1. Introduction
Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease (ICAD) represents a devastating pathology with high risk of recurrent cerebrovascular events, even with optimal medical therapy [
1]. SAMMPRIS and VISSIT trials were multicenter randomized controlled trials which compared optimal medical therapy versus endovascular revascularization in ICAD patients [
2,
3]. Both trials concluded that optimal medical therapy was better than endovascular revascularization regarding safety and efficacy. However, both trials received a lot of criticism regarding patient selection criteria and operators’ experience [
4,
5,
6,
7]. Seven-year data from the China Angioplasty and Stenting for Symptomatic Intracranial Severe Stenosis (CASSISS) trial indicate that intracranial stenting offers no additional benefits for patients with intracranial stenosis [
8]. This conclusion was reached despite using a refined methodology [
6]. On the contrary, another trial conducted in a single centre in China randomized patients with Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) stenosis to either optimal medical therapy or endovascular revascularization [
9]. They concluded that endovascular revascularization can be performed safely in carefully selected patients with MCA stenosis. Additionally, the results of Wingspan stEnt system post-mArket surVEillance (WEAVE) trial showed extremely low periprocedural adverse events rate (2.6%), suggesting that proper patient selection and operators’ experience may maximize benefit from endovascular revascularization [
10]. The recently published Balloon Angioplasty for Symptomatic Intracranial Artery Stenosis (BASIS) trial demonstrated that combining balloon angioplasty with optimal medical management significantly reduced the risk of adverse events compared to optimal medical management alone [
11]. These adverse events included any stroke or death within the first 30 days, as well as ischemic stroke or the need for revascularization of the qualifying artery between 30 days and 12 months post-treatment. In the current stroke guidelines, the usefulness of endovascular revascularization for ICAD patients is considered unknown and investigational [
12,
13,
14].
Controversies usually arise regarding the relationship between clinical outcome and the volume of specific surgical procedures or medical conditions treated in a given site. Few investigators have addressed this point for the endovascular treatment of ICAD [
10,
15,
16]. Learning curve for mastering the safety precautions of intracranial stenting is crucial. High-volume sites may guarantee the success and safety of intracranial stenting and maintain the continuity of operators’ experience. Our study question was whether outcomes were similar among centres that treated high and low volumes of patients.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
We retrospectively recruited 36 patients with symptomatic severe ICAD who underwent attempted intracranial angioplasty and / or stenting from January 2014 to June 2016. Only patients who had a TIA or ischaemic stroke attributed to advanced intracranial atherosclerotic lesions (≥70% stenosis) were included. Analysis was performed by reviewing data in previously maintained databases at four centres with comprehensive neuroendovascular services. Clinical data were treated in respect of the local hospital rules. All clinical data analyzed were collected as part of routine diagnosis and treatment. We identified demographic, clinical, and radiological data including vascular risk factors, qualifying event, other non-qualifying events, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), modified Rankin Scale (mRS), antithrombotic therapy at time of qualifying event, vascular imaging, brain parenchymal imaging (CT or MRI).
The high-volume centre was defined in this study as a centre with an annual volume of ≥ 300 general neuroendovascular treatments per year including at least ten endovascular treatments for intracranial atherosclerosis per year. Our study centres were one high-volume centre which treated 26 patients with intracranial atherosclerosis over a period of 30 months and three low-volume centres which collectively treated 21 patients with intracranial atherosclerosis over the same period. Patients who underwent intracranial angioplasty and / or stenting as a rescue treatment in the setting of acute stroke treatment were excluded (n=11). Thirty-six patients were grouped accordingly into two groups; patients treated in high-volume centre (group HV, n=18), and patients treated in low-volume centre (group LV, n=18).
While the decision to proceed with intracranial stenting should come from recurrent events despite aggressive medical therapy, this was not consistently implemented in our study as in SAMMPRIS trial. All patients were managed by vascular neurologists prior to their referral for endovascular treatment according to every local institutional protocol. The protocol was variable among our recruitment sites. In some patients presenting with hemodynamic infarctions that might be related to a low flow situation based on a critical stenosis with insufficient collateral flow, endovascular treatment could relieve the patients’ symptoms dramatically. Those patients could not benefit from medical therapy especially if this medical therapy requires lowering blood pressure. Additionally, few patients were switched to oral anticoagulation after failure of dual antiplatelet before their referral for endovascular treatment.
2.2. Brain Parenchymal Imaging Analysis and the Most Likely Stroke Mechanisms
We defined the most likely mechanism of stroke related to ICAD according to infarct pattern on brain parenchymal imaging as follows: (1) artery-to-artery embolism for single or multiple scattered infarcts located in the territory supplied by a single intracranial artery either cortical, subcortical or both,(2) perforator occlusion for lacune-like lesions in the territory of perforating vessels that originate at the site of stenosis,(3) insitu thrombotic occlusion for infarctions that extensively involve the entire or most of the stenosed arterial territory, (4) hypoperfusion for borderzone infarcts occur at the junction of two arterial territories, either cortical borderzone or internal borderzone and (5) mixed mechanisms for multiple infarct patterns.
