Submitted:
17 December 2024
Posted:
18 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Electronic Arts (EA) has recently unveiled a concept video titled "Imagination to Creation " [7], which demonstrates the potential of generating real-time interactive game scenarios. It showcases two players who collaboratively articulate their vision for a game world, which is then rapidly materialized into a cardboard maze and two gun-wielding characters. As the players navigate the emergent game world, they continue to expand upon it, illustrating the capability of users to create game assets from scratch using natural language prompts.
- "AI Dungeon 2" is a text adventure game crafting personalized and dynamic storylines [8]. It uses language models to generate narratives and outcomes, enabling players to perform any action they can articulate, with the AI dungeon master generating responses accordingly. This transcends the limitations of predefined storylines, offering a unique gaming experience where the story evolves in countless ways, leading to an infinite variety of adventures.
- "Eden Island" leverages generative AI to imbue its Non-Player Characters (NPCs) with autonomous and self-evolving behaviors [7]. Autonomous behaviors refer to the NPCs’ ability to make decisions and take actions without direct player intervention. Self-evolving behaviors allow the NPCs to update themselves after being created and deployed, learning from experience and deliberately improving their performance. This creates a more realistic and immersive gaming environment, where NPCs are not just reactive but also proactive, exhibiting a level of agency that brings the game’s world to life.
2. The Evolution of Generative AI’s Applications in Games
2.1. Phase 1: Proof of Concept (2015–2019)
2.2. Phase 2: Language-Controllable Generation (2020–2022)
2.3. Phase 3: Large Model & Multimodal Enhancement (2023 to Mid-2024)
2.4. Phase 4: Efficiency & Innovation (Mid-2024 to Present)
3. Key Features of Generative Games
3.1. Real-time Interactive Scenarios
3.2. Personalized and Dynamic Storylines
3.3. Autonomous and Self-evolving Character Behaviors
4. Challenges
4.1. Technical Challenges
-
Content Consistency
- –
- Visual Consistency: Maintaining coherence in generated images, scenes, and animations is critical. Abrupt or unrealistic transitions can disrupt immersion and break the player’s connection to the game.
- –
- Semantic Consistency: Long-context coherence in generated text and stories remains a challenge. Ensuring that narrative and dialogue align with logical, extended contexts is essential to preserve storytelling quality.
-
Computational Cost and Real-Time Performance
- –
- High Computational Cost: Training and deploying generative AI models demand extensive computational resources, significantly increasing development costs.
- –
- Real-Time Performance: Generating content dynamically in real-time can strain hardware, impacting game frame rates and fluidity. Handling complex tasks in this manner risks lag or stuttering during gameplay.
- Stability The integration of new characters or storylines into a generative framework can challenge the stability and coherence of the existing game structure, making updates and expansions difficult to manage without disrupting player experiences.
4.2. Limitations
- Ethical and Social Concerns Generative content risks perpetuating biases or producing harmful outputs, posing threats to social values and fairness. Ensuring the ethical deployment of generative AI is an ongoing challenge.
- Constraints on Innovation While generative AI excels in producing vast quantities of content, it often relies on patterns from existing data. This tendency may limit its ability to deliver genuinely innovative game concepts, characters, or narratives, potentially leading to homogenized content that lacks originality.
- Complexity in Game Development The inherent opacity of generative AI models makes controlling their output challenging. This lack of interpretability complicates the development process, increasing the difficulty for developers to refine and direct the game’s generative systems.
