Submitted:
08 December 2024
Posted:
09 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized the financial services sector by enhancing data processing, decision-making, and customer interaction. Particularly in the insurance industry, LLMs facilitate significant advancements by automating complex processes and personalizing customer engagements, which increases efficiency and satisfaction. This paper explores the integration of LLMs within the insurance sector, highlighting their capabilities in sentiment analysis, risk assessment, and tailored service provision. However, deploying these models presents substantial challenges concerning data privacy, security, and the ethical implications of automated decision-making. Ensuring the fairness and transparency of AI-driven processes is imperative to address potential biases and maintain consumer trust. The paper also discusses robust risk management strategies essential for implementing LLMs in sensitive environments, focusing on continuous monitoring and the need for regular updates to security practices and compliance with data protection laws. The insurance industry can leverage LLMs to improve operational efficiencies and enhance customer service and risk management practices, positioning themselves at the forefront of technological innovation in the financial sector.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Development of Large Language Models
3. Application of LLMs in the Fintech Industry

- LLMs play an essential role in risk assessment and compliance monitoring. Analyzing vast amounts of transaction data and identifying patterns helps detect potential risks and fraud early [80,81]. This enables financial institutions to take preventive measures, reduce losses, and ensure regulatory compliance.
- LLMs can automatically process and analyze large volumes of complex financial documents and transaction data, reducing the human workload and improving processing speed and accuracy [82,83]. This capability is especially critical for financial institutions dealing with high-frequency transactions and cross-border activities.
- LLMs drive financial innovation and new product development. By analyzing market trends and consumer behavior data, LLMs help financial institutions design and promote new financial products and services, enabling them to respond more effectively to changing market demands [84].
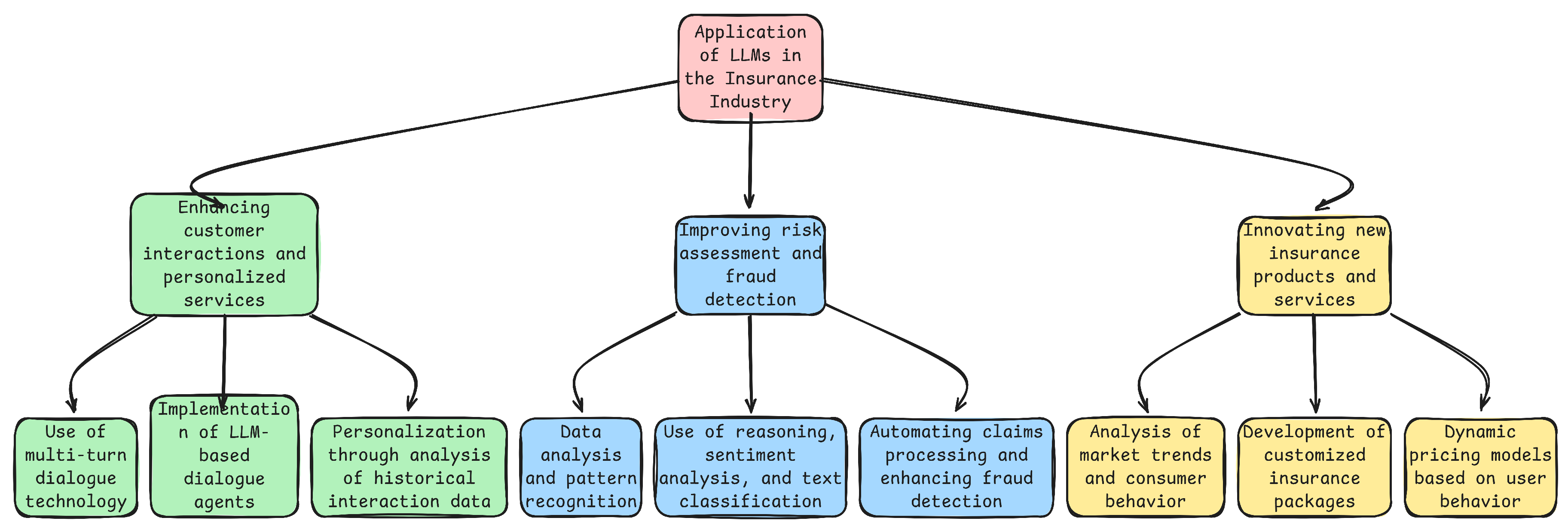
4. Application of LLMs in the Insurance Industry
- Improving Customer Service Response Times: Traditional customer service often suffers from lengthy response times and low efficiency. With LLM’s advanced text understanding and generation capabilities, real-time, automated customer responses become possible. LLMs can instantly answer customer queries and provide detailed information about insurance policies, using their deep understanding of natural language [106,107,108,109]. This immediate responsiveness greatly enhances customer satisfaction, optimizes the customer experience, reduces waiting times, and boosts overall service efficiency.
