Submitted:
30 December 2024
Posted:
31 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
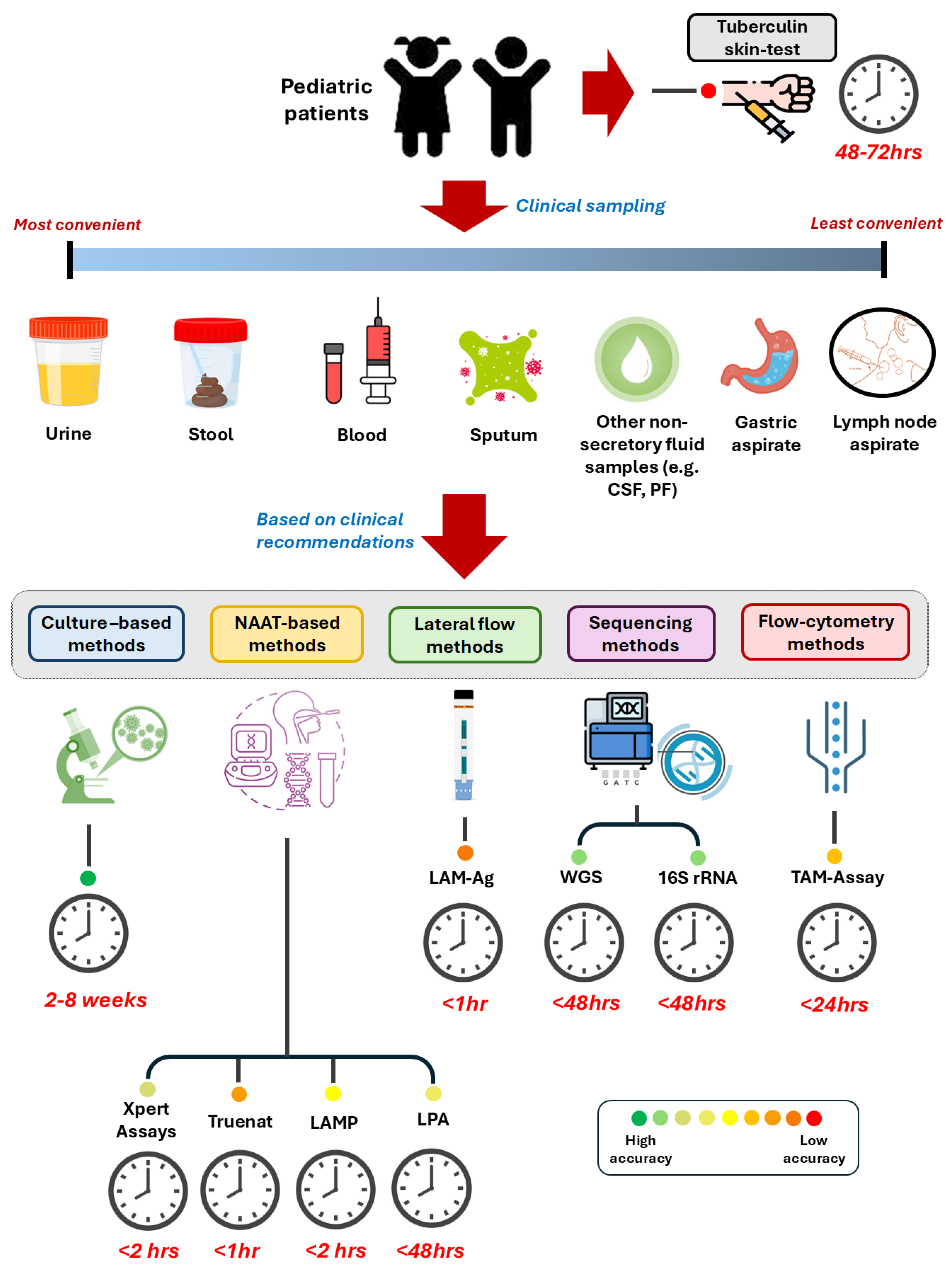
Introduction
Challenges in Pediatric TB Sampling
Existing Diagnostic Methods and Gaps
Traditional Diagnostic Methods for Pediatric TB
Molecular Diagnostic Techniques for Pediatric TB
Emerging Approaches in Pediatric TB Diagnosis
Balancing Speed, Accuracy and Cost of Diagnosis
Future Directions
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
References
- Basile, F.W.; Nabeta, P.; Ruhwald, M.; Song, R. Pediatric Tuberculosis Diagnostics: Present and Future. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc 2022, 11, S85–S93. [CrossRef]
- World Health organization https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/data. Geneva 2024,.
- Geneva: World Health Organization Diagnosis of Tuberculosis and Detection of Drug-Resistance: Rapid Communication.
- World Health Organization WHO TB Knowledge Sharing Platform.