2.3. Angiographic Analysis
Digital subtraction angiography was reviewed for each patient to determine the exact degree of stenosis according to WASID trial standards [
17]. Lesions were divided into three groups: 70–79%, 80–89%, and 90–99%. According to lesion length, lesions were divided into three groups: <5 mm, 5-10 mm, and >10 mm. Proximal vessels were considered tortuous if there were 2 or more acute curves that would be difficult to traverse.
2.4. Procedural Aspects
Detailed procedural aspects were obtained; including time from the qualifying event to the procedure, periprocedural antithrombotics, anaesthesia, intraprocedural adverse events, pre-stent angioplasty, stent type, stent size, poststent angioplasty, use of intermediate catheters, wire exchange, no. of lesion pass (single or multiple), combined treatment of other lesions, residual stenosis, and post-procedural brain imaging.
2.5. Follow-Up Data
Follow-up data including vascular adverse events, mRs, and vascular imaging were revised at least one year after the procedure. Post-stenting antiplatelet regime was variable among our recruitment sites. The patient would continue dual antiplatelet (aspirin 100-150 mg plus clopidogrel 75 mg or aspirin 100-150 mg plus ticlopidine 500 mg) for 3-6 months depending on follow-up vascular imaging, type of stent, and recurrent events. Patients would continue aspirin 100-150 mg for life. Patients with no follow-up at the outpatient service or by telephone contact were considered lost for follow-up.
2.6. Outcome Parameters
Outcome parameters included: successful revascularization with residual stenosis < 50%, occurrence of stroke, TIA and/or death after intervention or during the follow-up period, and restenosis (≥ 50%).
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Pre-coded data were entered on the computer using "Microsoft Office Excel Software" program (2016) for Windows. Data were coded and entered using the statistical package SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) version 24. Data were summarized using mean, standard deviation, median, and range for quantitative variables, and as frequency and percentage for categorical variables. Comparisons between quantitative variables were done using the non-parametric Mann-Whitney test. For comparing categorical data, Chi-square test was performed. Exact test was used instead when the expected frequency was less than 5. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
The age ranged from 37 to 81 years, with a mean age of 62.39 ± 11.2 Standard Deviation (SD). The median age was 63.5 years. There were 29 males (80.6%) and 7 females (19.4%). The most common risk factor among our study population was hypertension in 83.3 % (30/36) of patients followed by: dyslipidaemia 66.7% (24/36), diabetes mellitus 33.3 % (12/36), coronary artery disease 22.2 % (8/36), hyperuricaemia 8.3% (3/36), obesity (BMI ≥ 30) 5.6% (2/36), peripheral vascular disease 5.6% (2/36), hyperhomocystienaemia 5.6% (2/36), and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome 5.6% (2/36). Smoking history among our study population was as follows: current 41.7% (15/36), former 8.3% (3/36), and never 50% (18/36). The qualifying event was stroke in 63.9% (23/36), and TIA in 36.1% (13/36). Twenty-three patients (63.9%) had suffered previous cerebrovascular events (stroke or TIA) other than the qualifying event. Twenty-nine patients (80.6%) were already receiving antithrombotic therapy at the time of the qualifying event; 14 patients (38.9%) on single antiplatelet, 12 patients (33.3%) on double antiplatelet, 2 patients (5.6%) on single antiplatelet plus anticoagulation, and 1 patient (2.8%) on anticoagulation alone. Qualifying event severity, measured by NIHSS, was as follows: 14/36 (38.9%) mild with NIHSS <5, 15/36 (41.7%) moderate with NIHSS=5-14, 7/36 (19.4%) severe with NIHSS=15-24. Twenty-eight patients (77.8%) had preprocedural mRS ≤3. Eight patients (22.2%) had preprocedural mRS ˃3.
