Content Negotiation, Backward Compatibility, Software Maintenance
Introduction
APIs are mechanisms that enable two software components to communicate with each other using a set of definitions and protocols. For example, the weather bureau's software system contains daily weather data. The weather app on your phone “talks” to this system via APIs and shows you daily weather updates on your phone.
REST stands for Representational State Transfer, which refers to the transfer of a representational state. REST defines a set of functions, such as GET,POST, PUT, DELETE, etc., that clients can use to access data on the server. Clients and servers exchange data using the HTTP protocol.
API versioning isn't just a nice-to-have - it's crucial for developers working with APIs. Here's why:
- I.
Reasons to Version APIs
1. Breaking changes Sometimes you need to shake things up. Versioning lets you make big changes without breaking existing stuff. 2. New features Want to add cool new endpoints or data fields? Versioning lets you do it without forcing everyone to update at once. 3. Bug fixes and security updates Roll out critical fixes while keeping older versions stable. It's like having your cake and eating it too. 4. Gradual migration gives users time to move to newer versions. No sudden disruptions, no panic.As described in [
7], the principles of software versioning can significantly enhance API maintainability and evolution strategies.
||. Benefits of Versioning
Stability: Users can stick with what works for them.
Flexibility: Improve your API without breaking things.
Clear communication: Version numbers make changes easy to track.
Easier maintenance: Support multiple versions side by side.[
6]
Spring Boot