- World Health organization Global Tuberculosis Report 2022.
- Olbrich, L.; Nliwasa, M.; Sabi, I.; Ntinginya, N.E.; Khosa, C.; Banze, D.; Corbett, E.L.; Semphere, R.; Verghese, V.P.; Michael, J.S.; et al. Rapid and Accurate Diagnosis of Pediatric Tuberculosis Disease: A Diagnostic Accuracy Study for Pediatric Tuberculosis. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2023, 42, 353–360. [CrossRef]
- Gebre, M.; Cameron, L.H.; Tadesse, G.; Woldeamanuel, Y.; Wassie, L. Variable Diagnostic Performance of Stool Xpert in Pediatric Tuberculosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Open Forum Infect Dis 2021, 8. [CrossRef]
- Togun, T.O.; Kampmann, B. Diagnostics for Childhood Tuberculosis: A Marathon Rather than a Sprint. Lancet Infect Dis 2024, 24, 110–112. [CrossRef]
- Wobudeya, E.; Bonnet, M.; Walters, E.G.; Nabeta, P.; Song, R.; Murithi, W.; Mchembere, W.; Dim, B.; Taguebue, J.-V.; Orne-Gliemann, J.; et al. Diagnostic Advances in Childhood Tuberculosis—Improving Specimen Collection and Yield of Microbiological Diagnosis for Intrathoracic Tuberculosis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 389. [CrossRef]
- Mesman, A.W.; Soto, M.; Coit, J.; Calderon, R.; Aliaga, J.; Pollock, N.R.; Mendoza, M.; Mestanza, F.M.; Mendoza, C.J.; Murray, M.B.; et al. Detection of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in Pediatric Stool Samples Using TruTip Technology. BMC Infect Dis 2019, 19, 563. [CrossRef]
- Walters, E.; Demers, A.-M.; van der Zalm, M.M.; Whitelaw, A.; Palmer, M.; Bosch, C.; Draper, H.R.; Gie, R.P.; Hesseling, A.C. Stool Culture for Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Children. J Clin Microbiol 2017, 55, 3355–3365. [CrossRef]
- Mafirakureva, N.; Klinkenberg, E.; Spruijt, I.; Levy, J.; Shaweno, D.; de Haas, P.; Kaswandani, N.; Bedru, A.; Triasih, R.; Gebremichael, M.; et al. Xpert Ultra Stool Testing to Diagnose Tuberculosis in Children in Ethiopia and Indonesia: A Model-Based Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e058388. [CrossRef]
- Gunasekera, K.S.; Vonasek, B.; Oliwa, J.; Triasih, R.; Lancioni, C.; Graham, S.M.; Seddon, J.A.; Marais, B.J. Diagnostic Challenges in Childhood Pulmonary Tuberculosis—Optimizing the Clinical Approach. Pathogens 2022, 11, 382. [CrossRef]
- Walters, E.; van der Zalm, M.M.; Palmer, M.; Bosch, C.; Demers, A.-M.; Draper, H.; Goussard, P.; Schaaf, H.S.; Friedrich, S.O.; Whitelaw, A.; et al. Xpert MTB/RIF on Stool Is Useful for the Rapid Diagnosis of Tuberculosis in Young Children With Severe Pulmonary Disease. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2017, 36, 837–843. [CrossRef]
- Mafirakureva, N.; Klinkenberg, E.; Spruijt, I.; Levy, J.; Shaweno, D.; de Haas, P.; Kaswandani, N.; Bedru, A.; Triasih, R.; Gebremichael, M.; et al. Xpert Ultra Stool Testing to Diagnose Tuberculosis in Children in Ethiopia and Indonesia: A Model-Based Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e058388. [CrossRef]
- Segala, F.V.; Papagni, R.; Cotugno, S.; De Vita, E.; Susini, M.C.; Filippi, V.; Tulone, O.; Facci, E.; Lattanzio, R.; Marotta, C.; et al. Stool Xpert MTB/RIF as a Possible Diagnostic Alternative to Sputum in Africa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Public Health 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Gonzales-Huerta, L.E.; Evans, C.A. The Potential for Testing Stool to Reduce Tuberculosis Missed Diagnoses and Misdiagnoses. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2018, 99, 243–245. [CrossRef]
- Jayagandan, S.; Singh, J.; Mudliar, S.R.; Shankar, P.; Maurya, A.K.; Malhotra, A.G.; Malik, S.; Purwar, S.; Singh, S. Evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF Assay on Stool Samples for the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis among the Pediatric Population. J Lab Physicians 2023, 15, 329–335. [CrossRef]
- Baghaei, P.; Tabarsi, P.; Farnia, P.; Radaei, A.; Kazempour, M.; Faghani, Y.; Mirsaeidi, M.; Novin, A.; Chitsaz, E.; Mansouri, D.; et al. Utility of Gastric Lavage for Diagnosis of Tuberculosis in Patients Who Are Unable to Expectorate Sputum. J Glob Infect Dis 2011, 3, 339. [CrossRef]
