filtering out noise. Specifically, they adapted the Smart Speech Enhancement (SSE) architecture [
46] for resource-constrained devices. SSE consisted of a classifier that detects emergency signals and a Deep Convolution Recurrent Network (DCRN) that operates in audio enhancement mode when emergency signal are detected or in speech enhancement mode otherwise. To adapt the SSE architecture for MCUs, the authors removed or modified several layers, reduced filter and kernel sizes, and modified activation functions in both the classifier and the DCRN. Furthermore, int8 quantization was applied to the classifier. The proposed system was deployed on an STM32H735 MCU, and achieved an inference time of 150 ms and an energy consumption of 48.07 mJ per inference. Additionally, it achieved results comparable to the reference model SSE and state-of-the art models, while using 634 KiB of Flash memory and 224 KiB of RAM.
4.5. Neural Machine Translation
Neural Machine Translation (NMT) allows automatic translation of text from one language to another. Transformer-based models are among the most common and effective models for NMT. Nevertheless, Transformers [
47] tends to be memory and time consuming on edge devices, so compression techniques are required.
To improve the efficiency of Transformers, the hidden size of the network can be scaled down; however, this often resulted in poorer performance. To address this issue and enhance performance without sacrificing efficiency, Tan et al. [
48] introduced dynamic multi-branch (DMB) layers and extended the Transformer architecture with these layers, creating the Transformer-DMB architecture. The proposed models based on Transformer-DMB were deployed on a Raspberry Pi 4B but did not achieve an optimal trade-off between latency and performance. While their performance slightly exceeded that of scaled-down Transformers, they exhibited higher latencies. [
48] also demonstrated that a better balance between model size and performance could be achieved by combining knowledge distillation with 8-bit quantization. This approach resulted in a model with a BLEU score of 25.3 and a footprint of 26.9 MB.
Li et al. [
49] did another attempt to bring NMT models to edge devices by proposing a Hybrid Tensor-Train (HTT) decomposition for compressing and accelerating Transformers. The resulting model, named Hypoformer, applied the HTT decomposition to achieve these goals. They trained Hypoformer-based models using sequence-level knowledge distillation [
50] and evaluated their deployment on a Raspberry Pi 4B. These models achieved BLEU scores comparable to standard Transformers while significantly reducing the number of parameters and improving inference speed.
4.6. Neural Style Transfer
Neural Style Transfer (NST) aims to apply a different style to an image using a style described in a text prompt or derived from another image. This technique can be useful for rendering images or performing anonymization tasks, as it enables the modification of sensitive data and personal information within an image. As discussed in
Section 3, performing this task on the device allows for the immediate removal of sensitive data at the exact moment the images are captured.
With the goal of anonymizing images by transferring the style of another image, Ancilotto et al. [
4] proposed a lightweight NST architecture based on XiNet [
51], a neural network designed for tiny devices, like MCUs. Their approach achieved performance comparable to other methods while using a tinier architecture, requiring only 0.60M parameters and 0.45G MAC operations. The 8-bit quantized model was deployed on a Raspberry Pi 4B and a STM32H743 MCU, achieving minimal energy consumption on both devices and latency of 165 ms and 998 ms, respectively. On STM32N6, one variant of it, achieved 10 fps taking advantage of its super integrated NPU.
Similarly, Huo et al. [
52] proposed a lightweight NST approach that transferred the style of an image to another. To achieve this, the authors distilled knowledge from VGG-19 based backbone and designed an efficient feature transformation module (FTM), which also enabled video style transfer. Their proposed video NST model achieved competitive results and has a size of 2.67 MB, making it suitable for deployment on edge devices. They evaluated the deployment of this model on an NVIDIA Jetson Nano and an NVIDIA Jetson TX2, where it performed video style transfer at almost 41 FPS.
On the other hand, the work of Suresh et al. [
53] focused on transferring style to an image starting from a text prompt. They introduced FastCLIPstyler and EdgeCLIPstyler. FastCLIPstyler built on CLIPstyler [
54], one of the first models to perform style transfer given a text prompt, while also incorporating a pre-trained vision-based style transfer network into its framework. EdgeCLIPstyler, in turn, was based on FastCLIPstyler but used a more resource-efficient text-embedded model [
55], making it suitable for deployment on edge devices. Both FastCLIPstyler and EdgeCLIPstyler achieved performance comparable to CLIPstyler in terms of quantitative metrics and human evaluation. Additionally, they evaluated the deployment of EdgeCLIPstyler on a Raspberry Pi 3B+, achieving an inference time of 15 seconds. While this demonstrated the model’s suitability for edge deployment, further optimization was required to reduce inference time.
Ganugula et al. [
56] also focused on transferring style based on a text prompt, but their approach enabled assigning different styles to individual objects within an image. They proposed an efficient pipeline that incorporated a segmentation module and evaluated its deployment on a Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 processor, achieving a latency of 236 ms.
4.7. Face Swapping
Alongside NST, face swapping is another technique that enables the anonymization of images or videos, especially when performed directly on edge devices at the moment of the image capture. This process involves replacing the face in a target image with another face, preserving the individual’s facial expression and pose while protecting their identity. While face swapping plays a fundamental role in preventing the storage or transmission of sensitive information when executed at the moment of capture, it also raises concerns about potential misuse, which requires careful consideration in studies addressing this topic.
An early study on face swapping that explored the deployment on edge devices was conducted by Xu et al. [
57]. Their framework for video face swapping achieves a frame rate of 26 fps on a mobile phone equipped with a MediaTek Dimensity 1100 chipset, without leveraging optimizations such as quantization or pruning. Two subsequent models, PhiNet-GAN [
58] and XimSwap [
59], were developed with the aim of anonymizing data at the source. Both models employed an encoder-decoder architecture, and quantization techniques were explored. While PhiNet-GAN achieved a frame rate of 16.4 fps on a Kendryte K210 MCU, the smallest version of XimSwap was deployed on a Raspberry Pi 4 and an STM32H743 microcontroller, demonstrating latencies of 52 ms and 818 ms, respectively.
4.8. Visual Processing Tasks
GenAI models can be used to process, restore, and enhance images and videos. Deploying these models on edge devices, such as smartphones, addresses all the main concerns associated with the cloud deployment. In this context, 31 different papers that addressed the design and deployment of these kinds of models on edges devices have been collected. All of them are listed in
Table 3 which also indicates the task addressed in each paper, the devices used for deployment, and the contributions brought by the papers, consisting of a brief description of the approach adopted and the results achieved. A significant portion of the papers in the table proposed multiple models with varying sizes and evaluated them on images of different resolutions. In each paper, the performance and latency achieved by each model depended on its size and the resolution of the images considered, with larger models achieving the best performance while incurring in higher latencies.
As shown in the last column of the table, most of the collected papers evaluated the deployment of the devised models on smartphones, achieving inference times ranging from a few milliseconds to a couple of seconds. For example, Berger et al. reported latencies of less than 10 ms on a Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 chipset [
60], while Conde et al. achieved a runtime of 1.5 s on the GPU of the OnePlus Nord 2 5G smartphone [
61]. Notably, Li et al. tested the deployment of their proposed model, TinyLUT, on both a Xiaomi 11 smartphone and a Raspberry Pi 4B [
62]. The compact version of TinyLUT trained for single-image super-resolution (SISR) was characterized by a model footprint of only 37 KiB and achieved a runtime of 88 ms on the Raspberry Pi and 29 ms on the smartphone.
Nearly half of the papers listed in
Table 3 addressed the task of super-resolution (SR). Two competitions organized as part of the Mobile AI & AIM 2022 Workshops and Challenges have contributed to this area: Quantized Image Super-Resolution on Mobile NPUs [
63] and Power Efficient Video Super-Resolution on Mobile NPUs [
64]. The goals of these competitions were to design deep learning-based solutions for image super-resolution and video super-resolution, respectively, that could run efficiently on mobile devices. In the first competition, the efficiency of the proposed solutions was evaluated on the Synaptics Dolphin platform, while in the second competition used the MediaTek Dimensity 9000 mobile SoC. Winners were determined based on a score that accounted for both performance and runtime on the target device. The following competitions were also part of the Mobile AI & AIM 2022 Workshops and Challenges:
Learned Smartphone ISP on Mobile GPUs [
65]
Realistic Bokeh Effect Rendering on Mobile GPUs [
66]
Efficient Single-Image Depth Estimation on Mobile Devices [
67]
Super-Resolution of Compressed Image and Video [
68]
Reversed Image Signal Processing and RAW Reconstruction [
69]
Instagram Filter Removal [
70]
4.9. Image Generation
Image generation refers to the process of creating visual content, such as pictures, illustrations, or graphics, using computer algorithms and software. This can be done through various methods, including:
AI and ML: Techniques like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) can create realistic images by learning from a large dataset of existing images.
