Submitted:
11 November 2024
Posted:
12 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Automation Testing Principles
- (a)
- Test cases are pre-written and not ambiguous.
- (b)
- Test cases are autonomous
- (c)
- Each test case can run independently.
- (d)
- Test cases may not cover end to end scenarios.
- (e)
- Keep test tests short
- (f)
- Each test case can cover only one functionality.
- (g)
- Test cases are idempotent
- (h)
- Minimize incident Test coverage.
- (i)
- Automation testing tool selected via proper research.
- (j)
- Coding standards should define for script writing.
2.1. When to Automate?
2.2. Architecture and Flow
- Reusability
- Maintainability
- Flexibility
2.3. Architecture Diagram
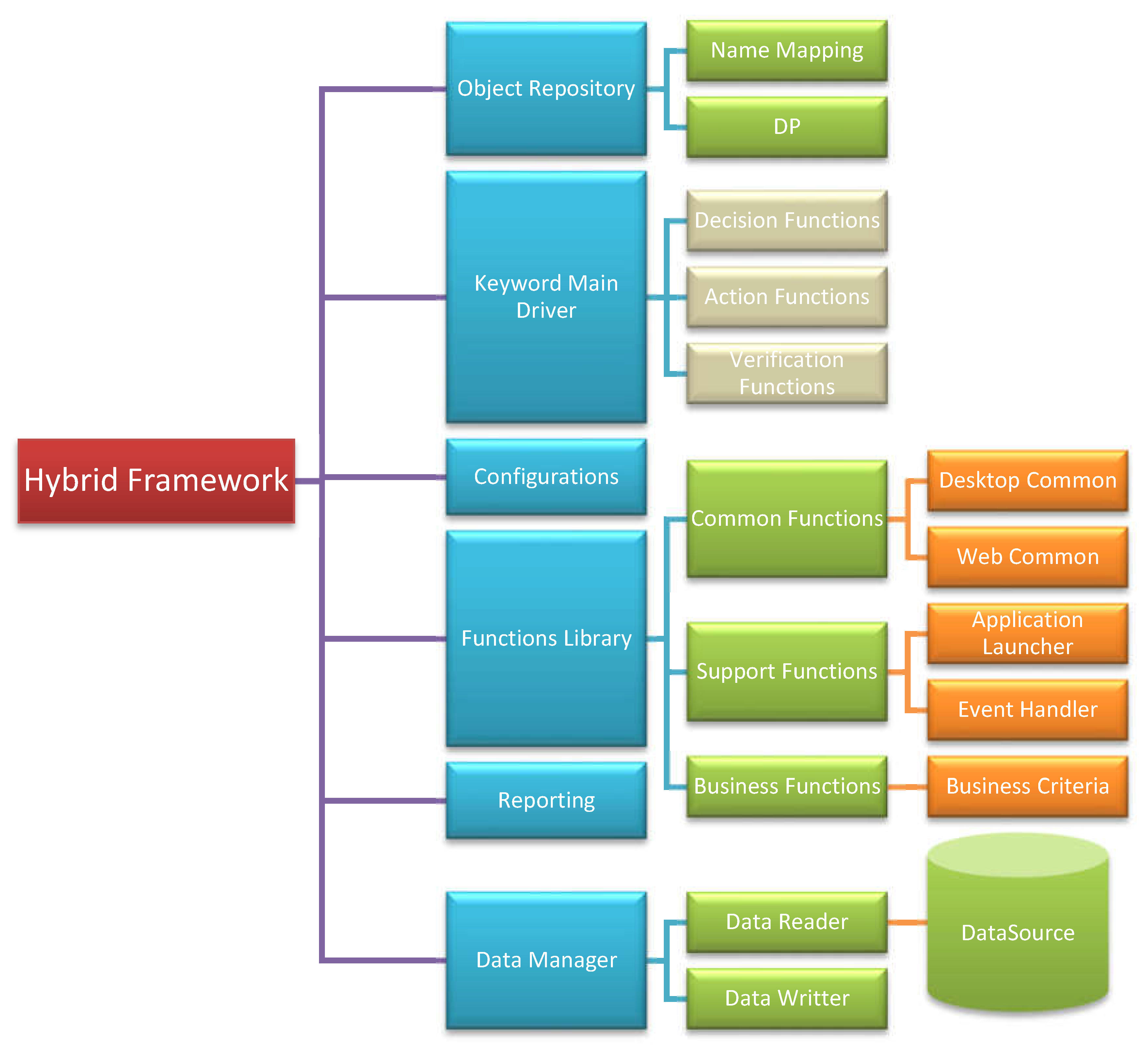
2.4. Control Flow of Hybrid Automation Testing Framework
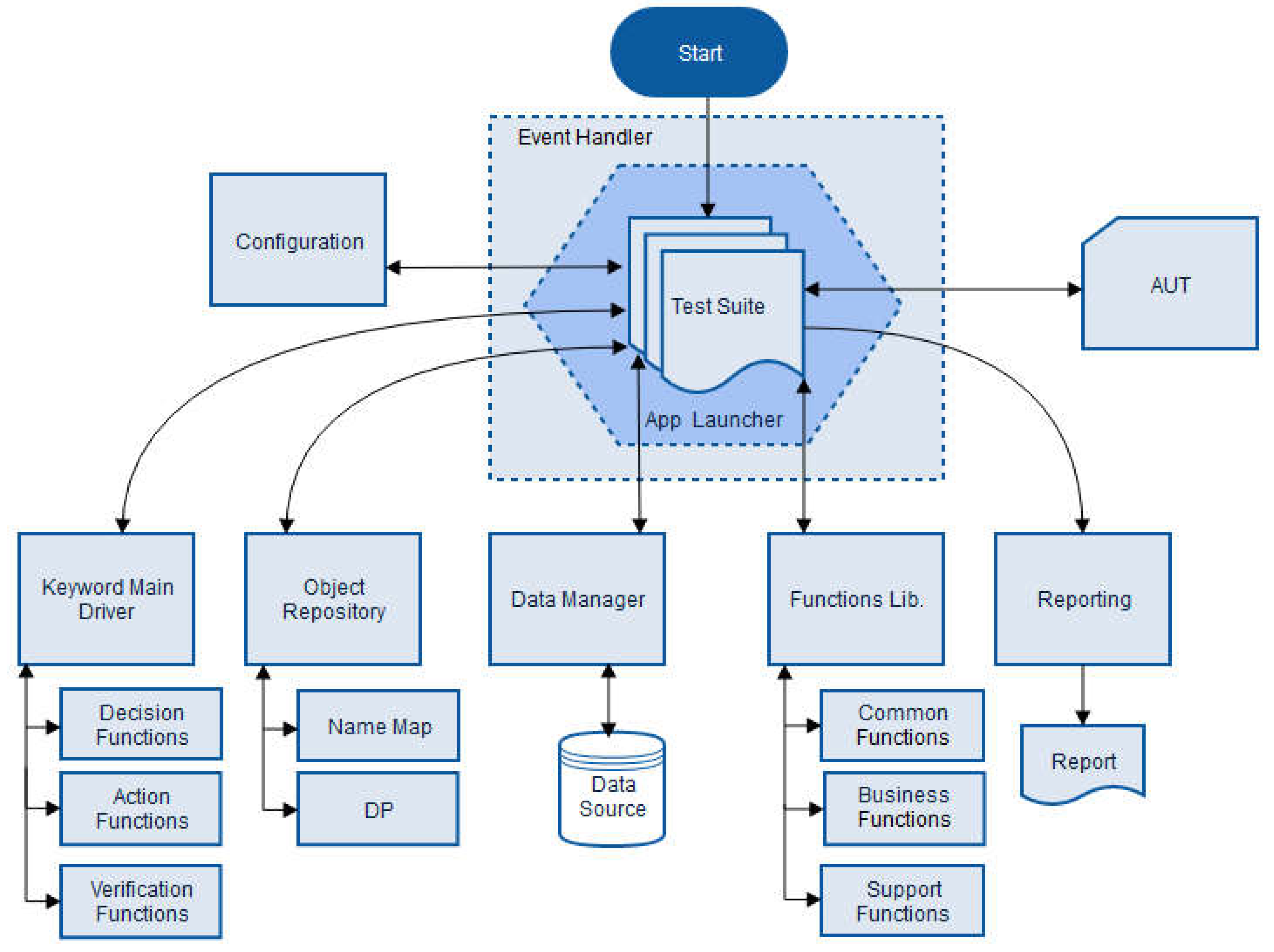
2.5. Object Repository
2.6. Name Mapping
2.7. Mapped objects
2.8. Aliases
2.9. Descriptive Programming
2.10. Functions Library
2.11. Common Functions
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| SelectDropDownItem | It’s a function which can be used to select item from drop down List. Usage: SelectDropDownItem(Object,Val) |
| GetSelectedItemValue | It’s a function which can be used to get selected item from drop down list. Usage: GetSelectedItemValue (Object) |
| SetText | It’s a function which can be used to set text into required object. Usage: SetText(Object,Val) |
| GetText | It’s a function which can be used to get text from required object. Usage: GetText(Object) |
| FindRow | It’s a function which can be used to find row number from Grid/Table. Usage: FindRow(Object,ColName,Val) |
| ClickCell | It’s a function which can be used to click on specific grid cell. Usage: ClickCell(Object,RowID,ColName,Val) |
| DoubleClickCell | It’s a function which can be used to double click on grid cell. Usage: DoubleClickCell(Object,RowID,ColName,Val) |
| ClickTab | It’s a function which can be used to click on tab control. Usage: ClickTab(Object,Item) |
| ClickRibbonButton | It’s a function which can be used to click on ribbon. Usage: ClickRibbonButton(ButtonName) |
| ClickRibbonMenu | It’s a function which can be used to click on ribbon menu item. Usage: ClickRibbonMenu(Object,MenuItem) |
| ClickToolBarButton | It’s a function which can be used to click on tool bar button. Usage: ClickToolBarButton(Object) |
| clickMsgPopups | It’s a function which can be used to click on MsgPopups button. Usage: ClickMsgPopups(Object,buttonname) |
| getRowCount | It’s a function which can be used to get page row count from grid. Usage: GetRowCount (Object) |
| getCellValue | It’s a function which can be used to get cell value from grid. Usage: getCellValue(Grid,RowIndex,ColIndex) |
