Submitted:
08 January 2025
Posted:
09 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
First-principles calculations are performed to examine the physical features of full Heusler ln2MnW. The WIEN2K code is utilized with the variety of approximations, including the GGA and GGA + U, to examine the structural, electronic, and magnetic properties. The unit cell is optimized to achieve the ground state energy level. The calculated ΔH for In2MnW is -0.189 eV. This negative ΔH value signifies the thermodynamic stability of the compound. The metallic behavior of the investigated compound is confirmed by the calculated band structure (BS) with both potentials. These potentials are also used to calculate the total density of the state, which confirm their metallic nature. Total magnetic moment value is recorded as 4.3 µB while addition of U parameter slightly enhances its value to 4.4 µB. These studied properties indicate that ln2MnW has a metallic ferromagnetic character and is ideally appropriate for the usage of mass storage devices as a ferromagnetic material.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Computational Method
3. Results and Discussion
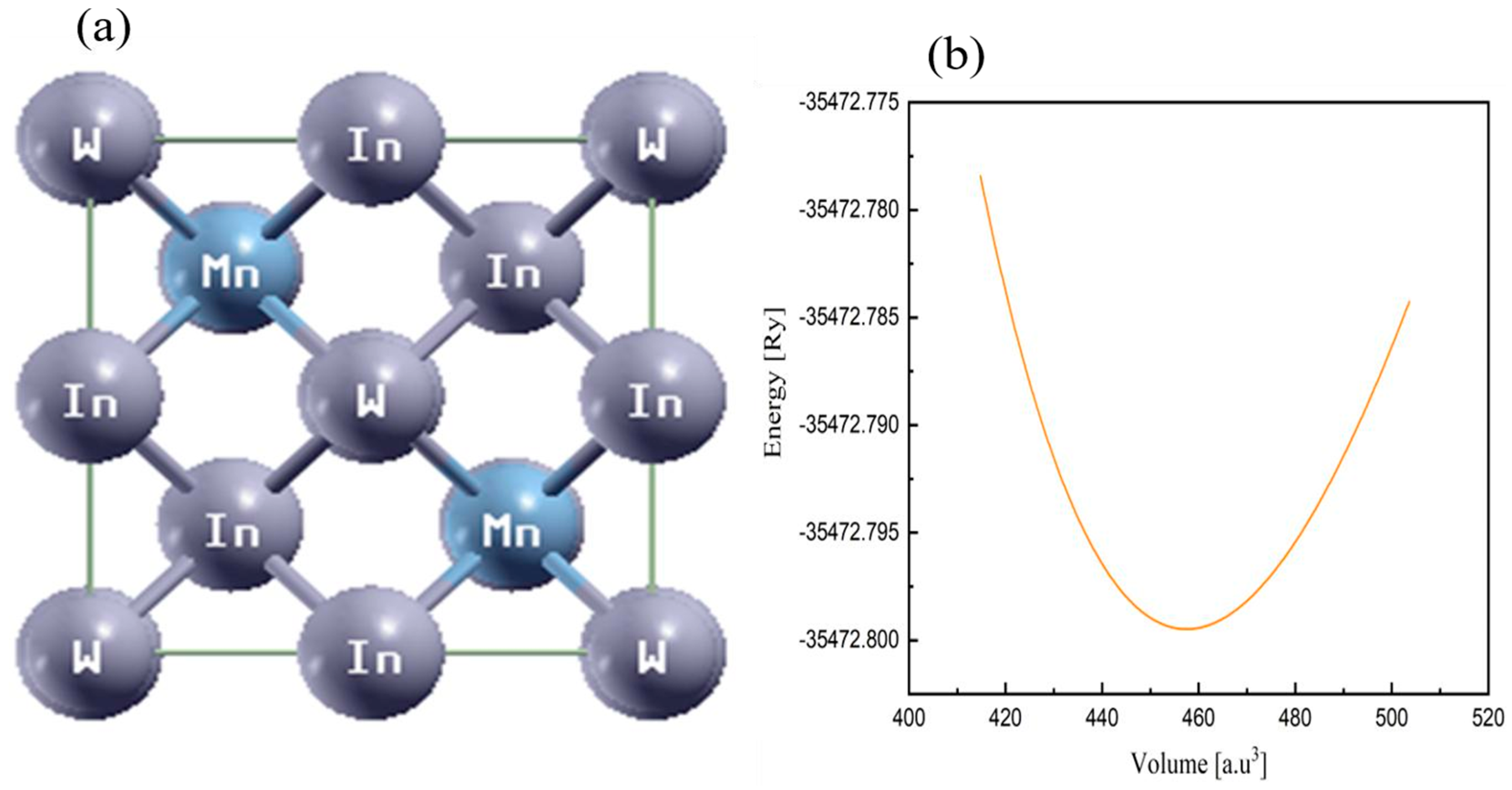
3.1. Structural Properties
3.1.1. Lattice Parameters
3.2. Electronic Characteristics
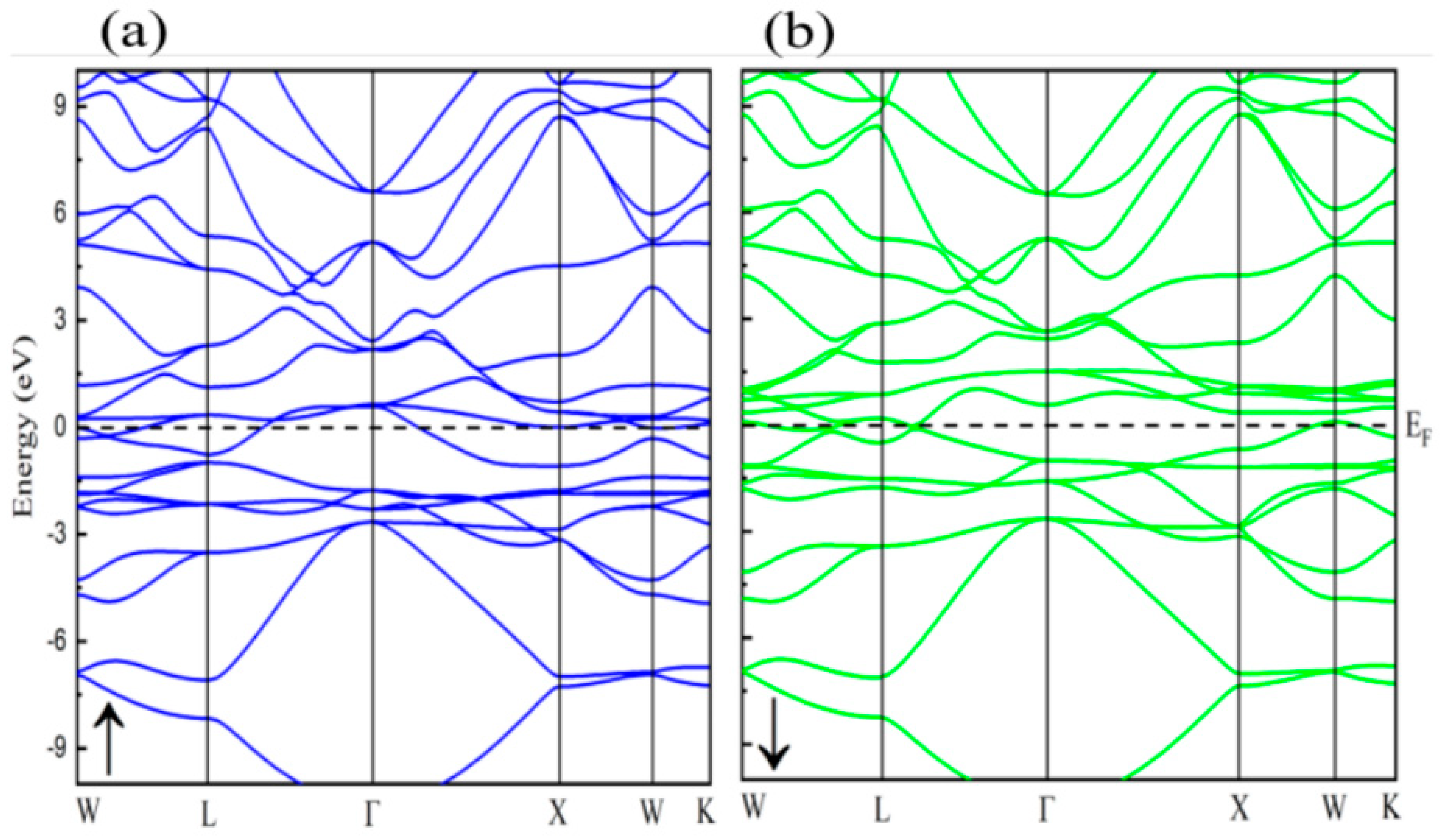
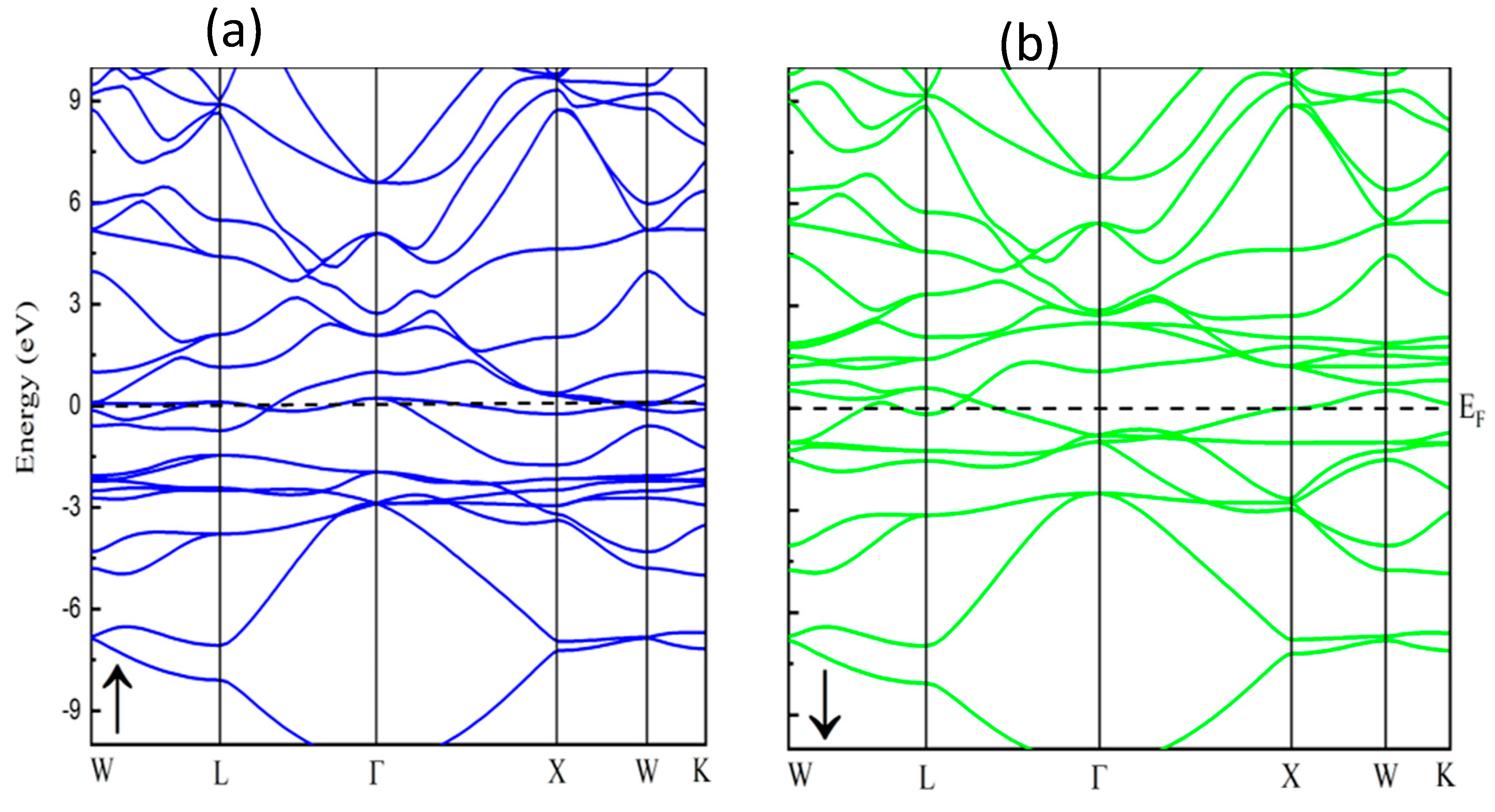
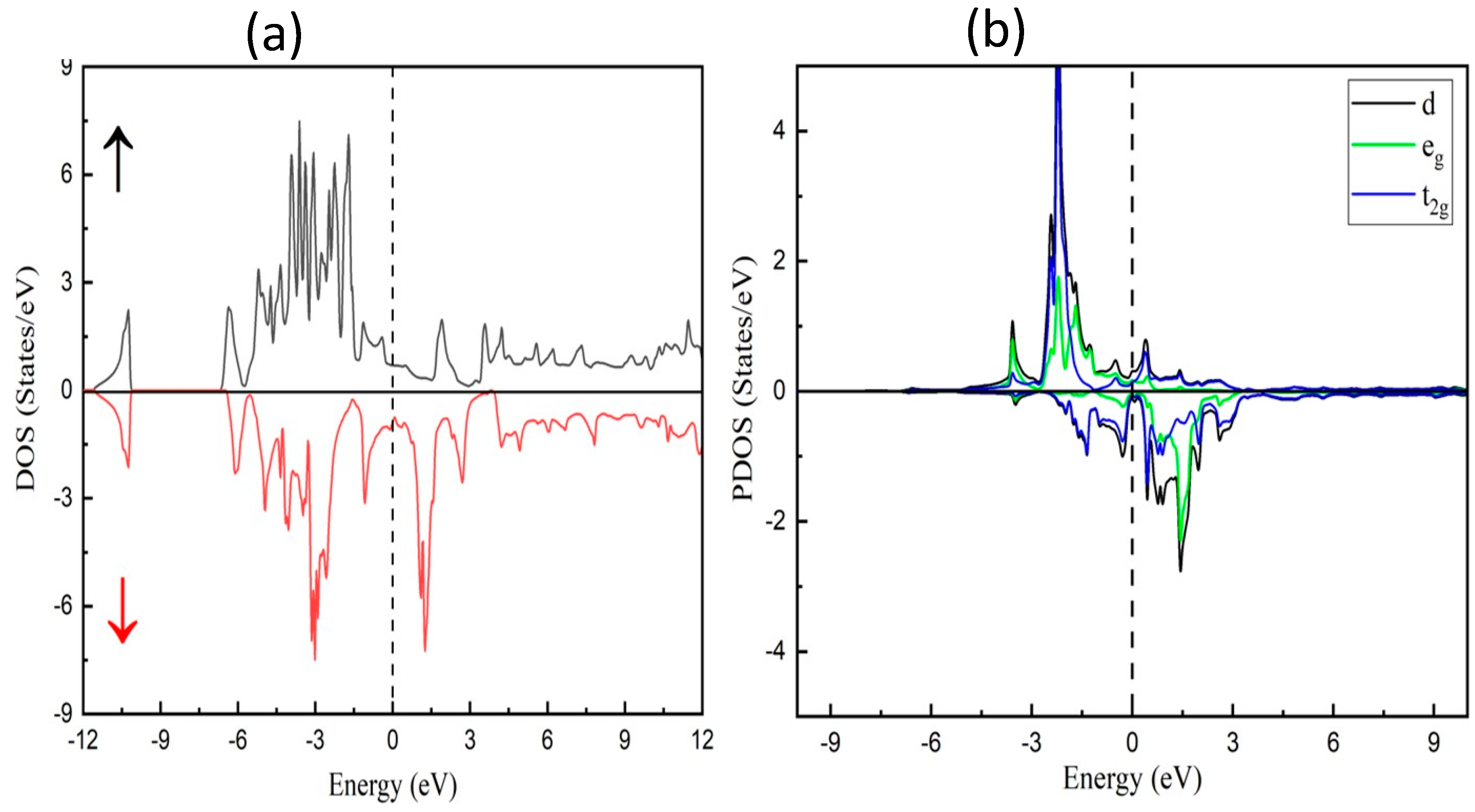