Procedural Generation: Creating images algorithmically based on a set of rules or parameters, often used in video games and simulations.
AI and ML models for image generation can be either unconditioned or conditioned, such as generating images based on a text prompt or another image. Various networks and approaches exist, with the most common being GANs, VAEs, and Diffusion Models. A Diffusion Model is a type of probabilistic model used in ML and statistics to describe how data points spread out over time. In the context of ML, Diffusion Models have gained attention for their ability to generate high-quality synthetic data. They work by modeling the process of gradually adding noise to data and then learning to reverse this process to recover the original data. This approach can be used for tasks like image generation, where the model learns to generate realistic images by reversing the diffusion process. Seven papers focusing on the deployment of image generation models on edge devices have been identified and are listed and compared in
Table 4. All these studies proposed text-to-image Diffusion Models, enabling the generation of images based on a text prompt. Moreover, all of them tested the deployment of the proposed models on smartphones. Unlike for the visual processing tasks described in
4.8 where some papers proposed GAN-based models, no studies were found that explored the use of GANs or other types of networks for image generation on edge devices.
Diffusion Models have recently demonstrated impressive generative capabilities, surpassing GANs in both the quality and heterogeneity of generated images. Due to their excellent performance, they are ideal candidates for image generation on edge devices. However, two main factors hinder their deployment on such devices: the complexity of their network architecture, which involves a substantial number of parameters, and the high latencies caused by the iterative denoising process. Stable Diffusion (SD) [
98] is one of the most well-known open-source Diffusion Models for text-to-image generation. Specifically, it is a latent diffusion model with over one billion parameters, consisting of a text encoder, an image decoder, and a UNet responsible for progressive denoising. Early efforts to deploy Stable Diffusion on mobile devices are documented in the blog articles "Stable Diffusion with Core ML on Apple Silicon" [
99] and "World’s First On-Device Demonstration of Stable Diffusion on an Android Phone" [
100]. These articles describe the optimizations implemented to run Stable Diffusion on an Apple Neural Engine and a Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 Mobile Platform, respectively. Specifically, the optimizations adopted by Hou and Asghar to run Stable Diffusion on an Android phone concern int8 post-training quantization, compilation, and hardware acceleration, enabling the generation of 512×512 images in under 15 seconds [
100]. Chen et al. [
101] and Choi et al. [
102] also proposed a series of optimizations for deploying Stable Diffusion on mobile devices. The different approaches are compared in the paper by Choi et al. The other approaches adopted in the collected papers mainly focused on designing efficient network architectures or applying techniques to reduce the number of steps in the denoising process. All models in the collected papers were trained to generate 512×512 images, with the exception of SnapGen [
103], which was trained to generate 1024×1024 images.
4.10. Small Language Models
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in running Language Models (LMs) on edge devices, driven by the numerous advantages this offers. An increasing number of studies have been released that organize various strategies and approaches to enable LMs on edge devices [
108,
109] or compare the performance of existing models on different devices [
110,
111]. This trend is further highlighted since the major smartphone manufacturers are actively developing LMs for deployment on their devices, such as Google’s integration of Gemini Nano into Pixel phones.
LMs can be broadly categorized into Large Language Models (LLMs) and Small Language Models (SLMs). While there isn’t a consensual definition for SLMs, they can be described as models whose size ranges from the minimum necessary to effectively perform a given task to the maximum feasible within limited resource constraints, as proposed by Wang et al. [
112]. SLMs typically have fewer parameters than LLMs, are more efficient, and have reduced memory and energy consumption. These attributes render them particularly well-suited for deployment on edge devices, unlike LLMs, whose high computational and memory requirements make such deployment challenging. Additionally, their smaller size reduces the computational cost of fine-tuning, a common practice to enhance the performance of LMs in specialized domains or for specific tasks.
Despite the existence of numerous SLMs designed for resource-constrained devices, only five papers were identified that both proposed models and also deployed them on edge devices, therefore reporting their performance. These papers are listed and compared in
Table 5, along with the models they proposed and their on-device performance. Notably, all these papers provide publicly available code or models. All models listed in
Table 5 utilize a Transformer architecture, which is commonly employed for SLMs. Furthermore, all models have been deployed on smartphones and, with the exception of those proposed by Liu et al. [
113], incorporate quantization prior to deployment to further reduce storage consumption.
5. Common Optimizations
The previous section models subject of various optimization techniques adopted during the development of GenAI models for edge deployment, specifically aimed at reducing implementation costs. This section identifies and provides a concise overview of the main optimization techniques utilized in the approaches discussed in
Section 4.
The most common approach to developing a GenAI model for specific tasks on edge devices involves identifying an efficient and lightweight network architecture to reduce resource usage and inference time. At the same time, the network architecture must achieve good performance, ensuring an optimal balance between efficiency, resource usage, and task execution. Additionally, the operations supported by the target device must be considered during the network design.
Nearly half of papers presented in
Section 4 explored the use of quantization, an optimization technique often employed to reduce the memory footprint of the models. This well known technique involves lowering the precision of weights, biases, and activations in a model, such as converting 32-bit floating values into 8-bit integers. Various kinds of quantization exist, but their application can often lead to performance degradation, therefore a thorough analysis of how quantization impacts performance is often required. Another technique frequently adopted in the papers discussed in
Section 4 is knowledge distillation. This technique, explored in nearly 20 papers, involves transferring knowledge from a large and resource-intensive model, known as the teacher model, to a smaller and more efficient model, referred to as the student model. Through this process, the performance of tinier models, suitable for edge deployment, can be improved by leveraging the optimal performance of larger models. The distillation of knowledge from the teacher model to the student model can be carried out in different ways. Notably, some papers performing image generation described in
4.9 applied a form of distillation to reduce the number of denoising steps, therefore decreasing the inference time of the proposed Diffusion Models.
A less frequently adopted optimization technique among the papers presented in
Section 4 is pruning, which was explored in nearly 5 papers. This technique involves selectively removing unimportant connections or neurons within a network, thereby resulting in a smaller and faster model. Alongside the optimization techniques mentioned above, pruning can also be explored to facilitate the deployment of GenAI models on edge devices.
