Submitted:
29 November 2024
Posted:
02 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
MSC: 68Q11; 68T05; 68T01
1. Introduction
1.1. Contribution
- We Introduce an innovative decentralized blockchain protocol enabling autonomous energy exchanges between sensor nodes, significantly enhancing the sustainability of wireless sensor systems through smart contracts and an efficient Proof-of-Stake verification process with mathematical approach.
- We also proposing a hybrid energy harvesting system that brings together different renewable sources like solar, radio frequency, and piezoelectric power along with blockchain-enabled redistribution to maximize usage and extend function in resource-limited settings dynamically.
- We observed that a 20% increase in operating time by allowing sensor devices to monitor autonomously and trade power reserves, preventing depletion and hotspots from ensuring continuous, energy-efficient performance over longer durations with proof of mathematics constraints.
- We developed a scalable, efficient, and secure blockchain solution adapted for the emerging Internet of Things applications, including intelligent urban infrastructures involving environmental monitoring, where self-sufficiency of energy resources and tamper-proof decentralized oversight are mission critical.
2. Related Work
3. Systematic Theoretical Analysis
3.1. Energy Consumption Model
3.2. Energy Harvesting Model
3.3. Energy Update for Nodes
3.4. Energy Deficit and Surplus
3.5. Energy Swapping Between Nodes
