Submitted:
12 January 2025
Posted:
13 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Targeting Molecules and Signaling Pathways in Neuroinflammation Intervention
2.1. Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB): A Central Player in the Development of Neuroinflammation and Neurodegenerative Conditions
2.2. Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 (Nrf2): A Novel Approach to Address Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Disorders
2.3. Impact of the NLR (Nucleotide-Binding Domain and Leucine-Rich Repeat Containing) Family Pyrin Domain Containing 3 (NLRP3) Inflammasome on Neuroinflammation: Exploring a Promising Therapeutic Target for Neuroinflammation
2.4. JAK/STAT: An Evergreen and Unconventional Pathway in Neuroinflammation and Neurological Dysfunctions
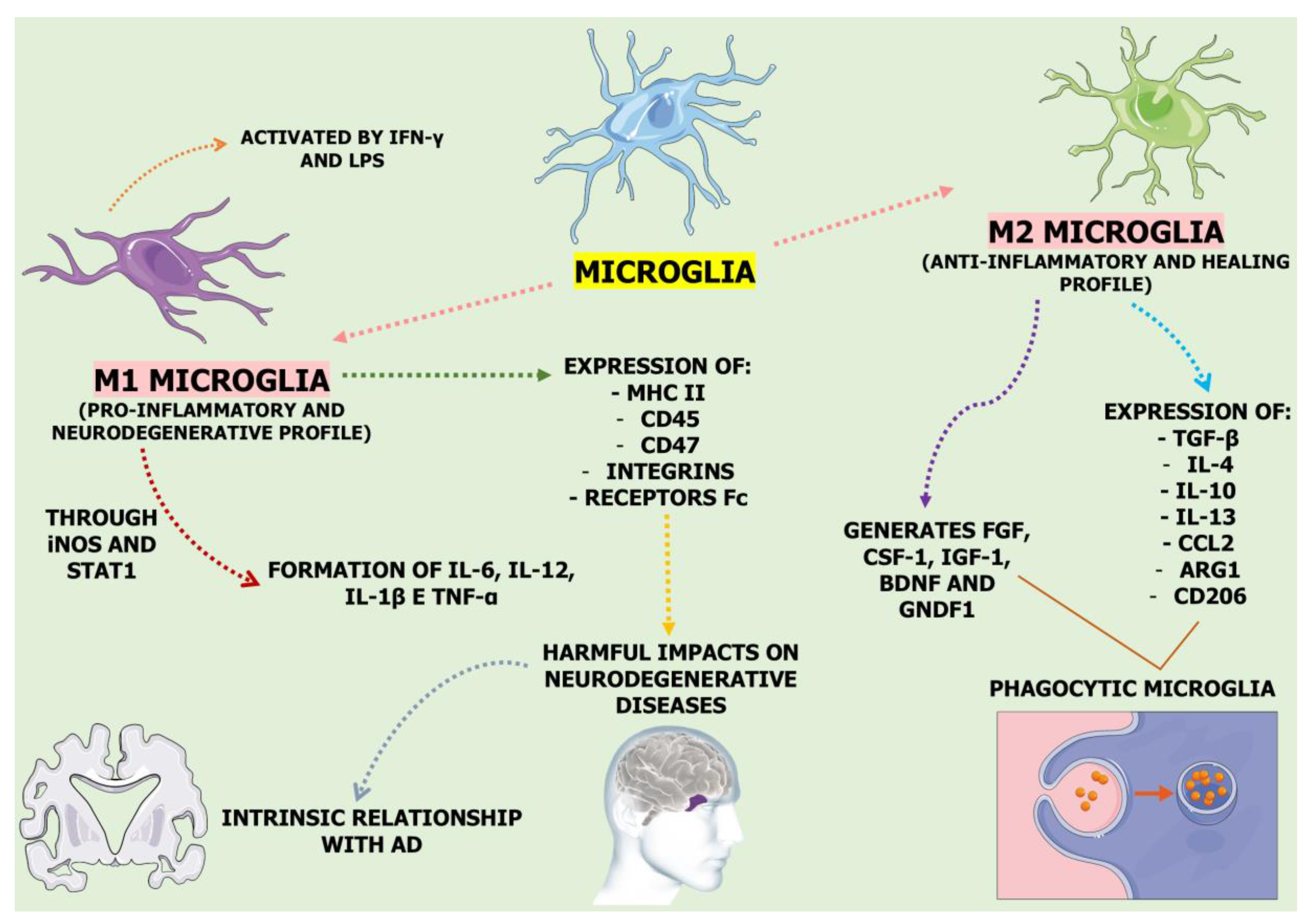
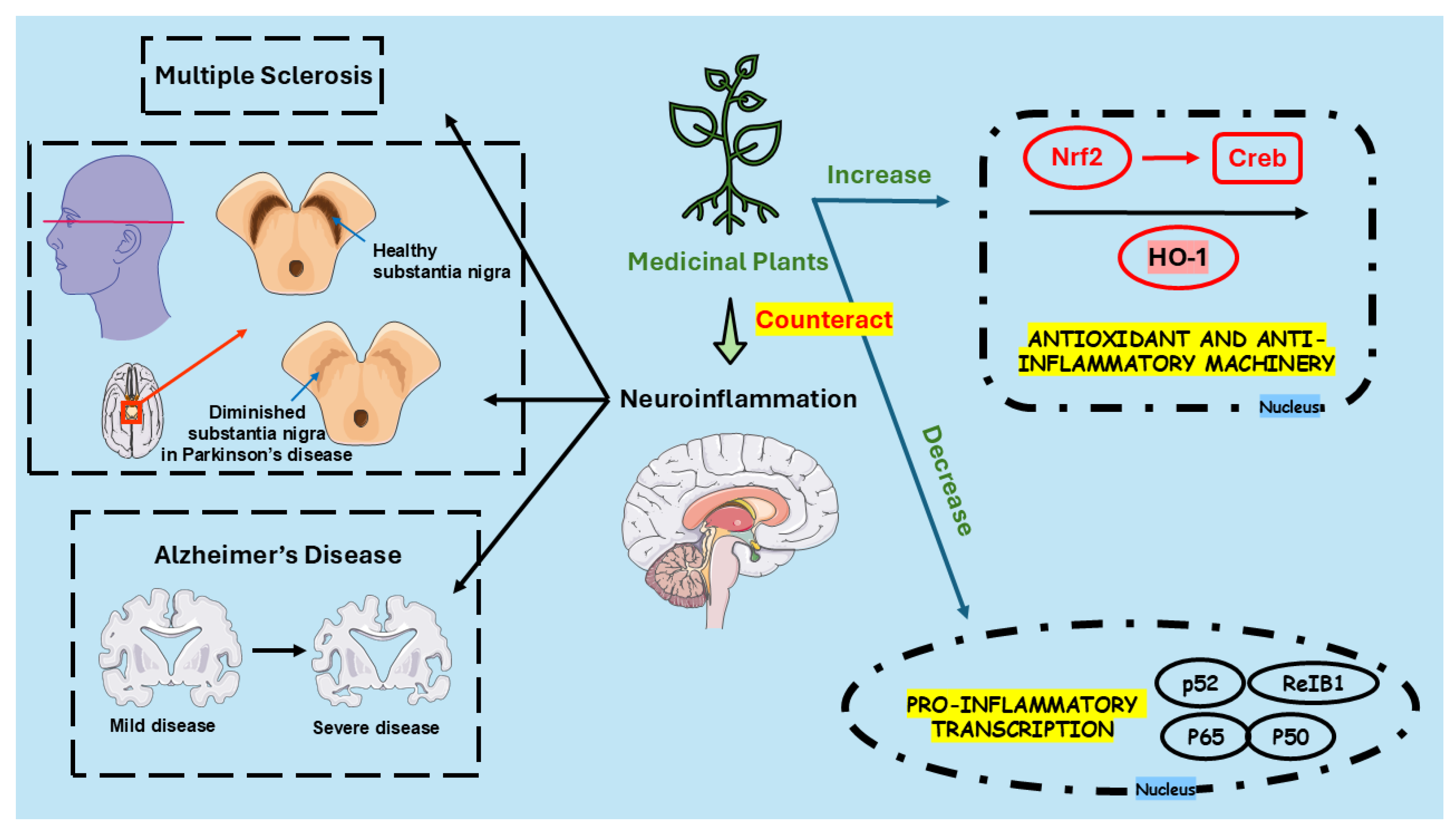
3. Neuroinflammation and Microglial Activation: Charting the Path Forward Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease, and Multiple Sclerosis
4. Exploring Medicinal Plants in Neuroinflammation: Comprehensive Insights on Effects, Dosage, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications
5. Conclusions and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davinelli, S.; Maes, M.; Corbi, G.; Zarrelli, A.; Willcox, D.C.; Scapagnini, G. Dietary phytochemicals and neuro-inflammaging: from mechanistic insights to translational challenges. Immun Ageing 2016, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, T.; Xiao, Q.; Fan, H.J.; Xu, L.; Qin, S.C.; Yang, L.X.; Jin, X.M.; Xiao, B.G.; Zhang, B.; Ma, C.G., et al. Wuzi Yanzong Pill relieves MPTP-induced motor dysfunction and neuron loss by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation. Metab Brain Dis 2023. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. A Decade of Dedication: Pioneering Perspectives on Neurological Diseases and Mental Illnesses. Biomedicines 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Revolutionizing our understanding of Parkinson's disease: Dr. Heinz Reichmann's pioneering research and future research direction. Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996) 2024. [CrossRef]
- Rink, C.; Khanna, S. Significance of brain tissue oxygenation and the arachidonic acid cascade in stroke. Antioxid Redox Signal 2011, 14, 1889–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozumi, T.; Preziosa, P.; Meani, A.; Albergoni, M.; Margoni, M.; Pagani, E.; Filippi, M.; Rocca, M.A. Influence of cardiorespiratory fitness and MRI measures of neuroinflammation on hippocampal volume in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2023. [CrossRef]
- Abadin, X.; de Dios, C.; Zubillaga, M.; Ivars, E.; Puigròs, M.; Marí, M.; Morales, A.; Vizuete, M.; Vitorica, J.; Trullas, R. , et al. Neuroinflammation in Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases: Role of Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants (Basel) 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solleiro-Villavicencio, H.; Rivas-Arancibia, S. Effect of Chronic Oxidative Stress on Neuroinflammatory Response Mediated by CD4(+)T Cells in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front Cell Neurosci 2018, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Direito, R.; Barbalho, S.M.; Figueira, M.E.; Minniti, G.; de Carvalho, G.M.; de Oliveira Zanuso, B.; de Oliveira Dos Santos, A.R.; de Góes Corrêa, N.; Rodrigues, V.D.; de Alvares Goulart, R. , et al. Medicinal Plants, Phytochemicals and Regulation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Metabolites 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleanu, D.M.; Niculescu, A.G.; Lungu, II; Radu, C.I.; Vladâcenco, O.; Roza, E.; Costăchescu, B.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, R.I. An Overview of Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, E.P.; Moretti, R.C., Jr.; Torres Pomini, K.; Laurindo, L.F.; Sloan, K.P.; Sloan, L.A.; Castro, M.V.M.; Baldi, E., Jr.; Ferraz, B.F.R.; de Souza Bastos Mazuqueli Pereira, E. , et al. Glycolipid Metabolic Disorders, Metainflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Cardiovascular Diseases: Unraveling Pathways. Biology 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girotto, O.S.; Furlan, O.O.; Moretti Junior, R.C.; Goulart, R.A.; Baldi Junior, E.; Barbalho-Lamas, C.; Fornari Laurindo, L.; Barbalho, S.M. Effects of apples (Malus domestica) and their derivatives on metabolic conditions related to inflammation and oxidative stress and an overview of by-products use in food processing. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition 2024, 10.1080/10408398.2024.2372690, 1-32. [CrossRef]
