Introduction
Many countries, including Uzbekistan, are enriched with domestic tourism which is useful in building the cultural and economic atmosphere. In recent years, the demand for domestic tourism has been on the rise, and in any tourism activity, the effects on local culture and communities should be understood. The impact of international tourism on Uzbekistan on the other hand is being assessed. Only a few scientific studies show a clear understanding of the effect of external tourism on the communities and the local culture. Focus has in the past been more on international tourism and its merits or demerits while the social impacts of local tourism have been left unattended (Orzikulov, 2024). American domestic tourists have an idea about what local tourism has done to the respective regions. Other areas that there is a need for focus include how domestic tourism may have a negative impact on the culture, the social networks, the environment, and wealth distribution in the region. However, the growth of local tourism may trigger cultural erosion, environmental pollution, and the disintegration of societies (Daukayeva et al., 2020). The current research is meant to address this gap in knowledge by looking into the policies meant to limit internal tourism in Uzbekistan and seeing it through the eyes of the local perspective. In this research, the authors attempt to address the people regarding the issues of cultural trauma and economic disparity, environmental factors, social relationships, and the wider effects of domestic tourism in the area. The main objective of this research is to examine the issues of analysis of domestic tourism in Uzbekistan and ignore them. A systematic approach is of more importance as it corresponds to the already existing framework for the development of historical and cultural tourism in the country. The study emphasizes the need to promote such forms of tourism which can negate negative influences such as depletion of the ecosystem and social injustices. The author mentions in his articles the issues arising from internal tourism in Uzbekistan which today consists more of migrant exiles, ethnological tourists, and moving artists who number in the hundreds on their visit to Uzbekistan’s archeological sites. Furthermore, the analysis of the impact of domestic tourism on the community and cultural contexts is also well substantiated. Practical measures are formulated to apply in resolving and addressing some of the problems discussed during this research.
Literature Review
Tourism is endowed with relevance in a large number of countries across the world as it is considered to enhance the economic and cultural development of the nation and its people. Domestic tourism is on the rise and although it adds potential for growth of the economy and the culture such an industry also creates hurdles when it comes to community development and environmental conservation within the area. According to the study of Ibrokhimov and Rotich, the aim was the demonstration of the role of tourism in the growth of cultural change between Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. Their research endeavors to explore how tourism might support cultural decision-making and understanding through historical context, current tourism development efforts, and its economic components. Important themes like cultural integration, economic effect, and business issues were identified (Ibrokhimov & Rotich, 2024). Tourism is the fifth-largest and fastest-growing segment of the global economy. Today, the concepts of sustainable development have emerged as a great focus on the issue of public concern. Recent researches and studies have started showing the shape for the sustainability of tourism concerning social, economic, and cultural variables. Ji Young and other authors(2023) did a remarkable research paper to identify the main issues and develop appropriate cultural strategies to meet expectations in Uzbekistan. Amonboyev provided more information in his research work(2022) that historical and cultural tourism is one of the main drivers of the tourism industry. The historical and cultural role and spread of tourism in the overall development, and its potential that is some of the main focuses of researchers and scholars in the field of tourism marketing. This study, comparatively new regarding the tourism of Uzbekistan, shifts the focus from the historical and cultural monuments and landmarks of the country to a different aspect. From this point of view, the focus is on those countries that can attract the maximum number of tourists from across the world and accordingly the capability of holiday sites to entice visitors. Environmental consequences of tourism have received attention in several studies in the past. Using social exchange theory, tourism affects the lifestyles of the residents of Samarkand and Bukhara. Due to the rise in tourism activities in Uzbekistan, World Heritage Sites along the Intangible Cultural Heritage have been so far the most popular areas as well. However, the results show the need of both visitors and residents for the maintenance of conservation in the framework of ICH. These positive attitudes encourage people to support tourism development. Therefore, this suggests how tourism development policies should be analyzed to ensure that tourism is addressed according to local people’s perceptions of their cultural values(Allaberganov & Catterall, 2023). The purpose of the other study by Nazarov is to analyze the strengths of cultural and historical tourism in the region and to determine their regional characteristics in Uzbekistan. It describes tourism and recreation in the Kashkadarya region, which is important for the development of tourism in Uzbekistan due to its natural resources, and is analyzed from the perspective of culture and technology in urban and rural areas. The study of the state continues to ensure that the region has a lot to offer, more so because of its multicultural and recreational chances (Nazarov et al., 2020). Many scholars interested in cultural heritage conservation, cultural heritage, and tourism have studied the area of expertise of Uzbekistan. Nevertheless, some tourism studies highlight the impact of tourism on local cultures and communities but only a small number of them have addressed the issue. The present study fills this gap by examining the influence of cultural, and local factors, and values of individuals and social organizations.
