1. Introduction
Digital transformation has become a crucial aspect of organizational progress today, markedly changing operational frameworks and redefining performance metrics. The integration of digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, cloud computing, and big data analytics, has revolutionized the operational structures of service-oriented businesses globally. In Bangladesh, a developing economy increasingly emphasizing digitalization, service-oriented enterprises have been using technological advancements to sustain competitiveness and improve efficiency. This study investigates the influence of digital transformation on enhancing operational efficiency within Bangladeshi service enterprises, a sector with considerable potential for growth and innovation. The article recognizes the critical importance of digital transformation in rectifying inefficiencies, enhancing consumer satisfaction, and improving organizational productivity, providing a comprehensive understanding of its applications and impacts in an expanding economy.
The increasing digitization of service delivery processes has profoundly transformed the operations and interactions of enterprises with their stakeholders. Digital transformation encompasses several strategies, including customer service automation and supply chain optimization, which significantly improve company productivity (Emon & Khan, 2024). Service-oriented organizations in Bangladesh, including banks, healthcare facilities, educational institutions, and e-commerce platforms, have started the use of digital technology to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve customer experiences (Emon, 2023). Technological adoptions are often driven by the need to address operational inefficiencies, adapt to evolving consumer behaviors, and maintain competitiveness in a more digital economy. Recent studies highlight the transformative impact of digital technologies on organizational processes, demonstrating their ability to minimize redundancy, enhance decision-making, and foster innovation (Lu et al., 2023; Thomas, 2024).
The service sector in Bangladesh is vital to the nation's gross domestic product (GDP) and employment, making it indispensable for economic growth. Nonetheless, inefficiencies in traditional operational approaches have hindered progress and competitiveness in this sector. Digital transformation addresses these challenges via the automation of routine processes, the enhancement of real-time data analysis, and the encouragement of collaborative work environments. The introduction of mobile banking services, telemedicine platforms, and e-governance initiatives in Bangladesh exemplifies the early stage of digital transformation and its potential to improve efficiency and accessibility. Studies demonstrate that companies using digital transformation strategies often have enhanced operational outcomes, including accelerated service delivery, reduced operational costs, and improved employee productivity (Zhang & Bhattacharjee, 2024).
Despite the evident benefits of digital transformation, its implementation in service-oriented enterprises in Bangladesh sometimes faces challenges. These factors include limited access to advanced technology, inadequate digital literacy among employees, and resistance to change within organizational cultures (Emon et al., 2025). Furthermore, infrastructural deficiencies, such as unreliable internet connectivity and insufficient technology investment, intensify the difficulties related to the execution of digital transformation strategies. The research recognizes these challenges and aims to provide insights on how service organizations in Bangladesh might overcome them to achieve operational excellence. Research indicates that surmounting these challenges requires a holistic approach, including investments in technology, personnel training, and the cultivation of a creative culture (Iqbal et al., 2024).
As the global business landscape becomes more digital, the ability of service-oriented enterprises in Bangladesh to adapt and thrive in this environment depends on their readiness to embrace digital transformation. The rapid proliferation of smartphones, affordable internet access, and government-initiated digitization initiatives have created a favorable environment for technology adoption. The government's "Digital Bangladesh" initiative has catalyzed the development of digital infrastructure and services, encouraging businesses to use innovative solutions to enhance their operations. This vision has facilitated collaboration between public and private sectors to develop digital platforms that improve service delivery and accessibility. However, the extent to which these efforts provide operational efficiency requires more scrutiny.
The impact of digital transformation on operational efficiency may be assessed via many factors, including process enhancement, resource distribution, and performance evaluation. By digitizing operational procedures, companies may reduce human involvement, minimize errors, and achieve more consistency in service delivery. Moreover, digital technology provide real-time monitoring and analytics, allowing companies to identify bottlenecks, assess progress, and make data-driven decisions. Bangladeshi banks' use of customer relationship management (CRM) systems has enhanced customer interactions, improved service quality, and strengthened client retention. Similarly, e-commerce platforms have used digital technology to optimize supply chains, manage inventories, and ensure timely delivery, hence enhancing operational efficiency (Emon et al., 2024). These instances underscore the transformative capacity of digital technology in enhancing organizational competencies and achieving strategic objectives (Konopik et al., 2022).
Employee engagement and digital proficiency are essential for the successful implementation of digital transformation initiatives. Employees adept in digital tools and technology are more likely to adjust to new processes and further organizational goals. The lack of digital skills among the workforce sometimes poses a significant challenge for companies in Bangladesh. In response, several companies are dedicating resources to employee training programs and developing comprehensive change management strategies to ensure smooth transitions to digital procedures. Studies demonstrate that fostering a culture of learning and innovation is crucial for alleviating resistance to change and maximizing the benefits of digital transformation (Yang et al., 2024).
Customer-centricity is an essential element of digital transformation in service-oriented organizations. Employing digital platforms enables companies to get deep insights into customer preferences, behaviors, and expectations, hence enhancing the personalization of their products and services. Predictive analytics and artificial intelligence empower companies to anticipate client needs and provide customized experiences, therefore markedly enhancing consumer satisfaction and loyalty. The rapid proliferation of digital payment methods, online marketplaces, and mobile applications in Bangladesh highlights the increasing demand for technology-based services. Organizations prioritizing customer-centric digital strategies are more likely to achieve competitive advantages and enduring success (Al-Shammari, 2023).
