Submitted:
23 January 2025
Posted:
24 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
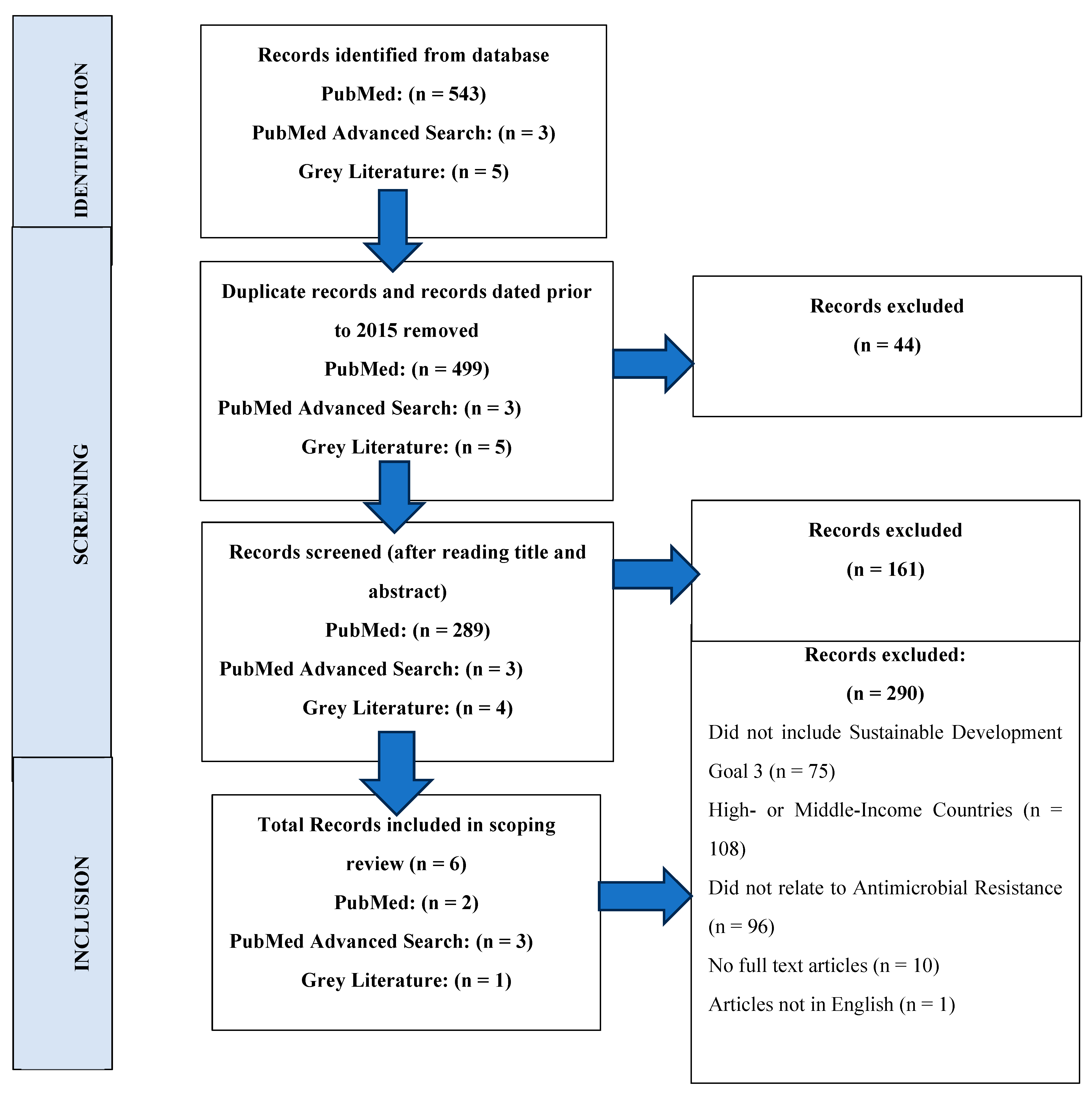
Background: The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs) are designed to be achieved by the year 2030, however, inadequate policies and lack of proper implementation of practices to control Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) has led to the failure of these SDG 3 targets. The targets and the control parameters align with each other as both pose the same challenges to the health sector by increasing morbidity and mortality and making sustainable development impossible. The aim of the study is to directly address the scope of literature available on the effect of AMR on UN SDG 3 targets. Methods: Free-access database with advanced search strategy for peer-reviewed literature and official websites are used to include six full-text publications following Cochrane guidelines for scoping review. The searches are conducted in January 2025; and results from 2015 to 2025 are considered. Results are filtered and extracted for relevant data, and was the identification and screening process was charted using a flow diagram. Results: A total of 543 results are identified from PubMed search, 3 from PubMed Advanced Search and 5 from organization websites. These are narrowed down after rigorous screening and filtration to include 6 publications in total, both from peer-reviewed journals and grey literature. The comparison of SDG 3 targets with AMR shows eight targets (3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4, 3.6 ,3.7 ,3.8, and 3.B), are directly or indirectly impacted by AMR. The interface of AMR and SDG 3 targets presents overlapping challenges, calling for improved policies to curb AMR and encourage SDG 3 target related efforts. Conclusion: The scoping review sums up the extent and nature of available data on this aspect. This provides a comprehensive insight into the evidence of the current status of SDG 3 targets in relation to AMR, highlighting the need of further research and policy amendments.
