Submitted:
09 November 2024
Posted:
12 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Quantum image computing has attracted attention due to its vast storage and faster processing of image data than classical computers. Although classical computing power has grown substantially in the last decade, its abilities have plateaued, struggling to meet the needs of huge datasets. Quantum computers, on the other hand, take advantage of unique qualities like quantum parallelism, superposition, and entanglement to provide faster solutions to complicated problems. Managing huge image data in classical systems necessitates significant memory and hardware resources, which makes quantum computing a possible alternative. Several approaches have arisen for encoding and compressing classical images in the quantum processor. However, one of the most significant limitations is the complexity of quantum state preparation, which translates pixel coordinates to corresponding quantum circuits. Current approaches for representing large-scale images require a huge number of quantum resources including qubit, and qubit connection, which presents significant hurdles. Therefore, this article aims to overview the pixel intensity and state preparation circuit that needs fewer connections, i.e., quantum gates to represent quantum image data, and then explore and design effective compression and processing methods for medium and high-resolution images. This work specializes in emerging quantum models’ potential for enhancing image representation and compression capabilities. It also conducts a comprehensive study of quantum image representation and compression techniques, categorizing existing methods by grayscale and color image types and evaluating their methods, strengths, and limitations. It focuses on crucial difficulties, such as high qubit requirements and complex state preparation, that limit scalability for huge images. This paper also assesses each model’s compression efficacy, which will help future research focus on efficient circuit designs with lower complexity for medium to high-resolution images. It is an essential reference for advancing quantum image processing research since it provides a systematic framework for evaluating quantum image compression and representation algorithms.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
|
|
2. Existing Standards for Quantum Image Compression and Representation, and Their Limitations
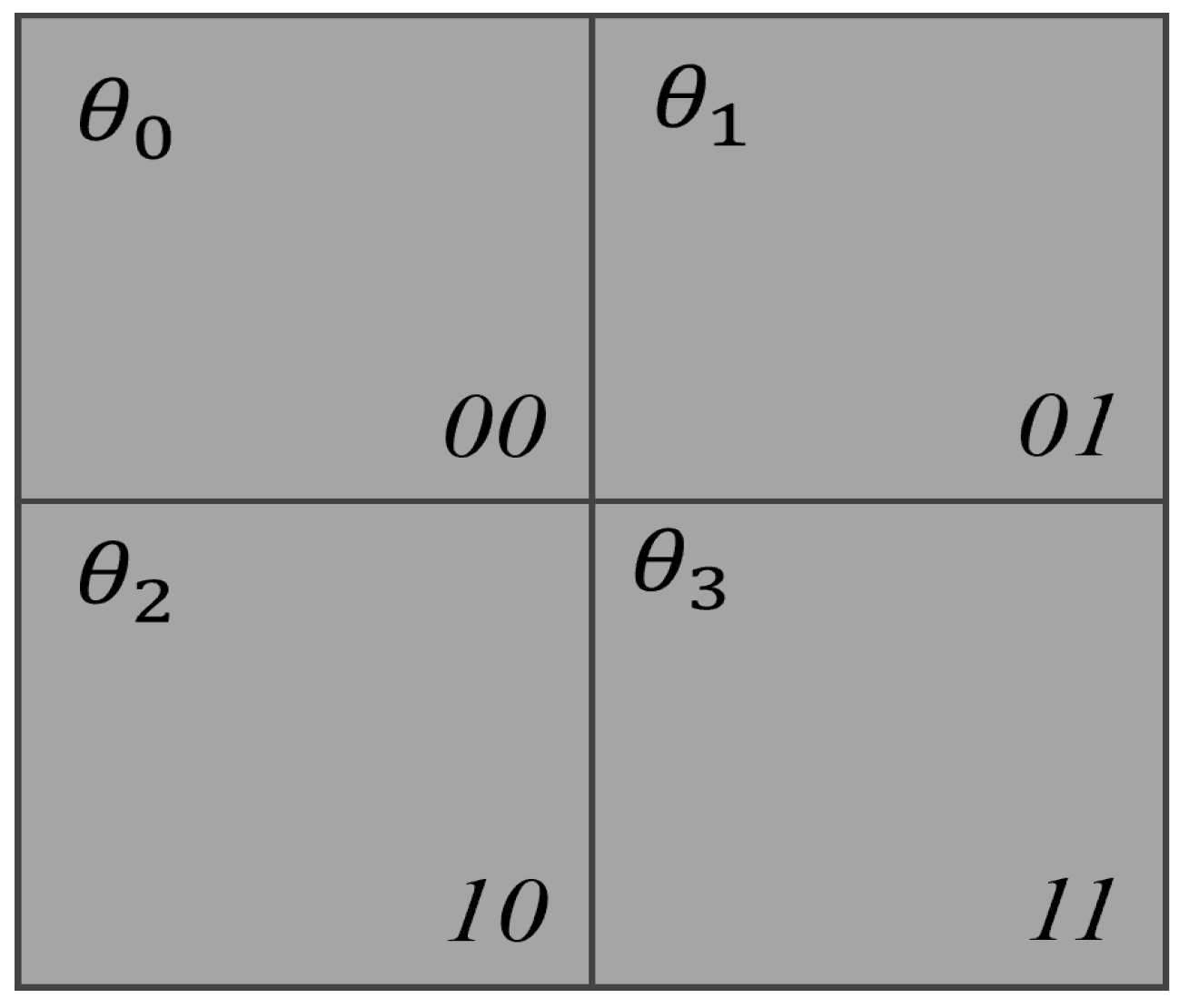
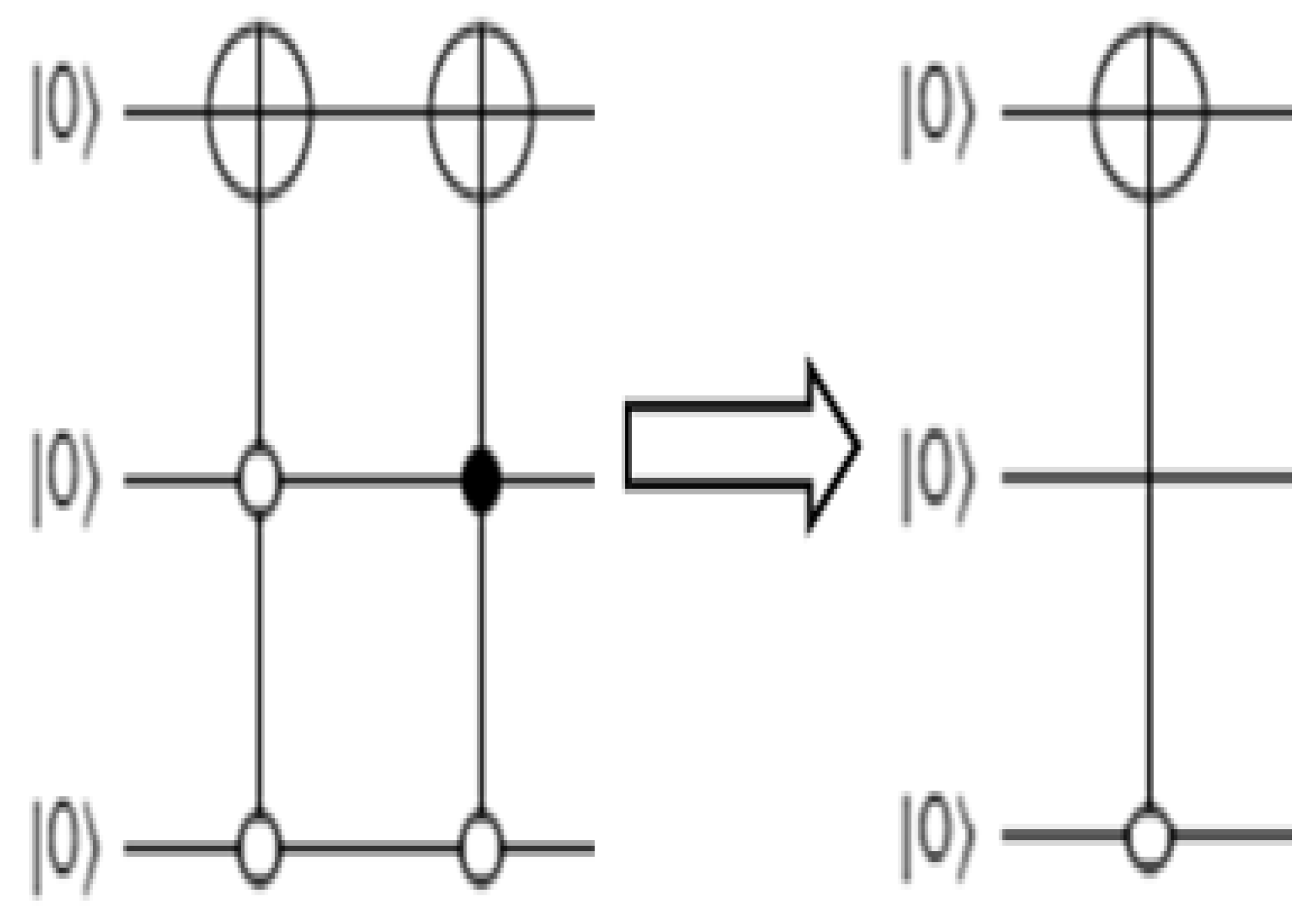
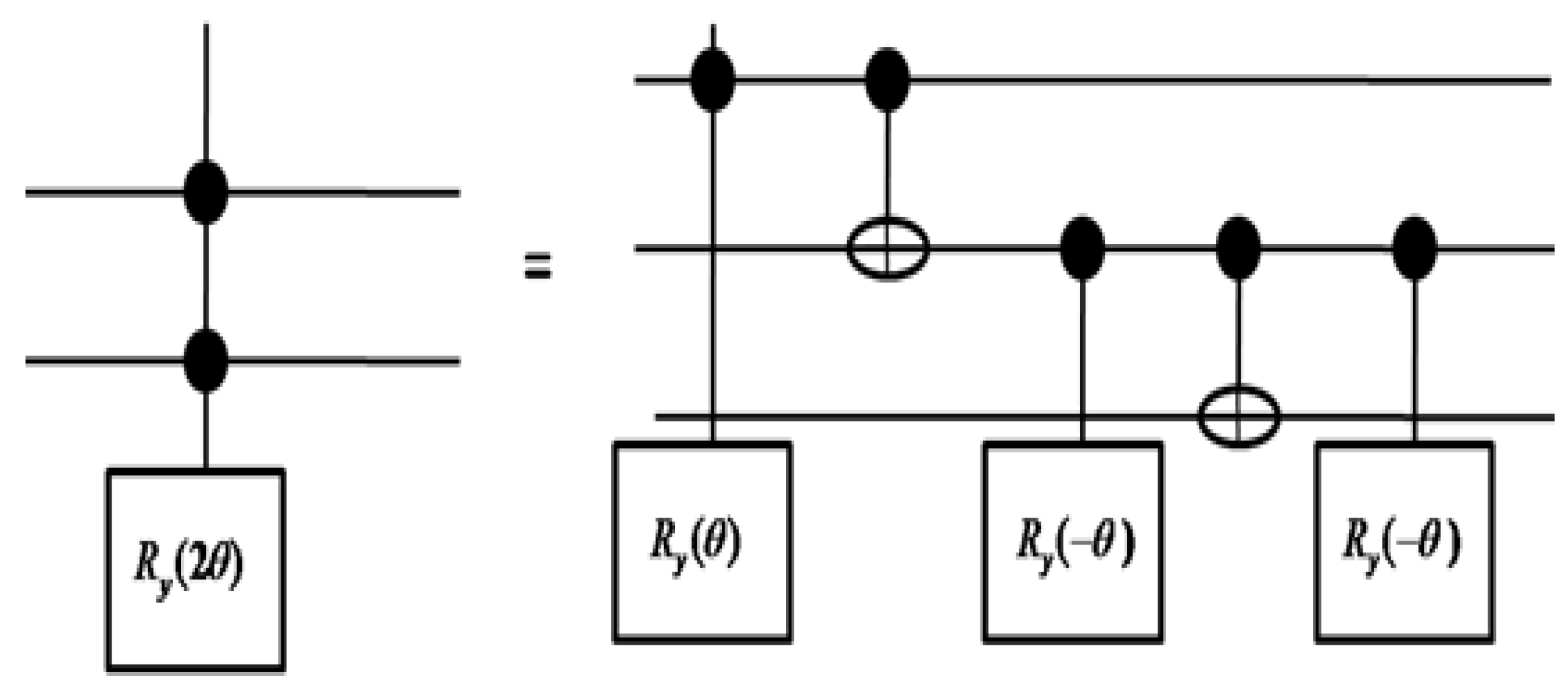
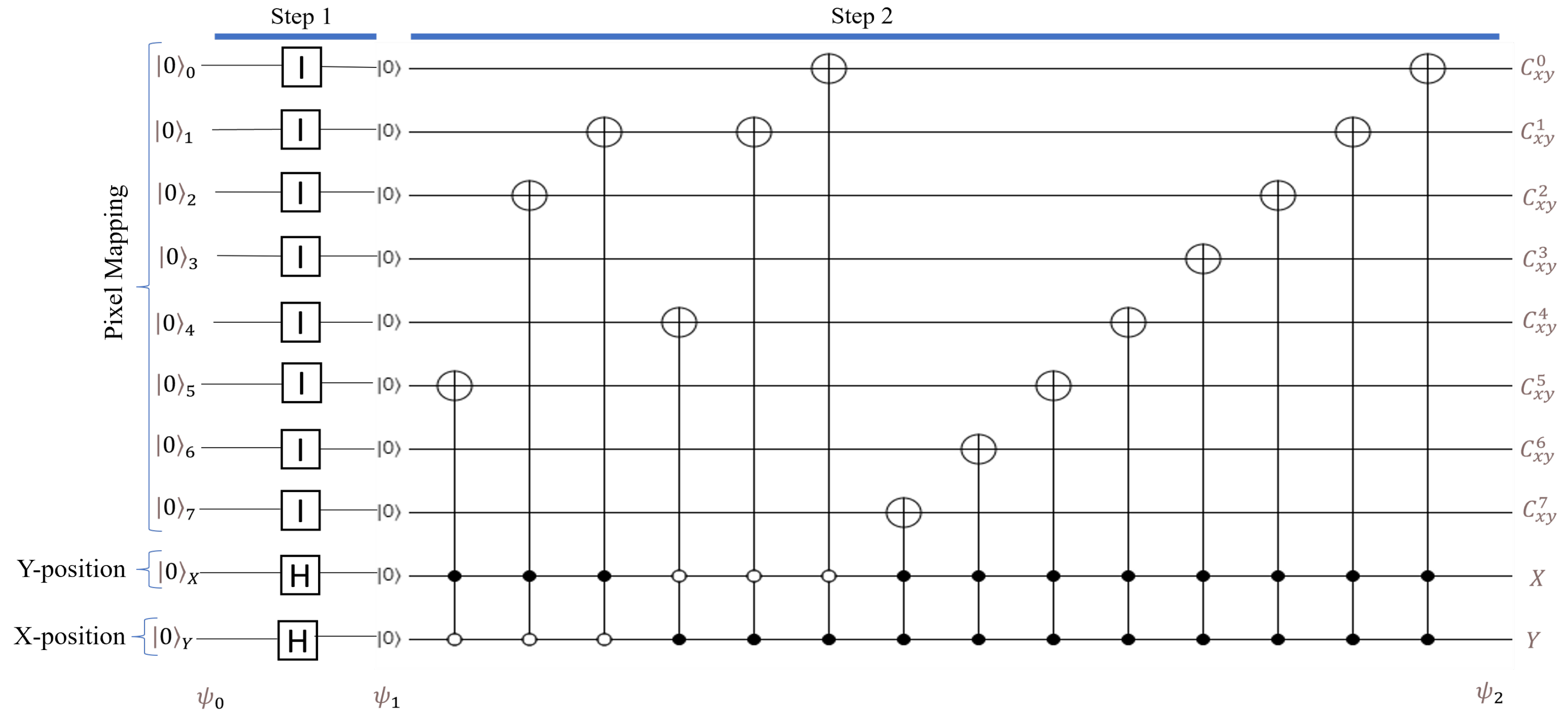
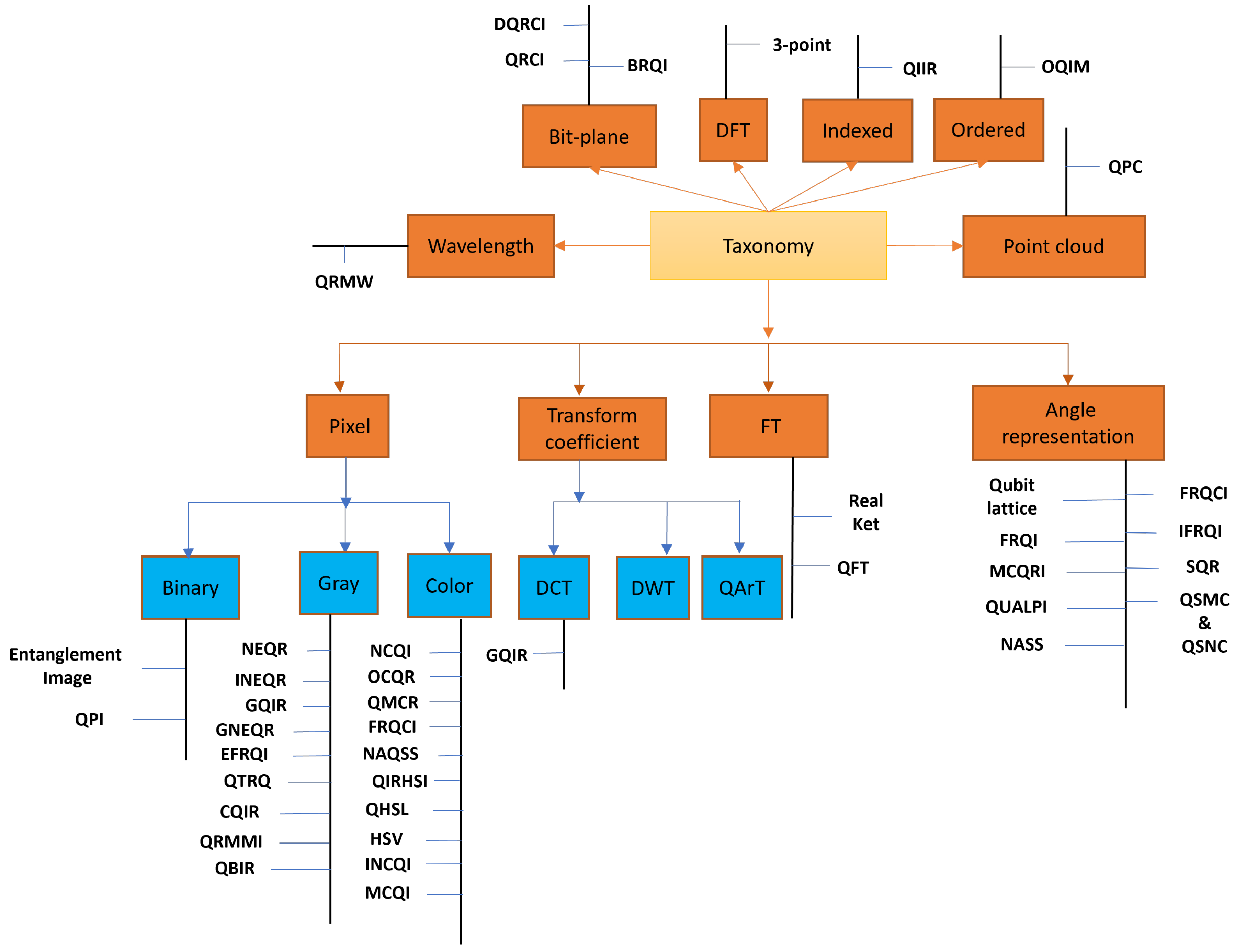
3. Taxonomy of the Quantum Image Compression and Representation Approaches