6. Discussion and Future Directions
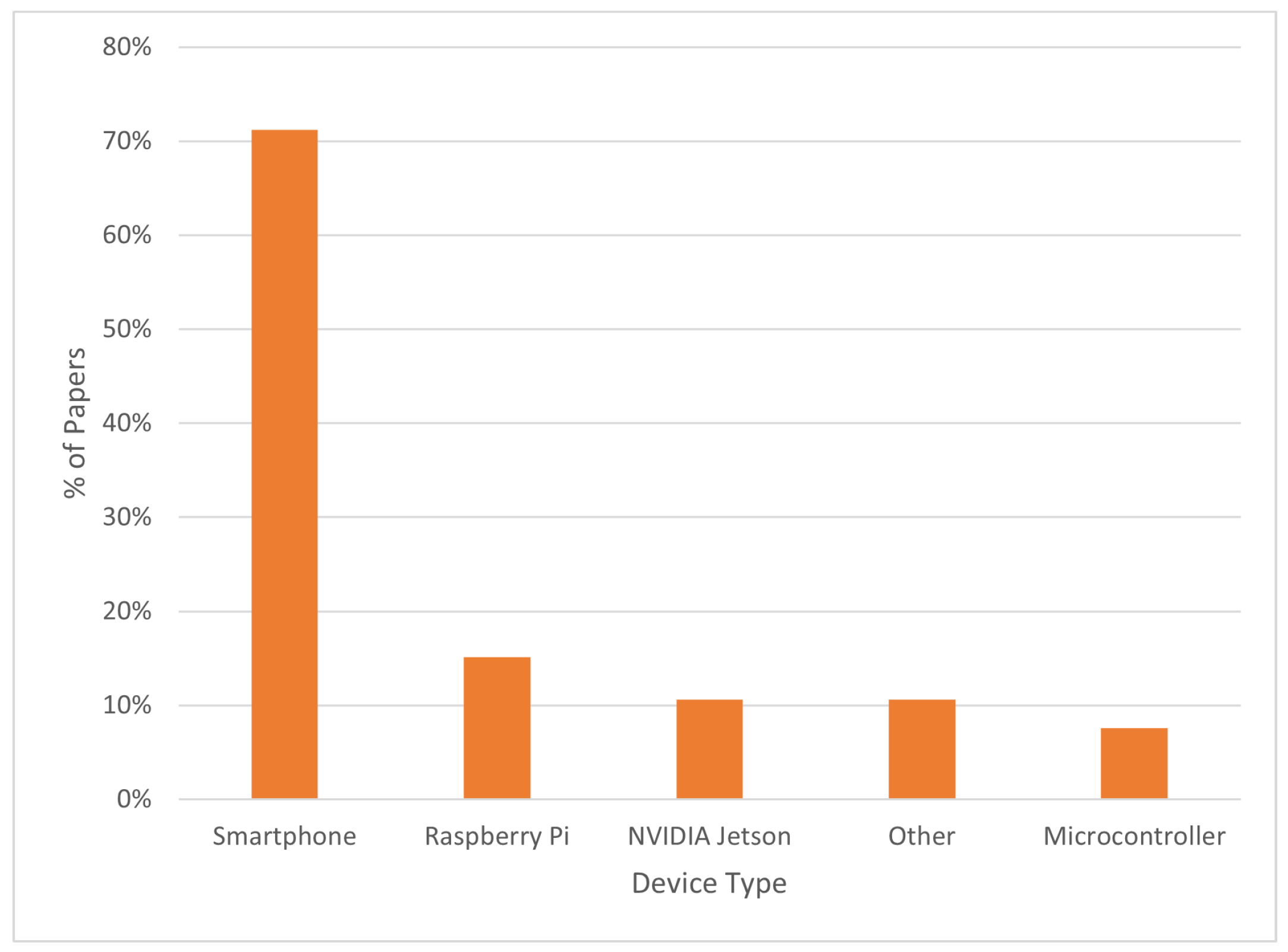
For this review paper, a total of 66 manuscripts were collected, each focusing on the design of GenAI models and their deployment on edge devices. A significant portion of these papers investigated the deployment of the proposed models on smartphones and their application processors. As illustrated in
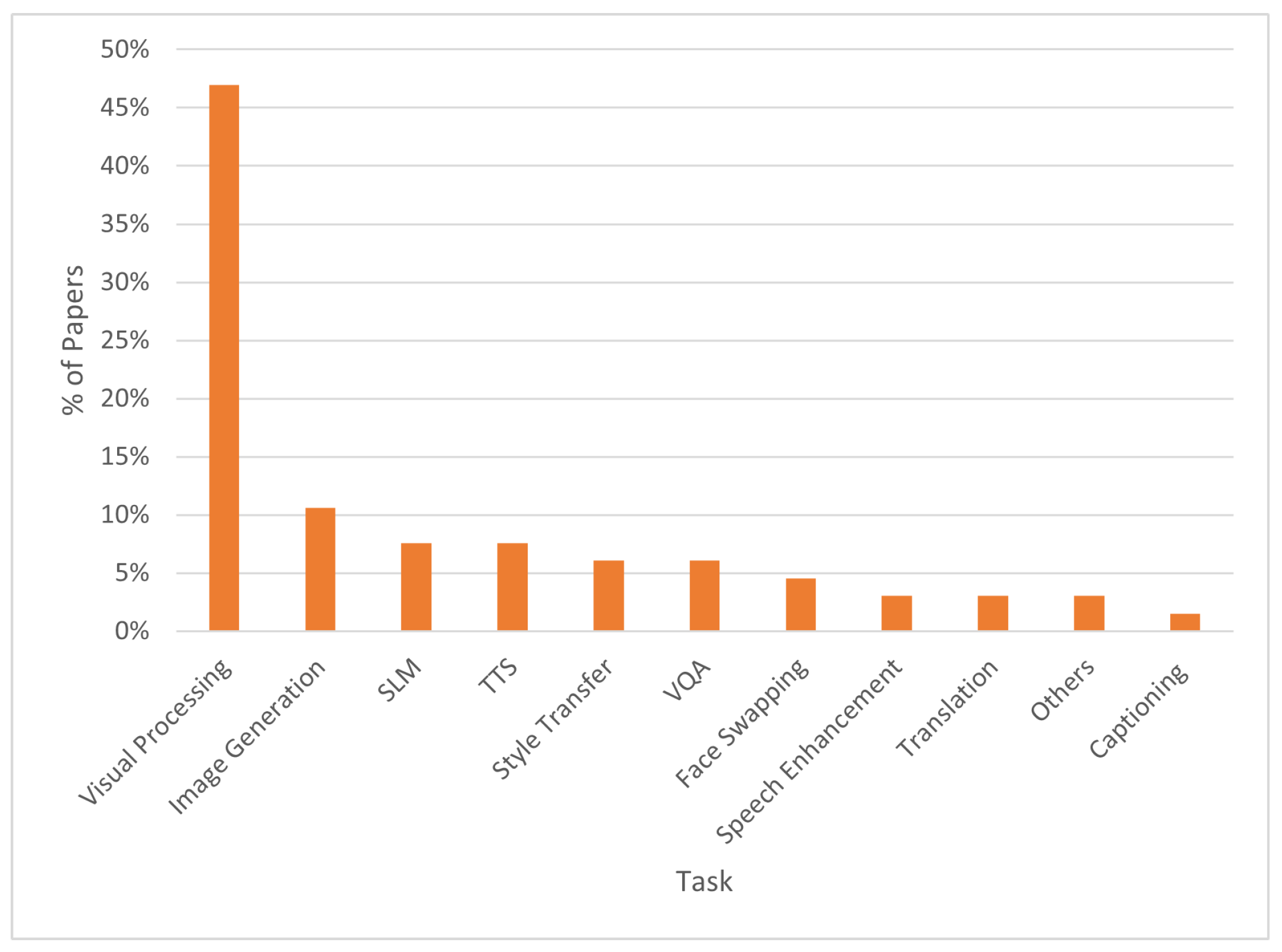
Figure 2, devices such as Raspberry Pi and NVIDIA Jetson boards were less frequently utilized, while only a small fraction of papers explored deployment on MCUs. Nearly half of the collected papers focused on visual processing tasks, whereas each of the other tasks was addressed by a handful of papers. The graph in
Figure 3 illustrates the percentage of collected papers focusing on each task. While the addressed task was always indicated in the papers, the use case or application domain were rarely mentioned. Although studies on the design and edge deployment of GenAI models are still limited, there is a growing interest and effort in the field. With the application of appropriate methods and optimization techniques, these deployments can become increasingly feasible. The field of Edge GenAI is in its initial stages, since started on March 2024 by the EdgeAI Foundation, and further research and techniques are required to develop models with enhanced efficiency and performance on increasingly resource-constrained devices. Additionally, it is important for future studies to provide a detailed analysis of models’ performance on deployment devices, including information on latency, model size, storage usage, and energy consumption. Given the need for Edge GenAI models to be energy-efficient, particularly when operating on battery-powered devices, an important research direction also involves studying the energy consumption of these models in comparison to those running on cloud servers, both for training and inference workloads. Exploring whether EdgeAI can contribute to reducing the carbon footprint in the AI field can be a valuable area of investigation.
This paper underscores the growing interest in deploying GenAI models on embedded devices, alongside cloud servers where scaling laws can be leveraged to achieve superior performance. Since larger networks and datasets cannot be exploited, optimal performance must be attained through careful and tailored approaches. Despite the challenges posed by limited resources, there are numerous use cases, benefits, and advances that would otherwise be infeasible. Edge GenAI has the potential to advance Agentic AI, a burgeoning area of interest within the AI field. Agentic AI refers to systems capable of continuous learning, real-time adaptability to their environment, and autonomous decision-making and action, marking the transition from static to dynamic AI. Edge GenAI represents a significant step forward in developing these systems and enabling their operation on embedded devices, thereby making autonomous and dynamic AI feasible without relying on the vast resources of the cloud.
7. Conclusions
This paper seeks to evaluate the progress made to date in the field of Edge GenAI, an emerging area of research in the domain of EdgeAI. To capture the latest innovations in the field, only papers released between 2022 and 2024 were considered. During this period, several reviews in the domain of EdgeAI and TinyML have emerged. However this review uniquely focuses on GenAI models, identifying and comparing studies that addressed their design and deployment on edge devices. While reviews on LMs on embedded devices are relatively common, comprehensive reviews on Edge GenAI as a whole remain scarce. This review is among the first to systematically collect GenAI models deployed on edge devices, describing their approach and performance.