- Valotto Neto, L.J.; Reverete de Araujo, M.; Moretti Junior, R.C.; Mendes Machado, N.; Joshi, R.K.; Dos Santos Buglio, D.; Barbalho Lamas, C.; Direito, R.; Fornari Laurindo, L.; Tanaka, M. , et al. Investigating the Neuroprotective and Cognitive-Enhancing Effects of Bacopa monnieri: A Systematic Review Focused on Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Apoptosis. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira Rossi, J.L.; Barbalho, S.M.; Reverete de Araujo, R.; Bechara, M.D.; Sloan, K.P.; Sloan, L.A.J.D.m.r. ; reviews. Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases: Going beyond traditional risk factors. 2022, 38, e3502. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, M.; Szabó, Á.; Vécsei, L. Redefining Roles: A Paradigm Shift in Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolism for Innovative Clinical Applications. International journal of molecular sciences 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, E.P.; Tanaka, M.; Lamas, C.B.; Quesada, K.; Detregiachi, C.R.P.; Araújo, A.C.; Guiguer, E.L.; Catharin, V.; de Castro, M.V.M.; Junior, E.B. , et al. Vascular Impairment, Muscle Atrophy, and Cognitive Decline: Critical Age-Related Conditions. Biomedicines 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, D.S.A.; Oliver, P.L. ROS Generation in Microglia: Understanding Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Neurodegenerative Disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabisiak, T.; Patel, M. Crosstalk between neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in epilepsy. Front Cell Dev Biol 2022, 10, 976953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Lopez, A.; Torres-Paniagua, A.M.; Acero, G.; Díaz, G.; Gevorkian, G. Increased TSPO expression, pyroglutamate-modified amyloid beta (AβN3(pE)) accumulation and transient clustering of microglia in the thalamus of Tg-SwDI mice. J Neuroimmunol 2023, 382, 578150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurindo, L.F.; de Carvalho, G.M.; de Oliveira Zanuso, B.; Figueira, M.E.; Direito, R.; de Alvares Goulart, R.; Buglio, D.S.; Barbalho, S.M. Curcumin-Based Nanomedicines in the Treatment of Inflammatory and Immunomodulated Diseases: An Evidence-Based Comprehensive Review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Battaglia, S.; Giménez-Llort, L.; Chen, C.; Hepsomali, P.; Avenanti, A.; Vécsei, L. Innovation at the Intersection: Emerging Translational Research in Neurology and Psychiatry. Cells 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Chen, C. Editorial: Towards a mechanistic understanding of depression, anxiety, and their comorbidity: perspectives from cognitive neuroscience. Frontiers in behavioral neuroscience 2023, 17, 1268156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornari Laurindo, L.; Aparecido Dias, J.; Cressoni Araújo, A.; Torres Pomini, K.; Machado Galhardi, C.; Rucco Penteado Detregiachi, C.; Santos de Argollo Haber, L.; Donizeti Roque, D.; Dib Bechara, M.; Vialogo Marques de Castro, M. , et al. Immunological dimensions of neuroinflammation and microglial activation: exploring innovative immunomodulatory approaches to mitigate neuroinflammatory progression. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1305933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Wang, F.; Han, K. Silencing of SH3BP2 Inhibits Microglia Activation Via the JAK/STAT Signaling in Spinal Cord Injury Models. Inflammation 2024. [CrossRef]