- Streamlining the Claims Process: The claims handling process is typically complex and time-consuming, requiring substantial manual document processing. LLMs utilize their natural language processing capabilities to automate the processing and review of claim documents, identify key information, and accelerate the document workflow [110,111,112,113]. This automation reduces the workload on human staff and increases processing speed and accuracy, making the claims process more efficient and customer-friendly.
- Enhancing the Accuracy of Risk Assessment: Traditional risk assessment methods often rely on outdated data and limited analytical capabilities, which can lead to inaccurate risk predictions. LLMs, with their pattern recognition and data analysis capabilities, analyze vast amounts of historical data and behavioral patterns. Through precise data analysis and trend prediction, they enhance the accuracy of risk assessments. More accurate risk assessments help insurance companies optimize their insurance products and pricing strategies, reduce unnecessary losses, and offer more reasonable insurance services to customers, thereby increasing customer trust and satisfaction.
5. Opportunities for LLM in the Insurance Industry
5.1. Establishing Dialogue Agents to Enhance Customer Interaction and Personalized Services
5.2. Improving Risk Assessment and Fraud Detection
- Mathematical Reasoning: Mathematical reasoning enables LLMs to handle complex calculations and statistical analyses required for risk assessment [116,117,118]. For instance, LLMs can evaluate the probability of certain events based on historical data, such as the likelihood of a fraudulent claim based on past claim patterns and financial behaviors. This type of reasoning helps insurers quantify risk levels and make decisions based on statistical evidence, thereby improving the precision of risk assessments.
- Textual Reasoning: Textual reasoning involves understanding and interpreting written content within context [119,120,121,122]. In the realm of insurance, this ability allows LLMs to analyze the textual data from claims or customer interactions to identify signs of possible fraud. For example, discrepancies in incident reports or claims that deviate from typical patterns can be flagged for further investigation. Textual reasoning helps LLMs understand the nuances of language used in claims, spotting inconsistencies and anomalies that could indicate fraudulent activities.
- Symbolic Reasoning: Symbolic reasoning refers to the ability of LLMs to manipulate and reason with symbols, typically used in logical deduction and problem-solving scenarios [123,124,125]. In insurance, symbolic reasoning can be applied to automate and refine the decision-making processes. For example, by defining certain rules and conditions for what constitutes a high-risk claim, LLMs can apply these criteria systematically, checking claims against established risk indicators. This type of reasoning ensures that decisions are consistent and based on defined insurance policy parameters, reducing human error and bias in fraud detection and risk assessment processes.
5.3. Innovating New Insurance Products and Services Through LLM Insights
5.3.1. Emotional Analysis for Consumer Insight
5.3.2. Synthetic Data for Market Simulation
5.3.3. Time Series Analysis for Market Trends
6. Security, Risks, and Ethical Concerns
6.1. Data Privacy and Security Challenges with LLMs
6.2. Ethical Implications of Automated Decision-Making in Insurance
6.3. Risk Management Strategies for Deploying LLMs in Sensitive Environments
References
- Chang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhu, K.; Chen, H.; Yi, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; others. A survey on evaluation of large language models. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology 2024, 15, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaee, S.; Mikolov, T.; Nikzad, N.; Chenaghlu, M.; Socher, R.; Amatriain, X.; Gao, J. Large language models: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.06196, arXiv:2402.06196 2024.
- Gao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Gao, X.; Jia, K.; Pan, J.; Bi, Y.; Dai, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, H. Retrieval-augmented generation for large language models: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.10997, arXiv:2312.10997 2023.
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Ding, H.; Chen, H. Large language models in finance: A survey. Proceedings of the fourth ACM international conference on AI in finance, 2023, pp. 374–382.
- Nie, Y.; Kong, Y.; Dong, X.; Mulvey, J.M.; Poor, H.V.; Wen, Q.; Zohren, S. A Survey of Large Language Models for Financial Applications: Progress, Prospects and Challenges. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.11903, arXiv:2406.11903 2024.
- Hadi, M.U.; Al Tashi, Q.; Shah, A.; Qureshi, R.; Muneer, A.; Irfan, M.; Zafar, A.; Shaikh, M.B.; Akhtar, N.; Wu, J. ; others. Large language models: a comprehensive survey of its applications, challenges, limitations, and future prospects. Authorea Preprints.
