Submitted:
27 January 2025
Posted:
28 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
This paper presents a cost-effective approach for the automated surface quality measurement in reamed bores. The study involved drilling 4,000 holes into 42CrMo S4V steel, of which 3,600 underwent subsequent reaming. Utilizing a CNC-controlled gantry coupled with a mobile roughness measurement device through a compliant mechanism, surface data of every bore was efficiently gathered and processed. Additionally, analytical methods are presented that extend beyond standardized, aggregated metrics, enabling the evaluation of correlations to other quality characteristics and sensor data, such as the formation of grooves, positional deviations, and the process forces that occur during the reaming process. This approach aims to enhance understanding of the reaming process, ultimately improving bore quality, reducing component rejects, and extending tool lifespan.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1 Reaming Process
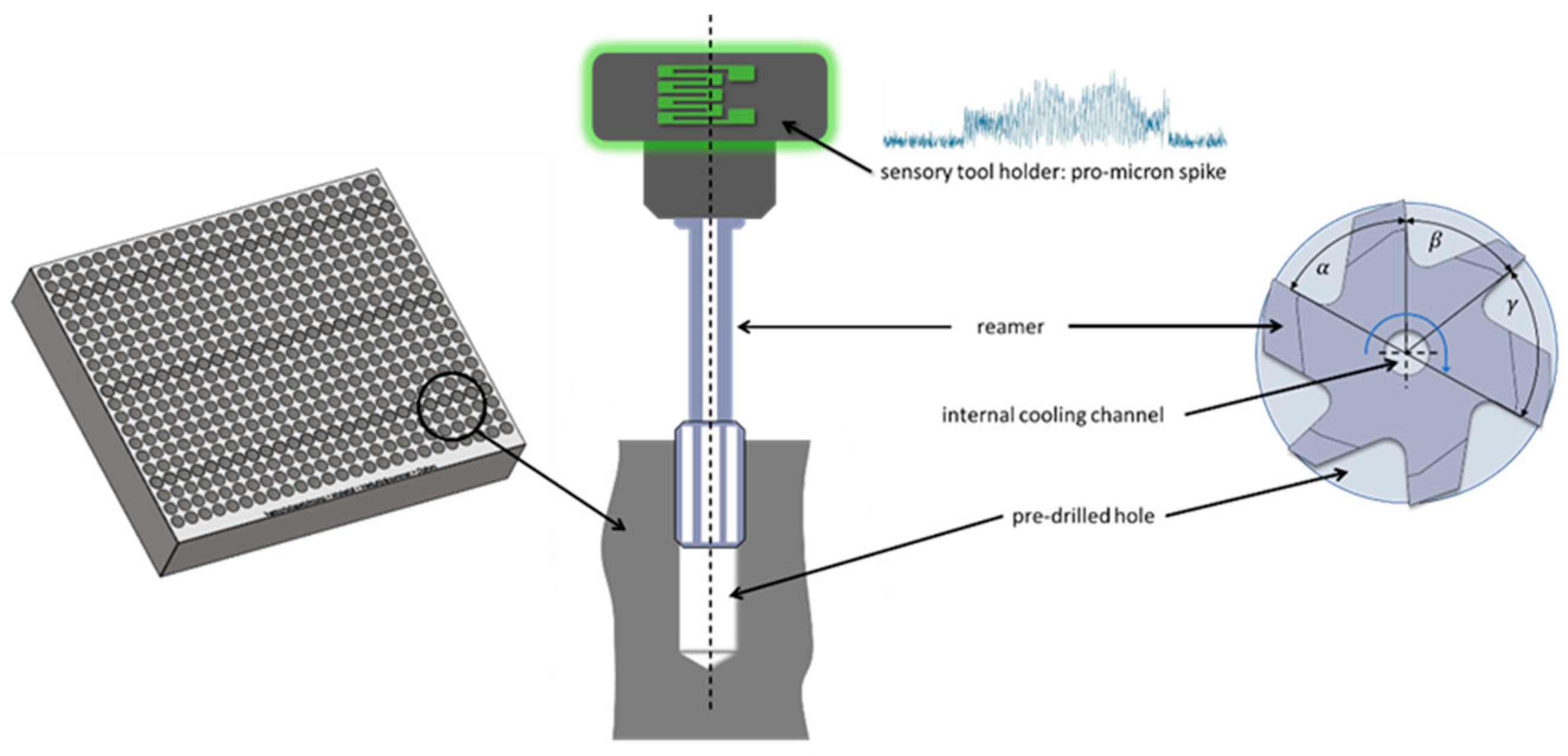
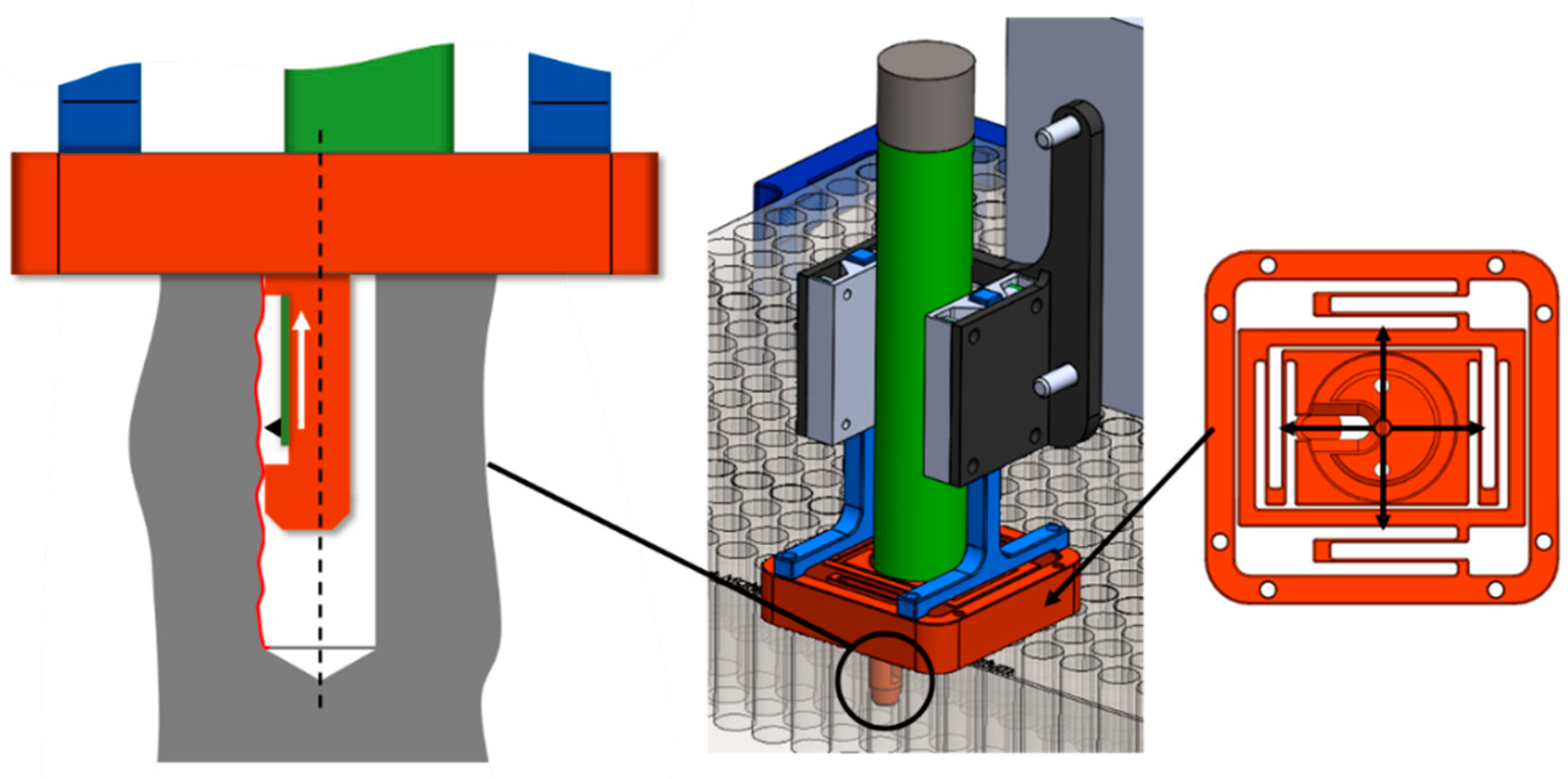
2.2 Automated Surface Measurement
3. Results
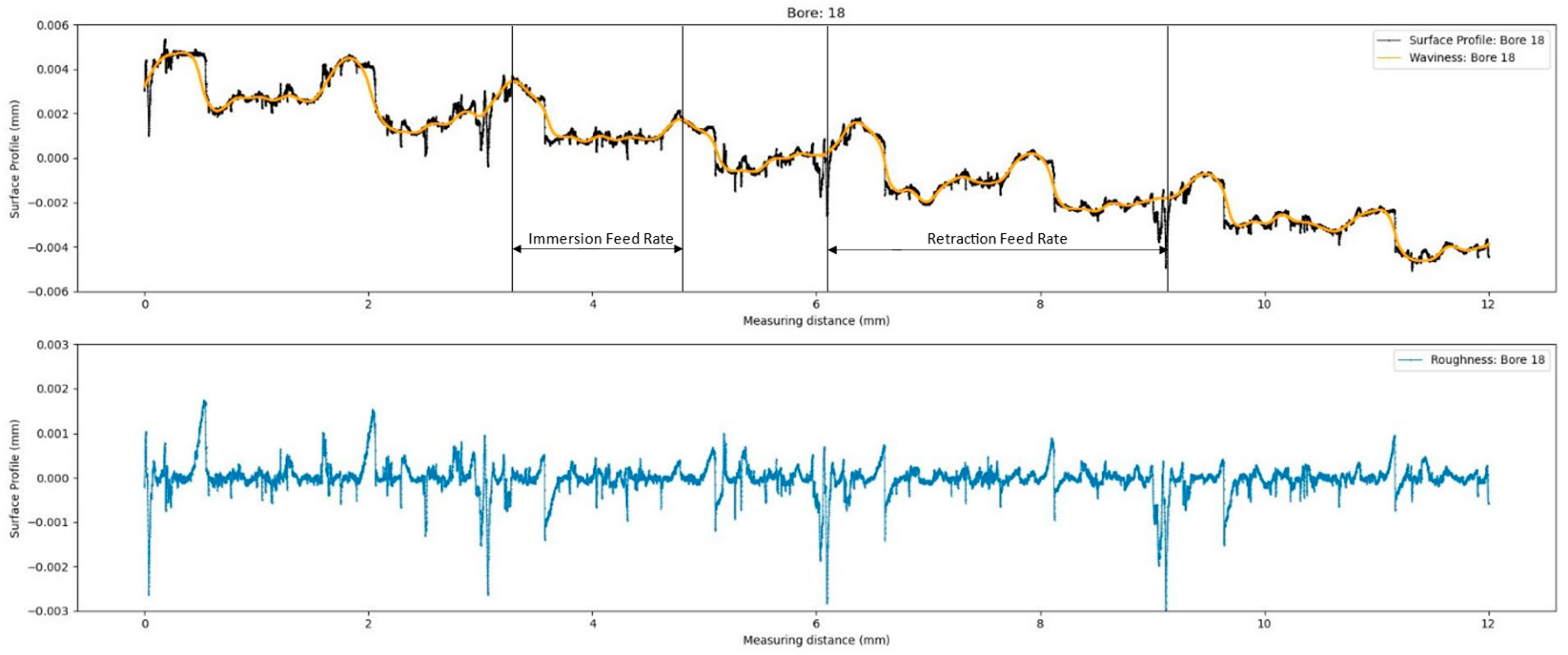