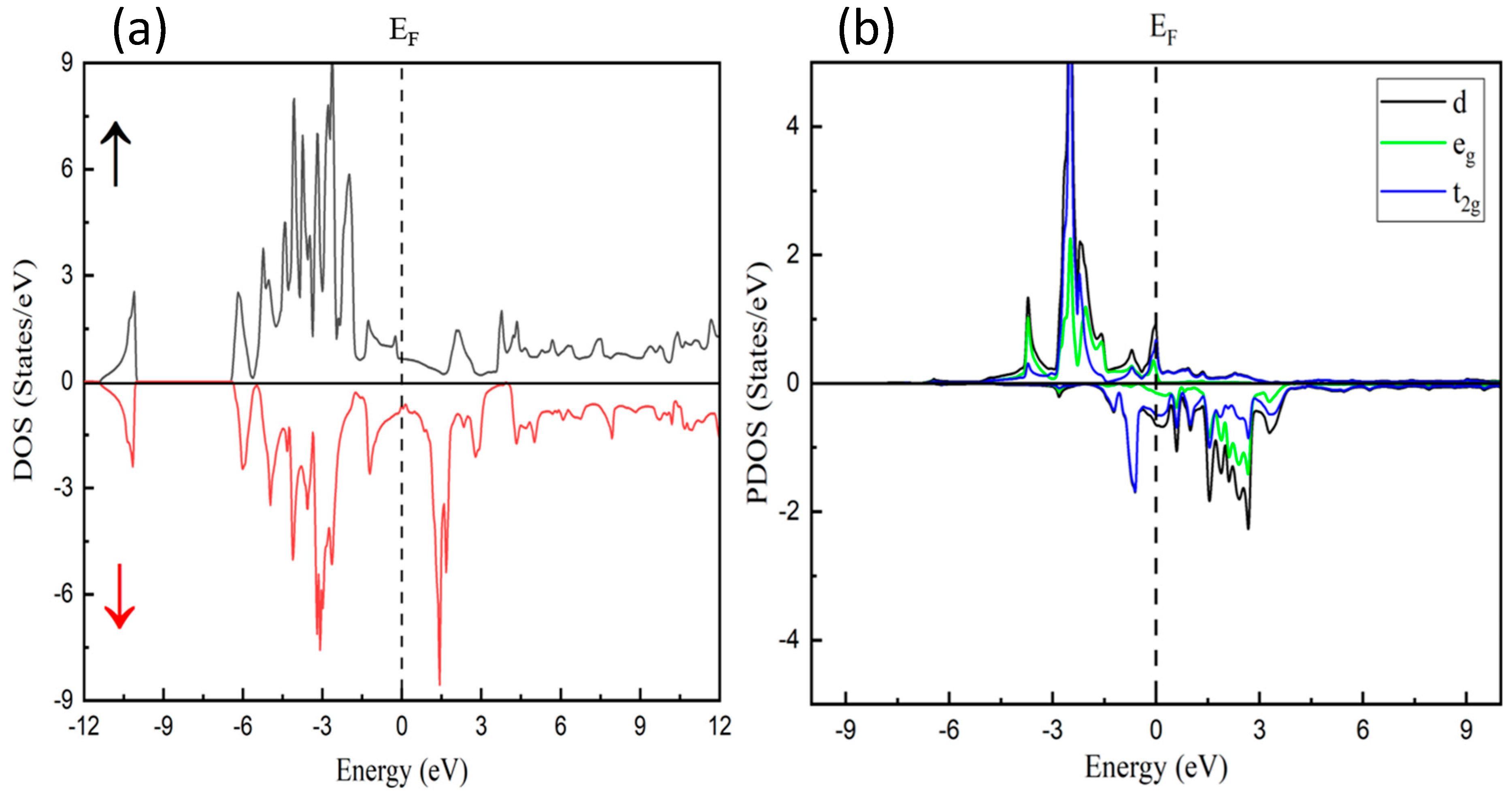
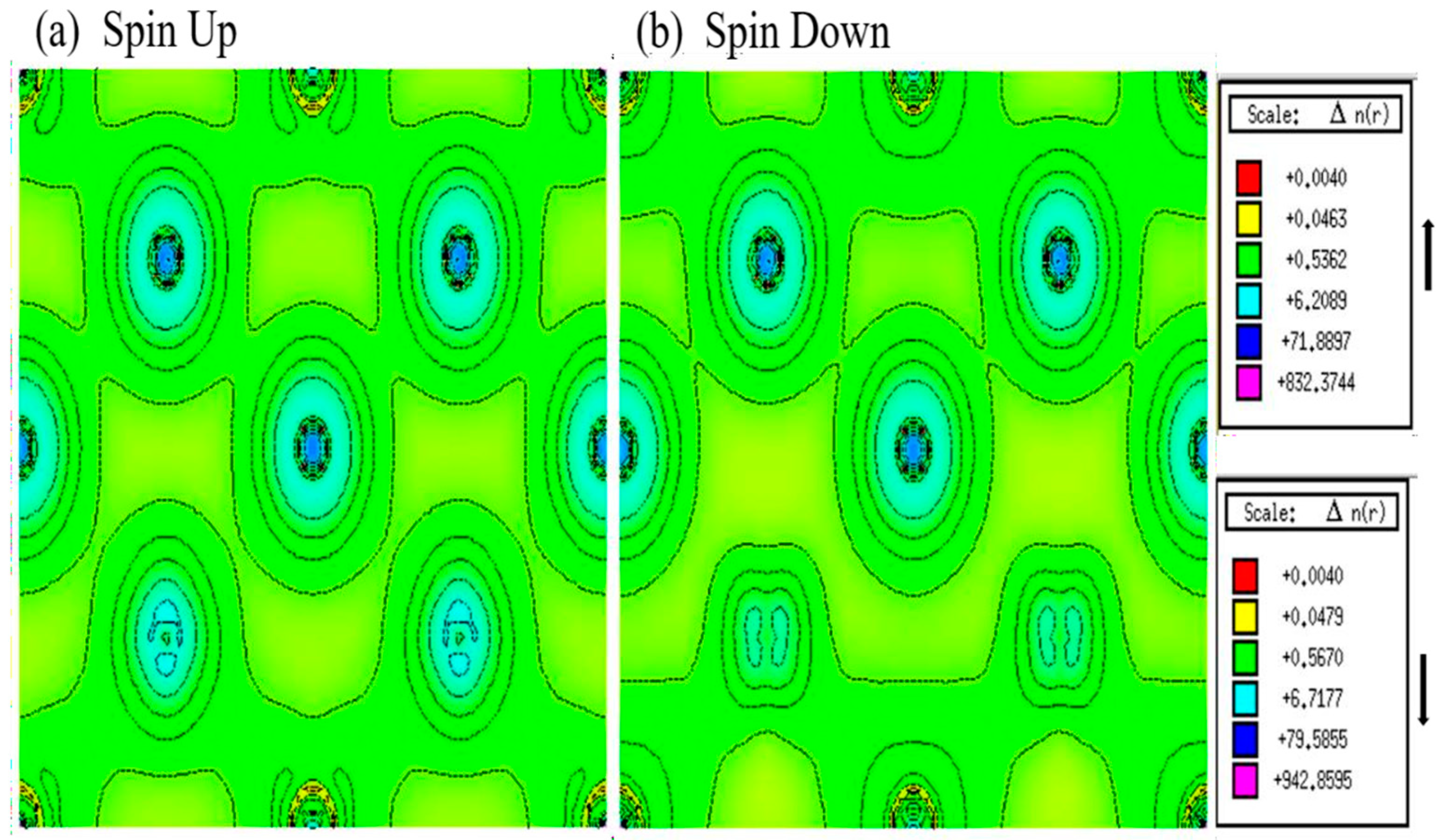
3.3. Magnetic Properties
4. Conclusions
Data Availability Statement
Conflict of Interest
References
- T. Graf, C. Felser, S.S.P. Parkin, Heusler Compounds: Applications in Spintronics, in: Handbook of Spintronics, Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, 2016: pp. 335–364. [CrossRef]
- G. Bulman, B. Cook, High-efficiency energy harvesting using TAGS-85/half-Heusler thermoelectric devices, in: N.K. Dhar, P. Balaya, A.K. Dutta (Eds.), 2014: p. 911507. [CrossRef]
- A. Erkisi, G. Surucu, The investigation of electronic, magnetic, mechanical, and lattice dynamical properties of Pd MX ( M = Cr, Fe and X = Si and Ge) ferromagnetic half-Heusler metallics: an ab initio study, Mater Res Express 4 (2017) 066504. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Meyer, N. Teichert, A. Auge, E. Rausch, B. Balke, A. Hütten, G.H. Fecher, C. Felser, Heusler nanoparticles for spintronics and ferromagnetic shape memory alloys, Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, Nanotechnology and Microelectronics: Materials, Processing, Measurement, and Phenomena 32 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Hirohata, H. Sukegawa, H. Yanagihara, I. Zutic, T. Seki, S. Mizukami, R. Swaminathan, Roadmap for Emerging Materials for Spintronic Device Applications, IEEE Trans Magn 51 (2015) 1–11. [CrossRef]
- N.S. Chauhan, Y. N.S. Chauhan, Y. Miyazaki, Contrasting role of bismuth doping on the thermoelectric performance of VFeSb half-Heusler, J Alloys Compd 908 (2022) 164623. [CrossRef]
- R.O. Agbaoye, P.O. R.O. Agbaoye, P.O. Adebambo, B.I. Adetunji, O. Osafile, G.A. Adebayo, Thermoelectric properties, optimal doping levels and high figure of merit in Cobalt-based Half/Full Heusler alloys by First-Principles calculations, Materials Science and Engineering: B 248 (2019) 114409. [CrossRef]
- P.O. Adebambo, O.E. P.O. Adebambo, O.E. Osafile, J.A. Laoye, M.A. Idowu, G.A. Adebayo, Electronic fitness function, effective mass and thermoelectric properties of Rh-based (-ScTe; -TiSb; -VSn) alloys for thermoelectric generator applications, Computational Condensed Matter 26 (2021) e00523. [CrossRef]