- Cokdinleyen, M.; Dos Santos, L.C.; de Andrade, C.J.; Kara, H.; Colás-Ruiz, N.R.; Ibañez, E.; Cifuentes, A. A Narrative Review on the Neuroprotective Potential of Brown Macroalgae in Alzheimer's Disease. Nutrients 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, S.; Avenanti, A.; Vécsei, L.; Tanaka, M. Neurodegeneration in Cognitive Impairment and Mood Disorders for Experimental, Clinical and Translational Neuropsychiatry. Biomedicines 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopper, A.T.; Campbell, B.M.; Kao, H.; Pintchovski, S.A.; Staal, R.G.W. Chapter Four - Recent Developments in Targeting Neuroinflammation in Disease. In Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry, Desai, M.C., Ed. Academic Press: 2012; Vol. 47, pp. 37-53.
- Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Luo, N.; Fu, Y.; Qiu, F.; Pan, Z.; Li, X.; Jian, W.; Yang, X.; Xue, Q. , et al. An Fgr kinase inhibitor attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy by ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation via the SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling pathway. J Transl Med 2023, 21, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bássoli, R.; Audi, D.; Ramalho, B.; Audi, M.; Quesada, K.; Barbalho, S.J.J.o.H.M. The Effects of Curcumin on Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review. 2023, 42, 100771.
- Barbalho, S.M.; Direito, R.; Laurindo, L.F.; Marton, L.T.; Guiguer, E.L.; Goulart, R.d.A.; Tofano, R.J.; Carvalho, A.C.; Flato, U.A.P.; Capelluppi Tofano, V.A.J.A. Ginkgo biloba in the aging process: A narrative review. 2022, 11, 525.
- de Oliveira Zanuso, B.; Dos Santos, A.R.d.O.; Miola, V.F.B.; Campos, L.M.G.; Spilla, C.S.G.; Barbalho, S.M.J.E.g. Panax ginseng and aging related disorders: A systematic review. 2022, 161, 111731.
- Rangaraju, S.; Dammer, E.B.; Raza, S.A.; Rathakrishnan, P.; Xiao, H.; Gao, T.; Duong, D.M.; Pennington, M.W.; Lah, J.J.; Seyfried, N.T. , et al. Identification and therapeutic modulation of a pro-inflammatory subset of disease-associated-microglia in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurodegener 2018, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank-Stein, N.; Mass, E. Macrophage and monocyte subsets in response to ischemic stroke. Eur J Immunol 2023, 10.1002/eji.202250233, e2250233. [CrossRef]
- Cotoia, A.; Charitos, I.A.; Corriero, A.; Tamburrano, S.; Cinnella, G. The Role of Macronutrients and Gut Microbiota in Neuroinflammation Post-Traumatic Brain Injury: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarsaiya, S.; Jain, A.; Shu, F.; Jia, Q.; Gong, Q.; Wu, Q.; Shi, J.; Chen, J. Unveiling the potential of dendrobine: insights into bioproduction, bioactivities, safety, circular economy, and future prospects. Crit Rev Biotechnol 2025. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Ma, Q.; Ye, L.; Piao, G. The Traditional Medicine and Modern Medicine from Natural Products. Molecules 2016, 21, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: an overview. Journal of Nutritional Science 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, A.A.; Shah, Z.A. A Review of the Consequences of Gut Microbiota in Neurodegenerative Disorders and Aging. Brain Sci 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K. The Role of Dietary Phytochemicals: Evidence from Epidemiological Studies. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buglio, D.S.; Marton, L.T.; Laurindo, L.F.; Guiguer, E.L.; Araújo, A.C.; Buchaim, R.L.; Goulart, R.A.; Rubira, C.J.; Barbalho, S.M. The Role of Resveratrol in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review. J Med Food 2022, 25, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalho, S.M.; Bueno Ottoboni, A.M.M.; Fiorini, A.M.R.; Guiguer, E.L.; Nicolau, C.C.T.; Goulart, R.d.A.; Flato, U.A.P.J.C.r.i.f.s. ; nutrition. Grape juice or wine: which is the best option? 2020, 60, 3876–3889. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laurindo, L.F.; Direito, R.; Bueno Otoboni, A.M.; Goulart, R.A.; Quesada, K.; Barbalho, S.M.J.F.R.I. Grape processing waste: effects on inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer. 2024, 40, 336-369.