3.1. Pre-Processing: Filtering According to Standards
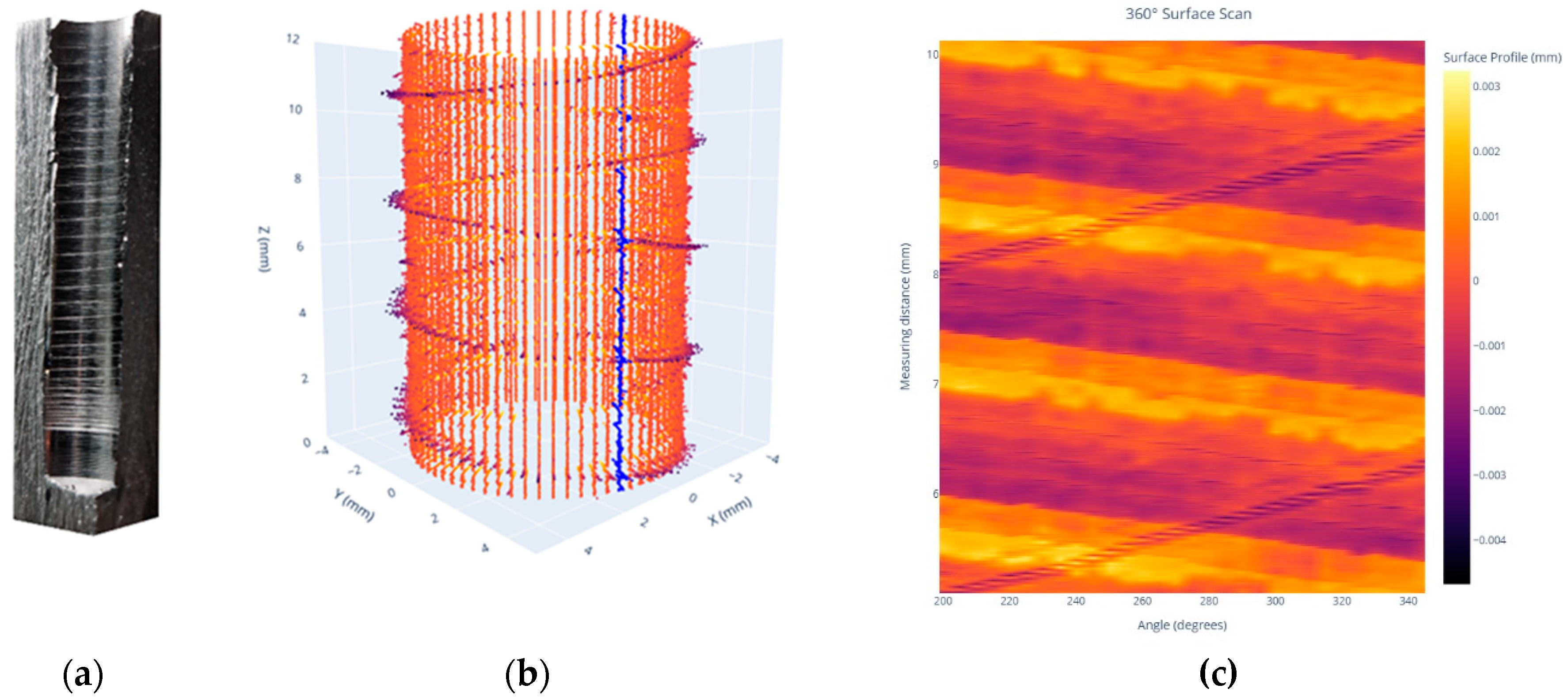
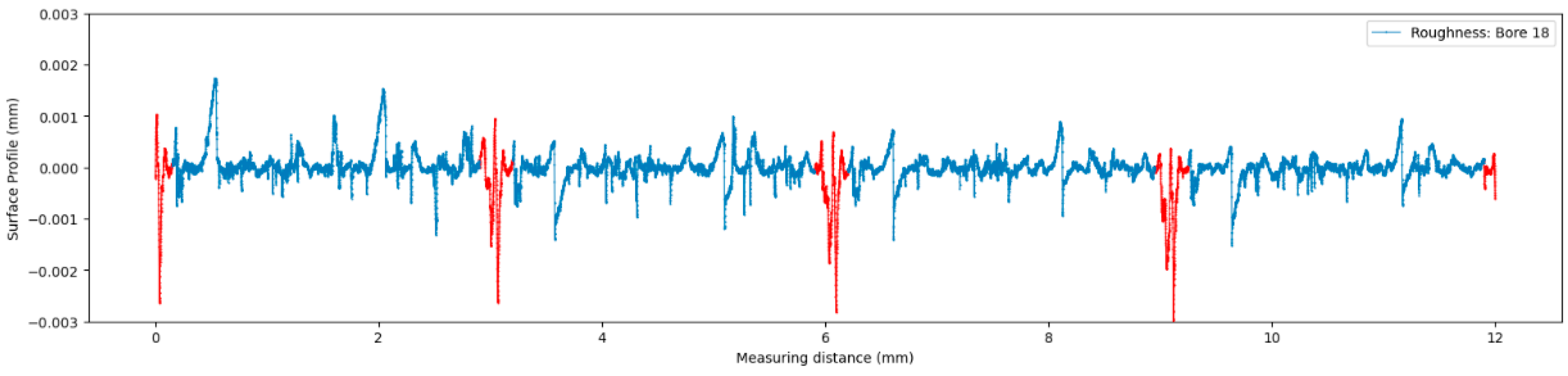
3.2. Analysis of Retraction Grooves in the Roughness profile
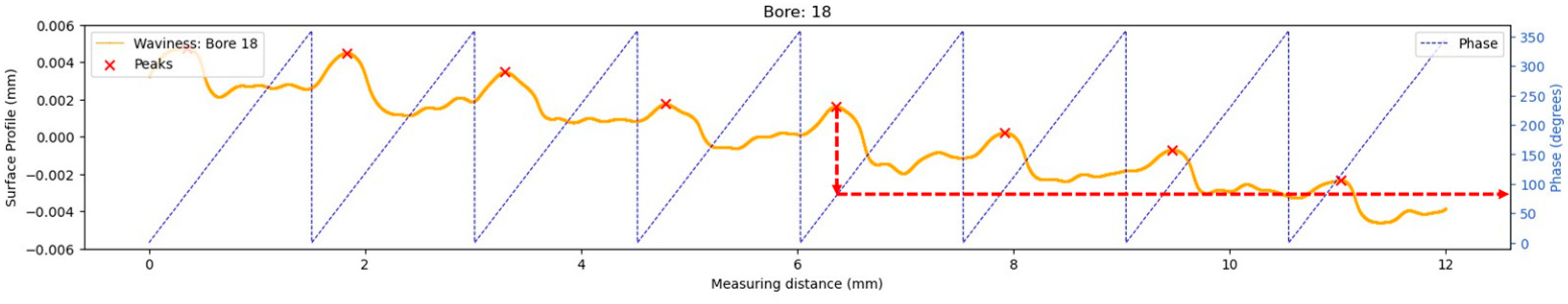
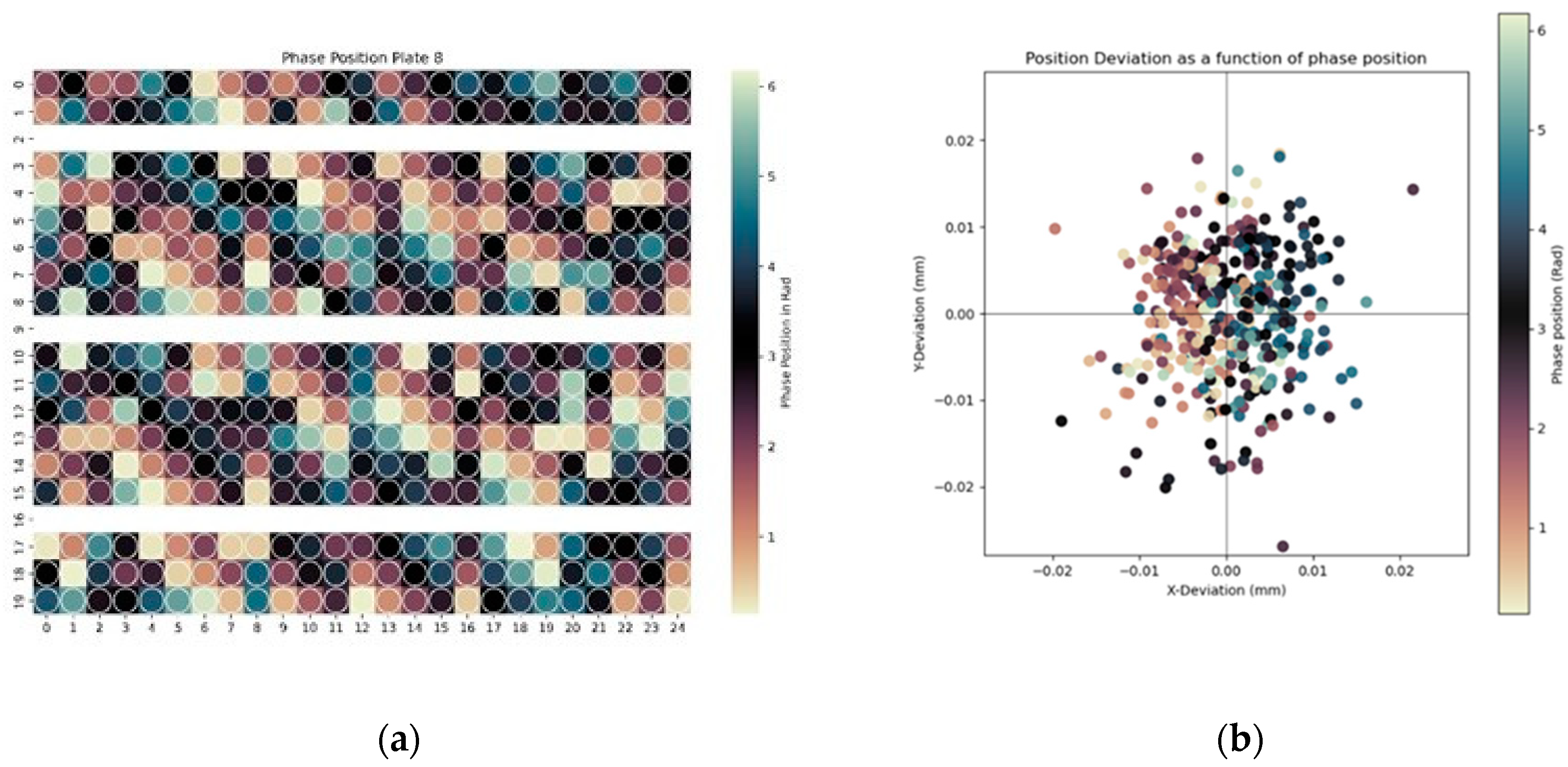
3.3. Analysis of Phase Position in Waviness