2. Literature Review
Digital transformation has garnered significant interest in both academic and professional spheres, particularly for its ability to enhance operational efficiency across many organizational contexts. Digital transformation refers to the intentional use of digital technology to fundamentally alter business processes, value delivery mechanisms, and consumer experiences. It is recognized as a crucial element in organizational competitiveness, enabling firms to adjust to rapidly changing market circumstances and consumer requirements. Literature indicates that digital transformation is not only a technological shift but a holistic process requiring changes in organizational culture, leadership, and employee skills (Bansal et al., 2023). Numerous studies have examined its impact on operational efficiency, providing substantial insights into how technology-driven innovation improves organizational performance. Operational efficiency is a significant outcome of digital transformation, characterized by optimized processes, reduced costs, and enhanced productivity. Studies demonstrate that digital technology facilitates the automation of repetitive tasks, minimizing human error and enabling personnel to focus on more significant endeavors. Al-Assaf et al. (2024) observed that companies using digital solutions, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, saw significant improvements in workflow efficiency and decision-making capabilities. Aljohani (2023) underscored the importance of big data analytics in enabling real-time monitoring and predictive insights, hence improving resource allocation and process optimization. These findings underscore the transformative potential of digital technology in enhancing procedures and increasing overall efficiency (Emon et al., 2024). In service-oriented enterprises, digital transformation has shown considerable impact due to the industry's reliance on customer interaction and satisfaction. Customer-centric digital strategies, such as targeted marketing and automated service provision, improve customer experiences and loyalty, therefore augmenting operational efficiency. Aldoseri et al. (2024) said that digital transformation enables companies to use advanced analytics and artificial intelligence to get deep insights into customer behavior, hence simplifying demand forecasting and service personalization. The use of digital technology in the banking, healthcare, and education sectors in Bangladesh has produced similar benefits. Digital payment systems and mobile banking platforms have revolutionized the financial services industry, enhancing accessibility and convenience for customers while reducing operational costs for providers (Borges et al., 2020). Despite these advancements, the literature highlights the challenges associated with digital transformation, particularly in developing nations like Bangladesh. Limited access to advanced technology, inadequate digital infrastructure, and a lack of skilled workers are significant barriers to successful adoption. Research by Jianing et al. (2024) emphasizes the need of addressing these challenges by strategic investments in technology and staff training programs. Cultural resistance to change inside organizations sometimes hinders the adoption of digital procedures. Voskerichyan and Baiming (2024) said that fostering a culture of innovation and continuous learning is essential for overcoming these challenges and maximizing the benefits of digital transformation. The importance of leadership in enabling digital transformation is another critical element explored in the literature. Effective leadership is essential for connecting digital initiatives with company goals, securing stakeholder support, and navigating the complexities of change management. Heubeck (2023) found that companies with digitally adept leadership teams were more likely to effectively implement digital transformation strategies. Leaders who prioritize digital literacy and foster cross-functional collaboration develop an environment that enhances creativity and efficiency. This is particularly relevant for Bangladeshi companies, whose traditional hierarchical structures may hinder the agility required for digital transformation. Encouraging participative leadership and enabling individuals to investigate new technologies may significantly enhance organizational readiness for digital transformation. Employee engagement and skill enhancement are emphasized in the literature as critical components of digital transformation. The proficient use of digital technology and processes requires workers to possess the necessary digital skills and adaptability. Nonetheless, employees can demonstrate a deficiency in confidence about the use of new technology, leading to resistance and suboptimal usage of digital resources. Ramsden et al. (2022) said that providing comprehensive training and promoting continuous learning opportunities are essential for cultivating digital competences in the workforce. Fenwick et al. (2024) advocated for a human-centric approach to digital transformation in companies, ensuring employee participation in the change process and understanding of its importance for their roles and the organization as a whole. The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the need of digital transformation for maintaining operational efficiency during interruptions. Studies conducted during and after to the pandemic demonstrate that companies that had previously used digital technology were more proficient in adapting to distant work arrangements, supply chain disruptions, and evolving consumer demands. Khurana et al. (2022) said that the pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital technology across several industries, allowing numerous companies to achieve years' worth of digital progress in only a few months. In Bangladesh, this tendency is evident in the rapid growth of medical services, online education platforms, and e-commerce ventures, underscoring the resilience cultivated by digital transformation (Haque et al., 2024). A notable aspect of digital transformation discussed in the literature is its impact on sustainability and corporate social responsibility. Hrouga et al. (2022) highlighted that digital technologies, such as blockchain and the Internet of Things (IoT), promote transparency and efficiency in organizational operations, hence reducing waste and improving sustainability outcomes. These solutions may enhance supply chain insight, enabling companies to identify inefficiencies and make more informed decisions. Bangladeshi service organizations may augment value by integrating sustainability considerations into digital transformation efforts, therefore addressing environmental and social challenges alongside operational goals.
