Submitted:
10 January 2025
Posted:
11 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction and State of the Art
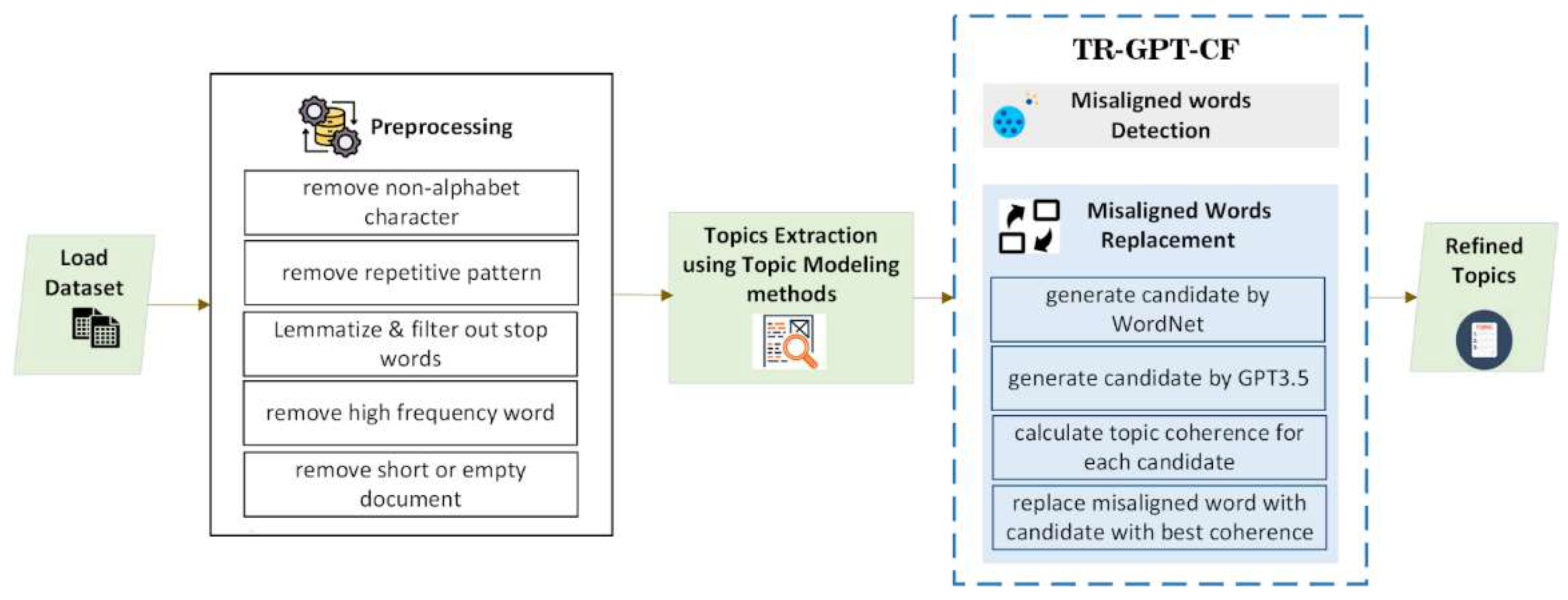
2. Materials and Methods
- Removing high-frequency words: Identifies and removes the most frequent words in the corpus, based on TF-IDF scores. This procedure prevents the model from focusing on very common words (e.g., “the”, “and”)
- Eliminating repetitive pattern: Eliminate redundant sequences such as like “hahahaha” or “hihihhihi” that contribute unnecessary noise to the corpus. This procedure uses regular expression to replace any character repeated three or more times with a single occurrence.
- Removing non-alphabet character: Employs regular expression to eliminate non-alphabetic characters.
- Eliminating very short document: Exclude documents that are excessively brief or potentially consist of solely of nonsensical content, which might not be meaningful for topic modeling.
