1. Basics of Chemical Thermodynamics
Chemical thermodynamics is an interdisciplinary science that combines thermodynamics, physical chemistry, statistical and chemical physics, and some other scientific areas. The main tasks of chemical thermodynamics are to determine thermodynamic functions, study the transformations of various forms of energy during chemical reactions and phase transitions, predict the feasibility and direction of chemical processes, and study the ability of chemical systems to perform useful work [
1,
2]. A section of chemical thermodynamics is thermochemistry, which studies the thermal effects of chemical reactions and physicochemical processes.
Chemical thermodynamics considers isolated, closed, and open systems. In an isolated system, there is no exchange of energy and matter with the external environment. In a closed system, there is no exchange of matter, but energy exchange with the external environment is carried out. In an open system, the exchange of both matter and energy with the external environment is possible.
There are also laws of thermodynamics. The zeroth law of thermodynamics states that an isolated thermodynamic system spontaneously passes over time into a state of thermodynamic equilibrium.
The first law of thermodynamics states that the heat received by a system from outside is used to increase the internal energy of the system and to perform work by this system.
According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat or thermal energy cannot spontaneously pass from a cooler body to a hotter body. Another formulation of the second thermodynamic law is as follows: in a nonequilibrium isolated system, entropy increases and reaches a maximum when thermodynamic equilibrium is established. The consequence of the second law is that a perpetual motion machine of the second kind is impossible.
The third law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of any equilibrium system, as the temperature approaches absolute zero, ceases to depend on any state parameters and tends to a certain limit close to zero. Moreover, all processes near absolute zero that transfer the system from one equilibrium state to another occur without changing the entropy.
Chemical thermodynamics operates with several terms, parameters, and thermodynamic functions such as temperature (T), pressure (P), volume (V), work (A), heat (Q), kinetic energy (Ek), internal energy (U), enthalpy (H), entropy (S), free energy or potential of Helmholtz (F) and Gibbs (G), etc.
In the case of an isolated system, the change in internal energy is zero: ΔU=0.
For a reaction occurring in closed or open systems at constant temperature and volume, the thermal effect (∆Q) of this reaction is equal to the change in the internal energy (∆U) of the system, i.e.,
If a reaction occurs in an open system at constant temperature and pressure, then from the first law of thermodynamics it follows:
Denoting U + PV = H, where H is called enthalpy, we obtain:
Thus, in an open system at P=const, the thermal effect of the reaction is equal to the enthalpy change.
As a result of a chemical reaction, enthalpy can decrease (∆rН < 0) when heat is released, or increase (∆rН > 0) when heat is absorbed from outside. According to the Lavoisier-Laplace law, the thermal effect of a forward reaction is always equal to the thermal effect of a reverse reaction with the opposite sign. The second law of thermochemistry, proposed by Hess, states that the thermal effect of a reaction depends only on the initial and final state and does not depend on the intermediate stages of the reaction. There is also another formulation of this law, namely: if a chemical process occurs in several stages, then the overall thermal effect of the process is equal to the algebraic sum of the thermal effects of the individual, intermediate stages.
Two important consequences follow from Hess's law. Firstly. The thermal effect of a chemical reaction (∆
rН) is equal to the difference between the sums of the combustion enthalpies (∆
cН
r) of the starting reagents and the combustion enthalpies (∆
cН
p) of the reaction products, taking into account their stoichiometric coefficients:
Secondly. The thermal effect of a chemical reaction is equal to the difference between the sums of the formation enthalpies (∆
fН
p) of the reaction products and the formation enthalpies (∆
fН
r) of the starting reagents, taking into account their stoichiometric coefficients.
Numerical values of standard formation enthalpy for various substances under standard conditions (T
o=298.15 K, P
o = 0.1 MPa) are given in reference books.
The concept of entropy was first introduced by Rudolf Clausius in the late 19th century. Entropy is considered a function of the state of a thermodynamic system, related to the reduced thermal energy:
From the second law of thermodynamics, it follows that the spontaneous transfer of heat from a hotter region to a colder one is determined by the increase in the entropy of the system.
According to the Ludwig Boltzmann concept, entropy is a function of system state, characterizing the degree of statistical disorder (W) in the arrangement of elements of a system, ions, atoms, molecules, etc.:
If at Р = constant the temperature rises, then the disorder in the arrangement of atoms or molecules increases, which leads to an increase in the entropy, namely:
where C
p is the specific heat capacity; and T
2 >T
1.
If the open system at Р = const is in equilibrium state, then the following equality is true:
For example, at equilibrium between liquid and vapor at T
c, the change in entropy during vapor condensation (∆S
c) can be calculated if the condensation enthalpy (∆Н
c) is known:
Similarly, one can find the change in entropy during melting at T
m of a crystalline substance:
If a chemical reaction occurs, the change in entropy can be found using an equation similar to the Hess equation:
where S
p and S
r are entropy values for obtaining products and starting reagents, respectively.
Numerical values of standard entropy for various substances under standard conditions (To=298.15 K, Po = 0.1 MPa) are given in reference books.
Chemical thermodynamics can be also used to predict the feasibility and direction of chemical processes. For this purpose, special thermodynamic functions of the system state are used, which reflect the influence of two factors on the process, energy and entropy. These special thermodynamic functions have the property that their sign is a criterion for the feasibility or non-feasibility of a spontaneous reaction.
For isothermal reactions occurring at constant volume, such a function is the Helmholtz free energy, which is calculated using the equation:
In the case of isothermal reactions occurring at constant pressure, a criterion for the feasibility of a spontaneous reaction is the Gibbs free energy or potential. The change in the Gibbs potential during the reaction is determined by the equation:
These special thermodynamic functions characterize the degree of non-equilibrium of the reaction system. The more negative their values are, the greater the deviation of the system from equilibrium and the greater the probability of the reaction being feasible. The feasibility of a reaction is facilitated by a decrease in the internal energy or enthalpy and an increase in the disorder of the system, characterized by the entropy factor.
Thus, the criterion for the feasibility of a reaction in systems at constant volume is ∆
rF< 0. This can happen in the following cases:
For open systems proceeding at constant pressure, the criterion for reaction feasibility is ∆
rG < 0. This can happen when:
If the reaction is reversible and an equilibrium is established between the forward and reverse reactions, such an equilibrium is characterized by a constant K
eq. According to Van't Hoff, the equilibrium constant of a chemical reaction is an exponential function of the thermodynamic potential:
Vice versa, if the value of the equilibrium constant is known, then the thermodynamic potential of the reversible reaction can be calculated, as follows:
To describe the state of the multi-component system with a variable number of different components, a partial thermodynamic function of a component called chemical potential is used:
Such a function determines the change in thermodynamic potential when the number of components in the system changes. The importance of chemical potential is that one of the conditions of equilibrium in a system is the equality of the chemical potential of any component of the system in different phases and at different points of one phase. This function is widely used in physical chemistry to study the processes of dissolution, sorption, etc. For example, for a solution in equilibrium state at P and T = const, the following relationship exists:
where P
s is the vapor pressure of the solvent above the solution, and P
o is the vapor pressure of the pure solvent.
If Ps < Po the Δμs < 0, which is a criterion for good compatibility between the solvent and the polymer.
Thermodynamic analysis of nanoscale particles must take into account a great specific surface area (S
sp) of such particles and its change in various processes:
where σ is the specific surface energy of particles; V
m is the molar volume.
Such nanoparticles tend to aggregate, which is thermodynamically favorable since this process leads to a decrease in the specific surface area (ΔSsp < 0) and provides the negative value of the thermodynamic potential (∆Gn < 0).