Data and Methodology
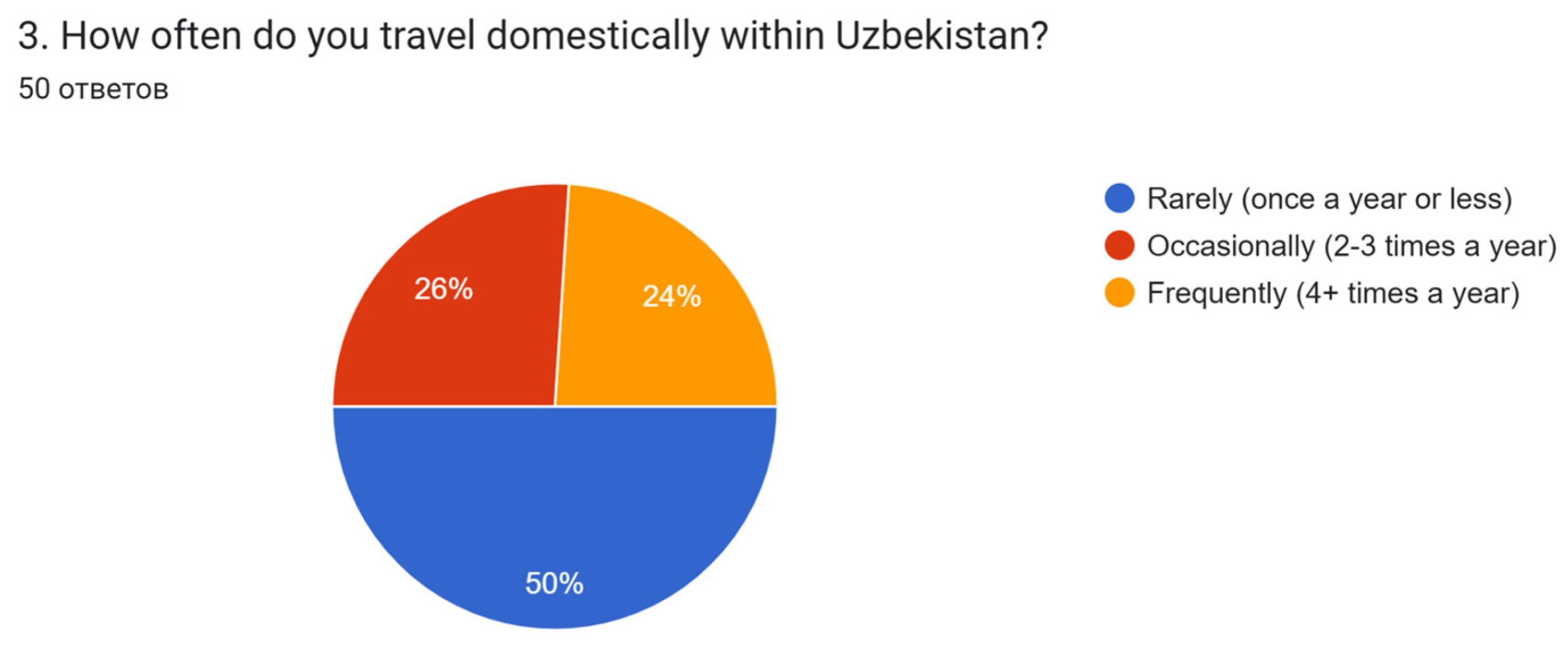
This study learns the situation of the impact on culture and community by the domestic tourism actions. To get much probing, useable for exploratory purposes, small sample, large data from respondents, and subjective, interpretive, and flexible answers this research explored through a survey method which consists of 20 questions. The study examines the influence of various factors on tourists` traveling decisions among visitors in Uzbekistan. The analysis utilizes primary qualitative data gathered from a sample of 50 domestic tourists, consisting of 76% urban area residents and 24% persons from rural sides. Data collection occurred onsite in Samarkand.