3.1. Angle-Based Compression and Representation Approach
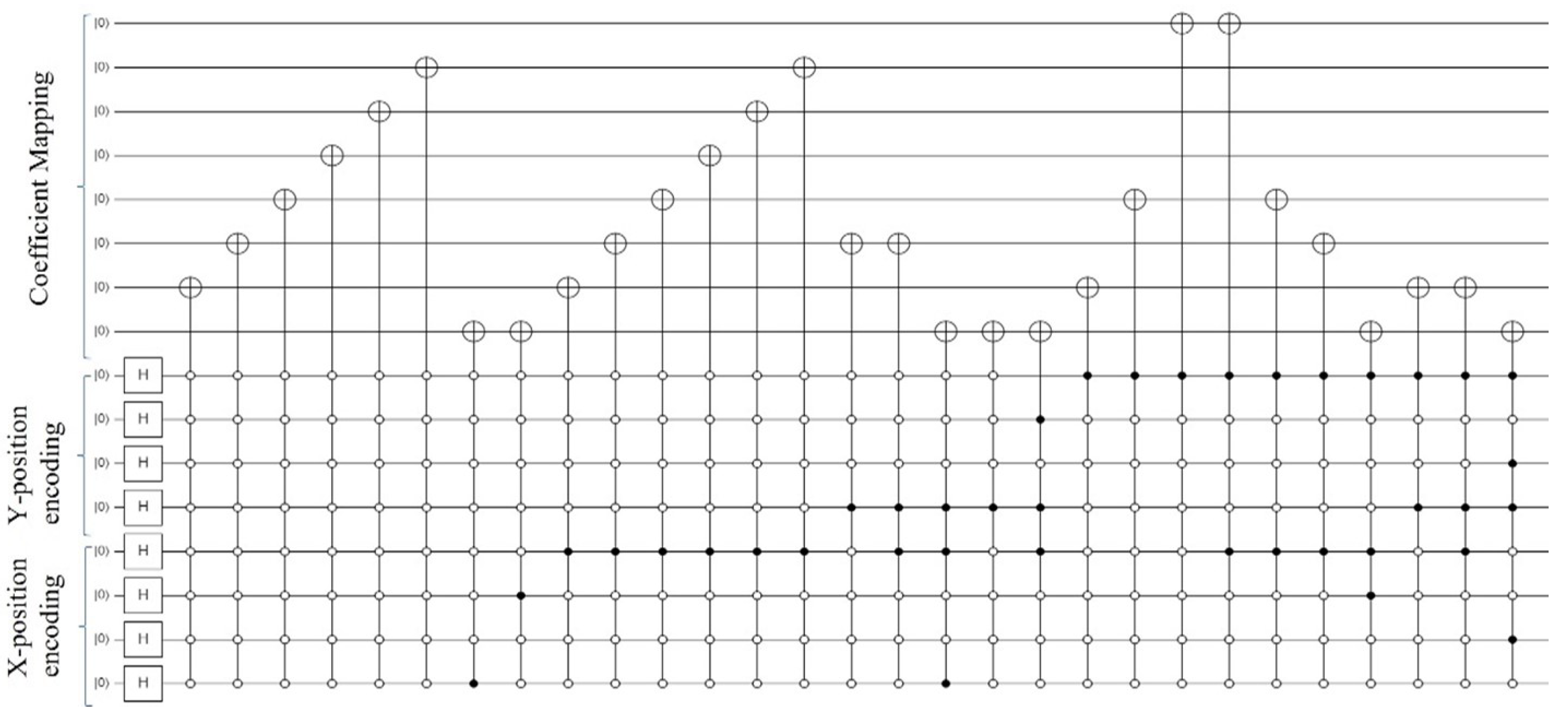
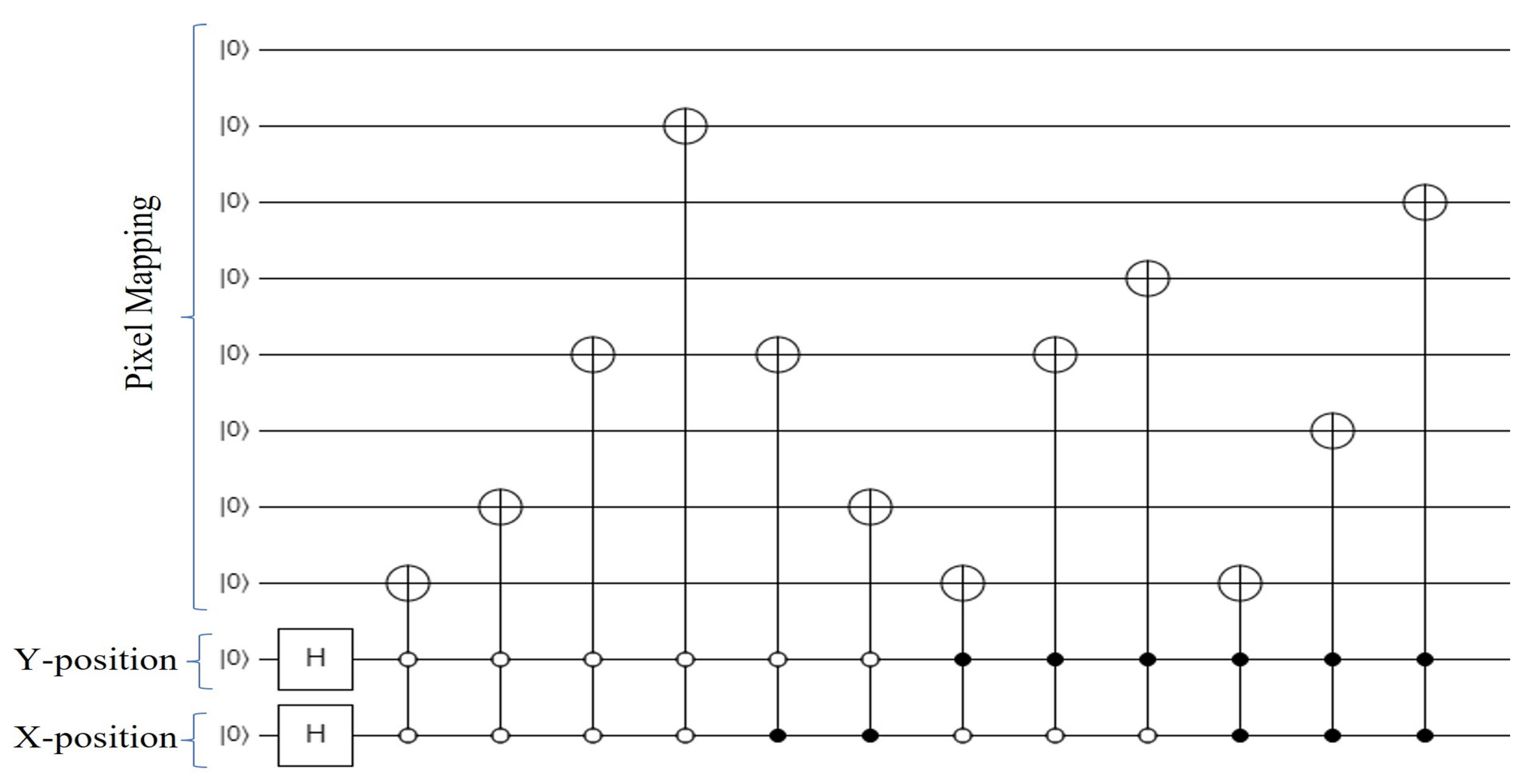
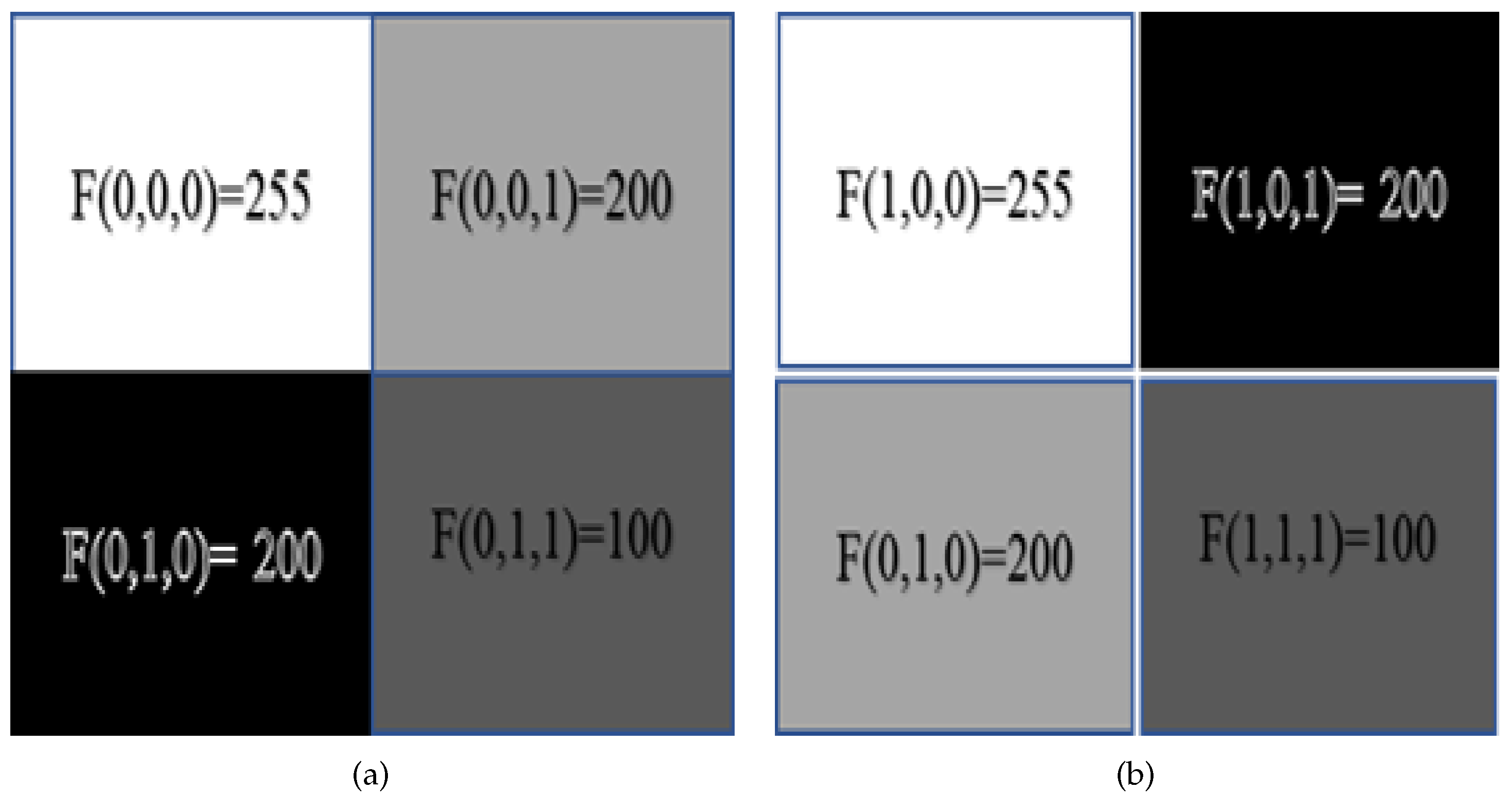
3.2. Overview of Pixel-Based Representation and Compression Approach
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Z. Xu, M. Wang, and Y.Zhang, Review of quantum image processing. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering 2022, 29, 737–761. [CrossRef]
- P.W., Shor, "Fine particles, thin films, and exchange anisotropy",n Proceedings 35th annual symposium on foundations of computer science, pp.124–134, 1994.
- L. K. Grover, "A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search", Proceedings of the twenty-eighth annual ACM symposium on Theory of computing,pp.212–219, 1996.
- I. S. Jacobs, Fine particles, thin films, and exchange anisotropy. Magnetism 1963, 3, 271–350.