Another example is the Gibbs-Thomson equation, according to which the melting point decreases with decreasing size of nanocrystallites. It was found that ∆G
n depends on the temperature change, as follows: ∆G
n = Δ
mH (ΔT/T
m). On the other hand, for nano- particles ΔS
sp = 4/L. Substituting the right parts of ∆G
n and ΔS
sp into eq. (21), the Gibbs-Thomson equation can be obtained:
where T
n and T
m are the melting points of nano-crystallites and macrocrystals, L is the size of nano-crystallite, and Δ
mH is the melting enthalpy.
2. Methods for Determining the Thermodynamic Characteristics of Substances
Values of standard thermodynamic functions (TDFs), such as the standard formation enthalpy (Δ
fH
o) and entropy (S
o), for various substances, can be found in reference books. However, if reference data is not available, the values of these TDFs are determined experimentally. The standard formation enthalpy of an organic substance C
xH
yO
z can be calculated from the experimentally determined combustion enthalpy (Δ
cH
o) of this substance at standard conditions (T
o=298.15 K, P=0.1 MPa). The combustion process of the substance is:
The standard formation enthalpy of this substance can be calculated, as follows:
where Δ
fH
o(CO
2, g) = -393.51 kJ/mol and Δ
fH
o(H
2O, l) = -285.83 kJ/mol are standard enthalpies of the formation of carbon dioxide and liquid water, respectively.
Precision oxygen bomb calorimeters of various designs can be used to burn samples [
3]. Typically, it consists of a strong stainless-steel bomb, which is placed in a water calorimeter. A small sample (0.5-1 g) is put in a crucible inside the bomb and 1 ml of water is added. Oxygen is pumped into the bomb to provide a pressure of 2.5 to 3 MPa. After temperature equilibrium is established, the sample is ignited, the temperature rise is measured with an accuracy of ±0.001 K, and the combustion enthalpy is calculated. The true mass of the used sample is determined from the mass of the produced CO
2. The corrections for ignition and forming of acid traces should be made. To adjust the enthalpy of combustion to standard conditions (T
o=298.15 K, P=0.1 MPa) the Washburn correction, as well as the correction for the change in the number of moles of gases before and after combustion are introduced. For each sample, several experiments are performed to obtain a reliable value of the combustion enthalpy and standard deviation.
To measure the specific heat capacity (C
p) of the dry sample, a scanning adiabatic vacuum calorimeter is used [
3,
4]. The experiments usually are carried out in the temperature range of 80-340 K. Below 80 K, C
p values can be estimated by the method of Kelly, et al. [
5]. The accuracy of C
p determination is ±0.005 J/mol K. For each sample, several experiments should be performed to find the reliable C
p value and standard deviation.
The entropy value of the sample at temperature T is calculated, as follows:
If T is the standard temperature, T
o = 298.15 K, then the result of the calculation is the standard entropy of the sample, S
o.
Along with the bomb calorimeter and the scanning adiabatic calorimeter, other types of calorimeters are also used to study the thermochemical properties of samples. For example, to measure the enthalpy of sample wetting and dissolution, isothermal or adiabatic calorimeters, as well as microcalorimeters can be applied [
6,
7].
For example, to determine the wetting enthalpy of cellulose, a small sample (ca 1 g) is prepared. Before starting experiments, the air-dry sample is weighed into a special glass ampoule and dried in a vacuum at 378 K to a constant weight. The glass ampoule containing the dry sample is sealed and introduced into the calorimetric cell filled with distilled water. The calorimeter is thermostated at 298.15 K to achieve an equilibrium state. Thereafter, the sealed ampoule with the dry sample is broken to ensure that the sample is wetted with water. The released exothermic heat effect of wetting is measured with accuracy ±0.01 J. Several of the same samples usually are tested to calculate an average enthalpy value and standard deviation.
In addition to calorimetry, several other methods can be used to characterize samples. These methods may include X-ray scattering, NMR, FTIR-spectroscopy, DTA, electron microscopy, sorption, etc. [
8,
9,
10,
11].
This review article will show how thermochemical methods can be applied to the study of plant biomass and its main components, cellulose, hemicelluloses, lignin, etc. Considerable attention will be paid to the thermodynamics of physicochemical and chemical transformations of cellulose and nanocellulose, as well as other components of plant biomass. The thermodynamics of second solid, liquid, and gaseous biofuels released from the initial biomass was also considered.
3. Thermochemistry of Plant Biomass
There are many applications of chemical thermodynamics to various substances and diverse reaction classes (synthesis, decomposition, substitution, exchange, oxidation, reduction, etc.). Currently, due to the depletion of fossil fuel reserves and the harm that their use causes to the environment, much attention is paid to the use of renewable natural resources, including plant biomass.
The existence and further development of the present civilization require expanded consumption of energy, chemicals, and materials. Nowadays, the main energy sources are still fossil fuels, namely coal, petroleum, and natural gas [
12]. However, the increased use of fossil fuels is causing acute environmental problems, since the combustion of such fuels is accompanied by the emission of carbon dioxide triggering the greenhouse effect and global warming.
An additional problem is that fossil resources are not reproduced in nature. Therefore, their reserves are exhausted and run down in an essentially permanent manner [
13]. To eliminate the imbalance in the fossil sources, an increased utilization of alternative sources of energy and raw materials is required. Considerable attention in recent years has been given to plant biomass, which in contrast to fossil sources is continuously renewed in nature [
14].
The total resources of plant biomass reach 1.5 trillion tons [
15]. The potential resources of biomass among alternative and renewable energy sources is above 70% [
16], while its share in the production of alternative energy exceeds 50% [
17]. Despite advances in solar and wind energy, in many countries plant biomass still accounts for a significant share of energy production [
17]. So in Africa, up to 60% of energy is generated from biomass. East Asia countries and China receive up to 25% of energy from biomass, while in Latin America, the share of biomass energy is 18%. Only in the USA, the European Union, and other developed regions and countries, the share of biomass in energy production is small and does not exceed 3%.
The plant biomass is formed in nature from carbon dioxide and water by photosynthesis absorbing solar energy. When the plant biomass is burned, it releases the accumulated solar energy in the form of heat, along with the release of used water and carbon dioxide stored in the biomass. Therefore, plant biomass is considered a CO
2-neutral source of renewable energy [
17,
18].
Currently implemented technologies for the production of liquid biofuels are based on the transformation of carbohydrates into bioethanol and vegetable oils into biodiesel fuel. The main sources of these carbohydrates are juices of sugarcane, sugar beet, and sweet sorghum, as well as starches of corn, wheat, potatoes, and some other agricultural plants. Since these carbohydrates and vegetable oils are required in the food industry, their use for the production of biofuels is limited. Moreover, further expansion of the production to a higher volume of bioethanol and/or biodiesel will cause a shortage of land areas, exhaustion of the soil, excessive consumption of water and energy, deficits of food and feed products, and increase their prices [
19].
An alternative way to obtain biofuels without competing with the food and feed industry is the use of inedible biomass, which is an abundant, renewable, and inexpensive plant material. This biomass type involves energy crops (e.g., miscanthus, switchgrass, Bermuda grass,
etc.), forest residues (e.g., sawdust, twigs, shrubs,
etc.), residues of agricultural plants (
e.g. stalks, husks, cobs,
etc.), residues of textile, pulp, and paper, municipal paper waste, etc. Moreover, huge amounts of algae can be used as appropriate feedstock for the production of bioenergy or chemicals. The total resources of inedible biomass accumulated annually are estimated at 10 billion tons, the combustion of which could potentially generate about 150 EJ of bio-energy [
20].
The main components of plant biomass are cellulose, hemicelluloses, and lignin (
Table 1).