- Xing, F.Z.; Cambria, E.; Welsch, R.E. Natural language based financial forecasting: a survey. Artificial Intelligence Review 2018, 50, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Irsoy, O.; Lu, S.; Dabravolski, V.; Dredze, M.; Gehrmann, S.; Kambadur, P.; Rosenberg, D.; Mann, G. Bloomberggpt: A large language model for finance. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.17564, arXiv:2303.17564 2023.
- Zhang, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, K. Enhancing Risk Assessment in Transformers with Loss-at-Risk Functions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.02558, arXiv:2411.02558 2024.
- Zhao, H.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, T.; Shu, P.; Xu, S.; Dai, H.; Zhao, L.; Mai, G. ; others. Revolutionizing finance with llms: An overview of applications and insights. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.11641, arXiv:2401.11641 2024.
- Kasneci, E.; Seßler, K.; Küchemann, S.; Bannert, M.; Dementieva, D.; Fischer, F.; Gasser, U.; Groh, G.; Günnemann, S.; Hüllermeier, E.; others. ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education. Learning and individual differences 2023, 103, 102274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jin, H.; Tang, R.; Han, X.; Feng, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zhong, S.; Yin, B.; Hu, X. Harnessing the power of llms in practice: A survey on chatgpt and beyond. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data 2024, 18, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, H.C.; Lu, B.; Li, M. Evaluation of asphalt pavement texture using multiview stereo reconstruction based on deep learning. Construction and Building Materials 2024, 412, 134837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbayoglu, A.M.; Gudelek, M.U.; Sezer, O.B. Deep learning for financial applications: A survey. Applied soft computing 2020, 93, 106384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, C.; Liu, S. Textual sentiment in finance: A survey of methods and models. International Review of Financial Analysis 2014, 33, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, H.; Khan, A.U.; Qiu, S.; Saqib, M.; Anwar, S.; Usman, M.; Akhtar, N.; Barnes, N.; Mian, A. A comprehensive overview of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.06435, arXiv:2307.06435 2023.
- Girotra, K.; Meincke, L.; Terwiesch, C.; Ulrich, K.T. Ideas are dimes a dozen: Large language models for idea generation in innovation. Available at SSRN 4526071 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bao, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Feng, F.; He, X. Is chatgpt fair for recommendation? evaluating fairness in large language model recommendation. Proceedings of the 17th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, 2023, pp. 993–999.
- Wang, P.; Li, L.; Chen, L.; Cai, Z.; Zhu, D.; Lin, B.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, T.; Sui, Z. Large language models are not fair evaluators. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.17926, arXiv:2305.17926 2023.
- Yao, Y.; Duan, J.; Xu, K.; Cai, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y. A survey on large language model (llm) security and privacy: The good, the bad, and the ugly. High-Confidence Computing, 1002. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Zhang, M.; Ji, S.; Yang, M. Privacy risks of general-purpose language models. 2020 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1314–1331.
- Liu, X.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y.; Zou, J.; Xiong, J.; Ying, Z.; Vasilakos, A.V. Privacy and security issues in deep learning: A survey. IEEE Access 2020, 9, 4566–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, M.U.; Qureshi, R.; Shah, A.; Irfan, M.; Zafar, A.; Shaikh, M.B.; Akhtar, N.; Wu, J.; Mirjalili, S. ; others. A survey on large language models: Applications, challenges, limitations, and practical usage. Authorea Preprints.
- Zhao, W.X.; Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Tang, T.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Min, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Z. ; others. A survey of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.18223, arXiv:2303.18223 2023.
- Gillioz, A.; Casas, J.; Mugellini, E.; Abou Khaled, O. Overview of the Transformer-based Models for NLP Tasks. 2020 15th Conference on computer science and information systems (FedCSIS). IEEE, 2020, pp. 179–183.
- Vaswani, A. Attention is all you need. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kalyan, K.S.; Rajasekharan, A.; Sangeetha, S. Ammus: A survey of transformer-based pretrained models in natural language processing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.05542, arXiv:2108.05542 2021.
- Ansar, W.; Goswami, S.; Chakrabarti, A. A Survey on Transformers in NLP with Focus on Efficiency. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.16893, arXiv:2406.16893 2024.
- Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Vincent, P. Representation learning: A review and new perspectives. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2013, 35, 1798–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Liu, J.; Bu, X.; He, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, Z.; Su, W.; Ge, T.; Zheng, B. ; others. Mt-bench-101: A fine-grained benchmark for evaluating large language models in multi-turn dialogues. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.14762, arXiv:2402.14762 2024.
