Submitted:
21 November 2024
Posted:
25 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
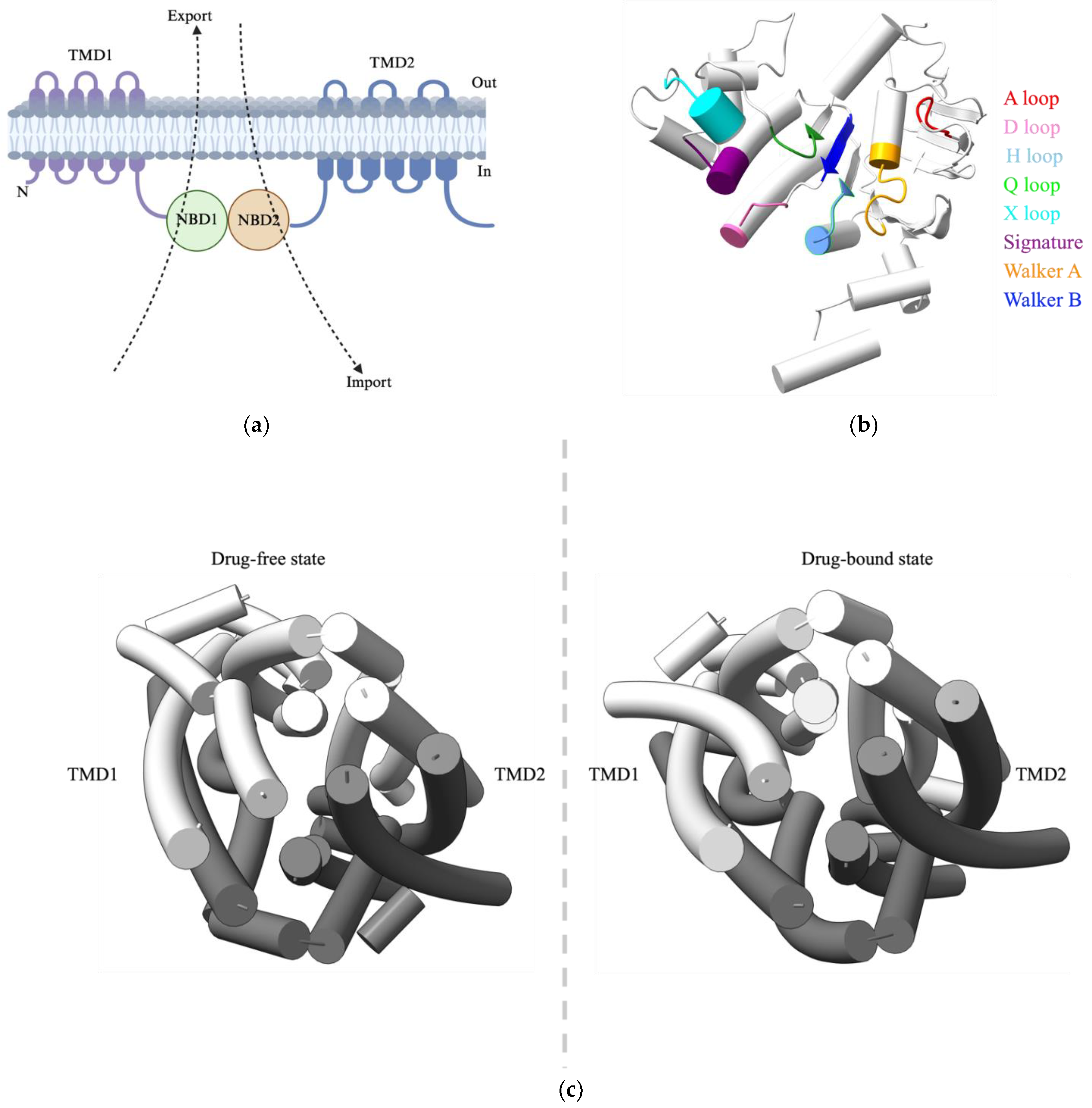
The general architecture of ABC transporters
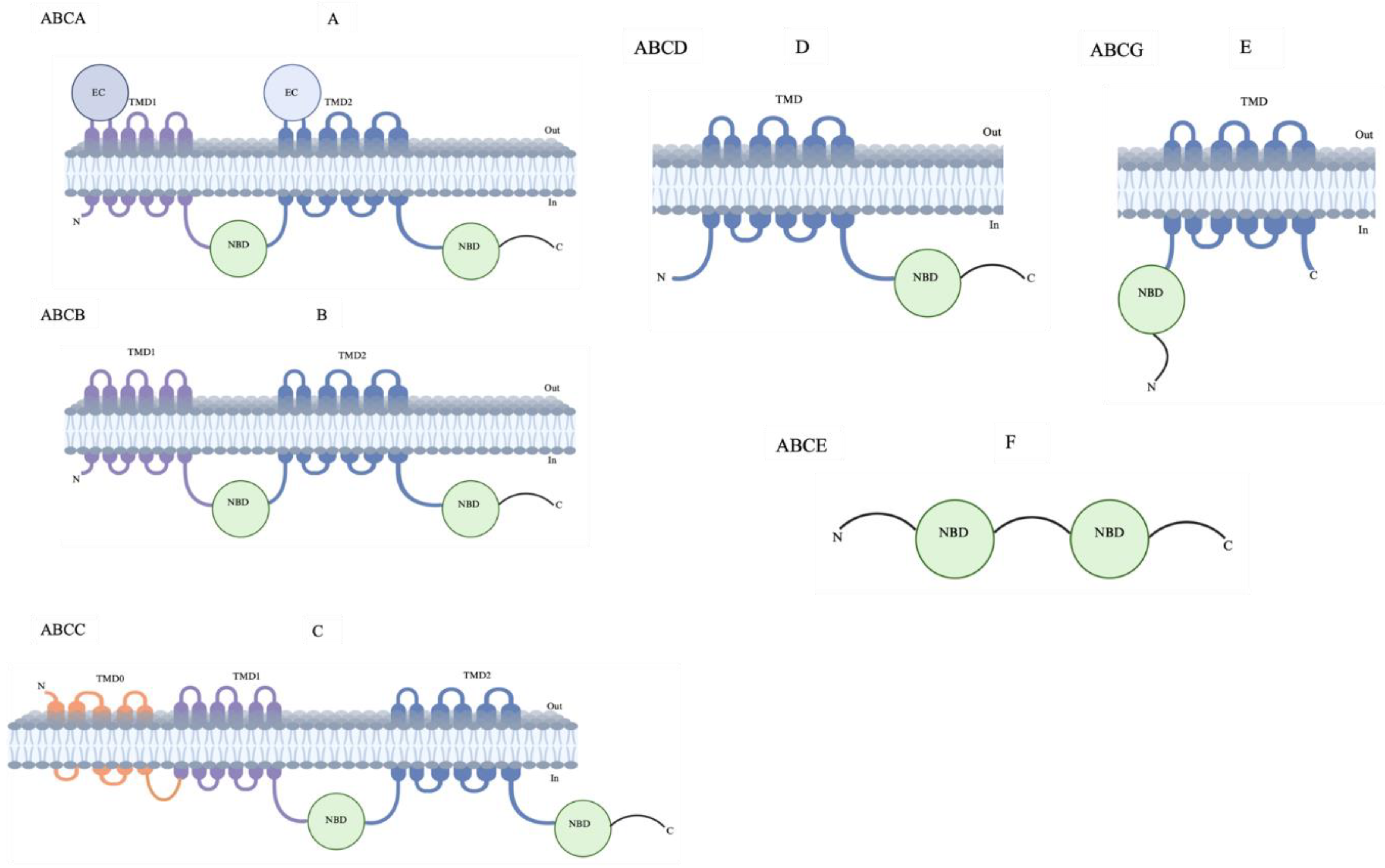
Classification of ABC Transporters
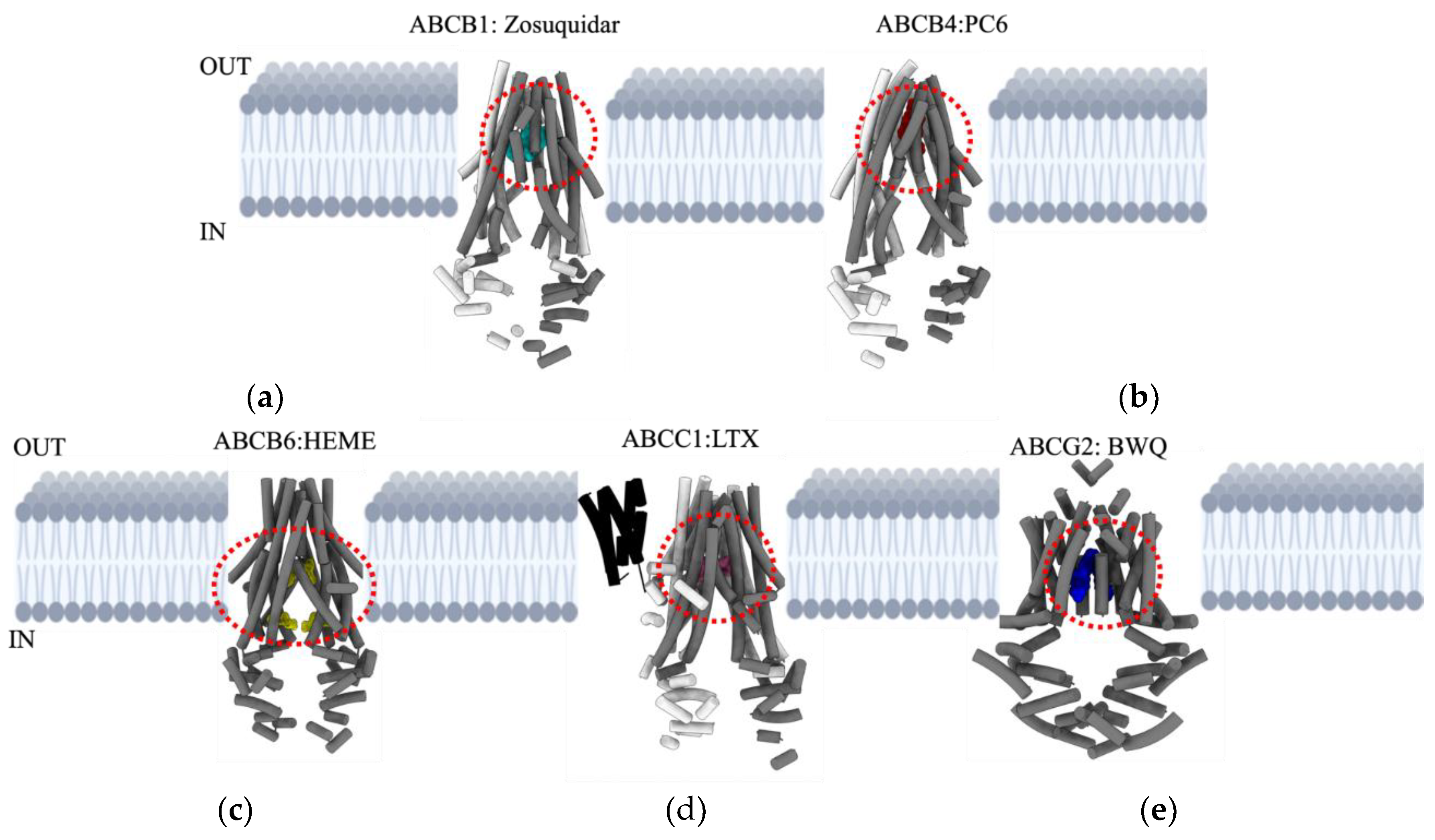
ABCB1
ABCB4
ABCB6
ABCC1
ABCG2
Mechanistic Overview of Drug Transport
Translational role and Therapeutic Targeting Strategies for ABC Transporters
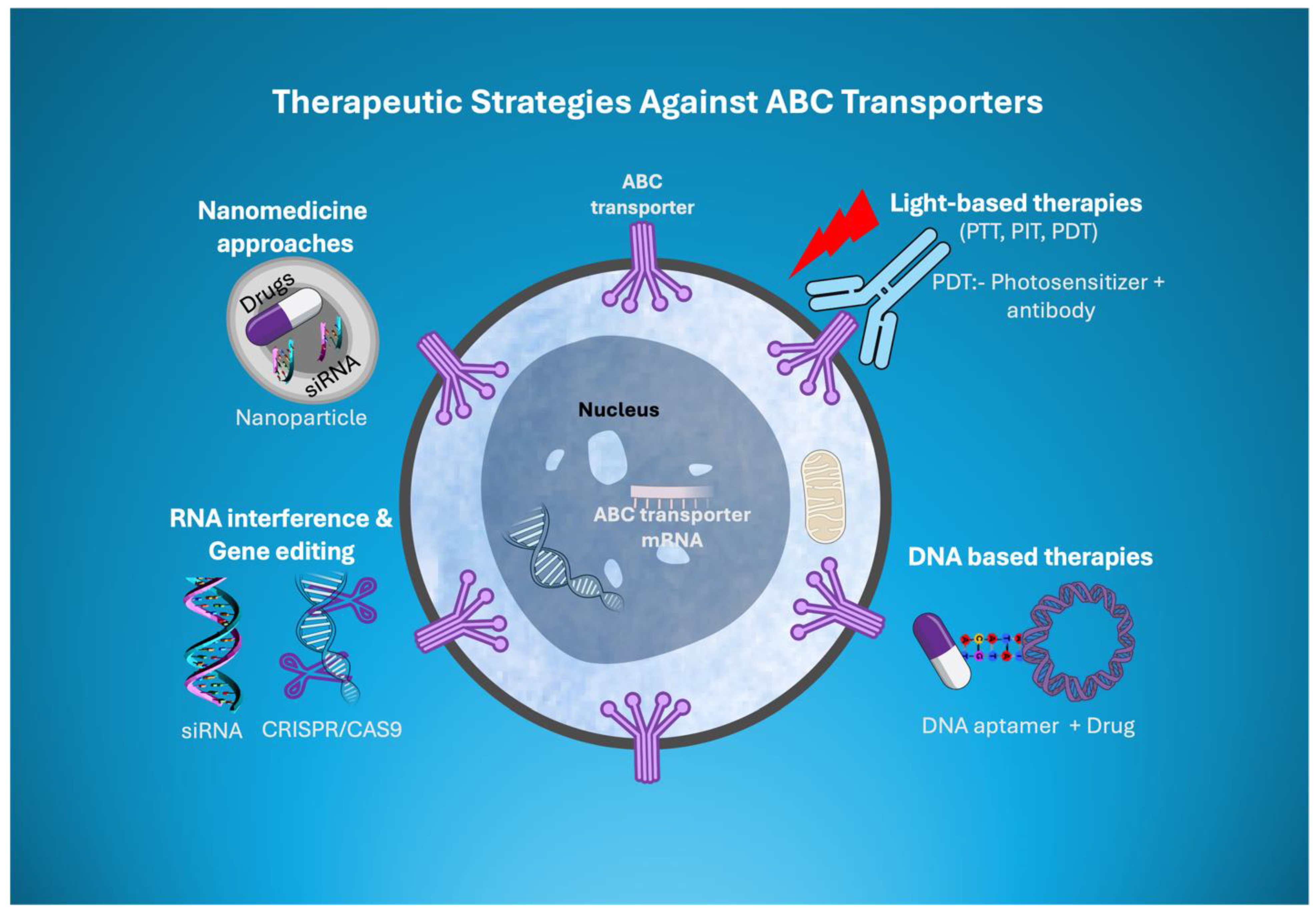
Novel Therapeutic Strategies Targeting ABC Transporters
Light-Based Therapies Coupled with ABC Transporter Inhibitors
DNA-Based Therapeutics
Nanomedicine Approaches
RNA Interference and Gene Editing
miRNA Targeting ABC Transporters
CRISPR/Cas9 Targeting ABC Transporter
Conclusions, Open Questions, and Future Perspectives
References
- Jokhadze, N., A. Das, and D.S. Dizon, Global cancer statistics: A healthy population relies on population health. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024. 74(3): p. 224-226. [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L., et al., Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin, 2023. 73(1): p. 17-48.