Cellulose is a linear, stereoregular, semicrystalline polysaccharide consisting of anhydroglucose units (AGUs) having a “chair” conformation and linked to each other in long macromolecules by chemical β-1,4-glycosidic bonds in a head-to-tail manner [
16,
22,
23,
24,
25]. Macromolecules of natural cellulose from various origins may include 2,000 to 30,000 AGUs. During the process of cellulose isolation from plant materials and cellulose modification, partial depolymerization of the macromolecules is observed. Each AGU of cellulose contains three hydroxyl functional groups: one primary and two secondary groups. Hydroxyl groups of adjacent chains are linked by strong hydrogen bonds, which leads to the formation of thread-like elementary nanofibrils and their bundles, called microfibrils, which contain nanocrystallites and non-crystalline domains. Besides, hydroxyl groups can be replaced by various substituents, resulting in the formation of cellulose derivatives, such as ethers, esters, etc. [
26,
27].
Hemicelluloses are highly amorphous heteropolysaccharides [
16,
22,
23,
28,
29]. In the cell walls of plant fibers, hemicelluloses fulfill the function of binder between cellulose fibrils and lignin. The chemical structure of hemicelluloses consists of chains of a variety of pentoses or hexoses units. Various plants and also its tissues contain different types of hemicelluloses. Agricultural and herbaceous plants, as well as hardwoods, contain mainly xylan, pentosan-type hemicellulose, while softwoods are enriched with mannan, which is hexosan-type hemicellulose. Hemicelluloses are heteropolymers. Xylan, for example, can be present in the form of glucuronoxylan (in hardwoods) or arabinoxylan (in grasses and grains), while mannan presents in the form of glucomannan (in softwoods) or galactomannan (in carob tree). The polysaccharide complex of biomass containing cellulose and hemicelluloses is called holocellulose.
Lignin is an aromatic, amorphous, and hydrophobic polymer [
16,
22,
23,
30,
31]. It is a complex biopolymer of phenylpropane units, which are linked to each other with a variety of different chemical bonds with the formation three-dimensional network. Due to such structural organization, lignin is resistant to some chemical reagents and enzymes. This biopolymer consists of three main phenylpropane units such as guaiacyl (G), syringyl (S), and hydroxyphenyl (H). The relative ratios of these units can vary for different biomass sources. Lignin of softwoods is mainly of G-type, whereas lignin of hardwoods contains a mixture of G-and S-units. Lignin of herbaceous plants consists usually of all three types of phenylpropane units.
In addition to the main components, biomasses may contain inorganic substances (ash), organic extractives (lipids, waxes, and resins), starch, pectin, etc. If the initial biomass is subjected to chemical, physicochemical, or biological treatment, its chemical composition changes.
The chemical composition directly affects the calorific value of biomass. Increased content of lignin, lipids, resins, and waxes contributes to achieving a high calorific value of biomass [
22,
23,
32]. This is due to the increased value of combustion enthalpy of lignin, Δ
cH from -25 to -26 MJ/kg [
33] compared with polysaccharides, Δ
cH from -17.4 to -17.6 MJ/kg [
3]. In addition, extractive substances of biomass, lipids, waxes, and resins have Δ
cH from -36 to -38 MJ/kg [
20,
34,
35,
36], which is much higher than that combustion enthalpy of polymeric components of the biomass, lignin, and polysaccharides.
Numerous experiments on measuring the combustion enthalpy or gross heating value (GHV) have shown that for dry wood samples of different species, the difference in the calorific values is small [
37,
38]. Softwood samples have an average value of Δ
cH = -20.5 MJ/kg, while hardwood samples have an average value of Δ
cH = -19.7 MJ/kg [
38] (
Table 2). Forest residues have a lower GHV with Δ
cH = -18.8 MJ/kg [
39]. The calorific value of biomass of cereal crops and herbaceous plants turned out to be lower than that of woody biomass [
20,
40]. The lowest GHV was observed for paper waste containing a large amount of inorganic fillers [
20,
22,
23], while olive samples having increased content of lignin and lipids are distinguished by quite high value of combustion enthalpy (
Table 2).
There are several known methods for extracting energy from biomass. The most well-known method is the use of biomass as solid biofuel. In addition, biomass can be a feedstock for obtaining secondary biofuels from it, such as biochar, bio-oil, bioethanol, biodiesel, and biogas.
However, the direct use of biomass as a solid fuel raises several problems. The initial biomass is a non-dense and heterogeneous material consisting of pieces of various sizes [
18]. Moreover, it can contain moisture and inorganic substances. These features of the initial biomass worsen its fuel properties, since moisture and inorganic admixtures decrease the calorific value, and the low bulk density of the initial biomass declines the density of thermal energy, which significantly reduces the productivity of furnaces.
To improve the fuel performance, the initial biomass should be demineralized, dried, and densified into briquets and pellets [
41,
42,
43,
44,
45]. For example, it was shown that the initial unpressed Switchgrass biomass has unsatisfactory characteristics: bulk density, BD = 98 kg/m
3, and thermal energy density, ED = 1.8 GJ/m
3, while after pelletization these features increased 5 times [
46]. When plastic waste is used as a binder, these features of the pelletized solid biofuel increase by 8 times, which is also accompanied by a rise in the GHV of the pellets.
Along with experimental methods, numerous attempts have been made to calculate the combustion heat of biomass. The most common approach is to use several correlation equations to calculate the calorific value of each type of biomass [
32,
33,
47,
48,
49,
50]. For the calculation, diverse variables were used such as ash content and moisture; individual biomass components, such as lignin; volatile matter and fixed carbon; various physical properties, etc. In addition, correlation equations based on the determination of the elemental composition of biomass were proposed [
47,
51,
52,
53]. However, since the amount of plant biomass species is unlimited, the number of correlation equations can also be unlimited. In addition, the articles [
32,
33,
47] do not provide a critical analysis of the various mathematical models and correlation equations, so it is impossible to identify the equation that is best suited for specific biomass types. Analyzing calculation results of GHV for various biomasses [
32,
48], Park and co-authors [
50] concluded that the discrepancies between calculations and experimental data are high, over 10%.
To improve the accuracy of calculations, it is necessary to use another method than finding correlations with some randomly selected biomass characteristics. In our studies, we used a method based on the rule of additive contributions [
20]:
where C
i is the percentage content of components (see e.g.,
Table 3); Δ
cH
i is GHV of the component of the biomass (
Table 4).
The results revealed that the calculation method based on the rule of additive contributions gives values of combustion enthalpy for biomass samples that are very close to the experimental data (
Table 3). More detailed studies have shown that the average deviation between calculated and experimental results does not exceed 3% [
54].
Based on the carbon content [
20,
47,
49], it can be calculated that burning 1 ton of plant biomass will release an average of 900 m
3 of carbon dioxide, which is half the volume of this greenhouse gas produced by burning 1 ton of such solid fossil fuel as coal.
4. Thermal Energy Potential of Secondary Biofuels
Plant biomass is also a feedstock for producing secondary biofuels, such as biochar, bio-oil, and biogas. For this purpose, the initial biomass is pyrolyzed, i.e. subjected to heat treatment in the absence or lack of oxygen [
16,
22,
55,
56].
Slow pyrolysis of biomass is carried out with a heating rate below 60 degrees/min at temperatures of about 500
oC and residence time of 10-20 min with the formation of biochar, bio-oil, and biogas in approximately the same amounts. If slow pyrolysis is processed at high temperatures, from 600 to 1000
oC, then strong gasification of biomass with a predominant hydrogen fraction occurs [
57,
58]. Hydrothermal gasification of biomass, especially in the presence of a catalyst, significantly increases the hydrogen content in biogas.
Fast pyrolysis is performed at temperatures from 500 to 650oC for short contact time. This pyrolysis type produces usually 60% bio-oil, 20% biochar, and 20% biogas.
