Submitted:
27 January 2025
Posted:
29 January 2025
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
I. Introduction
II. Classification of ERP Systems
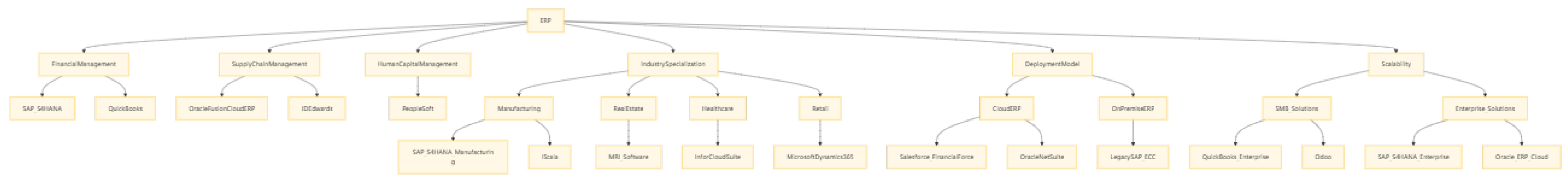
- SAP S/4HANA: This system is renowned for its robust integration of real-time accounting, budgeting, and compliance modules. It is particularly favored by multinational corporations due to its ability to handle complex financial operations across various geographies and currencies. It integrates real-time accounting, budgeting, and compliance modules, favored by multinational corporations. [9]For instance, a global manufacturing company with operations in multiple countries can use SAP S/4HANA to streamline its financial processes, ensuring compliance with local regulations and optimizing financial reporting.
- QuickBooks: QuickBooks is a cost-effective ERP solution for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), offering core accounting features like invoicing, payroll, and basic financial reporting. Recent updates and third-party integrations have expanded its capabilities in supply chain analytics and inventory management. For instance, a small retail business can use QuickBooks to manage daily financial transactions, payroll, and gain insights into inventory levels and sales trends.
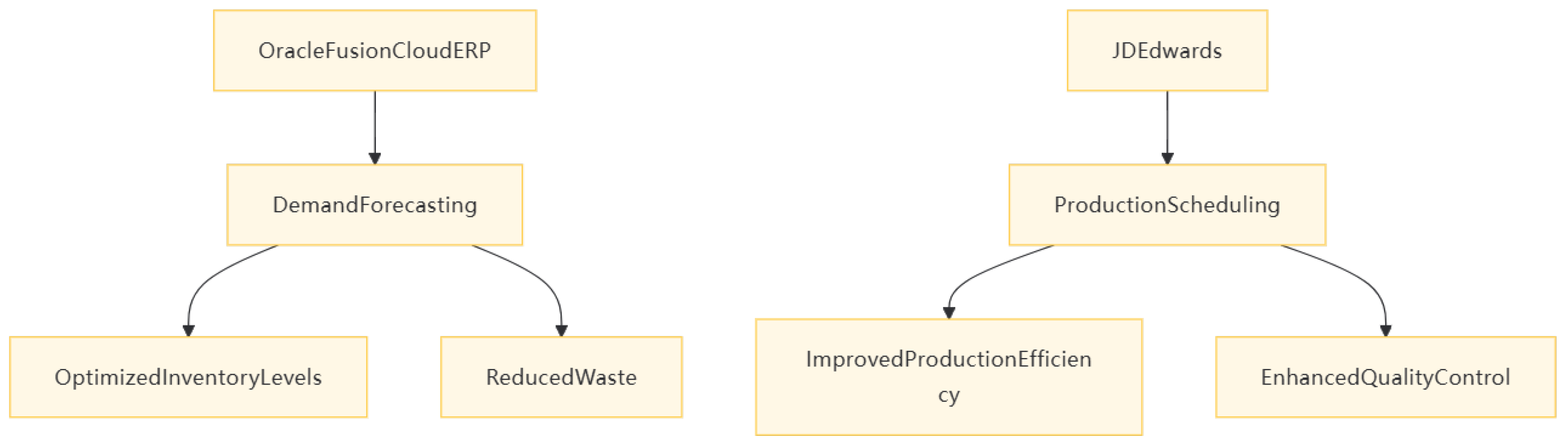
- Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP: This system stands out for its advanced supply chain management capabilities, particularly in procurement and logistics.[8] It leverages AI-driven demand forecasting to optimize inventory levels and reduce waste. For example, a retail company can use Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP to predict consumer demand based on historical sales data and market trends, allowing it to maintain optimal inventory levels and avoid stockouts or overstock situations.