- Ferlay J, E.M., Lam F, Laversanne M, Colombet M, Mery L, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Soerjomataram I, Bray F Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. . 2024.
- Ahmed, S., et al., Anticancer Potential of Furanocoumarins: Mechanistic and Therapeutic Aspects. Int J Mol Sci, 2020. 21(16). [CrossRef]
- Housman, G., et al., Drug resistance in cancer: an overview. Cancers (Basel), 2014. 6(3): p. 1769-92. [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, B., et al., The Different Mechanisms of Cancer Drug Resistance: A Brief Review. Adv Pharm Bull, 2017. 7(3): p. 339-348. [CrossRef]
- Cancer multidrug resistance. Nature Biotechnology, 2000. 18(10): p. IT18-IT20.
- Emran, T.B., et al., Multidrug Resistance in Cancer: Understanding Molecular Mechanisms, Immunoprevention and Therapeutic Approaches. Front Oncol, 2022. 12: p. 891652nce in Cancer: Understanding Molecular Mechanisms, Immunoprevention and Therapeutic Approaches. Front Oncol, 2022. 12: p. 891652.
- Debela, D.T., et al., New approaches and procedures for cancer treatment: Current perspectives. SAGE Open Medicine, 2021. 9: p. 20503121211034366. [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.I., et al., ABC transporters in cancer: more than just drug efflux pumps. Nat Rev Cancer, 2010. 10(2): p. 147-56. [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q., et al., Gaseous signaling molecules and their application in resistant cancer treatment: from invisible to visible. Future Med Chem, 2019. 11(4): p. 323-336. [CrossRef]
- Doyle, L.A., et al., A multidrug resistance transporter from human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1998. 95(26): p. 15665-70. [CrossRef]
- Allikmets, R., et al., A human placenta-specific ATP-binding cassette gene (ABCP) on chromosome 4q22 that is involved in multidrug resistance. Cancer Res, 1998. 58(23): p. 5337-9.
- Giacomini, K.M., et al., New and Emerging Research on Solute Carrier and ATP Binding Cassette Transporters in Drug Discovery and Development: Outlook From the International Transporter Consortium. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2022. 112(3): p. 540-561. [CrossRef]
- Stockner, T., R. Gradisch, and L. Schmitt, The role of the degenerate nucleotide binding site in type I ABC exporters. FEBS Lett, 2020. 594(23): p. 3815-3838. [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.F., et al., Three-dimensional Structures of the Mammalian Multidrug Resistance P-glycoprotein Demonstrate Major Conformational Changes in the Transmembrane Domains upon Nucleotide Binding*. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2003. 278(10): p. 8294-8299. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C., et al., Structural and functional diversity calls for a new classification of ABC transporters. FEBS Lett, 2020. 594(23): p. 3767-3775. [CrossRef]
- Borst, P. and R.O. Elferink, Mammalian ABC transporters in health and disease. Annu Rev Biochem, 2002. 71: p. 537-92. [CrossRef]
- Murina, V., et al., ABCF ATPases Involved in Protein Synthesis, Ribosome Assembly and Antibiotic Resistance: Structural and Functional Diversification across the Tree of Life. J Mol Biol, 2019. 431(18): p. 3568-3590. [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Quiles, C., E. Mateo-Bonmatí, and J.L. Micol, ABCE Proteins: From Molecules to Development. Front Plant Sci, 2018. 9: p. 1125. [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, M.L., Z. Mujawar, and N. Tamehiro, ABC transporters, atherosclerosis and inflammation. Atherosclerosis, 2010. 211(2): p. 361-70.
- Xie, T., et al., Cryo-EM structures of the human surfactant lipid transporter ABCA3. Sci Adv, 2022. 8(14): p. eabn3727. [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.G., A. Geier, and R.P. Oude Elferink, ABC of oral bioavailability: transporters as gatekeepers in the gut. Gut, 2003. 52(12): p. 1788-95. [CrossRef]
- Durmus, S., J.J. Hendrikx, and A.H. Schinkel, Apical ABC transporters and cancer chemotherapeutic drug disposition. Adv Cancer Res, 2015. 125: p. 1-41.
- (USFDA), U.F.A.C.D.E.R., Invitro drug interaction studies—cytochrome P450 enzyme- and transporter-mediated drug interactions: guidance for industry. Guidance Doc., US FDA., 2020.
- Wang, J.Q., et al., Multidrug resistance proteins (MRPs): Structure, function and the overcoming of cancer multidrug resistance. Drug Resist Updat, 2021. 54: p. 100743. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.S., et al., Characterization of the transport properties of human multidrug resistance protein 7 (MRP7, ABCC10). Mol Pharmacol, 2003. 63(2): p. 351-8. [CrossRef]
- Hopper-Borge, E., et al., Human multidrug resistance protein 7 (ABCC10) is a resistance factor for nucleoside analogues and epothilone B. Cancer Res, 2009. 69(1): p. 178-84.