In addition, flash pyrolysis is known, proceeding at temperatures higher than 650oC with a contact time of less than 1 sec. The main product of flash pyrolysis is biogas.
It was found that biochar has GHV ca -27 MJ/kg [
22]. The bio-oil is a dark and thick liquid containing a complex mixture of water and various organic substances (tar, hydrocarbons, furan derivatives, aldehydes, ketones, phenols, organic acids, methanol, etc.) with GHV ca -16 MJ/kg [
22].
The biogas is a mixture, containing CO
2, CO, H
2, and CH
4, with a GHV ca -10 MJ/m
3 [
16,
22]. This biogas is formed as a result of the following processes [
16]:
- 1).
Oxidation of biochar at increased temperature
C + 0.5 O2 → CO with ΔrH (T) = -103.9 kJ/mol
C + O2 → CO2 with ΔrH (T) = -370.1 kJ/mol
- 2).
Reduction reactions of gases at increased temperature
C + CO2 2CO with ΔrH (T) = 162.4 kJ/mol
C + H2O CO + H2 with ΔrH (T) = 131.9 kJ/mol
CO + H2O CO2 + H2 with ΔrH (T) = -30.5 kJ/mol
C + 2H2 CH4 with ΔrH (T) = -65 kJ/mol
The average gasification temperature is 800
oC or 1073 K [
57,
58]. Therefore, instead of the standard enthalpies of reactions, Δ
rH
o, at 298.15 K, the enthalpies of these reactions, Δ
rH (T), at a temperature of T = 1073 K should be used. The calculated values of Δ
rH (T) are shown near the equation of the corresponding reaction.
To implement endothermic reactions that have positive values of reaction enthalpy, they must absorb thermal energy from the outside. Exothermic reactions can occur spontaneously without heat absorption from the outside, but often a temperature rise is necessary to increase the rate of such reactions.
Using slow pyrolysis of 100 kg woody biomass, the following yield of secondary biofuel was determined: 30 kg biochar, 18.1 kg bio-oil, and 14 m
3 biogas [
59]. It can be calculated that the total content of thermal energy (TEC) of such biofuel will be TEC = - 1.24 GJ, which is only 62% of the thermal energy content in 100 kg initial biomass equal to -2 GJ.
Another study [
57] found that the yield of biogas after the gasification of pine wood was ca 37 m
3 from 100 kg of wood. In this case, the TEC of such biogas volume does not exceed 20% of the TEC in 100 kg initial wood.
Biogas enriched with methane can be obtained by anaerobic digestion [
60]. This process is performed at a pH 6-7 under the action of mesophilic bacteria at a temperature of 30-40 °C or thermophilic bacteria at a temperature of 50-60 °C. As a feedstock for biogas production, MSW, waste paper, residue of pulp and paper, agricultural waste, etc. can be used [
16,
60,
61]. Lignocellulosic biomass is pretreated to loosen its physical structure and reduce the content of lignin hindering the bioconversion process. The pretreated biomass is diluted with water to prepare aqueous dispersion for anaerobic digestion.
The process of anaerobic biodegradation of organic substances usually takes 3 - 4 weeks and occurs in several stages. In the first stage, called hydrolysis, the complex organic molecules (СM) break down into simple molecules (SM). At the second stage, called acidogenesis, deeper biodegradation occurs with the release of volatile products and the formation of carboxylic acids (CA). In the third stage, called acetogenesis, simple molecules and carboxylic acids are converted to acetic acid (AA). In the last stage, called methanogenesis, acetic acid is converted to biogas (BG) containing mainly methane and carbon dioxide.
Thus, the anaerobic digestion process of biomass can be expressed, as follows:
For example, in the first stage, cellulose and other C6-polysaccharides split into monomeric glucose (GL). Further, glucose forms carboxylic acids and acetic acid, which is transformed into biogas.
The theoretical yield of this biogas from 1 t cellulose is 830 m3 and their thermal energy content TEC = -14.9 GJ, ca 86% from the TEC of initial cellulosic feedstock with TEC = - 17.4 GJ. However, due to increased cellulose crystallinity, the actual yield of biogas and its TEC from cellulose are 1.5 - 2 times lower than the theoretical values. An even lower biogas yield is observed during the anaerobic digestion of lignocellulosic raw materials.
To extract energy from plant biomass, it can be also hydrolyzed and transformed into monosaccharides, mainly glucose, followed by fermentation to produce bioethanol.
Features of the enzymatic hydrolysis of various plant materials have been discussed in many studies [
62,
63,
64,
65,
66]. To implement the effective hydrolysis of biomass, enzyme preparations were used, which include at least three types of specific enzymes, such as endo-1,4-β-glucanases, exo-1,4-β-glucanases, and β-glucosidases. These enzymes act synergistically because endo-acting enzymes generate new chain ends for the exo-acting enzymes, which release the oligosaccharides that are converted into glucose by β-glucosidases [
64].
The enzymatic hydrolysis of biomass is usually carried out at a temperature of 50 °C and pH 5 using a dose of enzyme preparation of 10 to 40 mg of protein per 1 g of substrate. It has been found that to achieve maximum glucose concentration during enzymatic hydrolysis, the optimal loading of the cellulose-containing substrate in the aqueous enzyme system should be at least 150 g/L [
62,
63,
64]. At a higher substrate loading, enzymatic hydrolysis ceases due to a significant reduction in the mass transfer and inhibition of cellulolytic enzymes by a large amount of formed glucose [
67].
In addition, it was established that the initial plant biomass exhibits high resistance to enzymatic cleavage due to the compact structure of the plant material and the presence of lignin and other non-cellulosic components hindering the hydrolysis process. Therefore, the plant biomass is pretreated to loosen its physical structure, eliminate non-cellulosic components, and increase cellulose accessibility to cellulolytic enzyme molecules. To reduce biomass recalcitrance, various pretreatment methods can be used such as steam explosion, acid hydrolysis, alkaline extraction, oxidation, and combined methods [
68,
69,
70,
71,
72,
73,
74]. After the acidic pretreatment of the biomass, predominantly hemicelluloses are removed, which leads to an increase in the cello-lignin content. During alkaline and oxidative pretreatments, partial removal of hemicelluloses and lignin from the biomass occurs, which is accompanied by an increase in the cellulose content in the pretreated biomass and a reduction of biomass recalcitrance to enzymatic hydrolysis.
Combined pretreatment methods are considered the most effective for removing non-cellulosic components from biomass and improving enzymatic hydrolyzability. For example, 1 kg of switchgrass biomass was treated with dilute nitric acid and then with dilute alkali solution [
46]. The result was 410 g of cellulose-enriched pre-treated biomass (PTB). After enzymatic hydrolysis of PTB, 320 g of glucose was obtained. In the fermentation stage, glucose produces 163 g bioethanol with a thermal energy content of TEC = -4.9 MJ, which however is only 27% of the TEC in 1 kg initial biomass equal to -18.3 MJ.
Special plant types containing vegetable oil are well known such as soybeans, rapeseed, olives, sunflower, palms, etc. However, these oil plants are in demand in the food industry, and their use for energy production is limited. For this purpose, it is desirable to use non-edible lipid sources such as camelina, jatropha, pongamia legume, crabapple, jojoba, castor oil plant, tung, algae, etc. Tall oil and waste cooking and frying oils are considered suitable feedstocks for biofuel production.
Though vegetable oils, technical oils, and other lipids have a high calorific value (-35 to -40 MJ/kg), they are less suitable as diesel fuel due to relatively low cetane number, low volatility, high flash point, and increased viscosity [
22]. To improve fuel characteristics, lipids are subjected to transesterification. This process is carried out by reacting triglycerides (TGL) of lipids with alcohols, usually with methanol (MET), in the presence of catalysts. The final products are glycerol (GL) and ester of methanol and fatty acid (e.g. linoleic acid) used as a biodiesel fuel (BDF):
The glycerol fraction is separated from biodiesel fuel and the excess alcohol is removed by distillation or partial evaporation [
16].