- Khambati, N.; Song, R.; MacLean, E.L.-H.; Kohli, M.; Olbrich, L.; Bijker, E.M. The Diagnostic Yield of Nasopharyngeal Aspirate for Pediatric Pulmonary Tuberculosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Global and Public Health 2023, 1, 18. [CrossRef]
- MacLean, E.; Broger, T.; Yerlikaya, S.; Fernandez-Carballo, B.L.; Pai, M.; Denkinger, C.M. A Systematic Review of Biomarkers to Detect Active Tuberculosis. Nat Microbiol 2019, 4, 748–758. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ai, L.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z.; Wang, F. Review and Updates on the Diagnosis of Tuberculosis. J Clin Med 2022, 11, 5826. [CrossRef]
- Brent, A.J.; Mugo, D.; Musyimi, R.; Mutiso, A.; Morpeth, S.C.; Levin, M.; Scott, J.A.G. Bacteriological Diagnosis of Childhood TB: A Prospective Observational Study. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 11808. [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Click, E.S.; McCarthy, K.D.; Heilig, C.M.; Mchembere, W.; Smith, J.P.; Fajans, M.; Musau, S.K.; Okeyo, E.; Okumu, A.; et al. Sensitive and Feasible Specimen Collection and Testing Strategies for Diagnosing Tuberculosis in Young Children. JAMA Pediatr 2021, 175, e206069. [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, O.; Moses, N.; Sanga, D.; Annie, W. The Effect of Empirical and Laboratory-Confirmed Tuberculosis on Treatment Outcomes. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 14854. [CrossRef]
- Detjen, A.K.; DiNardo, A.R.; Leyden, J.; Steingart, K.R.; Menzies, D.; Schiller, I.; Dendukuri, N.; Mandalakas, A.M. Xpert MTB/RIF Assay for the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Respir Med 2015, 3, 451–461. [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Katoch, C.D.S.; Kumar, M.; Dhole, T.N.; Sharma, Y.K. Evaluation of Microscopic Observation Drug Susceptibility (MODS) Assay as a Rapid, Sensitive and Inexpensive Test for Detection of Tuberculosis and Multidrug Resistant Tuberculosis. Med J Armed Forces India 2019, 75, 58–64. [CrossRef]
- Hamada, Y.; Kontsevaya, I.; Surkova, E.; Wang, T.T.; Liu, V.; Ziganshina, L.E.; Rangaka, M.X.; Denkinger, C.; Abubakar, I. WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis Module 3: Diagnosis. Tests for TB Infection Web Annex B Safety of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Antigen-Based Skin Tests: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis; 2021; ISBN 9789240056602.
- Mastrolia, M.V.; Sollai, S.; Totaro, C.; Putignano, P.; de Martino, M.; Galli, L.; Chiappini, E. Utility of Tuberculin Skin Test and IGRA for Tuberculosis Screening in Internationally Adopted Children: Retrospective Analysis from a Single Center in Florence, Italy. Travel Med Infect Dis 2019, 28, 64–67. [CrossRef]
- Machingaidze, S.; Wiysonge, C.S.; Gonzalez-Angulo, Y.; Hatherill, M.; Moyo, S.; Hanekom, W.; Mahomed, H. The Utility of an Interferon Gamma Release Assay for Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Disease in Children. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2011, 30, 694–700. [CrossRef]
- Pai, M.; Dewan, P.K.; Swaminathan, S. Transforming Tuberculosis Diagnosis. Nat Microbiol 2023, 8, 756–759. [CrossRef]
- Nurwidya, F.; Handayani, D.; Burhan, E.; Yunus, F. Molecular Diagnosis of Tuberculosis. Chonnam Med J 2018, 54, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Kohli, M.; Schiller, I.; Dendukuri, N.; Yao, M.; Dheda, K.; Denkinger, C.M.; Schumacher, S.G.; Steingart, K.R. Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra and Xpert MTB/RIF Assays for Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis and Rifampicin Resistance in Adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Ngangue, Y.R.; Mbuli, C.; Neh, A.; Nshom, E.; Koudjou, A.; Palmer, D.; Ndi, N.N.; Qin, Z.Z.; Creswell, J.; Mbassa, V.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of the Truenat MTB Plus Assay and Comparison with the Xpert MTB/RIF Assay to Detect Tuberculosis among Hospital Outpatients in Cameroon. J Clin Microbiol 2022, 60. [CrossRef]