- Leslie, E.M., R.G. Deeley, and S.P. Cole, Multidrug resistance proteins: role of P-glycoprotein, MRP1, MRP2, and BCRP (ABCG2) in tissue defense. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2005. 204(3): p. 216-37. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., et al., Characterization of the kinetic cycle of an ABC transporter by single-molecule and cryo-EM analyses. eLife, 2020. 9: p. e56451. [CrossRef]
- Quazi, F., S. Lenevich, and R.S. Molday, ABCA4 is an N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylethanolamine importer. Nat Commun, 2012. 3: p. 925. [CrossRef]
- van Roermund, C.W., et al., The human peroxisomal ABC half transporter ALDP functions as a homodimer and accepts acyl-CoA esters. Faseb j, 2008. 22(12): p. 4201-8.
- van Roermund, C.W., et al., Differential substrate specificities of human ABCD1 and ABCD2 in peroxisomal fatty acid β-oxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2011. 1811(3): p. 148-52.
- Xu, D., et al., Cryo-EM structure of human lysosomal cobalamin exporter ABCD4. Cell Research, 2019. 29(12): p. 1039-1041.
- Liang, X., et al., p62/mTOR/LXRα pathway inhibits cholesterol efflux mediated by ABCA1 and ABCG1 during autophagy blockage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2019. 514(4): p. 1093-1100. [CrossRef]
- Hegyi, Z. and L. Homolya, Functional Cooperativity between ABCG4 and ABCG1 Isoforms. PLoS One, 2016. 11(5): p. e0156516.
- Leslie, E.M., R.G. Deeley, and S.P.C. Cole, Multidrug resistance proteins: role of P-glycoprotein, MRP1, MRP2, and BCRP (ABCG2) in tissue defense. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2005. 204(3): p. 216-237.
- Mo, W. and J.T. Zhang, Human ABCG2: structure, function, and its role in multidrug resistance. Int J Biochem Mol Biol, 2012. 3(1): p. 1-27.
- Szakács, G., et al., The role of ABC transporters in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity (ADME–Tox). Drug Discovery Today, 2008. 13(9): p. 379-393. [CrossRef]
- Kadioglu, O., et al., Effect of ABC transporter expression and mutational status on survival rates of cancer patients. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020. 131: p. 110718. [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, M.N., I.J. Slotnick, and L.J. Journey, In vitro studies with HeLa cell line sensitive and resistant to actinomycin D. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 1960. 89: p. 474-83. [CrossRef]
- Juliano, R.L. and V. Ling, A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1976. 455(1): p. 152-62. [CrossRef]
- Fromm, M.F., Importance of P-glycoprotein at blood-tissue barriers. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2004. 25(8): p. 423-9. [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S., et al., DrugBank: a comprehensive resource for in silico drug discovery and exploration. Nucleic Acids Res, 2006. 34(Database issue): p. D668-72. [CrossRef]
- Giacomini, K.M., et al., Membrane transporters in drug development. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2010. 9(3): p. 215-236. [CrossRef]
- Robey, R.W., et al., Revisiting the role of ABC transporters in multidrug-resistant cancer. Nat Rev Cancer, 2018. 18(7): p. 452-464. [CrossRef]
- Gottesman, M.M. and V. Ling, The molecular basis of multidrug resistance in cancer: the early years of P-glycoprotein research. FEBS Lett, 2006. 580(4): p. 998-1009. [CrossRef]
- Aller, S.G., et al., Structure of P-glycoprotein reveals a molecular basis for poly-specific drug binding. Science, 2009. 323(5922): p. 1718-22.
- Jin, M.S., et al., Crystal structure of the multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein from Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature, 2012. 490(7421): p. 566-569. [CrossRef]
- Kodan, A., et al., Structural basis for gating mechanisms of a eukaryotic P-glycoprotein homolog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2014. 111(11): p. 4049-54. [CrossRef]
- Alam, A., et al., Structural insight into substrate and inhibitor discrimination by human P-glycoprotein. Science, 2019. 363(6428): p. 753-756. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y. and J. Chen, Molecular structure of human P-glycoprotein in the ATP-bound, outward-facing conformation. Science, 2018. 359(6378): p. 915-919. [CrossRef]
- Waghray, D. and Q. Zhang, Inhibit or Evade Multidrug Resistance P-Glycoprotein in Cancer Treatment. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2018. 61(12): p. 5108-5121. [CrossRef]
- Nosol, K., et al., Cryo-EM structures reveal distinct mechanisms of inhibition of the human multidrug transporter ABCB1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2020. 117(42): p. 26245-26253. [CrossRef]
- Dash, R.P., R. Jayachandra Babu, and N.R. Srinivas, Therapeutic Potential and Utility of Elacridar with Respect to P-glycoprotein Inhibition: An Insight from the Published In Vitro, Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 2017. 42(6): p. 915-933. [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, N.R., Understanding the role of tariquidar, a potent Pgp inhibitor, in combination trials with cytotoxic drugs: What is missing? Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2016. 78(5): p. 1097-1098.
- Alam, A., et al., Structure of a zosuquidar and UIC2-bound human-mouse chimeric ABCB1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2018. 115(9): p. E1973-e1982. [CrossRef]
- Martino, E., et al., Vinca alkaloids and analogues as anti-cancer agents: Looking back, peering ahead. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2018. 28(17): p. 2816-2826. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X., et al., Double-sides sticking mechanism of vinblastine interacting with α,β-tubulin to get activity against cancer cells. J Biomol Struct Dyn, 2019. 37(15): p. 4080-4091.
- Crowley, E., C.A. McDevitt, and R. Callaghan, Generating inhibitors of P-glycoprotein: where to, now? Methods Mol Biol, 2010. 596: p. 405-32.
- Hyafil, F., et al., In vitro and in vivo reversal of multidrug resistance by GF120918, an acridonecarboxamide derivative. Cancer Res, 1993. 53(19): p. 4595-602.
- Cripe, L.D., et al., Zosuquidar, a novel modulator of P-glycoprotein, does not improve the outcome of older patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group 3999. Blood, 2010. 116(20): p. 4077-85. [CrossRef]
- Mechetner, E.B. and I.B. Roninson, Efficient inhibition of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance with a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1992. 89(13): p. 5824-8. [CrossRef]
- Morita, S.Y. and T. Terada, Molecular mechanisms for biliary phospholipid and drug efflux mediated by ABCB4 and bile salts. Biomed Res Int, 2014. 2014: p. 954781. [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.J., et al., MDR3 P-glycoprotein, a phosphatidylcholine translocase, transports several cytotoxic drugs and directly interacts with drugs as judged by interference with nucleotide trapping. J Biol Chem, 2000. 275(31): p. 23530-9. [CrossRef]
- Sticova, E. and M. Jirsa, ABCB4 disease: Many faces of one gene deficiency. Annals of Hepatology, 2020. 19(2): p. 126-133. [CrossRef]
- Morita, S.Y., et al., Bile salt-stimulated phospholipid efflux mediated by ABCB4 localized in nonraft membranes. J Lipid Res, 2013. 54(5): p. 1221-30. [CrossRef]
- Smit, J.J., et al., Homozygous disruption of the murine mdr2 P-glycoprotein gene leads to a complete absence of phospholipid from bile and to liver disease. Cell, 1993. 75(3): p. 451-62. [CrossRef]
- Boyer, J.L., Bile formation and secretion. Compr Physiol, 2013. 3(3): p. 1035-78. [CrossRef]
- Fagerberg, L., et al., Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics, 2014. 13(2): p. 397-406. [CrossRef]
- de Vree, J.M., et al., Mutations in the MDR3 gene cause progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1998. 95(1): p. 282-7. [CrossRef]
- Oude Elferink, R.P. and C.C. Paulusma, Function and pathophysiological importance of ABCB4 (MDR3 P-glycoprotein). Pflugers Arch, 2007. 453(5): p. 601-10.