Spring Boot helps you to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring-based applications that you can run. We take an opinionated view of the Spring platform and third-party libraries, so that you can get started with minimum fuss. Most Spring Boot applications need very little Spring configuration.
Spring Boot also provides built-in tools such as Spring Boot Actuator for monitoring and managing applications, and Spring Initializr, which allows developers to generate project structures and configurations with ease. It integrates seamlessly with the entire Spring ecosystem, making it ideal for building microservices, RESTful APIs, and enterprise-level applications.
API Versioning in Spring Boot
- 1)
URI Versioning:
URI path versioning is one of the most basic and widely used methods. The version number is in the URI path, making it clear and easy to read. Simple to implement and understand.
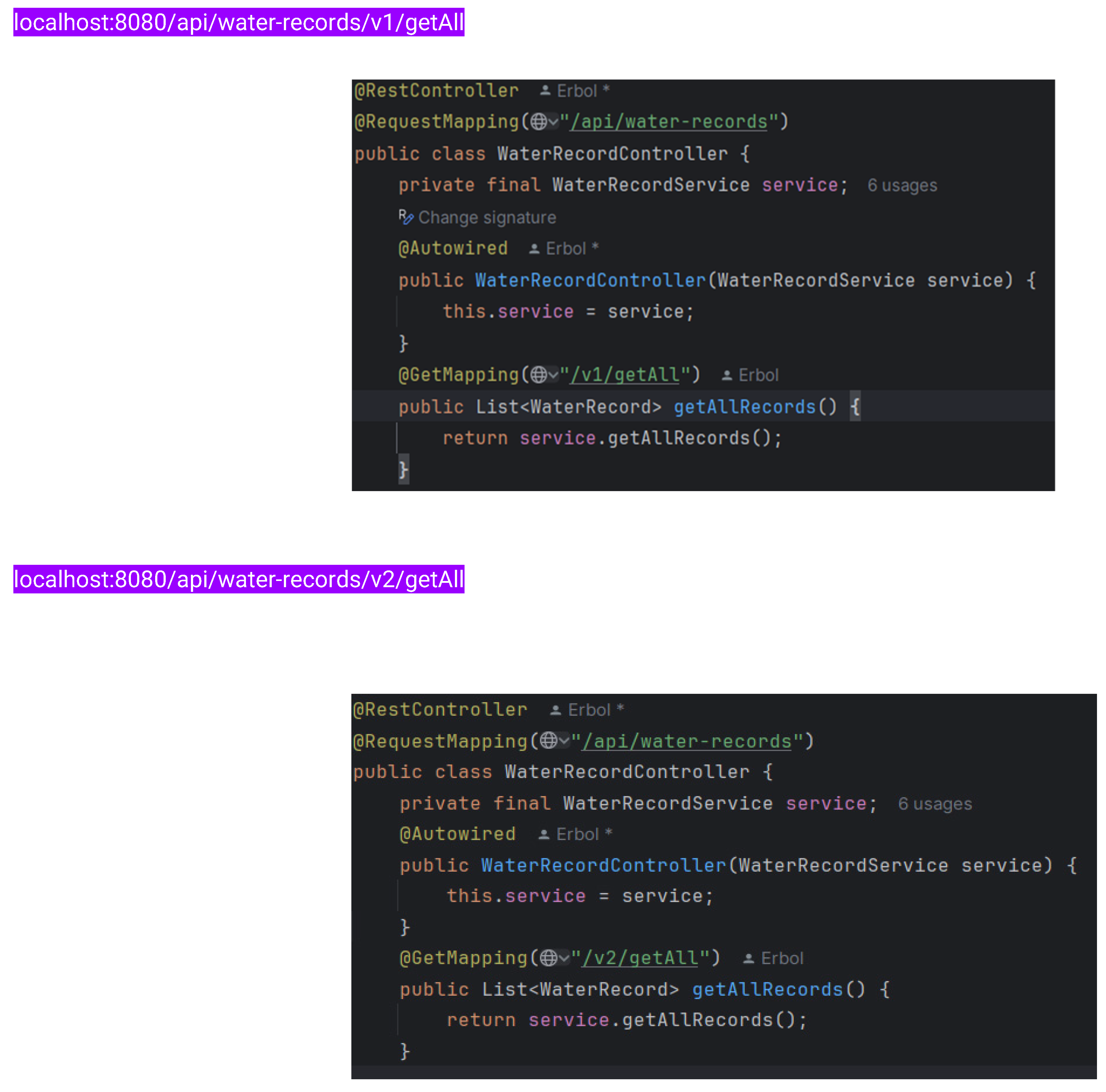
Changes in the URI structure can affect caching.