- Sen, T.; Samanta, S.K. Medicinal plants, human health and biodiversity: a broad review. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 2015, 147, 59–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Tian, Q.; Ran, Q.; Gan, Q.; Hu, Y.; Du, D.; Qin, Z.; Duan, X.; Zhu, X.; Huang, W. Z-Ligustilide: A Potential Therapeutic Agent for Atherosclerosis Complicating Cerebrovascular Disease. Biomolecules 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montazeri-Khosh, Z.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Keshavarz, M.; Sheybani-Arani, M.; Samiei, A. Combination therapies and other therapeutic approaches targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome and neuroinflammatory pathways: a promising approach for traumatic brain injury. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 2025, 10.1080/08923973.2024.2444956, 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Pagotto, G.L.O.; Santos, L.; Osman, N.; Lamas, C.B.; Laurindo, L.F.; Pomini, K.T.; Guissoni, L.M.; Lima, E.P.; Goulart, R.A.; Catharin, V. , et al. Ginkgo biloba: A Leaf of Hope in the Fight against Alzheimer's Dementia: Clinical Trial Systematic Review. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaachouay, N.; Zidane, L. Plant-Derived Natural Products: A Source for Drug Discovery and Development. Drugs and Drug Candidates 2024, 3, 184–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Assale, T.; Afrang, N.; Wissfeld, J.; Cuevas-Rios, G.; Klaus, C.; Linnartz-Gerlach, B.; Neumann, H. Neuroprotective role of sialic-acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-11 in humanized transgenic mice. Front Neurosci 2024, 18, 1504765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Lim, J.; Oh, J. Taming neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease: The protective role of phytochemicals through the gut-brain axis. Biomed Pharmacother 2024, 178, 117277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisioglu, B.; Onal, E.; Karabulut, D.; Onbasilar, I.; Akyol, A. Neuroprotective Roles of Lauric Acid and Resveratrol: Shared Benefits in Neuroinflammation and Anxiety, Distinct Effects on Memory Enhancement. Food Sci Nutr 2024, 12, 9735–9748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Lei, D.; Liu, J.; Fei, Y.; Wang, C.; Han, C. Resveratrol ameliorates postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged mice by regulating microglial polarization through CX3CL1/CX3CR1 signaling axis. Neurosci Lett 2024, 847, 138089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lang, Y.; Ding, S. Dihydro-resveratrol ameliorates NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation via Bnip3-dependent mitophagy in Alzheimer's disease. Br J Pharmacol 2024. [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.L.; Wang, C.C.; Liang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Sun, Y.E.; Huang, Y.L.; Ma, Z.L. Analgesic Effect of Dehydrocorydaline on Chronic Constriction Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain via Alleviating Neuroinflammation. Chin J Integr Med 2025. [CrossRef]
- Carles, A.; Freyssin, A.; Guehairia, S.; Reguero, T.; Vignes, M.; Hirbec, H.; Rubinstenn, G.; Maurice, T. Neuroprotection by chronic administration of Fluoroethylnormemantine (FENM) in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 2025, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, S.; Avenanti, A.; Vécsei, L.; Tanaka, M. Neural Correlates and Molecular Mechanisms of Memory and Learning. International journal of molecular sciences 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, S.E.B.; Tyler, L.D.K. Pathways to healing: Plants with therapeutic potential for neurodegenerative diseases. IBRO Neurosci Rep 2023, 14, 210–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, K. Regulation of neuroinflammation by herbal medicine and its implications for neurodegenerative diseases. A focus on traditional medicines and flavonoids. Neurosignals 2005, 14, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janpaijit, S.; Sillapachaiyaporn, C.; Theerasri, A.; Charoenkiatkul, S.; Sukprasansap, M.; Tencomnao, T. Cleistocalyx nervosum var. paniala Berry Seed Protects against TNF-α-Stimulated Neuroinflammation by Inducing HO-1 and Suppressing NF-κB Mechanism in BV-2 Microglial Cells. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janpaijit, S.; Lertpatipanpong, P.; Sillapachaiyaporn, C.; Baek, S.J.; Charoenkiatkul, S.; Tencomnao, T.; Sukprasansap, M. Anti-neuroinflammatory effects of Cleistocalyx nervosum var. paniala berry-seed extract in BV-2 microglial cells via inhibition of MAPKs/NF-κB signaling pathway. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; Lee, Y.S.; Yoon, D.; Kim, G.S.; Lee, D.Y. The ethanolic extract of Curcuma longa grown in Korea exhibits anti-neuroinflammatory effects by activating of nuclear transcription factor erythroid-2-related factor 2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling pathway. BMC complementary medicine and therapies 2022, 22, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eun, C.S.; Lim, J.S.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.P.; Yang, S.A. The protective effect of fermented Curcuma longa L. on memory dysfunction in oxidative stress-induced C6 gliomal cells, proinflammatory-activated BV2 microglial cells, and scopolamine-induced amnesia model in mice. BMC complementary and alternative medicine 2017, 17, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgonetti, V.; Benatti, C.; Governa, P.; Isoldi, G.; Pellati, F.; Alboni, S.; Tascedda, F.; Montopoli, M.; Galeotti, N.; Manetti, F. , et al. Non-psychotropic Cannabis sativa L. phytocomplex modulates microglial inflammatory response through CB2 receptors-, endocannabinoids-, and NF-κB-mediated signaling. Phytotherapy research : PTR 2022, 36, 2246–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Jakaria, M.; Yu, Y.J.; Ahn, J.Y.; Kim, I.S.; Choi, D.K. Dioscorea nipponica Makino Rhizome Extract and Its Active Compound Dioscin Protect against Neuroinflammation and Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficits. International journal of molecular sciences 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Zhou, Y.L.; He, D.H.; Liu, W.; Fan, X.Z.; Wang, Q.; Pan, H.F.; Cheng, Y.X.; Liu, Y.Q. Centipeda minima extract exerts antineuroinflammatory effects via the inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway. Phytomedicine : international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology 2020, 67, 153164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.H.; Li, W.; Go, Y.; Oh, Y.C. Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba Attenuates Neuroinflammation in BV2 Microglia upon LPS Stimulation by Inducing HO-1 Activity and Inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK. International journal of molecular sciences 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.H.; Ma, S.X.; Ko, Y.H.; Seo, J.Y.; Lee, B.R.; Lee, T.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, C.G. Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb. Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Activity by Inhibiting NF-κB Activation in BV-2 Microglial Cells. Biomolecules & therapeutics 2016, 24, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.H.; Ma, S.X.; Hong, S.I.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, C.G. Lonicera japonica THUNB. Extract Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Inflammatory Responses by Suppressing NF-κB Signaling in BV-2 Microglial Cells. Journal of medicinal food 2015, 18, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, H.W.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Seong, S.J.; Jin, M.L.; Ryu, E.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, S.J. Bambusae Caulis in Taeniam modulates neuroprotective and anti-neuroinflammatory effects in hippocampal and microglial cells via HO-1- and Nrf-2-mediated pathways. International journal of molecular medicine 2012, 30, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.W.; Yoon, C.H.; Park, K.M.; Han, H.S.; Park, Y.K. Hexane fraction of Zingiberis Rhizoma Crudus extract inhibits the production of nitric oxide and proinflammatory cytokines in LPS-stimulated BV2 microglial cells via the NF-kappaB pathway. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 2009, 47, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, R.; Baltimore, D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell 1986, 47, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, E.; Motolani, A.; Campos, L.; Lu, T. The Pivotal Role of NF-kB in the Pathogenesis and Therapeutics of Alzheimer's Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nennig, S.E.; Schank, J.R. The Role of NFkB in Drug Addiction: Beyond Inflammation. Alcohol Alcohol 2017, 52, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. Targeting NF-kappaB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2020, 5, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.C. The non-canonical NF-kappaB pathway in immunity and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 2017, 17, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, R.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, C.M. NF-kappaB Signaling Pathways in Neurological Inflammation: A Mini Review. Front Mol Neurosci 2015, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zusso, M.; Lunardi, V.; Franceschini, D.; Pagetta, A.; Lo, R.; Stifani, S.; Frigo, A.C.; Giusti, P.; Moro, S. Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin attenuate microglia inflammatory response via TLR4/NF-kB pathway. J Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabab, T.; Khanabdali, R.; Moghadamtousi, S.Z.; Kadir, H.A.; Mohan, G. Neuroinflammation pathways: a general review. Int J Neurosci 2017, 127, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, C.K.; Saijo, K.; Winner, B.; Marchetto, M.C.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell 2010, 140, 918–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano-Silva, M.E.; Rund, L.A.; Vailati-Riboni, M.; Pacheco, M.T.B.; Johnson, R.W. Copper-Binding Peptides Attenuate Microglia Inflammation through Suppression of NF-kB Pathway. Mol Nutr Food Res 2021, 65, e2100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badenetti, L.; Manzoli, R.; Rubin, M.; Cozza, G.; Moro, E. Monitoring Nrf2/ARE Pathway Activity with a New Zebrafish Reporter System. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, M.; Patil, J.; D'Angelo, B.; Weber, S.G.; Mallard, C. NRF2-regulation in brain health and disease: implication of cerebral inflammation. Neuropharmacology 2014, 79, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Xia, M. Cell-Based Assays to Identify Modulators of Nrf2/ARE Pathway. Methods Mol Biol 2022, 2474, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivandzade, F.; Prasad, S.; Bhalerao, A.; Cucullo, L. NRF2 and NF-қB interplay in cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative disorders: Molecular mechanisms and possible therapeutic approaches. Redox Biol 2019, 21, 101059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordoe, C.; Wang, X.; Lin, P.; Wang, Z.; Hu, J.; Wang, D.; Fang, Y.; Liang, F.; Ye, S.; Chen, J. , et al. Non-mitogenic fibroblast growth factor 1 protects against ischemic stroke by regulating microglia/macrophage polarization through Nrf2 and NF-kappaB pathways. Neuropharmacology 2022, 212, 109064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; An, C.; Gao, Y.; Leak, R.K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F. Emerging roles of Nrf2 and phase II antioxidant enzymes in neuroprotection. Prog Neurobiol 2013, 100, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Duan, H.; Li, R.; Peng, W.; Wu, C. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress. J Adv Res 2021, 34, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, Z. The Nrf2 Pathway in Liver Diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol 2022, 10, 826204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, K.; Motohashi, H.; Yamamoto, M. Molecular mechanisms of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in stress response and cancer evolution. Genes Cells 2011, 16, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayalan Naidu, S.; Muramatsu, A.; Saito, R.; Asami, S.; Honda, T.; Hosoya, T.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Suzuki, T.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. C151 in KEAP1 is the main cysteine sensor for the cyanoenone class of NRF2 activators, irrespective of molecular size or shape. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 8037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Long, D. Nrf2 and Ferroptosis: A New Research Direction for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front Neurosci 2020, 14, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, S.; Gupta, D. Crosstalk of toll-like receptors signaling and Nrf2 pathway for regulation of inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother 2018, 108, 1866–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cores, Á.; Piquero, M.; Villacampa, M.; León, R.; Menéndez, J.C. NRF2 Regulation Processes as a Source of Potential Drug Targets against Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomolecules 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, L.; Johnson, J.A. Oxidative damage and the Nrf2-ARE pathway in neurodegenerative diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014, 1842, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.J.; Lv, C.H.; Chen, Z.; Shi, M.; Zeng, C.X.; Hou, D.X.; Qin, S. The Regulatory Effect of Phytochemicals on Chronic Diseases by Targeting Nrf2-ARE Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoroso, R.; Maccallini, C.; Bellezza, I. Activators of Nrf2 to Counteract Neurodegenerative Diseases. Antioxidants (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, J.K.; Kang, H.C.; Cho, Y.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.Y. Therapeutic regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in chronic inflammatory diseases. Arch Pharm Res 2021, 44, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.; Kanneganti, T.D. Inflammasome activation and assembly at a glance. J Cell Sci 2017, 130, 3955–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, K.V.; Deng, M.; Ting, J.P. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat Rev Immunol 2019, 19, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Callaway, J.B.; Ting, J.P. Inflammasomes: mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics. Nat Med 2015, 21, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulte, D.; Rigamonti, C.; Romano, A.; Mortellaro, A. Inflammasomes: Mechanisms of Action and Involvement in Human Diseases. Cells 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wu, H. Structural Mechanisms of NLRP3 Inflammasome Assembly and Activation. Annu Rev Immunol 2023, 41, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, N.; Li, T. Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome by Phosphorylation. Front Immunol 2018, 9, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Zheng, C.; Xu, J.; Ma, S.; Jia, H.; Yan, M.; An, F.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, J.; Bian, H. Race between virus and inflammasomes: inhibition or escape, intervention and therapy. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2023, 13, 1173505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, F.L.; Biggs, K.E.; Rankin, B.E.; Havrda, M.C. NLRP3 inflammasome in neurodegenerative disease. Transl Res 2023, 252, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, S.; Kim, J.K.; Silwal, P.; Sasakawa, C.; Jo, E.K. An update on the regulatory mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Mol Immunol 2021, 18, 1141–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Li, Q.; Xu, G.; Xiao, X.; Bai, Z. The mechanism of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and its pharmacological inhibitors. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 1109938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasizzo, M.; Kopitar-Jerala, N. Interplay Between NLRP3 Inflammasome and Autophagy. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 591803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, C.; Antonioli, L.; Lopez-Castejon, G.; Blandizzi, C.; Fornai, M. Canonical and Non-Canonical Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome at the Crossroad between Immune Tolerance and Intestinal Inflammation. Front Immunol 2017, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhao, W. NLRP3 Inflammasome-A Key Player in Antiviral Responses. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zito, G.; Buscetta, M.; Cimino, M.; Dino, P.; Bucchieri, F.; Cipollina, C. Cellular Models and Assays to Study NLRP3 Inflammasome Biology. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Mei, X. Role of NLRP3 Inflammasomes in Neuroinflammation Diseases. Eur Neurol 2020, 83, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.Q.; Le, W. NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Related Mitochondrial Impairment in Parkinson's Disease. Neurosci Bull 2023, 39, 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X. Interaction between autophagy and the NLRP3 inflammasome in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. Front Aging Neurosci 2022, 14, 1018848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soraci, L.; Gambuzza, M.E.; Biscetti, L.; Laganà, P.; Lo Russo, C.; Buda, A.; Barresi, G.; Corsonello, A.; Lattanzio, F.; Lorello, G. , et al. Toll-like receptors and NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pathways in Parkinson's disease: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. J Neurol 2023, 270, 1346–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Ng, W.L.; Goh, S.Y.; Gulam, M.Y.; Wang, L.F.; Tan, E.K.; Ahn, M.; Chao, Y.X. Targeting the inflammasome in Parkinson's disease. Front Aging Neurosci 2022, 14, 957705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barczuk, J.; Siwecka, N.; Lusa, W.; Rozpedek-Kaminska, W.; Kucharska, E.; Majsterek, I. Targeting NLRP3-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's Disease Treatment. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severini, C.; Barbato, C.; Di Certo, M.G.; Gabanella, F.; Petrella, C.; Di Stadio, A.; de Vincentiis, M.; Polimeni, A.; Ralli, M.; Greco, A. Alzheimer's Disease: New Concepts on the Role of Autoimmunity and NLRP3 Inflammasome in the Pathogenesis of the Disease. Curr Neuropharmacol 2021, 19, 498–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, Q.; Wang, L. The Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Alzheimer's Disease and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 845185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wei, S.; Deng, J.; Feng, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, M. A novel strategy for bioactive natural products targeting NLRP3 inflammasome in Alzheimer's disease. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 1077222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.; Cai, X.; Jin, K.; Wang, Q. Editorial: The NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation and its related mitochondrial impairment in neurodegeneration. Front Aging Neurosci 2022, 14, 1118281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, D.; Guan, R.; Zou, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J. NLRP3 deficiency protects against hypobaric hypoxia induced neuroinflammation and cognitive dysfunction. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2023, 255, 114828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Zhao, T.; Liu, M.; Cao, D.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Xia, M.; Wang, X.; Zheng, T.; Liu, C. , et al. Targeting NLRP3 Inflammasome in Translational Treatment of Nervous System Diseases: An Update. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 707696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarapultsev, A.; Gusev, E.; Komelkova, M.; Utepova, I.; Luo, S.; Hu, D. JAK-STAT signaling in inflammation and stress-related diseases: implications for therapeutic interventions. Mol Biomed 2023, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardona, K.; Medina, J.; Orrego-Cardozo, M.; Restrepo de Mejía, F.; Elcoroaristizabal, X.; Naranjo Galvis, C.A. Inflammatory gene expression profiling in peripheral blood from patients with Alzheimer's disease reveals key pathways and hub genes with potential diagnostic utility: a preliminary study. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, M.; Singh, M.K.; Shyam, H.; Mishra, A.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, A.; Kushwaha, J. Role of JAK/STAT in the Neuroinflammation and its Association with Neurological Disorders. Ann Neurosci 2021, 28, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.L.; Zhou, M.; Chin, E.W.M.; Amarnath, G.; Cheah, C.H.; Ng, K.P.; Kandiah, N.; Goh, E.L.K.; Chiam, K.H. Alzheimer's Disease Blood Biomarkers Associated With Neuroinflammation as Therapeutic Targets for Early Personalized Intervention. Front Digit Health 2022, 4, 875895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, V.R.; Desai, R.J.; Navakkode, S.; Wong, L.W.; Anerillas, C.; Loeffler, T.; Schilcher, I.; Mahesri, M.; Chin, K.; Horton, D.B. , et al. Hydroxychloroquine lowers Alzheimer's disease and related dementias risk and rescues molecular phenotypes related to Alzheimer's disease. Mol Psychiatry 2023, 28, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusek, M.; Smith, J.; El-Khatib, K.; Aikins, K.; Czuczwar, S.J.; Pluta, R. The Role of the JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease: New Potential Treatment Target. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevado-Holgado, A.J.; Ribe, E.; Thei, L.; Furlong, L.; Mayer, M.A.; Quan, J.; Richardson, J.C.; Cavanagh, J.; Consortium, N.; Lovestone, S. Genetic and Real-World Clinical Data, Combined with Empirical Validation, Nominate Jak-Stat Signaling as a Target for Alzheimer's Disease Therapeutic Development. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porro, C.; Cianciulli, A.; Trotta, T.; Lofrumento, D.D.; Panaro, M.A. Curcumin Regulates Anti-Inflammatory Responses by JAK/STAT/SOCS Signaling Pathway in BV-2 Microglial Cells. Biology (Basel) 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Gibson, S.A.; Buckley, J.A.; Qin, H.; Benveniste, E.N. Role of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in regulation of innate immunity in neuroinflammatory diseases. Clin Immunol 2018, 189, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Li, J.; Fu, M.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway: from bench to clinic. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2021, 6, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal-Itriago, A.; Radford, R.A.; Aramideh, J.A.; Maurel, C.; Scherer, N.M.; Don, E.K.; Lee, A.; Chung, R.S.; Graeber, M.B.; Morsch, M. Microglia morphophysiological diversity and its implications for the CNS. Frontiers in immunology 2022, 13, 997786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullotta, G.S.; Costantino, G.; Sortino, M.A.; Spampinato, S.F. Microglia and the blood–brain barrier: An external player in acute and chronic neuroinflammatory conditions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 9144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.; Yeo, I.-J.; Hong, J.-T.; Eo, S.-K.; Lee, D.; Kim, K. Side-Chain Immune Oxysterols Induce Neuroinflammation by Activating Microglia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 15288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Che, J.; Zhang, J. Emerging non-proinflammatory roles of microglia in healthy and diseased brains. Brain Research Bulletin 2023, 199, 110664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, J.; Xu, Z.; Yan, H.; Tang, B.; Liu, C.; Chen, C.; Meng, Q. Microglia-containing human brain organoids for the study of brain development and pathology. Molecular Psychiatry 2023, 28, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colonna, M.; Butovsky, O. Microglia function in the central nervous system during health and neurodegeneration. Annual review of immunology 2017, 35, 441–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsudaira, T.; Prinz, M. Life and death of microglia: Mechanisms governing microglial states and fates. Immunology Letters 2022, 245, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright-Jin, E.C.; Gutmann, D.H. Microglia as dynamic cellular mediators of brain function. Trends in Molecular Medicine 2019, 25, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, J.; Martins, S.; Ferreira, P.A.; Cardoso, A.M.; Guedes, J.R.; Peça, J.; Cardoso, A.L. The