- JD Edwards: Specializing in manufacturing and distribution, JD Edwards provides tools for shop floor management, production scheduling, and quality control. [8]It is particularly useful for companies that need to manage complex manufacturing processes and ensure high product quality. For instance, an automotive parts manufacturer can use JD Edwards to track production progress, manage quality inspections, and optimize production schedules to meet customer demands.
- PeopleSoft: As Oracle’s HR-focused system, PeopleSoft supports comprehensive talent management and payroll automation. [8]It offers features such as employee performance tracking, training management, and benefits administration. For example, a large healthcare organization can use PeopleSoft to manage its workforce, ensuring that employees receive the necessary training and that payroll is processed accurately and efficiently.
B. By Industry Specialization
- SAP S/4HANA: In the manufacturing sector, SAP S/4HANA supports IoT-enabled production planning and quality control. It allows manufacturers to connect their production equipment and collect real-time data, enabling them to optimize production processes and improve product quality. For example, a smart factory can use SAP S/4HANA to monitor machine performance, predict maintenance needs, and adjust production schedules based on real-time data.
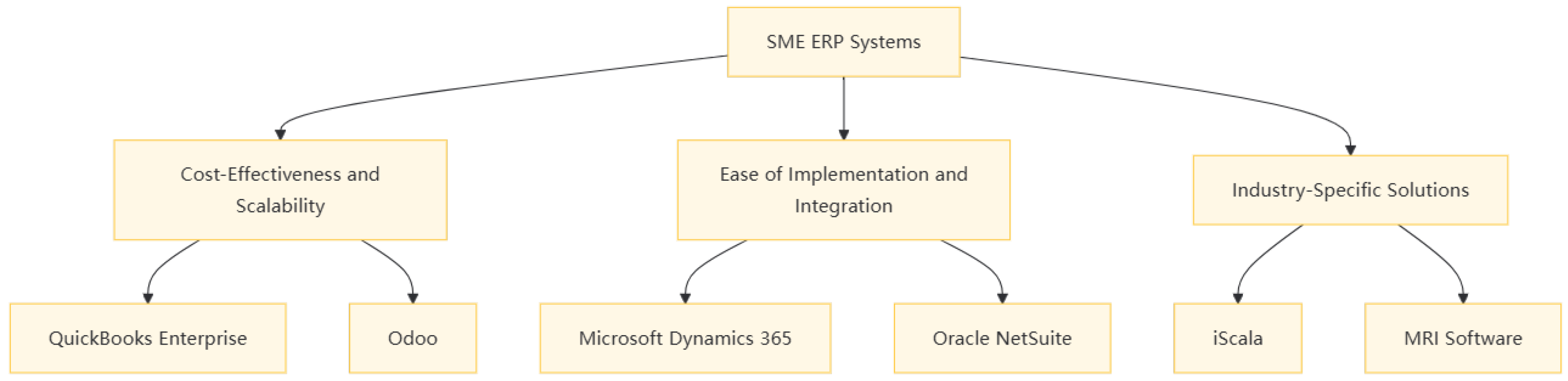
- iScala: Targeting mid-market manufacturers, iScala offers modular production and distribution modules that can be customized to meet specific business needs.[4] It provides functionalities such as production scheduling, inventory management, and customer relationship management. For instance, a mid-sized furniture manufacturer can use iScala to manage its production workflow, track inventory levels, and improve customer satisfaction by ensuring timely deliveries.
- MRI Software: This system is designed to streamline lease accounting, portfolio management, and compliance for real estate firms. It offers features such as lease abstraction, rent roll management, and financial reporting. [7] For example, a real estate management company can use MRI Software to manage its lease agreements, track rental income, and ensure compliance with accounting standards such as ASC 842.