| getColIndexByName | It’s a function which can be used to get column index by its name from grid Usage: getColIndexByName(Grid,colName) |
| getColumnCount | It’s a function which can be used to get column count from grid Usage: getColumnCount (Grid) |
| getDropDownValueInGrid | It’s a function which can be used to get drop down value from grid Usage: getDropDownValueInGrid (Grid,rowIndex,ColName) |
| selectDropDownValueInGrid | It’s a function which can be used to select drop down value from grid Usage: selectDropDownValueInGrid (Grid,rowIndex,ColName,Value) |
2.12. Support Functions
2.13. Events
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| OnLogMessage | It occurs when an informative message is posted to the test log. Usage: GeneralEvents_OnLogMessage(Sender, LogParams) |
| OnLogCheckpoint | It occurs when a checkpoint message is posted to the test log. Usage: GeneralEvents_OnLogCheckpoint(Sender, LogParams) |
| OnLogError | It occurs when an error message is posted to the test log. Usage: GeneralEvents_OnLogError(Sender, LogParams) |
| OnLogEvent | It occurs when an event notification is posted to the test log. Usage: GeneralEvents_OnLogEvent(Sender, LogParams) |
| OnLogWarning | It occurs when a warning message is posted to the test log. Usage: GeneralEvents_OnLogWarning(Sender, LogParams) |
| OnStartTest | It occurs when TestComplete starts a test run. Usage: GeneralEvents_OnStartTest(Sender) |
| OnStopTest | It occurs when a test run is over. Usage: GeneralEvents_OnStopTest(Sender) |
2.14. Application Launcher
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Launcher | It’s a function that starts the application, checks the availability of network and the Database. Usage: ApplicationLauncher(Process Name) |
| Network Availability | It’s a function which checks the Network Availability. Usage: NetworkAvailability() |
| Database Availability | This function is use to check Database Availability Usage: Function DatabaseAvailability() |
2.15. Business Functions
2.16. Data Manager
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| GetDriver | This function will be used to create a driver Usage: GetDriverInstance(DataSourceType,DataSourceName) |
| SetSourceData | This function will set a data source and filter can also be applied on that data source. Usage: SetSourceData(DriverObj,DataFilter,DataFilterColumn) |
| GetItemValue | This function will get data from a particular cell of Recordset. Usage: GetItemValue(RecordSet, ColumnName, RowId) |
| GetRowCount | This function will return the number of rows of RecordSet. Usage: GetRowCount(RecordSet) |