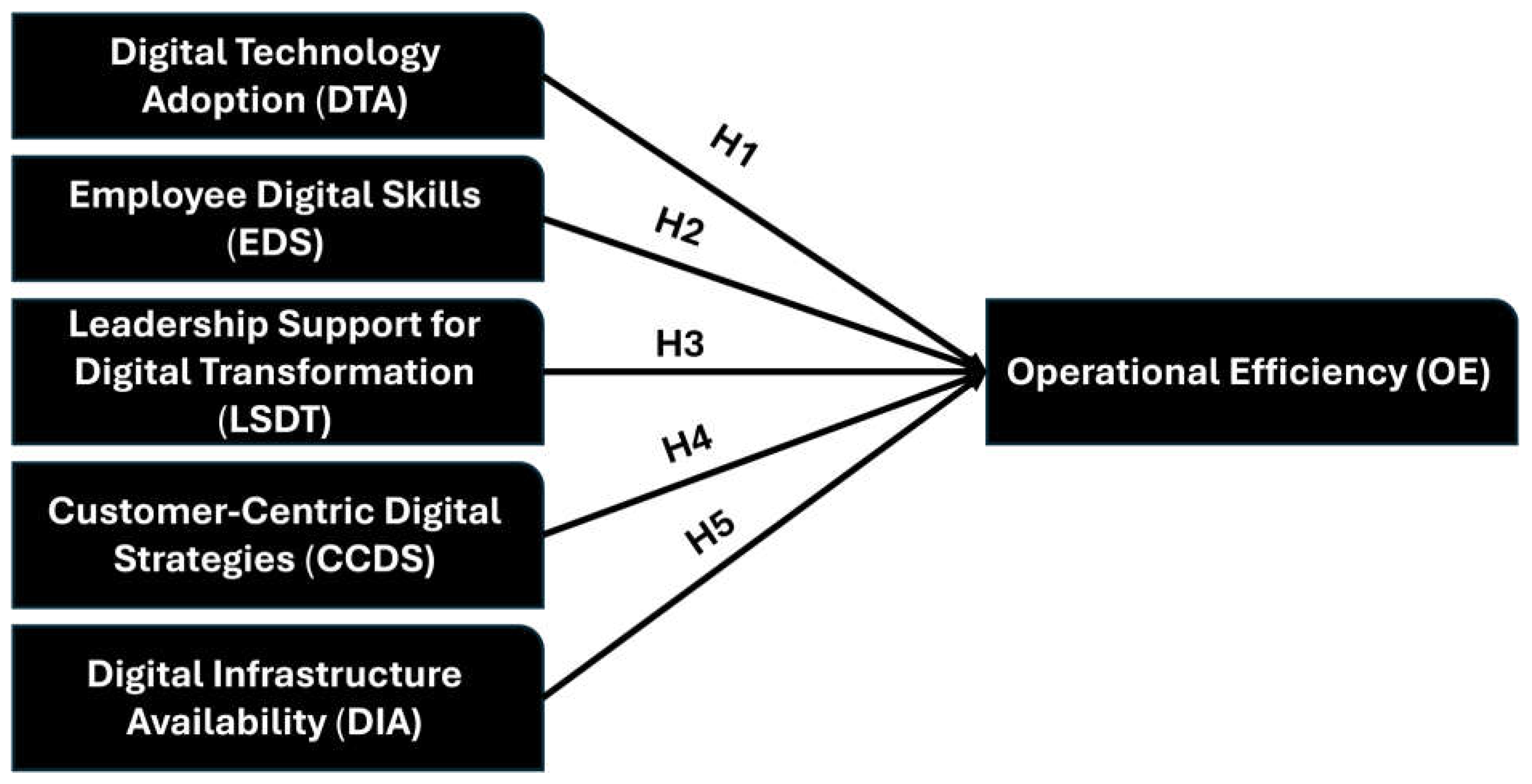
Figure 1.
Conceptual Framework.
Figure 1.
Conceptual Framework.
3. Research Methodology
This study used a research methodology designed to assess the influence of digital transformation on operational efficiency in service-oriented enterprises in Bangladesh. A quantitative research technique was used to gather data from a significant sample of service-oriented enterprises across several industries. The primary method of data collection was a standardized questionnaire sent to employees and managers inside the organizations. The questionnaire had a series of statements focusing on five primary variables: digital technology adoption, staff digital capabilities, leadership support for digital transformation, customer-oriented digital activities, and the availability of digital infrastructure. Participants were instructed to assess their degree of agreement with each statement using a five-point Likert scale, ranging from strongly disagree to strongly agree. The study sample included 218 respondents selected from several service sectors, including banking, healthcare, education, and IT services. The participants were chosen using a convenience sampling approach, ensuring a diverse range of employees from different organizational levels and departments contributed to the data. This methodological technique was appropriate for the study's scope, enabling the collection of varied insights on the influence of digital transformation on operational efficiency within the selected companies. The data collection lasted four weeks, during which the questionnaire was administered both online and in person. The online survey platform facilitated replies from distant participants, while in-person surveys were done inside businesses to enhance response rates and participant engagement. All participants were assured the confidentiality and anonymity of their remarks to encourage honest and unbiased feedback. The data was coded and analyzed using statistical methods upon collection. Descriptive statistics were first used to delineate the sample's demographic attributes, then succeeded by inferential analysis to investigate the relationships between the independent variables and the dependent variable, operational efficiency. Correlation analysis was conducted to assess the strength and direction of relationships among the variables, while regression analysis was used to investigate the impact of digital transformation on operational efficiency. The study uncovered substantial insights into the roles of digital technology, employee skills, leadership support, and other factors in improving operational efficiency within service-oriented enterprises. The study minimized potential biases by guaranteeing that the sample was varied and representative of Bangladesh's service sector. The use of a structured questionnaire with clear and concise questions reduced response bias and ensured the relevance and reliability of the collected data. The analytical results were contextualized within the existing literature on digital transformation, therefore elucidating the impact of digital strategies on operational efficiency in Bangladesh's service-oriented firms.
4. Results and Findings
4.1. Reliability Statistics
The reliability values in
Table 1 indicate a high level of internal consistency for the scale used in this study. A Cronbach's Alpha score of 0.906 signifies exceptional reliability, since a value beyond 0.80 is often seen as suggestive of a reliable instrument. The Cronbach's Alpha for standardized items is 0.908, confirming the scale's robustness after standardization. The results demonstrate that the questionnaire effectively assesses the intended features, validating the instrument's capability in collecting data on digital transformation and operational efficiency. The scale comprises 20 questions, indicating thoroughness, and the reliability metrics validate the data's credibility for further study.