- T. D. Ladd et. al., Quantum computers. nature 2010, 464, 45–53. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandrà, S.; Guerreschi, G.G.; Aspuru-Guzik, A. Faster than classical quantum algorithm for dense formulas of exact satisfiability and occupation problems. New J. Phys. 2016, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. E. Venegas-Andraca and S. Bose, Storing, processing, and retrieving an image using quantum mechanics. Quantum information and computation 2003, 5105, 137–147.
- Latorre, J. I. Image compression and entanglement. arXiv 2005, arXiv:quant-ph/0510031. [Google Scholar]
- Le, P. Q., Dong, F., & Hirota, K. A flexible representation of quantum images for polynomial preparation, image compression, and processing operations. Quantum Information Processing 2011, 10(1), 63–84. [CrossRef]
- Sun B, Iliyasu AM, Le P, Dong F, Hirota K (2011) A multichannel representation for images on quantum computers using the rgbα color space. In: IEEE 7th International Symposium on Intelligent, Signal Processing, Malta, Floriana, pp 160–165.
- Zhang Y, Lu K, Gao Y, Xu K A novel quantum representation for log-polar images. Quant Inf Process 2013, 12, 3103–3126.15. [CrossRef]
- Li HS, Zhu Q, Zhou RG, Li MC, Song L, Ian H Multidimensional color image storage, retrieval, and compression based on quantum amplitudes and phases. Inf Sci 2014, 273, 212–232. [CrossRef]
- Li, P., Xiao, H., & Li, B. Quantum representation and watermark strategy for color images based on the controlled rotation of qubits. Quantum Information Processing 2016, 15(11), 4415–4440. [CrossRef]
- Jiang N, Wang J, Mu Y Quantum image scaling up based on nearest-neighbor interpolation with integer scaling ratio. Quant Inf Process 2015, 14, 4001–4026. [CrossRef]
- Liu K, Zhang Y, Lu K, Wang X, Wang X An optimized quantum representation for color digital images. Quant Inf Process, 2018; 57, 2938–2948.