- Tougeron, D., et al., ABCB4/MDR3 gene mutations and cholangiocarcinomas. J Hepatol, 2012. 57(2): p. 467-8.
- Mhatre, S., et al., Common genetic variation and risk of gallbladder cancer in India: a case-control genome-wide association study. Lancet Oncol, 2017. 18(4): p. 535-544. [CrossRef]
- Kiehl, S., et al., ABCB4 is frequently epigenetically silenced in human cancers and inhibits tumor growth. Sci Rep, 2014. 4: p. 6899. [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.A., et al., Structure of the human lipid exporter ABCB4 in a lipid environment. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2020. 27(1): p. 62-707(1): p. 62-70. [CrossRef]
- Nosol, K., et al., Structures of ABCB4 provide insight into phosphatidylcholine translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2021. 118(33). [CrossRef]
- Ishigami, M., et al., ATPase activity of nucleotide binding domains of human MDR3 in the context of MDR1. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2013. 1831(4): p. 683-90. [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, Z.M., et al., Role of Multidrug Resistance Protein 3 in Antifungal-Induced Cholestasis. Mol Pharmacol, 2016. 90(1): p. 23-34. [CrossRef]
- Frampton, J.E. and L.J. Scott, Posaconazole : a review of its use in the prophylaxis of invasive fungal infections. Drugs, 2008. 68(7): p. 993-1016.
- Kiss, K., et al., Role of the N-terminal transmembrane domain in the endo-lysosomal targeting and function of the human ABCB6 protein. Biochem J, 2015. 467(1): p. 127-39. [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, Y., et al., Conserved intramolecular disulfide bond is critical to trafficking and fate of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters ABCB6 and sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1)/ABCC8. J Biol Chem, 2011. 286(10): p. 8481-8492.
- Boswell-Casteel, R.C., Y. Fukuda, and J.D. Schuetz, ABCB6, an ABC Transporter Impacting Drug Response and Disease. Aaps j, 2017. 20(1): p. 8. [CrossRef]
- Minami, K., et al., Expression of ABCB6 is related to resistance to 5-FU, SN-38 and vincristine. Anticancer Res, 2014. 34(9): p. 4767-73.
- Yasui, K., et al., Alteration in copy numbers of genes as a mechanism for acquired drug resistance. Cancer Res, 2004. 64(4): p. 1403-10. [CrossRef]
- Rakvács, Z., et al., The human ABCB6 protein is the functional homologue of HMT-1 proteins mediating cadmium detoxification. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2019. 76(20): p. 4131-4144. [CrossRef]
- Burke, M.A. and H. Ardehali, Mitochondrial ATP-binding cassette proteins. Transl Res, 2007. 150(2): p. 73-80. [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, P. and J.D. Schuetz, The role of ABCG2 and ABCB6 in porphyrin metabolism and cell survival. Curr Pharm Biotechnol, 2011. 12(4): p. 647-55. [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, P., T. Xie, and J.D. Schuetz, The role of transporters in cellular heme and porphyrin homeostasis. Pharmacol Ther, 2007. 114(3): p. 345-58. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., et al., ABCB6 mutations cause ocular coloboma. Am J Hum Genet, 2012. 90(1): p. 40-8. [CrossRef]
- Andolfo, I., et al., Missense mutations in the ABCB6 transporter cause dominant familial pseudohyperkalemia. Am J Hematol, 2013. 88(1): p. 66-72. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C., et al., Mutations in ABCB6 cause dyschromatosis universalis hereditaria. J Invest Dermatol, 2013. 133(9): p. 2221-8. [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, P.C., et al., Identification of a mammalian mitochondrial porphyrin transporter. Nature, 2006. 443(7111): p. 586-9. [CrossRef]
- Polireddy, K., et al., A novel flow cytometric HTS assay reveals functional modulators of ATP binding cassette transporter ABCB6. PLoS One, 2012. 7(7): p. e40005. [CrossRef]
- Park, S., et al., Gene expression profiling of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters as a predictor of the pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2006. 99(1): p. 9-17. [CrossRef]
- Januchowski, R., et al., Microarray-based detection and expression analysis of ABC and SLC transporters in drug-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines. Biomed Pharmacother, 2013. 67(3): p. 240-5. [CrossRef]
- Varatharajan, S., et al., ATP-binding casette transporter expression in acute myeloid leukemia: association with in vitro cytotoxicity and prognostic markers. Pharmacogenomics, 2017. 18(3): p. 235-244. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C., et al., Cryo-electron microscopy structure of human ABCB6 transporter. Protein Sci, 2020. 29(12): p. 2363-2374. [CrossRef]
- Song, G., et al., Molecular insights into the human ABCB6 transporter. Cell Discovery, 2021. 7(1): p. 55. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S., et al., Structural Insights into Porphyrin Recognition by the Human ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter ABCB6. Mol Cells, 2022. 45(8): p. 575-587.
- Lee, S.S., et al., W546 stacking disruption traps the human porphyrin transporter ABCB6 in an outward-facing transient state. Commun Biol, 2023. 6(1): p. 960. [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H., et al., Cryo-EM structure of cadmium-bound human ABCB6. Communications Biology, 2024. 7(1): p. 672. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, Z.L. and J. Chen, Structural Basis of Substrate Recognition by the Multidrug Resistance Protein MRP1. Cell, 2017. 168(6): p. 1075-1085.e9. [CrossRef]
- Conseil, G., et al., Structure-guided probing of the leukotriene C(4) binding site in human multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1; ABCC1). Faseb j, 2019. 33(10): p. 10692-10704. [CrossRef]
- Bakos, E., et al., Characterization of the amino-terminal regions in the human multidrug resistance protein (MRP1). J Cell Sci, 2000. 113 Pt 24: p. 4451-61. [CrossRef]
- Slot, A.J., S.V. Molinski, and S.P. Cole, Mammalian multidrug-resistance proteins (MRPs). Essays Biochem, 2011. 50(1): p. 179-207. [CrossRef]
- Seelig, A., A general pattern for substrate recognition by P-glycoprotein. Eur J Biochem, 1998. 251(1-2): p. 252-61. [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.Y., et al., Characterization and analyses of multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1/ABCC1) polymorphisms in Chinese population. Pharmacogenet Genomics, 2009. 19(3): p. 206-16.
- Taylor, N.M.I., et al., Structure of the human multidrug transporter ABCG2. Nature, 2017. 546(7659): p. 504-509. [CrossRef]
- Kowal, J., et al., Structural Basis of Drug Recognition by the Multidrug Transporter ABCG2. J Mol Biol, 2021. 433(13): p. 166980.