| Algorithm 1. Pre-processing |
| Input: Corpus D, stop words SW, Minimum word count min_word_count Output: Preprocessed corpus Dprocessed |
| For each document dm ∈ D: convert dm to lowercase remove non-alphabetic characters from dm remove repetitive pattern from dm tokenize dm into words lemmatize each word w remove stop words w ∈ SW end for Compute high-frequency word vectorize D, using TF-IDF to obtain BoW calculate word frequencies freq(w) for all words w ∈ BoW identify most frequent word HF remove high frequency words w ∈ HF Filter short or empty document remove dm if |words(dm)| < min_word_count Return preprocessed corpus Dprocessed |
2.1. Misaligned Word Detection
| Algorithm 2. TR-GPT-CF |
| Input: A set of topics T = {t1, t2, …, tK}, Embedding model M, Corpus C, Large Language Model L, WordNet W, Z-score threshold θz, Inverse document frequency threshold θf` Output: Refine topics T’ = {{t’1, t’2, …, t’K}. 1: Initialize the set of refine topics T’ ← Ø 2: For each topic ti ∈ T do 3: Initialize the refined topic t’i ← ti 4: Compute the topic centroid using word embedding from M(ti) 5: For each word wj ∈ t’i: 6: Compute the centroid c ← mean M(ti) 7: Compute the cosine similarity s between wj and the centroid c 8: Compute Z-score z of similarities s 9: Compute IDF value IDF (wij, C) 10: if zij < θz and IDF (wij) > θf` then 11: mark wij as a misaligned word wmisaligned 12: for each detected misaligned word wmisaligned do 13: initialize WordNet W ← Ø 14: select wc most similar to the centroid c 15: retrieve a hypernym or hyponym of wc from WordNet W 16: generate via prompt L to provide alternative for wc in the context of ti 17: combine all candidates:WK ∪ LK 18: calculate the coherence score of all candidates 19: check if replacement word improves overall coherence score 20: replace wmisaligned in ti with whighest_coherence score else 21: retain wmisaligned 22: Update the refined topic t’i 23: End if no further improvement in coherence is observed 24: End for (for all topics in T) 25: Return the set of refined topics T’ |
2.2. Misaligned Word Replacement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluating Topic Coherence Improvement Across Datasets
3.1.1. Improvement of Topic Coherence in AGNews Dataset
3.1.2. Improvement of Topic Coherence in TagMyNews Dataset
3.1.3. Improvement of Topic Coherence in YahooAnswer Dataset
3.1.4. Improvement of Topic Coherence in Newsgroup Dataset
3.1.5. Improvement of Topic Coherence in SMS Spam Dataset
3.1.6. Improvement of Topic Coherence in Science Article Dataset
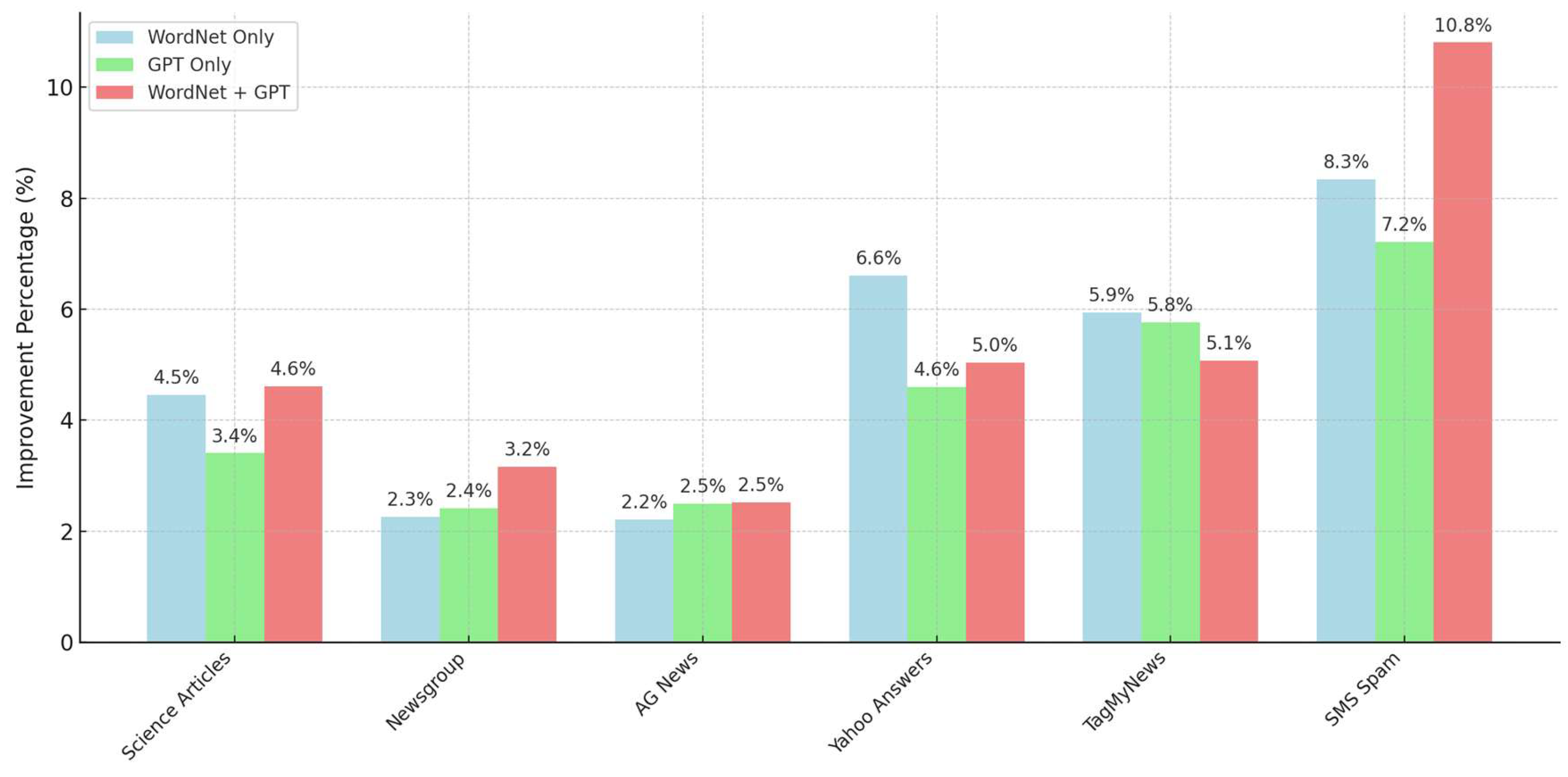
3.2. Evaluating Topic Coherence Improvements by Candidate Word Replacement: WordNet, GPT, and Combine Approaches