- Infor CloudSuite: In the healthcare industry, Infor CloudSuite ensures HIPAA compliance and patient data security.[12] It provides functionalities such as electronic health record (EHR) management, revenue cycle management, and supply chain management. For example, a hospital can use Infor CloudSuite to manage patient information securely, optimize its supply chain operations, and ensure compliance with healthcare regulations.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: This system enhances inventory optimization and customer analytics for retail businesses.[6] It offers features such as demand forecasting, inventory management, and customer relationship management. For example, a retail chain can use Microsoft Dynamics 365 to analyze customer purchasing patterns, optimize inventory levels, and improve customer engagement through personalized marketing campaigns.
C. By Deployment Model
- Salesforce (FinancialForce): As a SaaS-based ERP with CRM integration, Salesforce (FinancialForce) is ideal for subscription businesses. [10] It offers functionalities such as financial management, billing, and customer relationship management. For example, a software-as-a-service (SaaS) company can use Salesforce (FinancialForce) to manage its subscription-based revenue model, track customer interactions, and optimize billing processes.
- Oracle NetSuite: This scalable cloud ERP is designed for SMEs and offers multi-entity financial consolidation.[8] It provides functionalities such as financial management, inventory management, and order management. For example, a growing e-commerce business can use Oracle NetSuite to manage its financial operations, track inventory levels, and consolidate financial data from multiple entities.
- QuickBooks Enterprise: This solution is designed to bridge the gap between basic accounting and full-fledged ERP systems for growing businesses. It offers a range of functionalities including financial management, inventory management, and payroll processing. For instance, a small manufacturing business can use QuickBooks Enterprise to manage its financial operations, track inventory levels, and process payroll as it grows. The system is particularly favored for its ease of use and affordability, making it accessible to SMEs with limited IT resources.
- Odoo: As a modular open-source ERP, Odoo provides a wide range of functionalities that can be customized to meet specific business needs. It offers affordable pricing and flexibility, which are crucial for SMEs looking to control costs while maintaining the ability to scale. For example, a startup can use Odoo to manage its financial operations, customer relationships, and inventory management without incurring high costs. Odoo’s modular design allows businesses to add or remove modules as their needs change, ensuring that the system grows with the business.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: This system is known for its robust integration capabilities and ease of use. It offers a suite of applications that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of SMEs. For example, a retail business can use Microsoft Dynamics 365 to optimize inventory levels, manage customer relationships, and analyze sales data. The system’s cloud-based architecture makes it easy to implement and scale, reducing the need for extensive IT infrastructure.
- Oracle NetSuite: This scalable cloud ERP is designed for SMEs and offers multi-entity financial consolidation. It provides functionalities such as financial management, inventory management, and order management. For example, a growing e-commerce business can use Oracle NetSuite to manage its financial operations, track inventory levels, and consolidate financial data from multiple entities. The system’s cloud-based nature ensures that businesses can quickly implement and scale their operations without significant upfront costs.
- iScala: Targeting mid-market manufacturers, iScala offers modular production and distribution modules that can be customized to meet specific business needs. It provides functionalities such as production scheduling, inventory management, and customer relationship management. For instance, a mid-sized furniture manufacturer can use iScala to manage its production workflow, track inventory levels, and improve customer satisfaction by ensuring timely deliveries.
- MRI Software: This system is designed to streamline lease accounting, portfolio management, and compliance for real estate firms. It offers features such as lease abstraction, rent roll management, and financial reporting. For example, a real estate management company can use MRI Software to manage its lease agreements, track rental income, and ensure compliance with accounting standards such as ASC 842.
E. By Scalability
- QuickBooks Enterprise: This solution bridges basic accounting and ERP needs for growing businesses. [5]It offers functionalities such as financial management, inventory management, and payroll processing. For example, a small manufacturing business can use QuickBooks Enterprise to manage its financial operations, track inventory levels, and process payroll as it grows.