3.6. Blockchain-Based Energy Trading
3.7. Validator Selection in Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
3.8. Transaction Validation and Block Formation
3.9. Energy Flow Continuity
3.10. Energy Depletion Function
3.11. Time Complexity of Algorithms
3.12. Energy Balance
4. Dataset Description and Preprocessing
4.1. Mathematical Framework for Data Preprocessing
4.2. Data Normalization
- : Original value of the feature.
- : Minimum value of the feature in the dataset.
- : Maximum value of the feature in the dataset.
4.3. Outlier Detection and Removal
4.4. Feature Engineering
4.5. Time-Series Smoothing
- : Smoothed energy level for node at time .
- : Window size for the moving average.
4.6. Data Transformation for Energy Prediction
4.7. Scaling for Blockchain Transactions
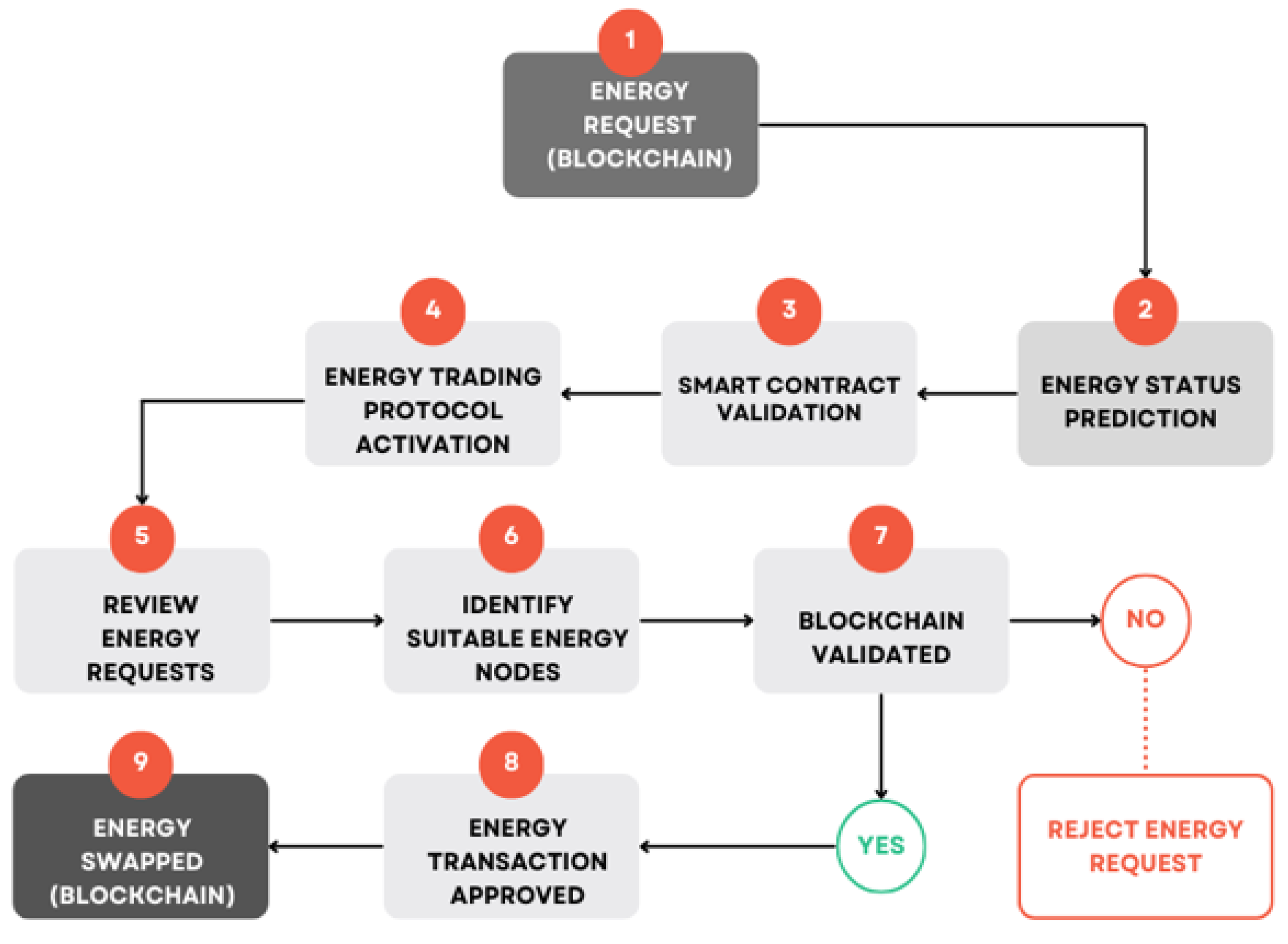
5. Proposed Model
 |
 |
 |
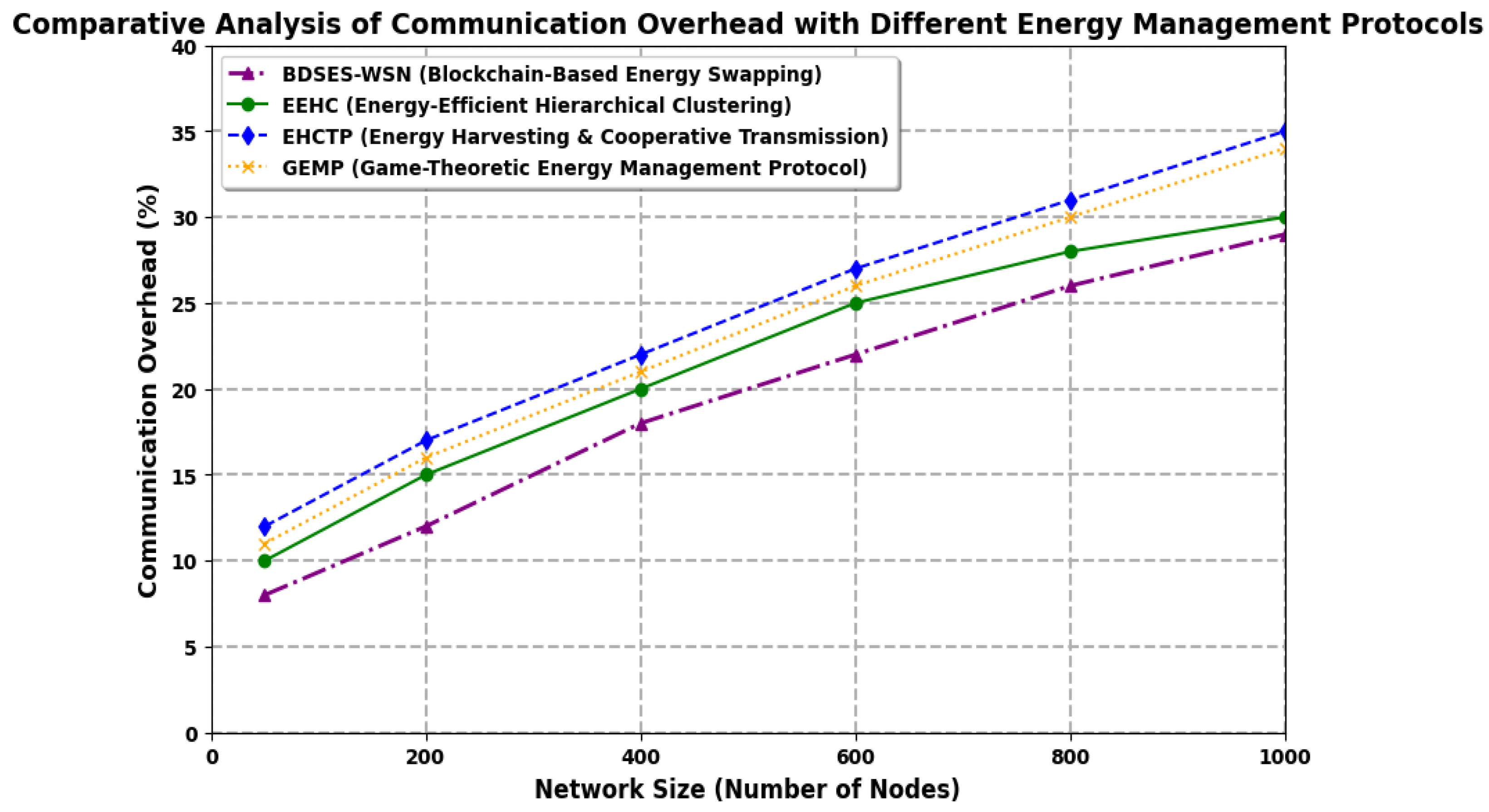
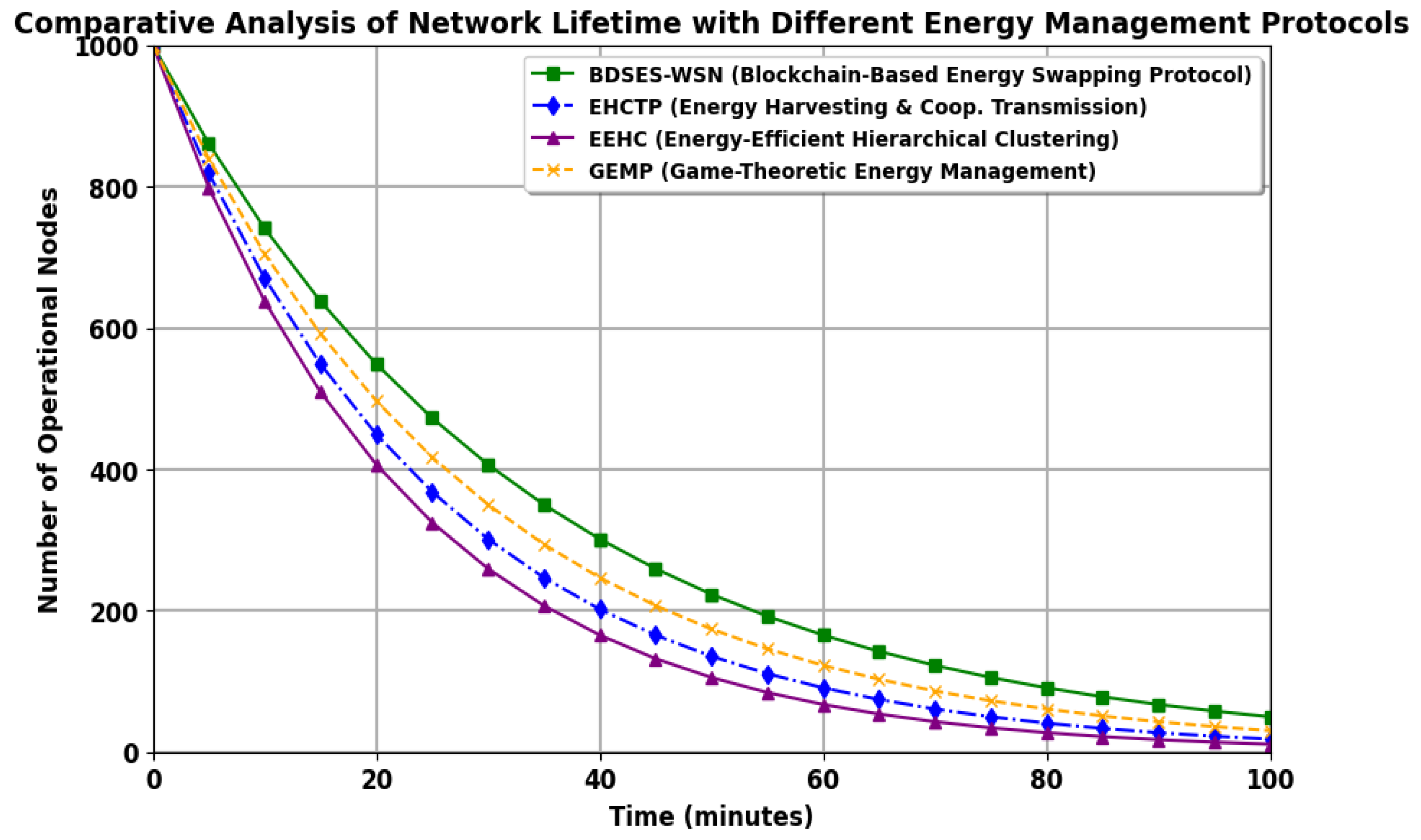
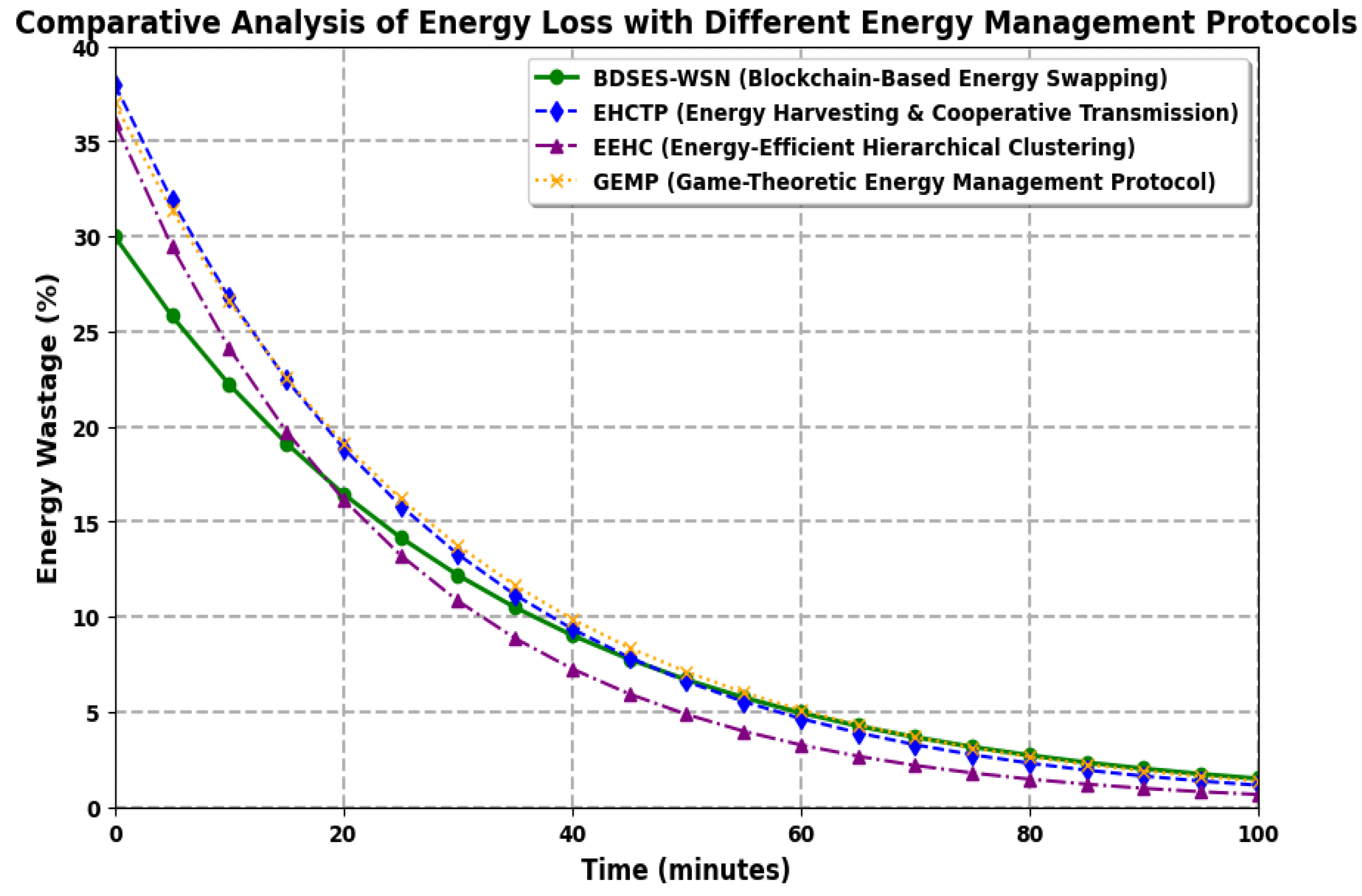
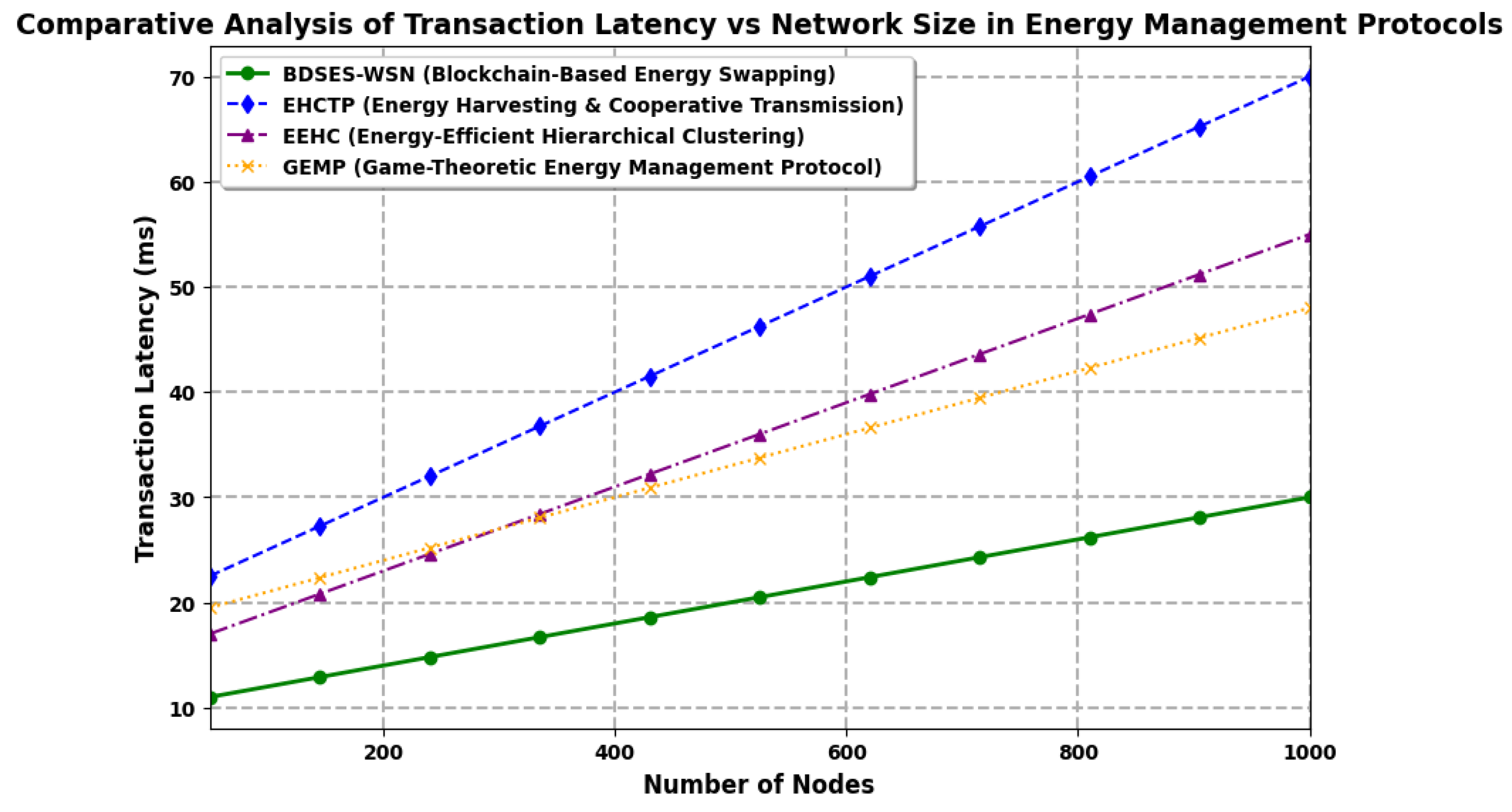
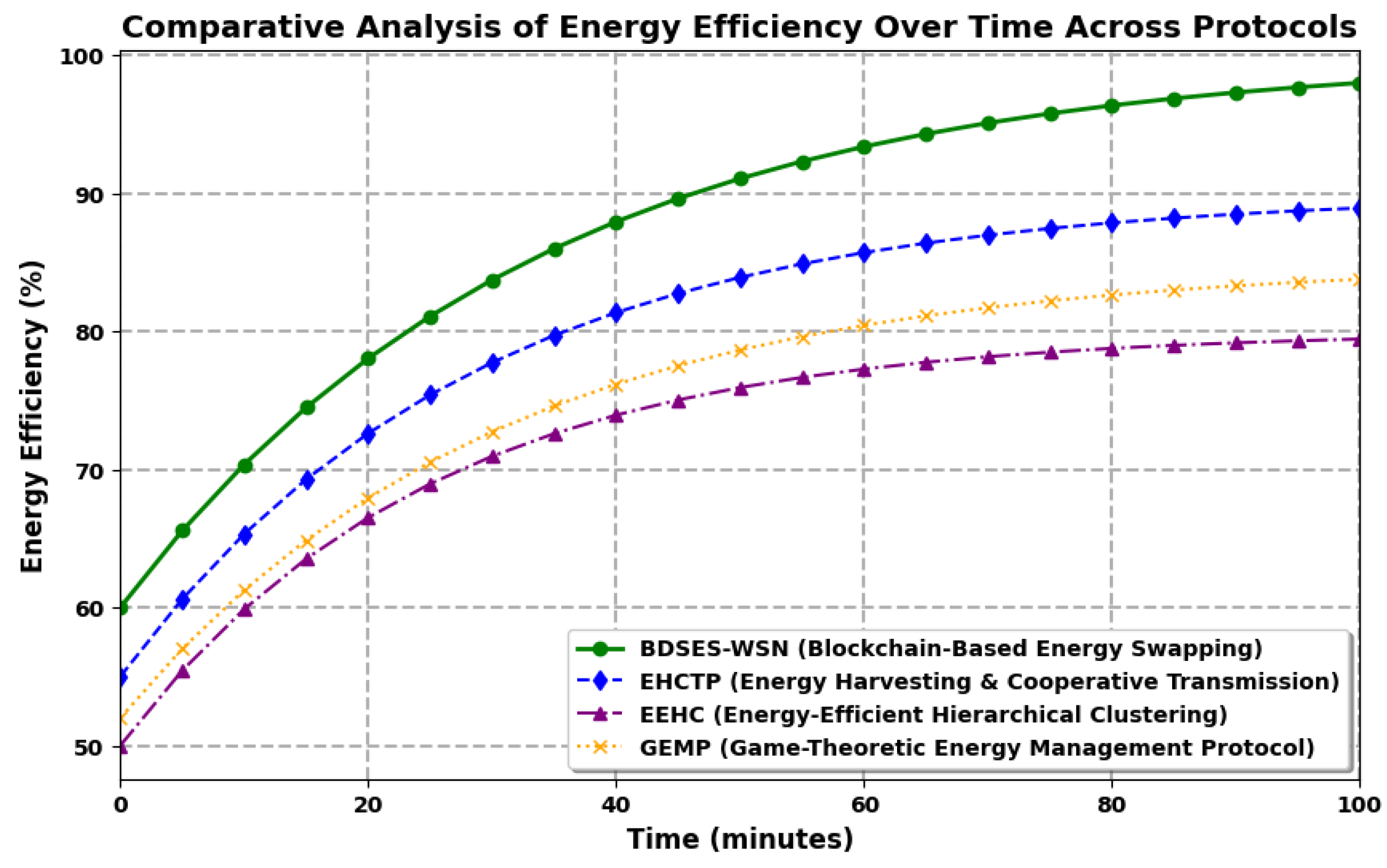
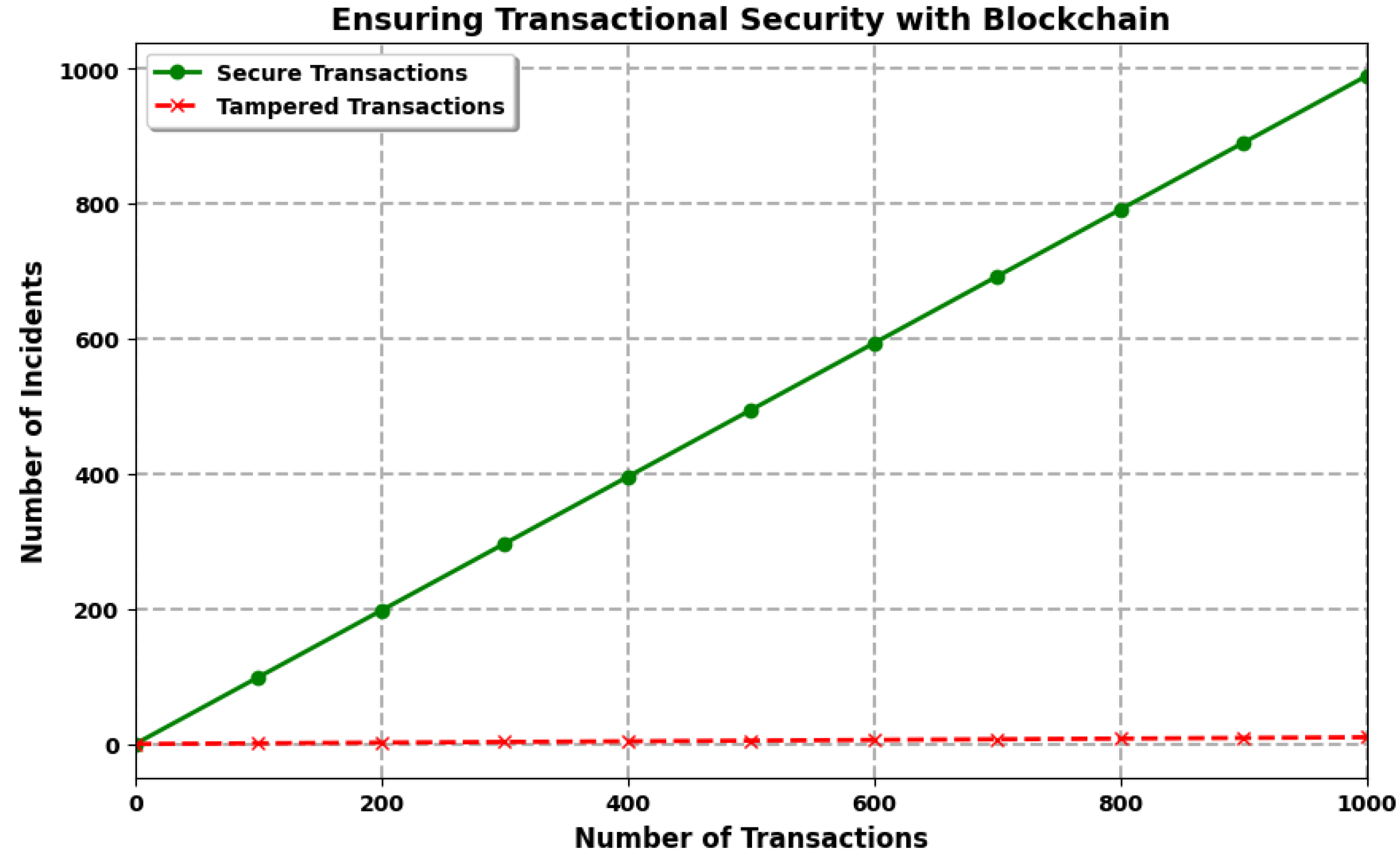
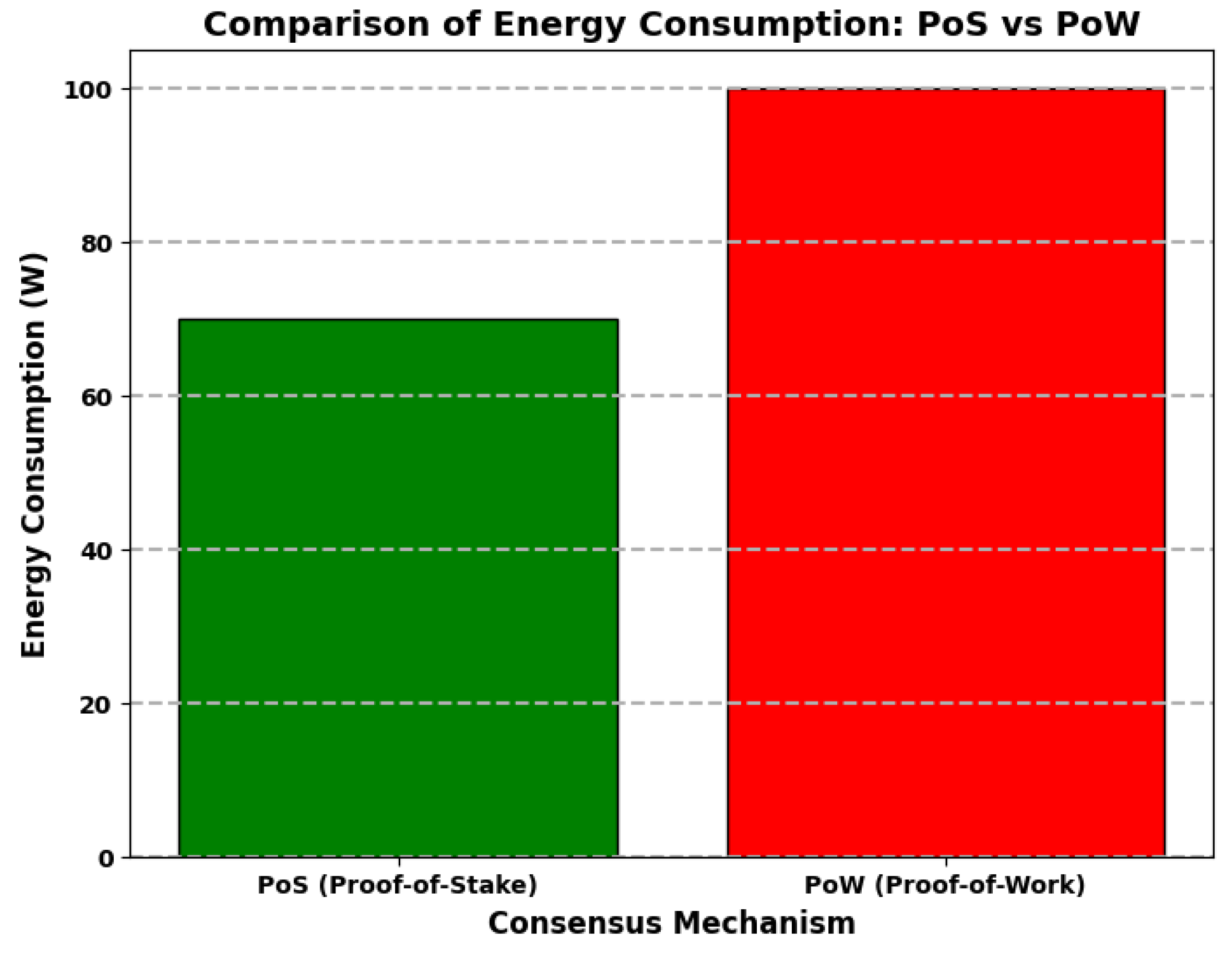
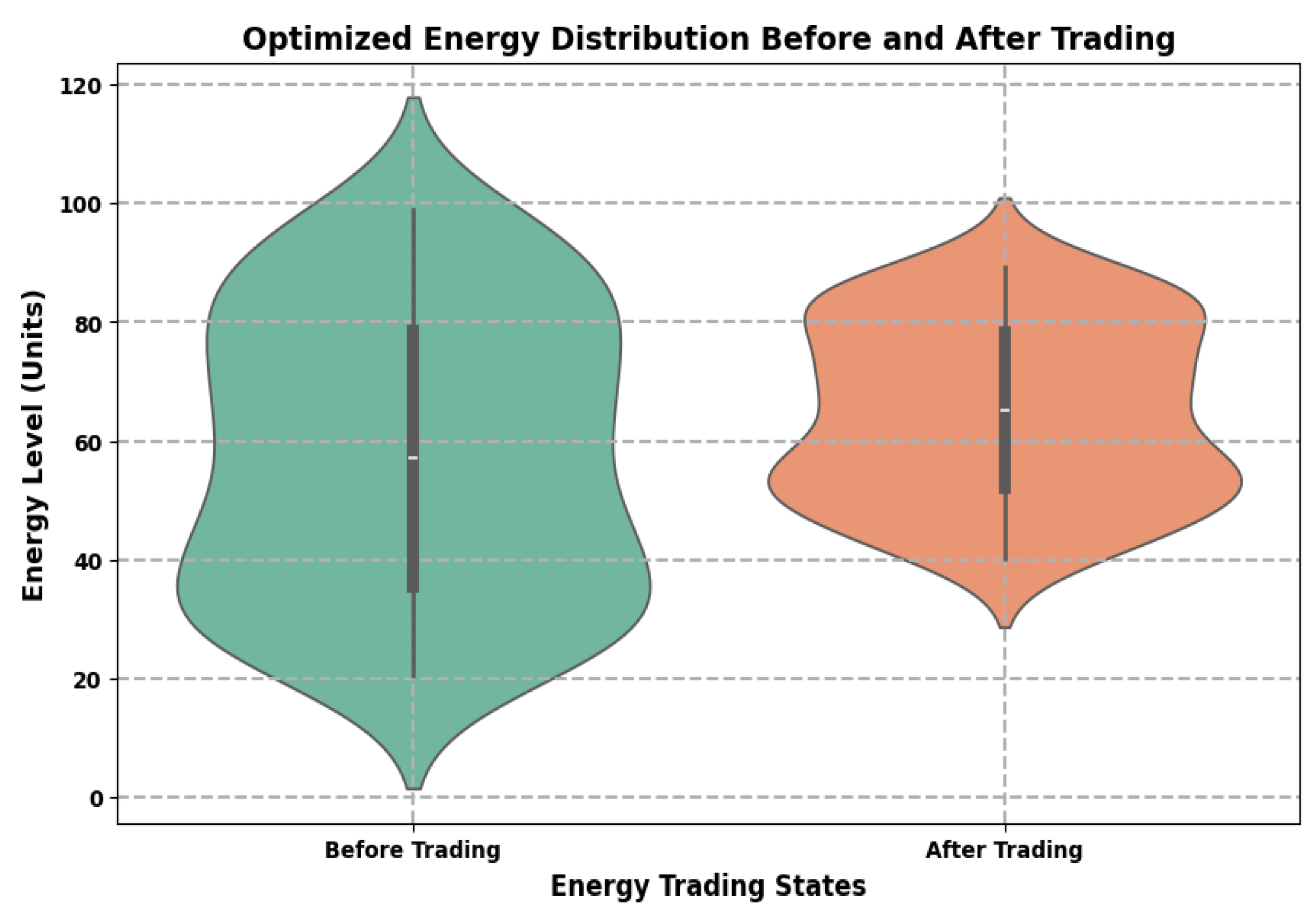
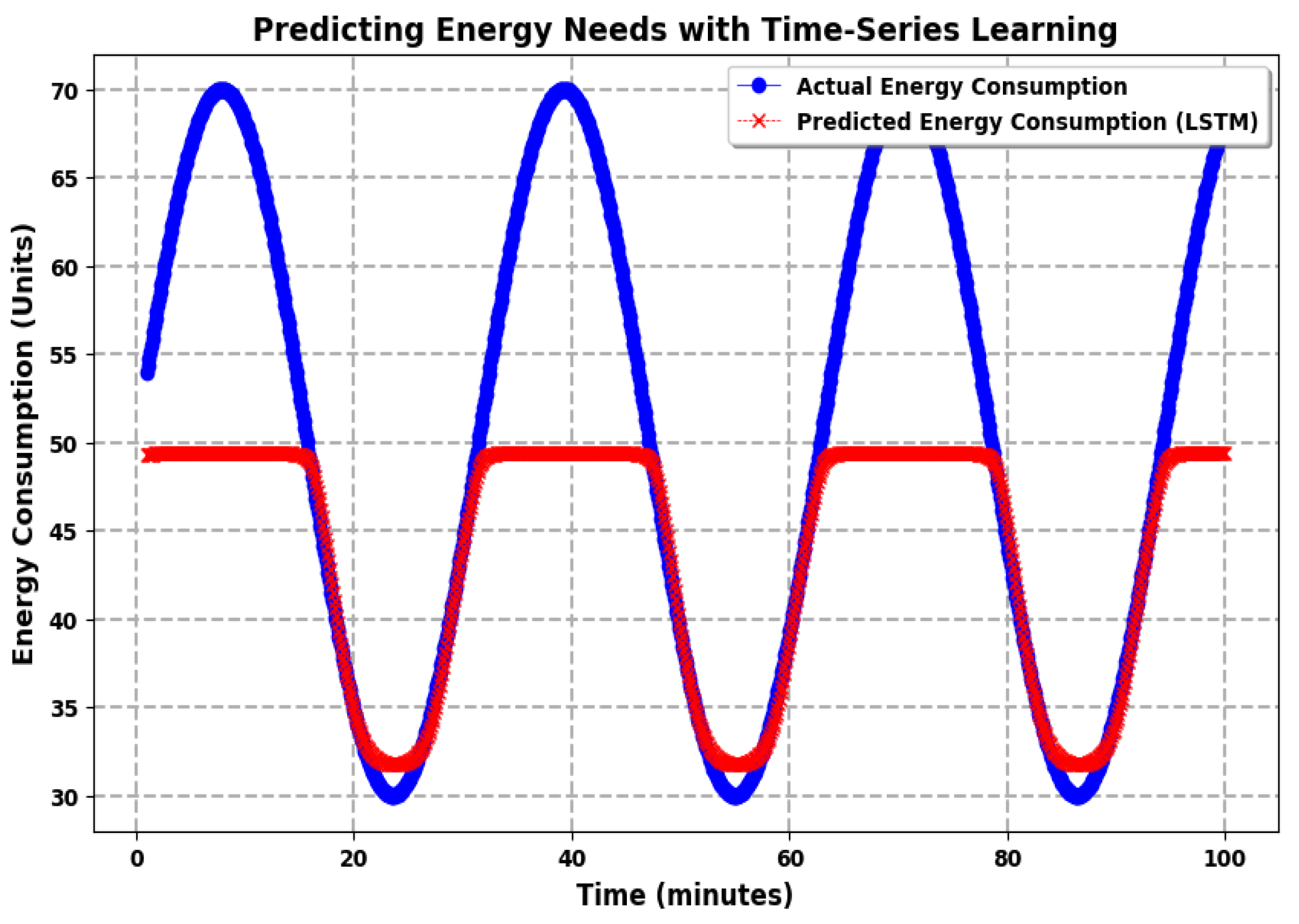
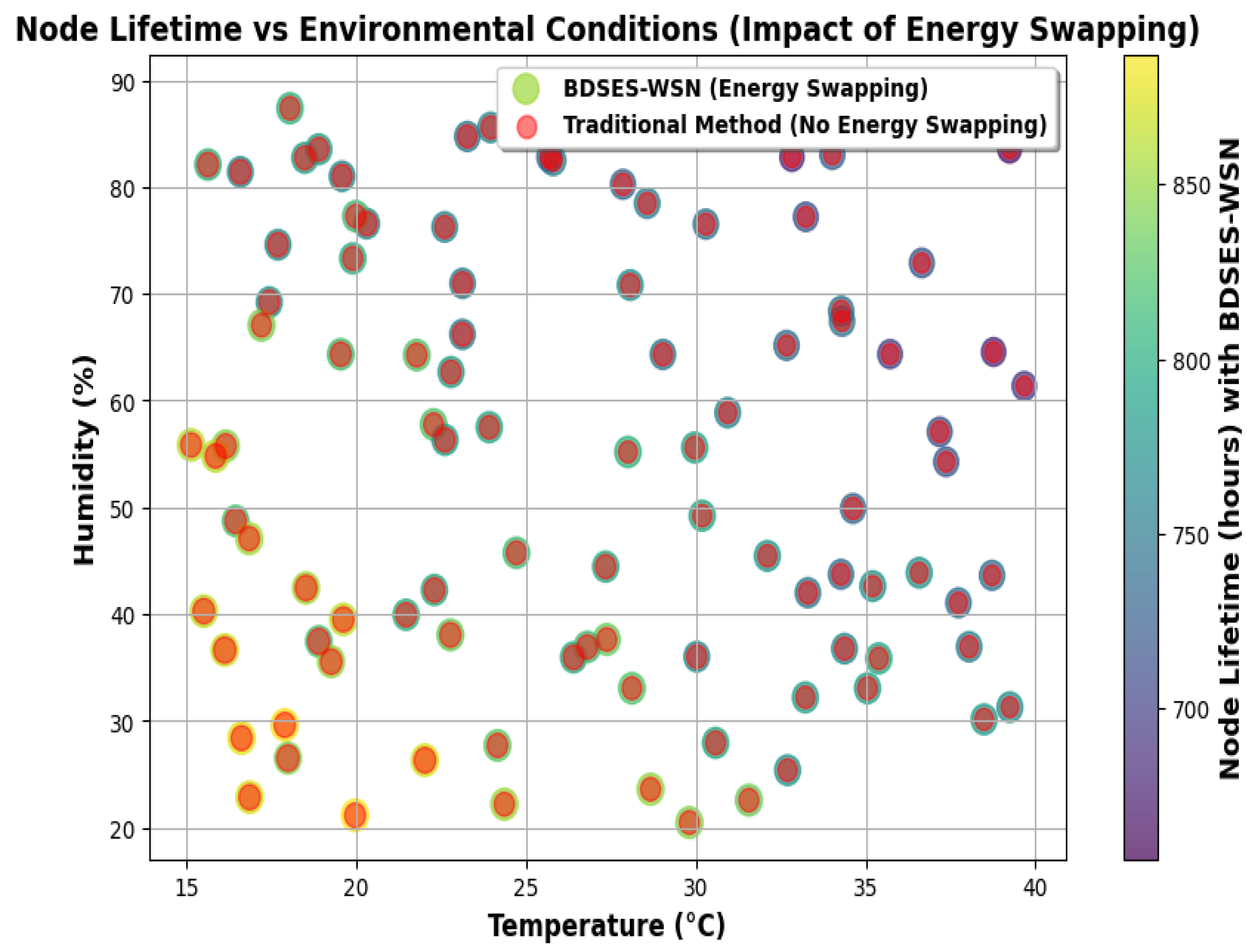
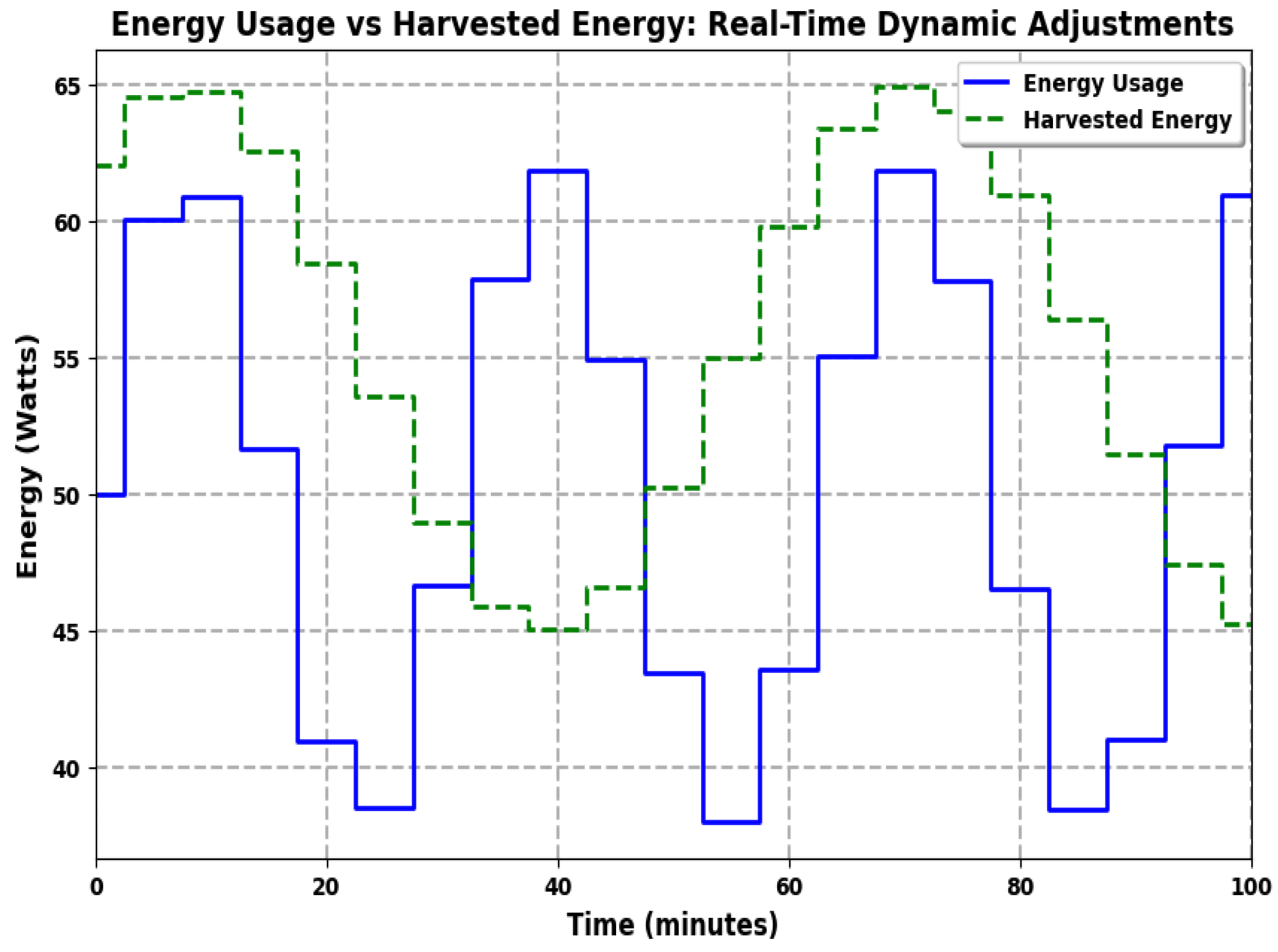
6. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alshmeel, G.H.A., Al-Doori, A.S.B., Ahmed, S.R., Ibrahim, Z.A., Ghaffoori, A.J., & Hussain, A.S.T. (2024, May). Self-Sustaining Buoy System: Harnessing Water Wave Energy for Smart, Wireless