3.3. Evaluating Topic Coherence by Qualitative Comparison
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- K. Taghandiki and M. Mohammadi, “Topic Modeling: Exploring the Processes, Tools, Challenges and Applications,” Authorea Preprints, Oct. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Meddeb and L. Ben Romdhane, “Using Topic Modeling and Word Embedding for Topic Extraction in Twitter,” Procedia Comput Sci, vol. 207, pp. 790–799, Jan. 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Li, Y. Qian, Y. Jiang, Y. Liu, and F. Zhou, “A novel label-based multimodal topic model for social media analysis,” Decis Support Syst, vol. 164, p. 113863, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. Zankadi, A. Idrissi, N. Daoudi, and I. Hilal, “Identifying learners’ topical interests from social media content to enrich their course preferences in MOOCs using topic modeling and NLP techniques,” Educ Inf Technol (Dordr), vol. 28, no. 5, pp. 5567–5584, May 2023. [CrossRef]
- “Sentiment Analysis and Topic Modeling Regarding Online Classes on the Reddit Platform: Educators versus Learners | Enhanced Reader.”.
- E. Rijcken, U. Kaymak, F. Scheepers, P. Mosteiro, K. Zervanou, and M. Spruit, “Topic Modeling for Interpretable Text Classification From EHRs,” Front Big Data, vol. 5, p. 846930, May 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Somani, M. M. van Buchem, A. Sarraju, T. Hernandez-Boussard, and F. Rodriguez, “Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Analysis of Statin-Related Topics and Sentiments on Social Media,” JAMA Netw Open, vol. 6, no. 4, p. e239747, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Boyd-Graber, Y. Hu, and D. Mimno, “Applications of Topic Models,” Foundations and Trends® in Information Retrieval, vol. 11, no. 2–3, pp. 143–296, 2017. [CrossRef]
- D. M. Blei, A. Y. Ng, and J. B. Edu, “Latent Dirichlet Allocation,” Journal of Machine Learning Research, vol. 3, no. Jan, pp. 993–1022, 2003.
- D. M. Blei, “Probabilistic topic models,” Commun ACM, vol. 55, no. 4, pp. 77–84, Apr. 2012. [CrossRef]
- L. Liu, L. Tang, W. Dong, S. Yao, and W. Zhou, “An overview of topic modeling and its current applications in bioinformatics,” SpringerPlus 2016 5:1, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 1–22, Sep. 2016. [CrossRef]
- D. M. Blei and J. D. Lafferty, “A correlated topic model of Science,” https://doi.org/10.1214/07-AOAS114, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 17–35, Jun. 2007. [CrossRef]
- Z. Fang, Y. He, and R. Procter, “BERTTM: Leveraging Contextualized Word Embeddings from Pre-trained Language Models for Neural Topic Modeling,” May 2023, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2305.09329.