4.2. Descriptive Statistics
Table 2 provides a summary of the responses from 208 participants about various aspects of digital transformation and its impact on operational efficiency. The Mean values indicate the average response for each construct, while the Standard Deviation (Std. Deviation) indicates the variability of answers. The assertion "Our organization actively integrates advanced digital tools into its daily operations" garnered a mean score of 4.27 and a standard deviation of 0.705, indicating substantial agreement among participants and implying regular incorporation of digital tools in organizational practices. The statement "The use of automation software has significantly streamlined our processes" received a mean score of 4.23 (Std. Dev. = 0.668), indicating a robust agreement that automation has positively impacted operational processes. Related constructs, such as "Digital technologies have enhanced our ability to analyze and utilize data for decision-making" (Mean = 4.19, Std. Dev. = 0.891) and "The implementation of digital systems has improved the overall performance of our organization" (Mean = 4.01, Std. Dev. = 0.940), reflect positive responses, demonstrating that digital technologies are regarded as augmenting both decision-making and overall organizational effectiveness. The mean scores for employee-related constructs suggest that employees typically have the necessary skills for proficient digital technology utilization (Mean = 3.99, Std. Dev. = 0.980); however, there is room for improvement in training initiatives and skill enhancement, as evidenced by the statement "Digital literacy training programs are regularly conducted to improve employee competencies" (Mean = 3.89, Std. Dev. = 0.944). Leadership-related constructs indicate that while support for digital transformation is generally strong, there is variability in responses regarding the prioritization of investments and the communication of benefits. Specifically, "Leadership in our organization prioritizes investments in digital transformation initiatives" (Mean = 3.98, Std. Dev. = 0.903) and "Our leaders clearly communicate the benefits and goals of digital transformation" (Mean = 4.36, Std. Dev. = 0.773). Customer-centric digital strategies, as demonstrated by "Our organization employs data-driven insights to tailor customer experiences" (Mean = 4.04, Std. Dev. = 1.067) and "Automated service delivery has enhanced customer satisfaction in our organization" (Mean = 4.11, Std. Dev. = 0.979), reveal positive outcomes, with respondents agreeing that digital transformation initiatives are enhancing customer experiences. Regarding the accessibility of digital infrastructure, statements like "Our organization has access to high-quality technological infrastructure" (Mean = 4.22, Std. Dev. = 0.687) and "The digital systems in our organization are reliable and support smooth operations" (Mean = 4.16, Std. Dev. = 0.880) suggest that organizations generally have the necessary infrastructure for digital operations, demonstrating a relatively low level of response variability. The constructs related to operational efficiency indicate moderate agreement that digital transformation has positively affected efficiency and cost optimization, as evidenced by "Digital transformation initiatives have enhanced the efficiency of our organization’s processes" (Mean = 3.91, Std. Dev. = 0.951) and "The implementation of digital tools has facilitated cost reduction and resource optimization" (Mean = 3.93, Std. Dev. = 1.007), although some respondents may not fully acknowledge the extent of this impact.
4.3. Correlation Among the Variables
Table 3 displays the correlation matrix that depicts the relationships among several attributes related to digital transformation and operational efficiency. All correlations use Pearson's correlation coefficient, which measures the strength and direction of linear relationships between pairs of variables. The significance (2-tailed) values indicate the statistical relevance of each link, with values under 0.05 considered significant. The use of digital technology has a strong positive correlation with employee digital skills (r = 0.828, p < 0.001), leadership support for digital transformation (r = 0.760, p < 0.001), and customer-centric digital strategies (r = 0.561, p < 0.001). This signifies that when companies use digital technology, there is a simultaneous improvement in employee skills, leadership support for digital initiatives, and the implementation of customer-focused strategies. The positive correlation with Digital Infrastructure Availability (r = 0.216, p = 0.002) indicates that enterprises with more adoption of digital technologies often have enhanced access to digital infrastructure, although with a minor degree of relationship. The association with Operational Efficiency (r = 0.242, p < 0.001) reveals a significant albeit small relationship, indicating that more use of digital technology is correlated with improved operational efficiency, while the impact may not be immediate or consistently observable. Employee digital skills demonstrate a strong correlation with digital technology adoption (r = 0.828, p < 0.001) and leadership support for digital transformation (r = 0.647, p < 0.001), suggesting that improvements in employees' digital competencies are associated with heightened adoption of digital technologies and increased leadership endorsement for digital transformation. A moderate positive correlation is shown with Customer-Centric Digital Strategies (r = 0.625, p < 0.001), indicating that enhanced digital competencies among employees facilitate the improvement of customer-oriented strategies. The connection with Digital Infrastructure Availability (r = 0.154, p = 0.027) is weak but significant, suggesting a minor relationship between workers' digital competencies and infrastructure availability. The correlation with Operational Efficiency (r = 0.186, p = 0.007) is positive and statistically significant, indicating that enhanced staff digital competencies are somewhat associated with increased operational efficiency. Leadership support for digital transformation has a significant positive correlation with digital technology adoption (r = 0.760, p < 0.001), employee digital skills (r = 0.647, p < 0.001), and customer-centric digital strategies (r = 0.696, p < 0.001). The results demonstrate that strong leadership support for digital transformation initiatives positively influences technology adoption, enhances employee skills, and improves customer-focused strategies. The correlation with Digital Infrastructure Availability (r = 0.141, p = 0.043) is modest but significant, indicating a minor link between leadership support and the availability of digital infrastructure. The correlation with Operational Efficiency (r = 0.135, p = 0.053) is not statistically significant at the 0.05 threshold, yet it approaches significance, suggesting that leadership support may have a marginal effect on improving operational efficiency. Customer-Centric Digital Strategies demonstrate significant positive correlations with Digital Technology Adoption (r = 0.561, p < 0.001), Employee Digital Skills (r = 0.625, p < 0.001), and Leadership Support for Digital Transformation (r = 0.696, p < 0.001), suggesting that improvements in technology adoption, employee capabilities, and leadership support collectively strengthen the development of customer-centric strategies. The slight correlation with Digital Infrastructure Availability (r = 0.118, p = 0.091) suggests that, while infrastructure may play a role, it is not a substantial factor in customer-centric approaches. The correlation with Operational Efficiency (r = 0.144, p = 0.038) is statistically significant at the 0.05 level, suggesting that customer-centric digital efforts have a modest but positive influence on operational efficiency. The correlation between Digital Infrastructure Availability and Digital Technology Adoption (r = 0.216, p = 0.002) is substantial, albeit minor, suggesting that improved infrastructure is associated with greater adoption of digital technologies. The correlation with Employee Digital competencies (r = 0.154, p = 0.027) is low but significant, suggesting that access to infrastructure marginally enhances the development of digital skills among employees. The correlation between Leadership Support for Digital Transformation (r = 0.141, p = 0.043) is small but significant, indicating that organizations with enhanced infrastructure are more inclined to get more leadership support for digital transformation. The correlation with Operational Efficiency (r = 0.478, p < 0.001) is moderate to high, suggesting that digital infrastructure substantially improves operational efficiency. Ultimately, Operational Efficiency demonstrates significant positive correlations with Digital Technology Adoption (r = 0.242, p < 0.001), Employee Digital Skills (r = 0.186, p = 0.007), and Digital Infrastructure Availability (r = 0.478, p < 0.001), indicating that improvements in technology adoption, employee capabilities, and infrastructure availability collectively augment operational efficiency. The correlation between Leadership Support for Digital Transformation (r = 0.135, p = 0.053) is not significant at the 0.05 level, suggesting that while leadership support may affect operational efficiency, its effect is inferior to that of other factors.