- OpenAI. New and Improved Embedding Model. https://openai.com/index/new-and-improved-embedding-model/, 2024.
- Yuan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, H. Rhyme-aware Chinese lyric generator based on GPT. Fourth International Conference on Advanced Algorithms and Neural Networks (AANN 2024). SPIE, 2024, Vol. 13416, pp. 667–672.
- Li, S.; He, Y.; Guo, H.; Bu, X.; Bai, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Qu, X.; Li, Y.; Ouyang, W. ; others. GraphReader: Building Graph-based Agent to Enhance Long-Context Abilities of Large Language Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.14550, arXiv:2406.14550 2024.
- Gao, M.; Wei, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, B.; Zheng, C.; Mulati, A. A survey of machine learning algorithms for defective steel plates classification. International Conference on Computing, Control and Industrial Engineering. Springer, 2024, pp. 467–476.
- Liu, Y.; Han, T.; Ma, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Tian, J.; He, H.; Li, A.; He, M.; Liu, Z. ; others. Summary of chatgpt-related research and perspective towards the future of large language models. Meta-Radiology, 1000. [Google Scholar]
- Mahowald, K.; Ivanova, A.A.; Blank, I.A.; Kanwisher, N.; Tenenbaum, J.B.; Fedorenko, E. Dissociating language and thought in large language models. Trends in Cognitive Sciences 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaddour, J.; Harris, J.; Mozes, M.; Bradley, H.; Raileanu, R.; McHardy, R. Challenges and applications of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.10169, arXiv:2307.10169 2023.
- Wang, Z.; Yan, H.; Wei, C.; Wang, J.; Bo, S.; Xiao, M. Research on autonomous driving decision-making strategies based deep reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.03084, arXiv:2408.03084 2024.
- Min, B.; Ross, H.; Sulem, E.; Veyseh, A.P.B.; Nguyen, T.H.; Sainz, O.; Agirre, E.; Heintz, I.; Roth, D. Recent advances in natural language processing via large pre-trained language models: A survey. ACM Computing Surveys 2023, 56, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Bu, X.; Yu, T.; Yuan, J.; Jia, Y. Learning a robust representation via a deep network on symmetric positive definite manifolds. Pattern Recognition 2019, 92, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Gao, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.Q. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning for large models: A comprehensive survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.14608, arXiv:2403.14608 2024.
- Zhang, S.; Dong, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Hu, R.; Zhang, T.; Wu, F. ; others. Instruction tuning for large language models: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.10792, arXiv:2308.10792 2023.
- Ziegler, D.M.; Stiennon, N.; Wu, J.; Brown, T.B.; Radford, A.; Amodei, D.; Christiano, P.; Irving, G. Fine-tuning language models from human preferences. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.08593, arXiv:1909.08593 2019.
- Feng, W.; Bu, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. Beyond bounding box: Multimodal knowledge learning for object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.04072, arXiv:2205.04072 2022.
- Lin, Z.; Akin, H.; Rao, R.; Hie, B.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, W.; dos Santos Costa, A.; Fazel-Zarandi, M.; Sercu, T.; Candido, S.; others. Language models of protein sequences at the scale of evolution enable accurate structure prediction. BioRxiv 2022, 2022, 500902. [Google Scholar]
- Creswell, A.; Shanahan, M. Faithful reasoning using large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.14271, arXiv:2208.14271 2022.
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Jin, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, K. Prototypical Reward Network for Data-Efficient RLHF. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.06606, arXiv:2406.06606 2024.
- Petroni, F.; Rocktäschel, T.; Lewis, P.; Bakhtin, A.; Wu, Y.; Miller, A.H.; Riedel, S. Language models as knowledge bases? arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.01066, arXiv:1909.01066 2019.
- Brants, T.; Popat, A.; Xu, P.; Och, F.J.; Dean, J. Large language models in machine translation. Proceedings of the 2007 Joint Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and Computational Natural Language Learning (EMNLP-CoNLL), 2007, pp. 858–867.
- Kocmi, T.; Federmann, C. Large language models are state-of-the-art evaluators of translation quality. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.14520, arXiv:2302.14520 2023.
- Mo, F.; Mao, K.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Huang, K.; Nie, J.Y. ConvGQR: generative query reformulation for conversational search. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15645, arXiv:2305.15645 2023.
- Bu, X.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Jia, Y. Deep convolutional network with locality and sparsity constraints for texture classification. Pattern Recognition 2019, 91, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Chen, X.; Shan, X. Enhancing large language models with evolutionary fine-tuning for news summary generation. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems.