- M. Bewong et al., “DATM: A Novel Data Agnostic Topic Modeling Technique With Improved Effectiveness for Both Short and Long Text,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 32826–32841, 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. Marani and E. P. S. Baumer, “A Review of Stability in Topic Modeling: Metrics for Assessing and Techniques for Improving Stability,” ACM Comput Surv, vol. 56, no. 5, Feb. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Chang, S. Gerrish, C. Wang, J. Boyd-graber, and D. Blei, “Reading Tea Leaves: How Humans Interpret Topic Models,” Adv Neural Inf Process Syst, vol. 22, 2009.
- T. Y. Lee, A. Smith, K. Seppi, N. Elmqvist, J. Boyd-Graber, and L. Findlater, “The human touch: How non-expert users perceive, interpret, and fix topic models,” Int J Hum Comput Stud, vol. 105, pp. 28–42, Sep. 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. El-Assady, R. Kehlbeck, C. Collins, D. Keim, and O. Deussen, “Semantic concept spaces: Guided topic model refinement using word-embedding projections,” IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 1001–1011, Jan. 2020. [CrossRef]
- F. Sperrle, H. Schäfer, D. Keim, and M. El-Assady, “Learning Contextualized User Preferences for Co-Adaptive Guidance in Mixed-Initiative Topic Model Refinement,” Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 40, no. 3, pp. 215–226, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. M. H. Ur Rehman and K. Wakabayashi, “Keyphrase-based Refinement Functions for Efficient Improvement on Document-Topic Association in Human-in-the-Loop Topic Models,” Journal of Information Processing, vol. 31, pp. 353–364, 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Chang, R. Wang, P. Ren, and H. Huang, “Enhanced Short Text Modeling: Leveraging Large Language Models for Topic Refinement,” ArXiv, Mar. 2024, Accessed: Nov. 30, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.17706v1.
- “News-Classification/train_data.csv at master · vijaynandwani/News-Classification · GitHub.” Accessed: Dec. 05, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://github.com/vijaynandwani/News-Classification/blob/master/train_data.csv.
- “SMS Spam Collection Dataset.” Accessed: Dec. 05, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/uciml/sms-spam-collection-dataset.
- “Topic Modeling for Research Articles.” Accessed: Dec. 05, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/blessondensil294/topic-modeling-for-research-articles?select=train.csv.
- X. Wu, C. Li, Y. Zhu, and Y. Miao, “Short Text Topic Modeling with Topic Distribution Quantization and Negative Sampling Decoder,” EMNLP 2020 - 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Proceedings of the Conference, pp. 1772–1782, 2020. [CrossRef]
- W. Xu, X. Liu, and Y. Gong, “Document clustering based on non-negative matrix factorization,” pp. 267–273, Jul. 2003. [CrossRef]
- M. Grootendorst, “BERTopic: Neural topic modeling with a class-based TF-IDF procedure,” Mar. 2022, Accessed: Jun. 20, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.05794v1.
- R. Wang et al., “Neural Topic Modeling with Bidirectional Adversarial Training,” Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 340–350, Apr. 2020. [CrossRef]
- G. A. Miller, “WordNet,” Commun ACM, vol. 38, no. 11, pp. 39–41, Nov. 1995. [CrossRef]
- “API platform | OpenAI.” Accessed: Dec. 17, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://openai.com/api/.
- S. Bhatia, J. H. Lau, and T. Baldwin, “Topic Intrusion for Automatic Topic Model Evaluation,” Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, EMNLP 2018, pp. 844–849, 2018. [CrossRef]
- A. Thielmann, A. Reuter, Q. Seifert, E. Bergherr, and B. Säfken, “Topics in the Haystack: Enhancing Topic Quality through Corpus Expansion,” Computational Linguistics, vol. 50, no. 2, pp. 619–655, Jun. 2024. [CrossRef]
- J. Devlin, M. W. Chang, K. Lee, and K. Toutanova, “BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding,” NAACL HLT 2019 - 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies - Proceedings of the Conference, vol. 1, pp. 4171–4186, Oct. 2018, Accessed: Dec. 17, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805v2.