- Odoo: As a modular open-source ERP, Odoo offers affordable pricing and a wide range of functionalities that can be customized to meet specific business needs. [11]For example, a startup can use Odoo to manage its financial operations, customer relationships, and inventory management without incurring high costs.
- SAP S/4HANA: This system handles complex global operations with custom workflows. It offers advanced functionalities for financial management, supply chain management, and human capital management. [9]For example, a global conglomerate can use SAP S/4HANA to manage its diverse business operations, optimize supply chain processes, and ensure compliance with international regulations.
- Oracle ERP Cloud: Supporting large-scale financial and supply chain management, Oracle ERP Cloud offers robust functionalities for financial management, procurement, and logistics. [8]For example, a large retail corporation can use Oracle ERP Cloud to manage its financial operations, optimize procurement processes, and ensure efficient logistics management.
| Industry | ERP System | Effect Indicator | Numerical Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | SAP S/4HANA | Reduction in inventory holding costs | 20% |
| Manufacturing | SAP S/4HANA | Improvement in order fulfillment accuracy | 15% |
| Retail | Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP | Improvement in demand forecasting accuracy | 90% |
| Retail | Microsoft Dynamics 365 | Improvement in cash flow forecasting accuracy | 90% |
| Healthcare | Infor CloudSuite | HIPAA compliance improvement | 100% |
| Real Estate | MRI Software | Lease accounting standard compliance improvement | 100% |
| Financial Services | Oracle ERP Cloud | Fraud transaction detection accuracy improvement | Real-time detection |
III. ERP Systems in Financial Management: Key Roles
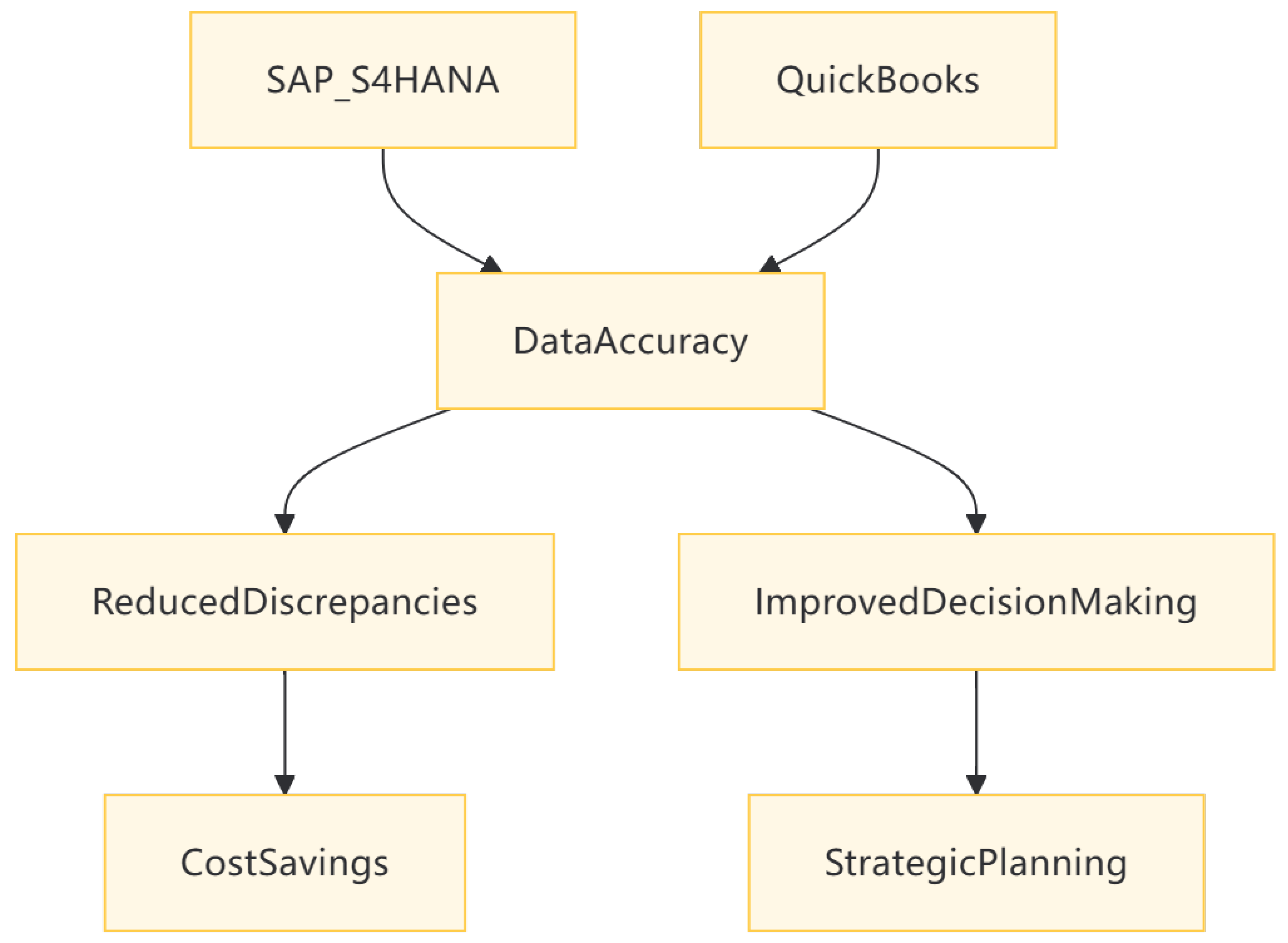
A. Enhanced Data Accuracy and Transparency
- Case Study – SAP: A manufacturing firm reduced financial discrepancies by 40% through automated data synchronization [9].This improvement allowed the company to have a more accurate view of its financial health, leading to better decision-making and reduced costs associated with financial errors.For instance, SAP S/4HANA’s real-time accounting module ensures that all financial transactions are recorded and updated in real-time, providing a continuous and accurate financial overview.