- Zhang, W.; Deng, Y.; Liu, B.; Pan, S.J.; Bing, L. Sentiment analysis in the era of large language models: A reality check. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15005, arXiv:2305.15005 2023.
- Mao, R.; Liu, Q.; He, K.; Li, W.; Cambria, E. The biases of pre-trained language models: An empirical study on prompt-based sentiment analysis and emotion detection. IEEE transactions on affective computing 2022, 14, 1743–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, Q.; Yu, W.; He, T.; Wang, H.; Peng, W.; Liu, M.; Qin, B.; Liu, T. A survey of chain of thought reasoning: Advances, frontiers and future. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.15402, arXiv:2309.15402 2023.
- Wei, J.; Wang, X.; Schuurmans, D.; Bosma, M.; Xia, F.; Chi, E.; Le, Q.V.; Zhou, D.; others. Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. Advances in neural information processing systems 2022, 35, 24824–24837. [Google Scholar]
- Self-Reflection, S. Self-Contrast: Better Reflection Through Inconsistent Solving Perspectives.
- Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; Anadkat, S. ; others. Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.08774, arXiv:2303.08774 2023.
- Lin, J.; Nogueira, R.; Yates, A. Pretrained transformers for text ranking: Bert and beyond; Springer Nature, 2022.
- Team, G.; Anil, R.; Borgeaud, S.; Alayrac, J.B.; Yu, J.; Soricut, R.; Schalkwyk, J.; Dai, A.M.; Hauth, A.; Millican, K. ; others. Gemini: a family of highly capable multimodal models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.11805, arXiv:2312.11805 2023.
- Team, G.; Mesnard, T.; Hardin, C.; Dadashi, R.; Bhupatiraju, S.; Pathak, S.; Sifre, L.; Rivière, M.; Kale, M.S.; Love, J. ; others. Gemma: Open models based on gemini research and technology. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.08295, arXiv:2403.08295 2024.
- Weise, K. Amazon Has New Chatbot For Shoppers. The New York Times.
- Syaqih, K.N.; Qaisara, A.D.; Lail, M. Character. Ai: Analisis Penyalahgunaan Chatbot Artificial Intelligence Untuk Kepuasan Seksual Pada Remaja Perempuan Daerah Jakarta. ADAPTASI: Jurnal Sosial Humaniora Dan Keagamaan 2024, 1, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Character.AI. https://character.ai/. Accessed: 2023-10-15.
- Ahmed, S.; Alshater, M.M.; El Ammari, A.; Hammami, H. Artificial intelligence and machine learning in finance: A bibliometric review. Research in International Business and Finance 2022, 61, 101646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodell, J.W.; Kumar, S.; Lim, W.M.; Pattnaik, D. Artificial intelligence and machine learning in finance: Identifying foundations, themes, and research clusters from bibliometric analysis. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance 2021, 32, 100577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Guo, L.; Zhou, S.; Song, R.; Niu, K. Enterprise supply chain risk management and decision support driven by large language models. Applied Science and Engineering Journal for Advanced Research 2024, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, D.; Rao, S.; Lim, W.M.; Mangla, S.K. Past, present, and future of sustainable finance: insights from big data analytics through machine learning of scholarly research. Annals of Operations Research.
- Xu, W.; Xiao, J.; Chen, J. Leveraging Large Language Models to Enhance Personalized Recommendations in E-commerce. arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.12829, arXiv:2410.12829 2024.
- Khodadadi, A.; Ghandiparsi, S.; Chuah, C.N. A Natural Language Processing and deep learning based model for automated vehicle diagnostics using free-text customer service reports. Machine Learning with Applications 2022, 10, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, F.; Mao, K.; Zhao, Z.; Qian, H.; Chen, H.; Cheng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Dou, Z.; Nie, J.Y. A survey of conversational search. arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.15576, arXiv:2410.15576 2024.
- Xie, Q.; Han, W.; Zhang, X.; Lai, Y.; Peng, M.; Lopez-Lira, A.; Huang, J. Pixiu: A large language model, instruction data and evaluation benchmark for finance. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.05443, arXiv:2306.05443 2023.
- Abu-Salih, B.; Alweshah, M.; Alazab, M.; Al-Okaily, M.; Alahmari, M.; Al-Habashneh, M.; Al-Sharaeh, S. Natural language inference model for customer advocacy detection in online customer engagement. Machine Learning 2024, 113, 2249–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Fei, H.; Ji, D. A semantic and syntactic enhanced neural model for financial sentiment analysis. Information Processing & Management 2022, 59, 102943. [Google Scholar]
- Doerr, S.; Gambacorta, L.; Garralda, J.M.S. Big data and machine learning in central banking. BIS Working Papers 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Petropoulos, A.; Siakoulis, V.; Stavroulakis, E.; Vlachogiannakis, N.E. Predicting bank insolvencies using machine learning techniques. International Journal of Forecasting 2020, 36, 1092–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mo, F.; Ma, W.; Sun, P.; Zhang, M.; Nie, J.Y. A User-Centric Multi-Intent Benchmark for Evaluating Large Language Models. Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2024, pp. 3588–3612.