The following standard formation enthalpies were found or determined from combustion enthalpies of the starting reagents and products of this reaction (
Table 5).
Using values of standard enthalpies, the enthalpy of the transesterification reaction was calculated as follows:
As a result, it was found that the enthalpy of transesterification reaction Δ
rH
o = -363 kJ/mol. Thus, this reaction is exothermic and can proceed spontaneously without a temperature increase. However, to speed up the process, it is heated to 50-70
oC [
16,
75].
As with other types of biofuels, the TEC of biodiesel fuel can be also compared to the TEC of initial feedstock. Let's say, for example, that the source of vegetable oil is fallen olive fruits. From one ton of these fruits, 230 kg of oil can be extracted and subjected to transesterification. The calculations showed that the resulting biodiesel fuel will have a thermal energy content TEC= -7.4 GJ, which is however significantly less than the amount of energy TEC= -26. 1 GJ that can be obtained by burning 1 ton of fallen olives.
Although biomass is considered CO
2 neutral and the secondary biofuels extracted from it are CO
2 tolerant, the increasing greenhouse effect requires a reduction in CO
2 concentration in the atmosphere. Therefore, the process of converting carbon dioxide into biomethane, known as the Sabatier reaction, has attracted considerable attention [
76,
77].
The Sabatier reaction is expressed by the following equation:
Thus, it is the hydrogenation process of carbon dioxide. However, at normal or slightly increased temperatures and pressures, the rate of direct reaction probable is negligible, and the process is shifted to the left. To ensure the conversion of CO
2 to CH
4, the reaction should be carried out at elevated temperatures and pressures in the presence of a catalyst [
78,
79,
80]. Studies have shown that a high yield of synthetic methane, over 90% of the theoretical yield. can be achieved if the reaction temperature is about 400
oC (673.15 K) and the pressure is about 3 MPa [
79]. As catalysts, Ni and Ru on alumina and some others are used [
76,
80].
The Sabatier reaction most likely occurs in two stages. In the first stage, carbon dioxide is reduced with hydrogen to carbon monoxide, and in the second stage, carbon monoxide is converted to methane.
It was found that the Sabatier reaction is exothermic [
76]. Several references also indicated that the standard enthalpy of the Sabatier reaction, Δ
rH
o = -165 kJ/mol CH
4 when formed water is in the gaseous (vapor) state [
76,
81,
82,
83,
84,
85,
86]. The standard Gibbs potential of this reaction was also estimated [
85]. Unfortunately, in the case, when the formed water vapor condenses into liquid, the calculation of the standard enthalpy and Gibbs potential of the reaction was not performed. However, thermodynamic analysis requires calculating three thermodynamic functions, enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs potential, not only for standard temperature and pressure but also for real conditions occurring at high temperature and pressure. For this purpose, a complete thermodynamic analysis of the Sabatier reaction was carried out under standard and real reaction conditions [
87].
Using reference books, the standard enthalpies of formation (Δ
fH
o) and the standard enthalpies (S
o) for reagents and products of the Sabatier reaction were found (
Table 6) and used for further calculations.
Thermodynamic analysis in the case of the gaseous (vapor) phase state of the formed water
The standard enthalpy of the Sabatier reaction was calculated using the equation:
Similarly, the standard entropy of this reaction was calculated, as follows:
In addition, the Gibbs potential of the reaction was found:
where T
o = 298.15 K is the standard temperature.
Substituting the values of the required TDFs of reagents and products from
Table 6 into these equations, the standard TDFs of the Sabatier reaction were obtained (
Table 7).
Thermodynamic analysis in the case of the liquid phase state of the formed water
The calculations were performed using similar equations with the difference that standard TDF of liquid (l) water was used instead of gaseous (g) water.
The calculation results are presented in
Table 7. When the resulting water is liquid, the exothermic thermal effect of the reaction is higher than in the case of gaseous water. The same relationship is observed for the Gibbs potential of the Sabatier reaction. A more negative value of the Gibbs potential means that the process that forms liquid water is more favorable than the process that produces gaseous water (vapor).
Despite the negative value of the Gibbs potential, the process of carbon dioxide hydrogenation under standard conditions, T
o= 298.15 K and P
o = 0.1 MPa, cannot be implemented, due to kinetic limitations [
80]. As the temperature rises, the reaction rate increases, especially in the presence of a catalyst [
76,
78,
79,
80]. In addition, the elevation of pressure shifts the equilibrium of the reaction to the right and increases the methane yield [
85,
86].
Thermodynamic analysis of catalyzed Sabatier reaction at high temperatures and pressures
These calculations were carried out for real conditions of the Sabatier reaction, T
r = 673.15 K and P
r = 3 MPa in the catalyst presence, when the reaction rate is high enough to ensure a high yield of the formed methane. Under these conditions, the water is in a gaseous phase state. As is known, enthalpy is almost independent of pressure and the main influence on the enthalpy value is exerted by temperature. The enthalpy value of a gaseous substance at pressure P
r and temperature T
r can be found using the following equation:
Unlike enthalpy, the entropy depends on both pressure and temperature. The value of enthalpy at pressure P
r = 3 MPa and standard temperature T
o = 298.15 K was calculated using the equation:
where standard pressure P
o=0.1 MPa, and R=8.3145 (J/mol K) is the gas constant.
The calculated values of S(P
r,T
o) at P
r = 3 MPa for the studied substances are shown in
Table 8.
Further, the entropy value of the gaseous substance at pressure P
r and temperature T
r was calculated, as follows:
where C
p is the specific heat capacity of gaseous reagents and products.
The calculation results of TDFs are shown in
Table 9.
Using these TDFs of gaseous substances, the enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs potential of the Sabatier reaction at high temperature and pressure were obtained [
87] (
Table 10).
These results showed that the Sabatier reaction is highly exothermic also at increased temperature and pressure, while reaction entropy is negative. In addition, the Gibbs potential under these conditions is negative. Thus, the process of methane synthesis from carbon dioxide and hydrogen at elevated temperature T
r = 673.15 K and pressure P
r =3 MPa is energetically and thermodynamically favorable. Using the Van 't Hoff equation, it was found that the equilibrium constant of the reaction K
eq is 2.04 x 10
3 [
87]. Such a value of the equilibrium constant indicates that under real conditions the equilibrium of the Sabatier reaction is shifted to the right with the formation of methane and water vapor.
Calculations also showed that heating a compressed initial gas mixture from To to Tr requires the expenditure of 61.1 kJ/mol of thermal energy, which is 3 times less than the thermal energy released by the exothermic Sabatier reaction.
The Sabatier process continues to be improved. New designs of CO
2 hydrogenation reactors with an improved heat exchange have been proposed [
76,
83,
88]. In addition, more efficient catalytic systems and the removal of resulting water vapor allow for optimization of reaction conditions and enhance methane yield [
76,
80,
88,
89]. The thermal energy of the Sabatier process can be utilized to heat the initial gas mixture and electrolyze water [
90]. Moreover, constructions are being developed that combine a CO
2 hydrogenation reactor with a fuel combustion furnace [
76], an electrolyzer [
76,
90], or an electrochemical cell [
81,
82].
7. Discussion
As is known, renewable plant biomass is considered CO2-neutral. Therefore, its combustion does not increase the concentration of this greenhouse gas in the atmosphere. It should also be noted that the volume of carbon dioxide formed during the combustion of 1 t biomass (ca 900 m3 CO2) is two times less than when burning 1 t such solid fossil fuel as coal (ca 1870 m3 CO2) and even 1.7 times less when burning 1 t of liquid or gaseous fossil fuels (ca 1600 m3 CO2). In addition, CO2 released during the combustion of plant biomass can be converted into gaseous biofuel, for example, bio-methane, using the Sabatier reaction.