- QuickBooks Integration: AI tools like Grabb AI improve expense tracking accuracy by 25% through automated data entry.[3]This not only saves time but also ensures that all expenses are accurately recorded, providing a clearer picture of the company’s financial outlays.For example, QuickBooks’ invoicing module, when integrated with AI, can automatically categorize expenses and generate detailed financial reports, enhancing the accuracy and transparency of financial data.
- Cost Management Module: SAP S/4HANA’s cost management module provides detailed insights into cost centers and cost objects, enabling organizations to optimize their cost structures. For example, a manufacturing company can use this module to analyze production costs, identify inefficiencies, and implement cost-saving measures. This level of detail and accuracy is crucial for strategic financial planning and budgeting.
- Budget Control Module: Oracle ERP Cloud’s budget control module allows organizations to set and monitor budgets in real-time, ensuring that financial goals are met and deviations are promptly addressed. For instance, a retail corporation can use this module to track monthly sales against budgeted targets, identify variances, and adjust strategies accordingly. This real-time monitoring enhances financial control and transparency.
B. Risk Mitigation and Compliance
- Oracle ERP Cloud: Detects fraudulent transactions in real-time using machine learning [8].For example, Oracle Cloud Risk Management uses data science to automate and digitize security and audit activities, protecting against fraud and error by continuously monitoring transactions and sensitive ERP data. Additionally, recent advancements in AI have enabled more sophisticated risk prediction models. For instance, a financial institution using an AI-driven ERP system was able to predict and prevent a potential fraud scheme by analyzing unusual transaction patterns and behavioral data, saving millions of dollars in potential losses.
- MRI Software: Automates lease accounting standards (ASC 842) for real estate compliance [7].This ensures that companies in the real estate sector can easily adhere to complex accounting standards, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties.
C. Strategic Decision Support
- Predictive Analytics: Microsoft Dynamics 365 forecasts cash flow trends with 90% accuracy.[6]This allows businesses to have a clear view of their future financial status, enabling them to make informed decisions about investments, budgeting, and financial planning.
- Scenario Modeling: JD Edwards simulates production costs under supply chain disruptions [8].For instance, in the case of supply chain disruptions, JD Edwards can model different scenarios to help businesses understand the potential impact on production costs and identify the most cost-effective strategies to mitigate these risks.