- Mo, F.; Nie, J.Y.; Huang, K.; Mao, K.; Zhu, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, Y. Learning to relate to previous turns in conversational search. Proceedings of the 29th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 2023, pp. 1722–1732.
- Yuan, T.; He, Z.; Dong, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Xia, T.; Xu, L.; Zhou, B.; Li, F.; Zhang, Z. ; others. R-judge: Benchmarking safety risk awareness for llm agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.10019, arXiv:2401.10019 2024.
- Tang, X.; Jin, Q.; Zhu, K.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Qu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Z. ; others. Prioritizing safeguarding over autonomy: Risks of llm agents for science. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.04247, arXiv:2402.04247 2024.
- Wang, Y.; Gangi Reddy, R.; Mujahid, Z.M.; Arora, A.; Rubashevskii, A.; Geng, J.; Afzal, O.M.; Pan, L.; Borenstein, N.; Pillai, A. ; others. Factcheck-gpt: End-to-end fine-grained document-level fact-checking and correction of llm output. arXiv e-prints, 2311. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, A.; Talukdar, W. Robustness of Structured Data Extraction from In-Plane Rotated Documents Using Multi-Modal Large Language Models (LLM). Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Singh, P.V.; Srinivasan, K. How Much Should We Trust LLM Results for Marketing Research? Available at SSRN 4526072 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dercon, S. Risk, insurance, and poverty: a review. Insurance against poverty.
- Levy, H.; Meltzer, D. The impact of health insurance on health. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2008, 29, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, F.D. Dependents and the demand for life insurance. The American economic review 1989, 79, 452–467. [Google Scholar]
- Zelizer, V.A.R. Morals and markets: The development of life insurance in the United States; Columbia University Press, 2017.
- Gerber, H.U. Life insurance mathematics; Springer Science & Business Media, 2013.
- Straub, E.; of Actuaries (Zürich), S.A. Non-life insurance mathematics; Springer, 1988.
- Council, N.R. ; others. Science and Judgment in Risk Assessment, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Zio, E. The future of risk assessment. Reliability Engineering & System Safety 2018, 177, 176–190. [Google Scholar]
- Dimri, A.; Paul, A.; Girish, D.; Lee, P.; Afra, S.; Jakubowski, A. A multi-input multi-label claims channeling system using insurance-based language models. Expert Systems with Applications 2022, 202, 117166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.; Woensel, W.V.; Seneviratne, O. Using Large Language Models for Generating Smart Contracts for Health Insurance from Textual Policies. In AI for Health Equity and Fairness: Leveraging AI to Address Social Determinants of Health; Springer, 2024; pp. 129–146.
- Balona, C. ActuaryGPT: Applications of large language models to insurance and actuarial work. Available at SSRN 4543652 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S. Using chatgpt for insurance: Current and prospective roles. Available at SSRN 4405394 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, F.; Qu, C.; Mao, K.; Zhu, T.; Su, Z.; Huang, K.; Nie, J.Y. History-Aware Conversational Dense Retrieval. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.16659, arXiv:2401.16659 2024.
- Chen, H.; Mo, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Nie, J.Y.; Wang, C.; Cui, J. A customized text sanitization mechanism with differential privacy. arXiv preprint arXiv:2207.01193, arXiv:2207.01193 2022.
- Mao, K.; Qian, H.; Mo, F.; Dou, Z.; Liu, B.; Cheng, X.; Cao, Z. Learning denoised and interpretable session representation for conversational search. Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023, 2023, pp. 3193–3202. [Google Scholar]
- Hofert, M. Assessing ChatGPT’s proficiency in quantitative risk management. Risks 2023, 11, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troxler, A.; Schelldorfer, J. Actuarial applications of natural language processing using transformers: Case studies for using text features in an actuarial context. British Actuarial Journal 2024, 29, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Chen, Z.; Ling, Y.; Dong, S.; Liu, Z.; Lu, Y. Temporal Data Meets LLM–Explainable Financial Time Series Forecasting. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.11025, arXiv:2306.11025 2023.