- Toyoda, Y., T. Takada, and H. Suzuki, Inhibitors of Human ABCG2: From Technical Background to Recent Updates With Clinical Implications. Front Pharmacol, 2019. 10: p. 208. [CrossRef]
- Houghton, P.J., et al., Imatinib mesylate is a potent inhibitor of the ABCG2 (BCRP) transporter and reverses resistance to topotecan and SN-38 in vitro. Cancer Res, 2004. 64(7): p. 2333-7. [CrossRef]
- Candeil, L., et al., ABCG2 overexpression in colon cancer cells resistant to SN38 and in irinotecan-treated metastases. Int J Cancer, 2004. 109(6): p. 848-54. [CrossRef]
- Hillgren, K.M., et al., Emerging transporters of clinical importance: an update from the International Transporter Consortium. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2013. 94(1): p. 52-63. [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, A., et al., The controversial role of ABC transporters in clinical oncology. Essays Biochem, 2011. 50(1): p. 209-32. [CrossRef]
- Robey, R.W., et al., ABC transporters: unvalidated therapeutic targets in cancer and the CNS. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 2010. 10(8): p. 625-33. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S., et al., The ABC transporter Bcrp1/ABCG2 is expressed in a wide variety of stem cells and is a molecular determinant of the side-population phenotype. Nature Medicine, 2001. 7(9): p. 1028-1034.
- Lee, J.Y., et al., Crystal structure of the human sterol transporter ABCG5/ABCG8. Nature, 2016. 533(7604): p. 561-4.
- Rosenberg, M.F., et al., Three-dimensional structure of the human breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) in an inward-facing conformation. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 2015. 71(Pt 8): p. 1725-35. [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.M., et al., Structural basis of small-molecule inhibition of human multidrug transporter ABCG2. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2018. 25(4): p. 333-340. [CrossRef]
- Manolaridis, I., et al., Cryo-EM structures of a human ABCG2 mutant trapped in ATP-bound and substrate-bound states. Nature, 2018. 563(7731): p. 426-430.
- Yu, Q., et al., Structures of ABCG2 under turnover conditions reveal a key step in the drug transport mechanism. Nature Communications, 2021. 12(1): p. 4376.
- Puentes, C.O., et al., Solid phase synthesis of tariquidar-related modulators of ABC transporters preferring breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2). Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2011. 21(12): p. 3654-7. [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.D., et al., Potent and specific inhibition of the breast cancer resistance protein multidrug transporter in vitro and in mouse intestine by a novel analogue of fumitremorgin C. Mol Cancer Ther, 2002. 1(6): p. 417-25.
- Weidner, L.D., et al., The Inhibitor Ko143 Is Not Specific for ABCG2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2015. 354(3): p. 384-93. [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Puentes, C., et al., Benzanilide-Biphenyl Replacement: A Bioisosteric Approach to Quinoline Carboxamide-Type ABCG2 Modulators. ACS Med Chem Lett, 2013. 4(4): p. 393-6. [CrossRef]
- Roe, M., et al., Reversal of P-glycoprotein mediated multidrug resistance by novel anthranilamide derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 1999. 9(4): p. 595-600. [CrossRef]
- Köhler, S.C. and M. Wiese, HM30181 Derivatives as Novel Potent and Selective Inhibitors of the Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP/ABCG2). J Med Chem, 2015. 58(9): p. 3910-21. [CrossRef]
- Miyata, H., et al., Identification of Febuxostat as a New Strong ABCG2 Inhibitor: Potential Applications and Risks in Clinical Situations. Front Pharmacol, 2016. 7: p. 518. [CrossRef]
- Ji, N., et al., VS-4718 Antagonizes Multidrug Resistance in ABCB1- and ABCG2-Overexpressing Cancer Cells by Inhibiting the Efflux Function of ABC Transporters. Front Pharmacol, 2018. 9: p. 1236. [CrossRef]
- Alam, A. and K.P. Locher, Structure and Mechanism of Human ABC Transporters. Annu Rev Biophys, 2023. 52: p. 275-300. [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.M. and A.M. George, The Switch and Reciprocating Models for the Function of ABC Multidrug Exporters: Perspectives on Recent Research. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023. 24(3): p. 2624. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T., et al., Oxidative stress-mediated up-regulation of ABC transporters in lung cancer cells. J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2022. 36(8): p. e23095. [CrossRef]
- Sajid, A., H. Rahman, and S.V. Ambudkar, Advances in the structure, mechanism and targeting of chemoresistance-linked ABC transporters. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2023. 23(11): p. 762-779. [CrossRef]
- Lainey, E., et al., Erlotinib antagonizes ABC transporters in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Cycle, 2012. 11(21): p. 4079-4092. [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, I.S., W. He, and L. Yin, Insight on Multidrug Resistance and Nanomedicine Approaches to Overcome MDR. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst, 2020. 37(5): p. 473-509. [CrossRef]
- Pote, M.S. and R.N. Gacche, ATP-binding cassette efflux transporters and MDR in cancer. Drug Discovery Today, 2023. 28(5): p. 103537. [CrossRef]
- Cui, H., et al., ABC Transporter Inhibitors in Reversing Multidrug Resistance to Chemotherapy. Curr Drug Targets, 2015. 16(12): p. 1356-71. [CrossRef]
- Falasca, M. and K.J. Linton, Investigational ABC transporter inhibitors. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 2012. 21(5): p. 657-6666. [CrossRef]
- Friedenberg, W.R., et al., Phase III study of PSC-833 (valspodar) in combination with vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone (valspodar/VAD) versus VAD alone in patients with recurring or refractory multiple myeloma (E1A95). Cancer, 2006. 106(4): p. 830-838. [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.J., et al., A Pharmacodynamic Study of Docetaxel in Combination with the P-glycoprotein Antagonist Tariquidar (XR9576) in Patients with Lung, Ovarian, and Cervical Cancer. Clinical Cancer Research, 2011. 17(3): p. 569-580. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-L., et al., Reversal of MRP7 (ABCC10)-Mediated Multidrug Resistance by Tariquidar. PLOS ONE, 2013. 8(2): p. e55576. [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, A., et al., The controversial role of ABC transporters in clinical oncology. Essays in Biochemistry, 2011. 50: p. 209-232. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H., et al., Clinically-Relevant ABC Transporter for Anti-Cancer Drug Resistance. Front Pharmacol, 2021. 12: p. 648407. [CrossRef]
- Yu, M., A. Ocana, and I.F. Tannock, Reversal of ATP-binding cassette drug transporter activity to modulate chemoresistance: why has it failed to provide clinical benefit? Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2013. 32(1-2): p. 211-27.
- Krapf, M.K., et al., Synthesis and biological evaluation of quinazoline derivatives - A SAR study of novel inhibitors of ABCG2. Eur J Med Chem, 2019. 161: p. 506-525. [CrossRef]
- Mohajeri, M. and A. Sahebkar, Protective effects of curcumin against doxorubicin-induced toxicity and resistance: A review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2018. 122: p. 30-51. [CrossRef]
- Omori, M., et al., Inhibitors of ABCB1 and ABCG2 overcame resistance to topoisomerase inhibitors in small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer, 2022. 13(15): p. 2142-2151. [CrossRef]
- Yarla, N.S., Bioactive Flavonoids as ABC Transporters Inhibitors for Reversion of Multidrug Resistance in Cancer. Journal of Marine Science: Research & Development, 2013. 4: p. 1-2.