- Abdolmaleky M, Naseri M, Batle J, Farouk A, Gong LH (2017), Red-green-blue multi-channel quantum representation of digital images. Opt: Int J Light Electron 128:121–132. [CrossRef]
- Li P, Liu X (2018a), Color image representation model and its application based on an improved FRQI. Int J Quant Inf 16(1):1850005. [CrossRef]
- Yan, F., Li, N., & Hirota, K. (2021). QHSL: A quantum hue, saturation, and lightness color model.Information Sciences, 577, 196-213. [CrossRef]
- Chen, G. L., Song, X. H., Venegas-Andraca, S. E., El-Latif, A., & Ahmed, A. (2022). QIRHSI: novel quantum image representation based on HSI color space model. Quantum Information Processing, 21(1), 1-31. [CrossRef]
- Sun, B., Iliyasu, A., Yan, F., Dong, F., & Hirota, K. (2013). An RGB multi-channel representation for images on quantum computers. J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform, 17(3). [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, C.; Lu, S.; Li, L. An improved novel quantum image representation and its experimental test on IBM quantum experience. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11(1), 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang N, Hu H, Dang Y, Zhang W Quantum point cloud and its compression. Int J Theor Phys 2017, 56, 3147–3163. [CrossRef]
- Li H-S, Chen X, Xia H-Y, Liang Y, Zhou Z (2018), A quantum image representation based on bitplanes. IEEE Access, 6:62396–62404. [CrossRef]
- Sahin E, YILMAZ I (2018), Qrmw: quantum representation of multi-wavelength images. Turk J Elect Eng Comput Sci 26(2):768–779. [CrossRef]
- Khan, R. A. (2019), An improved flexible representation of quantum images. Quantum Information Processing, 18(7), 1-19. [CrossRef]
- Li, H. S. et al. Image storage, retrieval, compression, and segmentation in a quantum system. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 2269–2290. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S. Z. et al. SQR: A simple quantum representation of infrared images. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 1353–1379. [CrossRef]
- Venegas-Andraca, S.E.; Ball, J.L. Processing images in entangled quantum systems. Quantum Inf. Process. 2009, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurel, C.O.; Dong, S.-H.; Cruz-Irisson, M. Equivalence of a Bit Pixel Image to a Quantum Pixel Image. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2015, 64(5), 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Lu K, Gao Y, Wang M Neqr: a novel enhanced quantum representation of digital images. Quant Inf Process 2013, 12, 2833–2860.
- Jiang N, Wang L Quantum image scaling using nearest neighbor interpolation. Quant Inf Process 2015, 14, 1559–1571. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Lu, X.; Hu, H.; Dang, Y.; Cai, Y. A Novel Quantum Image Compression Method Based on JPEG. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2017, 57, 611–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li HS, Fan P, Xia HY, Peng H, Song S Quantum implementation circuits of quantum signal representation and type conversion. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regular Papers 2019, 66, 341–354. [CrossRef]
- Nasr, N.; Younes, A.; Elsayed, A. Efficient representations of digital images on quantum computers. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2021, 80(25), 34019–34034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Lu, D.; Li, C. A novel qutrit representation of quantum image. Quantum Inf. Process. 2022, 21(3), 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ran, Q.; Ma, J.; Yu, S.; Tan, L. QRCI: A new quantum representation model of color digital images. Opt. Commun. 2019, 438, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang B, Hao M-Q, Li P-C, Liu Z-B Quantum representation of indexed images and its applications. Int J Theor Phys 2020, 59, 374–402. [CrossRef]
- Xu G, Xu X, Wang X, Wang X Order-encoded quantum image model and parallel histogram specification. Quant Inf Process 2019, 18, 1–26.
- Grigoryan AM, Agaian SS, New look on quantum representation of images: fourier transform representation. Quant Inf Process 19(5), 2020. [CrossRef]
- Wang L, Ran Q, Ma J (2020), Double quantum color images encryption scheme based on DQRCI. Multimed Tools Appl 79(9–10):6661–6687. [CrossRef]
- S. Caraiman and V. Manta, Image representation and processing using ternary quantum computing, in Adaptive and Natural Computing Algo- rithms, vol. 7824. Springer, Apr. 2013, pp. 366-375. [Online]. Available: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-3-642-37213-1_38. 1007.