| GetColumnCount | This function will return the number of columns of RecordSet. Usage: GetColumnCount(RecordSet) |
| GetItemRowIndex | This function will return the row number of RecordSet. Usage: GetItemRowIndex(RecordSet,ColumnName,Value) |
| GetColumnIndex | This function will return the column number of RecordSet. Usage: GetColumnIndex(RecordSet,ColumnName) |
| DataWriter | This function will write the data in data source. Usage: DataWriter (DataSourceType, DataSourceName, RowId, ColumnName, Value, Appendmode) |
2.17. Decision Functions
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| EvaluateObjectType (Decision) | It is used to decide the execution based on the ObjectType Keywords. Usage: fnSet (object, Action, Data) Note: Few functions will be developed such as fnClick, fnVerifyValue, fnVerifyExists etc |
| EvaluateAction (Decision) | It is used to decide the execution based on the Action Keywords. Usage: EvaluateAction (object, Action, Data) |
2.18. Action Functions
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| FnTextBox_Set | It provides the ability to perform the required action/activity e.g. Textbox Set etc. It is the actual implementation of performing the actions. Usage: FnTextBox_Set (object, Data) |
| FnComboBox_Set | It provides the ability to perform the required action/activity e.g, Combobox Set etc. It is the actual implementation of performing the actions. Usage: FnComboBox_Set (object, Data) |
2.19. Verification Functions
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| FnVerifyValue | It provides the ability to perform the required verifications e.g. VerifyValue etc. It is the actual implementation of performing the verifications. Usage: FnVerifyValue (object, Data) |
| FnVerifyExists | It provides the ability to perform the required verifications e.g. VerifyExists etc. It is the actual implementation of performing the verifications. Usage: FnVerifyExists (object, Data) |
| FnVerifyState | It provides the ability to perform the required verifications e.g. VerifyState etc. It is the actual implementation of performing the verifications. Usage: FnVerifyState (object, Data) |
2.20. Configuration
3. Characteristics of Hybrid Automation Framework
3.1. Introduction to Hybrid Automation Testing Framework
- Reusability
- Maintainability
- Flexibility
- Adoptability,
- Hybrid (Adopt the good things of other frameworks and remove the limitations of other frame work )
3.2. Reusability
- Base Common functions are those functions which are used throughout the application, each function should describe in separate unit/file/class. Other functionalities of that particular function for example dialogue handling etc. should also describe in the same class.