- Gopalaswamy, R.; Kumar, N.; Vashistha, H.; Rajendran, P.; Kayesth, J.; Peravali, C.J.; Kashyap, S.; Ghosh, S.; Yumo, H.; Moore, M.; et al. Comprehensive Assessment of Invalid and Indeterminate Results in Truenat MTB-RIF Testing across Sites under the National TB Elimination Program of India. Front Public Health 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Opota, O.; Mazza-Stalder, J.; Greub, G.; Jaton, K. The Rapid Molecular Test Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra: Towards Improved Tuberculosis Diagnosis and Rifampicin Resistance Detection. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2019, 25, 1370–1376. [CrossRef]
- Kaso, A.W.; Hailu, A. Costs and Cost-Effectiveness of Gene Xpert Compared to Smear Microscopy for the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis Using Real-World Data from Arsi Zone, Ethiopia. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0259056. [CrossRef]
- Bouzouita, I.; Ghariani, A.; Dhaou, K. Ben; Jemaeil, S.; Essaalah, L.; Bejaoui, S.; Draoui, H.; El Marzouk, N.; Mehiri, E.; Slim-Saidi, L. Usefulness of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for Rapid Diagnosis of Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis in Tunisia. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 2217. [CrossRef]
- Waters, R.; Laubscher, M.; Dunn, R.N.; Adikary, N.; Coussens, A.K.; Held, M. Higher Sensitivity of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra Over Tuberculosis Culture for the Diagnosis of Spinal Tuberculosis With Open or Computed Tomography–Guided Biopsies. Open Forum Infect Dis 2024, 11. [CrossRef]
- Slail, M.J.; Booq, R.Y.; Al-Ahmad, I.H.; Alharbi, A.A.; Alharbi, S.F.; Alotaibi, M.Z.; Aljubran, A.M.; Aldossary, A.M.; Memish, Z.A.; Alyamani, E.J.; et al. Evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for the Diagnosis of Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis: A Retrospective Analysis in Saudi Arabia. J Epidemiol Glob Health 2023, 13, 782–793. [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Kumarasamy, N.; Resch, S.C.; Sivaramakrishnan, G.N.; Mayer, K.H.; Tripathy, S.; Paltiel, A.D.; Freedberg, K.A.; Reddy, K.P. Rapid, Point-of-Care Diagnosis of Tuberculosis with Novel Truenat Assay: Cost-Effectiveness Analysis for India’s Public Sector. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0218890. [CrossRef]
- Desikan, P.; Panwalkar, N.; Mirza, S.; Chaturvedi, A.; Ansari, K.; Varathe, R.; Chourey, M.; Kumar, P.; Pandey, M. Line Probe Assay for Detection of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Complex: An Experience from Central India. Indian Journal of Medical Research 2017, 145, 70. [CrossRef]
- Ssengooba, W.; Katamba, A.; Sserubiri, J.; Semugenze, D.; Nyombi, A.; Byaruhanga, R.; Turyahabwe, S.; Joloba, M.L. Performance Evaluation of Truenat MTB and Truenat MTB-RIF DX Assays in Comparison to Gene XPERT MTB/RIF Ultra for the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Uganda. BMC Infect Dis 2024, 24, 190. [CrossRef]
- Nathavitharana, R.R.; Cudahy, P.G.T.; Schumacher, S.G.; Steingart, K.R.; Pai, M.; Denkinger, C.M. Accuracy of Line Probe Assays for the Diagnosis of Pulmonary and Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. European Respiratory Journal 2017, 49, 1601075. [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Kanade, S.; Nataraj, G. Performance of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Diagnosis of Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis and Antituberculosis Treatment Initiation. The International Journal of Mycobacteriology 2021, 10, 373–378. [CrossRef]
- Nagai, K.; Horita, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Tsukahara, T.; Nagakura, H.; Tashiro, K.; Shibata, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Nakashima, K.; Ushio, R.; et al. Diagnostic Test Accuracy of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 39090. [CrossRef]