Nevertheless, increased amounts of moisture and mineral impurities (ash) reduce the energy potential of biomass. Examples of such types of biomasses are fresh wood with high moisture content and office paper or rice husks with high ash content. On the other hand, it has been established that lipids, organic extractive substances, and lignin have increased calorific value, so their high content in biomass contributes to the extraction of elevated amounts of thermal energy during biomass combustion.
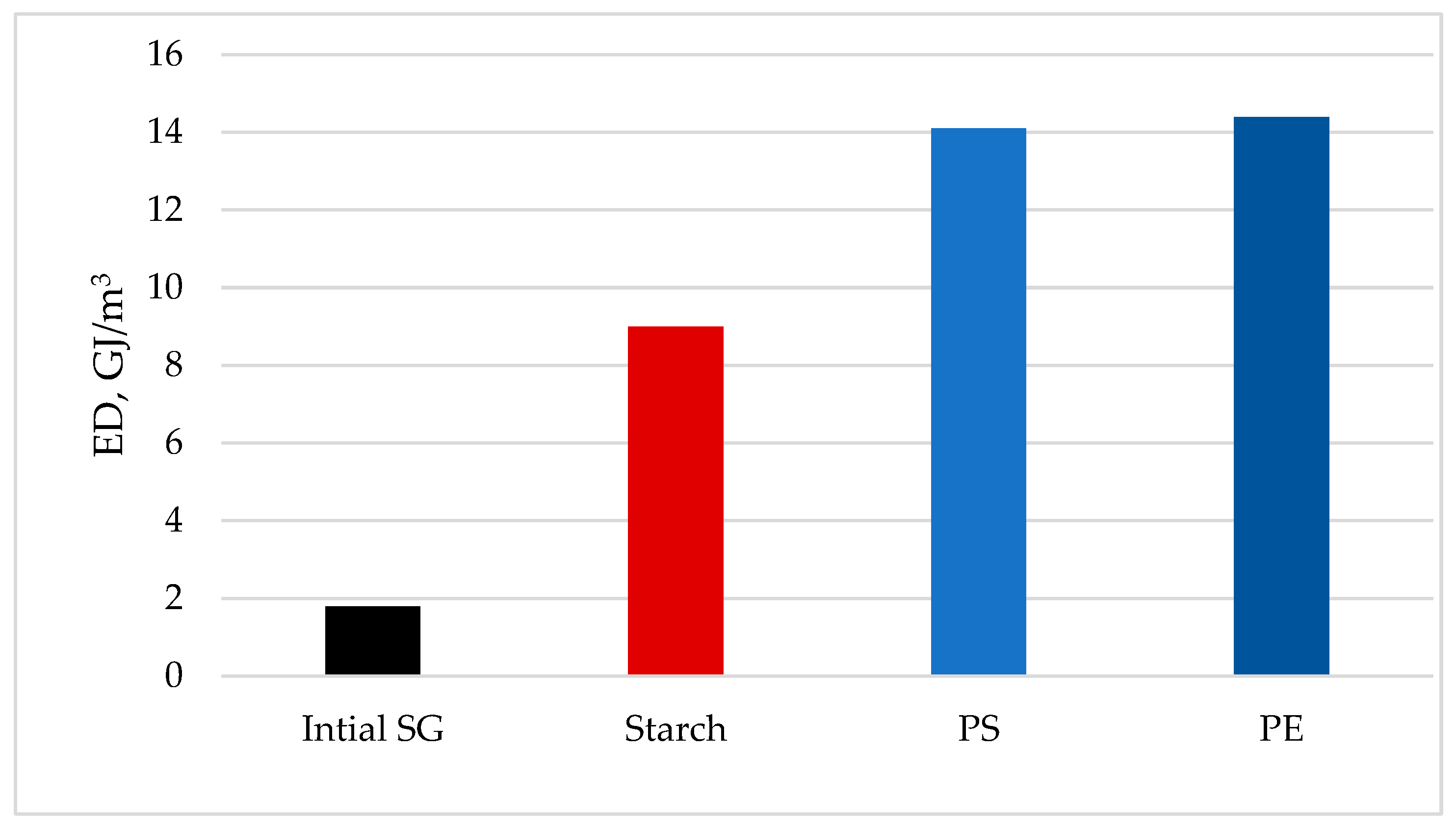
An additional problem is that the initial plant biomass is a loose and non-uniform material consisting of pieces of different sizes with low bulk density. These features of the biomass decline the density of thermal energy (ED), significantly reducing the productivity of the furnaces. To improve the fuel characteristics, the initial plant biomass should be demineralized, dried, and compacted. For example, if pelletize dried Switchgrass (SG) biomass with the addition of various binders such as starch and waste plastics, polystyrene (PS), and polyethylene (PE), then the density of thermal energy can be increased by 5-8 times (
Figure 4). In terms of ED and GHV, biomass pelletized together with plastic binders is not inferior to coal, a traditional solid fossil fuel.
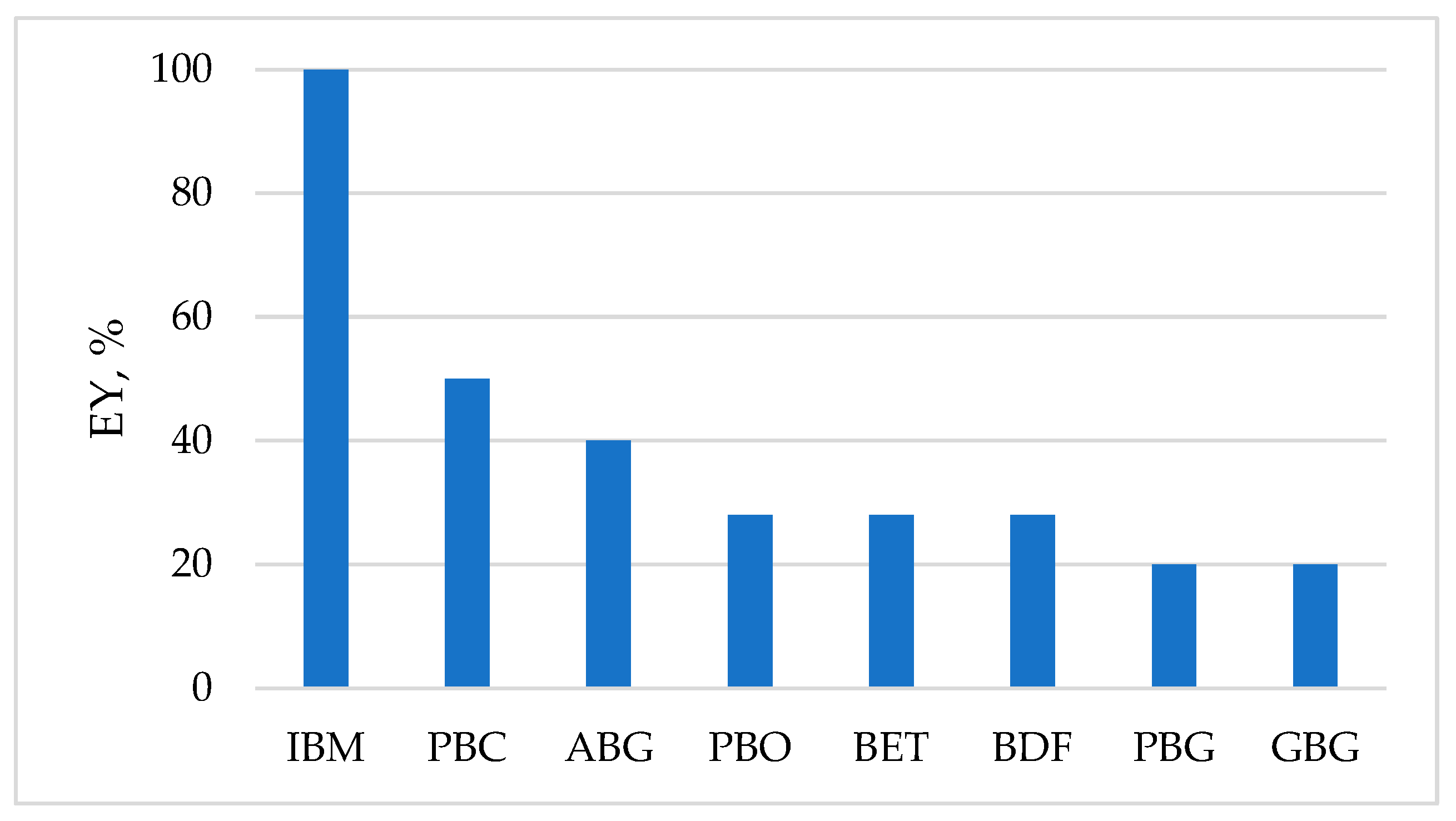
Initial plant biomass can be also a feedstock for producing secondary biofuels, such as biochar, bio-oil, bioethanol, biodiesel fuel, and biogases. From the chart (
Figure 5), one can understand how profitable it is to produce various types of secondary biofuels. The following secondary biofuels were analyzed: biochar (PBC), bio-oil (PBO), and biogas (PBG) of slow pyrolysis of biomass; biogas produced by biomass gasification (GBG); biogas of anaerobic digestion of biomass (ABG); bioethanol (BET) and biodiesel fuel (BDF).
