Submitted:
04 December 2024
Posted:
05 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
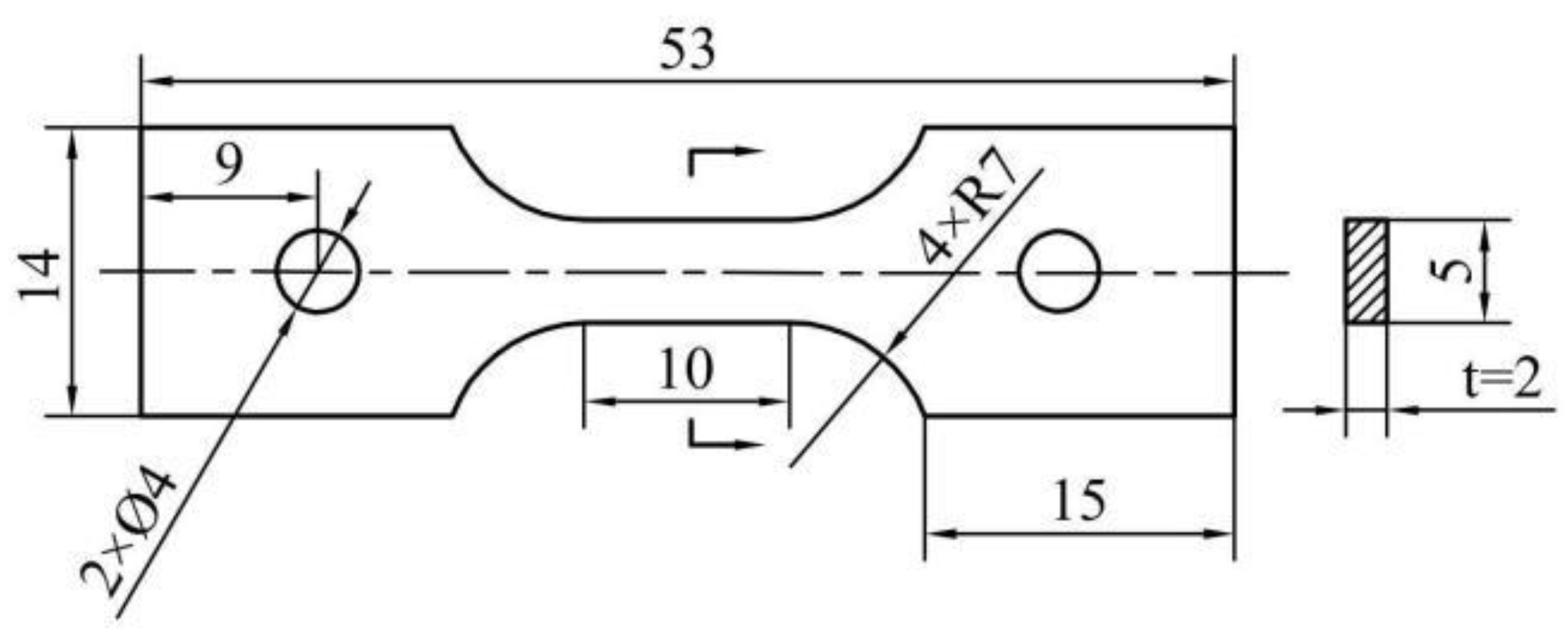
2.1. Materials preparation
2.2. Experimental procedure
3. Results and Discussion
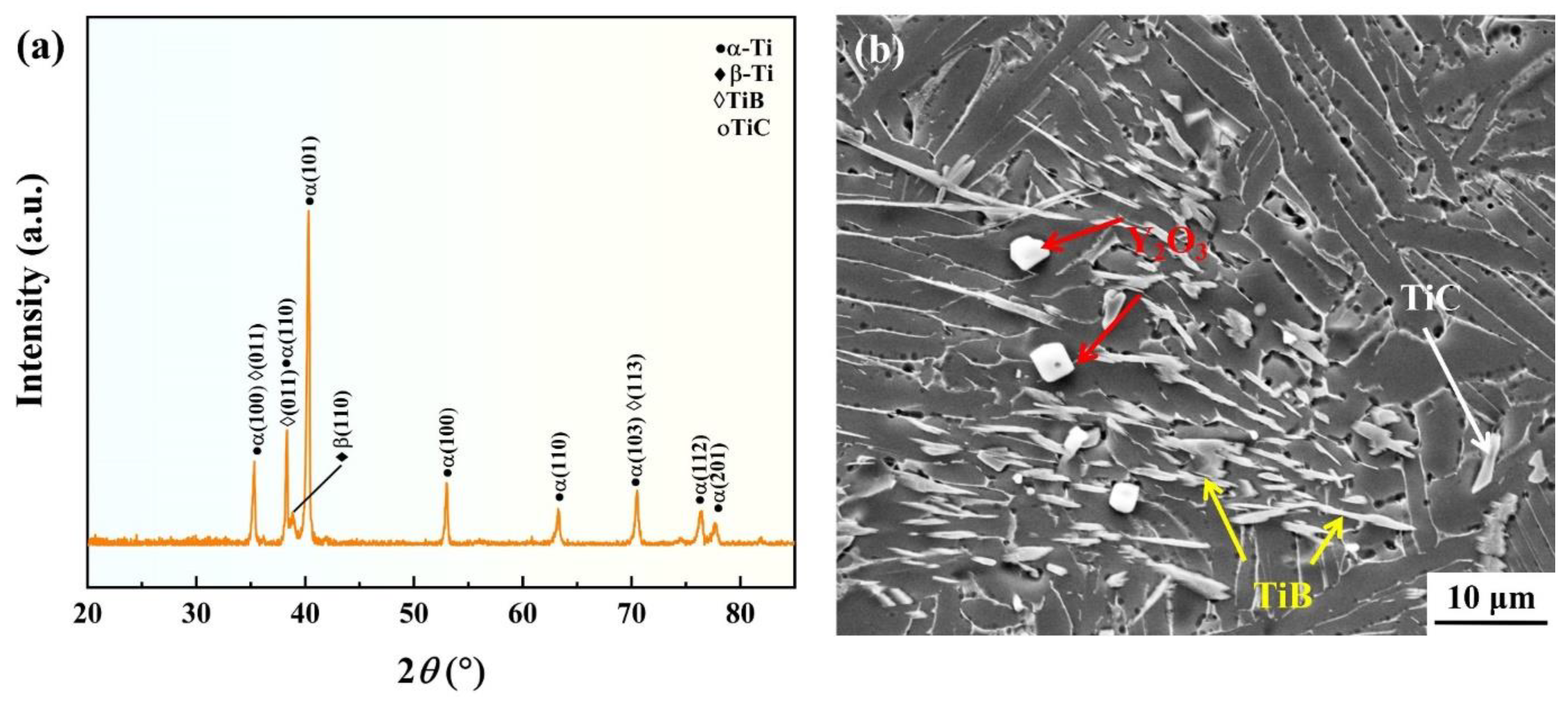
3.1. Constituent phase identification and original microstructure
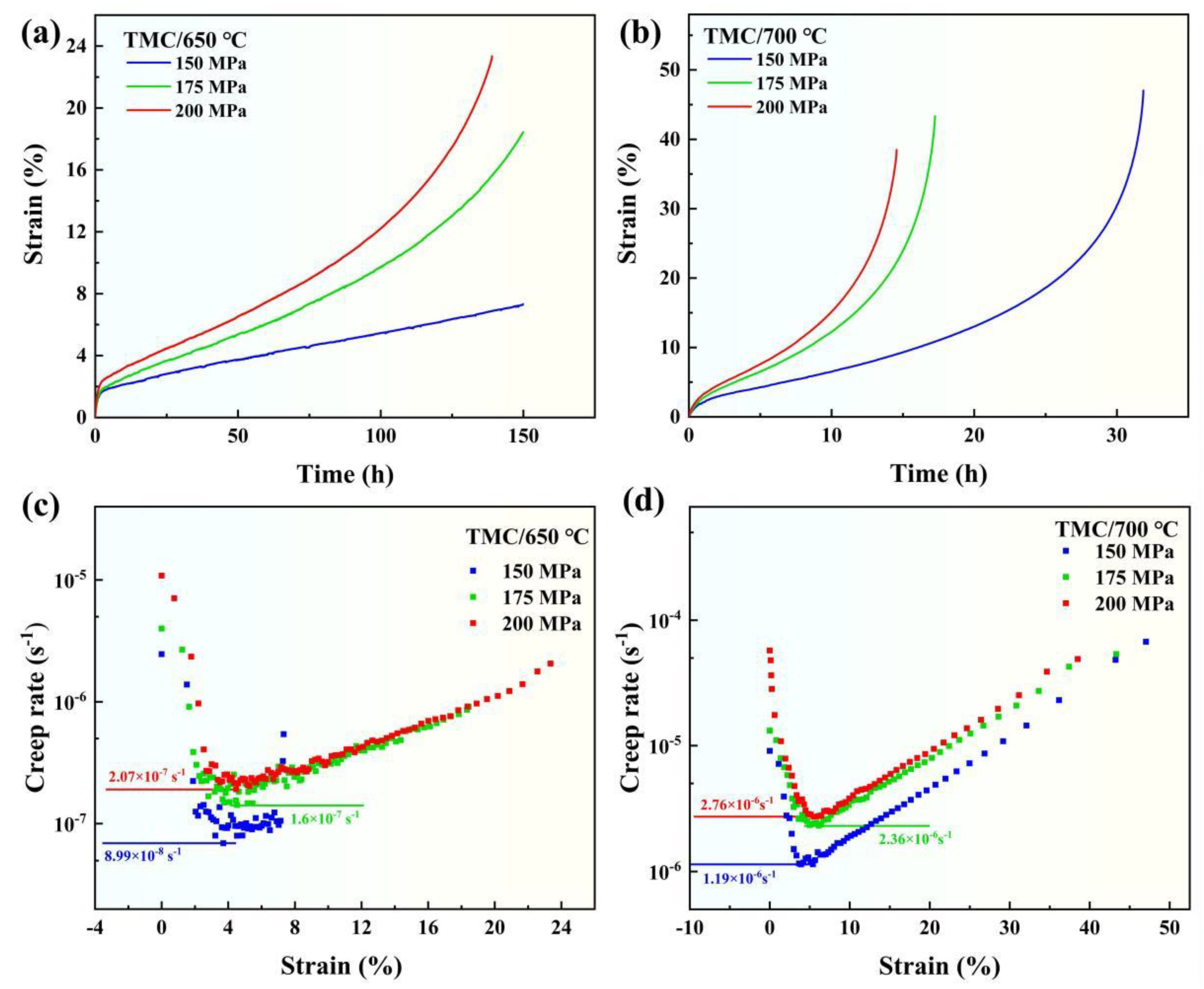
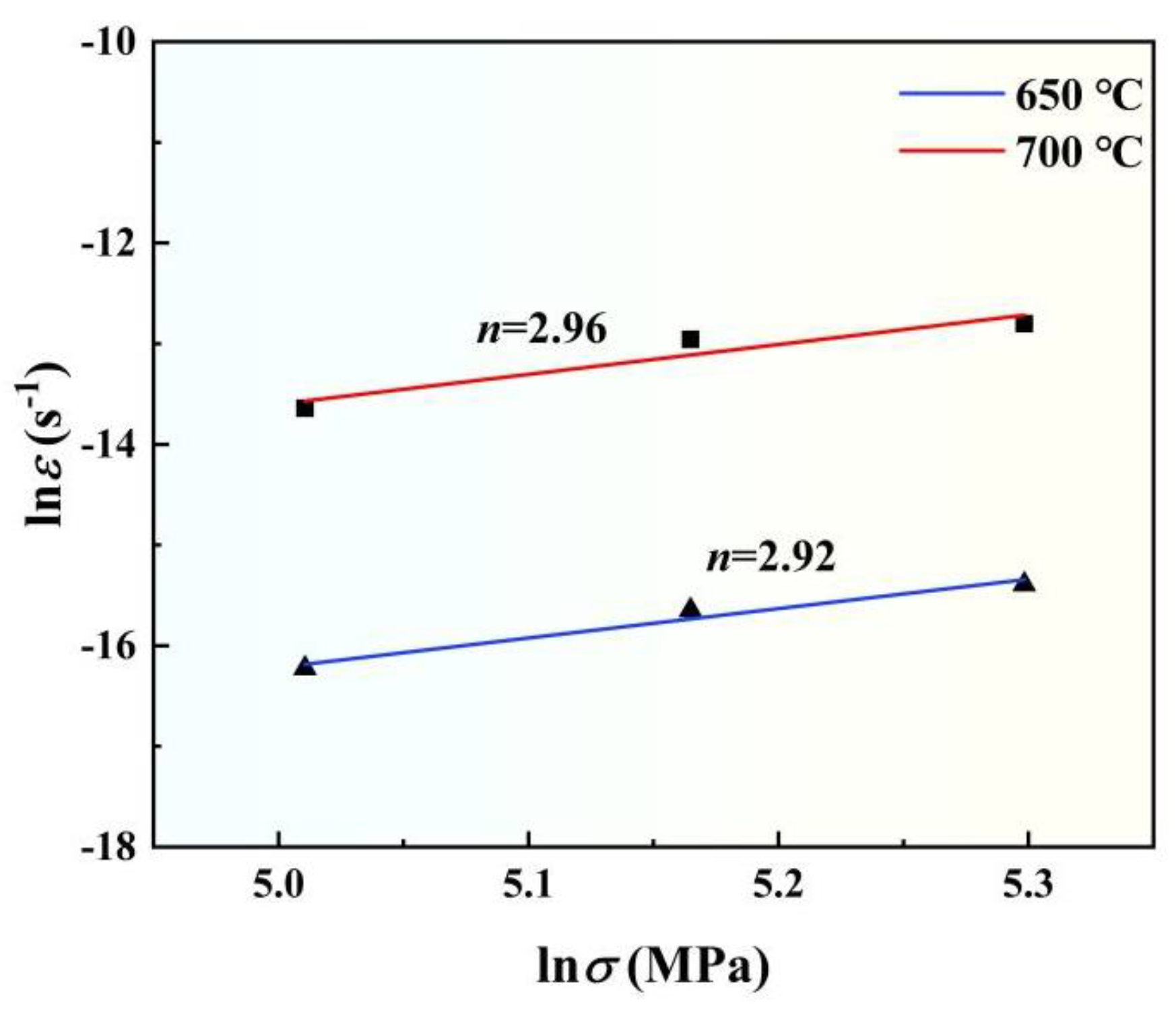
3.2. High temperature tensile creep properties
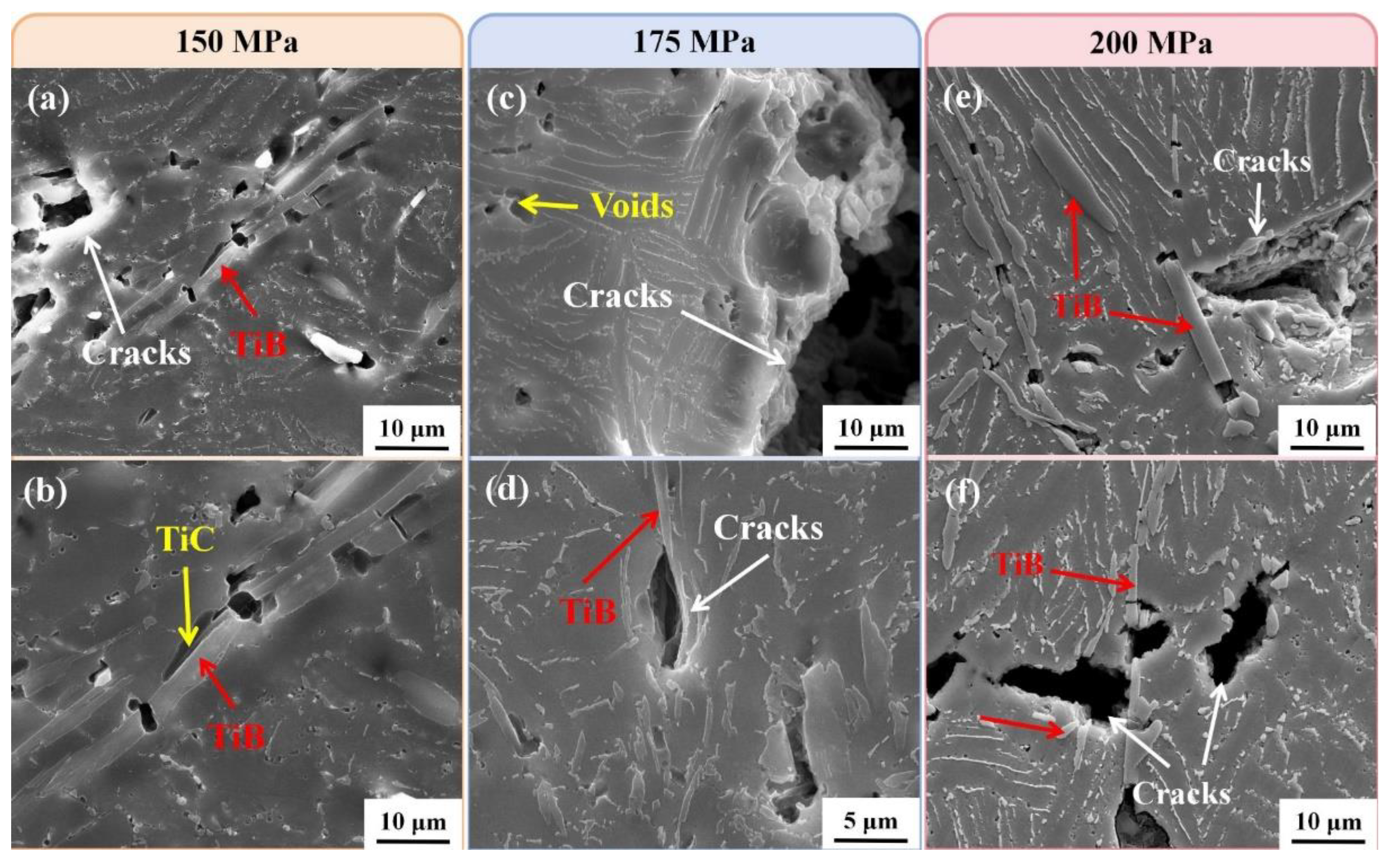
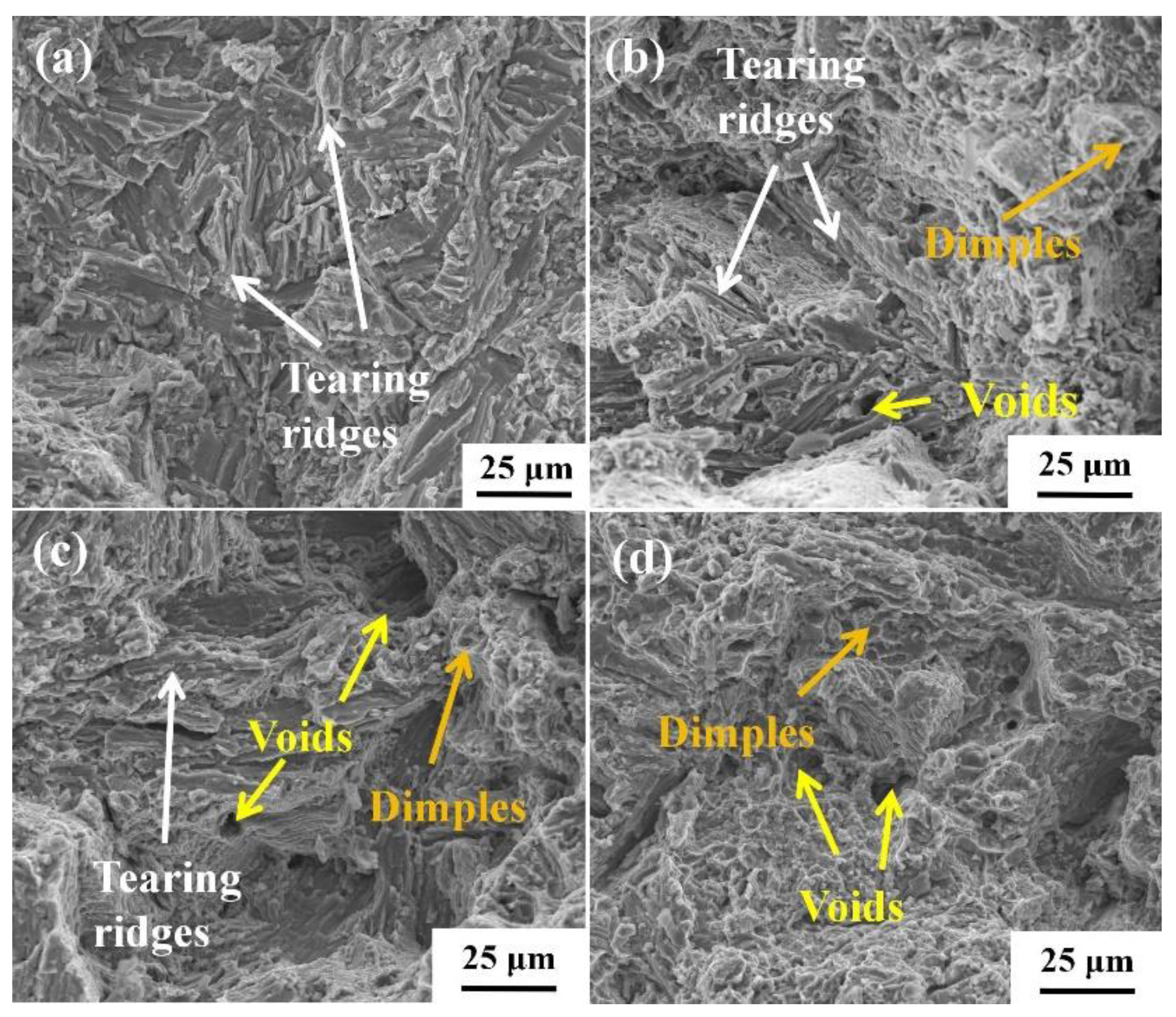
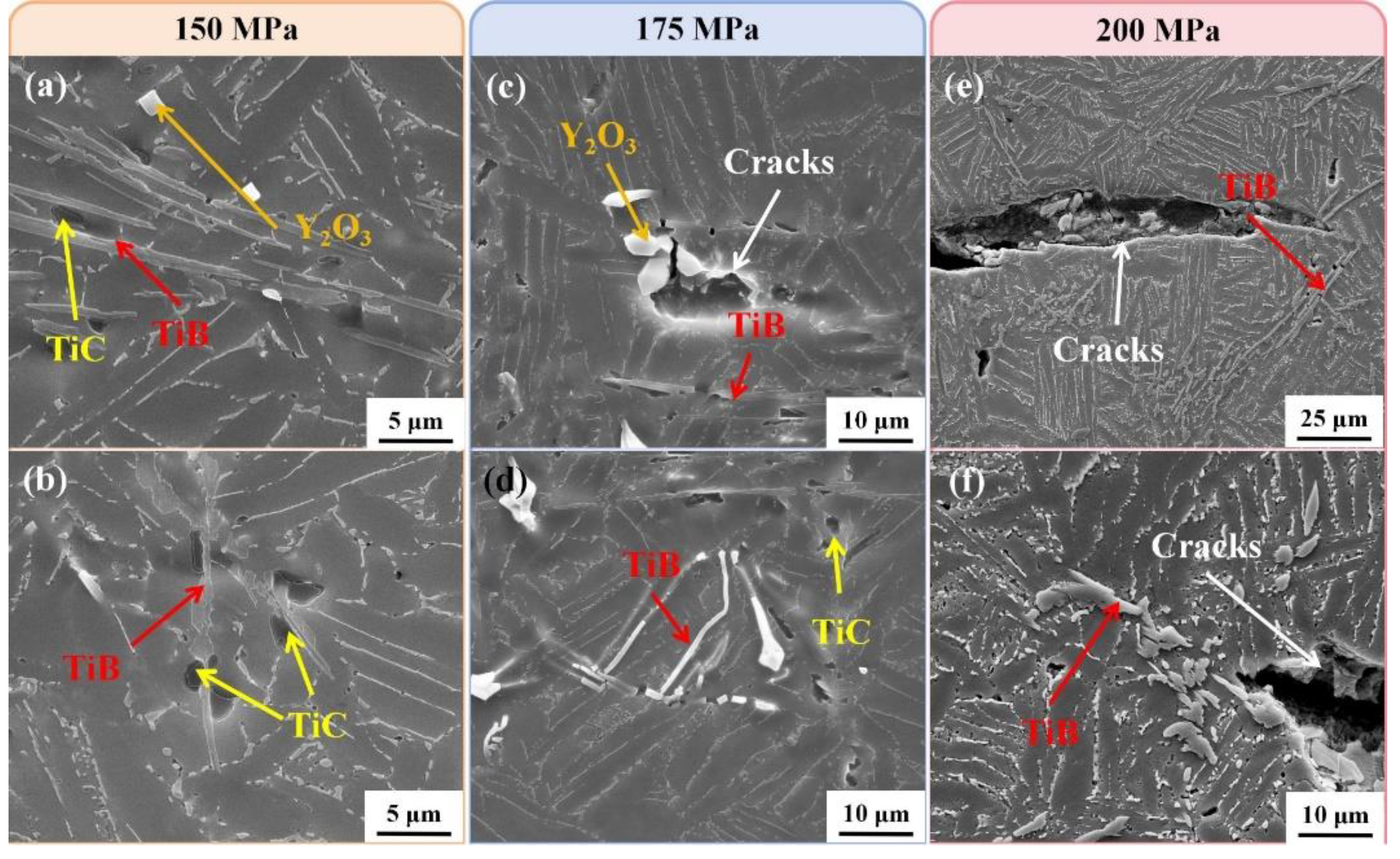
3.3. Creep deformed microstructure and fracture morphology
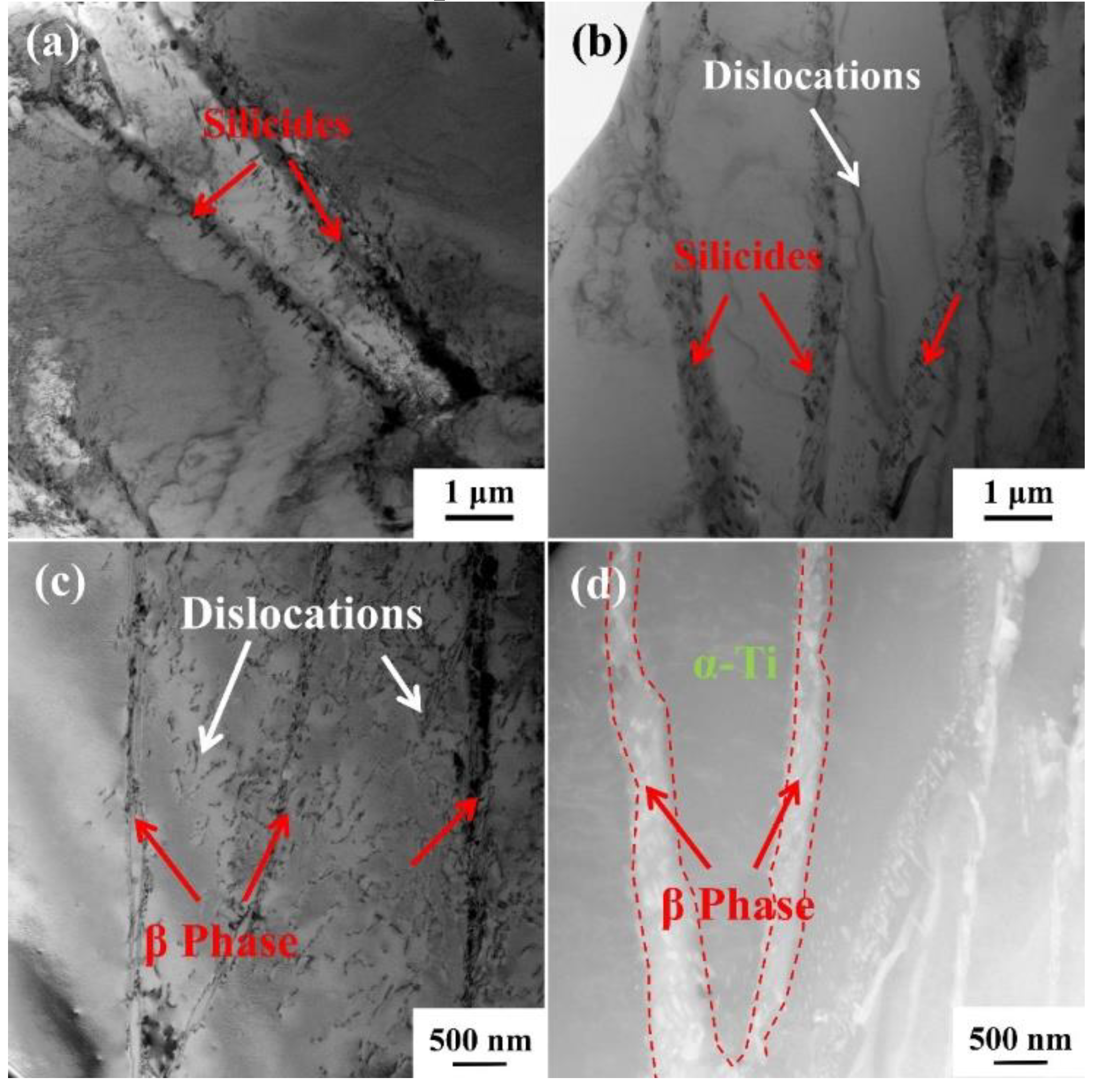
3.4. Microstructure evolution during creep
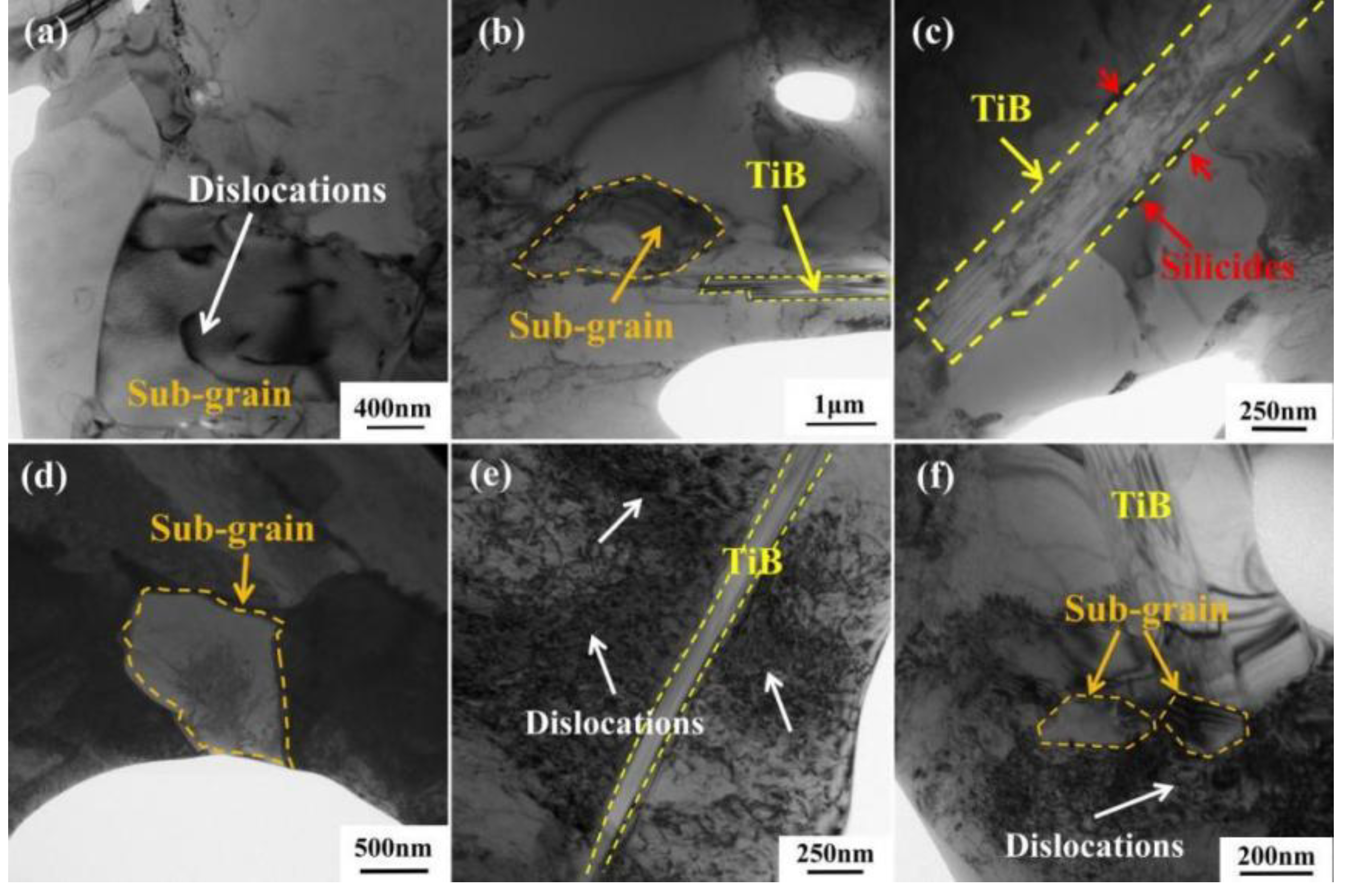
3.5. The influence of reinforcements on microstructure and creep properties
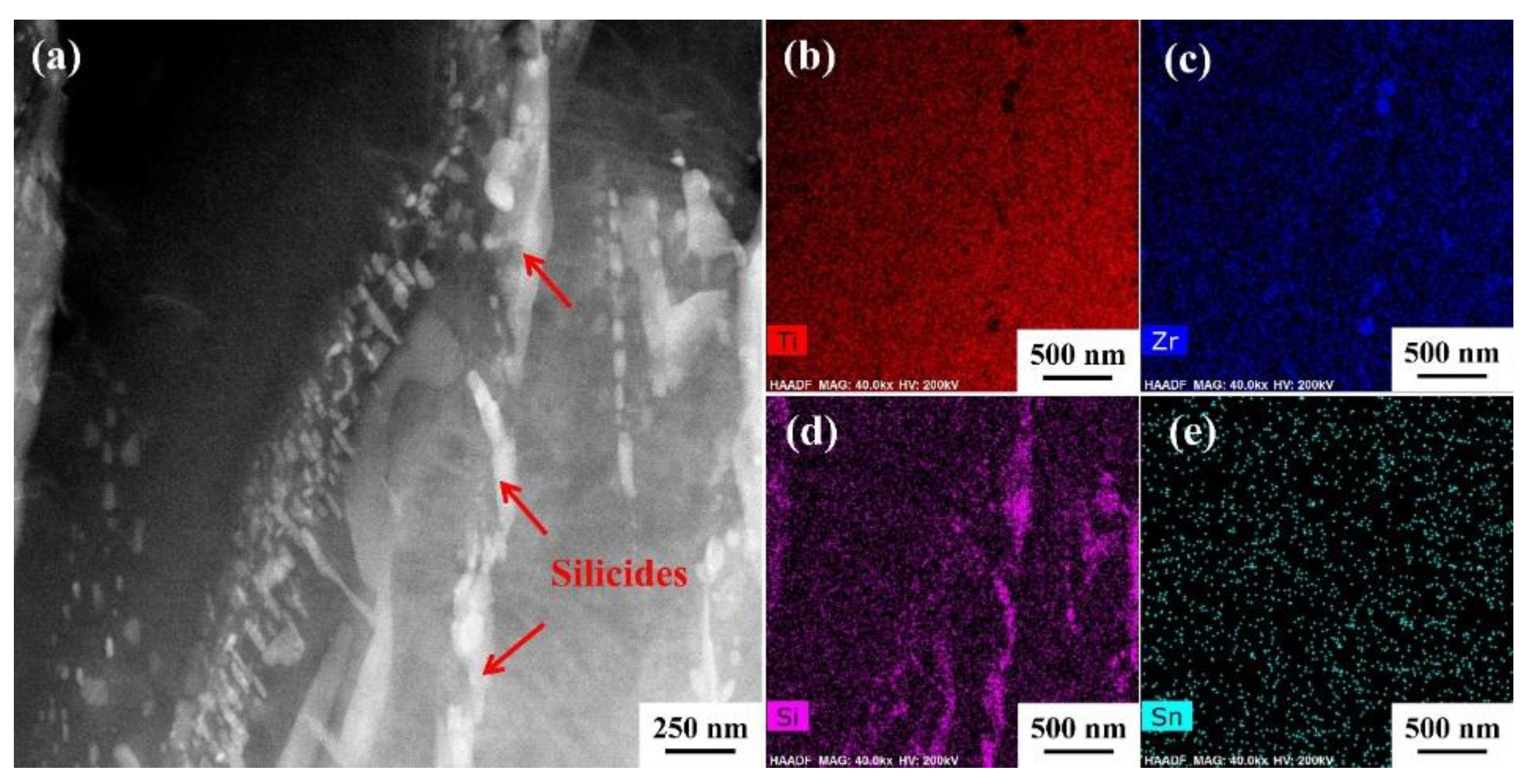
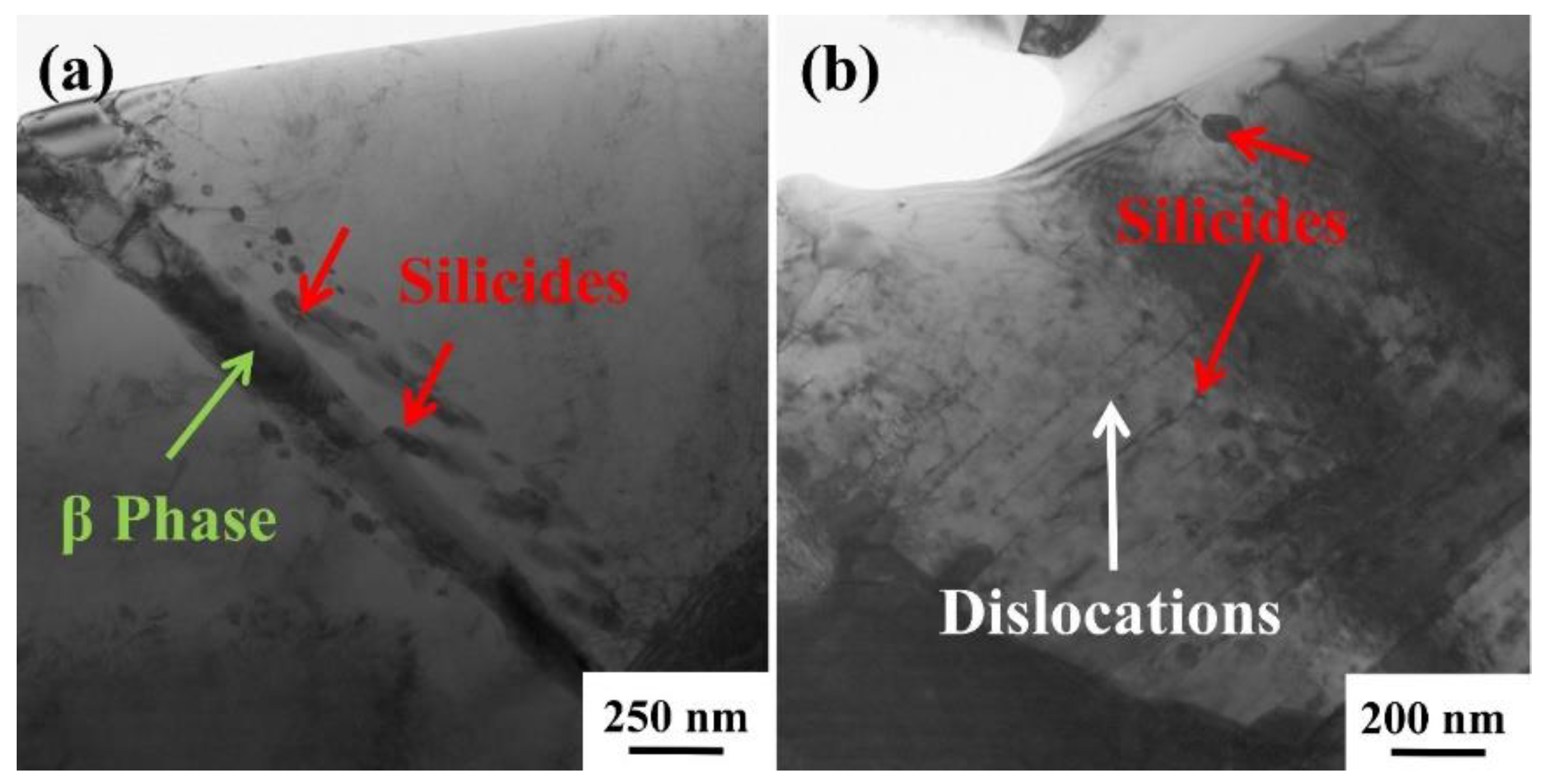
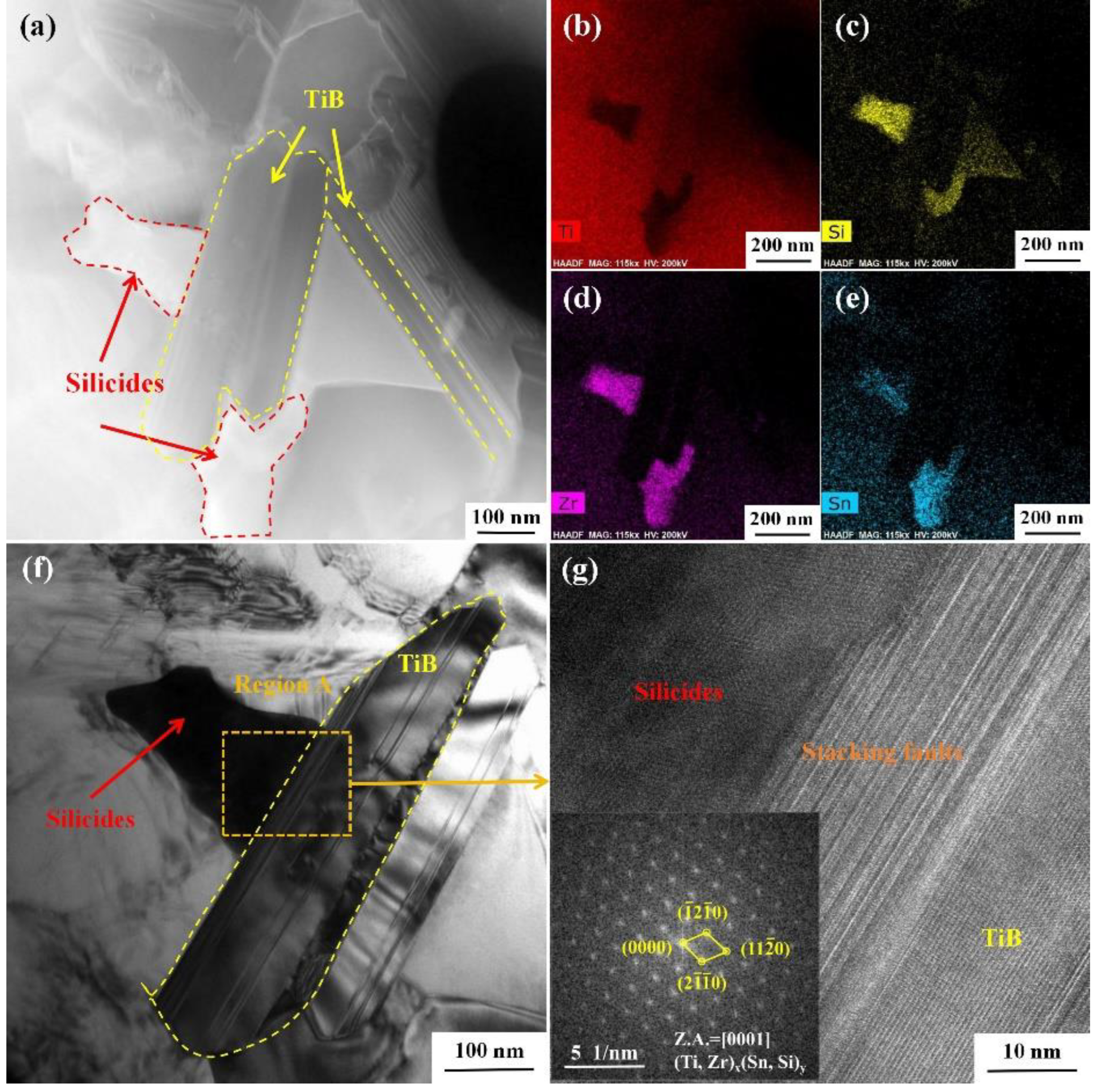
3.6. Precipitation of silicides
3.7. Effect of silicides on creep behavior
4. Conclusion
- The as-cast microstructure of the composites is basket-weave structure, the main phase composition is lamellar α phase and a relatively low content of β phase, TiB is a whisker with large aspect ratio, TiC is equiaxed and mostly distributed near TiB, Y2O3 is micron-meter granular.
- When the temperature increases from 650 °C to 700 °C, the steady-state creep rate of the composites increases by 1-2 orders of magnitude, and the creep life decreases significantly. After creep, TiB fractures and there is debonding between TiC and the matrix, while Y2O3 remains intact and has good bonding with the matrix.
- The creep stress exponent of the composites at 650 °C and 700 °C is 2.92 and 2.96 respectively, indicating the main creep mechanism of this composites is dislocation slip. Temperature and stress have no significant effect on the creep mechanism of the composites.