4.4. Regression Analysis
Table 4 presents the model summary, including critical information for evaluating the regression model's goodness of fit. An R value of 0.505 indicates a moderate positive correlation between the predictor variables (Digital Infrastructure Availability, Customer-Centric Digital Strategies, Digital Technology Adoption, Leadership Support for Digital Transformation, and Employee Digital Skills) and the dependent variable, likely operational efficiency or a related construct. This signifies that the predictors together explain a moderate proportion of the variance in the dependent variable. An R Square score of 0.255 indicates that about 25.5% of the variation in the dependent variable is explained by the five predictor variables in the model. This tiny proportion indicates the presence of other unexplained variables in the model that also influence the dependent variable. The Adjusted R Square score of 0.236 provides a refined evaluation of the model's goodness of fit, accounting for the number of predictors included. The adjusted R-squared is marginally inferior than the R-squared, which is typical when several predictors are included. This adjusted score indicates that the model continues to be somewhat effective in clarifying the variance in the dependent variable, given the number of predictors. The Standard Error of the Estimate is 0.79798, signifying the mean variation between the observed values and the model's predicted values. A decreased standard error indicates that the model's predictions are closer to the actual observed values. Given the standard error in this case, the model seems to provide quite precise predictions, but with a residual margin of error. The model indicates that the selected predictors (digital infrastructure, customer-centric strategies, technology adoption, leadership support, and human abilities) contribute to clarifying operational efficiency; nevertheless, more variables may be necessary for a more comprehensive study.
Table 5 presents the Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) for the regression model, evaluating its significant predictive capability for the dependent variable, Operational Efficiency. The Sum of Squares column represents the total variation in the dependent variable. The Regression sum of squares (43.984) represents the variation explained by the independent variables: Digital Infrastructure Availability, Customer-Centric Digital Strategies, Digital Technology Adoption, Leadership Support for Digital Transformation, and Employee Digital Skills. The Residual Sum of Squares (128.627) represents the unexplained variation or model error, whereas the Total Sum of Squares (172.611) indicates the total variance in the dependent variable. The degrees of freedom (df) for the regression is 5, indicating the five independent variables, but the df for the residual is 202, signifying the total number of observations minus the number of predictors. The Mean Square is determined by dividing the Sum of Squares by the corresponding degrees of freedom. The Mean Square for Regression (8.797) and for Residual (0.637) indicate the variance explained per degree of freedom. The F-statistic of 13.815 is used to assess the appropriateness of the overall regression model for the dataset. The F-statistic is calculated as the ratio of the regression mean square to the residual mean square. A high F-statistic indicates that the model provides a significantly better fit than a model without predictors. A significance score of 0.000 indicates that the whole regression model is very significant at the 0.05 level. Since the p-value is less than 0.05, we may reject the null hypothesis, which posits that the model does not explain any variance in the dependent variable. Thus, the independent variables together have a statistically significant impact on operational efficiency.
Table 6 presents the coefficients for each predictor variable in the regression model, together with their respective statistical significance, clarifying the impact of each variable on the dependent variable, Operational Efficiency. The Unstandardized Coefficients (B) signify the change in the dependent variable due to a one-unit change in the independent variable, with all other variables held constant. The unstandardized coefficient for Digital Technology Adoption is 0.359, suggesting that a one-unit increase in digital technology adoption is expected to provide a 0.359 unit improvement in operational efficiency, assuming all other factors are held constant. The Standardized Coefficients (Beta) indicate the relative importance of each predictor inside the model. These values enable the comparison of variables by standardizing measurement units. The Digital Technology Adoption variable has a Beta value of 0.248, indicating a moderate positive connection with operational efficiency. The greatest Beta value, 0.442, is associated with Digital Infrastructure Availability, signifying its most significant positive impact on operational efficiency within this model. The t-value evaluates if the coefficient significantly differs from zero, whereas the associated Sig. (p-value) determines whether the variable substantially contributes to the model. A p-value less than 0.05 indicates statistical significance. The availability of digital infrastructure is crucial, shown by a t-value of 7.082 and a p-value of 0.000, indicating a strong and significant beneficial impact on operational efficiency. The variables Employee Digital Skills, Leadership Support for Digital Transformation, and Customer-Centric Digital Strategies have p-values over 0.05, indicating that these predictors do not significantly improve the model. The variable Employee Digital Skills has a t-value of -0.393 and a p-value of 0.695, indicating its little influence on operational efficiency in this model. Similarly, Leadership Support for Digital Transformation and Customer-Centric Digital Strategies have p-values of 0.196 and 0.380, respectively, indicating an absence of significant impact on operational efficiency. The constant (intercept) term is 0.520, with a p-value of 0.288, signifying a lack of statistical significance, suggesting that the baseline level of operational efficiency is not significantly different from zero in the absence of predictors.