- Aracena, C.; Rodríguez, N.; Rocco, V.; Dunstan, J. Pre-trained language models in Spanish for health insurance coverage. Proceedings of the 5th Clinical Natural Language Processing Workshop, 2023, pp. 433–438.
- Wu, J.; Yang, S.; Zhan, R.; Yuan, Y.; Wong, D.F.; Chao, L.S. A survey on llm-gernerated text detection: Necessity, methods, and future directions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.14724, arXiv:2310.14724 2023.
- Jin, M.; Wang, S.; Ma, L.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, J.Y.; Shi, X.; Chen, P.Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.F.; Pan, S. ; others. Time-llm: Time series forecasting by reprogramming large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.01728, arXiv:2310.01728 2023.
- Cao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W. Mitigating Knowledge Conflicts in Language Model-Driven Question Answering. arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.11344, arXiv:2411.11344 2024.
- Mo, F.; Yi, B.; Mao, K.; Qu, C.; Huang, K.; Nie, J.Y. Convsdg: Session data generation for conversational search. Companion Proceedings of the ACM on Web Conference 2024, 2024, pp. 1634–1642. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Wang, H.; Feng, Z.; Fu, M.; Ma, C.; Pan, H.; Xu, B.; Li, N. A novel texture extraction method for the sedimentary structures’ classification of petroleum imaging logging. Pattern Recognition: 7th Chinese Conference, CCPR 2016, Chengdu, China, -7, 2016, Proceedings, Part II 7. Springer, 2016, pp. 161–172. 5 November.
- Huang, K.; Mo, F.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, W.; Mao, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Xu, J. ; others. A Survey on Large Language Models with Multilingualism: Recent Advances and New Frontiers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.10936, arXiv:2405.10936 2024.
- Tao, T.; Wang, X.; Mei, Q.; Zhai, C. Language model information retrieval with document expansion. Proceedings of the Human Language Technology Conference of the NAACL, Main Conference, 2006, pp. 407–414.
- Tirumala, K.; Simig, D.; Aghajanyan, A.; Morcos, A. D4: Improving llm pretraining via document de-duplication and diversification. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2023, 36, 53983–53995. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, J.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, Z. Artistic Neural Style Transfer Algorithms with Activation Smoothing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.08014, arXiv:2411.08014 2024.
- Yasunaga, M.; Leskovec, J.; Liang, P. Linkbert: Pretraining language models with document links. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.15827, arXiv:2203.15827 2022.
- Yu, S.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, C.; Feng, T.; Liu, Z. Few-shot conversational dense retrieval. Proceedings of the 44th International ACM SIGIR Conference on research and development in information retrieval, 2021, pp. 829–838.
- Wu, Y.; Ma, X.; Yang, D. Personalized response generation via generative split memory network. Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, 2021, pp. 1956–1970.
- Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Cheng, X.; Tan, Z.; Nong, Q.; Lu, W. Multi-view reasoning: Consistent contrastive learning for math word problem. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.11694, arXiv:2210.11694 2022.
- Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Bu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Bai, Z.; Chen, H.; Ge, T. ; others. Conceptmath: A bilingual concept-wise benchmark for measuring mathematical reasoning of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.14660, arXiv:2402.14660 2024.
- Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Hou, G.; Wang, K.; Lu, W. Specialized Mathematical Solving by a Step-By-Step Expression Chain Generation. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing.
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Ren, W.; Jiang, L.; Wang, D.; Liu, K. RATT: AThought Structure for Coherent and Correct LLMReasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.02746, arXiv:2406.02746 2024.
- Huang, J.; Chang, K.C.C. Towards reasoning in large language models: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.10403, arXiv:2212.10403 2022.
- Zhang, J.; Mo, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, K. Thought space explorer: Navigating and expanding thought space for large language model reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.24155, arXiv:2410.24155 2024.
- Huang, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Lian, D.; Wang, Y.; Tang, R.; Chen, E. Understanding the planning of LLM agents: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.02716, arXiv:2402.02716 2024.
- Lu, P.; Gong, R.; Jiang, S.; Qiu, L.; Huang, S.; Liang, X.; Zhu, S.C. Inter-GPS: Interpretable geometry problem solving with formal language and symbolic reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.04165, arXiv:2105.04165 2021.
- Besold, T.R.; d’Avila Garcez, A.; Bader, S.; Bowman, H.; Domingos, P.; Hitzler, P.; Kühnberger, K.U.; Lamb, L.C.; Lima, P.M.V.; de Penning, L. ; others. Neural-symbolic learning and reasoning: A survey and interpretation 1. In Neuro-Symbolic Artificial Intelligence: The State of the Art; IOS press, 2021; pp. 1–51.