- The α/β interface has a hindering effect on the dislocation movement. With the increase of temperature or stress, the dissolution degree of the β phase increases, the α/β colonies is destroyed, and the limiting effect on the dislocation movement is weakened. Therefore, the increase of the dissolution degree of the β phase is one of the main reasons for the decrease of the creep life of the composites.
- The reinforcements can improve composites structure, withstand loads and hinder the dislocation movement during the creep process. Silicides precipitated near TiB and the α/β interface during creep can also restrict dislocation movement, thus reducing the creep rate and extending the creep life.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiao, Y.; Huang, L.; Geng, L. Progress on discontinuously reinforced titanium matrix composites. J. Alloys. Compd. 2018, 767, 1196–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, J.; Han, Y.; Qiu, P.; Huang, G.; Mao, j.; Lu, W. The Impact of matrix texture and whisker orientation on property anisotropy in titanium matrix composites: Experimental and computational evaluation. Compos. Part. B-eng 2021, 212, 108682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Liu, H.; Ma, Z.; Ma, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X. Microstructure and properties of high entropy alloy reinforced titanium matrix composites. Mater. Charact. 2022, 187, 111856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zeng, W.; Qi, Y.; Zhao, Y. The influence of thermomechanical processing on microstructural evolution of Ti600 titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 8410–8416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zeng, W.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Q. A study of epitaxial growth behaviors of equiaxed alpha phase at different cooling rates in near alpha titanium alloy. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yue, K.; Yu, J.; Huang, Z.; Teng, A. Research overview and application of high-temperature titanium alloy and titanium matrix (Ti-Al) composites for aerospace. The Chinese Society for Metals. Proceedings of the 14th China Iron and Steel Annual Conference, 6: steel materials and applications, 2023, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kurita, H.; Suzuki, S.; Kikuchi, S.; Yodoshi, N.; Gourdet, S.; Narita, F. Strengthening Mechanism of Titanium Boride Whisker-Reinforced Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Matrix Composites with the TiB Orientation Perpendicular to the Loading Direction. Materials 2019, 12, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Chang, Y.; He, Y.; Sui, Y.; Wei, F.; Meng, Q.; Wei, Z. Effect of Zr, Mo and TiC on microstructure and high-temperature tensile strength of cast titanium matrix composites. Mater. Des. 2016, 99, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Peng, H.; Miao, K.; Gao, B.; Wu, H.; Yang, J.; Fan, G. Significant enhancement in high-temperature tensile strength of trace nano-Y2O3-reinforced TiAl alloy prepared by selective electron beam melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 875, 145086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Ma, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Shi, L.; Liu, M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Y2O3 reinforced Ti6Al4V composites fabricated by spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys. Compd 2018, 768, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xu, L.; Chi, D.; Liang, Z.; Han, S.; Xue, X.; Xiao, S.; Tian, J.; Chen, Y. Tensile and creep properties under different temperature conditions of titanium matrix composites reinforced by TiB and TiC. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 860, 144279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Gao, Z.; Fan, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of in-situ hybrid reinforced (TiB plus TiC)/Ti composites prepared by laser powder bed fusion. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 9258–9237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kondoh, K.; Imai, H.; Chen, B.; Jia, L.; Umeda, J.; Fu, Y. Strengthening behavior of in situ-synthesized (TiC-TiB)/Ti composites by powder metallurgy and hot extrusion. Mater. Des. 2016, 95, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Xu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liang, Z.; Chi, D.; Tian, J.; Xiao, S. Short-time creep behavior of (TiB + TiC + Y2O3) reinforced titanium matrix composites in the range of 600 °C to 700 °C, Mater. Charact. 2024, 210, 113785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Ji, X.; Zhang, S.; Feng, H.; Han, J.; Peng, P.; Wang, T. Microstructural evolution and silicide precipitation behavior of TiCp/near-α titanium matrix composites during hot compression. Mater. Charact. 2022, 189, 1119333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, N.; Mahoney, M. Creep of titanium-silicon alloys. Metall. Trans. A. 1976, 7, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xu, L.; Yu, J.; Liang, Z.; Xue, X.; Xiao, S.; Tian, J.; Chen, Y. Effect of TiB, TiC and Y2O3 on tensile properties and creep behavior at 650 °C of titanium matrix composites. J. Alloys. Compd 2022, 908, 164699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Xue, X.; Xiao, S.; Tian, J.; Chen, Y. Effects of hybrid reinforcements to the high temperature tensile and creep properties of a (TiB + TiC + Y2O3)/α-Ti composites. Mater. Charact. 2022, 190, 112067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, L.; Qian, M.; Zou, J. High tensile-strength and ductile titanium matrix composites strengthened by TiB nanowires, Scr. Mater. 2017, 141, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Mao, L.; Xu, D.; Qin, J.; Zhang, D. Microstructural characterization of Y2O3 in in situ synthesized titanium matrix composites. J. Alloys. Compd. 