D. Cross-Module Integration and Organizational Efficiency
Practical Case Studies and Visual Aids
Case Study: Oracle ERP Cloud in Action
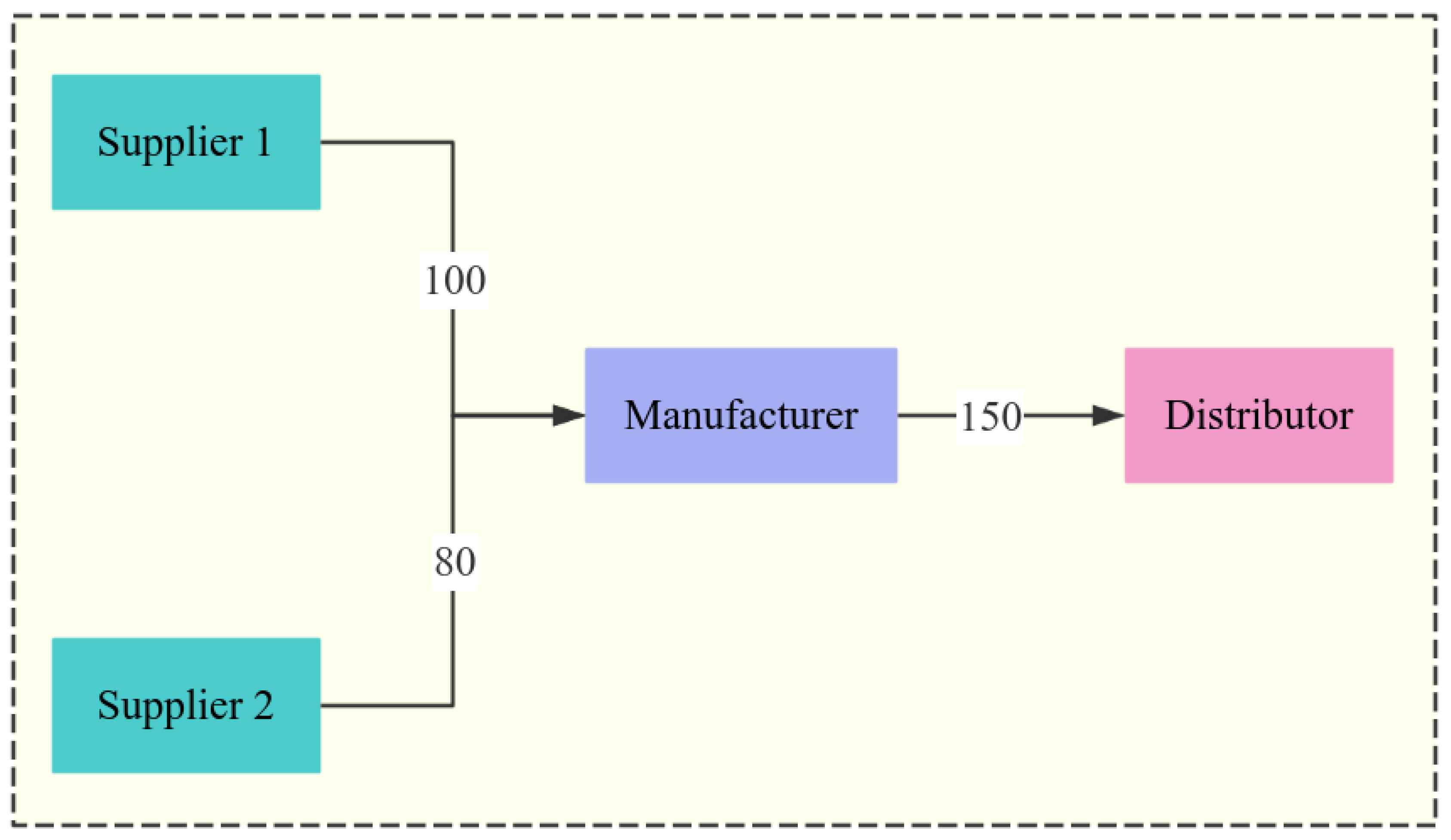
Inventory Management with AI
Predictive Maintenance with AI
IV. AGI/ASI Integration: Redefining ERP Capabilities
A. AGI-Driven Automation
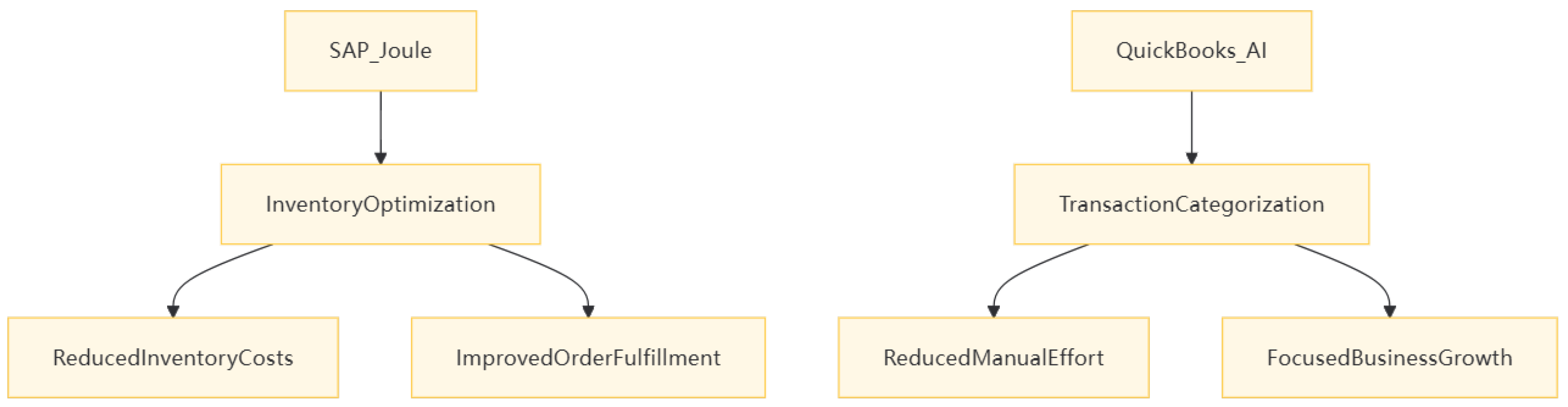
- SAP’s Joule: AGI optimizes inventory levels by analyzing supplier lead times and demand patterns [9].For example, a manufacturing company utilized SAP’s Joule to analyze historical sales data and supplier performance, resulting in a 20% reduction in inventory holding costs and a 15% improvement in order fulfillment accuracy.
- QuickBooks + AI: Automates transaction categorization, reducing manual effort by 30% .[3]A small business owner reported that after integrating QuickBooks with AI tools, they were able to save over 10 hours per week on bookkeeping tasks, allowing them to focus more on business growth strategies.
| System | Function | Effect Indicator | Numerical Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAP S/4HANA | AGI-driven inventory optimization | Reduction in inventory holding costs | 20% |
| QuickBooks + AI | Automated transaction categorization | Reduction in manual effort | 30% |
| Oracle ERP Cloud | Cross-border tax optimization | Annual cost savings | $2M |
| Salesforce Einstein AI | Customer churn prediction accuracy improvement | Reduction in customer churn rate | 30% |
B. ASI and Global Optimization
- Oracle’s Adaptive Intelligence: ASI models solve cross-border tax optimization, saving enterprises $2M annually.[8]A multinational corporation implemented Oracle’s Adaptive Intelligence to analyze tax regulations across different countries and optimize their tax strategies, resulting in significant cost savings and improved compliance.
- Ethical Challenges: Unregulated ASI may prioritize profit over ethical sourcing, necessitating governance frameworks. [1] For instance, a study highlighted the need for ethical guidelines in AI-driven supply chain management to ensure fair labor practices and environmental sustainability. To address these challenges, future ERP systems should integrate explainable AI (XAI) frameworks to audit decision logic, ensuring transparency and accountability. Additionally, blockchain-integrated ERPs can provide immutable audit trails for compliance, enhancing ethical and sustainable business practices.