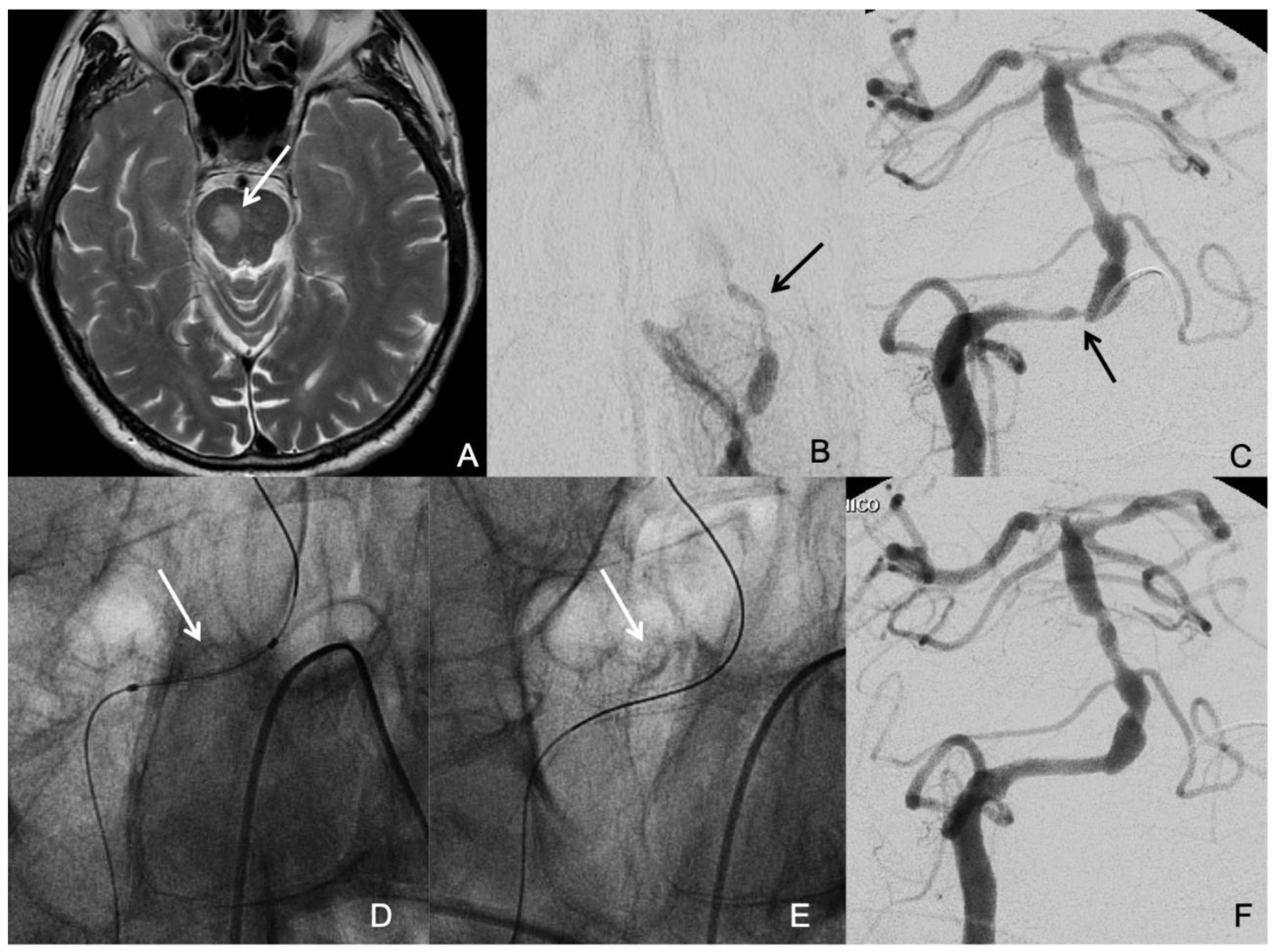
The symptomatic qualifying artery was basilar artery in 15 patients (41.7%), intracranial vertebral artery in 13 patients (36.1%), middle cerebral artery in 3 patients (8.3%), and intracranial internal carotid artery in 5 patients (13.9%). The mean degree of stenosis was 86.6 % ± 8.7 SD. The mean lesion length was 7.34 mm ± 3.2 SD. The time from the qualifying event to intervention ranged from 2-78 days, with a mean time of 24.6 days ± 21.9 SD, and a median time of 17 days. The most likely stroke mechanisms related to ICAD were mixed mechanisms in 47.2% (17/36), hypoperfusion in 27.8% (10/36), and artery-to-artery embolism in 25% (9/36). Neither perforator occlusion nor insitu thrombotic occlusion was present as the sole stroke mechanism in any patient of our study population. Thirteen patients (36.1%) had multiple significant ICAD (
Figure 1). Five patients (13.9%) had concomitant significant Extracranial Atherosclerotic Disease (ECAD). Two patients (5.6%) had significant stenosis (≥70%) proximal to the target lesion i.e. tandem stenosis. Twenty-one patients (58.3%) had tortuous proximal vessels (≥ 2 acute curves).
3.2. Procedure Characteristics
All procedures were done under general anaesthesia. Different endovascular treatment modalities were used. Primary balloon angioplasty without stenting was done in 3 patients (8.3%). The stents used were either balloon-expandable coronary or self-expanding neurovascular stents. Balloon-expandable coronary stents were used in 24 patients; 19 bare-metal (52.8 %) and 5 drug-eluting (13.9%). Bare-metal coronary stents included: 15 PRO-Kinetic Energy® (BiotroniK), and 4 Liberté® (Boston Scientific). Drug-eluting coronary stents included: 2 Resolute Onyx® (Medtronic), 2 Resolute Integrity® (Medtronic), and 1 Xience Prime® (Abbott Vascular). Self-expanding stents were used in 9 patients (25%). Self-expanding stents included: 4 LVIS Jr® (MicroVention), 3 LEO Baby® (Balt), and 2 Wingspan® (Stryker). Pre-stent angioplasty was performed in 18 patients (50%). Six patients (16.7%) underwent complex revascularization procedures including combined treatment of other significant lesions either to bypass severe tandem stenosis or to improve collateral circulation. Intermediate catheter was required in 3 patients (8.3%). Over-the-wire exchange was performed in 16 patients (44.4%). Regarding the no. of lesion pass, it was a single pass in 30 patients (83.3%), and multiple passes in 6 patients (16.7%). Intraprocedural adverse events occurred during 2 procedures (5.6 %) including distal embolization, and branch occlusion.