- T. Graf, S.S.P. T. Graf, S.S.P. Parkin, C. Felser, Heusler Compounds—A Material Class With Exceptional Properties, IEEE Trans Magn 47 (2011) 367–373. [CrossRef]
- W. Xie, A. W. Xie, A. Weidenkaff, X. Tang, Q. Zhang, J. Poon, T. Tritt, Recent Advances in Nanostructured Thermoelectric Half-Heusler Compounds, Nanomaterials 2 (2012) 379–412. [CrossRef]
- Osafile, J.O. Azi, Structural, electronic, elastic and mechanical properties of novel ZrMnAs half Heusler alloy from first principles, Physica B Condens Matter 571 (2019) 41–49. [CrossRef]
- B.D. Terris, T. B.D. Terris, T. Thomson, Nanofabricated and self-assembled magnetic structures as data storage media, J Phys D Appl Phys 38 (2005) R199–R222. [CrossRef]
- Page, C. Uher, P.F. Poudeu, A. Van der Ven, Phase separation of full-Heusler nanostructures in half-Heusler thermoelectrics and vibrational properties from first-principles calculations, Phys Rev B 92 (2015) 174102. [CrossRef]
- G. Rogl, A. G. Rogl, A. Grytsiv, M. Gürth, A. Tavassoli, C. Ebner, A. Wünschek, S. Puchegger, V. Soprunyuk, W. Schranz, E. Bauer, H. Müller, M. Zehetbauer, P. Rogl, Mechanical properties of half-Heusler alloys, Acta Mater 107 (2016) 178–195. [CrossRef]
- R. Dahal, G. R. Dahal, G. Chandra Kaphle, V. Kumar Jha Binod Adhikari Kapil Adhikari, STRUCTURAL, ELECTRONIC AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF XYZ TYPE HALF-HEUSLER ALLOYS, 2019.