Keywords:
Introduction
Methodology
Study Design
Literature Search Strategy
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Results
Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgements
Competing Interests
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Consent for Publication
Availability of Data and Materials
References
- Alleyne G, Beaglehole R, Bonita RJTL. Quantifying targets for the SDG health goal. 2015;385(9964):208-9. [CrossRef]
- Mantegazza L, De Pascali AM, Munoz O, Manes C, Scagliarini A, Capua IJFiC, et al. Circular Health: exploiting the SDG roadmap to fight AMR. 2023;13:1185673. [CrossRef]
- Kiggundu R, Lusaya E, Seni J, Waswa J, Kakooza F, Tjipura D, et al. Identifying and addressing challenges to antimicrobial use surveillance in the human health sector in low-and middle-income countries: experiences and lessons learned from Tanzania and Uganda. 2023;12(1):9. [CrossRef]
- Pokharel S, Raut S, Adhikari BJBgh. Tackling antimicrobial resistance in low-income and middle-income countries. BMJ Specialist Journals; 2019. p. e002104. [CrossRef]
- Lewnard JA, Charani E, Gleason A, Hsu LY, Khan WA, Karkey A, et al. Burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in low-income and middle-income countries avertible by existing interventions: an evidence review and modelling analysis. 2024;403(10442):2439-54. [CrossRef]
- Kanan M, Ramadan M, Haif H, Abdullah B, Mubarak J, Ahmad W, et al. Empowering low-and middle-income countries to combat AMR by minimal use of antibiotics: A way forward. 2023;12(10):1504. [CrossRef]
- Zhou N, Cheng Z, Zhang X, Lv C, Guo C, Liu H, et al. Global antimicrobial resistance: a system-wide comprehensive investigation using the Global One Health Index. 2022;11(1):92. [CrossRef]
- Organization WH. Antimicrobial resistance and the United Nations sustainable development cooperation framework: Guidance for United Nations Country teams: World Health Organization; 2021.
- Gajdács M, Urbán E, Stájer A, Baráth ZJEJoIiH, Psychology, Education. Antimicrobial resistance in the context of the sustainable development goals: A brief review. 2021;11(1):71-82. [CrossRef]
- Shamas N, Stokle E, Ashiru-Oredope D, Wesangula EJIPiP. Challenges of implementing antimicrobial stewardship tools in Low to Middle Income Countries (LMICs). 2023;5(4):100315. [CrossRef]
- Armstrong R, Hall BJ, Doyle J, Waters EJJoph. ‘Scoping the scope’of a cochrane review. 2011;33(1):147-50. [CrossRef]
- Tang KWK, Millar BC, Moore JEJBJoBS. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR). 2023;80:11387.
- Sdg UJTeprTS. Sustainable development goals. 2019;7:805-14.
- Mahida N, Winzor G, Wilkinson M, Jumaa P, Gray JJJoHI. Antimicrobial stewardship in the post COVID-19 pandemic era: an opportunity for renewed focus on controlling the threat of antimicrobial resistance. 2022;129:121-3. [CrossRef]
- Stenberg K, Hanssen O, Edejer TT-T, Bertram M, Brindley C, Meshreky A, et al. Financing transformative health systems towards achievement of the health Sustainable Development Goals: a model for projected resource needs in 67 low-income and middle-income countries. 2017;5(9):e875-e87. [CrossRef]
- Humphreys G, Fleck FJWHOBotWHO. United Nations meeting on antimicrobial resistance. 2016;94(9):638. [CrossRef]
- Jasovský D, Littmann J, Zorzet A, Cars OJUjoms. Antimicrobial resistance—a threat to the world’s sustainable development. 2016;121(3):159-64. [CrossRef]
- Ferdinand A, Coppo M, Howden B, Browning G. Tackling antimicrobial resistance by integrating one health and the sustainable development goals. BMC Global Public Health. 2023; 1 (1): 11. [CrossRef]
- Hanefeld J, Khan M, Tomson G, Smith R. Trade is central to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals: A case study of antimicrobial resistance. BMJ 358: j3505. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Organization WH. Monitoring and evaluation of the global action plan on antimicrobial resistance: framework and recommended indicators. 2019.
- Mphande FA. Sustainable Health in Low and Middle Income Countries; Focus on SDG Target 3.3, 3b, 3c and 3d. Sustainable Health in Low and Middle Income Countries: Achieving SDG3 in the (Post) Pandemic World: Springer; 2023. p. 1-12.