2007, 433, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zeng, F.; Qi, Y.; Xia, C.; Xiong, X. Tensile creep behavior of heat-treated TC11 titanium alloy at 450-550 °C. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 575, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, Z.; Gray, V.; Whittaker, M.; Perkins, K. A critical analysis of the conventionally employed creep lifing methods. Materials 2014, 5, 3371–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Shin, Y. The influences of melting degree of TiC reinforcements on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser direct deposited Ti6Al4VTiC composites, Mater. Des. 2017, 136, 185–195. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Yang, M.; Yang, Z. Microstructural evolution and mechanical of titanium matrix composites with second-phase dendritic TiC improved through B4C additions. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 17482–17491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Xu, Y.; Pan, C.; Liang, L.; Wang, X. Microstructural Modeling and Strengthening Mechanism of TiB/Ti-6Al-4V Discontinuously-Reinforced Titanium Matrix Composites. Materials 2019, 12, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Huang, L.; An, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gong, D.; Cui, L.; Geng, L.; Hong, C. Wire-arc additive manufacturing of TiB/Ti6Al4V composites using Ti-TiB2 cored wire: processing, microstructure and mechanical properties. Virtual and Physical Prototyping 2024, 19, e2383287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, E.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Yu. Recent advances in silicon containing high temperature titanium alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 3029–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, P.; Mao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xin, S. Effect of Si addition on the microstructure and creep properties of the forged