- Bjerrum, S.; Schiller, I.; Dendukuri, N.; Kohli, M.; Nathavitharana, R.R.; Zwerling, A.A.; Denkinger, C.M.; Steingart, K.R.; Shah, M. Lateral Flow Urine Lipoarabinomannan Assay for Detecting Active Tuberculosis in People Living with HIV. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2019, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Broger, T.; Koeppel, L.; Huerga, H.; Miller, P.; Gupta-Wright, A.; Blanc, F.X.; Esmail, A.; Reeve, B.W.P.; Floridia, M.; Kerkhoff, A.D.; et al. Diagnostic Yield of Urine Lipoarabinomannan and Sputum Tuberculosis Tests in People Living with HIV: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Individual Participant Data. Lancet Glob Health 2023, 11, e903–e916. [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Hanrahan, C.; Wang, Z.Y.; Dendukuri, N.; Lawn, S.D.; Denkinger, C.M.; Steingart, K.R. Lateral Flow Urine Lipoarabinomannan Assay for Detecting Active Tuberculosis in HIV-Positive Adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016. [CrossRef]
- Schwab, T.C.; Perrig, L.; Göller, P.C.; Guebely De la Hoz, F.F.; Lahousse, A.P.; Minder, B.; Günther, G.; Efthimiou, O.; Omar, S.V.; Egger, M.; et al. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing to Diagnose Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2024, 24, 1162–1176. [CrossRef]
- Dookie, N.; Khan, A.; Padayatchi, N.; Naidoo, K. Application of Next Generation Sequencing for Diagnosis and Clinical Management of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis: Updates on Recent Developments in the Field. Front Microbiol 2022, 13. [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.; Ndlovu, Z.; Sharma, J.; Mansoor, H.; Bharati, M.; Kolan, S.; Morales, M.; Das, M.; Issakidis, P.; Ferlazzo, G.; et al. Operationalising Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing for Routine Diagnosis of Drug-Resistant TB. Public Health Action 2023, 13, 43–49. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.I.M.; Ziegler, C.; Held, K.; Dubinski, I.; Ley-Zaporozhan, J.; Geldmacher, C.; von Both, U. The TAM-TB Assay—A Promising TB Immune-Diagnostic Test With a Potential for Treatment Monitoring. Front Pediatr 2019, 7. [CrossRef]
- Portevin, D.; Moukambi, F.; Clowes, P.; Bauer, A.; Chachage, M.; Ntinginya, N.E.; Mfinanga, E.; Said, K.; Haraka, F.; Rachow, A.; et al. Assessment of the Novel T-Cell Activation Marker–Tuberculosis Assay for Diagnosis of Active Tuberculosis in Children: A Prospective Proof-of-Concept Study. Lancet Infect Dis 2014, 14, 931–938. [CrossRef]
- Trenti, T. Synergy Between Point-of-Care Testing and Laboratory Consolidations. EJIFCC 2021, 32, 328–336.
- Hong, J.M.; Lee, H.; Menon, N. V.; Lim, C.T.; Lee, L.P.; Ong, C.W.M. Point-of-Care Diagnostic Tests for Tuberculosis Disease. Sci Transl Med 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Lewinsohn, D.M.; Leonard, M.K.; Lobue, P.A.; Cohn, D.L.; Daley, C.L.; Desmond, E.; Keane, J.; Lewinsohn, D.A.; Loeffler, A.M.; Mazurek, G.H.; et al. Official American Thoracic Society/Infectious Diseases Society of America/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Clinical Practice Guidelines: Diagnosis of Tuberculosis in Adults and Children. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2017, 64, e1–e33.
- Graham, S.M.; Oliwa, J.N. DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS A DESK GUIDE FOR PRIMARY HEALTH CARE WORKERS Fourth Edition 2023; 2023;
- World Health Organization Guidance for National Tuberculosis Programmes on the Management of Tuberculosis in Children; World Health Organization, 2015; ISBN 9789241548748.
- World Health Organization WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis Module 5: Management of Tuberculosis in Children and Adolescents; 2022;
- Yerlikaya, S.; Broger, T.; Isaacs, C.; Bell, D.; Holtgrewe, L.; Gupta-Wright, A.; Nahid, P.; Cattamanchi, A.; Denkinger, C.M. Blazing the Trail for Innovative Tuberculosis Diagnostics. Infection 2024, 52, 29–42. [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tan, G.; Ma, J.; Yang, J.; Guo, Y.; Lu, H.; Ke, H.; Li, M.; Tang, Y.-W.; Sha, W.; et al. Assessment of the Cepheid 3-Gene Host Response Fingerstick Blood Test (MTB-HR) on Rapid Diagnosis of Tuberculosis. Emerg Microbes Infect 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, J.S.; van der Spuy, G.; Gindeh, A.; Thuong, N.T.T.; Namuganga, A.; Owolabi, O.; Mayanja-Kizza, H.; Nsereko, M.; Thwaites, G.; Winter, J.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of the Cepheid 3-Gene Host Response Fingerstick Blood Test in a Prospective, Multi-Site Study: Interim Results. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2022, 74, 2136–2141. [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Li, K.; Li, Y.; Guo, D.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Gong, W. CRISPR-Based Diagnostics: A Potential Tool to Address the Diagnostic Challenges of Tuberculosis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1211. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Pan, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, H. A New Method for the Detection of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Based on the CRISPR/Cas System. BMC Infect Dis 2023, 23, 680. [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, S.; Li, C.; Pang, Y. Development and Clinical Evaluation of a CRISPR/Cas13a-Based Diagnostic Test to Detect Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in Clinical Specimens. Front Microbiol 2023, 14. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; LaCourse, S.M.; Kay, A.W.; Stern, J.; Escudero, J.N.; Youngquist, B.M.; Zheng, W.; Vambe, D.; Dlamini, M.; Mtetwa, G.; et al. CRISPR Detection of Circulating Cell-Free Mycobacterium Tuberculosis DNA in Adults and Children, Including Children with HIV: A Molecular Diagnostics Study. Lancet Microbe 2022, 3, e482–e492. [CrossRef]
- Manyelo, C.M.; Solomons, R.S.; Snyders, C.I.; Mutavhatsindi, H.; Manngo, P.M.; Stanley, K.; Walzl, G.; Chegou, N.N. Potential of Host Serum Protein Biomarkers in the Diagnosis of Tuberculous Meningitis in Children. Front Pediatr 2019, 7. [CrossRef]
- Nathavitharana, R.R.; Garcia-Basteiro, A.L.; Ruhwald, M.; Cobelens, F.; Theron, G. Reimagining the Status Quo: How Close Are We to Rapid Sputum-Free Tuberculosis Diagnostics for All? EBioMedicine 2022, 78, 103939. [CrossRef]
- Walzl, G.; McNerney, R.; du Plessis, N.; Bates, M.; McHugh, T.D.; Chegou, N.N.; Zumla, A. Tuberculosis: Advances and Challenges in Development of New Diagnostics and Biomarkers. Lancet Infect Dis 2018, 18, e199–e210. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization WHO on tuberculosis (Module 2: Screening); 2021;
- Kazemzadeh, S.; Kiraly, A.P.; Nabulsi, Z.; Sanjase, N.; Maimbolwa, M.; Shuma, B.; Jamshy, S.; Chen, C.; Agharwal, A.; T. Lau, C.; et al. Prospective Multi-Site Validation of AI to Detect Tuberculosis and Chest X-Ray Abnormalities. NEJM AI 2024, 1. [CrossRef]
- Nijiati, M.; Ma, J.; Hu, C.; Tuersun, A.; Abulizi, A.; Kelimu, A.; Zhang, D.; Li, G.; Zou, X. Artificial Intelligence Assisting the Early Detection of Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis From Chest X-Rays: A Population-Based Study. Front Mol Biosci 2022, 9. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Sharma, N.; Chauhan, R.; Thapliyal, S.; Gupta, R. Tuberculosis Classification Using EfficientNet B3 Deep Learning Architecture. In Proceedings of the 2023 Global Conference on Information Technologies and Communications (GCITC); IEEE, December 1 2023; pp. 1–6.
- Kaviani, P.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Bizzo, B.C.; Reddy, B.; Tadepalli, M.; Putha, P.; Jagirdar, A.; Ebrahimian, S.; Kalra, M.K.; Dreyer, K.J. Performance of a Chest Radiography AI Algorithm for Detection of Missed or Mislabeled Findings: A Multicenter Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2086. [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.Z.; Ahmed, S.; Sarker, M.S.; Paul, K.; Adel, A.S.S.; Naheyan, T.; Barrett, R.; Banu, S.; Creswell, J. Tuberculosis Detection from Chest X-Rays for Triaging in a High Tuberculosis-Burden Setting: An Evaluation of Five Artificial Intelligence Algorithms. Lancet Digit Health 2021, 3, e543–e554. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Kwak, N.; Yoon, S.H.; Park, N.; Kim, Y.R.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, Y.; Kang, Y.A.; Kim, S.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Based Radiographic Extent Analysis to Predict Tuberculosis Treatment Outcomes: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 13162. [CrossRef]
- David, P.M.; Onno, J.; Keshavjee, S.; Ahmad Khan, F. Conditions Required for the Artificial-Intelligence-Based Computer-Aided Detection of Tuberculosis to Attain Its Global Health Potential. Lancet Digit Health 2022, 4, e702–e704.