The analysis of thermal energy yield from initial biomass (IBM) and secondary biofuels shows that it is most advantageous to produce biochar of slow pyrolysis and, maybe, biogas by anaerobic digestion of cellulose or other polysaccharides. However, in general, one can conclude that if the ultimate goal is to obtain the maximum amount of thermal energy, then it is more profitable to directly burn the initial biomass (preferably in the form of pellets) than to burn such an amount of secondary solid, liquid or gaseous biofuel that can be extracted from this biomass.
As known, the most important component of biomass is cellulose. It is a semicrystalline biopolymer, many properties of which depend on crystallinity. Unfortunately, currently, existing research methods allow to determine only an estimated characteristic of cellulose crystallinity, the so-called crystallinity index. Therefore, to determine the crystallinity degree, a new thermochemical method was developed based on the measurement of the enthalpy of wetting of cellulose samples. This new method provides the determination degree of cellulose crystallinity with a standard deviation of no more than ±0.01. The thermochemical method is direct, simple, fast, accurate, reliable, and reproducible. It does not require special models, complex software, and calculations. In addition, this method does not have special requirements for the shape, size, morphology, and type of crystalline allomorph of cellulose samples.
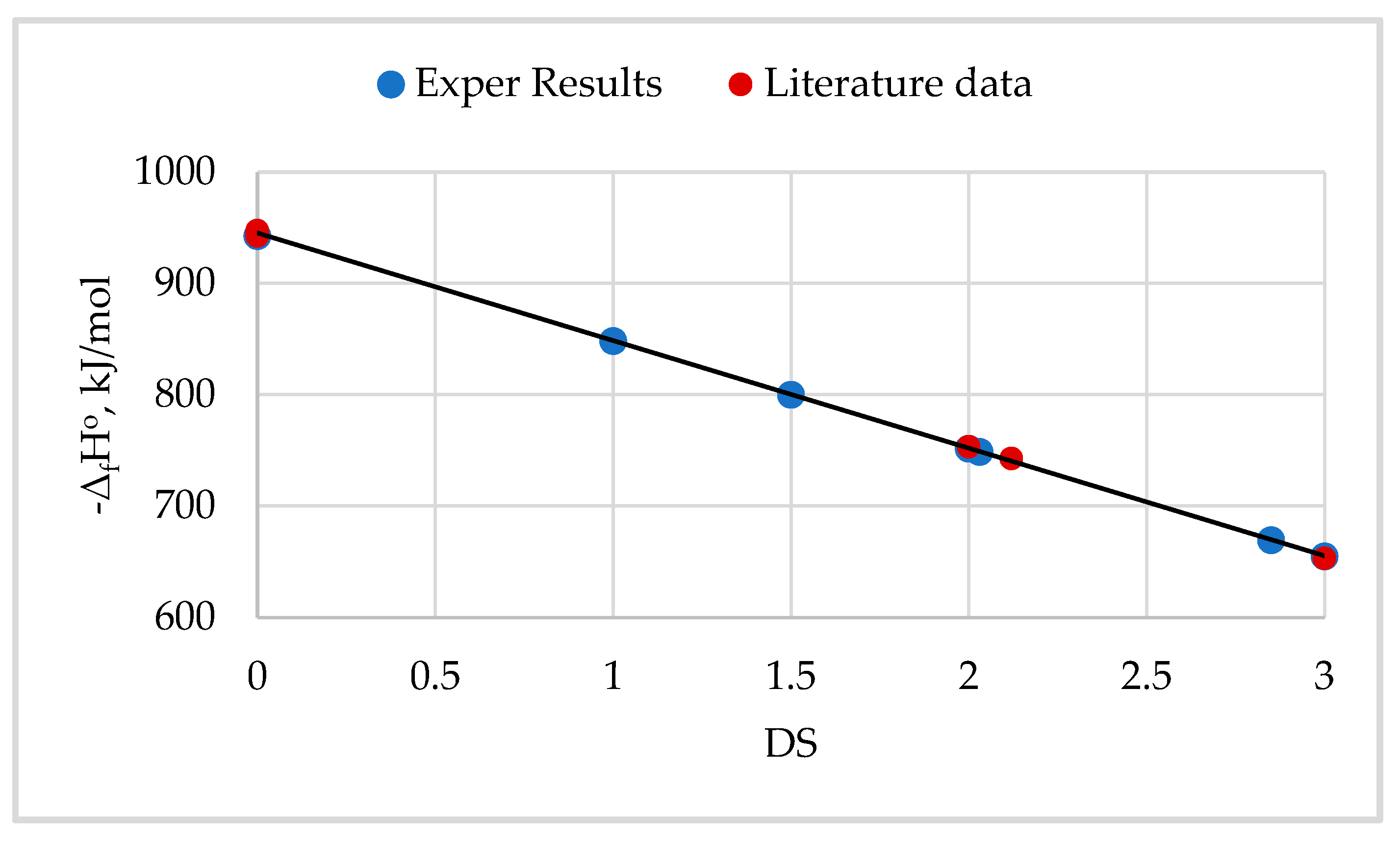
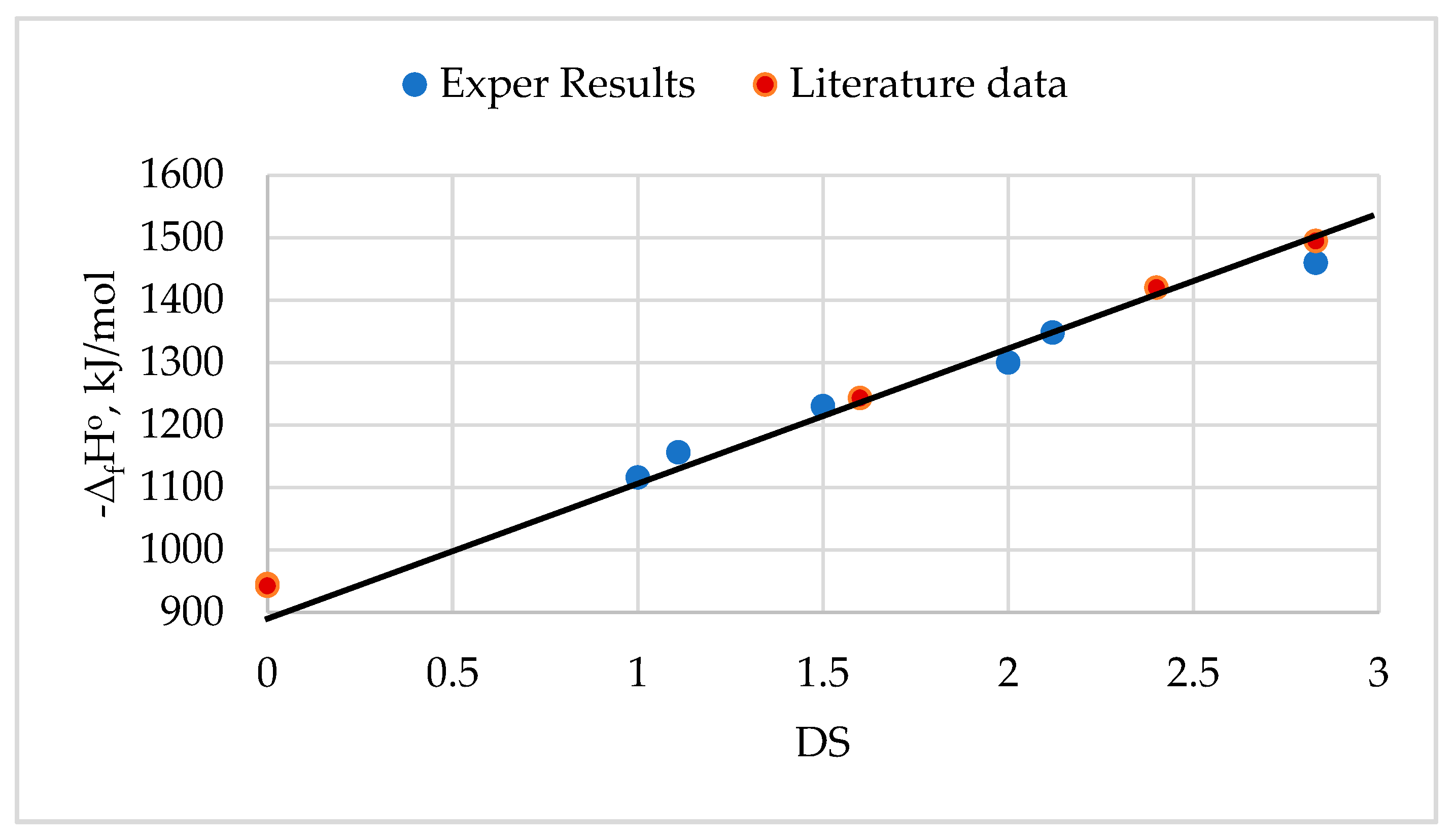
In addition to determining the degree of crystallinity, a thermochemical method was used to characterize the thermodynamic stability of cellulose crystallites with different types of crystalline allomorphs (CAs), I
β, II, III, IV, and amorphous cellulose (AMC). The results showed that the relative thermodynamic stability of cellulose CAs and AMC decreases in the following order:
On the other hand, the relative reactivity decreases in the reverse order:
The obtained thermodynamic characteristics allow to explain the phase transitions and reactivity of AMC and cellulose samples with different crystalline allomorphs.
When discussing the thermodynamic properties of cellulose nanocrystallites, the Gibbs-Thomson theory should be used. This theory allows one to explain various specific features of the nanocrystallites such as their spontaneous aggregation, a decrease in the melting temperature and an increase in solubility with a decrease in the crystallites size, the phase transition of small nanocrystallites of CA III into larger crystallites of CA IV during high-temperature treatment, and other properties.
To study the thermodynamics of chemical reactions involving biomass and its components, it is necessary to know the standard thermodynamic functions (TDFs) such as the enthalpy of formation (Δ
fH
o) and the entropy (S
o) for the starting materials, reagents, and reaction products. The enthalpy of the formation of the main components of plant biomass, cellulose, lignin, hemicelluloses, and other organic substances, can be determined experimentally by studying the enthalpy of combustion (Δ
cH
o):
where Δ
fH
o(CO
2,g) = -393.51 kJ/mol and Δ
fH
o(H
2O,l) = -285.83 kJ/mol are standard enthalpies of the formation of carbon dioxide and liquid water, respectively.
To determine the standard entropy of a substance, measurements of its specific heat capacity are usually carried out using a scanning vacuum adiabatic calorimeter in the temperature range from 0 to standard temperature, 298.15 K.