Ordinal logistics regression has been employed to estimate the relationship between domestic tourism and community-culture influencing factors.
Ordinal logistic regression has been effectively used in diverse research studies to analyze ordered categorical data. Researchers in Taiwan and China use logistic regression to examine the impact of regional organizations on cultural heritage conservation. This study shows that various factors such as school climate and culture influence.
| Parameter Estimates |
| |
Estimate |
Std. Error |
Wald |
df |
Sig. |
95% Confidence Interval |
| Lower Bound |
Upper Bound |
| Threshold |
[LocalComImpact = Negative] |
-16,285 |
5,452 |
8,921 |
1 |
,003 |
-26,972 |
-5,599 |
| [LocalComImpact = Neutral] |
-7,380 |
2,549 |
8,382 |
1 |
,004 |
-12,376 |
-2,384 |
| Location |
[ResidentPlace=rural area] |
-4,268 |
2,075 |
4,231 |
1 |
,040 |
-8,335 |
-,201 |
| [TourismBenefits=Agree] |
-4,255 |
1,936 |
4,831 |
1 |
,028 |
-8,049 |
-,461 |
| [CostOfLiving=Decreased slightly] |
6,486 |
3,617 |
3,216 |
1 |
,073 |
-,603 |
13,575 |
| [TraditionalCulture=Cultural preservation, but commercialization risks.] |
7,476 |
4,380 |
2,913 |
1 |
,088 |
-1,108 |
16,060 |
| [TraditionalCulture=Festivals] |
8,438 |
4,853 |
3,024 |
1 |
,082 |
-1,073 |
17,949 |
| [TraditionalCulture=Positive] |
6,989 |
3,941 |
3,144 |
1 |
,076 |
-,736 |
14,714 |
| [TraditionalCulture=Yes] |
11,068 |
5,303 |
4,356 |
1 |
,037 |
,674 |
21,462 |
| [RecommendationLikelihood=likely] |
-5,717 |
2,459 |
5,406 |
1 |
,020 |
-10,536 |
-,898 |
| [RecommendationLikelihood=unlikely] |
-10,848 |
4,894 |
4,913 |
1 |
,027 |
-20,441 |
-1,255 |
| Link function: Logit. |
| a. This parameter is set to zero because it is redundant. |
The above table summarizes the outcomes of the ordinal logistic regression analysis which aimed at evaluating the effects of domestic tourism on local culture and community. Some of the high points include the First Variables: Furthermore, the variable Communities where the variable residents have been rated as negative and neutral has significant results with p value less than 005. Second Variables Third, it was found that residents in rural areas have statistically significant results p-value of 040, this implies that rural areas have an extreme view of the impacts tourism has. Third: Also, the benefits hit tourism are significant P 028 which ok people are optimistic about the input by the tourism sector towards tourism. Fourth rated cultural and economic impacts: Variables concerning preservation of culture traditional culture festivals and positive changes of the living standards over the costs for example minimal drop in living standards were found to be of p < 1 and near and statistically significant p < 1. Fifth, Risks associated with the commercialization of culture preservation were also very significant P: Always in consideration of the above Ukrainian variables: Sixth, the Likelihood ratio also indicated significance with 05207. Seventh, these results inform on how tourism and community, cultural, and economic variables are related in a complex way.
Result
The table analysis of the results from multinomial logistic regression presents parameter estimates for each predictor and its respective category.
Firstly Local Community impact is statistically significant at [0.05] level, we accept Ha and reject H0 meaning that there is a negative relationship between local community impact and logistic regression.
Negative: Estimate = – 16.285, p = 0.003, which suggests large effects in the negative direction.
Neutral: Estimate = – 7.380, p = 0.004
Other categories, namely Positive and Very Negative, do not achieve statistical significance.
The second one Resident Location is statistically nonsignificant at [0.1] level we accept H0, meaning that there is no association between Resident Location and Logistic
Farmers’ residents show a significant negative estimate of about - 4.268 (P = 0.040) which means their perception is different from urban residents.
The next Tourism Benefits participants who Agree that tourism offers benefits show a significant negative estimate of -4.255, (p = 0.028).