The paper begins by introducing the context and defining the key concepts. The challenges and several benefits of deploying GenAI models on edge devices were also highlighted in this introductory part. Specifically, notable benefits include independence from an Internet connection, enhanced privacy, low latency, reduced costs, and improved scalability. Subsequently, concrete use cases and applications of Edge GenAI were presented. These examples underscore the necessity of deploying GenAI models on edge devices, enabling applications that would otherwise be infeasible with models running on cloud servers. Edge GenAI will also pave the way for new and previously unimagined applications and use cases.
In
Section 4, the papers collected for the review were described and categorized according to the task they addressed. This section constitute the core of this review, gathering and comparing various approaches and results related to the design of GenAI models and their deployment on edge devices. The subsequent section highlighted the optimization techniques explored in the papers described in
Section 4. These techniques are crucial in EdgeAI, as they aim to reduce the resource usage of models, thereby facilitating deployment on edge devices. Finally, a discussion on the studies reviewed and their implications was provided, along with potential future research directions in the field of Edge GenAI.
Although Edge GenAI is a newly emerging field, this reviews demonstrates that it is a promising area of research with the potential to offer numerous advantages. Several researchers and organizations are increasingly interested in and committed to advancing its progress.
8. Patents
There are no patents either filed or pending resulting from the work reported in this manuscript.
Author Contributions
For research articles with several authors, a short paragraph specifying their individual contributions must be provided. The following statements should be used “Conceptualization, G.Giorgetti and D.Pau; methodology, G.Giorgetti and D.Pau; software, G.Giorgetti and D.Pau; validation, G.Giorgetti and D.Pau; formal analysis, G.Giorgetti and D.Pau; investigation, G.Giorgetti and D.Pau; resources, D. Pau; data curation, G. Giorgetti; writing—original draft preparation, G. Giorgetti and D.Pau; writing—review and editing, G. Giorgetti and D.Pau; supervision, D. Pau; project administration, D. Pau; funding acquisition, D. Pau. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.’
Funding
This research received any funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study did not require any ethical approval, since not applicable and not involving humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
This work did not involve humans, vegetables or animals to support the studies reported by this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The authors of this article declare that no new datasets were generated to support the findings reported by this paper.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to MDPI to have fully waived the publication costs associated to this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare under their responsibility no conflict of interests, personal circumstances or interest that may be perceived as inappropriately influencing the representation or interpretation of reported research results.
References
- Fiorenza, G.; Pau, D.P.; Schettini, R. Action Prediction with Edge Generative AI for Mice Pre-clinical Studies. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI). IEEE, 2024.
- EDGE AI FOUNDATION. https://www.edgeaifoundation.org/about, 2024. Accessed on 4 December 2024.
- About the EDGE AI FOUNDATION. https://www.edgeaifoundation.org/, 2024. Accessed on 4 December 2024.
- Ancilotto, A.; Farella, E. Painting the Starry Night using XiNets. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops and other Affiliated Events (PerCom Workshops). IEEE, 2024, pp. 684–689.
- Cao, Q.; Khanna, P.; Lane, N.D.; Balasubramanian, A. Mobivqa: Efficient on-device visual question answering. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies 2022, 6, 1–23. [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Bansal, M. Lxmert: Learning cross-modality encoder representations from transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.07490 2019. [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Lu, J.; Schwenk, D.; Hajishirzi, H.; Kembhavi, A. X-lxmert: Paint, caption and answer questions with multi-modal transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.11278 2020. [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Son, B.; Kim, I. Vilt: Vision-and-language transformer without convolution or region supervision. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2021, pp. 5583–5594.
- Yu, Z.; Jin, Z.; Yu, J.; Xu, M.; Wang, H.; Fan, J. Bilaterally Slimmable Transformer for Elastic and Efficient Visual Question Answering. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 2023, 25, 9543–9556. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yu, J.; Cui, Y.; Tao, D.; Tian, Q. Deep modular co-attention networks for visual question answering. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2019, pp. 6281–6290.
- Chen, Y.C.; Li, L.; Yu, L.; El Kholy, A.; Ahmed, F.; Gan, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J. Uniter: Universal image-text representation learning. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision. Springer, 2020, pp. 104–120.
- Shen, S.; Li, L.H.; Tan, H.; Bansal, M.; Rohrbach, A.; Chang, K.W.; Yao, Z.; Keutzer, K. How much can clip benefit vision-and-language tasks? arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.06383 2021. [CrossRef]
- Rashid, H.A.; Sarkar, A.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Rahnemoonfar, M.; Mohsenin, T. TinyVQA: Compact Multimodal Deep Neural Network for Visual Question Answering on Resource-Constrained Devices. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.03574 2024. [CrossRef]
- Rahnemoonfar, M.; Chowdhury, T.; Sarkar, A.; Varshney, D.; Yari, M.; Murphy, R.R. Floodnet: A high resolution aerial imagery dataset for post flood scene understanding. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 89644–89654. [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Chowdhury, T.; Murphy, R.R.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Rahnemoonfar, M. Sam-vqa: Supervised attention-based visual question answering model for post-disaster damage assessment on remote sensing imagery. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2023, 61, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Agarwala, A.; Tiwari, U.; Rajendiran, V.N.; Miriyala, S.S. Efficient Visual Question Answering on Embedded Devices: Cross-Modality Attention With Evolutionary Quantization. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). IEEE, 2024, pp. 2142–2148.
- Goyal, Y.; Khot, T.; Summers-Stay, D.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D. Making the v in vqa matter: Elevating the role of image understanding in visual question answering. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2017, pp. 6904–6913.
- Safiya, K.; Pandian, R. Computer Vision and Voice Assisted Image Captioning Framework for Visually Impaired Individuals using Deep Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th IEEE Global Conference for Advancement in Technology (GCAT). IEEE, 2023, pp. 1–7.
- Wang, Y.; Lou, S.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Liu, H. Automatic Captioning based on Visible and Infrared Images. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). IEEE, 2024, pp. 11312–11318.
- Gao, C.; Dong, Y.; Yuan, X.; Han, Y.; Liu, H. Infrared Image Captioning with Wearable Device. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). IEEE, 2023, pp. 8187–8193.
- Arystanbekov, B.; Kuzdeuov, A.; Nurgaliyev, S.; Varol, H.A. Image Captioning for the Visually Impaired and Blind: A Recipe for Low-Resource Languages. In Proceedings of the 2023 45th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC). IEEE, 2023, pp. 1–4.
- Uslu, B.; Çaylı, Ö.; Kılıç, V.; Onan, A. Resnet based deep gated recurrent unit for image captioning on smartphone. Avrupa Bilim ve Teknoloji Dergisi 2022, pp. 610–615. [CrossRef]
- Kılcı, M.; Çaylı, Ö.; Kılıç, V. Fusion of High-Level Visual Attributes for Image Captioning. Avrupa Bilim ve Teknoloji Dergisi 2023, pp. 161–168.
- Nguyen, H.; Huynh, T.; Tran, N.; Nguyen, T. MyUEVision: an application generating image caption for assisting visually impaired people. Journal of Enabling Technologies 2024, 18, 248–264. [CrossRef]
- Aydın, S.; Çaylı, Ö.; Kılıç, V.; Onan, A. Sequence-to-sequence video captioning with residual connected gated recurrent units. Avrupa Bilim ve Teknoloji Dergisi 2022, pp. 380–386.
- Pezzuto Damaceno, R.J.; Cesar Jr, R.M. An End-to-End Deep Learning Approach for Video Captioning Through Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the Iberoamerican Congress on Pattern Recognition. Springer, 2023, pp. 715–729.
- Huang, L.H.; Lu, C.H. Average Sparse Attention for Dense Video Captioning From Multiperspective Edge-Computing Cameras. IEEE Systems Journal 2024. [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.H.; Lu, C.H. Sequence-Aware Learnable Sparse Mask for Frame-Selectable End-to-End Dense Video Captioning for IoT Smart Cameras. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2023. [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.H.; Fan, G.Y. Environment-aware dense video captioning for IoT-enabled edge cameras. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2022, 9, 4554–4564. [CrossRef]
- Yousif, A.J.; Al-Jammas, M.H. A Lightweight Visual Understanding System for Enhanced Assistance to the Visually Impaired Using an Embedded Platform. Diyala Journal of Engineering Sciences 2024, pp. 146–162.
- Wang, N.; Xie, J.; Luo, H.; Cheng, Q.; Wu, J.; Jia, M.; Li, L. Efficient image captioning for edge devices. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2023, Vol. 37, pp. 2608–2616.