Values of standard TDFs for cellulose and other components of plant biomass can be also found in scientific literature. In addition, standard TDFs for most reagents and reaction products are given in handbooks on chemical thermodynamics.
These TDFs are used to calculate the enthalpy (Δ
rH
o) and entropy (Δ
rS
o) values of diverse chemical reactions. For example, let a chemical reaction occur between a feedstock (F) and a reagent (R) to form a reaction product (P):
Then, the change in reaction enthalpy will be:
while the change in reaction entropy:
The Gibbs potential of the reaction is calculated as follows
Such a potential is used to predict the feasibility of a chemical reaction, namely, if the Gibbs potential has a negative value, then the reaction can occur, and in the case of a positive value of this potential, the reaction cannot proceed. Almost all reactions considered in this review article are feasible and therefore have a negative Gibbs potential.
In addition, the Gibbs potential determines the value of the equilibrium constant (K
eq) of reversible reactions:
where EXP is the Euler's number “e”.
The more negative the value of ΔrGo, the greater the value of the equilibrium constant, and when the value of ΔrGo reaches -100, the reaction becomes practically irreversible. A typical example of such an irreversible reaction is the conversion of glucose solution into bioethanol with ΔrGo = -114.9 kJ/mol, the equilibrium constant of which has a very large value, Keq = 1.35 x 1020 (see section 6.1).
On the other hand, the value of Gibbs potential for the reaction of enzymatic hydrolysis of starch is not so large, ΔrGo = -19.54 kJ/mol; and therefore, the equilibrium constant of this process has a moderate value of Keq = 2.64 x 103, which indicates the possibility of reversibility of this reaction and a decrease in the yield of produced glucose compared to the theoretical value. The reaction of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose is also partially reversible.
Another important characteristic is the temperature coefficient of the reaction, which depends on the reaction enthalpy:
This coefficient allows to recommend whether to increase the reaction temperature or not. If the reaction is endothermic, then with increasing temperature the coefficient K
Т will increase, which improves the implementation of such a reaction. However, for exothermic reactions, an increase in temperature will cause a decrease in the coefficient K
T, which means a deterioration in the implementation of such a reaction.
An example of an endothermic reaction is the process of hydrothermal gasification of biochar obtained from plant biomass by the slow pyrolysis method:
It can be calculated that with an increase in the temperature of the gasification process from 973 to 1273 K, the value of the temperature coefficient will increase by 47 times, which should improve the yield of formed syngas. Further, this syngas can be used, e.g., for the synthesis of artificial hydrocarbon fuel by the Fischer-Tropsch method.
Almost all reactions involving cellulose considered in this review article are exothermic (
Table 24). Therefore, an increase in the temperature of the cellulose reactions reduces the thermal coefficient, which indicates a deterioration in the implementation of these reactions. For this reason, cellulose reactions occur at normal or moderate temperatures, usually in the range of 293 to 333 K.