- Murphy, K.; Habib, S.S.; Zaidi, S.M.A.; Khowaja, S.; Khan, A.; Melendez, J.; Scholten, E.T.; Amad, F.; Schalekamp, S.; Verhagen, M.; et al. Computer Aided Detection of Tuberculosis on Chest Radiographs: An Evaluation of the CAD4TB v6 System. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 5492. [CrossRef]
- Biewer, A.; Tzelios, C.; Tintaya, K.; Roman, B.; Hurwitz, S.; Yuen, C.M.; Mitnick, C.D.; Nardell, E.; Lecca, L.; Tierney, D.B.; et al. Accuracy of Digital Chest X-Ray Analysis with Artificial Intelligence Software as a Triage and Screening Tool in Hospitalized Patients Being Evaluated for Tuberculosis in Lima, Peru. medRxiv 2023. [CrossRef]
- Kazemzadeh, S.; Yu, J.; Jamshy, S.; Pilgrim, R.; Nabulsi, Z.; Chen, C.; Beladia, N.; Lau, C.; McKinney, S.M.; Hughes, T.; et al. Deep Learning Detection of Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis at Chest Radiography Matched the Clinical Performance of Radiologists. Radiology 2023, 306, 124–137. [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, A.; Thompson, R.; De Vos, M.; David, A.; Schumacher, S.; Sohn, H. Determining Cost and Placement Decisions for Moderate Complexity NAATs for Tuberculosis Drug Susceptibility Testing. PLoS One 2023, 18, e0290496. [CrossRef]
- Cates, L.; Crudu, V.; Codreanu, A.; Ciobanu, N.; Fosburgh, H.; Cohen, T.; Menzies, N.A. Laboratory Costs of Diagnosing TB in a High Multidrug-Resistant TB Setting. The International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2021, 25, 228–230. [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H.; Puri, L.; Nguyen, N.A.T.; Van’t Hoog, A.H.; Nguyen, V.A.T.; Nliwasa, M.; Nabeta, P. Cost and Affordability Analysis of TB-LAMP and Xpert MTB/RIF Assays as Routine Diagnostic Tests in Peripheral Laboratories in Malawi and Vietnam. Journal of Global Health Science 2019, 1. [CrossRef]
- Theron, G.; Venter, R.; Smith, L.; Esmail, A.; Randall, P.; Sood, V.; Oelfese, S.; Calligaro, G.; Warren, R.; Dheda, K. False-Positive Xpert MTB/RIF Results in Retested Patients with Previous Tuberculosis: Frequency, Profile, and Prospective Clinical Outcomes. J Clin Microbiol 2018, 56. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.A. Challenges in Diagnosing Childhood Tuberculosis HHS Public Access; 2016; Vol. 25;.
- Sohn, H.; Sweeney, S.; Mudzengi, D.; Creswell, J.; Menzies, N.A.; Fox, G.J.; MacPherson, P.; Dowdy, D.W. Determining the Value of TB Active Case-Finding: Current Evidence and Methodological Considerations. The International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2021, 25, 171–181. [CrossRef]
- Weyer, K.; Mirzayev, F.; Migliori, G.B.; Van Gemert, W.; D’Ambrosio, L.; Zignol, M.; Floyd, K.; Centis, R.; Cirillo, D.M.; Tortoli, E.; et al. Rapid Molecular TB Diagnosis: Evidence, Policy Making and Global Implementation of Xpert MTB/RIF. European Respiratory Journal 2013, 42, 252–271. [CrossRef]
- Medina-Marino, A.; Bezuidenhout, D.; Bezuidenhout, C.; Facente, S.N.; Fourie, B.; Shin, S.S.; Penn-Nicholson, A.; Theron, G. In-Home TB Testing Using GeneXpert Edge Is Acceptable, Feasible, and Improves the Proportion of Symptomatic Household Contacts Tested for TB: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Open Forum Infect Dis 2024, 11. [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.J.; Babirye, D.; Armstrong-Hough, M.; Mark, D.; Ayakaka, I.; Katamba, A.; Haberer, J.E.; Davis, J.L. Text Messages Sent to Household Tuberculosis Contacts in Kampala, Uganda: Process Evaluation. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2018, 6, e10239. [CrossRef]
- Maphalle, L.N.F.; Michniak-Kohn, B.B.; Ogunrombi, M.O.; Adeleke, O.A. Pediatric Tuberculosis Management: A Global Challenge or Breakthrough? Children 2022, 9, 1120. [CrossRef]
| Test | Technology | Time taken | Age | Symptoms and medical history | Target Population | Sample | Accuracy | Technical Simplicity | Recommendations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pediatric | Adolescents | Adults | |||||||||
| ±Xpert MTB/ RIF and/ or Xpert Ultra | qPCR | <2 h | >15 years | Signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB | - | √ | √ | Sputum | High | Moderately simple; requires moderate training | Initial Diagnosis Strongly recommended |
| <15 years | Signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB | √ | Sputum, gastric aspirate, nasopharyngeal aspirate and stool | Moderate to Low | Strongly recommended | ||||||
| >15 years | Signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB and without a prior history of TB (≤5 years) or with a remote history of TB treatment (>5 years since end of treatment) | - | √ | √ | Sputum | High | Initial Diagnosis Strongly recommended |
||||
| >15 years | Signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB and with a prior history of TB and an end of treatment <5 years | - | √ | √ | Sputum | High | Initial Diagnosis Strongly recommended |
||||
| All | Signs and symptoms of TB meningitis | √ | √ | √ | Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) | Moderate to Low | Strongly recommended | ||||