Sensing and Data Transmission. In Proceedings of the Cognitive Models and Artificial Intelligence Conference (pp. 349–356).
- Ismail, S.; Dawoud, D.W.; Reza, H. Securing wireless sensor networks using machine learning and Blockchain: A review. Future Internet 2023, 15, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipon, W.H. (2023). Self-Sustaining Multi-Sensing and Wireless Communication System Powered by Efficient Energy Harvesting from Road Traffic and Heat (Doctoral dissertation, The University of Texas at San Antonio).
- Arachchige, K.G.; Branch, P.; But, J. Evaluation of Correlation between Temperature of IoT Microcontroller Devices and Blockchain Energy Consumption in Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2023, 23, 6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaragoez, Y., Pollin, S., & Schreurs, D. (2024, June). Integrated Dual-Mode Energy Harvesting for Self-Sustaining Sensor Nodes: Synergy of Solar and RF Energies. In 2024 IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium-IMS 2024 (pp. 273–276). IEEE.
- Huang, X.; Zhao, W.; Yuan, M.; Sun, K.; Yang, B. A self-sustaining wireless sensing and flight control device for beetles. AIP Advances 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankar, C., Subramanian, E.K., Sarala, V., Moorthy, A., & Purushothaman, N. (2024, July). Optimizing Power Consumption in Wireless Sensor Networks for Prolonged Sustainability. In 2024 Second International Conference on Advances in Information Technology (ICAIT) (Vol. 1, pp. 1–4). IEEE.