This can lead to duplication of resources if not managed properly.
2)
Header-based Versioning
In header versioning, the version number is specified in the HTTP request headers. This technique removes versioning information from the URI and keeps it clean.Clean and uncluttered URIs.Flexible and easily extensible.
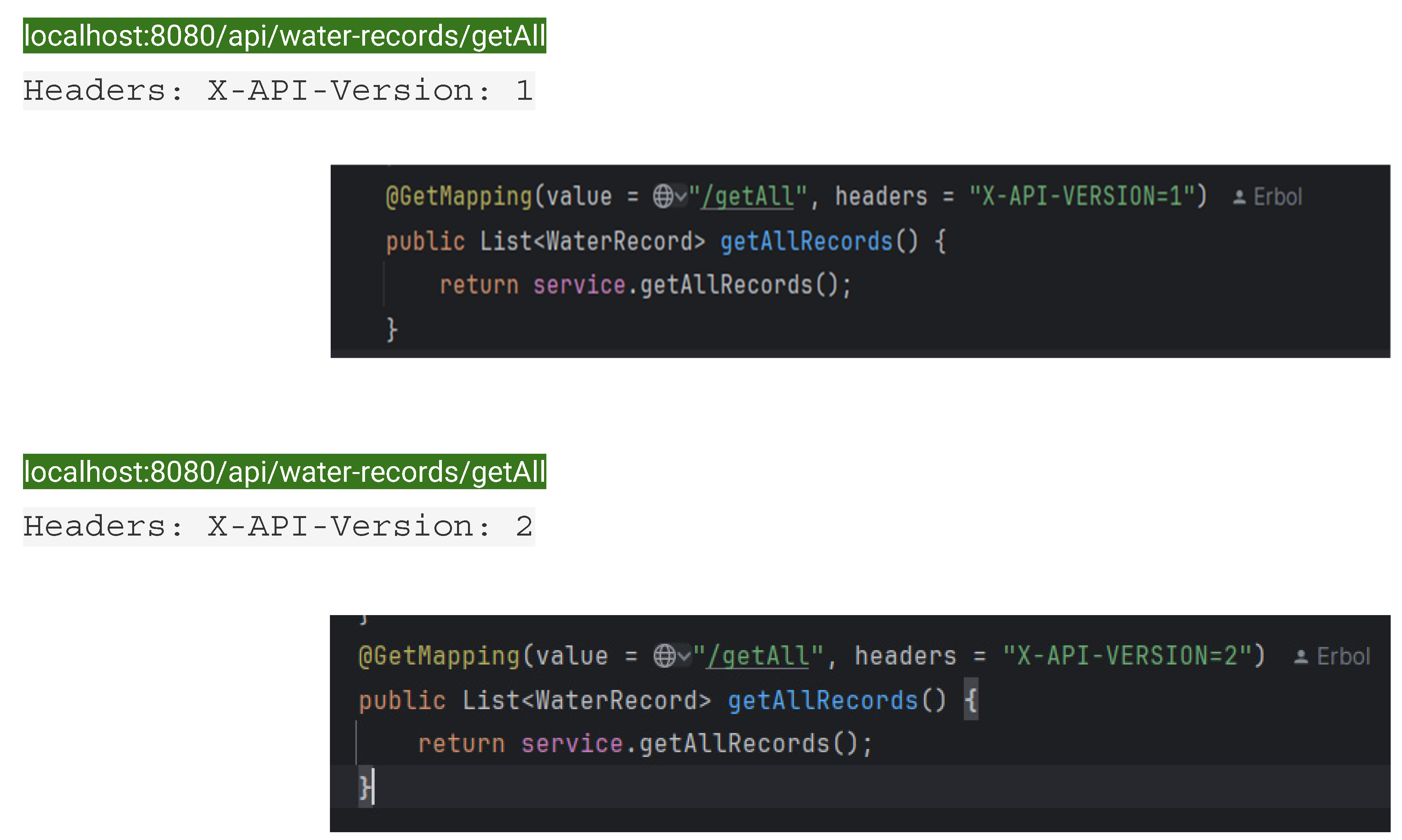
Less visible, making it harder for developers to know which version they are using.
Requires custom logic to handle headers.
3)
Query Parameter Versioning
The process in which version number is passed as a query or request parameter. It is less impertinent approach than URI Path Versioning. It is not as much helpful for consumers.In this method, the version is specified as a query parameter in the request URL.
Pros:
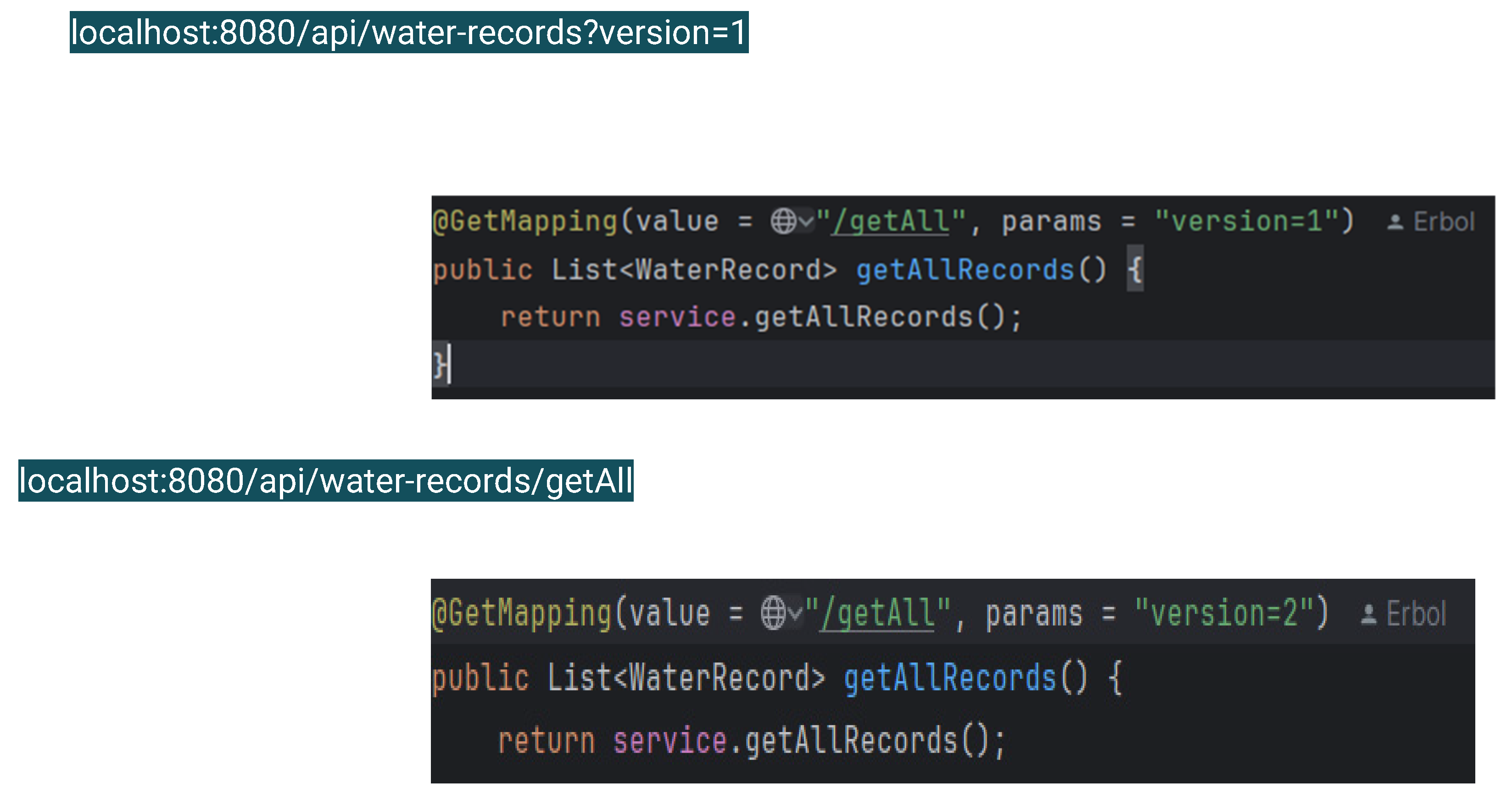
Less visible than URI path versioning.
This can complicate URI management and routing logic.
