Submitted:
24 December 2024
Posted:
25 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
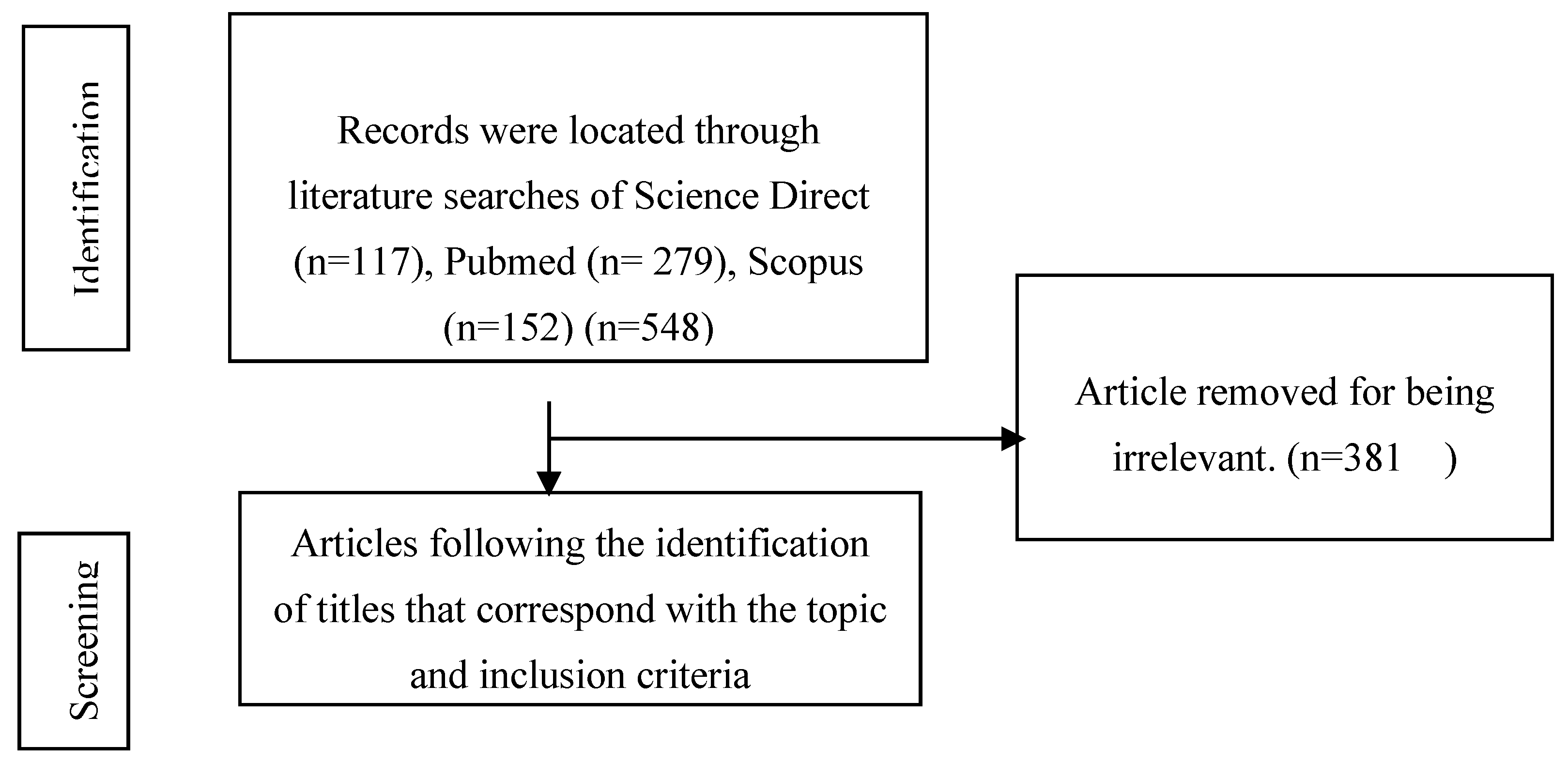
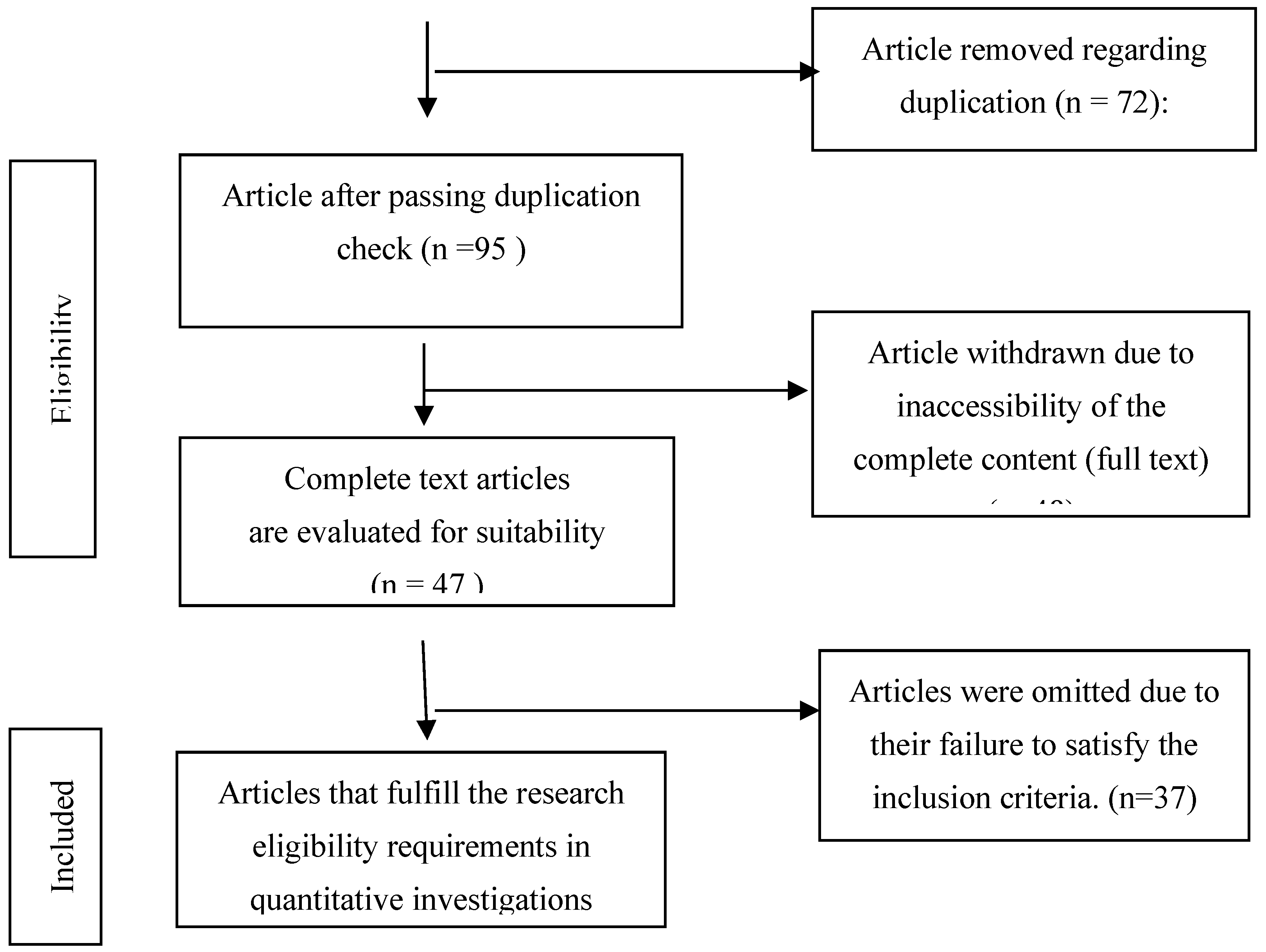
| No | Nama Peneliti | Tahun | Nama Jurnal | Judul Jurnal | Ringkasan Hasil Penelitian |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zaqhini et al | 2020 | International Journal of Nursing Studies 1 | The relationship between nurse managers’ leadership style and patients’ perception of the quality of the care provided by nurses: Cross sectional survey | The findings of the research indicated that when nurses are content with their leadership, they experience reduced fatigue and tension in their interpersonal relationships, they exhibit a lower level of negative behavior, and consequently, patients express higher satisfaction with the quality of care delivered by nurses. |
| 2 | Heryanoor, Nursalam | 2021 | Journal of International Dental and Medical Research | Culture-Based Situational Leadership Model in Improving the Organization Nurse Performance | The situational leadership framework for organizations has the capability to improve nurse performance by 53. 4%. This improvement is linked to factors associated with internal leadership, individual nurses, job characteristics, and the organization's culture. Recent findings concerning the situational leadership framework based on organizational culture indicate that nurse performance is affected by internal leadership factors and individual nurse factors, which contribute positively to organizational culture, situational leadership, and performance. The innate traits of leaders (motivation and self-perception) as well as individual nurse characteristics (knowledge and expectations) can enhance performance by implementing a situational leadership strategy rooted in organizational culture that prioritizes innovation and risk-taking, attention to detail, results focus, people focus, team focus, assertiveness, and stability. Utilizing a situational leadership framework grounded in organizational culture is expected to improve performance in aspects such as caring, collaboration, empathy, responsiveness, courtesy, and sincerity. |
| 3 | (Ansar Abbas, Muhammad Saud, Dian Ekowati and Indrianawati Usman, 2021) | 2021 | Int. J. Productivity and Quality Management | Servant leadership: a strategic choice for organisational performance. An empirical discussion from Pakistan |