- Ravikumar, C.V., Sathish, K., & Su, C. (2024, October). Design and Analysis of Piezoelectric Energy Harvester for Wireless Sensor Networks. In International Conference on Data Security and Privacy Protection (pp. 239–254). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
- Paulraj, D., Lavanya, R., Jayasudha, T., Niranjana, M.I., Daniya, T., & Shadrach, F.D. (2023, February). Blockchain-based wireless sensor network security through authentication and cluster head selection. In 2023 IEEE International Conference on Integrated Circuits and Communication Systems (ICICACS) (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
- Draz, U., Ali, T., Yasin, S., Naseer, N., & Waqas, U. (2018, February). A parametric performance evaluation of SMDBRP and AEDGRP routing protocols in an underwater wireless sensor network for data transmission. In 2018 international conference on advancements in computational sciences (ICACS) (pp. 1–8). IEEE.
- Zhou, X.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, K. Remote radio frequency unit selection of self-sustaining distributed base-station system based on downlink physical layer secure transmission. Wireless Networks 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.N.; Kader, K.A.; Ali, M.S.; Ullah, A.; Al Dodaev, Z. An Extensive Analysis of the Significance and Difficulties of Microgrids Based on Renewable Energy in Wireless Sensor Networks. Control Systems and Optimization Letters 2024, 2, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentivogli, A.; Polonelli, T.; Magno, M.; Comai, G. (2023). Check for Enabling Predictive Maintenance on Electric Motors Through a Self-sustainable Wireless Sensor Node. Applications in Electronics Pervading Industry, Environment and Society: APPLE PIES 2022, 1036, 3.
- Ning, T.; Lin, C.; Cai, G.; Xie, K.; He, J.; Huang, C.; Debbah, M.R. Energy Buffer-Aided Wireless-Powered Relaying System for Self-Sustainable Implant WBAN. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, P.; Magno, M.; Benini, L. Self-sustaining ultrawideband positioning system for event-driven indoor localization. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2023, 11, 1272–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoor, F.; Shafik, W. Harvesting energy overview for sustainable wireless sensor networks. Journal of Smart Cities and Society 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srividya, P. Self-Powered Wireless Sensor Networks in Cyber-Physical System. Self-Powered Cyber-Physical Systems, 2023; 41–56. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.A.; Amjad, S.; Ahmed, F.; Almasoud, A.M.; Imran, M.; Javaid, N. A blockchain-based deep-learning-driven architecture for quality routing in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 31036–31051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, M.; Orman, A. Bbap-win: a new blockchain-based authentication protocol for wireless sensor networks. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, M.; Husnain, G. Blockchain-Based Multi-hop Routing and Cost-Effective Decentralized Storage System for Wireless Sensor Networks. Wireless Personal Communications 2023, 131, 3009–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draz, U.; Ali, T.; Yasin, S.; Waqas, U.; Rafiq, U. (2019, February). EADSA: Energy-aware distributed sink algorithm for hotspot problem in wireless sensor and actor networks. In 2019 International Conference on Engineering and Emerging Technologies (ICEET) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
- Almasabi, S.; Shaf, A.; Ali, T.; Zafar, M.; Irfan, M.; Alsuwian, T. Securing smart grid data with Blockchain and wireless sensor networks: A collaborative approach. IEEE Access 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, V.; Pandimurugan, V.; Rajasoundaran, S.; Rodrigues, P.; Kumar, S.S.; Selvi, M.; Loganathan, V. Enriched energy-optimized LEACH protocol for efficient data transmission in a wireless sensor network. Wireless Networks 2024, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draz, U., Yasin, S., Ali, A., Khan, M.A., & Nawaz, A. (2021, January). Traffic agents-based analysis of hotspot effect in IoT-enabled wireless sensor network. In 2021 International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technologies (IBCAST) (pp. 1029–1034). IEEE.
- Fu, X.; Pace, P.; Aloi, G.; Li, W.; Fortino, G. Toward robust and energy-efficient clustering wireless sensor networks: A double-stage scale-free topology evolution model. Computer Networks 2021, 200, 108521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilhore, U.K.; Khalaf, O.I.; Simaiya, S.; Tavera Romero, C.A.; Abdulsahib, G.M.; Kumar, D. A depth-controlled and energy-efficient routing protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks 2022, 18, 15501329221117118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, D.J.; Lakshmanan, L. A novel method for optimizing energy consumption in wireless sensor networks using genetic algorithm. Microprocessors and Microsystems 2023, 96, 104749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draz, U.; Ali, T.; Asghar, K.; Yasin, S.; Sharif, Z.; Abbas, Q.; Aman, S. A Comprehensive Comparative Analysis of Two Novel Underwater Routing Protocols. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathish Kumar, L.; Ahmad, S.; Routray, S.; Prabu, A.V.; Alharbi, A.; Alouffi, B.; Rajasoundaran, S. Modern Energy Optimization Approach for Efficient Data Communication in IoT-Based Wireless Sensor Networks. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing 2022, 2022, 7901587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Byun, H.; Zhang, L. Energy-balanced cluster-routing protocol based on particle swarm optimization with five mutation operators for wireless sensor networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, T.; Yasin, S.; Draz, U.; Ayaz, M. Towards formal modelling of subnet-based hotspot algorithm in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications 2019, 107, 1573–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draz, U.; Ali, T.; Yasin, S.; Fareed, A.; Shahbaz, M. (2019, July). Watchman-based data packet forwarding algorithm for underwater wireless sensor and actor networks. In 2019 International Conference on electrical, communication, and computer engineering (ICECCE) (pp. 1–7). IEEE.
- Kathiroli, P.; Selvadurai, K. Energy-efficient cluster head selection using improved Sparrow Search Algorithm in Wireless Sensor Networks. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences 2022, 34, 8564–8575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim Mohammed, L.A.; Hasan, A.M.; Hamza, E.K. Pruning and Validation Techniques Enhanced Genetic Algorithm for Energy Efficiency in Wireless Sensor Networks. Ingénierie des Systèmes d'Information 2024, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Senkumar, M.R.; Arafat, I.S.; Nathiya, R.; Nishath, S.M. Enhanced Energy Efficient Clustering and Routing Algorithm in Wireless Sensor Network. Wireless Personal Communications 2024, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, V.; Singh, D.; Pandey, S.; Singh, S.; Singh, P.K. Energy-Optimization Route and Cluster Head Selection Using M-PSO and GA in Wireless Sensor Networks. Wireless Personal Communications 2024, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takale, D.G.; Mahalle, P.N.; Gawali, P.P.; Deshmukh, G.B.; Banchhor, C.O.; Mehta, P.S. (2024). Innovative and Sustainable Energy-Efficient Wireless Sensor Networks: Design and Techniques. In Edge Computational Intelligence for AI-Enabled IoT Systems (pp. 281–319). CRC Press.
- Suman MA, N.; Geethasri, V.; Pavan, A.S. A Routing Protocol for Efficiently Managing Energy In Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks With Depth Control. Journal of Science & Technology (JST) 2024, 9, 59–73. [Google Scholar]
- Draz, U. , Ali, T., Yasin, S., Waqas, U., & Rafiq, U. (2019, February). Towards formalism of link failure detection algorithm for wireless sensor and actor networks. In 2019 International Conference on Engineering and Emerging Technologies (ICEET) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
- Draz, U.; Ali, T.; Ahmad Zafar, N.; Saeed Alwadie, A.; Irfan, M.; Yasin, S.; Khan Khattak, M.A.; et al. Energy efficient watchman-based flooding algorithm for IoT-enabled underwater wireless sensor and actor networks. ETRI Journal 2021, 43, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draz, U. , Ali, T., Yasin, S., & Waqas, U. (2018, December). Towards formal modelling of hotspot issue by watch-man nodes in wireless sensor and actor-network. In 2018 International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology (FIT) (pp. 321–326). IEEE.