old guard: Age-related changes in microglia and their consequences. Mechanisms of ageing and development 2021, 197, 111512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Onaizi, M.; Al-Khalifah, A.; Qasem, D.; ElAli, A. Role of microglia in modulating adult neurogenesis in health and neurodegeneration. International journal of molecular sciences 2020, 21, 6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, G.; Marrocco, F.; Limatola, C. Microglial cells: sensors for neuronal activity and microbiota-derived molecules. Frontiers in immunology 2022, 13, 1011129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Mao, Y.; Peng, B. Novel microglia-based therapeutic approaches to neurodegenerative disorders. Neuroscience bulletin 2023, 39, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Taso, O.; Wang, R.; Bayram, S.; Graham, A.C.; Garcia-Reitboeck, P.; Mallach, A.; Andrews, W.D.; Piers, T.M.; Botia, J.A. Trem2 promotes anti-inflammatory responses in microglia and is suppressed under pro-inflammatory conditions. Human molecular genetics 2020, 29, 3224–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strizova, Z.; Benesova, I.; Bartolini, R.; Novysedlak, R.; Cecrdlova, E.; Foley, L.K.; Striz, I. M1/M2 macrophages and their overlaps - myth or reality? Clin Sci (Lond) 2023, 137, 1067–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Jiang, J.; Tan, Y.; Chen, S. Microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: mechanism and potential therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2023, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Shui, X.; Sun, R.; Wan, L.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, B.; Luo, Z. Microglial Phenotypic Transition: Signaling Pathways and Influencing Modulators Involved in Regulation in Central Nervous System Diseases. Front Cell Neurosci 2021, 15, 736310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lis-López, L.; Bauset, C.; Seco-Cervera, M.; Cosín-Roger, J. Is the Macrophage Phenotype Determinant for Fibrosis Development? Biomedicines 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, C.; Ferreira, R.; George, J.; Sanches, R.; Rodrigues, D.I.; Gonçalves, N.; Cunha, R.A. Activation of microglial cells triggers a release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) inducing their proliferation in an adenosine A2A receptor-dependent manner: A2A receptor blockade prevents BDNF release and proliferation of microglia. Journal of Neuroinflammation 2013, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, C.; Valle, M.S.; Russo, A.; Malaguarnera, L. The interplay between ghrelin and microglia in neuroinflammation: implications for obesity and neurodegenerative diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 13432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Tong, F.; Li, H.; Bin, Y.; Ding, P.; Peng, L.; Liu, Z.; Dong, X. Maturation, morphology, and function: the decisive role of intestinal flora on microglia: a review. Journal of Integrative Neuroscience 2023, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.Y.; McNeely, T.L.; Baker, D.J. Untangling senescent and damage-associated microglia in the aging and diseased brain. The FEBS journal 2023, 290, 1326–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpierre, A.D.; Wu, L.J. How microglia sense and regulate neuronal activity. Glia 2021, 69, 1637–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristovska, I.; Robert, M.; Combet, K.; Honnorat, J.; Comte, J.; Pascual, O. Sleep decreases neuronal activity control of microglial dynamics in mice. Nature communications 2022, 13, 6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikegami, A.; Kato, D.; Wake, H. Microglial process dynamics depend on astrocyte and synaptic activity. Nagoya Journal of Medical Science 2023, 85, 772. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, K.; Lee, S.J.; Mook-Jung, I. White matter-associated microglia: New players in brain aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res Rev 2022, 75, 101574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.; Victor, M.B.; Park, Y.P.; Xiong, X.; Scannail, A.N.; Leary, N.; Prosper, S.; Viswanathan, S.; Luna, X.; Boix, C.A. , et al. Human microglial state dynamics in Alzheimer's disease progression. Cell 2023, 186, 4386–4403.e4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, R.; Joers, V.; Tansey, M.G.; McKernan, D.P.; Dowd, E. Microglial Phenotypes and Their Relationship to the Cannabinoid System: Therapeutic Implications for Parkinson's Disease. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Revolutionizing our understanding of Parkinson's disease: Dr. Heinz Reichmann's pioneering research and future research direction. Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996) 2024, 131, 1367–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harry, G.J. Microglia in Neurodegenerative Events-An Initiator or a Significant Other? Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofaris, G.K. Initiation and progression of α-synuclein pathology in Parkinson's disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 2022, 79, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toni, M. Special Issue "Neurobiology of Protein Synuclein". Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badanjak, K.; Fixemer, S.; Smajić, S.; Skupin, A.; Grünewald, A. The Contribution of Microglia to Neuroinflammation in Parkinson's Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basellini, M.J.; Kothuis, J.M.; Comincini, A.; Pezzoli, G.; Cappelletti, G.; Mazzetti, S. Pathological Pathways and Alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson's Disease: A View from the Periphery. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2023, 28, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Han, T.; Liu, H.; Sun, L.; Hong, J.; Hashimoto, M.; Wei, J. The reciprocal interactions between microglia and T cells in Parkinson’s disease: a double-edged sword. Journal of Neuroinflammation 2023, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.Q.; Zheng, R.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Lin, Z.H.; Xue, N.J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, B.R.; Pu, J.L. Parkin regulates microglial NLRP3 and represses neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e13834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Hamade, M.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Axtell, R.; Giri, S.; Mao-Draayer, Y. Current and Future Biomarkers in Multiple Sclerosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charabati, M.; Wheeler, M.A.; Weiner, H.L.; Quintana, F.J. Multiple sclerosis: Neuroimmune crosstalk and therapeutic targeting. Cell 2023, 186, 1309–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mey, G.M.; Mahajan, K.R.; DeSilva, T.M. Neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. WIREs Mech Dis 2023, 15, e1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Dai, C.; Zhou, X.; Barnes, J.A.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Shingu, T.; Heimberger, A.B.; Chen, Y. , et al. Qki is an essential regulator of microglial phagocytosis in demyelination. J Exp Med 2021, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, F.; Sun, M.; Wu, N.; Liu, B.; Yi, X.; Ge, R.; Fan, X. Microglia in the context of multiple sclerosis. Front Neurol 2023, 14, 1157287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Fang, X.; Liu, W.; Sun, R.; Zhou, J.; Pu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Sun, D.; Xiang, Z.; Liu, P. , et al. Microglia Regulate Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity via MiR-126a-5p/MMP9 Axis during Inflammatory Demyelination. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2022, 9, e2105442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Szabó, Á.; Vécsei, L. Preclinical modeling in depression and anxiety: Current challenges and future research directions. Advances in clinical and experimental medicine : official organ Wroclaw Medical University 2023, 32, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, Y.C.; Mendes, N.M.; Pereira de Lima, E.; Chehadi, A.C.; Lamas, C.B.; Haber, J.F.S.; Dos Santos Bueno, M.; Araújo, A.C.; Catharin, V.C.S.; Detregiachi, C.R.P. , et al. Curcumin: A Golden Approach to Healthy Aging: A Systematic Review of the Evidence. Nutrients 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróbel-Biedrawa, D.; Podolak, I. Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effects of Adaptogens: A Mini-Review. Molecules 2024, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Plant Species | Organ Harvested | Main Bioactive Compounds | Models | Effective Dose (s) / Treatment (s) | Mechanisms | Clinical Implications | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cleistocalyx nervosum var. paniala |