- P. D. Domanski, “Statistical outlier labelling - A comparative study,” 7th International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies, CoDIT 2020, pp. 439–444, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Röder, A. Both, and A. Hinneburg, “Exploring the space of topic coherence measures,” WSDM 2015 - Proceedings of the 8th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 399–408, Feb. 2015. [CrossRef]
| Dataset | Description | Content Type | Average Length (word) | Size (document/article) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGNews | News of articles across major topics | News articles | 30 | 120,000 |
| SMS Spam | Message labeled as spam or ham | Short text messages | 10-20 | 5,574 |
| TagMyNews | English news articles | News headlines | 15-20 | 32,000 |
| YahooAnswer | User-generated Q&A | Question and answer pairs | 100 | 1,400,000 |
| 20Newsgroup | Newsgroup posts across 20 topics | Full news posts and threads | 200 | 18,000 |
| Kaggle’s Research Article | Research articles for topic modeling exercises |
Title and Abstract of Research Article | 200 | 20,972 |
| Aspect | LDA | NMF | BERTopic | G-BAT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Model | Probabilistic | Matrix Decomposition | Neural (Embedding+Clustering) |
Neural (VAE+Adversarial) |
| Input representation |
Bag of Words | TF-IDF Matrix | Contextual Embeddings |
Pre-trained Embeddings |
| Output |
|
|
|
|
| Topic Representation |
Topic-word | Topic-word | Cluster centers and their representative words | Latent space clusters |
| Strength |
|
|
|
|
| Weakness |
|
|
|
|
| Best Use Cases |
|
|
|
|
| Application |
|
|
|
|
| Word | Cosine similarity | Z-score |
|---|---|---|
| Word A | 0.85 | 0.40 |
| Word B | 0.87 | 0.50 |
| Word C | 0.83 | 0.30 |
| Word D | 0.90 | 0.65 |
| Word E | 0.40 | - 1.85 |
| Model | t-statistic | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| LDA | -2.723 | 0.042 |
| BERTopic | -3.491 | 0.017 |
| G-BAT | -3.251 | 0.023 |
| NMF | -2.318 | 0.068 |
| Model | Before Refinement | After Refinement | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDA | 0.591 | 0.617 | 4.40 |
| BERTopic | 0.897 | 0.901 | 0.45 |
| G-BAT | 0.453 | 0.471 | 3.97 |
| NMF | 0.771 | 0.790 | 2.45 |
| Model | Before Refinement | After Refinement | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDA | 0.336 | 0.431 | 28.27 |
| BERTopic | 0.539 | 0.572 | 6.12 |
| G-BAT | 0.646 | 0.650 | 0.62 |
| NMF | 0.589 | 0.604 | 2.55 |
| Model | Before Refinement | After Refinement | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDA | 0.485 | 0.503 | 3.71 |
| BERTopic | 0.706 | 0.745 | 5.52 |
| G-BAT | 0.468 | 0.492 | 5.13 |
| NMF | 0.564 | 0.581 | 3.01 |
| Model | Before Refinement | After Refinement | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDA | 0.583 | 0.602 | 3.26 |
| BERTopic | 0.823 | 0.839 | 1.94 |
| G-BAT | 0.209 | 0.293 | 40.19 |
| NMF | 0.743 | 0.743 | 0.00 |
| Model | Before Refinement | After Refinement | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDA | 0.461 | 0.487 | 5.64 |
| BERTopic | 0.506 | 0.552 | 9.09 |
| G-BAT | 0.494 | 0.570 | 15.38 |
| NMF | 0.427 | 0.483 | 13.11 |
| Model | Before Refinement | After Refinement | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDA | 0.526 | 0.544 | 3.42 |
| BERTopic | 0.731 | 0.740 | 1.23 |
| G-BAT | 0.265 | 0.341 | 28.68 |
| NMF | 0.614 | 0.619 | 0.81 |
| Dataset | Model | Extracted Topic | Refined Topic | Misaligned Word | Replacement Word |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGNews | LDA | year, u, sale, percent, share, cut, inc, profit, china, report | sales_event, u, sale, percent, share, cut, inc, profit, china, report | year, report | sales_event, |
| NMF | president, bush, state, afp, election, united, Kerry, talk, john, nuclear | president, bush, state, senator, election, united, Kerry, talk, john, nuclear | afp | senator | |
| BERTopic | tendulkar, test, sachin, cricket, zealand, Australia, wicket, Nagpur, ponting, mcgrath | trial_run, test, sachin, cricket, zealand, Australia, wicket, nagpur, ponting, mcgrath | tendulkar | trial_run | |