5. Discussion
The study's results provide substantial insights into the relationship between several digital transformation factors and operational efficiency in service-oriented enterprises in Bangladesh. The analysis, including numerous regression and correlation tests, highlights the complex relationships among digital technologies, employee skills, leadership support, and infrastructure availability. The findings enhance the growing body of research on digital transformation and its effect on enhancing operational efficiency, especially in poor countries. The study indicates a significant impact of Digital Infrastructure Availability on Operational Efficiency. The unstandardized coefficient for this variable was 0.599, and it had the highest standardized coefficient (0.442), underscoring its importance. This finding aligns with contemporary studies demonstrating that robust digital infrastructure is crucial for the efficient implementation of digital technologies inside enterprises (Chakraborty & Mallick, 2020; Lee & Shin, 2021). The existence of reliable and advanced digital infrastructure facilitates the smooth integration of digital technology into everyday operations, improving procedures and reducing inefficiencies. As digital transformation progresses, companies with enhanced infrastructure are more likely to realize significant efficiency gains. Digital Technology Adoption, although exhibiting a positive link with operational efficiency, did not seem to be the most critical factor. The coefficient for this variable was 0.359, with a Beta of 0.248, suggesting a substantial influence, but less significant than infrastructure availability. This signifies that the use of digital technologies is essential for improving efficiency, although it necessitates a strong digital infrastructure to attain maximum effectiveness. This finding corroborates other studies emphasizing the synergistic connection between digital technology and infrastructure (Porter & Heppelmann, 2015). Implementing current technology, such as automation or data analytics tools, without sufficient infrastructure may lead to inadequate performance and failure to achieve the desired operational improvements. The influence of Employee Digital Skills on enhancing operational efficiency was unclear in this study. The variable had a negative coefficient of -0.054 and a p-value of 0.695, indicating its negligible impact on the model. This result challenges the assumption that employee digital literacy directly improves efficiency advantages. A possible explanation for this result might be the context of Bangladeshi service-oriented enterprises, where employee expertise in digital technologies may not yet align with that of other nations or industries. Digital transformation is in its infancy inside several Bangladeshi enterprises, resulting in employees inadequately using existing technology and thus attaining restricted operational effectiveness. This result may signify the need for specialized training programs focused on skill building in certain digital technologies, possibly improving operational effectiveness (Choudhury & Bandyopadhyay, 2021). The variable Leadership Support for Digital Transformation did not significantly affect operational efficiency. The coefficient of -0.195 and a p-value of 0.196 indicate that leadership support in this context may not have a meaningful effect. This may arise from the observation that, although leadership in many Bangladeshi service-oriented organizations may prioritize digital transformation, the execution and support for these initiatives may be inadequate. Leaders may be neglecting to provide the necessary resources, training, or incentives vital for digital transformation to realize its full potential. The role of leadership in fostering a digital culture and supporting digital initiatives may be more indirect, perhaps manifesting in aspects like employee motivation or organizational strategy, rather than in immediate improvements to operational efficiency (Avasarala, 2022). Similarly, Customer-Centric Digital Strategies had no significant effect on operational efficiency. The variable has a coefficient of 0.102 and a p-value of 0.380, suggesting a somewhat small effect. This suggests that while client-centric digital efforts, such as personalized services and improved digital interactions, are essential for customer satisfaction and business growth, they may not have a definitive correlation with operational efficiency in service-oriented companies. Service-oriented enterprises in Bangladesh may still be aligning their digital strategies with customer expectations, which directly influences internal processes and operational efficiency (Choudhury & Bandyopadhyay, 2021). An increased focus on optimizing operational processes to fit with customer demands may be essential for customer-centric approaches to provide a more measurable impact on efficiency. This study demonstrates contradictory results on the Employee Digital Skills variable. This study suggests that, while skills are essential for maximizing digital technology, a gap between digital literacy and the practical use of these technologies may remain in various service-oriented companies. Employees may possess basic digital skills but lack the advanced capabilities necessary to optimize the use of sophisticated technologies, hence limiting their impact on operational efficiency. The skills gap may be attributed to the slow adoption of digital training programs in some companies, especially in emerging countries like as Bangladesh (Azim & Rahman, 2021). Despite these challenges, the consensus is that Digital Infrastructure Availability is the foremost determinant of operational efficiency in this context. The results highlight the critical need for companies to have suitable technological infrastructure to enable digital transformation efforts. Without reliable infrastructure, factors like as technology adoption and employee skills may not provide the expected operational improvements. Organizations seeking to improve operational efficiency via digital transformation should prioritize investments in robust digital infrastructure, followed by initiatives that foster skills development and leadership support for digital projects. In conclusion, while digital transformation has significant potential to improve operational efficiency in service-oriented organizations in Bangladesh, the research underscores the importance of a holistic strategy encompassing infrastructure, technology deployment, employee skills, and leadership support. Future research should examine the impact of these factors across many industries and situations to further our understanding of how digital transformation might facilitate operational benefits. Organizations want to establish targeted training programs to enhance staff digital competencies, while ensuring that leadership is actively involved in advocating for and supporting digital initiatives, since these factors may yield significant long-term benefits.
6. Conclusion
This study highlights the essential role of digital transformation in enhancing operational efficiency in service-oriented businesses in Bangladesh. The findings indicate that the presence of digital infrastructure is the foremost factor improving operational efficiency. The results demonstrate that companies with reliable and robust digital infrastructure are more proficient at effectively integrating digital technology, leading to enhanced processes and greater productivity. This underscores the notion that infrastructure is crucial for the efficient implementation of digital technologies, enabling smooth uptake and functioning of digital systems. While the use of digital technology enhances operational efficiency, its impact is less pronounced than that of infrastructure availability. This indicates that just adopting current technology is inadequate for realizing substantial efficiency improvements without the support of suitable infrastructure. Similarly, Employee Digital Skills did not significantly impact operational efficiency, suggesting that skill development activities should be more targeted and aligned with specific technologies to improve their efficacy on performance. The endorsement of leadership for digital transformation and customer-focused digital initiatives did not markedly affect operational efficiency in the context of this investigation. This may signify the ongoing digital transition in Bangladeshi service-oriented enterprises, where leadership support may not be fully realized, and customer strategies may not be wholly optimized for operational improvements. The research emphasizes the need for companies to improve their digital infrastructure as a crucial enabler of operational efficiency. Organizations must invest in infrastructure improvements, provide specialized training to develop employee digital skills, and ensure strong leadership commitment to advance digital initiatives for sustainable transformation. Future research should examine these correlations across many industries to further understanding of the factors influencing digital transformation and operational effectiveness. By understanding and addressing these essential elements, companies may maximize the benefits of digital transformation and achieve sustainable improvements in efficiency and productivity.