titanium alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys, 2024, 317, 129212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Ma, Y.; Lei, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, A.; Rugg, D.; Yang, R. A Comparative study on dwell fatigue of Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-xMo (x=2 to 6) alloys on a microstructure-normalized basis. Metal. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, 45, 6075–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, L.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, R.; Liu, B.; Sun, F.; An, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Geng, L. Microstructure evolution and tensile properties of as-rolled TiB/TA15 composites with network microstructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 804, 140783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Q.; Li, X. A rapid route to fabricate in situ TiB-whisker-reinforced Ti-6Al-4V alloy composites by spark plasma sintering and heat treatment. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 1265d3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Kong, F.; Xiao, S.; Zhao, E.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y. Evolution of microstructure and tensile properties of in situ titanium matrix composites with volume fraction of (TiB + TiC) reinforcements. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 548, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, V.; Leguey, T.; Muñoz, A.; Monge, M.; Pareja, R. Microstructure and tensile properties of Y2O3-dispersed titanium produced by arc melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 422, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Fu, B.; Wang, Y.; Dong, T.; Li, J.; Li, G.; Liu, J. Effect of Y Content on Precipitation Behavior, Oxidation and Mechanical Properties of As-Cast High-Temperature Titanium Alloys. Materials 2023, 16, 