- Joshi MP, Alombah F, Konduri N, Ndiaye A, Kusu N, Kiggundu R, et al. Moving from assessments to implementation: promising practices for strengthening multisectoral antimicrobial resistance containment capacity. 2023;5(1):7. [CrossRef]
- Sulis G, Sayood S, Gandra SJEroa-it. Antimicrobial resistance in low-and middle-income countries: current status and future directions. 2022;20(2):147-60. [CrossRef]
| Search String 1 (PubMed) | Effect of Antimicrobial Resistance on Sustainable Development Goals |
| Search String 2 for advanced search (PubMed Advanced Search) | (sustainable development goal) AND (antimicrobial resistance) |
| Limits | Title/Abstract |
| Filters | Year: 2015 – 2025, Language: English only, Articles: Full-text articles excluding preprints |
| No. of SDG 3 Targets | SDG 3 Target Title | Relation with AMR |
| Target 3.1 | Reduce Maternal Mortality | Increases maternal death rates by making infections harder to treat, leading to severe complications and treatment failures. |
| Target 3.2 | End all Preventable Deaths under 5 Years of Age | Makes common childhood infections, like pneumonia and diarrhea, harder to treat, leading to higher mortality rates in young children. |
| Target 3.3 | Fight Communicable Diseases | Reduces the effectiveness of antimicrobial drugs, making it more difficult to manage infections, control outbreaks, and prevent the spread of resistant pathogens. |
| Target 3.4 | Reduce Mortality from Non-Communicable Diseases and Promote Mental Health | Impedes the treatment of Non-Communicable Diseases like organ transplant and cancer during pre- and post-therapy antibiotic administrations. |
| Target 3.5 | Prevent and Treat Substance Abuse | N/A |
| Target 3.6 | Reduce Road Injuries and Deaths | Limiting the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy leading to longer recovery times and higher mortality rates. |
| Target 3.7 | Universal Access to Sexual and Reproductive Care, Family Planning and Education | Increases the incidence of Sexually Transmitted Diseases, perinatal and postnatal infections and deaths. |
| Target 3.8 | Achieve Universal Health Coverage | Increases the complexity and cost of treating infections, straining healthcare systems, and limiting access to effective treatments. |
| Target 3.9 | Reduce Illness and Death from Hazardous Chemicals and Pollution | N/A |
| Target 3.A | Implement the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control | N/A |
| Target 3.B | Support Research, Development and Universal Access to Affordable Vaccines and Medicines | Diverts resources and research efforts toward combating resistance, potentially slowing the development of new medicines and vaccines. |
| Target 3.C | Increase Health Financing and Support Health Workforce in Developing Countries | N/A |
| Study title | Authors (Year) | Study design | SDGs discussed | SDG 3 findings |
| Antimicrobial Resistance in the Context of the Sustainable Development Goals: A Brief Review | Gajdács, M., Urbán, E., Stájer, A., & Baráth, Z. (2021). | A perspective and a non-systematic review of the peer-reviewed and grey Literature |
SDG 1, 2, 3, 6, 8, 10, 12, 13, 17 | SDG 3 is only achievable when disadvantageous developments in antimicrobial resistance and related death toll issues are addressed. |
| AMR and Sustainable Development Goals: at a crossroads | Aslam, B., Asghar, R., Muzammil, S., Shafique, M., Siddique, A. B., Khurshid, M., ... & Baloch, Z. (2024). | A review including peer-reviewed research that addresses pre-formulated research questions | SDG 1, 2, 3, 6, 8, 10, 13, 17 | Equitable health service provision and universal access to antimicrobial drugs is vital to achieving SDG 3. |
| Antimicrobial resistance—a threat to the world's sustainable development | Jasovský, D., Littmann, J., Zorzet, A., & Cars, O. (2016). | A detailed commentary based on peer-reviewed and grey literature | SDG 3, and 1, 2, 6, 8, 12, 17 | Emergence of AMR not only poses a threat to universal health coverage, but also to the treatment of maternal and child health, communicable and non-communicable diseases. |
| Trade is central to achieving the sustainable development goals: a case study of antimicrobial resistance | Hanefeld, J., Khan, M., Tomson, G., & Smith, R. (2017). | A case study and analysis the importance of intelligence and resource trade for achieving SDGs | SDG 3, SDG 11, and SD 16 | In the light of SDG 3, access to health goods and medical intellects across the borders is vital to achieving control over AMR. |
| Tackling antimicrobial resistance by integrating One Health and the Sustainable Development Goals | Ferdinand, A. S., Coppo, M. J., Howden, B. P., & Browning, G. F. (2023). | A detailed commentary on SDGs affected by AMR | SDG 2, 3,6,and 17 | Supports One Health nature of AMR programs to incorporate SDG 3 and tackle challenges of these targets equitably around the globe. |
| Progress and Info - Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages | World Health Organization | A website publication based on research to assess the progress of SDG 3 | SDG 3 | Assessment of the progress of all targets of SDG 3. |
| Antimicrobial resistance and the United Nations sustainable development cooperation framework: guidance for United Nations country teams | United Nations SDGs | An advocacy brief with editors from WHO, FAO, OIE, and UNEP | All 17 SDGs | Highlights two main SDG indicators for AMR and pinpoints the dependence of LMICs on out-of-pocket healthcare payments is linked to antimicrobial resistance (AMR). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





