Submitted:
16 December 2024
Posted:
25 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Background: Leadership constitutes an endeavor to sway collective actions. Leadership entails the capacity to achieve consensus on shared objectives. Leadership is an attempt to steer others toward attaining specific aims. Leadership represents the most impactful connection between a leader and their followers. While it may be challenging to encapsulate, fundamentally, leadership pertains to the act of one person influencing the actions of others for a specific reason. However, this does not imply that everyone who sways others for a reason qualifies as a leader. Objective: To outline the philosophical viewpoint of leadership in enhancing nurse performance: a literature review methodology.Method: A literature review study utilizing databases from Google Scholar, PubMed, and ProQuest with the search terms "leadership" and "nurse performance." Results: From a philosophical standpoint, leadership is a notion that necessitates profound contemplation regarding the essence, purposes, and fundamental principles that inform an individual's leadership. Philosophical viewpoints emphasize the moral, ethical, and ontological dimensions of leadership, as well as the way individuals perceive their duties and interactions with others.Conclusion: In philosophical terms, leadership revolves around establishing significance, providing guidance, and leading with integrity. Leaders bear the responsibility not only for attaining tangible objectives but also for fostering a more equitable, harmonious, and humane world. This philosophical insight reminds us that leadership transcends mere action; it also involves serving as a model for subordinates in elevating performance.
Keywords:
Introduction
Method
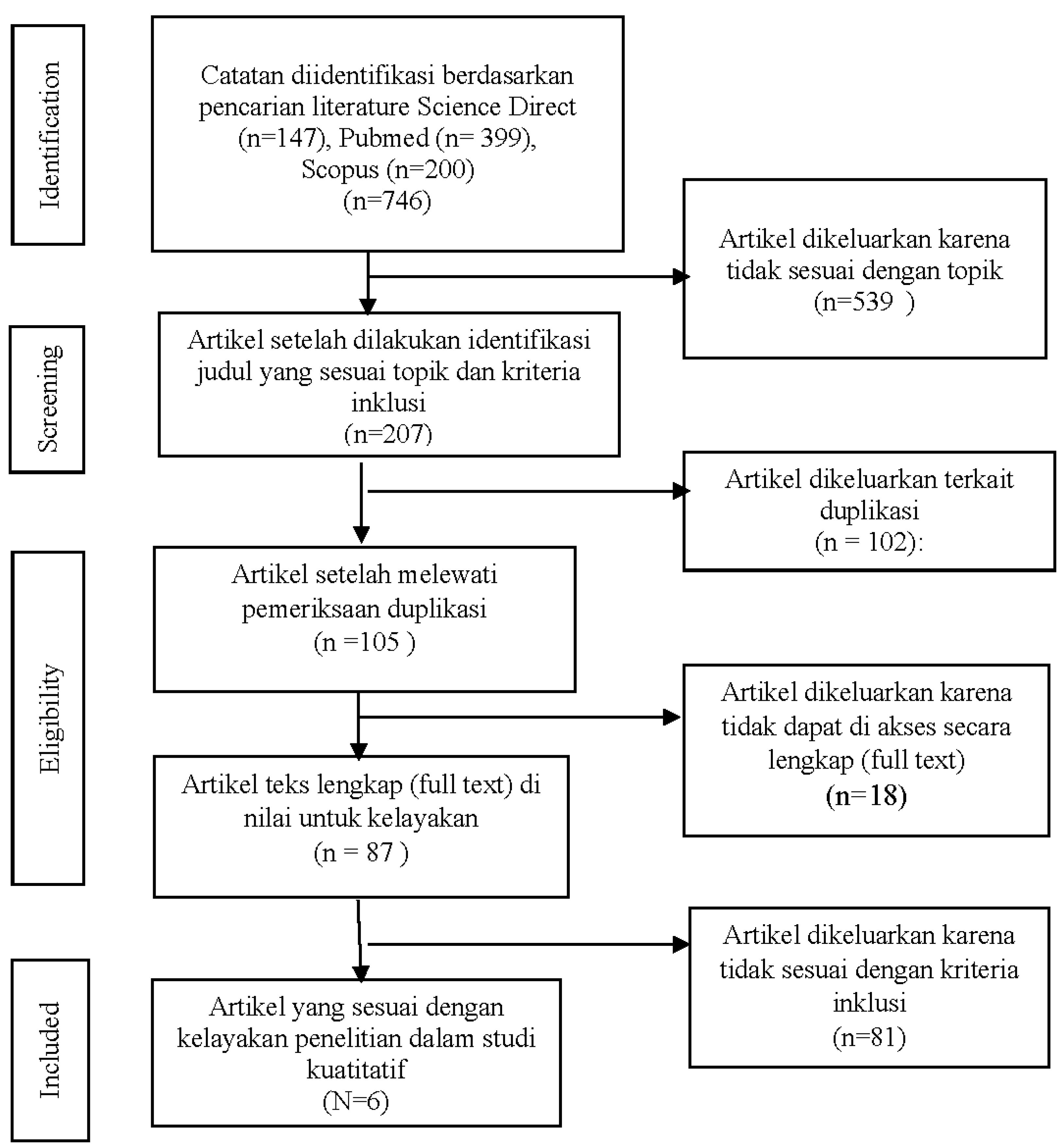
Results
| No | Researcher Name | Year | Journal Name | Title Journal | Summary of Research Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zaqhini et al | 2020 | International Journal of Nursing Studies 1 |
The relationship between nurse managers' leadership style and patients' perception of the quality of the care provided by nurses: Cross sectional survey |
Research findings indicate that when nurses are content with their leadership, they experience less fatigue and tension in their interpersonal relationships, are less engaged in negative behaviors, and consequently, patients are more satisfied with the quality of care provided by the nurses. |
| 2 | Heryanoor , Nursalam | 2021 | Journal of International Dental and Medical Research | Culture Based Situational Leadership Model in Improving the Organization Nurse Performance |
Model can enhance nurse performance by 53. 4%. This improvement is attributed to internal leadership factors, individual nurse factors, job characteristics, and organizational culture. Recent discoveries regarding the organizational culture-based situational leadership model and its impact on nurse performance are influenced by internal leadership factors and individual nurse factors that positively affect organizational culture, situational leadership, and performance. Internal leadership aspects (motivation and self-concept) and individual nurse aspects (knowledge and expectations) can boost performance through the application of organizational culture-based situational leadership founded on innovation and risk-taking, attention to detail, results orientation, people orientation, team orientation, aggressiveness, and stability. The use of organizational culture-based situational leadership will enhance performance through caring, collaboration, empathy, responsiveness, courtesy, and sincerity. |
| 3 | (Ansar Abbas, Muhammad Saud, Dian Ekowati and Indrianawati Usman, 2021) | 2021 | Int. J. Productivity and Quality Management | Servant leadership: a strategic choice fororganizational performance. An empirical discussion from Pakistan |
More correlation strong between performance, compared with commitment, and gender is visible clear. This own significant relationship with variable demographic like level education and income Respondents. Performance and commitment own connection negative with service and the positive with gender. Performance shows significant correlation with age and marital status, reported as coefficient correlation. This result confirm characteristic all variables in the sector education. Can concluded that with improvement experience, desire For increase performance and commitment on the spot Work decreased in employees; the same thing has reported with performance, age, and marital status. Age, marital status, and education own correlation significant positive with income, while gender, commitment, leadership servants, and nature connection performance share positive and significant relationship. |