4)
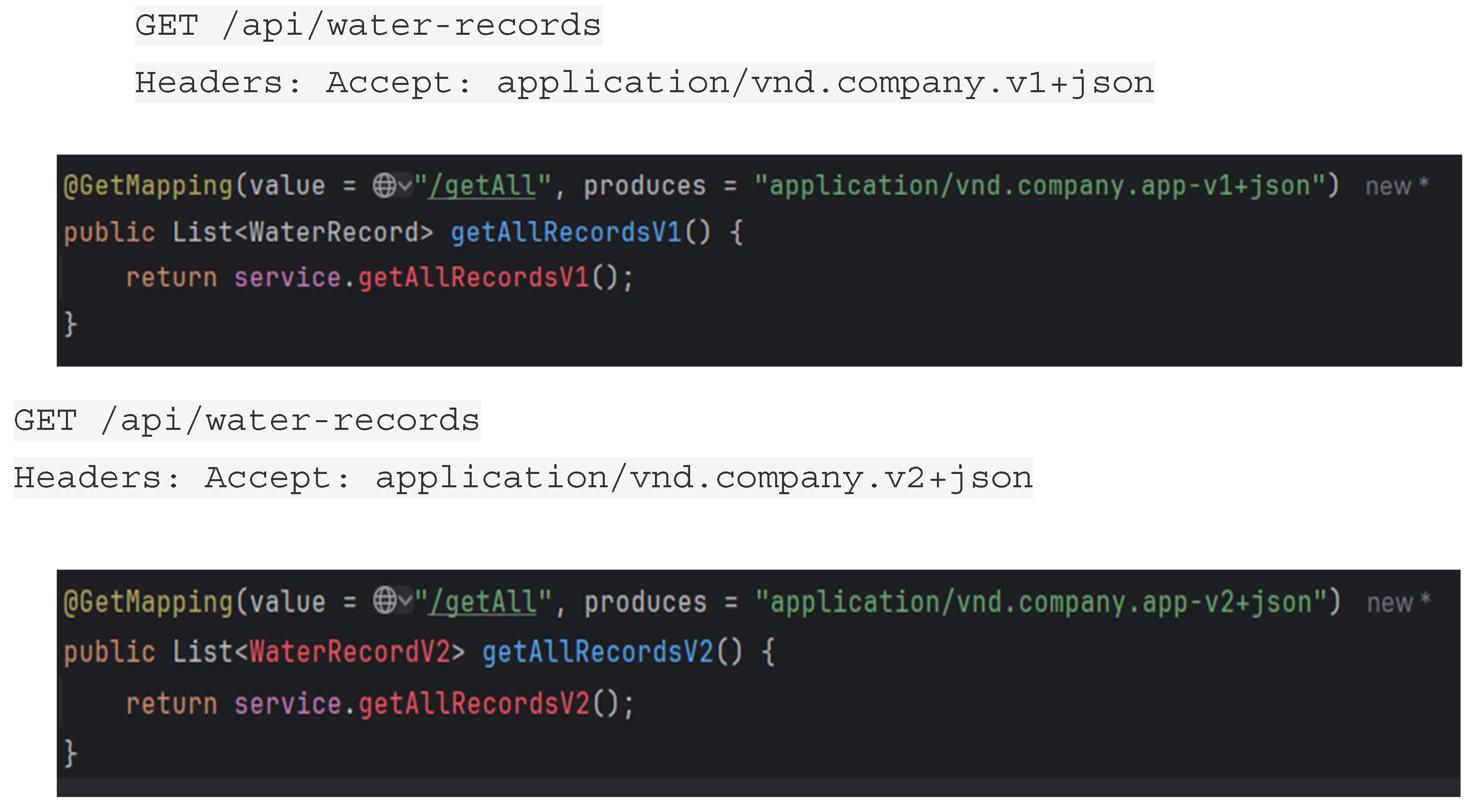
Content Negotiation Versioning
Content negotiation uses the Accept header to specify the desired version of the API. In this method, version is a part of content Negotiation.
Clean URIs.
Standard HTTP mechanism for versioning.
Reasons to Version APIs
As discussed in [
8], the use of voice assistants, like the Holographic Intellectual Voice Assistant (HIVA), emphasizes the importance of maintaining user-friendly, adaptable systems that evolve without disrupting existing services. Similarly, API versioning in distributed systems ensures backward compatibility, allowing for the seamless introduction of new features while preserving stability for current users.