Berry seed | Ferulic acid, aurentiacin, brassitin, ellagic acid, alpinetin and resveratrol | TNF-α-stimulated BV-2 cells in vitro | 5, 10 or 25 μg/mL CNSE incubated for 24 h in vitro | ↓ COX-2 activation, ↓ iNOS function, ↓ TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β mRNA expression, ↓ p38MAPK and ERK 1/2 phosphorylation, ↓ NF-κB activation, ↓ p65 and IκB phosphorylation, ↑ HO-1 induction (in vitro) | Potential for new anti-inflammatory agents targeting neurodegenerative diseases. Could pave the way for natural, multi-targeted treatments. | [58] |
| Berry seed | LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells in vitro | 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, or 100 μg/mL CNSE incubated for 24 h in vitro | ↓ NO production, ↓ iNOS mRNA expression, ↓ TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β mRNA expression, ↓ MAPK phosphorylation, ↓ p-JNK, p-ERK 1/2 and p-p38 levels, ↓ NF-κB activation (in vitro) | This could contribute to developing targeted anti-inflammatory therapies with fewer side effects. | [59] | ||
|
Curcuma longa |
Rhizome | Curcumin, demethoxycurcumin and bisdemethoxycurcumin | LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells in vitro | 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 150, or 200 μg/mL CLE incubated for 24 h in vitro | ↓ NO production, ↓ PGE2 production, ↓ iNOS and COX-2 expression, ↓ TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β mRNA expression, ↓ NF-κB activation, ↓ IκB-α phosphorylation and degradation, ↓ p65 nuclear translocation, ↓ MAPK (p38, ERK, and JNK) phosphorylation, ↑ HO-1 expression, ↑ Nrf2 nuclear translocation (in vitro) | It could enhance treatments for neuroinflammation and oxidative stress-related disorders, offering a natural alternative to synthetic drugs. | [60] |
| Rhizome | LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells in vitro and scopolamine-induced male ICR mice in vivo | 1, 10, 50, or 50 μg/mL FCL incubated for 24 h in vitro and 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg FCL in vivo | ↓ NO production, ↓ PGE2 production, ↓ iNOS and COX-2 expression, ↑ AP-1 inhibition, ↓ NF-κB activation, ↓ p-MAPKs, ↑ AChE inhibition (in vitro), and ↑ pCREB and BDNF expression (in vivo) | It may offer new avenues for treating cognitive deficits and memory impairments associated with neurodegenerative conditions. | [61] |
||
|
Cannabis sativa |
Dried inflorescence | Cannabidiol, cannabigerol, cannabidiolic acid, tetrahydrocannabinol, β-caryophyllene, caryophyllene-oxide, α-Humulene, and apigenin | LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells in vitro | 1 μg/mL CSE incubated for 24 h in vitro | ↓ TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β production, ↑ AEA and 2-AG expression, ↓ JNK and p38 activation, ↓ NF-κB nuclear translocation, ↓ ROS production (in vitro) | It could be a cornerstone for novel treatments targeting neuroinflammation and chronic pain, with potential applications in psychiatric and neurological disorders. | [62] |
| Dioscorea nipponica |
Rhizome | Dioscin | LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells in vitro and scopolamine-induced male C57BL mice in vivo | 10, 20, 50, or 100 μg/mL dioscin incubated for 24 h in vitro and 60 mg/kg dioscin in vivo | ↓ iNOS and COX-2 expression, ↓ NO and PGE2 production, ↓ TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β mRNA expression, ↓ NF-κB nuclear translocation, ↓ IκB phosphorylation, ↓ p65 nuclear translocation (in vitro) and ↑ BDNF and pCREB expression (in vivo) | It may support treatments to improve cognitive functions and mood disorders by targeting neuroinflammatory pathways. | [63] |
| Centipeda minima | Leaves | Chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, rutin, isochlorogenic acid A, isochlorogenic acid B, isochlorogenic acid C, and 6-O-angeloylplenolin | LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells in vitro and LPS-stimulated male C57BL/6J mice in vivo | 2, 4, or 6 μg/mL ECM incubated for 24 h in vitro and 100, 200 mg/kg ECM in vivo | ↓ NF-κB nuclear translocation, ↓ IκB phosphorylation, ↓ COX-2 and iNOS expression, ↓ NO and PGE2 production, ↓ NOX proteins (in vitro) and ↓ NO, PGE2, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β production, ↓ NF-κB nuclear translocation, ↓ iNOS, COX-2 and NOX2 and NOX4 expression (in vivo) | Potential to develop comprehensive anti-inflammatory therapies targeting multiple pathways involved in neuroinflammation. | [64] |
| Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba | Rhizome | Atractylenolide I, atractylenolide III, and atractylodin | LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells in vitro | 10, 50, or 100 μg/mL ARAE incubated for 24 h in vitro | ↓ NO production, ↓ TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β mRNA expression, ↓ iNOS and COX-2 expression, ↑ HO-1 mRNA expression, ↓ NF-κB activity, ↓ MAPK, p38, ERK and JNK activation (in vitro) | It may contribute to integrative approaches for treating neuroinflammation and related conditions. | [65] |
| Vaccinium bracteatum | Aboveground parts not specified) | Quercetin, chrysin, apigenin, kaempferol, and lutelin | LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells in vitro | 1, 2,5, 5, 10, or 20 µg/mL VBME incubated for 24 h in vitro | ↓ NO and PGE2 production, ↓ iNOS and COX-2 expression, ↓ NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation, ↓ TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β levels, ↓ ROS production (in vitro) | It may inspire new anti-inflammatory and antioxidant treatments with fewer side effects. | [66] |
| Lonicera japonica | Flower buds | Chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid,cryptochlorogenic acid, artichoke,isochlorogenic acid A,isochlorogenic acid B,isochlorogenic acid C, rutin,hibisin, and loganin | LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells in vitro | 0.5, 5, 2.5, 5, or 10 µg/mL LJ incubated for 24 h in vitro | ↓ NO and PGE2 production, ↓ iNOS and COX-2 mRNA expression, ↓ TNF-α, IL-1β, MCP-1 and MMP-9 production, ↓ ROS levels, ↓ p38 MAPKs, ERK 1/2, JNK and PI3K phosphorylation, ↓ JAK1/STAT1/3 phosphorylation, ↓ NF-κB nuclear translocation (in vitro) | This could lead to new treatments targeting both neuroinflammation and related oxidative stress. | [67] |
| Phyllostachys nigra var. henonis or Phyllostachys bambusoides | Caulis | (-)-7'-epi-lyoniresinol 4,9'-di-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (7), (-)-lyoniresinol 4,9'-di-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (8) and bambulignan A | LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells and glutamate-stimulated hippocampal HT22 cells in vitro | 10, 20, 40, 60 or 80 μg/mL BCE incubated for 24 h in vitro | ↓ NO, TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 levels, ↓ iNOS and COX-2 expression, ↓ ROS production, ↑ HO-1 mRNA expression, ↑ Nrf2 nuclear translocation (in vitro) | Potential for advancing treatments against neuroinflammation and oxidative damage through modulation of key inflammatory and oxidative pathways. | [68] |
| Zingiber officinale |
Rhizome | Gingerols and shogaol | LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells in vitro | 1, 5, or 10 μg/mL GHE incubated for 24 h in vitro | ↓ NO and PGE2 production, ↓ COX-2 mRNA expression, ↓ TNF-α and IL-1β production, ↓ MAPK molecules, ERK1/2, p38 MAPK, and JNK phosphorylation, ↓ NF-κB nuclear translocation (in vitro) | A promising candidate for developing interventions targeting neuroinflammatory processes and related molecular pathways. | [69] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