3.3. Clinical and Radiological Follow-Up
Three patients (8.3%) were lost for follow-up. The mean clinical follow-up time was 17.8 months ± 9.5 SD, median of 18 months. Follow-up vascular imaging was available for 30 patients (83.33%). The mean radiological follow-up time was 10.7 months ± 10.5 SD, median 12 months.
3.4. Outcome Parameters
Successful revascularization (Residual stenosis <50%) was obtained in 97.2 % (35/36). In one case with marked proximal vessel tortuosity, the self-expanding stent could not be advanced to stent a distal basilar artery stenosis. Neither a distal access catheter nor an intermediate catheter was available during this procedure due to insurance issues.
At 30 days, the rate of any death, stroke, and/or TIA was 13.9% (5/36), and the rate of any target territory related stroke and/or TIA was 11.1% (4/36). At a median clinical follow-up of 18 months, the rate of any death, stroke, and/or TIA was 27.8% (10/36). At 30 days, a fatal haemorrhagic stroke occurred in one patient, and fatal ischemic stroke occurred in two patients: all in the target territory. Two patients had a non-fatal ischaemic stroke at 30 days: one in the target territory and one in a territory other than the target territory. No TIAs or non-fatal haemorrhagic stroke occurred at 30 days. After 30 days, a fatal ischaemic stroke occurred in one patient, a non-fatal ischemic stroke occurred in two patients; all in the target territory, and three patients had TIAs; all in the target territory. A fatal haemorrhagic stroke after 30 days occurred in one patient as a complication of the antithrombotic therapy in a territory other than the target territory.
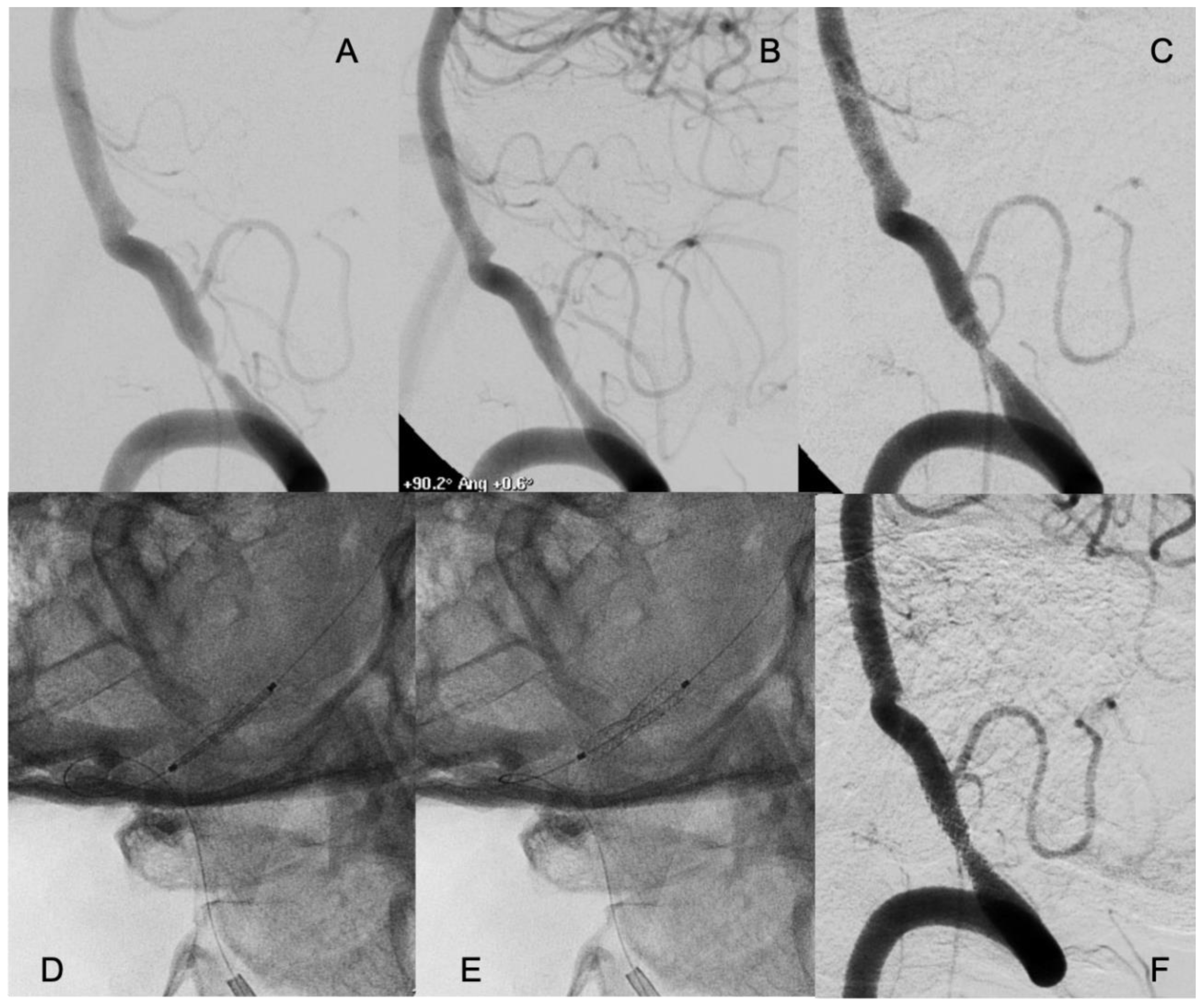
Restenosis (≥50%) at median radiological follow-up of 12 months was observed in 4 patients (11.1%): 2 patients were treated with self-expanding stents, and 2 patients with bare-metal stents). All four patients had symptomatic restenosis. Two of these restenoses required endovascular re-treatment; 1 patient was re-treated with balloon angioplasty, and 1 patient with drug-eluting stent (
Figure 2).
3.5. Comparison Between High- and Low-Volume Centers
A comparison between patients treated in the high-volume centre (group HV, n=18), and patients treated in low-volume centre (group LV, n=18) regarding baseline and procedure characteristics was done (
Table 1).
There was no statistically significant difference between both groups regarding baseline patient and lesion characteristics. Median age was 65 years in group HV versus 61 years in group LV (p = 0.606). The median time from the qualifying event to the procedure was 14 days in group HV versus 21 days in group LV (p = 0.556). The most likely stroke mechanisms related to ICAD were variable between both groups, but without reaching statistical significance (p = 0.124). Hypoperfusion was more frequently present in group HV versus group LV (38.9% and 16.7%, respectively). Conversely, artery-to-artery embolism was more frequently present in group LV versus group HV (38.9% and 11.1%, respectively). Mixed mechanisms were similarly present in both groups (50% for group HV and 44.4% for group LV).