- Lin, J.; Yin, H.; Ping, W.; Molchanov, P.; Shoeybi, M.; Han, S. Vila: On pre-training for visual language models. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2024, pp. 26689–26699.
- Lin, J.; Tang, J.; Tang, H.; Yang, S.; Chen, W.M.; Wang, W.C.; Xiao, G.; Dang, X.; Gan, C.; Han, S. AWQ: Activation-aware Weight Quantization for On-Device LLM Compression and Acceleration. Proceedings of Machine Learning and Systems 2024, 6, 87–100.
- Atienza, R. Efficientspeech: An on-device text to speech model. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). IEEE, 2023, pp. 1–5.
- Chevi, R.; Prasojo, R.E.; Aji, A.F.; Tjandra, A.; Sakti, S. Nix-TTS: Lightweight and end-to-end text-to-speech via module-wise distillation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT). IEEE, 2023, pp. 970–976.
- Kim, J.; Kong, J.; Son, J. Conditional variational autoencoder with adversarial learning for end-to-end text-to-speech. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2021, pp. 5530–5540.
- Piper. https://github.com/rhasspy/piper, 2022. Accessed on 9 January 2025.
- Kong, J.; Kim, J.; Bae, J. Hifi-gan: Generative adversarial networks for efficient and high fidelity speech synthesis. Advances in neural information processing systems 2020, 33, 17022–17033.
- Ren, Y.; Hu, C.; Tan, X.; Qin, T.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, T.Y. Fastspeech 2: Fast and high-quality end-to-end text to speech. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.04558 2020.
- Nguyen, V.T.; Pham, H.C.; Mac, D.K. How to Push the Fastest Model 50x Faster: Streaming Non-Autoregressive Speech Synthesis on Resouce-Limited Devices. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). IEEE, 2023, pp. 1–5.
- Yang, G.; Yang, S.; Liu, K.; Fang, P.; Chen, W.; Xie, L. Multi-band melgan: Faster waveform generation for high-quality text-to-speech. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT). IEEE, 2021, pp. 492–498.
- Ciapponi, S.; Paissan, F.; Ancilotto, A.; Farella, E. TinyVocos: Neural Vocoders on MCUs. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 5th International Symposium on the Internet of Sounds (IS2). IEEE, 2024, pp. 1–10.
- Park, S.; Choo, K.; Lee, J.; Porov, A.V.; Osipov, K.; Sung, J.S. Bunched LPCNet2: Efficient neural vocoders covering devices from cloud to edge. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.14416 2022.
- Chen, S.; Weng, J.; Hong, S.; He, Y.; Zou, Y.; Wu, K. TransFiLM: An Efficient and Lightweight Audio Enhancement Network for Low-Cost Wearable Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 21st International Conference on Mobile Ad-Hoc and Smart Systems (MASS). IEEE, 2024, pp. 150–158.
- Šljubura, N.; Šimić, M.; Bilas, V. Deep Learning Based Speech Enhancement on Edge Devices Applied to Assistive Work Equipment. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS). IEEE, 2024, pp. 1–6.
- Nossier, S.A.; Wall, J.A.; Moniri, M.; Glackin, C.; Cannings, N. Convolutional Recurrent Smart Speech Enhancement Architecture for Hearing Aids. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, 2022, pp. 5428–5432.
- Vaswani, A. Attention is all you need. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2017.
- Tan, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Q.; Sun, M.; Liu, Y. Dynamic multi-branch layers for on-device neural machine translation. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing 2022, 30, 958–967. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, P.; Gan, G.; Lv, X.; Wang, B.; Wei, J.; Jiang, X. Hypoformer: Hybrid decomposition transformer for edge-friendly neural machine translation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2022, pp. 7056–7068.
- Kim, Y.; Rush, A.M. Sequence-level knowledge distillation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1606.07947 2016.
- Ancilotto, A.; Paissan, F.; Farella, E. Xinet: Efficient neural networks for tinyml. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2023, pp. 16968–16977.
- Huo, J.; Kong, M.; Li, W.; Wu, J.; Lai, Y.K.; Gao, Y. Towards efficient image and video style transfer via distillation and learnable feature transformation. Computer Vision and Image Understanding 2024, 241, 103947. [CrossRef]
- Suresh, A.P.; Jain, S.; Noinongyao, P.; Ganguly, A.; Watchareeruetai, U.; Samacoits, A. Fastclipstyler: Optimisation-free text-based image style transfer using style representations. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2024, pp. 7316–7325.
- Kwon, G.; Ye, J.C. Clipstyler: Image style transfer with a single text condition. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022, pp. 18062–18071.
- Reimers, N. Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.10084 2019.
- Ganugula, P.; Kumar, Y.; Reddy, N.; Chellingi, P.; Thakur, A.; Kasera, N.; Anand, C.S. MOSAIC: Multi-object segmented arbitrary stylization using CLIP. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2023, pp. 892–903.
- Xu, Z.; Hong, Z.; Ding, C.; Zhu, Z.; Han, J.; Liu, J.; Ding, E. Mobilefaceswap: A lightweight framework for video face swapping. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2022, Vol. 36, pp. 2973–2981.
- Ancilotto, A.; Paissan, F.; Farella, E. PhiNet-GAN: Bringing real-time face swapping to embedded devices. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops and other Affiliated Events (PerCom Workshops). IEEE, 2023, pp. 677–682.
- Ancilotto, A.; Paissan, F.; Farella, E. Ximswap: Many-to-many face swapping for tinyml. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems 2024, 23, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Berger, G.; Dhingra, M.; Mercier, A.; Savani, Y.; Panchal, S.; Porikli, F. QuickSRNet: Plain Single-Image Super-Resolution Architecture for Faster Inference on Mobile Platforms. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2023, pp. 2187–2196.
- Conde, M.V.; Vasluianu, F.; Vazquez-Corral, J.; Timofte, R. Perceptual image enhancement for smartphone real-time applications. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2023, pp. 1848–1858.
- LI, H.; Guan, J.; Rui, L.; Ma, S.; Gu, L.; Zhu, Z. TinyLUT: Tiny Look-Up Table for Efficient Image Restoration at the Edge. In Proceedings of the The Thirty-eighth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2024.
- Ignatov, A.; Timofte, R.; Denna, M.; Younes, A.; Gankhuyag, G.; Huh, J.; Kim, M.K.; Yoon, K.; Moon, H.C.; Lee, S.; et al. Efficient and accurate quantized image super-resolution on mobile NPUs, mobile AI & AIM 2022 challenge: report. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 92–129.
- Ignatov, A.; Timofte, R.; Chiang, C.M.; Kuo, H.K.; Xu, Y.S.; Lee, M.Y.; Lu, A.; Cheng, C.M.; Chen, C.C.; Yong, J.Y.; et al. Power efficient video super-resolution on mobile npus with deep learning, mobile ai & aim 2022 challenge: Report. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 130–152.
- Ignatov, A.; Timofte, R.; Liu, S.; Feng, C.; Bai, F.; Wang, X.; Lei, L.; Yi, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. Learned smartphone ISP on mobile GPUs with deep learning, mobile AI & AIM 2022 challenge: report. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 44–70.
- Ignatov, A.; Timofte, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Yu, G.; Ma, Z.; Wang, H.; Kwon, M.; Qian, H.; Tong, W.; et al. Realistic bokeh effect rendering on mobile gpus, mobile ai & aim 2022 challenge: report. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 153–173.
- Ignatov, A.; Malivenko, G.; Timofte, R.; Treszczotko, L.; Chang, X.; Ksiazek, P.; Lopuszynski, M.; Pioro, M.; Rudnicki, R.; Smyl, M.; et al. Efficient single-image depth estimation on mobile devices, mobile AI & AIM 2022 challenge: report. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 71–91.
- Yang, R.; Timofte, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, F.; He, D.; Li, F.; Zheng, H.; Yuan, W.; et al. Aim 2022 challenge on super-resolution of compressed image and video: Dataset, methods and results. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 174–202.
- Conde, M.V.; Timofte, R.; Huang, Y.; Peng, J.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; Pérez-Pellitero, E.; Song, F.; Bai, F.; Liu, S.; et al. Reversed image signal processing and RAW reconstruction. AIM 2022 challenge report. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 3–26.
- Kınlı, F.; Menteş, S.; Özcan, B.; Kıraç, F.; Timofte, R.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; et al. AIM 2022 challenge on Instagram filter removal: methods and results. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 27–43.
- Sargsyan, A.; Navasardyan, S.; Xu, X.; Shi, H. Mi-gan: A simple baseline for image inpainting on mobile devices. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2023, pp. 7335–7345.