| G-BAT | bond, course, sale, poor, chief, charley, low, bay, coming, pick | bond, course, sale, poor, quest charley, low, bay, coming, pick | chief | quest | |
| TagMyNews | LDA | world, u, year, job, court, star, coach, musical, john, wednesday. | world, planet, year, job, court, star, coach, musical, john, earth. | u, wednesday | planet, earth |
| NMF | japan, nuclear, earthquake, plant, crisis, tsunami, radiation, stock, power, quake. | japan, nuclear, earthquake, ionizing radiation, crisis, tsunami, radiation, stock, power, quake. | plant | ionizing radiation | |
| BERTopic | trial, jury, insider, rajaratnam, guilty, former, blagojevich, prosecutor, lawyer, accused. | trial, jury, insider, rajaratnam, guilty, former, prosecuting_officer, prosecutor, lawyer, accused. | blagojevich | prosecuting_ officer |
|
| G-BAT | yankee, south, focus, abidjan, shuttle, stake, Bahrain, wont, coach, nuclear | yankee, south, focus, center, shuttle, stake, Bahrain, wont, coach, nuclear | abidjan | center | |
| YahooAnswer | LDA | range, x, water, b, weight, size, test, running, speed, force. | range, x, water, mass, weight, size, test, running, speed, force. | b | mass |
| NMF | help, thanks, plz, problem, tried, yahoo, appreciated, site, computer | help, thanks, lend a hand problem, tried, yahoo, appreciated, site, computer. |
plz | lend a hand | |
| BERTopic | guy, friend, love, girl, relationship, talk, boyfriend, together, he, married | guy, friend, love, girl, relationship, talk, boyfriend, together, he, young_man. | married | young_man | |
| G-BAT | ability, mac, common, test, time, shes, running, medicine, deal, maybe | ability, mac, common, test, time, trade, running, medicine, deal, maybe. | shes | trade | |
| Newsgroup | LDA | line, subject, organization, writes, article, like, one, dont, would, get. | line, subject, organization, writes, article, like, one, pay_back, would, get. | dont | pay_back |
| NMF | window, file, program, problem, use, application, using, manager, run, server. | window, file, program, problem, use, application, using, software, run, server. | manager | software | |
| BERTopic | printer, font, print, deskjet, hp, laser, ink, bubblejet, bj, atm | printer, font, print, deskjet, hp, laser, ink, bubblejet, laser printer, atm. | bj | laser printer | |
| G-BAT | drive, matthew, file, dead, clipper, ride, pat, drug, tax, manager. | drive, matthew, file, dead, repulse, ride, pat, drug, tax, manager. | clipper | repulse | |
|
SMS Spam |
LDA |
number, urgent, show, prize, send, claim, u, message, contact, sent. |
number, urgent, show, correspondence, send, claim, u, message, contact, sent. |
prize |
correspondence |
| NMF | ill, later, sorry, meeting, yeah, aight, tonight, right, meet, thing. | ill, later, sorry, meeting, yeah, match, tonight, right, meet, thing. | aight | match | |
| BERTopic | lunch, dinner, eat, food, pizza, hungry, weight, eating, lor, menu. | lunch, dinner, eat, food, pizza, hungry, weight, eating, selection, menu. | lor | selection | |
| G-BAT | abiola, loving, ltgt, player, cool, later, big, waiting, regard, dude. | abiola, loving, bed, player, cool, later, big, waiting, regard, dude. | ltgt | bed | |
| Science Article | LDA | state, system, phase, quantum, transition, field, magnetic, interaction, spin, energy. | state, system, phase, quantum, transition, changeover, magnetic, interaction, spin, energy. | field | changeover |
| NMF | learning, deep, task, training, machine, model, feature, neural, classification, representation. | learning, deep, task, training, machine, model, feature, neural, train, representation. | classification | train | |
| BERTopic | logic, program, language, semantic, automaton, proof, calculus, verification. | logic, program, language, semantic, reasoning, proof, calculus, verification. | automaton | reasoning | |
| G-BAT | graph, space, constraint, site, integer, logic, frame, patient, diffusion, clustering. | graph, space, constraint, site, integer, logic, frame, patient, diffusion, dispersal. | clustering | dispersal |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