Endovascular treatment modalities varied significantly between both groups (p < 0.001). Bare metal coronary stents were used as the sole treatment modality for patients treated in the high-volume centre. Conversely, modalities were variable among patients treated in low-volume centres including self-expanding stents (50 %), drug-eluting coronary stents (27.8%), bare metal coronary stents (5.6%), and primary balloon angioplasty (16.7%). There was no statistically significant difference between both groups regarding clinical and radiological follow-up durations. The median clinical follow-up duration was 18.5 months for group HV and 17 months for group LV (p = 0.276). Median radiological follow-up duration was the same (12 months) in both groups (p = 0.790).
Incidence of outcome parameters showed no statistically significant difference between patients treated in high-volume centre, and patients treated in low-volume centre. However, 30-days and 18-month rates of any death, stroke, and/or TIA were higher among patients treated in the low-volume centre versus those treated in the high-volume centre but without reaching statistical significance (22.2% versus 5.6%, p = 0.188; and 38.9% versus 16.7%, p = 0.137, respectively). Similarly, 30-days and 18-month rates of target territory related stroke and/or TIA were higher among patients treated in the low-volume centre versus those treated in the high-volume centre but without reaching statistical significance (16.7% versus 5.6%, p = 0.603; and 38.9% versus 16.7%, p = 0.137, respectively,
Table 2).
4. Discussion
Our study showed a 97.2% successful recanalization rate. The global rate for any death, stroke, and/or TIA within 30 days after endovascular treatment was 13.9%. At median clinical follow-up of 18 month, our study revealed 27.8 % any death, stroke, and/or TIA rate.
Our study question was whether outcomes were similar among centers that treated high and low volumes of patients. Our results showed that the incidence of intraprocedural adverse events, successful revascularization, and 30-day haemorrhagic stroke was not significantly different between both groups. However, 30-days rate of any death, stroke, and/or TIA was higher among patients treated in low-volume centre versus those treated in high-volume centre but without reaching statistical significance (22.2% versus 5.6%, p = 0.188). Similarly, the 18-month rate of any death, stroke, and/or TIA was higher among patients treated in low-volume centre versus those treated in high-volume centre but without reaching statistical significance (38.9% versus 16.7%, p = 0.137). The 5.6% any death, stroke, and/or TIA rate at 30 days obtained among patients treated in our high-volume centre is similar to the 4.3% rate reported in a previous Chinese multicentre registry [
18] and is lower than 30-day rates reported in the European INTRASTENT registry (12.4%) [
19], and the endovascular arm of SAMMPRIS (14.7%) [
2]. Similarly, at our high-volume centre, the rate of any death, stroke, and/or TIA at 18 months was 16.7%. This rate is lower compared to SAMMPRIS which showed a 24.1% probability of any stroke or death at 24 months among endovascularly treated patients [
20]. Also, it is considerably lower than the 36.2% any stroke or hard TIA rate at 12 months reported in the endovascular arm of VISSIT [
3].