| 4 | (Praptini Yulianti, 2019) | 2019 | International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change | Building Employee Creative Performance: through Person-Job Fit, Empowering |
Empowering leadership has a greater importance in affecting creative self-efficacy than Person-job fit from the perspectives of DA-fit and SV-fit. Similarly, creative self-efficacy has a notable effect on the performance of creative employees. The ability to foster creativity can be enhanced more effectively within a company, depending on the role of the leader. Empowering leadership can enhance employees' self-efficacy to innovate and ultimately boost the performance of creative employees. |
| 5 | (Dodot Adikoeswanto, Siti Nurjanah, Saparuddin Mukhtar, Anis Eliyana, *, 2024) | 2024 | International Journal of Advanced and Applied Sciences | Supportive leadership and voice behavior : The mediating role of work engagement |
There is a significant positive influence from supportive leadership on officer socialization and work engagement, a significant positive influence from work engagement to officer socialization of voice behavior, and a positive influence of supportive leadership on officer correctional voice behavior through work engagement within correctional offices in Aceh. |
| 6 | Yetty Dwi Lestari et al | 2021 | International Journal of Leadership in EducationTheory and Practice | Dynamic managerial capability, trust in leadership and performance: the role of cynicism toward change |
Findings study This demonstrate that trust in leadership is one of the fundamental aspects that affect organizational performance. Therefore, this trust in leadership needs to be taken into serious consideration (Lines et al. ,2005) as it plays an important role in creating a supportive environment (Gravenhorst et al. , 2003), which is essential for making change efforts successful. Interestingly, the results also indicate that there is no significant difference. |
Discussion
Conclusion
References
- Ansar Abbas, Muhammad Saud, Dian Ekowati and Indrianawati Usman, FS (2021) 'Servant leadership: a strategic choice for organizational performance. An empirical discussion from Pakistan', Int. J. Productivity and Quality Management , 34(4), pp. 469–485.
- Dodot Adikoeswanto, Siti Nurjanah, Saparuddin Mukhtar, Anis Eliyana, *, NLMK (2024) 'Supportive leadership and voice behavior: The mediating role of work engagement', International Journal of Advanced and Applied Sciences , 11(7), pp. 39–48.
- Gibson, JL, JMIvancecich, JHDonnelly, J. (2003) Organization, Behavior, Structure, Process. Jakarta: Bina Rupa Aksara .
- Gravenhorst et al, (2003). The change capacity of organisations: general assessment and five configurations. Applied Psychology, 52(1), 83-105.
- Hasibuan, MS. (2015) Basic Management, Definition, and Problems, . Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
- Heryanoor, Nursalam, Abdul Aziz Alimul Hidayat, Taufik Hidayat, Raziansyah, Zubaidah, P. (2021) 'Culture-Based Situational Leadership Model in Improving the Organization Nurse Performance', Journal of International Dental and Medical Research , 14(3), pp. 1251–1259. Available at: https://www.jidmr.com/journal/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/62-7.-2265_Culture-Based-Situational-Leadership-Model-in-Improving-the-Organization-Nurse-Performance_HERRYNOOR_28-Juli_rev.pdf.
- Kadarisman (2017) Human Resource Development Management . Jakarta: Raja Grafindo Rosada.
- Lines et al. (2005). The structure and function of attitudes toward organizational change. Human resource development review, 4(1), 8-32.
- Nursalam (2017) Nursing Management Application in Professional Nursing Practice. 4th edn. Jakarta: Salemba Medika.
- Praptini Yulianti, IU (2019) 'Building Employee Creative Performance: through Person-Job Fit, Em', International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change , 9(8), pp. 167–180.
- Yetty Dwi Lestari, Fiona Niska Dinda Nadia, Badri Munir Sukoco, David, Ahlstrom, Sunu Widianto, Ely Susanto, RAN& AMF (2021) 'Dynamic managerial capability, trust in leadership and performance: the role of cynicism toward change', International Journal of Educational Leadership , 11(4), pp. 49–62.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