5. Prospects
5.1. Generative Evolution of Game Development
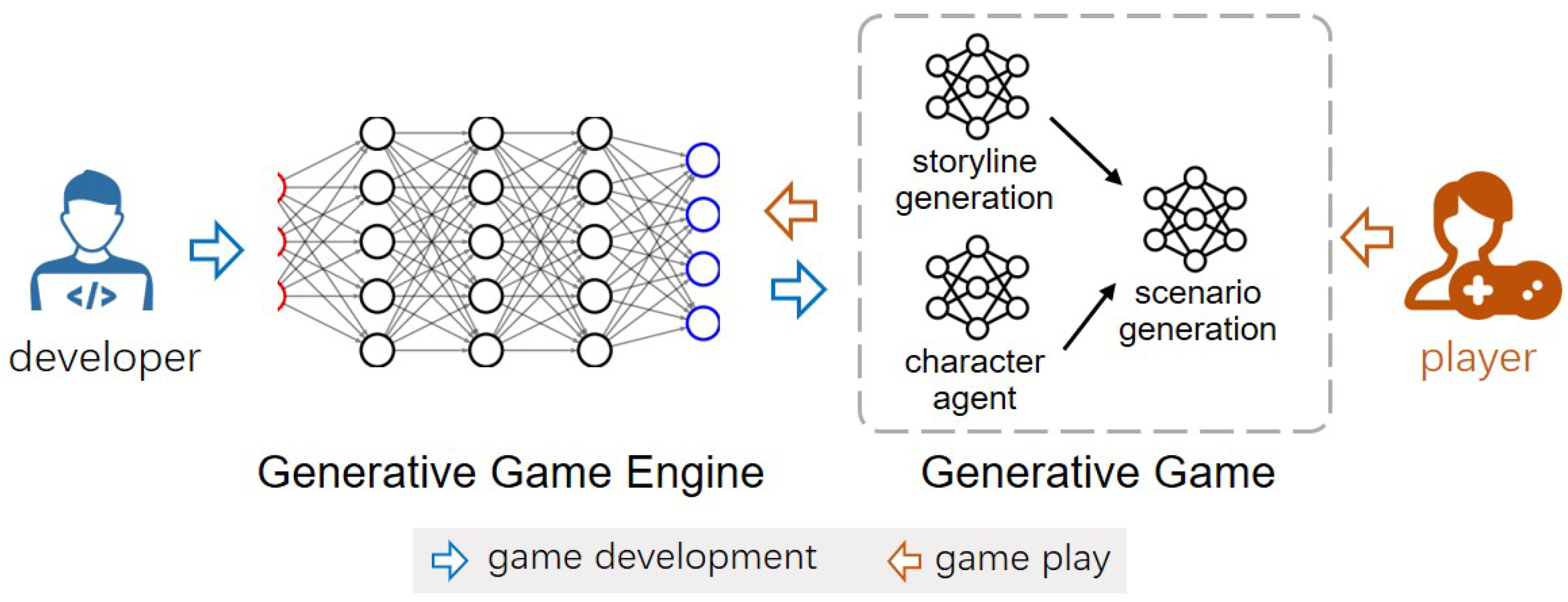
- Storyline Generation Model: This model controls the narrative progression, ensuring long-term coherence and addressing the lack of memory seen in works like GameGen-X.
- Character Agent Model: Responsible for managing the behaviors of key NPCs and main characters, this model ensures autonomous and self-evolving character actions.
- Scenario Generation Model: Taking inputs from both the storyline and character agent models, this model generates the game environment dynamically, ensuring visual and functional coherence.
5.2. When Generative Game Meets o1: from Outer Shell to Inner Soul
5.3. Gaming towards AGI
5.4. Beyond Entertainment: Games as a Pathway to Self-Actualization
References
- Taveekitworachai, P.; Gursesli, M.C.; Abdullah, F.; Chen, S.; Cala, F.; Guazzini, A.; Lanata, A.; Thawonmas, R. Journey of ChatGPT from Prompts to Stories in Games: The Positive, the Negative, and the Neutral. 2023 IEEE 13th International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Berlin (ICCE-Berlin). IEEE, 2023, pp. 202–203. [CrossRef]
- Sudhakaran, S.; González-Duque, M.; Glanois, C.; Freiberger, M.; Najarro, E.; Risi, S. Prompt-guided level generation. Proceedings of the Companion Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation, 2023, pp. 179–182. [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Shen, T.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Yin, K.; Li, D.; Litany, O.; Gojcic, Z.; Fidler, S. GET3D: A Generative Model of High Quality 3D Textured Shapes Learned from Images. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2022, NeurIPS 2022, New Orleans, LA, USA, November 28 - December 9, 2022, 2022.