Few investigators studied the relationship between the outcome of intracranial stenting and volume of patients treated in a given site. An analysis of the NIH Wingspan registry revealed that rates of all stroke and ischemic stroke in the target territory were significantly higher among patients treated in low enrolling sites (<10 patients) compared to high enrolling sites [
15]. Similarly, analysis of SAMMPRIS trial showed higher rates of hemorrhagic stroke in low enrolling sites (<12 patients) compared to high enrolling sites (9.8% versus 2.7%, p=0.043) [
16]. In the WEAVE trial, operators who had experience of >50 Wingspan cases before enrolment achieved a 0% periprocedural adverse events rate, while operators with <50 Wingspan cases before enrolment had a 4.8% periprocedural adverse events rate [
10].
Potential explanation for the statistical insignificance of our results might be related to the small sample size. Small sample size might limit statistical power and prevent outcome differences from being statistically significant. The trend of more death, Stroke, and TIAs among patients treated in LV centre might be related to type of stent, most likely stroke mechanism, and socioeconomic status variability among our recruitment sites. Half of patients in the LV group were treated using self-expanding stents. Generally, using balloon-mounted stents or primary balloon angioplasty is technically simpler and demands less procedural time than “multistep” self-expanding stents which require over wire catheter exchange with risk of wire perforation and haemorrhagic complications [
21,
22]. Among patients treated in our low-volume centers, four patients had death and/or stroke within 30 days after intervention. Three of them were treated using self-expanding stents. The most likely stroke mechanisms could also influence the difference in the results between the two groups. In our HV centre the main indication to the endovascular treatment of ICAD was hypoperfusion in territory supplied by the target vessel, a condition more prone to respond to endovascular revascularization [
23]. Conversely, artery-to-artery embolism was more frequently present in group LV. However, a recent subgroup analysis of SAMMPRIS trial couldn’t provide any evidence regarding the advantage of endovascular treatment over medical treatment in patients with hypoperfusion symptoms [
24]. Lastly, some adverse events after endovascular revascularization might be attributed to the patient’s non-compliance to antiplatelet therapy, risk factors control, or even follow-up visits [
25]. Socioeconomic status as a robust determinant of patient’s compliance was variable among our recruitment sites. This variability might also influence the incidence of post-procedural adverse events among our study groups.
Our study reported a restenosis rate of 11.1 % at median radiological follow-up of 12 months. This rate is at the lower end of the range of restenosis rates reported in the literature following balloon-mounted stents placement (10– 20%) [
26,
27,
28], and self-expanding stents placement (17.4–25%) [
29,
30]. The restenosis rate among HV group patients treated with bare-metal coronary stents as the sole treatment modality was 5.6% at a median radiological follow-up of 12 months. Among LV group patients treated with variable endovascular modalities, including 50% self-expanding stents, 27.8% drug-eluting coronary stents, and 16.7% primary balloon angioplasty, restenosis rate was higher (16.7%), but without reaching statistical significance (p =0.603). This may add to the growing evidence that restenosis is seen less frequently with balloon-mounted stents [
22,
31].
Our study was not without limitations. The limitations of the current study should be considered when interpreting the results. The main limitation of our study is the small sample size. Our study was a retrospective cohort study with a non-randomized design. Another limitation is that our definition of high- and low-volume centers considered the global experience within each center of treating intracranial atherosclerosis, and of neuroendovascular procedures in general. Lastly, our study population was heterogeneous. Patients were recruited from four different centres with ethnic, demographic, clinical, and procedural differences that may have influenced our study outcomes.
5. Conclusions
Our study showed a higher incidence of mortality and adverse events among ICAD patients treated in low-volume centre compared to those treated in high-volume centre without reaching statistical significance. Future prospective studies with larger sample size are warranted.
Author Contributions
All authors were engaged in the study's design, manuscript review, manuscript editing, and final approval of the manuscript. All authors were involved in data acquisition and organization. A.A., and G.P. drafted the article. A.A., and F.A. performed all the statistical analyses. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
In this retrospective cohort clinical study, analysis was performed by reviewing data in previously maintained databases. All clinical data analyzed were collected as part of routine diagnosis and treatment in respect of the local hospital rules. The policy of our hospitals does not require the ethics committee approval for retrospective clinical studies.
Informed Consent Statement
All patients signed the informed consent for the treatment and allowed anonymous use of their clinical and radiological data.