| All | Signs and symptoms of extrapulmonary TB | √ | √ | √ | Lymph node aspirate, lymph node biopsy, pleural fluid, peritoneal fluid, pericardial fluid, synovial fluid or urine specimens | Moderate to Low (Strong for rifampicin resistance) | Conditionally recommended (strongly recommended for Xpert MTB/RIF) | ||||
| All | Signs and symptoms of disseminated TB (HIV-positive) | √ | √ | √ | Blood | Moderate to Low | Conditionally recommended | ||||
| >15 years | General population who had either signs or symptoms of TB or chest radiograph with lung abnormalities or both | √ | √ | Blood | Moderate to Low | Conditionally recommended | |||||
| ±Truenat MTB, MTB plus, (Under development: MTB-Ultima, MTB-INH, MTB-BDQ, MTB TB-COVID-19) | Micro RT-PCR | <1 h | All | With signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB | √ | √ | √ | Sputum | Moderate | Moderately simple; requires moderate training | Conditionally recommended |
| ±Truenat MTB-RIF Dx | All | With signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB and a Truenat MTB or MTB Plus positive result | √ | √ | √ | Sputum | Low | Moderately simple; requires moderate training | Conditionally recommended | ||
| ±Moderate complexity automated nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) | High-throughput molecular PCR | 6-8 h | All | Signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB | √ | √ | √ | Respiratory samples | Moderate | Requires highly trained facility/ manpower | Conditionally recommended (also for isoniazid and rifampicin resistance) |
| ±Loopamp MTBC assay | Loop-mediated isothermal amplification | <2h | >15 years | Signs and symptoms consistent with TB | √ | √ | √ | Sputum | Low | Simple with moderate training | Conditionally recommended |
| >15 years | Necessary further testing of sputum smear-negative specimens | √ | √ | √ | Sputum | Low | Simple with moderate training | Conditionally recommended | |||
| ±LAM Ag assay | Lateral flow urine lipo-arabino-mannan assay | <1 h | All | In inpatient settings→HIV-positive adults and children with signs and symptoms of TB, CD4 cell count of less than 200 cells/mm3 | √ | √ | √ | Urine | Moderate to Low | Simple with minimal instructions | Conditionally recommended |
| All | In outpatient settings→HIV-positive adults and children with signs and symptoms of TB, CD4 cell count of less than 100 cells/mm3 | √ | √ | √ | Urine | Low | Conditionally recommended | ||||
| ±First-line line-probe assay (LPAs) | Multiplex PCR+ DNA strip reverse hybridization assay | < 48 h | All | Sputum smear-positive specimen or a cultured isolate of Mtb complex (MTBC) | √ | √ | √ | Sputum | Moderate | Requires highly trained facility/ manpower | Conditionally recommended (rifampicin/ isoniazid resistance) |
| Second-line line-probe assays (SL-LPAs)* | Multiplex PCR+ DNA strip reverse hybridization assay | < 48 h | All | Confirmed MDR/RR-TB | √ | √ | √ | Sputum | Moderate to low | Requires highly trained facility/ manpower | Conditionally recommended (Fluoroquinolone resistance detection) |
| ±High complexity reverse hybridization-based NAATs | Multiplex PCR+ DNA strip reverse hybridization assay (targeting the entire pncA gene) | Variable (<24 hrs) | All | Bacteriologically confirmed TB | √ | √ | √ | TB culture isolates | Low | Requires highly trained facility/ manpower | Conditionally recommended (Specialized for pyrazinamide resistance) |
| Next-generation sequencing | Whole genome/ targeted sequencing | < 48 h | All | NA | √ | √ | √ | Sputum, TB culture isolates | High | Requires highly trained facility/ manpower | NA |
| TAM TB assay* | Flow cytometry / TB specific biomarkers CD38/ CD27 | <24 h | All | NA | √ | √ | √ | Blood | Moderate to High | Requires highly trained facility/ manpower | NA |
| Tool | Accuracy | Input | Key Feature | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAD4TB (version 7) | 94% sensitivity and 84% specificity | Chest X-rays | Includes modules for registration, symptom screening, X-ray imaging, and integration with GeneXpert systems | [79] |
| EfficientNetB3 | high performance (highest Area Under Curve 0.999) | chest X-rays | A convolutional neural network structure that can accurately detect mislabeled and missed findings | [74]. |
| qSpot-TB | 96% sensitivity | chest X-ray analysis | Received FDA breakthrough device designation | [75] |
| InferRead DR (version 2) | 90% sensitivity and 70.4% specificity | chest X-ray analysis | Screening time is <1 min, no subsequent validation suggested | [76] |
| Lunit INSIGHT | ~89% sensitivity | chest X-ray analysis | Clinical evaluations worldwide show promise in conspicuity among other tools | [76] |
| JF CXR-1 | 94% sensitivity | chest X-rays | Clinical evaluations worldwide show promise working under limited resource | [76] |
| qXR | ~91% sensitivity | chest X-rays | Received FDA/CE clearances | [80] |
| Google Health AI system | Yet to be determined | chest X-rays | A deep learning-based system capable of personalized health management | [81] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