- van der Noord, V.E., et al., Systematic screening identifies ABCG2 as critical factor underlying synergy of kinase inhibitors with transcriptional CDK inhibitors. Breast Cancer Res, 2023. 25(1): p. 51.
- Liu, L., et al., IGHMBP2-related clinical and genetic features in a cohort of Chinese Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2 patients. Neuromuscul Disord, 2017. 27(2): p. 193-199. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C., et al., Near-infrared light induced in vivo photodynamic therapy of cancer based on upconversion nanoparticles. Biomaterials, 2011. 32(26): p. 6145-54. [CrossRef]
- Bui, K.C., et al., X-ray-irradiated K562 feeder cells for expansion of functional CAR-T cells. Biochem Biophys Rep, 2023. 33: p. 101399. [CrossRef]
- Du, J., et al., Comparative analysis of the immune responses in cancer cells irradiated with X-ray, proton and carbon-ion beams. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2021. 585: p. 55-60. [CrossRef]
- Kawanishi, M., M. Fujita, and K. Karasawa, Combining Carbon-Ion Irradiation and PARP Inhibitor, Olaparib Efficiently Kills BRCA1-Mutated Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Breast Cancer (Auckl), 2022. 16: p. 11782234221080553. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D., et al., Application of MOF-based nanotherapeutics in light-mediated cancer diagnosis and therapy. J Nanobiotechnology, 2022. 20(1): p. 421. [CrossRef]
- De Vera, A.A., et al., Immuno-oncology agent IPI-549 is a modulator of P-glycoprotein (P-gp, MDR1, ABCB1)-mediated multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer: In vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett, 2019. 442: p. 91-103.
- Bihorel, S., et al., Modulation of the brain distribution of imatinib and its metabolites in mice by valspodar, zosuquidar and elacridar. Pharm Res, 2007. 24(9): p. 1720-8. [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.H., et al., Direct toxicity of Rose Bengal in MCF-7 cell line: role of apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol, 2009. 47(4): p. 855-9. [CrossRef]
- He, J., et al., Recent progress of aptamer‒drug conjugates in cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2023. 13(4): p. 1358-1370. [CrossRef]
- Ma, W., et al., Self-Assembled Multivalent Aptamer Drug Conjugates: Enhanced Targeting and Cytotoxicity for HER2-Positive Gastric Cancer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2023. 15(37): p. 43359-43373. [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H., et al., Combining ABCG2 Inhibitors with IMMU-132, an Anti-Trop-2 Antibody Conjugate of SN-38, Overcomes Resistance to SN-38 in Breast and Gastric Cancers. Mol Cancer Ther, 2016. 15(8): p. 1910-9.
- Pieper, S., et al., Incorporation of doxorubicin in different polymer nanoparticles and their anticancer activity. Beilstein J Nanotechnol, 2019. 10: p. 2062-2072. [CrossRef]
- Lage, H., Gene Therapeutic Approaches to Overcome ABCB1-Mediated Drug Resistance. Recent Results Cancer Res, 2016. 209: p. 87-94.
- Varlas, S., T.J. Neal, and S.P. Armes, Polymerization-induced self-assembly and disassembly during the synthesis of thermoresponsive ABC triblock copolymer nano-objects in aqueous solution. Chem Sci, 2022. 13(24): p. 7295-7303. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P., S.V. Ambudkar, and N. Rajendra Prasad, Emerging nanotechnology-based therapeutics to combat multidrug-resistant cancer. J Nanobiotechnology, 2022. 20(1): p. 423. [CrossRef]
- Kunjachan, S., et al., Multidrug resistance: Physiological principles and nanomedical solutions. Adv Drug Deliv Rev, 2013. 65(13-14): p. 1852-1865. [CrossRef]
- de la Puente, P. and A.K. Azab, Nanoparticle delivery systems, general approaches, and their implementation in multiple myeloma. Eur J Haematol, 2017. 98(6): p. 529-541. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z., et al., The novel ABC transporter ABCH1 is a potential target for RNAi-based insect pest control and resistance management. Scientific Reports, 2015. 5(1): p. 13728. [CrossRef]
- Hokaiwado, N., et al., RNAi-based drug discovery and its application to therapeutics. IDrugs, 2008. 11(4): p. 274-8.
- Uchino, K., T. Ochiya, and F. Takeshita, RNAi therapeutics and applications of microRNAs in cancer treatment. Jpn J Clin Oncol, 2013. 43(6): p. 596-607. [CrossRef]
- Tong, A.W., Small RNAs and non-small cell lung cancer. Curr Mol Med, 2006. 6(3): p. 339-49.
- Cho, S.W., et al., Analysis of off-target effects of CRISPR/Cas-derived RNA-guided endonucleases and nickases. Genome Res, 2014. 24(1): p. 132-41. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-H., et al., Off-target Effects in CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Genome Engineering. Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids, 2015. 4: p. e264. [CrossRef]
- Wegler, C., et al., Expanding the Efflux In Vitro Assay Toolbox: A CRISPR-Cas9 Edited MDCK Cell Line with Human BCRP and Completely Lacking Canine MDR1. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2021. 110(1): p. 388-396. [CrossRef]
- Radtke, L., et al., CRISPR/Cas9-induced knockout reveals the role of ABCB1 in the response to temozolomide, carmustine and lomustine in glioblastoma multiforme. Pharmacol Res, 2022. 185: p. 106510. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H., et al., Infection risk in autoimmune hematological disorders with low-dose rituximab treatment. J Clin Lab Anal, 2020. 34(10): p. e23455.
- Wang, X. and M. Hong, Protein Kinases and Cross-talk between Post-translational Modifications in the Regulation of Drug Transporters. Mol Pharmacol, 2023. 103(1): p. 9-20. [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.L., et al., Physiological expression and function of the MDR1 transporter in cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med, 2020. 217(5). [CrossRef]
- Liang, C., et al., Development and Characterization of MDR1 (Mdr1a/b) CRISPR/Cas9 Knockout Rat Model. Drug Metab Dispos, 2019. 47(2): p. 71-79. [CrossRef]
- Norouzi-Barough, L., et al., CRISPR/Cas9, a new approach to successful knockdown of ABCB1/P-glycoprotein and reversal of chemosensitivity in human epithelial ovarian cancer cell line. Iran J Basic Med Sci, 2018. 21(2): p. 181-187.