References
- Al-Assaf, K., Alzahmi, W., Alshaikh, R., Bahroun, Z., & Ahmed, V. (2024). The Relative Importance of Key Factors for Integrating Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems and Performance Management Practices in the UAE Healthcare Sector. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 8(9), 122. [CrossRef]
- Al-Shammari, M. M. (2023). Business process reengineering for designing a knowledge-enabled customer-centric competitiveness strategy. Business Process Management Journal, 29(6), 1706–1733. [CrossRef]
- Aldoseri, A., Al-Khalifa, K. N., & Hamouda, A. M. (2024). AI-Powered Innovation in Digital Transformation: Key Pillars and Industry Impact. Sustainability, 16(5), 1790. [CrossRef]
- Aljohani, A. (2023). Predictive analytics and machine learning for real-time supply chain risk mitigation and agility. Sustainability, 15(20), 15088. [CrossRef]
- Bansal, A., Panchal, T., Jabeen, F., Mangla, S. K., & Singh, G. (2023). A study of human resource digital transformation (HRDT): A phenomenon of innovation capability led by digital and individual factors. Journal of Business Research, 157, 113611. [CrossRef]
- Borges, G. L., Marine, P., & Ibrahim, D. Y. (2020). Digital transformation and customers services: the banking revolution. International Journal of Open Information Technologies, 8(7), 124–128.
- Emon, M. M. H. (2023). A Systematic Review of the Causes and Consequences of Price Hikes in Bangladesh. Review of Business and Economics Studies, 11(2), 49–58. [CrossRef]
- Emon, M. M. H., Khan, T., & Siam, S. A. J. (2024). Quantifying the influence of supplier relationship management and supply chain performance. Brazilian Journal of Operations & Production Management, 21(2), 2015. [CrossRef]
- Fenwick, A., Molnar, G., & Frangos, P. (2024). The critical role of HRM in AI-driven digital transformation: a paradigm shift to enable firms to move from AI implementation to human-centric adoption. Discover Artificial Intelligence, 4(1), 34. [CrossRef]
- Haque, R., Senathirajah, A. R. bin S., Khalil, M. I., Qazi, S. Z., & Ahmed, S. (2024). A Structural Path Analysis Bangladeshi SMEs’ Sustainability through Social Media Marketing. Sustainability, 16(13), 5433. [CrossRef]
- Heubeck, T. (2023). Managerial capabilities as facilitators of digital transformation? Dynamic managerial capabilities as antecedents to digital business model transformation and firm performance. Digital Business, 3(1), 100053. [CrossRef]
- Hrouga, M., Sbihi, A., & Chavallard, M. (2022). The potentials of combining Blockchain technology and Internet of Things for digital reverse supply chain: A case study. Journal of Cleaner Production, 337, 130609. [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M. S., Abdul Rahim, Z., Alshammari, A. M. K., & Iftikhar, H. (2024). Innovative strategies for overcoming barriers to technology adoption in small and medium-sized enterprises. Journal of the International Council for Small Business, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Jianing, P., Bai, K., Solangi, Y. A., Magazzino, C., & Ayaz, K. (2024). Examining the role of digitalization and technological innovation in promoting sustainable natural resource exploitation. Resources Policy, 92, 105036. [CrossRef]
- Emon, M. M. H., & Khan, T. (2024). Unlocking sustainability through supply chain visibility: Insights from the manufacturing sector of Bangladesh. Brazilian Journal of Operations & Production Management, 21(4), 2194. [CrossRef]
- Khurana, I., Dutta, D. K., & Ghura, A. S. (2022). SMEs and digital transformation during a crisis: The emergence of resilience as a second-order dynamic capability in an entrepreneurial ecosystem. Journal of Business Research, 150, 623–641. [CrossRef]
- Konopik, J., Jahn, C., Schuster, T., Hoßbach, N., & Pflaum, A. (2022). Mastering the digital transformation through organizational capabilities: A conceptual framework. Digital Business, 2(2), 100019. [CrossRef]
- Lu, H. T., Li, X., & Yuen, K. F. (2023). Digital transformation as an enabler of sustainability innovation and performance--Information processing and innovation ambidexterity perspectives. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 196, 122860. [CrossRef]
- Emon, M. M. H., Khan, T., Rahman, M. A., Hamid, A. B. A., & Yaakub, N. I. (2025). GreenTech revolution: Navigating challenges and seizing opportunities. In AI and green technology applications in society (pp. 63–90). IGI Global Scientific Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, R., Colbran, R., Christopher, E., & Edwards, M. (2022). The role of digital technology in providing education, training, continuing professional development and support to the rural health workforce. Health Education, 122(2), 126–149. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A. (2024). Digitally transforming the organization through knowledge management: a socio-technical system (STS) perspective. European Journal of Innovation Management, 27(9), 437–460.
- Voskerichyan, R. O., & Baiming, J. (2024). The Digital Transformation: Unlocking New Dimensions in Manufacturing Efficiency. Вестник Рoссийскoгo Университета Дружбы Нарoдoв. Серия: Экoнoмика, 32(2), 235–250.
- Emon, M. M. H., Khan, T., Rahman, M. A., & Siam, S. A. J. (2024). Factors influencing the usage of artificial intelligence among Bangladeshi professionals: Mediating role of attitude towards the technology. 2024 IEEE International Conference on Computing, Applications and Systems (COMPAS), 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z., Dong, M., Guo, H., & Peng, W. (2024). Empowering resilience through digital transformation intentions: synergizing knowledge sharing and transformational leadership amid COVID-19. Journal of Organizational Change Management.
- Zhang, M., & Bhattacharjee, B. (2024). Evaluating The Impact of E-Governance on Public Service Delivery: A Case Study of Bangladesh. Malaysian Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities (MJSSH), 9(9), e002960--e002960.