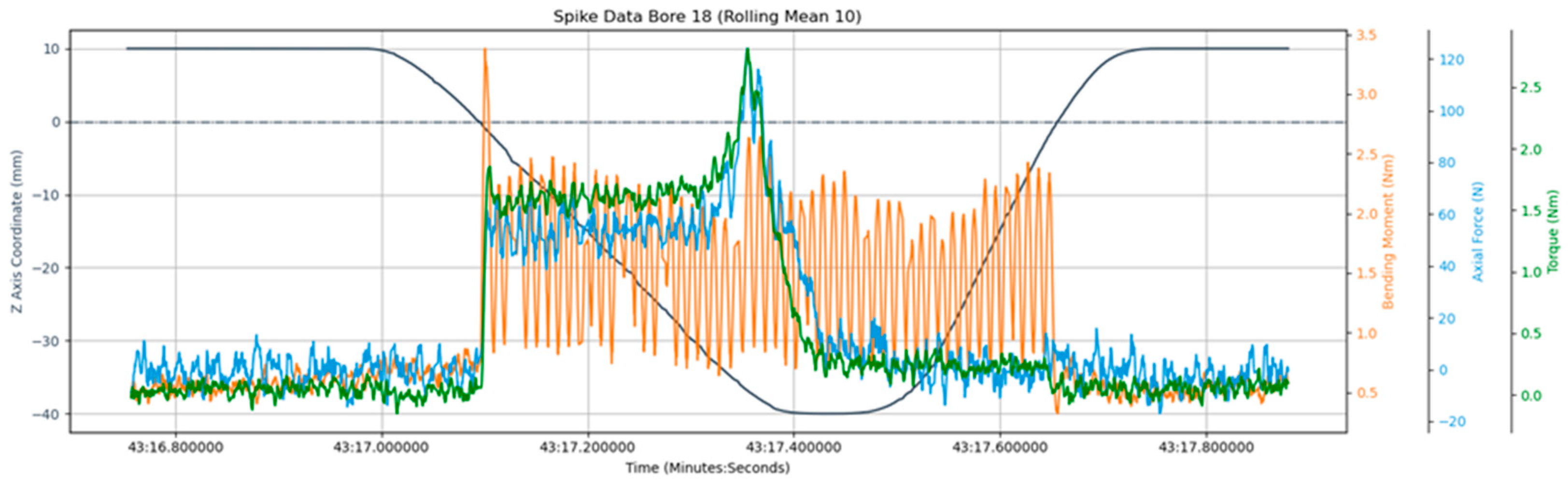
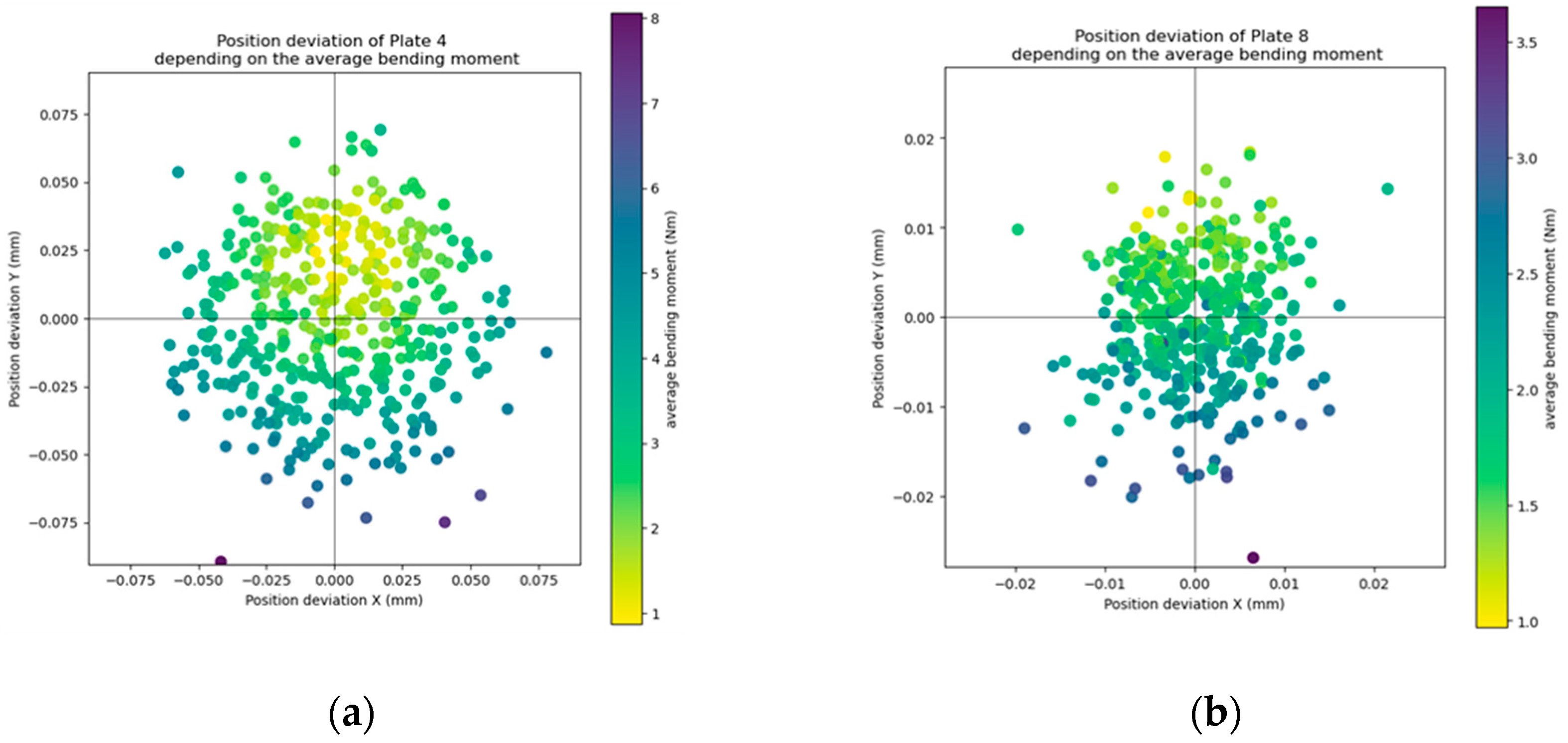
3.4. Analysis of Cutting Forces
4. Discussion
- An automated, cost-effective system was developed for surface quality measurement in reamed bores, using a NC-controlled gantry and a mobile stylus profilometer.