The situational leadership model in an organization can enhance nurse performance by 53. 4%. This improvement is attributed to internal leadership elements, individual nurse characteristics, job features, and the culture of the organization. Recent research on the organizational culture-focused situational leadership model regarding nurse performance is influenced by internal leadership factors and individual nurse traits that positively impact organizational culture, situational leadership, and overall performance. Leaders' internal factors (motivation and self-image) and individual nurse attributes (knowledge and expectations) can boost performance by applying organizational culture-driven situational leadership based on innovation and risk-taking, detail orientation, result orientation, people orientation, team orientation, assertiveness, and stability. Implementing organizational culture-centered situational leadership will enhance performance through caring, collaboration, empathy, responsiveness, politeness, and sincerity. |
| 4 | (Praptini Yulianti, 2019) | 2019 | International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change | Building Employee Creative Performance: through Person-Job Fit, Empowering | Empowering leadership has a greater impact on enhancing creative self-efficacy than Person-job fit when viewed through the lens of DA-fit and SV-fit. Consequently, creative self-efficacy plays a significant role in affecting employee creative performance. The potential for creativity to flourish within an organization is influenced by the leader's role. By fostering employee self-efficacy toward creativity, empowering leadership will ultimately boost employee creative performance. |
| 5 | (Dodot Adikoeswanto, Siti Nurjanah, Saparuddin Mukhtar, Anis Eliyana, *, 2024) | 2024 | International Journal of Advanced and Applied Sciences | Supportive leadership and voice behavior: The mediating role of work engagement | Supportive leadership has a notable positive effect on the voice behavior of correctional officers and their level of work engagement, a notable positive effect of work engagement on the voice behavior of correctional officers, and a positive effect of supportive leadership on the voice behavior of correctional officers mediated by work engagement across all correctional offices in Aceh. |
| 6 | Yetty Dwi Lestari et al | 2021 | International Journal of Leadership in Education Theory and Practice |
Dynamic managerial capability, trust in leadership and performance: the role of cynicism toward change | The results of this research suggest that confidence in leadership is a key element that impacts organizational performance. Consequently, it is essential to take trust in leadership seriously (Lines et al. , 2005) as it is crucial for creating a nurturing environment (Gravenhorst et al. , 2003) required for successful change initiatives. Notably, the findings also revealed that there was no meaningful difference |