- Pan, L.; Albalak, A.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.Y. Logic-lm: Empowering large language models with symbolic solvers for faithful logical reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.12295, arXiv:2305.12295 2023.
- Su, A.; Wang, A.; Ye, C.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, G.; Wang, H.; Xu, H.; Chen, H.; Li, H. ; others. TableGPT2: A Large Multimodal Model with Tabular Data Integration. arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.02059, arXiv:2411.02059 2024.
- Yin, P.; Neubig, G.; Yih, W.t.; Riedel, S. TaBERT: Pretraining for joint understanding of textual and tabular data. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.08314, arXiv:2005.08314 2020.
- Huang, X.; Khetan, A.; Cvitkovic, M.; Karnin, Z. Tabtransformer: Tabular data modeling using contextual embeddings. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.06678, arXiv:2012.06678 2020.
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Rekabdar, B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, K. Dynamic and Adaptive Feature Generation with LLM. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.03505, arXiv:2406.03505 2024.
- Lu, P.; Peng, B.; Cheng, H.; Galley, M.; Chang, K.W.; Wu, Y.N.; Zhu, S.C.; Gao, J. Chameleon: Plug-and-play compositional reasoning with large language models. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2024, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Mo, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, K. TIFG: Text-Informed Feature Generation with Large Language Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.11177, arXiv:2406.11177 2024.
- Hou, G.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xue, W.; Lu, W. Enhancing Emotion Recognition in Conversation via Multi-view Feature Alignment and Memorization. Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2023, 2023, pp. 12651–12663. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, H.C.; Huang, Z.; Lu, B.; Li, M. Image-driven prediction system: Automatic extraction of aggregate gradation of pavement core samples integrating deep learning and interactive image processing framework. Construction and Building Materials 2024, 453, 139056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Fan, X.; Yang, Y. Harnessing LLMs for API Interactions: A Framework for Classification and Synthetic Data Generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.11703, arXiv:2409.11703 2024.
- Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, J.; Bu, X.; Yang, C.; Zhong, H.S.; Ouyang, W. Iterative Length-Regularized Direct Preference Optimization: A Case Study on Improving 7B Language Models to GPT-4 Level. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.11817, arXiv:2406.11817 2024.
- Borisov, V.; Seßler, K.; Leemann, T.; Pawelczyk, M.; Kasneci, G. Language models are realistic tabular data generators. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.06280, arXiv:2210.06280 2022.
- Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Lu, W.; Zhuang, Y. Data-copilot: Bridging billions of data and humans with autonomous workflow. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.07209, arXiv:2306.07209 2023.
- Jones, E.; Palangi, H.; Simões, C.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Mukherjee, S.; Mitra, A.; Awadallah, A.; Kamar, E. Teaching language models to hallucinate less with synthetic tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.06827, arXiv:2310.06827 2023.
- Peng, C.; Yang, X.; Chen, A.; Smith, K.E.; PourNejatian, N.; Costa, A.B.; Martin, C.; Flores, M.G.; Zhang, Y.; Magoc, T.; others. A study of generative large language model for medical research and healthcare. NPJ digital medicine 2023, 6, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, C.D. Fingpt: Open-source financial large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.06031, arXiv:2306.06031 2023.
- Fan, X.; Tao, C.; Zhao, J. Advanced Stock Price Prediction with xLSTM-Based Models: Improving Long-Term Forecasting. Preprints 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, Z.; Chen, W.; Guo, X.; He, W.; Ding, Y.; Hong, B.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Jin, S.; Zhou, E. ; others. The rise and potential of large language model based agents: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.07864, arXiv:2309.07864 2023.
- Chang, C.; Peng, W.C.; Chen, T.F. Llm4ts: Two-stage fine-tuning for time-series forecasting with pre-trained llms. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.08469, arXiv:2308.08469 2023.
- Voigt, P.; Von dem Bussche, A. The eu general data protection regulation (gdpr). A Practical Guide, 1st Ed., Cham: Springer International Publishing 2017, 10, 10–5555. [Google Scholar]
- Sirur, S.; Nurse, J.R.; Webb, H. Are we there yet? Understanding the challenges faced in complying with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Proceedings of the 2nd international workshop on multimedia privacy and security, 2018, pp. 88–95.
- Gostin, L.O.; Levit, L.A.; Nass, S.J. Beyond the HIPAA privacy rule: enhancing privacy, improving health through research 2009.
- Benitez, K.; Malin, B. Evaluating re-identification risks with respect to the HIPAA privacy rule. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 2010, 17, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