4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Wang, L.; Qin, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, W.; Zhang, D. Microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of in situ synthesized (TiB + TiC)/TC18 composites, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 530, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xu, L.; Liang, Z.; Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Xiao, S.; Xue, X.; Tian, J.; Chen, Y. Investigation of three-step heat treatments on the microstructure and steady-state creep behaviors of (TiB + TiC + Y2O3)/α-Ti composites. Mater. Charact. 2023, 204, 113181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, E.; Sun, S.; Yu, J.; An, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, R. Dynamic recrystallization and silicide precipitation behavior of titanium matrix composites under different strains. T. Nonferr. Metal.Soc. 2021, 31, 3416–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, S.; Han, Y.; Huang, G.; Mao, J.; Wang, L.; Lu, W. In situ characterization of tensile fracture of TiB + La2O3 / Ti matrix composites and its mechanism. Hot Working Technology 2019, 48, 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Nartu, M.; Mantri, S.; Pantawane, M.; Ho, Y.; McWilliams, B.; Cho, K.; Dahotre, N.; Banerjee, R. In situ reactions during direct laser deposition of Ti-B4C composites. Scr. Mater. 2020, 183, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, L.; Cui, G.; Chen, W. Room-Temperature and High-Temperature Tensile Mechanical Properties of TA15 Titanium Alloy and TiB Whisker-Reinforced TA15 Matrix Composites Fabricated by Vacuum Hot-Pressing Sintering. Materials 2017, 10, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, M. Morphology and crystallographic orientation of the secondary α phase in a compressed α/β titanium alloy. Scr. Mater. 