- Li, X.; You, X.; Chen, S.; Taveekitworachai, P.; Thawonmas, R. Analyzing Audience Comments: Improving Interactive Narrative with ChatGPT. Interactive Storytelling - 16th International Conference on Interactive Digital Storytelling, ICIDS 2023, Kobe, Japan, November 11-15, 2023, Proceedings, Part II. Springer, 2023, Vol. 14384, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 220–228. [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, H.; Huo, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Gamegpt: Multi-agent collaborative framework for game development. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.08067 2023. [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Kleinman, E.; Harteveld, C. GPT for Games: A Scoping Review (2020-2023). IEEE Conference on Games, CoG 2024, Milan, Italy, August 5-8, 2024. IEEE, 2024, pp. 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Tencent. Eden Island, 2024.
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.C.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2014, December 8-13, 2014, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, 2014, pp. 2672–2680. 8 December.
- OpenAI.; Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Sandhini Agarwal, e.a. GPT-4 Technical Report, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2303.08774]. [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Metz, L.; Chintala, S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2016.
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), 2017, pp. 2223–2232. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Fu, X.; Wang, L.; Sun, X. Game environment style transfer using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 2019, pp. 0–0. [CrossRef]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aila, T. A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2019, pp. 4401–4410.
- Wang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, L. Learning to generate game environments with stylegan and cycle-consistency loss. 2020 IEEE Conference on Games (CoG). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1–8.
- van den Oord, A.; Vinyals, O.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Neural discrete representation learning. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2017, pp. 6306–6315.
- Razavi, A.; van den Oord, A.; Vinyals, O. Generating diverse high-fidelity images with vq-vae-2. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2019, pp. 14837–14847.
- Eslami, S.A.; others. Neural scene representation and rendering. Science 2018, 360, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siarohin, A.; Lathuilière, S.; Tulyakov, S.; Ricci, E.; Sebe, N. First Order Motion Model for Image Animation. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2019, pp. 7137–7147.
- Games, H. No Man’s Sky, 2016. Game, https://www.nomanssky.com.
- Corporation, N. NVIDIA AI Playground. 2018. Tech Demo, https://www.nvidia.com.
- NCSoft. Project M, 2018. Tech Demo, https://www.ncsoft.com.
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; others. Language models are few-shot learners. Advances in neural information processing systems 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; others. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2021, pp. 8748–8763.
- Ramesh, A.; Pavlov, M.; Goh, G.; Gray, S.; Voss, C.; Radford, A.; Chen, M.; Sutskever, I. Zero-shot text-to-image generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.12092 2021. [CrossRef]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.10752 2022. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, N.; Li, Y.; Goldman, Y.; Fineran, B.; Li, Z.; Shih, K.; Hanrahan, P.; Goldman, D. DreamBooth: Fine Tuning Text-to-Image Diffusion Models for Subject-Driven Generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.12242 2022. [CrossRef]
- Suarez, J.; Du, Y.; Zhu, C.; Mordatch, I.; Isola, P. The Neural MMO Platform for Massively Multiagent Research. Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems Track on Datasets and Benchmarks, 2021.
- Guo, J.; Yang, B.; Yoo, P.; Lin, B.Y.; Iwasawa, Y.; Matsuo, Y. Suspicion-Agent: Playing Imperfect Information Games with Theory of Mind Aware GPT-4. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.17277 2023. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Agrawala, M. Adding Conditional Control to Text-to-Image Diffusion Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.05543 2023. [CrossRef]
- OpenAI. Sora: OpenAI’s Text-to-Video Model. OpenAI Research 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, J.; others. Genie: Generative Interactive Environments. DeepMind Research 2024. [Google Scholar]
- OpenAI. GPT-4o. https://openai.com/index/hello-gpt-4o/, 2024.