Data Availability Statement
Additional data and materials may be available on request. Requests should be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chimowitz, M. I.; Lynn, M. J.; Howlett-Smith, H.; Stern, B. J.; Hertzberg, V. S.; Frankel, M.R.; Levine, S.R.; Chaturvedi, S.; Kasner, S.E.; Benesch, C.G.; et al. Comparison of Warfarin and aspirin for symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2005, 352, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimowitz, M.I.; Lynn, M.J.; Derdeyn, C.P.; Turan, T.N.; Fiorella, D.; Lane, B.F.; Janis, L.S.; Lutsep, H.L.; Barnwell, S.L.; Waters, M.F.; et al. Stenting versus Aggressive Medical Therapy for Intracranial Arterial Stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2011, 365, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidat, O.O.; Fitzsimmons, B.F.; Woodward, B.K.; Wang, Z.; Killer-Oberpfalzer, M.; Wakhloo, A.; Gupta, R.; Kirshner, H.; Megerian, J.T.; Lesko, J.; et al. Effect of a Balloon-Expandable Intracranial Stent vs Medical Therapy on Risk of Stroke in Patients With Symptomatic Intracranial Stenosis. JAMA. 2015, 313, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Chebl, A.; Steinmetz, H. Critique of “Stenting Versus Aggressive Medical Therapy for Intracranial Arterial Stenosis” by Chimowitz et al in the New England Journal of Medicine. Stroke. 2012, 43, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Al-Senani, F.M.; Husain, S.; Janjua, N.A.; Lanzino, G.; Lavados, P.M.; Nguyen, T.; Raymond, J.; Shah, Q.A.; Suarez, J.I.; et al. Intracranial Angioplasty and Stent Placement After Stenting and Aggressive Medical Management for Preventing Recurrent Stroke in Intracranial Stenosis (SAMMPRIS) Trial: Present State and Future Considerations. J Neuroimaging. 2012, 22, 22,1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.; Cai, Y.; Li, T.; Wu, W.; Shi, H.; He, W.; Zhu, F.; et al. China Angioplasty and Stenting for Symptomatic Intracranial Severe Stenosis (CASSISS): A new, prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled trial in China. Interv Neuroradiol. 2015, 21, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualhasan, A.; Abd-Allah, F.; Pero, G.; Sobh, K.; Mansour, O.; El-Serafy, O.; Boccardi, E. Intracranial Stenting: Is It Still an Option for Treatment of Patients With Intracranial Atherosclerosis? Front Neurol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; He, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Wang, D.; Shi, H.; Li, T.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, Y.; Wu, W.; et al. Stenting Plus Medical Therapy vs Medical Therapy Alone for Symptomatic Intracranial Artery Stenosis: Long-Term Results of a Multicentre, Randomised Controlled Trial. SSRN Preprint. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wu, H.; Bao, Y.; Jiao, L.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Hua, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; et al. Randomized Controlled Trial of Symptomatic Middle Cerebral Artery Stenosis. Stroke. 2012, 43, 3284–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.J.; Zauner, A.; Chaloupka, J.C.; Baxter, B.; Callison, R.C.; Gupta, R.; Song, S.S.; Yu, W.; Feng, L.; Bonovich, D.; et al. WEAVE Trial. Stroke. 2019, 50, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Sun, D.; Nguyen, T.N.; Tong, X.; Peng, G.; Liu, A.; Xu, Y.; et al. Balloon Angioplasty vs Medical Management for Intracranial Artery Stenosis. JAMA. 2024, 332, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psychogios, M.; Brehm, A.; López-Cancio, E.; De Marchis, G.M.; Meseguer, E.; Katsanos, A.H.; Kremer, C.; Sporns, P.; Zedde, M.; Kobayashi, A.; et al. European Stroke Organisation guidelines on treatment of patients with intracranial atherosclerotic disease. Eur Stroke J. 2022, 7, XLII–LXXX. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turan, T.N.; Zaidat, O.O.; Gronseth, G.S.; Chimowitz, M.I.; Culebras, A.; Furlan, A.J.; Goldstein, L.B.; Gonzalez, N.R.; Latorre, J.G.; Messé, S.R.; et al. Stroke Prevention in Symptomatic Large Artery Intracranial Atherosclerosis Practice Advisory. Neurology. 2022, 98, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleindorfer, D.O.; Towfighi, A.; Chaturvedi, S.; Cockroft, K.M.; Gutierrez, J.; Lombardi-Hill, D.; Kamel, H.; Kernan, W.N.; Kittner, S.J.; Leira, E.C.; et al. 2021 Guideline for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients With Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack: A Guideline From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2021, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahab, F.; Lynn, M.J.; Kasner, S.E.; Alexander, M.J.; Klucznik, R.; Zaidat, O.O.; Chaloupka, J.; Lutsep, H.; Barnwell, S.; Mawad, M.; et al. Risk factors associated with major cerebrovascular complications after intracranial stenting. Neurology. 