2013, 68, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhao, E.; Hua, C.; Ana, Y.; Chen, W. Precipitation behavior of silicide and synergetic strengthening mechanisms in TiB-reinforced high-temperature titanium matrix composites during multi-directional forging. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 867, 159051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, R.; Hu, Q. Alloying Effect on the Stability of Ti5Si3 from First-Principles Study. Phys. Status Solidi B 2022, 259, 2100434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartamyshev, A.; Poletaev, D.; Lipnitskii, A. The influence of lattice vibrations and electronic free energy on phase stability of titanium silicides and Si solubility in hcp titanium: a DFT study. Calphad. 2019, 65, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xin, S.; Zhao, Y.; Dang, B. Effect of Silicide and α2 Phase on the Creep Behavior of TC25G Alloy at High Temperature. Met. Mater. Int. 2024, 30, 2158–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Xiao, S.; Xue, X.; Tian, J. Impact of long-term thermal exposure on the microstructure and creep resistance of (TiB + TiC + Y2O3)/α-Ti composites. J. Alloys. Compd 2024, 990, 174496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liang, Z.; Han, S.; Xue, X.; Xiao, S.; Tian, J.; Chen, Y. Creep behavior and microstructure evolution of titanium matrix composites reinforced with TiB, TiC and Y2O3. T. Nonferr. Metal.Soc. 2023, 33, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Creep conditions | Strain/% | Steady state creep rate/s-1 | Creep time/h | Experimental state |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 650 °C/150 MPa | 7.3 | 8.99×10-8 | 150.0 | Abort |
| 650 °C/175 MPa | 18.4 | 1.60×10-7 | 150.0 | Abort |
| 650 °C/200 MPa | 23.3 | 2.07×10-7 | 139.0 | Sample fracture |
| 700 °C/150 MPa | 47.0 | 1.19×10-6 | 31.8 | Sample fracture |
| 700 °C/175 MPa | 43.3 | 2.36×10-6 | 17.2 | Sample fracture |
| 700 °C/200 MPa | 38.5 | 2.74×10-6 | 14.6 | Sample fracture |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