- Module Common functions are those functions which are used for that particular module only and should never be used in outside the module or some other module each function should describe in separate unit/file/class. Other functionalities of that particular function for example dialogue handling etc. should also describe in the same class.
- The naming conventions of common functions should be according to some pre-defined standards for example function name can be written as Pascal case like ClickButton() is a perfect example of a function which can click on desired button
3.3. Maintainability
3.4. Flexibility
3.5. Adoptability
3.6. Hybrid
4. Design Pattern Involved
4.1. Design Pattern (POM)
4.2. Page Object Model
4.3. Object Repository
4.4. Modular Driven Technique
4.5. Function Parameters
4.6. Constants
4.7. Data Driven Technique
4.8. Logging
- Explicit
- Implicit
4.9. Reporting
- Auto Generated Report
- Custom Report
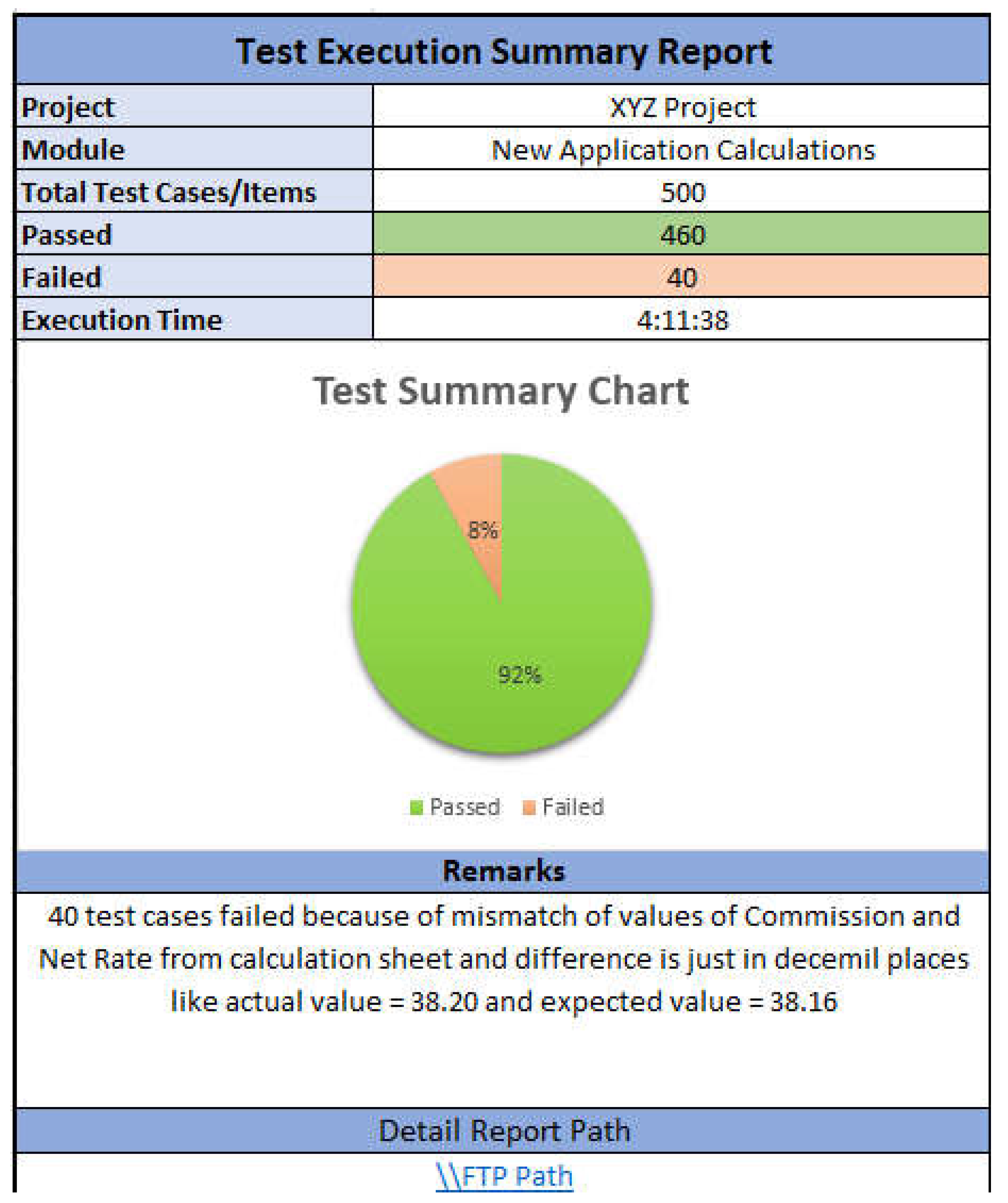
4.10. User Defined Functions
4.11. Exception Handling
5. Scripting
5.1. Scripting
5.2. Check Points
5.3. Exclusive Functions
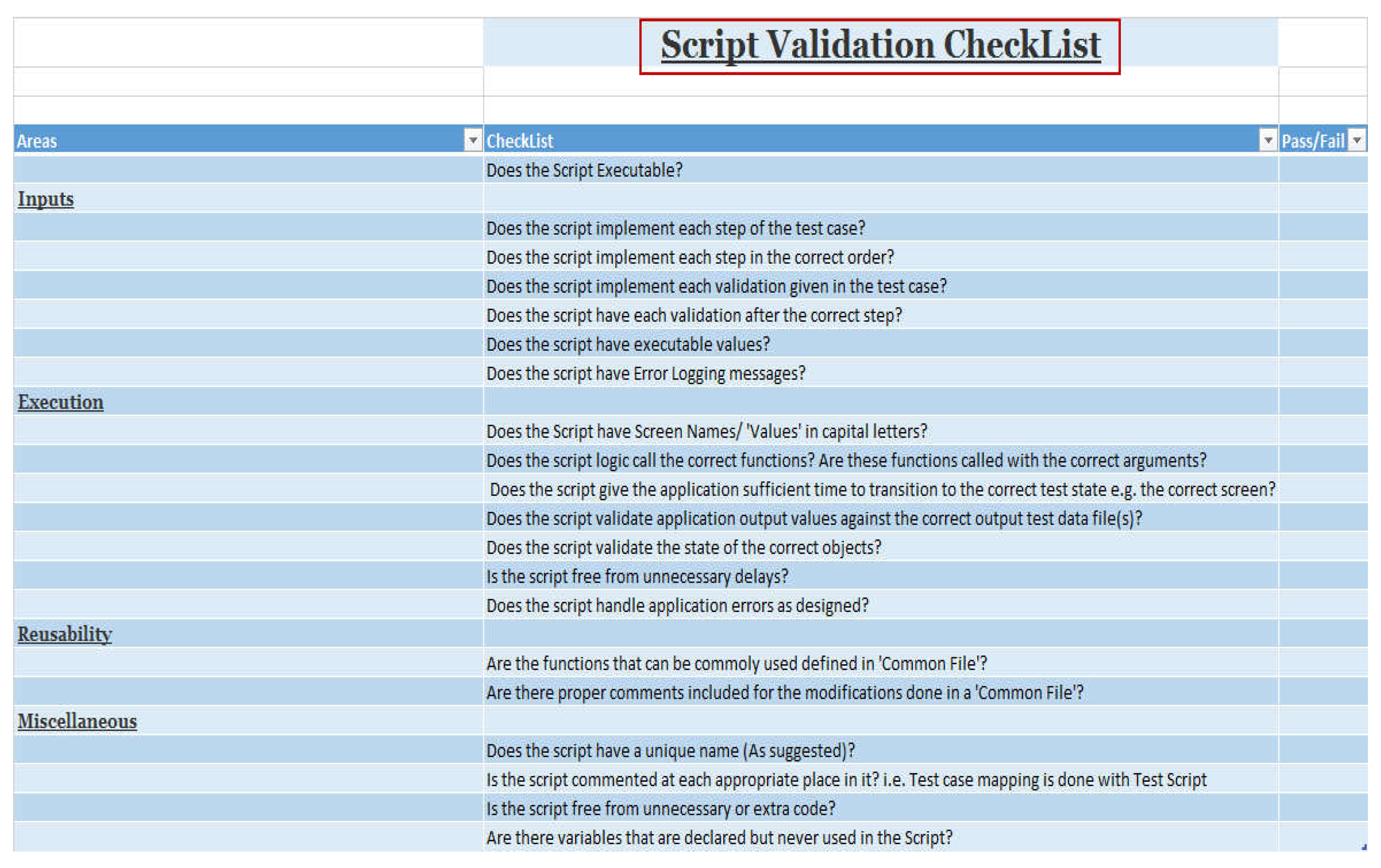
5.4. Script Validation Checklist
5.5. Performance of Application Under Testing
5.6. Identification of Interface Layers:
7. Coding Standards
Coding Standards
- 1.