| 7 | (Yetty Dwi Lestari, Fiona Niska Dinda Nadia, Badri Munir Sukoco, David, Ahlstrom, Sunu Widianto, Ely Susanto, 2021) | 2021 | International Journal of Leadership in Education Theory and Practice |
Dynamic managerial capability, trust in leadership and performance: the role of cynicism toward change | The results of this research suggest that confidence in leadership is a key element that affects organizational performance. As a result, confidence in leadership must be taken seriously (Lines et al. , 2005) as it contributes significantly to creating a supportive atmosphere (Gravenhorst et al. , 2003) essential for the success of change initiatives. Curiously, the findings additionally revealed that there was no notable difference |
| 8 | Alsadaan, N, et al | 2023 | INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing |
Impact of Nurse Leaders Behaviors on Nursing Staff Performance: A Systematic Review of Literature |
Nursing leadership plays a crucial role in shaping nurses' views on elements that affect their motivation to work. This influence can occur either directly or indirectly. Consequently, it is essential to have skilled nursing leaders to establish a practice environment that can nurture nurses' ability to attain success. In simpler terms, the connection between nursing leadership and nurse success is vital, and advancing leadership in the nursing field should be emphasized to reach the best possible patient outcomes. |
| 9 | (Moghaddam et al, 2021) | 2021 | BMC Nursing | Nurses’ trust in managers and its relationship with nurses’ performance behaviors: a descriptive-correlational study | Most nurses trust their head nurses and supervisors. The functional behaviors exhibited by most nurses were described as very good. There was no significant relationship between nurses' trust in head nurses and their functional behaviors, whereas the trust between nurses and supervisors did not significantly relate to nurses' functional behaviors. |
| 10 | (Dluha Mafula, Nursalam, Tintin Sukartini, 2020) |
2020 | Indonesian Nursing Journal of Education and Clinic |
Quality of Nursing Worklife Based on Caring Model for Improving Nurse Performance in Hospitals | A sum of 25 indicators were identified as valid (outer loading value > 0. 5) with a variable diversity of 24. 43%, thus internal, social, environmental, operational, and administrative factors influence nurse performance both directly and indirectly through QNWL-based caring. |
References
- Ansar Abbas, Muhammad Saud, Dian Ekowati and Indrianawati Usman, F. S. Servant leadership: a strategic choice for organisational performance. An empirical discussion from Pakistan’, Int. J. Productivity and Quality Management 2021, 34, 469–485.