- Robert, X. and P. Gouet, Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014. 42(W1): p. W320-W324. [CrossRef]
- Hrycyna, C.A., et al., Structural Flexibility of the Linker Region of Human P-Glycoprotein Permits ATP Hydrolysis and Drug Transport. Biochemistry, 1998. 37(39): p. 13660-13673. [CrossRef]
- Esser, L., et al., Structures of the Multidrug Transporter P-glycoprotein Reveal Asymmetric ATP Binding and the Mechanism of Polyspecificity*♦. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2017. 292(2): p. 446-461. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., et al., Placing steroid hormones within the human ABCC3 transporter reveals a compatible amphiphilic substrate-binding pocket. The EMBO Journal, 2023. 42(17): p. e113415. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, Z.L. and J. Chen, ATP Binding Enables Substrate Release from Multidrug Resistance Protein 1. Cell, 2018. 172(1): p. 81-89.e10. [CrossRef]
- Kroll, T. , et al., Structure and Function of Hepatobiliary ATP Binding Cassette Transporters. Chemical Reviews, 2021. 121(9): p. 5240-5288. [CrossRef]
- Bakos, É., et al., Functional Multidrug Resistance Protein (MRP1) Lacking the N-terminal Transmembrane Domain*. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1998. 273(48): p. 32167-32175. [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J., et al., Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature, 2021. 596(7873): p. 583-589. [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J., et al., Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature, 2024. 630(8016): p. 493-500. [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.A., et al., Structure of the human lipid exporter ABCB4 in a lipid environment. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2020. 27(1): p. 62-70. [CrossRef]
- Haenisch, S., A.N. Werk, and I. Cascorbi, MicroRNAs and their relevance to ABC transporters. Br J Clin Pharmacol, 2014. 77(4): p. 587-96. [CrossRef]
- Szczepanek, J., M. Skorupa, and A. Tretyn, MicroRNA as a Potential Therapeutic Molecule in Cancer. Cells, 2022. 11(6): p. 1008. [CrossRef]
| Name | Function | Molecular Weight kDa | Disease Association |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABCA2 | Lipid transporter | 269.8 | IDPOGSA |
| ABCA3 | Phospholipid transporter | 191.4 | SMDP3 |
| ABCB1 | Transports drugs & phospholipids | 141.4 | MDR |
| ABCB2 | Peptide transporter | 80.9 | BLS1 |
| ABCB5 | Multidrug exporter | 138.6 | MDR |
| ABCC1 | Exporter of anions and xenobiotics | 171.5 | MDR |
| ABCC2 | Transporter of bile acid conjugates | 174.2 | MDR |
| ABCC3 | Transporter of bile acid conjugates | 169.3 | MDR |
| ABCC4 | Transporter of metabolites | 149.5 | MDR |
| ABCC5 | Transporter of amnio acid metabolites | 160.6 | MDR |
| ABCC6 | Exporter of xenobiotics | 164.9 | PXE |
| ABCC10 | Transporter of glutathione conjugate | 161.6 | MDR |
| ABCG2 | Drug efflux pump | 72.3 | MDR |
| Transporters | Key residues within the binding pocket | Mediate through/ substrates | Current Drugs/Inhibitors under use or under clinical trials |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABCB1 | Y310, I340, F343, S344, Q347, Q725, Q946, Y953, F983, M9846, A987, Q990 [51] | A wide range of substrates. For example: Paclitaxel, Vincristine, Doxorubicin | Verapamil, Tariquidar, SelonsertibTepotinib, PND-1186, MK-8776, Rydapt, Erdafitinib, CGM097, Poziotinib, synthetic peptides, Nanobody nb-592, Biricodar, laniquidar, valspodar, querectin |
| ABCB4 | A737, G954, P726, T775, A286, R47, D243, S346, S 320, Q855, S978, A953, F357, A 346.[191] | Primarily involved in lipid transport. Depending on the need sometimes also mediates doxorubicin. | Curcumin |
| ABCB6 | T320, S322, T323, W546, A 492, G588, A681.[99] | Primarily involved in porphyrin transport. Depending on the need sometimes also mediates cisplatin, arsenic trioxide, vincristine, camptothecin, CPt-11, 5-Fu, SN-38, Doxorubicin, methotrexate, topotecan. | No known inhibitors so far. |
| ABCC1 | K332, H335, L381, F385, Y440, T550, W553, F594, M1092, R1196, Y1242, N1244, W1245, R1248. [103] | Transports leukotriene. Depending on the need sometimes also mediates vincristine, vinblastine, Doxorubicin, methotrexate, daunorubicin, etoposide, betulin | MK571, Flavopiridol, Apigenin, Chalcone, Kaempferol, Morin, Quercetin, GSK1940529A, Indomethacin, verapamil and its derivatives, macrocyclic peptides (CP11), sipholenol A, |
| ABCG2 | L405, F432, T435, N436, F439, S440, V442, T542, V546, M549 [109]. | Transports drugs. Such as topotecan, mitoxantrone, SN-38, OTS964, GSK1070916, Tivantinib, Pevonedistat, Imatinib. | KO143, FTC, Selonsertib, TAE684, M3814, CC-671, Antibody & Nanobody: 5D3, Nb8, Nb17, Nb96. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (Dacomitinib, pozoiotinib, venetoclax, olmutinib, gefitinib, quizartinib, novobiocin. |
| miRNA target | Targeting ABC transporter | Tested in |
|---|---|---|
| miR137 | ABCB1 | Human breast cancer cells MCF-7 |
| miR145 | ABCB1 | Human colon carcinoma cells, Caco-2 |
| miR200c | ABCB1 | Human breast cancer cells, MCF-7 |
| miR331-5p | ABCB1 | Chronic myelogenous leukaemia cells K562 |
| miR451 | ABCB1 | Human breast cancer cells, MCF-7 |
| miR1253 | ABCB1 | Human breast cancer cells, MDA-MB-231 |
| miR-271 | ABCB1 | Human oesophageal squamous cell lines ECA109 and TE-14 |
| ABCB1 | Human gastric cancer cell line MKN45 | |
| ABCB1 | Human Ovarian cancer cell line A2780 | |
| miR138 | ABCB1 | Human Leukaemia cell line HL-60 |
| miR296 | ABCB1 | Human oesophageal squamous cell lines ECA109 |
| miR451 | ABCB1 | Ovarian cancer cell line A2780 |
| miR223 | ABCB4 | Human liver cancer cell line |
| miR34a | ABCB4 | Human liver cancer cell line |
| miR1 | ABCB4 | Human liver cancer cell line |
| miR9 | ABCB4 | Human liver cancer cell line |
| miR449 | ABCB4 | Human liver cancer cell line |
| miR370 | ABCB6 | Human lung, liver cancer cell lines |
| miR27a | ABCB6 | Human lung, liver cancer cell lines |
| miR16 | ABCB6 | Human lung, liver cancer cell lines |
| miR181a | ABCB6 | Human lung, liver cancer cell lines |
| miR506 | ABCC1 | Human breast cancer cell line |
| miR27a | ABCC1 | Human breast, lung and cancer cell line |
| miR122 | ABCC1 | Human breast, lung and cancer cell line |
| miR370 | ABCC1 | Human breast, lung and cancer cell line |
| miR16 | ABCC1 | Human breast, lung and cancer cell line |
| miR328 | ABCG2 | Human breast, lung and cancer cell line |
| miR451 | ABCG2 | Human breast, lung and cancer cell line |
| miR506 | ABCG2 | Human breast, ovarian cancer cell line |
| miR34a | ABCG2 | Human breast, ovarian cancer cell line |
| miR30a | ABCG2 | Human breast, ovarian cancer cell line |
| miR9 | ABCG2 | Human breast, ovarian cancer cell line |
| miR138 | ABCG2 | Human breast, ovarian cancer cell line |
| miR204 | ABCG2 | Human breast, ovarian cancer cell line |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