- Indentation
- (a)
- Indentation of a code is a basic rule to improve the readability of code
- (b)
- Code in all routines/ functions will be indented with single tab. Code inside programming constructs such as If...Else, Switch, For, and Do...Loop will be indented one additional tab. Nested constructs will be indented an additional single tab for each level of nesting e.g.

- (c)
- Common Functions
- (d)
- Function Names PascalCase
- 1.
- Functions name should be meaningful
- 2.
- Functions name should be written in Pascal case i.e. first letter must be in upper case e.g. “AddFlatCancellation”

- (e)
- Use of Prefixes
- 1.
- Use “Can”, “Is” and “Has” prefixes with Boolean functions e.g. IsEnable()
- 2.
- Append computational qualifiers to function names like Average, Count, Sum, Min, and Max where appropriate e.g. SumTotalAmount()
- (f)
- Hungarian Notation
- (g)
- Class/Unit Name in Pascal Case
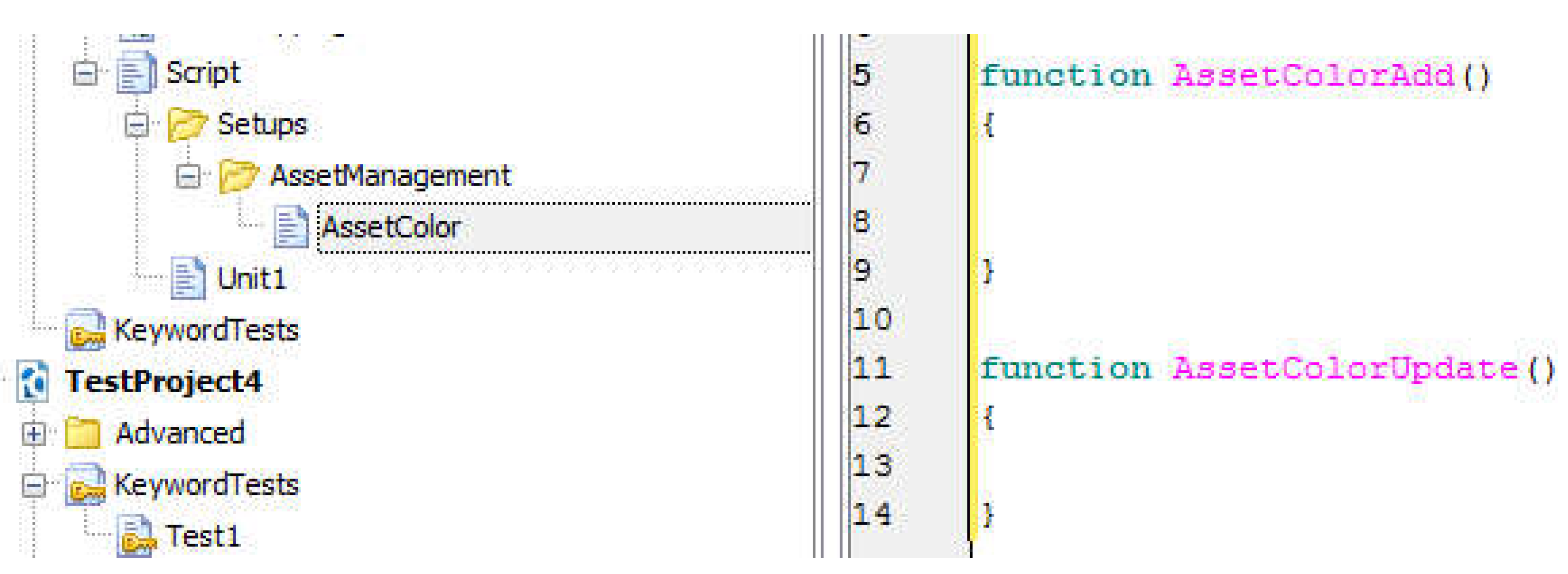
- (h)
- Code Organization
- 1
- Keep modules to a manageable size. If module become larger split into functional criteria.
- 2
- Small, cohesive modules are more manageable and easier to understand
- 3)
- Any if or else block should not be empty.
- 4
- Apply spaces liberally. Spaces break up the code, making it easier to read.
- 5
- There should not be any unreachable code in the script
- 6
- Add comments for anything ambiguous in script like use of abbreviations.
- 7
- In case of multiple if else statements, use switch statement.
- (i)
- Variable Names
- 1
- Variable Name should be Descriptive and Meaningful.
- 2
- Array should be declared using “Arr ” prefix
- 3
- Example: “arrName(Camels case) for local variables” and “ArrName(Pascal case) for global variables”
- 4
- Local Variables should be written in camel case i.e. addButton
- 5
- Global Variables should be in Pascal case i.e. AddButton.
- 6
- For longer variable names we should be using meaningful abbreviations. An abbreviation should not be greater than 5 characters. Moreover, for two characters abbreviations name should be in all caps and for greater the name should be in Pascal case. Also comments should be provided where abbreviations will be used
- 7
- Use “Can”, “Is” and “Has” prefixes with Boolean variables.