- G. Fiedler, P. G. Fiedler, P. Kratzer, Ternary Semiconductors NiZrSn and CoZrBi with half-Heusler structure: a first-principles study, (2016). [CrossRef]
- M. Wakeel, G. M. Wakeel, G. Murtaza, H. Ullah, S. Khan, A. Laref, Z. Ameer, S.A. Khan, Structural, electronic, and magnetic properties of palladium based full Heusler compounds: DFT study, Physica B Condens Matter 608 (2021) 412716. [CrossRef]
- K. Schwarz, P. K. Schwarz, P. Blaha, G.K.H. Madsen, Electronic structure calculations of solids using the WIEN2k package for material sciences, Comput Phys Commun 147 (2002) 71–76. [CrossRef]
- P. Blaha, K. P. Blaha, K. Schwarz, P. Sorantin, S.B. Trickey, Full-potential, linearized augmented plane wave programs for crystalline systems, Comput Phys Commun 59 (1990) 399–415. [CrossRef]
- J.P. Perdew, K. J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, M. Ernzerhof, Generalized gradient approximation made simple, Phys Rev Lett 77 (1996) 3865–3868. [CrossRef]
- Nasarullah, M. Yaseen, S.A. Aldaghfag, M. Zahid, Misbah, Physical characteristics of X2NaMoBr6 (X= K, Rb): A DFT study, Mater Sci Semicond Process 147 (2022). [CrossRef]
- T. Graf, F. T. Graf, F. Casper, J. Winterlik, B. Balke, G.H. Fecher, C. Felser, al Crystal, Crystal Structure of New Heusler Compounds, 635 (2009). [CrossRef]
- F. Birch, The effect of pressure upon the elastic parameters of isotropic solids, according to Murnaghan’s theory of finite strain, J Appl Phys 9 (1938) 279–288. [CrossRef]
- Osafile, J.O. Azi, Structural, electronic, elastic and mechanical properties of novel ZrMnAs half Heusler alloy from first principles, Physica B Condens Matter 571 (2019) 41–49. [CrossRef]
- S. Rauf, S. S. Rauf, S. Arif, M. Haneef, B. Amin, The first principle study of magnetic properties of Mn2WSn, Fe2YSn (Y=Ti, V), Co2YSn (Y=Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Mn) and Ni2YSn (Y=Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Mn) heusler alloys, Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids 76 (2015) 153–169. [CrossRef]
- M. Nazar, Nasarullah, S.A. Aldaghfag, M. Yaseen, M. Waqas, M.K. Butt, I. Boukhris, Electronic, Structural, Optical, and Magnetic Characteristics A2MgS4 of (A=Dy, Er) Spinel Sulfides: A Density Functional Theory Study, Phys Status Solidi B Basic Res (2023). [CrossRef]
- M. Nazar, Nasarullah, M.I. Shatha A. Aldaghfag, Muhammad Yaseen, S.N. Rasheed Ahmed Khera, M.H. Abdellattif, First-principles calculations to investigate structural, magnetic, optical, electronic and thermoelectric properties of X2MgS4(X=Gd, Tm) spinel sulfides, Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids 166 (2022). [CrossRef]
| Lattice parameters | Lattice constant | Vo | BP | B (Gpa) | E0 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM | FM | AFM | |||||
|
Pd2MnSb Exp.a,b |
6.33 6.413a 6.420c |
490.1032 ----------- |
5.00 ----------- |
203.9194 --------- |
-58182.48 ------------- |
-58182.51 ------------- |
-581821.51 -------------- |
| Parameter | GGA | GGA +U |
|---|---|---|
| Total magnetic moment | 4.33 | 4.408 |
| Magnetic moment of Mn | 4.1 | 4.1 |
| Magnetic moment of W | -0.02600 | -0.02500 |
| Magnetic moment of ln | 0.17218 | 0.15 |
| Interstitial | 0.17218 | 0.083 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