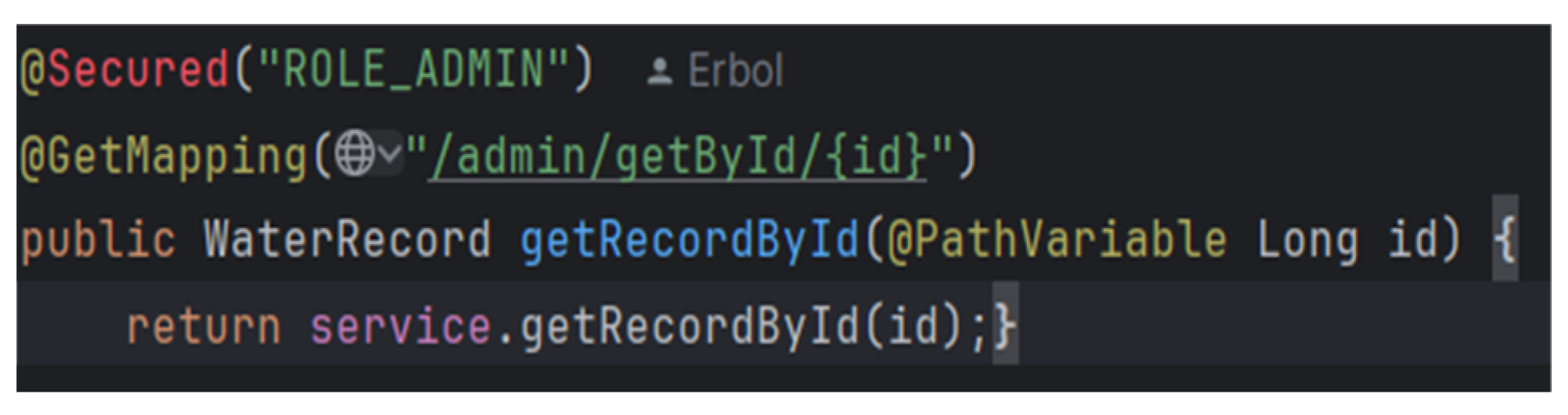
Secure REST Endpoints
Conclusion
"API versioning is very important for keeping an API strong and working well. By learning about different ways to version an API, developers can make changes easily without causing problems for users.
The best versioning method depends on what your API and its users need. You can choose methods like adding the version to the URL, using query parameters, headers, or content negotiation. The most important thing is to explain changes clearly and have good documentation.
To handle API versioning well, you should follow simple rules, like having a clear versioning plan, removing old versions slowly, and using simple version numbers. This will help both developers and users have a better experience."
References
- Available online: https://softwareguide.medium.com/securing-rest-apis-with-spring-boot-a-step-by-step-guide-5a754f821d0f.
- Available online: https://akadar899.medium.com/understanding-security-risks-of-exposing-entities-in-spring-boot-api-b6a57e3a45f.
- Available online: https://cyclr.com/blog/how-to-manage-api-versioning-a-technical-guide#:~:text=URI%20path%20versioning%20is%20one,explicit%20and%20easy%20to%20understand.&text=Pros%3A,Simple%20to%20implement%20and%20understand.
- Available online: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/spring-boot-versioning-a-rest-api/.
- Available online: https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/api/#:~:text =APIs%20are%20mechanisms%20that%20enable,weather%20updates%20on%20your%20phone.
- Available online: https://daily.dev/blog/api-versioning-strategies-best-practices-guide#:~:text=API%20versioning%20tracks%20changes%20to,gives%20users%20control%20over%20upgrades.
- Toktosunova, A.; Ergeshov, G. Esenalieva, A. Ermakov, R. Isaev, "Developing an Artificial Intelligence Tool for Image Generation Using a Unique Dataset with Image-to-Image Functionality," Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Systems and …, 2024. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=MEuCoikAAAAJ&pagesize=80&citation_for_view=MEuCoikAAAAJ:M3ejUd6NZC8C.
- Isaev R., R. G., Esenalieva G., M. R., D. E., Gulzada R. (2023). HIVA: Holographic Intellectual Voice Assistant. 17th International Conference on Electronics, Computer, and Computation.
- Available online: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=MEuCoikAAAAJ&pagesize=80&citation_for_view=MEuCoikAAAAJ:3fE2CSJIrl8C.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).