- Verma, S.; Sharma, A.; Sheshadri, R.; Raman, S. GraphFill: Deep Image Inpainting using Graphs. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2024, pp. 4996–5006.
- Ayazoglu, M.; Bilecen, B.B. Xcat-lightweight quantized single image super-resolution using heterogeneous group convolutions and cross concatenation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 475–488.
- Gendy, G.; Sabor, N.; Hou, J.; He, G. Real-time channel mixing net for mobile image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 573–590.
- Luo, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, Q.; Wen, Z.; Fan, H.; Liu, S. Fast nearest convolution for real-time efficient image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 561–572.
- Angarano, S.; Salvetti, F.; Martini, M.; Chiaberge, M. Generative adversarial super-resolution at the edge with knowledge distillation. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2023, 123, 106407. [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, H.; Gong, J.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Dehbi, L. Equivalent transformation and dual stream network construction for mobile image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2023, pp. 14102–14111.
- Deng, W.; Yuan, H.; Deng, L.; Lu, Z. Reparameterized residual feature network for lightweight image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2023, pp. 1712–1721.
- Gankhuyag, G.; Huh, J.; Kim, M.; Yoon, K.; Moon, H.; Lee, S.; Jeong, J.; Kim, S.; Choe, Y. Skip-concatenated image super-resolution network for mobile devices. IEEE Access 2022, 11, 4972–4982. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, X.; Zhou, L.; Li, C. Texture-Enhanced Framework by Differential Filter-Based Re-parameterization for Super-Resolution on PC/Mobile. Neural Processing Letters 2023, 55, 12183–12203. [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Wei, F.; Wang, Y. Two-stage deep single-image super-resolution with multiple blur kernels for Internet of Things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2023, 10, 16440–16449. [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Wu, B.; Lu, K.; Zhang, D.; Wang, N. RCBSR: re-parameterization convolution block for super-resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 540–548.
- Lian, W.; Lian, W. Sliding window recurrent network for efficient video super-resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 591–601.
- Xu, T.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, L.; Sun, H. Elsr: Extreme low-power super resolution network for mobile devices. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.14600 2022.
- Yue, S.; Li, C.; Zhuge, Z.; Song, R. Eesrnet: A network for energy efficient super-resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 602–618.
- Gou, W.; Yi, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Kong, D.; Xu, K. SYENet: A simple yet effective network for multiple low-level vision tasks with real-time performance on mobile device. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2023, pp. 12182–12195.
- Liao, J.; Peng, C.; Jiang, L.; Ma, Y.; Liang, W.; Li, K.C.; Poniszewska-Maranda, A. MWformer: a novel low computational cost image restoration algorithm. The Journal of Supercomputing 2024, pp. 1–25. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Shi, Z. Lightweight neural network for enhancing imaging performance of under-display camera. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 2023, 34, 71–84. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Song, M.; Ma, C.; Nasti, J.; Tyagi, V.; Lloyd, G.; Tang, W. An efficient hybrid model for low-light image enhancement in mobile devices. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022, pp. 3057–3066.
- A Sharif, S.; Myrzabekov, A.; Khudjaev, N.; Tsoy, R.; Kim, S.; Lee, J. Learning optimized low-light image enhancement for edge vision tasks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2024, pp. 6373–6383.
- Liu, Z.; Jin, M.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, C.; Xiong, H. Lightweight network towards real-time image denoising on mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). IEEE, 2023, pp. 2270–2274.
- Flepp, R.; Ignatov, A.; Timofte, R.; Van Gool, L. Real-World Mobile Image Denoising Dataset with Efficient Baselines. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2024, pp. 22368–22377.
- Xiang, L.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, H.; Hu, J.; Han, J.; Guo, Y.; Ding, G. ReMoNet: Recurrent multi-output network for efficient video denoising. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2022, Vol. 36, pp. 2786–2794.
- Ignatov, A.; Malivenko, G.; Timofte, R.; Tseng, Y.; Xu, Y.S.; Yu, P.H.; Chiang, C.M.; Kuo, H.K.; Chen, M.H.; Cheng, C.M.; et al. Pynet-v2 mobile: Efficient on-device photo processing with neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). IEEE, 2022, pp. 677–684.
- Ignatov, A.; Sycheva, A.; Timofte, R.; Tseng, Y.; Xu, Y.S.; Yu, P.H.; Chiang, C.M.; Kuo, H.K.; Chen, M.H.; Cheng, C.M.; et al. MicroISP: processing 32mp photos on mobile devices with deep learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 729–746.
- Raimundo, D.W.; Ignatov, A.; Timofte, R. LAN: Lightweight attention-based network for RAW-to-RGB smartphone image processing. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022, pp. 808–816.
- Zheng, J.; Fan, Z.; Wu, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, F. Residual Feature Distillation Channel Spatial Attention Network for ISP on Smartphone. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 635–650.
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2022, pp. 10684–10695.
- Orhon, A.; Siracusa, M.; Wadhwa, A. Stable Diffusion with Core ML on Apple Silicon. https://machinelearning.apple.com/research/stable-diffusion-coreml-apple-silicon, 2022. Accessed on 2 January 2025.
- Asghar, Z.; Hou, J. World’s first on-device demonstration of Stable Diffusion on an Android phone. https://www.qualcomm.com/news/onq/2023/02/worlds-first-on-device-demonstration-of-stable-diffusion-on-android, 2023. Accessed on 2 January 2025.
- Chen, Y.H.; Sarokin, R.; Lee, J.; Tang, J.; Chang, C.L.; Kulik, A.; Grundmann, M. Speed is all you need: On-device acceleration of large diffusion models via gpu-aware optimizations. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2023, pp. 4651–4655.
- Choi, J.; Kim, M.; Ahn, D.; Kim, T.; Kim, Y.; Jo, D.; Jeon, H.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, H. Squeezing large-scale diffusion models for mobile. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.01193 2023.
- Hu, D.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Coskun, H.; Sahni, A.; Gupta, A.; Goyal, A.; Lahiri, D.; Singh, R.; Idelbayev, Y.; et al. SnapGen: Taming High-Resolution Text-to-Image Models for Mobile Devices with Efficient Architectures and Training. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.09619 2024.
- Castells, T.; Song, H.K.; Piao, T.; Choi, S.; Kim, B.K.; Yim, H.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, T.H. EdgeFusion: On-Device Text-to-Image Generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.11925 2024.
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Jin, Q.; Hu, J.; Chemerys, P.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tulyakov, S.; Ren, J. Snapfusion: Text-to-image diffusion model on mobile devices within two seconds. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2024, 36.
- Kim, B.K.; Song, H.K.; Castells, T.; Choi, S. Bk-sdm: A lightweight, fast, and cheap version of stable diffusion. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2025, pp. 381–399.
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Jia, H.; Hou, T. Mobilediffusion: Instant text-to-image generation on mobile devices. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2025, pp. 225–242.
- Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, Q.; Gao, X.; Cai, Q.; Ling, Z. On-device language models: A comprehensive review. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.00088 2024.
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qian, B.; Shi, X.; Shu, Y.; Chen, J. A Review on Edge Large Language Models: Design, Execution, and Applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.11845 2024.
- Laskaridis, S.; Katevas, K.; Minto, L.; Haddadi, H. Melting point: Mobile evaluation of language transformers. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 30th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, 2024, pp. 890–907.
- Xiao, J.; Huang, Q.; Chen, X.; Tian, C. Large language model performance benchmarking on mobile platforms: A thorough evaluation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.03613 2024.
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Mo, T.; Lu, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, R.; Xu, J.; Tang, X.; et al. A comprehensive survey of small language models in the era of large language models: Techniques, enhancements, applications, collaboration with llms, and trustworthiness. arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.03350 2024.
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Iandola, F.; Lai, C.; Tian, Y.; Fedorov, I.; Xiong, Y.; Chang, E.; Shi, Y.; Krishnamoorthi, R.; et al. Mobilellm: Optimizing sub-billion parameter language models for on-device use cases. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.14905 2024.
- Abdin, M.; Aneja, J.; Awadalla, H.; Awadallah, A.; Awan, A.A.; Bach, N.; Bahree, A.; Bakhtiari, A.; Bao, J.; Behl, H.; et al. Phi-3 technical report: A highly capable language model locally on your phone. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.14219 2024.
- Hu, S.; Tu, Y.; Han, X.; He, C.; Cui, G.; Long, X.; Zheng, Z.; Fang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, W.; et al. Minicpm: Unveiling the potential of small language models with scalable training strategies. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.06395 2024.