- Governance Models: In addition to the IEEE Global Initiative, other governance models such as the EU’s Ethics Guidelines for Trustworthy AI and the OECD’s AI Principles also provide comprehensive frameworks for ethical AI development and deployment. These guidelines emphasize the importance of transparency, accountability, and fairness in AI systems. Future ERP systems should integrate these principles into their design and operation to ensure ethical and sustainable business practices.
V. Challenges and Ethical Considerations
D. Ethical AGI and Transparent Governance
VI. Conclusion
References
- Chen, B. (2025). The Pivotal Role of Accounting in Civilizational Progress and the Age of Advanced AI: A Unified Perspective.
- Chen, B. (2025). The Role of Accounting and Financial Management in Humanity's Transition to the Interstellar Era.
- Grabb. (2021). Top AI Apps for QuickBooks. Grabb AI Blog. https://grabb.ai/blog.
- iScala. (2025). iScala Manufacturing Solutions. Retrieved from https://www.iscala.com.
- L&Y Tax Advisors. (2023). QuickBooks Limitations. https://lytaxadvisors.com/quickbooks.
- Microsoft. (2024). AI in Dynamics 365. Microsoft Blog. https://www.microsoft.com/dynamics365.
- MRI Software. (2025). Real Estate ERP Solutions. https://www.mrisoftware.com.
- Oracle. (2025). Oracle Cloud ERP Features. Retrieved from https://www.oracle.com/erp.
- SAP. (2025). SAP S/4HANA Innovations. https://www.sap.com/s4hana.
- Salesforce. (2025). FinancialForce and AI. https://www.salesforce.com/financialforce.
- Odoo. (2025). Odoo ERP Solutions. Retrieved from https://www.odoo.com.
- Infor. (2025). Infor CloudSuite Self-Service Portal User Guide (Cloud). Retrieved from https://docs.infor.com/ssp/2025.x/en-us/cssplib/self_service_portal/cover.html.
- Deloitte. (2025). 2025 Tech Trends: AI in ERP. Deloitte Insights. https://www2.deloitte.com/tech-trends.
- Chen, B. (2025). The Significance of Internal Control in Business Management and the Application of Advanced AI in AGI, ASI, and UBI Eras.
- Chen, B. (2025). Leveraging Advanced AI in Activity-Based Costing (ABC) for Enhanced Cost Management.
- Chen, B. The Imperative Need for Tax Reform in China and Its Impact on Advancing Social Civilization.
- Lu, B. , Dan, H.-C., Zhang, Y., & Huang, Z. (2025). Journey into Automation: Image-Derived Pavement Texture Extraction and Evaluation. arXiv preprint: 2501.02414.
- Dan, H.-C.; Huang, Z.; Lu, B.; Li, M. Image-driven prediction system: Automatic extraction of aggregate gradation of pavement core samples integrating deep learning and interactive image processing framework. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oracle. (n.d.). City of Atlanta. Retrieved January 26, 2025, from https://www.oracle.com/sg/customers/city-of-atlanta/.
- Deloitte. (2025). ERP integration and digital transformation: Bridging silos for operational excellence. Deloitte Insights. https://www2.deloitte.com/erp-integration.
- Gartner. (2025). AI-driven ERP: Reshaping financial workflows. Gartner Research. https://www.gartner.com/ai-erp.
- McKinsey & Company. (2025). The future of finance: AI, ERP, and cross-functional collaboration. McKinsey Digital. https://www.mckinsey.com/future-finance.
- Ahex Technologies. (2025). Top 7 Use Cases of AI in ERP Systems: Insights and Case Studies for 2025. Retrieved from https://ahex.co/top-ai-in-erp-systems-use-cases/.
- Zhang, Z., Li, X., Cheng, Y., Chen, Z., & Liu, Q. (2025). Credit Risk Identification in Supply Chains Using Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.10348.
- Hu, Z., Yu, R., Zhang, Z., Zheng, H., Liu, Q., & Zhou, Y. (2024). Developing Cryptocurrency Trading Strategy Based on Autoencoder-CNN-GANs Algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.18202.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