2009, 72, 2014–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derdeyn, C.P.; Fiorella, D.; Lynn, M.J.; Barnwell, S.L.; Zaidat, O.O.; Meyers, P.M.; Gobin, Y.P.; Dion, J.; Lane, B.F.; Turan, T.N.; et al. Impact of operator and site experience on outcomes after angioplasty and stenting in the SAMMPRIS trial. J Neurointerv Surg. 2012, 5, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, O.B.; Joseph, G.J.; Lynn, M.J.; Smith, H.A.; Chimowitz, M.I. A Standardized Method for Measuring Intracranial Arterial Stenosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000, 21, 643–646. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shuai, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, K.; Liu, L.; Li, B.; Shi, X.; Gao, L.; et al. Thirty-Day Outcome of a Multicenter Registry Study of Stenting for Symptomatic Intracranial Artery Stenosis in China. Stroke. 2015, 46, 2822–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurre, W.; Berkefeld, J.; Brassel, F.; BrüNing, R.; Eckert, B.; Kamek, S.; Klein, G.E.; Knauth, M.; Liebig, T.; Maskova, J.; et al. In-Hospital Complication Rates After Stent Treatment of 388 Symptomatic Intracranial Stenoses. Stroke. 2010, 41, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derdeyn, C.P.; Chimowitz, M.I.; Lynn, M.J.; Fiorella, D.; Turan, T.N.; Janis, L.S.; Montgomery, J.; Nizam, A.; Lane, B.F.; Lutsep, H.L.; et al. Aggressive medical treatment with or without stenting in high-risk patients with intracranial artery stenosis (SAMMPRIS): the final results of a randomised trial. Lancet. 2013, 383, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, J.J. , Wojak J.C., Hoppe B.H. The Technique of Endovascular Intracranial Revascularization. Front Neurol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, M.; Milonia, L.; Cervo, A. , Modello, B.; Macera, A., Pero, G., Quilici, L., Boccardi, E., Eds.; Valvassori, L. Endovascular Treatment of Symptomatic Intracranial Vertebrobasilar Stenosis: A 10-Year Single Centre Experience Using Balloon-Expandable Coronary Artery Stents. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020, 30, 105431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.J. Intracranial stenting for intracranial atherosclerotic disease: still much to learn. J Neurointerv Surg. 2012, 4, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutsep, H.L.; Lynn, M.J.; Cotsonis, G.A.; Derdeyn, C.P.; Turan, T.N.; Fiorella, D.; Janis, L.S.; Lane, B.F.; Montgomery, J.; Chimowitz, M.I. Does the Stenting Versus Aggressive Medical Therapy Trial Support Stenting for Subgroups With Intracranial Stenosis? Stroke. 2015, 46, 3282–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, V.L.; Go, A.S.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Adams, R.J.; Berry, J.D.; Brown, T.M.; Carnethon, M.R.; Dai, S.; De Simone, G.; Ford, E.S.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2011 Update. Circulation. 2010, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorella, D.; Chow, M.M.; Anderson, M.; Woo, H.; Rasmussen, P.A.; Masaryk, T.J. A 7-year experience with balloon-mounted coronary stents for the treatment of symptomatic vertebrobasilar intracranial atheromatous disease. Neurosurgery. 2007, 61, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Z.R.; Feng, L.; Li, S.; Zhu, F.; Ji, X.; Jiao, L.; Ling, F. Treatment of symptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis with balloon-mounted stents: long-term follow-up at a single center. Neurosurgery. 2009, 64, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durst, C.R.; Geraghty, S.R.; Southerland, A.M.; Starke, R.M.; Rembold, K.; Malik, S.; Wintermark, M.; Liu, K.C.; Crowley, R.W.; Gaughen, J.; et al. Stenting of symptomatic intracranial stenosis using balloon mounted coronary stents: a single center experience. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014, 7, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidat, O.O.; Klucznik, R.; Alexander, M.J.; Chaloupka, J.; Lutsep, H.; Barnwell, S.; Mawad, M.; Lane, B.; Lynn, M.J.; Chimowitz, M. The NIH registry on use of the Wingspan stent for symptomatic 70–99% intracranial arterial stenosis. Neurology. 2008, 70, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costalat, V.; Maldonado, I.L.; Vendrell, J.F.; Riquelme, C.; Machi, P.; Arteaga, C.; Turjman, F.; Desal, H.; Sedat, J.; Bonafé, A. Endovascular treatment of symptomatic intracranial stenosis with the Wingspan stent system and Gateway PTA balloon: a multicenter series of 60 patients with acute and midterm results. J Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Yin, Q.; Xi, G.; Zhu, W.; Xu, G.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, M.; Jin, G.; Liu, X. Comparison of BMSs with SES for Symptomatic Intracranial Disease of the Middle Cerebral Artery Stenosis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010, 34, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).