- Thawakar, O.; Vayani, A.; Khan, S.; Cholakal, H.; Anwer, R.M.; Felsberg, M.; Baldwin, T.; Xing, E.P.; Khan, F.S. Mobillama: Towards accurate and lightweight fully transparent gpt. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.16840 2024.
- Yi, R.; Li, X.; Xie, W.; Lu, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhou, A.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Xu, M. Phonelm: an efficient and capable small language model family through principled pre-training. arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.05046 2024.
Figure 1.
Statistics of the 66 collected papers. (Left) Percentage of papers by type of publication. (Right) Percentage of papers coming from each source.
Figure 1.
Statistics of the 66 collected papers. (Left) Percentage of papers by type of publication. (Right) Percentage of papers coming from each source.
Figure 2.
Percentage of collected papers that investigated the deployment of the proposed models on each device type: smartphones and application processors, Raspberry Pi, NVIDIA Jetson, microcontrollers, and others. Some papers explored deployment on multiple device types; therefore, the sum of the percentages exceeds 100%.
Figure 2.
Percentage of collected papers that investigated the deployment of the proposed models on each device type: smartphones and application processors, Raspberry Pi, NVIDIA Jetson, microcontrollers, and others. Some papers explored deployment on multiple device types; therefore, the sum of the percentages exceeds 100%.
Figure 3.
Distribution of collected papers by the tasks addressed.
Figure 3.
Distribution of collected papers by the tasks addressed.
Table 1.
Papers proposing a VQA model for edge devices, adopted approach, number of parameters, model footprint, deployment devices, and achieved latency. MCAN-BTS (D,L) is the sub-model of width D and depth L derived from slimmable MCAN.
Table 1.
Papers proposing a VQA model for edge devices, adopted approach, number of parameters, model footprint, deployment devices, and achieved latency. MCAN-BTS (D,L) is the sub-model of width D and depth L derived from slimmable MCAN.
| Paper |
Approach |
Params |
Footprint |
Device |
Latency (ms) |
| Cao et al. [5] - |
Set of optimization applied to |
- |
- |
NVIDIA Jetson TX2 |
361 |
| MobiVQA |
LXMERT |
|
|
Pixel 3XL |
165 |
| |
Set of optimization applied to ViLT |
- |
- |
NVIDIA Jetson TX2 |
213 |
| Yu et al. [9] |
Slimmable framework applied to |
59 M |
- |
Snapdragon 888 |
167 |
| |
MCAN: MCAN-BTS (D = 512, L = 6) |
|
|
Dimensity 1100 |
361 |
| |
|
|
|
Snapdragon 660 |
439 |
| |
MCAN-BTS (1/4 D,L) |
- |
- |
Snapdragon 888 |
87 |
| |
|
|
|
Dimensity 1100 |
127 |
| |
|
|
|
Snapdragon 660 |
197 |
| |
MCAN-BTS (1/4 D, 1/6 L) |
9 M |
- |
Snapdragon 888 |
58 |
| |
|
|
|
Dimensity 1100 |
93 |
| |
|
|
|
Snapdragon 660 |
160 |
| Rashid et al. [13] - TinyVQA
|
Comapct Multimodal DNN developed through KD and int8 quantization |
- |
339 KiB |
GAP8 processor |
56 |
| Mishra et al. [16] |
Transformer-based architecture with int8 quantization |
- |
58 MB |
Samsung Galaxy S23 |
2.8 |
Table 2.
Papers proposing a TTS model for edge devices, adopted approach, number of parameters, model footprint, deployment devices, and achieved RTF.
Table 2.
Papers proposing a TTS model for edge devices, adopted approach, number of parameters, model footprint, deployment devices, and achieved RTF.
| Paper |
Approach |
Params |
Footprint |
Device |
RTF |
| Chevi et al. [35] - Nix-TTS
|
Non-autoregressive, end-to-end model developed through KD |
5. 23 M |
21.2 MB |
Raspberry Pi 3B |
1.97 |
| Atienza [34] - EfficientSpeech
|
non-autoregressive, two-stage model |
1.2 M |
- |
Raspberry Pi 4B |
1.7 |
| Nguyen et al. [40] - FastStreamSpeech
|
non-autoregressive, two-stage model |
- |
- |
MediaTek Helio G35 processor |
0.01 - 0.1 |
Table 3.
Papers proposing a visual processing model for edge devices, task addressed, contribution of the paper, and deployment devices.
Table 3.
Papers proposing a visual processing model for edge devices, task addressed, contribution of the paper, and deployment devices.
| Paper |
Task |
Contribution |
Devices |
| Sargsyan et al.
[71] - Mi-GAN
|
Image Inpaitning |
Combination of adversarial training, model reparametrization, and knowledge distillation for high-quality and efficient inpainting. |
iPhone7, iPhoneX, iPad mini (5th gen), iPhone 14-pro-max, Galaxy Tab S7+, Samsung Galaxy S8, vivo Y12 |
| Verma et al.
[72] - GraphFill
|
Image Inpaitning |
Coarser-to-finer method that employs a Graph Neural Network (GNN) and a GAN-based Refine Network, demonstrating
the effectiveness of GNNs for image inpainting. |
Samsung Galaxy S23 |
| Ayazoglu et al.
[73] - XCAT
|
Single-Image Super-Resolution |
Mobile device-friendly quantized network incorporating the proposed HXBlock. |
Mali-G71 MP2 GPU, Synaptics Dolphin NPU |
| Gendy et al.
[74] - CDFM-Mobile
|
Single-Image Super-Resolution |
SISR model incorporating the developed CDFM block for optimized performance and speed. |
Snapdragon 970, Synaptics VS680 board |
| Luo et al.
[75] - NCNet
|
Single-Image Super-Resolution |
Mobile-friendly fast nearest convolution plain network (NCNet) that achieves the same performance as nearest interpolation residual learning while being faster. |
Google Pixel 4 |
| Angarano et al.
[76] |
Single-Image Super-Resolution |
They proposed EdgeSRGAN, a GAN-based solution for SISR, along with EdgeSRGAN-tiny, obtained through KD from EdgeSRGAN. |
Google Coral Edge TPU USB Accelerator |
| Berger et al.
[60] - QuickSRNet
|
Single-Image Super-Resolution |
VGG-like architecture for SISR that demonstrates the effectiveness of simpler designs in achieving high levels of accuracy and on-device performance. |
Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 |
| Chao et al.
[77] - ETDS
|
Single-Image Super-Resolution |
Lightweight network named ETDS for real-time SR on mobile devices based on Equivalent Transformation and dual-stream networks, achieving superior speed and quality compared to previous lightweight SR methods. |
Dimensity 8100, Snapdragon 888, Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 |
| Deng et al.
[78] - RepRFN
|
Single-Image Super-Resolution |
They proposed a lightweight network structure based on reparameterization, named RepRFN, and designed a multi-scale feature fusion structure. RepRFN achieves a balance between performance and efficiency. |
Snapdragon 865, Snapdragon 820, Rockchips RK3588 |
| Gankhuyag et al.
[79] - SCSRN
|
Single-Image Super-Resolution |
Highly efficient SR network that can deliver high accuracy and fast speed, where element-wise addition operation is excluded, and lighter skip-concatenated layer is introduced. |
Galaxy Note20, Galaxy Z Fold4, Synaptics Dolphin smart
TV platform |
| Liu et al.
[80] - TELNet
|
Single-Image Super-Resolution |
They designed an SR network named TELNet based on the proposed RepDFSR framework to perform SR tasks on mobile devices. |
Huawei Mate 40 Pro, Synaptics VS680 board |
| Sun et al.
[81] - SSDSR
|
Single-Image Super-Resolution |
Two-stage semantic and spatial deep SR model suitable for the IoT environment and capable of handling a variety of blur kernels. |
NVIDIA Jetson Nano |
| Gao et al.
[82] - RCBSR
|
Video Super-Resolution |
Optimized ECBSR from three aspects: architecture, NAS, and training strategy. |
Dimensity 9000 |
| Lian et al.
[83] - SWRN
|
Video Super-Resolution |
They proposed a lightweight VSR network named SWRN that utilizes the proposed sliding-window strategy and can be easily deployed on mobile devices for real-time SR. |
Huawei Mate 10 Pro |
| Xu et al.
[84] - ELSR
|
Video Super-Resolution |
Network with 3×3 convolution, PReLU activation and pixel shuffle operation, which can run in real-time on mobile devices with very low power consumption. |
Dimensity 9000 |
| Yue et al.