- Smith, J.; others. Human-AI Collaboration Supporting GPT-4o Achieving Human-Level User Feedback in Emotional Support Conversations: Integrative Modeling and Prompt Engineering Approaches. AI Research Journal 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Electric Sheep. Electric Sheep’s AI Garden Robot, 2024.
- Yu, H.X.; Duan, H.; Herrmann, C.; Freeman, W.T.; Wu, J. WonderWorld: Interactive 3D Scene Generation from a Single Image. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.09394 2024. [CrossRef]
- Valevski, D.; Leviathan, Y.; Arar, M.; Fruchter, S. Diffusion Models Are Real-Time Game Engines. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.14837 2024. [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; He, X.; Liu, Q.; Jin, C.; Chen, H. GameGen-X: Interactive Open-world Game Video Generation, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CV/2411.00769]. [CrossRef]
- DecartAI. Oasis AI Minecraft: Play Game Online Demo, 2024.
- OpenAI. Introducing OpenAI o1-preview, 2024.
- Kim, S.W.; Lee, H.; Torr, P.; others. GameGAN: Learning to Play Pac-Man and Beyond. NVIDIA Research 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lab, U.A. UniSim: Predictive Video Continuation for Interactive Gaming. Interactive AI Research 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Team, D.A. Genie-2: Advancing the Frontiers of Interactive AI. Nature 2024, 568, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Lew, D.; Yu, K. LaSofa: Integrating Fantasy Storytelling in Human-Robot Interaction through an Interactive Sofa Robot. 2024, HRI ’24, p. 1168–1172.
- Yang, D.; Others. Snake Story: Integrating Path-Based Gameplay with Dynamic Narrative Generation. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Interactive Digital Entertainment, 2024, pp. 123–134.
- Wang, Y.; Others. Dynamic Plot Co-Authoring in StoryVerse: Collaborative Storytelling with AI. Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Interactive Storytelling, 2024, pp. 56–68.
- Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Fang, K.; Others. 1001 Nights: AI-Driven Co-Creative Storytelling in a Generative Game. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Interactive Digital Entertainment, 2023, pp. 425–436.
- Lima, E.; Others. ChatGeppetto: AI-Powered Interactive Storytelling through Dialogue. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Games, 2023, pp. 234–245.
- Agarwal, N. Infinite Craft. https://neal.fun/infinite-craft/, 2023.
- Park, J.S.; O’Brien, J.C.; Cai, C.J.; Ringel Morris, M.; Liang, P.; Bernstein, M.S. Generative Agents: Interactive Simulacra of Human Behavior. The 36th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology (UIST ’23), 2023.
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wadhwa, N.; Pritch, Y.; Jacobs, D.E.; Rubinstein, M.; Bansal, M.; Ruiz, N. Unbounded: A Generative Infinite Game of Character Life Simulation. arxiv 2024.
- GoodAI. AI People: Announcing the Next Evolution of Gaming AI NPCs. https://www.goodai.com/ai-people-announcing-the-next-evolution-of-gaming-ai-npcs/, 2024.
- Team, C. ChatWaifu, 2024.
- Sutton, R.S. The Alberta Plan for AI Research. https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.11173, 2023. Accessed: 2024-11-21.
- Banburski-Fahey, A. DreamGarden: A Designer Assistant for Growing Games from a Single Prompt, 2024, [2410.01791].
- Cursor. https://www.cursor.com/.
- Bolt.new. https://bolt.new/.
- Viswanathan, V.; Zhao, C.; Bertsch, A.; Wu, T.; Neubig, G. Prompt2Model: Generating Deployable Models from Natural Language Instructions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.12261 2023. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zeng, W.; Jin, S.; Qian, C.; Luo, P.; Liu, W. AutoMMLab: Automatically Generating Deployable Models from Language Instructions for Computer Vision Tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.15351 2024. [CrossRef]
- Portnoy, B. The Geometry of Wealth: How to shape a life of money and meaning; Harriman House, 2018.
- See-. https://www.taptap.cn/app/162251.


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