- Zhou, N. R. , Yan, X. Y., Liang, H. R., Tao, X. Y. & Li, G. Y. Multi-image encryption scheme based on quantum 3D Arnold transform and scaled Zhongtang chaotic system. Quantum Inf. Process. 17, 36. [CrossRef]
- Pivoluska, M., & Plesch. Implementation of quantum compression on IBM quantum computers. Scientific Reports 2022, 12(1), 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. B. , Xiao, D., Huang, W. & Liu, C. Quantum block image encryption based on Arnold transform and sine chaotification model. IEEE Access 7, 57188–57199. [CrossRef]
- Sang J, Wang S, Li Q A novel quantum representation of color digital images. Quant Inf Process 2017, 16, 42. [CrossRef]
- Li X-Z, Chen W-W, Wang Y-Q (2018) Quantum image compression-encryption scheme based on quantum discrete cosine transform. Int J Theor Phys 2018, 57, 2904–2919. [CrossRef]
- Pang CY, Zhou RG, Hu BQ, Hu WW, El-Rafei A Signal and image compression using quantum discrete cosine transform. Inf Sci 2019, 473, 121–141. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-S.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, R.-G.; Song, L.; Yang, X.-J. Multi-dimensional color image storage and retrieval for a normal arbitrary quantum superposition state, (in English). Quantum Inf. Process. 2013; 13, 991–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, E.; Paul, M.; Ulhaq, A.; Debnath, T. Advanced quantum image representation and compression using a DCT-EFRQI approach. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Strategy | pros | cons | compression |
| Venegas-Andraca et al.2003 [7] |
Qubit Lattice | Use multi-particle quantum mechanics system. Better reproduction of original values compare to classical. |
Use single qubit only. Four number of pixel values are converted randomly into quantum mechanics system. |
No |
| Le et al.2011 [9] | FRQI | Capture the image pixel color and its position. Convert the image into its normalized state. |
Mapping the pixel into angle using a single qubit. Use traditional Boolean expression compression approach. Unable to represent pixel-wise operation. |
Yes. |
| Sun et al.2011 [10] | MCRQI | Represent RGB quantum color image. Qubits represent the color space of the image. |
Insufficient qubit to represent to medium or big size images. Map the pixel values as an angle does not give sufficient knowledge to represent a big size image. |
No. |
| Zhang et al. 2013 [11] | QUALPI | Represent the image in log-polar coordinate system. Use geometric transformation to convert the image. array of image size was considered |
Generate more redundant information for position preparation. Nearly impossible to pixel wise representation of a medium or big size image. |
No. |
| Li et al. 2014 [12] | NASS | It represent multidimensional color image. Create arbitrary superposition. |
Pixels are directly converted into angle leading the question of originality of reproduction. How compression happens is not mentioned clearly. Applicable for very low-resolution images. |
Yes. |
| Li et al. 2016 [17] | FRQCI | Use two phases parameter to locate the RGB pixel value. |
Use single qubit lead the poor quality for its representation. Considered array size of the image which can carry a tiny amount of information for real application. Not suitable for big-size images due to generating huge amount of information for state preparation. |
No. |
| Khan et al.2019 [25] | IFRQI | Able to represent two bits as an angle | Only represent array of pixel image directly. Image reconstruction procedure is still missing. |
No. |
| Li et al.2013 [26] | QSMC & QSNC |
Represent pixel and state value. Image is segmented based quantum method. |
Use only array of image. Applicable for square size image. Reconstruction procedure is not mentioned properly. |
Yes |
| Yuan et al. 2014 [27] | SQR |
Represent and store the infrared image using Qubit lattice approach. |
Angle parameter is not mentioned clearly. Lack of information to represent a real image. |
No |
| Reference | Strategy | pros | cons | compression |
| Zhang et al. 2013 [30] | NEQR | Uses eight numbers of qubits to represent the gray image. |
Only applicable for square image. Mapping the pixel values directly leading the complexity of preparation. |
No. |
| Zhang et al. 2015 [31] | INEQR | Able to represent unequal horizontal and vertical coordinate image. |
Applicable for the small size of gray image for mapping. In what way, mapping of big size color image is still a gap? |
No. |
| Zhang et al. 2015a [32] | GQIR | Represent the rectangular image in any arbitrary shape. |
Generate more redundant information for position preparation. Nearly impossible to pixel wise image representation of a medium or big size image. |
No. |
| Li et al.2019 [33] | GNEQR | Represent real and complex value signal information. |
Applicable for square image. Complexity of preparation is very high, like NEQR. |
No. |
| Nasr et al. 2021 [34] | EFRQI | Use Toffili gate for state preparation. | Its increase the number of require gate compare to GQIR. Complexity become high when attempting to represent every pixel of an real application image |
No |
| Dong et al. 2022 [35] | QTRQ | Use ternary quantum system to store the formation. | Image is reconstructed procedure is not discussed. Exactly where and how the compression happens is not mentioned clearly. Nothing mentioned about quality measurement. |
Yes |
| Caraiman et al.2013 [41] | CQIR |
To store and process image use multi- label quantum system |
Higher preparation complexity. Did not mention how the image array is mapped. |
No |
| Zhou et al.2018 [42] | QRMMI |
Represent multiple image using 3D Arnold transform. |
Increase complexity mapping of sequence number. Limited to array size of image |
No |
| Liu et al.2019 [44] | QBIR | Represent pixel image as block-wise | Complexity is similar to NEQR. Map pixel value directly into quantum domain create higher preparation complexity for state connection |
No |
| Reference | Strategy | pros | cons | compression |
| Sang et al. 2017 [45] | NCQI | Represent the RGB value of color image separately. Decrease the time complexity compared to MCRQI. |
Although the author proposed color image representation, but it processes gray image for measurement. Require too many qubits to do the operation. Reconstruction of the image was not examined. How the required number of gates and PSNR are calculated is not mentioned. |
No. |
| Liu et al. 2018 [15] | OCQR | It require several qubits for representation compared to MCQI. Decrease the time complexity compared to MCRQI. |
Increase the complexity of operation due to counting channel swapping operation. |
No. |
| Abdolmaleky et al. 2017 [16] |
QMCR | Reduce the complexity of preparation compared to NEQR. |
More qubits is required compared to MCRQI. Quality of the reconstruction image is still issue. Working with pixel values conversion from classical to quantum leads the complexity of the preparation. |
No. |
| Li et al. 2016 [17] | FRQCI | Store the RGB value of the color image | Use probabilistic amplitude and phase against the pixels value information. Applicable for array image. How a higher resolution image is reconstructed still gap. |
No. |
| Yan et al.2021 [18] | QHSL | Map the image using Hue, Saturation, Lightness |
Only applicable for image. How mapping a big size image is still unclear |
No |
| Chen et al. 2021 [19] | QIRHSI | Represent image based on HSI (hue, saturation, intensity) method. Require less qubits compared to NCQI |
Use traditional BEC approach for optimization. Applicable for array size of image only Did not mention image reconstruction strategy |
No |
| Sun et al. 2013 [20] | MCQI | Represent multichannel color image | Only applicable for square image. limited to array size of image |
No |
| Su et al. 2021 [21] | INCQI | Represent color image. Use rectangular image |
Increase complexity due to considering accessory quantum bits. Applicable for array size of image |
No |
| Li et al.2014a [48] | NAQSS | Represent and segment the color image. | More complexity due to considering extra qubit for segmentation purpose. Quality is not measured after representation |
Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