[85] - SEESRNet
|
Video Super-Resolution |
They designed SEESRNet based on the proposed EESRNet, which can reduce power consumption while maintaining reasonably high performance. |
Dimensity 9000 |
| Gou et al.
[86] - SYENet
|
Multiple low-level vision tasks |
To handle multiple low-level vision tasks on mobile devices in real-time, they proposed SYENet, which consists of two asymmetrical branches fused with a Quadratic Connections Unit. |
Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 |
| Li et al.
[62] - TinyLUT
|
Image Restoration |
They proposed TinyLUT, which utilizes the proposed separable mapping strategy and dynamic discretization mechanism. TinyLUT achieved significant restoration accuracy with minimal storage consumption. |
Xiaomi 11, Raspberry Pi 4B |
| Liao et al.
[87] - MWformer
|
Image Restoration |
Algorithm named MWformer that combines wavelet transform and transformer to reduce computational overhead, achieving high performance in numerous image restoration tasks. |
NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX |
| Conde et al.
[61] - LPIENet
|
Image Enhancement |
Lightweight UNet-based architecture
characterized by the inverted residual attention (IRA)
block, achieving real-time performance on smartphones. |
Samsung A50, OnePlus Nord 2 5G, OnePlus 8 Pro, Realme 8 Pro |
| Li et al.
[88] |
Under-Display Camera (UDC) Image Enhancement |
They proposed a network that can restore UDC images in a blind manner and a lightweight variant, where the architectural redundancy in learning multi-scale features is reduced. |
Razen-Phone2 |
| Fu et al.
[89] - LLNet
|
Low-Light Image Enhancement (LLIE) |
Efficient hybrid model combining a lite CNN and a non-trainable linear transformation estimation model for image enhancement on mobile devices. |
SM8450 + Adreno660, SM8250 + Adreno650, SM7325 + Adreno642, SM7250 + Adreno620, SM6375 + Adreno619, SM6115 + Adreno610 |
| Sharif et al.
[90] |
Low-Light Image Enhancement (LLIE) |
LLIE learning framework for edge devices that incorporates a lightweight deep model (fully convolutional encoder-decoder architecture) and a deployment strategy. |
NVIDIA Jetson Orin |
| Liu et al.
[91] - MFDNet
|
Image Denoising |
They identified the network architectures and operations that can run on NPUs with low latency and built a mobile-friendly denoising network based on these findings. |
iPhone 11, iPhone 14 Pro |
| Flepp et al.
[92] - SplitterNet
|
Image Denoising |
They introduced MIDD, a large mobile image denoising dataset, and SplitterNet, an efficient baseline model that is optimized both in terms of denoising and inference performance. |
Snapdragon 8 Gen 1, 2 and 3, Snapdragon 888, Dimensity 9000, 9200 and 9300, Samsung Exynos 2100 and 2200, Google Tensor G1 and G2 |
| Xiang et al.
[93] - ReMoNet
|
Video Denoising |
Recurrent Multi-output Network (ReMoNet) composed of the Recurrent Temporal Fusion (RTF) block and the Multi-output Aggregation (MOA) block, and that achieves superior performance with significantly less computational cost. |
Snapdragon 888 |
| Ignatov et al.
[94] - PyNET-V2
|
Image Signal Processing |
Based on PyNET, they proposed PyNET-V2 Mobile CNN architecture which yields both good visual reconstruction results and low latency on mobile devices. |
Dimensity Next, 9000, 1000+ and 820, Exynos 990 and 2100, Kirin 9000, Snapdragon 888 Google Tensor |
| Ignatov et al.
[95] - MicroISP
|
Image Signal Processing |
DL-based image signal processing (ISP) architecture for mobile devices named MicroISP that
provides comparable or better visual results than traditional mobile ISP systems, while outperforming previous DL-based solutions. |
Dimensity 9000, 1000+ and 820, Exynos 990 and 2100, Kirin 9000, Snapdragon 888 Google Tensor |
| Raimundo et al.
[96] - LAN
|
Image Signal Processing |
Lightweight attention-based network (LAN) that improves performance without hindering inference time on smartphone devices. |
Dimensity 1000+ |
| Zheng et al.
[97] - RFDCSANet
|
Image Signal Processing |
Lightweight network named Residual Feature Distillation Channel Spatial Attention Network (RFDCSANet) for real-time smartphone ISP. |
Snapdragon 870, Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 |
| Chen et al.
[97] |
Single Image Bokeh Rendering |
Depth-guided deep filtering network (DDFN) for efficient bokeh effect synthesis on mobile devices. |
Snapdragon 865 |
Table 4.
Papers that focused on deploying a text-to-image model on an edge device, adopted approach, number of parameters, model size, deployment devices, and achieved latency.
Table 4.
Papers that focused on deploying a text-to-image model on an edge device, adopted approach, number of parameters, model size, deployment devices, and achieved latency.
| Paper |
Approach |
Params |
Footprint |
Device |
Latency (s) |
| Chen et al. [101] |
Series of implementation optimizations applied to SD v1.4. |
- |
2093 MB |
Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra |
11.5 |
| Choi et al. [102] - Mobile Stable Diffusion
|
Series of optimization techniques applied to SD v2.1, including pruning, mixed-precision quantization, and KD to reduce the number of denoising steps. |
- |
- |
Samsung Galaxy S23 |
7 |
| Castells et al. [104] - EdgeFusion
|
Employment of BK-SDM, a refined step distillation process for few-step inference, and optimization techniques, including mixed-precision post-training quantization. |
0.5 B |
- |
Samsung Exynos NPU |
0.7 |
| Hu et al. [103] - SnapGen
|
Efficient network architecture and improved training method consisting of multi-stage pre-training followed by KD and adversarial step distillation. |
0.4 B |
- |
iPhone 16 Pro Max |
1.2 - 2.3 |
| Li et al. [105] - |
Efficient network architecture, partic- |
1 B |
- |
iPhone 14 Pro |
2 |
| SnapFusion |
ularly through improvements to the |
|
|
iPhone 13 Pro Max |
2.7 |
| |
UNet, and improved step distillation to reduce the number of denoising steps. |
|
|
iPhone 12 Pro Max |
4.4 |
| Kim et al. [106] - BK-SDM
|
Compression of the SD UNet by removing architectural blocks (block |
0.5 B |
- |
NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin |
2.8 |
| |
pruning) and feature-level knowledge distillation retraining. |
|
|
iPhone 14 |
3.9 |
| Zhao et al. [107] - MobileDiffusion
|
Efficient and lightweight diffusion model architecture and a novel approach for developing highly efficient one-step diffusion-GAN models. |
0.4 B |
- |
iPhone 15 Pro |
0.2 |
Table 5.
Papers addressing the deployment of the proposed SLMs on edge devices, adopted approach, number of parameters, model footprint, deployment devices, and throughput (token/second).
Table 5.
Papers addressing the deployment of the proposed SLMs on edge devices, adopted approach, number of parameters, model footprint, deployment devices, and throughput (token/second).
| Paper |
Approach |
Params |
Footprint |
Device |
Throughput (token/s) |
| Abdin et al. [114] - Phi-3-mini
|
Transformer decoder architecture trained on a larger and more advanced dataset, 4-bit quantization applied before deployment. |
3.8 B |
1.8 GB |
iPhone 14 |
12 |
| Hu et al. [115] - |
Deep and thin network, embedding shar- |
2.4 B |
2 GB |
iPhone 15 Pro |
18 |
|
MiniCPM**
|
ing, and scalable training strategies, int4 |
|
|
iPhone 15 |
15 |
| |
quantization applied before deployment. |
|
|
OPPO Find N3 |
6.5 |
| |
|
|
|
Samsung S23 Ultra |
6.4 |
| |
|
|
|
iPhone 12 |
5.8 |
| Liu et al. [113] |
MobileLLM : Deep and thin Transformer architecture, embedding sharing and grouped-query attention mechanisms. |
125 M |
- |
iPhone 13 |
64.1* |
| |
MobileLLM-LS : MobileLLM with layer sharing. |
125 M |
- |
iPhone 13 |
62.5* |
| Thawakar et al. [116] - MobiLlama
|
Baseline architecture adapted from TinyLlama and Llama-2, parameter sharing scheme then employed, 4-bits quantization applied before deployment. |
0.5 B |
770 MB |
Snapdragon-685 |
7 |
| Yi et al. [117] - PhoneLM
|
Resurce-efficient Trasformer decoder architecture for smartphone hardware, mixed-precision quantization applied before deployment. |
1.5 B |
- |
Xiaomi 14 |
58 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).