- 8
- Append computational qualifiers to variable names like Average, Count, Sum, Min, and Max where appropriate.
- 9
- Do not use Hungarian Notation! Example: strName or iCount
- (j)
- Comments and Headers
- 1
- Add proper meaningful comments between coding statements.
- 2
- Use Proper English While Adding Comments. Don’t use Abbreviations while adding comments.
- 3
- On top of each script or function there should be a General information header. It should contains information such as description, summary, author name, reviewer name etc.
- 4
- This is very important that you explicitly mention the mapped FTCs ids in Script information header, since one ATS can mapped to multiple FTCs so use will mention all the FTCs ids that are covering in that particular ATS.


- (a)
- Debugging Statements
- (b)
- (Error Logging
8. Automation Scope/ Coverage
8.1. Defining Scope of Automation
8.2. Identification of Test Cases to Be Automated
- Test cases that are lengthy and complex and require human involvement.
- Test case which can take long time to be automated.
- Test cases which cannot be reused.
- Test cases for usability testing. Usability testing is supposed to be done in real time end user environment.
8.3. Test Cases Have Been Adjusted:
8.4. Choosing the Right Mode of Automation
8.5. HOW to Automate?
8.6. Following Scripting Standards:
8.7. Identifying Common Actions:
8.8. Development of Objects Repository
8.9. Extensibility
8.10. Custom Logs
8.11. Test Batch for Execution
8.12. Cleaning-Up
13. Conclusions & Recommendations
13.1. Conclusions
13.2. Is it All Beneficial?
- Testers will be sure about the level of testing they need to focus on.
- Application under testing will not be vulnerable in behavior, which will ultimately help the testers to use scripts for longer time period.
- Because application will be stable, scripts maintenance cost will reduce ultimately.
- Testers focus will be more on inner functionalities rather than GUIs. This will save a lot of time in developing scripts for core functionalities.
- The effort which was to be put in for development of complex and lengthy test cases can be put in development of smaller and easier test cases. It means more test cases will be covered in similar time period.
- Selected tool will definitely adhere to all testing requirements
- More reliable test cases will produce through which testers will ultimately target more sophisticated areas to be tested.
- If test cases are fine-tuned then test developers can also develop fine test scripts.
- It will be easier to extend the automation suite for test cases related to other versions of applications.
- More consistent test cases and test scripts will be developed throughout whole testing cycle.
- Re-Usability factors will definitely increase. Test Developers can access more objects and data, quickly and use easily.
- A lot of manual object creation activity will be decreased.
- Faults analysis will be easier with help of customized logs.
- The manual effort in script cleaning will be decreased eventually with development of clean-up scripts.
- There will be clarity in scope of automation. Testers will be confident about what they are going to automate.
References
- Gauf B, D. E. , Garrett T. (n.d.). Implementing automated software testing: How to save time and lower costs while raising quality. (Pearson Education). Pearson. https://books.google.com.my/books? 2009. [Google Scholar]
- A Literature Review on Automation Testing Using Selenium+Sikuli. (2022, ). SciSpace - Paper; IGI Global eBooks. 1 January. [CrossRef]
- Mitra, D.; Offshore, A. Organization Need Based Specific NDE Development Application Research on Key Performance Areas (KPA). e-Journal Nondestruct. Test. 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, S. A. , M. (2024). Challenges for the Development of Artificial Intelligence Models to Predict the Compressive Strength of Concrete Using Non-destructive Tests: A Review. In R. Gupta, M. Sun, S. Brzev, M. S. Alam, K. T. W. Ng, J. Li, A. El Damatty, & C. Lim (Eds.), Proceedings of the Canadian Society of Civil Engineering Annual Conference 2022 (Vol.; pp. 367839–857. [CrossRef]
- Ashish Lathwal. (n.d.). Ashish Lathwal | 2 Publications | 1 Citations | Related Authors. SciSpace - Author. Retrieved , 2024, from https://typeset. 5 November.
- Bedick, C.; Tulgestke, A.; Nie, K.; Ferguson, D.H. Comparisons of RDE inlet dynamics in a linear testing platform and models of varying complexity. AIAA SCITECH 2022 Forum. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE.
- Bennett, G.; Hall, T.; Winter, E.; Counsell, S. Semgrep*: Improving the Limited Performance of Static Application Security Testing (SAST) Tools. EASE 2024: 28th International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, ItalyDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 614–623.
- Bierig, R.; Brown, S.; Galván, E.; Timoney, J. Essentials of Software Testing; Cambridge University Press (CUP): Cambridge, United Kingdom, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, N.; Harris, R.; Marsh, D. Repurposing Spent Upper Stages into Platforms for In-Space Testing. AIAA SCITECH 2022 Forum. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- Braun, D.; Schwaiger, F.; Holzapfel, F.; Diepolder, J.; Ben-Asher, J.Z. Continuous Integration of Optimal Control Based Flight Control Law Clearance. AIAA SCITECH 2022 Forum. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE.