- Alsadaan, N. , Salameh, B., Reshia, F. A. A. E., Alruwaili, R. F., Alruwaili, M., Awad Ali, S. A.,... & Jones, L. K. Impact of nurse leaders behaviors on nursing staff performance: A systematic review of literature. INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing 2023, 60, 00469580231178528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dodot Adikoeswanto, Siti Nurjanah, Saparuddin Mukhtar, Anis Eliyana, *, N. L.M.K. ‘Supportive leadership and voice behavior: The mediating role of work engagement’, International Journal of Advanced and Applied Sciences 2024, 11, 39–48.
- Gibson, J.L., J. M.Ivancecich, J.H.Donnelly, J. Organisasi, Perilaku, Struktur, Proses. Jakarta: Bina Rupa Aksara, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hadi-Moghaddam, M. , Karimollahi, M., & Aghamohammadi, M. Nurses’ trust in managers and its relationship with nurses’ performance behaviors: a descriptive-correlational study. BMC nursing 2021, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hasibuan, M.S. Basic Management, Definition, and Problems,. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Heryyanoor, Nursalam, Abdul Aziz Alimul Hidayat, Taufik Hidayat, Raziansyah, Zubaidah, P. ‘Culture-Based Situational Leadership Model in Improving the Organization Nurse Performance’, Journal of International Dental and Medical Research 2021, 14, 1251–1259 Available online: https://wwwjidmrcom/journal/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/62-7.-2265_Culture-Based-Situational- Leadership-Model-in-Improving-the-Organization-Nurse-Performance_HERRYNOOR_28- Juli_rev.pdf.
- Kadarisman. Human Resource Development Management. Jakarta: Raja Grafindo Rosada, 2017.
- Lestari, Y. D. , Nadia, F. N. D., Sukoco, B. M., Ahlstrom, D., Widianto, S., Susanto, E.,... & Fauzi, A. M. Dynamic managerial capability, trust in leadership and performance: the role of cynicism toward change. International Journal of Leadership in Education 2024, 27, 1420–1450. [Google Scholar]
- Nursalam Manajemen Keperawatan Aplikasi dalam Praktik Keperawatan Profesional. 4th edn. Jakarta: Salemba Medika. 2017.
- Maf'ula, D.; Nursalam, N.; Sukartini, T. Quality of nursing worklife based on caring model for improving nurse performance in hospitals. Indonesian Nursing Journal of Education and Clinic (Injec) 2020, 5, 172–184. [Google Scholar]
- Nursalam. Nursing Management Applications in Professional Nursing Practice, 4th ed.; Jakarta: Salemba Medika, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Praptini Yulianti, I.U. Building Employee Creative Performance: through Person-Job Fit, Em’, International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change 2019, 9, 167–180.
- Yetty Dwi Lestari, Fiona Niska Dinda Nadia, Badri Munir Sukoco, David, Ahlstrom, Sunu Widianto, Ely Susanto, R. A.N.& A.M.F. ‘Dynamic managerial capability, trust in leadership and performance: the role of cynicism toward change’, Jurnal Internasional Kepemimpinan dalam Pendidikan 2021, 11, 49–62.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