- The analysis of the profile data and separation of surface profiles into roughness and waviness components, according to the demanding DIN EN ISO standards, enables a more targeted analysis of process-specific issues.
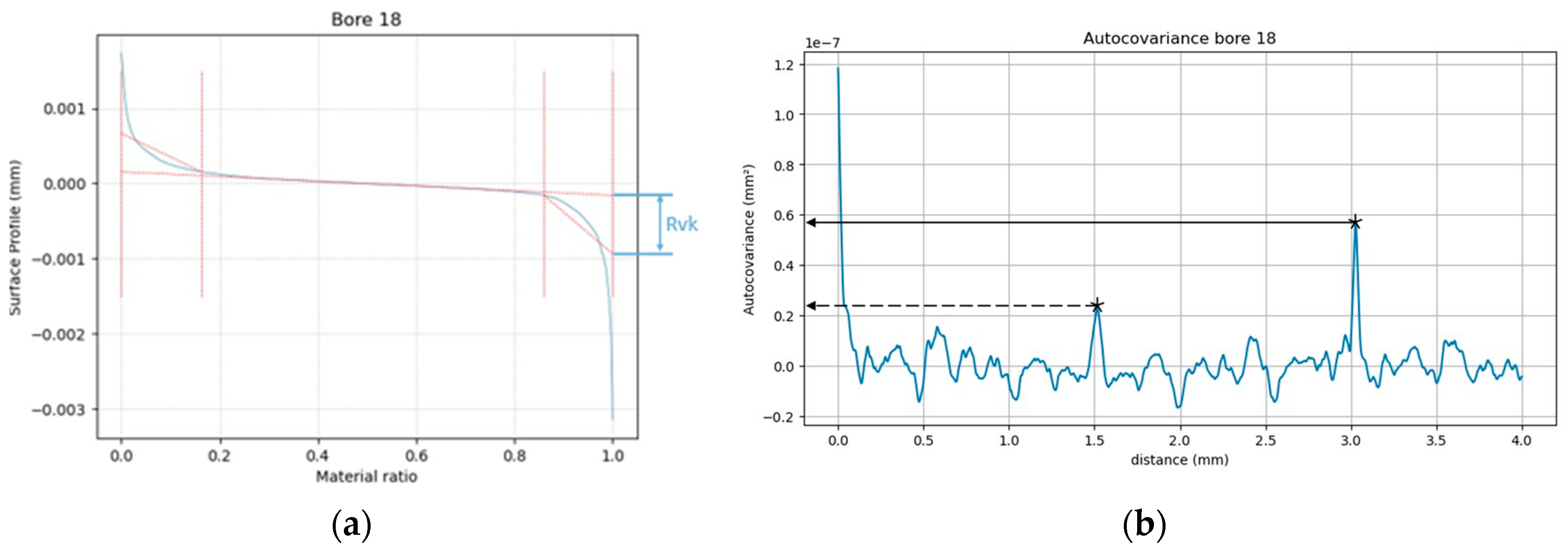
- Retraction grooves were clearly visualized using a 360° scan. An autocovariance-based approach was introduced to evaluate these grooves, offering a more specific assessment than standard metrics.
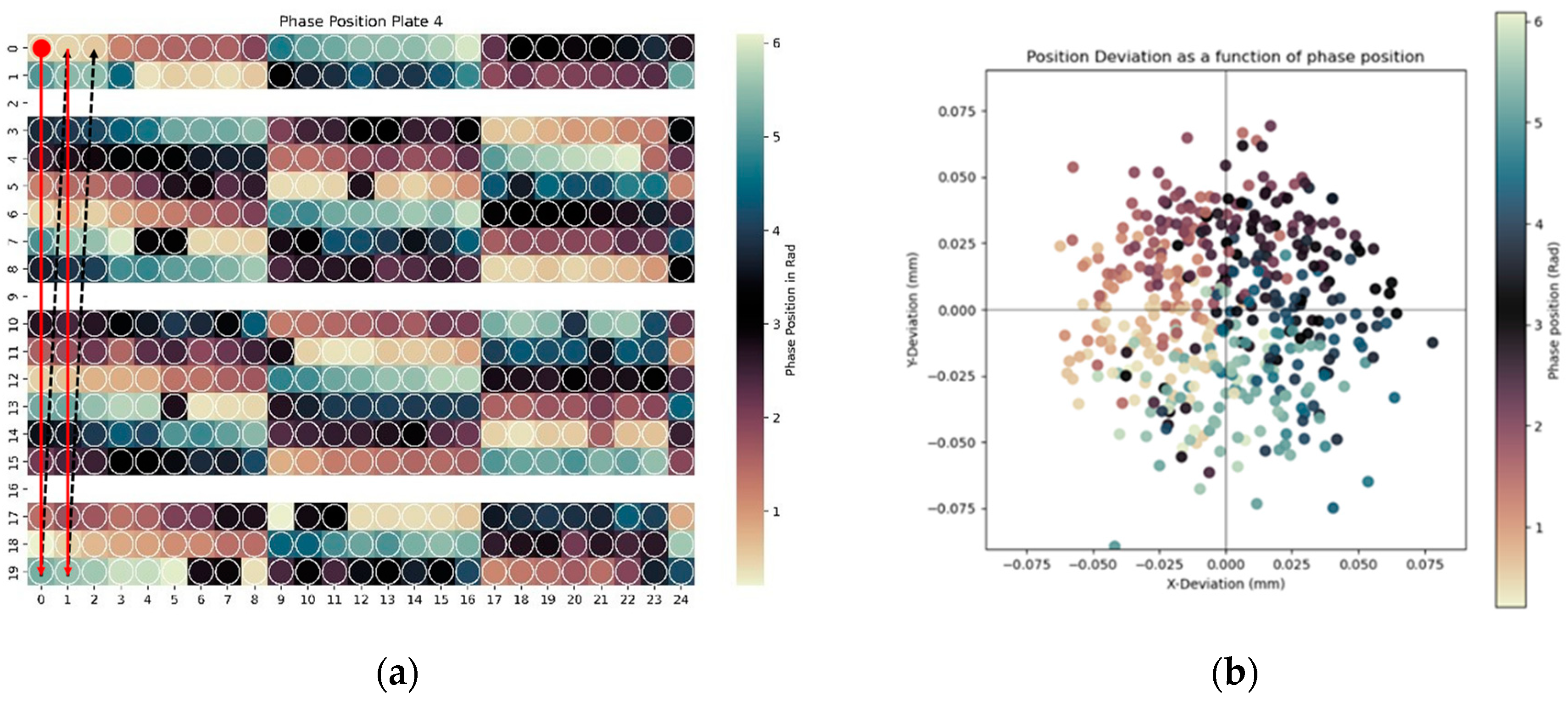
- The phase position of the waviness profile on the reamed surface correlates with tool entry angle and position deviation. By putting this phase position into context with the bore position in the workpiece, patterns associated with tool wear were identified, allowing for potential process improvements to reduce positional deviations.
- Process forces were measured and analysed to link bending moments with bore position deviations, revealing that bending moments increase significantly with larger positional deviations.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Unsin, S.; Dorer, C.; Müller, B.; Jung, T.; Limmer, A.; Schirmeier, F. Schritt für Schritt zur Zerspanungs-Ki. maschinenbau. 2024, 4, 10-15. https://www.springerprofessional.de/schritt-fuer-schritt-zur-zerspanungs-ki/27491970.
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y; Han, Z. Study on Characteristics for Reaming Titanium Alloy Ti6Al4V with Two Kinds of Cemented-Carbide Groove Reamers. Materials 2022, 15, 5027. [CrossRef]
- Lagoa Melo, T.F.; Ribeiro Filho, S.L.M.; Arruda, É.M.; Brandão, L.C. Analysis of the surface roughness, cutting efforts, and form errors in bore reaming of hardened steel using a statistical approach. Measurement. 