- Draz, U.; Ali, T.; Yasin, S.; Hussain, A.; Bukhari, S.; Nawaz, A.; Jung, L.T.; e, al. A novel layer-by-layer energy efficient watchman algorithm for wireless sensor and actor networks. Sci. Technol 2021, 24, 284–298. [Google Scholar]
- Draz, U.; Ali, T.; Yasin, S.; Chaudary, M.H.; Ayaz, M.; Aggoune EH, M.; Yasin, I. Hybridization and Optimization of Bioand Nature-Inspired Metaheuristic Techniques of Beacon Nodes Scheduling for Localization in Underwater IoT Networks. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draz, U. , Ali, T., Chaudary, M.H., Sohail, A., & Yasin, S. (2022, December). TARIQ: Towards Area Adjustment and Rounding of Intermediate Nodes for Quadrilateration in Blockchain Enabled Underwater Beacon Node Localization. In 2022 International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology (FIT) (pp. 41–46). IEEE.
| Ref. | Study Focus | Algorithm/Technique | Application Domain | Key Contribution | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Self-sustaining buoy system | Water wave energy harvesting | Smart, wireless sensing | Uses water wave energy for data transmission | Limited to specific environments |
| 2 | Securing WSNs using ML and Blockchain | Machine learning, Blockchain | WSNs | Uses ML and Blockchain for secure WSN communication | It does not focus on energy management |
| 3 | Self-sustaining multi-sensing system | Energy harvesting from road traffic | WSNs | Efficient energy harvesting from traffic and heat sources | Limited application to specific environments |
| 4 | Temperature and blockchain energy consumption | Correlation analysis | IoT microcontroller devices | Analyzes temperature effects on blockchain energy consumption | Focuses on correlation, not energy optimization |
| 5 | Dual-mode energy harvesting | Solar and RF energy harvesting | Self-sustaining sensor nodes | Integrates solar and RF energy harvesting | Limited to solar and RF energy sources |
| 6 | Self-sustaining wireless sensing for beetles | Energy harvesting for flight control | Wireless sensing | Uses energy harvesting for wireless flight control in beetles | Limited to specific biological systems |
| 7 | Optimizing power consumption in WSNs | Power optimization | WSNs | Prolongs sustainability through power optimization | Does not use Blockchain for energy management |
| 8 | Piezoelectric energy harvester for WSNs | Piezoelectric energy harvesting | WSNs | Design and analysis of piezoelectric energy harvesting for WSNs | Limited to piezoelectric sources |
| 9 | Blockchain-based WSN security | Blockchain, cluster head selection | WSNs | Uses Blockchain for WSN security through cluster head selection | No energy optimization addressed |
| 10 | Parametric performance evaluation of routing protocols | SMDBRP and AEDGRP | Underwater WSNs | Evaluates the performance of two underwater routing protocols | Focuses on performance, not energy trading |
| 11 | Remote RF unit selection for distributed base stations | RF unit selection | Self-sustaining distributed base stations | Secure transmission in self-sustaining distributed base stations | Limited to specific systems |
| 12 | Analysis of microgrids based on renewable energy | Microgrid analysis | Renewable energy in WSNs | Extensive analysis of microgrids based on renewable energy | Limited focus on WSN-specific challenges |
| 13 | Self-sustainable wireless sensor node for predictive maintenance | Predictive maintenance | Electric motors | Enables predictive maintenance through wireless sensor nodes | Limited to electric motor applications |
| 14 | Energy buffer-aided wireless-powered relaying | Energy buffer-aided relaying | Implant WBAN | Wireless-powered relaying for self-sustaining implant WBAN | Focuses on implant systems |
| 15 | Self-sustaining UWB positioning system | UWB positioning system | Indoor localization | Uses ultrawideband for self-sustaining indoor localization | Limited to indoor applications |
| 16 | Overview of energy harvesting for WSNs | Energy harvesting overview | WSNs | Overview of Sustainable Energy Harvesting Methods | Lacks blockchain integration |
| 17 | Self-powered WSNs in cyber-physical systems | Self-powered WSNs | Cyber-physical systems | Focus on self-powered wireless sensor networks | Limited to cyber-physical systems |
| 18 | Blockchain-based deep-learning for WSN routing | Blockchain, deep learning | WSNs | Uses Blockchain and deep learning for quality routing in WSNs | Focuses on routing, not energy management |
| 19 | Blockchain-based authentication protocol | Blockchain authentication | WSNs | New authentication protocol for WSNs using Blockchain | Focuses on security, not energy management |
| 20 | Blockchain-based routing and storage for WSNs | Blockchain, multi-hop routing | WSNs | Enhanced routing efficiency and secure decentralized storage | It does not focus on energy management |
| 21 | Energy-aware distributed sink algorithm | EADSA | WSNs | Mitigates hotspot problem by balancing energy distribution | Focused only on data routing |
| 22 | Securing smart grid data | Blockchain | WSNs | Secures decentralized energy management and data integrity | Energy management is not addressed |
| 23 | Energy-optimized LEACH protocol | LEACH Protocol | WSNs | Optimized data transmission and energy efficiency | Focuses on data communication, not energy swapping |
| 24 | Hotspot effect analysis in IoT-enabled WSNs | Traffic agents | IoT-based WSNs | Analyzed hotspot effects in IoT networks | No energy redistribution mechanism |
| 25 | Clustering model for energy efficiency | Double-stage scale-free topology | WSNs | Improved energy efficiency and robustness | Does not use Blockchain |
| 26 | Routing protocol for underwater WSNs | Energy-efficient routing | Underwater WSNs | Optimizes energy consumption in underwater networks | Limited to underwater environments |
| 27 | Genetic algorithm for optimizing energy | Genetic algorithm | WSNs | Optimized energy consumption using genetic algorithms | No security mechanisms are incorporated |
| 28 | Comparative analysis of underwater routing | Underwater routing protocols | Underwater WSNs | Comprehensive analysis of two underwater protocols | Focus on comparison, not energy trading |
| 29 | Energy optimization in IoT-based WSNs | Modern energy optimization approach | IoT-based WSNs | Optimized energy-efficient data communication | It does not address Blockchain for energy trading |
| 30 | Energy-balanced routing in WSNs | PSO with mutation operators | WSNs | Energy-balanced routing with particle swarm optimization | Limited application to general WSNs |
| 31 | Hotspot algorithm for energy distribution | Subnet-based hotspot algorithm | WSNs | Manages energy depletion in hotspots | Lacks decentralized energy trading |
| 32 | Packet forwarding in underwater WSNs | Watchman-based forwarding | Underwater WSNs | Improved energy-efficient data forwarding | It does not include energy management |
| 33 | Cluster head selection using the Sparrow Search Algorithm | Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm | WSNs | Energy-efficient cluster head selection | Focused on clustering, not energy redistribution |
| 34 | Energy-efficient genetic algorithm for WSNs | Genetic algorithm with pruning techniques | WSNs | Enhanced energy efficiency with validation techniques | No use of Blockchain for security |
| 35 | Clustering and routing algorithm for WSNs | Enhanced clustering and routing | WSNs | Improved energy usage and resilience | No blockchain application for decentralized management |
| 36 | Energy-optimization route and cluster selection | PSO and GA | WSNs | Optimized route and cluster head selection | No energy trading mechanism is included |
| 37 | Energy-efficient design for WSNs | Intelligent, sustainable design techniques | WSNs in IoT | Focus on sustainable, energy-efficient design for IoT systems | No blockchain or energy trading |
| Model | Hyperparameter | Optimal Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| WSN Node Configuration | Number of Nodes | 1000 |
| Initial Node Energy | 10 J | |
| Energy Threshold (E-threshold) | 2 J | |
| Communication Energy Consumption | 0.05 J/packet | |
| Sensing Energy Consumption | 0.02 J/sensor cycle | |
| Processing Energy Consumption | 0.01 J/operation | |
| Harvesting Energy Rate | Solar: 0.5 W, RF: 0.3 W | |
| Blockchain-Based Energy Swapping | Consensus Algorithm | Proof-of-Stake (PoS) |
| Number of Validators | 50 | |
| Transaction Fee | 0.1% of traded energy | |
| Block Size | 2 MB | |
| Validation Time | 2 seconds | |
| LSTM Neural Network (Energy Prediction) | Number of Layers | 3 |
| Number of Neurons per Layer | 64 | |
| Activation Function | ReLU | |
| Optimizer | Adam | |
| Learning Rate | 0.0005 | |
| Sequence Length | 100 | |
| Energy Harvesting Model | Solar Conversion Efficiency | 20% |
| RF Energy Conversion Efficiency | 15% | |
| Maximum Harvesting Capacity | 5 W | |
| Integration Strategy | Weight Adjustment Factor | Adaptive |
| Fitness Function Weights | α = 0.6, β = 0.4 | |
| Threshold for Convergence | 10⁻⁴ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