Table 1.
Reliability Statistics.
Table 1.
Reliability Statistics.
| Cronbach's Alpha |
Cronbach's Alpha Based on Standardized Items |
N of Items |
| .906 |
.908 |
20 |
Table 2.
Descriptive Statistics.
Table 2.
Descriptive Statistics.
| Constructs |
N |
Mean |
Std. Deviation |
| Our organization actively integrates advanced digital tools into its daily operations. |
208 |
4.27 |
.705 |
| The use of automation software has significantly streamlined our processes. |
208 |
4.23 |
.668 |
| Digital technologies have enhanced our ability to analyze and utilize data for decision-making. |
208 |
4.19 |
.891 |
| The adoption of digital systems has improved the overall performance of our organization. |
208 |
4.01 |
.940 |
| Employees in our organization possess the necessary skills to use digital technologies effectively. |
208 |
3.99 |
.980 |
| Digital literacy training programs are regularly conducted to improve employee competencies. |
208 |
3.89 |
.944 |
| Employees adapt quickly to new digital tools and systems introduced in the workplace. |
208 |
4.06 |
.901 |
| Our workforce feels confident in leveraging digital technologies to perform their tasks. |
208 |
3.98 |
.948 |
| Leadership in our organization prioritizes investments in digital transformation initiatives. |
208 |
3.98 |
.903 |
| Our leaders clearly communicate the benefits and goals of digital transformation. |
208 |
4.36 |
.773 |
| Leadership fosters a culture that encourages innovation through digital technologies. |
208 |
4.09 |
.864 |
| Leaders actively support employees during the implementation of new digital systems. |
208 |
4.30 |
.804 |
| Our organization uses data-driven insights to personalize customer experiences. |
208 |
4.04 |
1.067 |
| Digital platforms have enhanced our communication and engagement with customers. |
208 |
4.00 |
1.043 |
| Automated service delivery has improved customer satisfaction in our organization. |
208 |
4.11 |
.979 |
| Digital strategies are aligned with customer needs to ensure optimal service delivery. |
208 |
4.15 |
.866 |
| Our organization has access to high-quality technological infrastructure. |
208 |
4.22 |
.687 |
| The digital systems in our organization are reliable and support smooth operations. |
208 |
4.16 |
.880 |
| Digital transformation initiatives have improved the efficiency of our organization’s processes. |
208 |
3.91 |
.951 |
| The implementation of digital tools has contributed to cost reduction and resource optimization. |
208 |
3.93 |
1.007 |
| Valid N (listwise) |
208 |
|
|
Table 3.
Correlations.
| |
Digital Technology Adoption |
Employee Digital Skills |
Leadership Support for Digital Transformation |
Customer-Centric Digital Strategies |
Digital Infrastructure Availability |
Operational Efficiency |
| Digital Technology Adoption |
Pearson Correlation |
1 |
.828**
|
.760**
|
.561**
|
.216**
|
.242**
|
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
|
.000 |
.000 |
.000 |
.002 |
.000 |
| N |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
| Employee Digital Skills |
Pearson Correlation |
.828**
|
1 |
.647**
|
.625**
|
.154*
|
.186**
|
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
.000 |
|
.000 |
.000 |
.027 |
.007 |
| N |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
| Leadership Support for Digital Transformation |
Pearson Correlation |
.760**
|
.647**
|
1 |
.696**
|
.141*
|
.135 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
.000 |
.000 |
|
.000 |
.043 |
.053 |
| N |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
| Customer-Centric Digital Strategies |
Pearson Correlation |
.561**
|
.625**
|
.696**
|
1 |
.118 |
.144*
|
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
.000 |
.000 |
.000 |
|
.091 |
.038 |
| N |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
| Digital Infrastructure Availability |
Pearson Correlation |
.216**
|
.154*
|
.141*
|
.118 |
1 |
.478**
|
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
.002 |
.027 |
.043 |
.091 |
|
.000 |
| N |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
| Operational Efficiency |
Pearson Correlation |
.242**
|
.186**
|
.135 |
.144*
|
.478**
|
1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
.000 |
.007 |
.053 |
.038 |
.000 |
|
| N |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
208 |
| **. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed). |
| *. Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed). |
Table 4.
Model Summary.
| Model |
R |
R Square |
Adjusted R Square |
Std. Error of the Estimate |
| 1 |
.505a
|
.255 |
.236 |
.79798 |
| a. Predictors: (Constant), Digital Infrastructure Availability, Customer-Centric Digital Strategies, Digital Technology Adoption, Leadership Support for Digital Transformation, Employee Digital Skills |
Table 5.
ANOVA.
| Model |
Sum of Squares |
df |
Mean Square |
F |
Sig. |
| 1 |
Regression |
43.984 |
5 |
8.797 |
13.815 |
.000b
|
| Residual |
128.627 |
202 |
.637 |
|
|
| Total |
172.611 |
207 |
|
|
|
| a. Dependent Variable: Operational Efficiency |
| b. Predictors: (Constant), Digital Infrastructure Availability, Customer-Centric Digital Strategies, Digital Technology Adoption, Leadership Support for Digital Transformation, Employee Digital Skills |
Table 6.
Coefficients.
| Model |
Unstandardized Coefficients |
Standardized Coefficients |
t |
Sig. |
| B |
Std. Error |
Beta |
| 1 |
(Constant) |
.520 |
.488 |
|
1.065 |
.288 |
| Digital Technology Adoption |
.359 |
.192 |
.248 |
1.876 |
.062 |
| Employee Digital Skills |
-.054 |
.136 |
-.046 |
-.393 |
.695 |
| Leadership Support for Digital Transformation |
-.195 |
.150 |
-.142 |
-1.298 |
.196 |
| Customer-Centric Digital Strategies |
.102 |
.116 |
.080 |
.879 |
.380 |
| Digital Infrastructure Availability |
.599 |
.085 |
.442 |
7.082 |
.000 |
| a. Dependent Variable: Operational Efficiency |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).