The Other categories, such as Disagree and Neutral, are not statistically significant.
Following this statement Cost of Living, in most categories is not statistically significant, except for
Decreased slightly estimate = 6.486, p = 0.073 (marginally significant).
Subsequently, Traditional Culture certain responses reveal significant effects, such as a positive connection between tourism and traditional culture, Estimate = 11.068, p = 0.037
In addition, other responses (e.g., cultural exchange or preservation) lack statistical significance, likely due to smaller sample sizes.
Upcoming Tourism Promotion Categories like HA and Not Sure Category are not significant.
Immediately after this statement, the Recommendation Likelihood is statistically insignificant.
Likely: Estimate= -5.717, p = 0.020 which states that there is a large negative relationship.
Unlikely: Estimate= -10.848, p = 0.027 which also gives a strong negative effect on the outcome.
To summarise. Significant predictors of perceptions include Local Community Impact, Resident Location (Rural and Urban), and select categories within Tourism Benefits, Traditional Culture, and Recommendation Likelihood. Positive responses, such as "Yes" for Traditional Culture or higher Recommendation Likelihood, are associated with greater perceived benefits of tourism.
Negative impacts are identified in certain aspects of cost of living and local community variables.
Conclusion and Policy Implication
This research analyzes the economic and social consequences of domestic tourism, particularly its importance in bringing about income, creating jobs, and improving infrastructure. It determines the average level of domestic tourism participation among older people compared to the younger generation, utilizing both quantitative and qualitative data to explore these relationships. Some crucial factors such as age, living costs, and residential location are assessed alongside qualitative elements like cultural events and tourism management practices. The research scrutinizes the economic and social consequences of domestic tourism, particularly its role in generating income, job creation, and improvement of infrastructure.
The results of the survey supply a critical perception of the factors affecting attitudes towards local tourism. The analysis shows a statistically significant negative reaction related to the impact of tourism on local communities, suggesting that some aspects related to tourism are viewed unfavorably by the population. This is noticeable among rural people and they are skeptical about the advantages of travelling. By contrast, positive feelings accompany characterizing with the traditional cultural features. It comes as no surprise that respondents who perceive cultural heritage in a more positive light also appreciate the role of tourism more.
To put it in one word, this study offers relevant data on the correlation between intern tourism and its socio-economic and cultural effects and gives substantive hints on ways of enhancing tourist strategies that are beneficial to the locals and inclusive of development goals.
References
- Allaberganov, A., & Catterall, P. (2023). Using social exchange theory to examine residents’ responses to heritage tourism: case studies of Samarqand and Bukhara in Uzbekistan. Journal of Heritage Tourism, 18(6), 846-863.
- Bakhrom, Orzikulov. (2024). Issues of attention to examples of intangible cultural heritage in new uzbekistan. Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities Research Fundamentals, 4(5):23-26. [CrossRef]
- Daukaeva, Khalida, Ibrakhimovna., Mirboboeva, Dilfuza, Bakhtiyorovna. (2020). Cultural Tourism as a Means of Development of Regional Tourism. 5. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J. Y., Karimov, M., Sobirov, Y., Saidmamatov, O., & Marty, P. (2023). Evaluating centralization strategies for sustainable tourism development in Uzbekistan. Sustainability, 15(9), 7727.
- MDPI. (n.d.). Improving the sustainability effectiveness of traditional arts and crafts using supply–demand and ordered logistic regression techniques in Taiyuan, China. Retrieved from https://www.mdpi.com.
- Mukhammadsiddik, A., Bobir, T., & Shohruzbek, R. (2022). Main Tendencies of Historical and Cultural Tourism Development in Uzbekistan. In Event Tourism in Asian Countries (pp. 9-37). Apple Academic Press.
- Nazarov, M. I., Jumaev, H. H., Turdimambetov, I. R., Yanchuk, S. L., & Egamberdieva, M. M. (2020). Development of tourism in Uzbekistan and cultural-historical tourist resource potential of Kashkadarya region. Journal of Environmental Management and Tourism, 11(4), 794-801.
- Nodirbek, I., & Laban, R. K. (2024). Tourism as a Factor in the Development of Cultural Integration between Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. Journal of Tourism and Environmental Sustainability, 1(1), 1-9.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).