2019, 134, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, A.A.; Machado, A.R.; Souza, A.M.; Ezugwu, E.O. Effects of machining parameters when reaming aluminium-silicon (SAE 322) alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 112, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheleznov, G.S.; Andreeva, S.G. Final Surface Roughness in Reaming Holes. Russ. Eng. Res. 2013, 33, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, P.; Genta, G.; Barbato, G.; De Chiffre, L.; Levi, R. Reaming process improvement and control: An application of statistical engineering. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2012, 5(3), 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, P.; De Chiffre, L. Reproducibility of surface roughness in reaming. Proceedings of the 4. Swedish Production Symposium. 2011.
- Wang, Y.; Cui, X.; Xu, H.; Jiang, K. Cutting force analysis in reaming of ZL102 aluminium cast alloys by PCD reamer. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 67, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretz, A.; Abele, E.; Weigold, M. Measuring the bore straightness during reaming with sensoric tools. 2020, Prod. Eng. Res. Devel. 14, 535–544. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, O.; Jun, M.B.; Kapoor, S.G.; DeVor, R.E. The effects of process faults and misalignments on the cutting force system and hole quality in reaming. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, R.C.; Bekinal, S.; Bhat, R.; Naik, N.; Kuttan, A. Dynamic Force Modelling and Experimental Analysis of Reaming. Engineered Science. 2021, 15, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakshith, M.C.; Kamath, R.C.; Vijay, G.S. Prediction of the Reaming Torque Using Artificial Neural Network and Random Forest Algorithm: Comparative Performance Analysis. Eng. Proc. 2023, 59, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