- Ciptaningtyas, H.T.; Husni, M.; Rosyadi, F.D.; Qudus, R. Web based Application Quality from End User Perspective: Case Study - Assignment Letter LPPM ITS. The 7th Engineering International Conference (EIC), Engineering International Conference on Education, Concept and Application on Green Technology. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, IndonesiaDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 365–373.
- Corbelli, G. (2024). reflectR: Automatic Scoring of the Cognitive Reflection Test (p. 2.1.3) [Dataset]. [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, M.; Nigam, N.; Mukhopadhaya, J.; Alonso, J.J.; Ayyalasomayajula, S.K. Multi-Fidelity Probabilistic Aerodynamic Database Generation with the ProForMA Tool. AIAA SCITECH 2023 Forum. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE.
- Desai, P. (2024). Selenium in Cross-Browser Testing: Challenges and Solutions. International Journal of Advanced and Innovative Research, 10(1), 10.
- Fatima, S.; Mansoor, B.; Ovais, L.; Sadruddin, S.A.; Hashmi, S.A. Automated Testing with Machine Learning Frameworks: A Critical Analysis. International Electrical Engineering Conference. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE; p. 12.
- García, B.; Munoz-Organero, M.; Alario-Hoyos, C.; Kloos, C.D. Automated driver management for Selenium WebDriver. Empir. Softw. Eng. 2021, 26, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garousi, V. , Joy, N. 0 arXiv:2409.00411). arXiv. http://arxiv.org/abs/2409, 0411.
- Garousi, V. , Joy, N. 0 arXiv:2409.00411). arXiv. http://arxiv.org/abs/2409, 0411.
- Halani, K.R. ; Kavita; Saxena, R. Critical Analysis of Manual Versus Automation Testing. 2021 International Conference on Computational Performance Evaluation (ComPE). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, IndiaDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 132–135.
- Jain, J. (2022). Tools, Frameworks, and Libraries. In J. Jain, Learn API Testing (pp. 41–73). Apress. [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Feng, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, B. Automated Testing for Machine Translation via Constituency Invariance. 2021 36th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, AustraliaDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 468–479.
- Jones, H.W. Fault Tolerance Should No Longer Be Used. ASCEND 2022. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, United StatesDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- Kedward, L.; Allen, C.B. Optimisation of a Finite-Volume Test-bench Code for Highly Parallel Architectures. AIAA Scitech 2021 Forum. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- Kim, H.; Swan, C.A. Development of a Web-based Test Procedure Authoring and Execution Environment for Space Systems. AIAA SCITECH 2023 Forum. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- Kumar, P.; Singh, S. An efficient security testing for android application based on behavior and activities using RFE-MLP and ensemble classifier. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2024, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manukonda, K.R.R. A COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF SELENIUM WEBDRIVER FOR CROSS-BROWSER TEST AUTOMATION: PERFORMANCE, RELIABILITY, AND USABILITY. J. Artif. Intell. Mach. Learn. Data Sci. 2023, 1, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, S. (2024). An Overview on Testing using Selanium. Computer Science and Mathematics. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.; Hartman, M.; Johnson, D.; Allamraju, R.; Jacob, J.D.; Epperson, K. Testing and Evaluation of UTM Systems in a BVLOS Environment. AIAA AVIATION 2020 FORUM. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- S, S. Enhancing Performance of Software Testing Automation using Selenium Web Grid. Int. Res. J. Adv. Eng. Hub (IRJAEH) 2023, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, D.D.; Shaw-Lecerf, M.; Lash, E.L.; Lyons, K.; Roozeboom, N.; Li, J.; Califano, N.; Stremel, P.; Baerny, J.; Barreras, C.; et al. Implementation of the Lifetime Method in Unsteady Pressure-Sensitive Paint Measurements. AIAA SCITECH 2023 Forum. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- Prof. B K Srinivas4, R. S. N. Prof. B K Srinivas4, R. S. N. (2023). Dynamic Resource Allocation in Cloud Environments. International Journal for Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET), 11(6 Jun 2023), 45–98.
- Ricca, F.; Marchetto, A.; Stocco, A. AI-based Test Automation: A Grey Literature Analysis. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Software Testing, Verification and Validation Workshops (ICSTW). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, BrazilDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 263–270.
- Roopa Devi, E. M. , Shanthakumari, R., Dhanushya, S., & Kiruthika, G. (2024). AI Models for Predictive Maintenance. In A. Kumar Tyagi, S. Tiwari, & G. Soni, Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence for Predictive Maintenance in Smart Manufacturing (1st ed., pp. 69–94). CRC Press. [CrossRef]
- Schmiechen, K.; Schwaiger, F.; Wechner, M.A.; Holzapfel, F. Combining ALM and MBD Tools for Continuous Requirement Validation Tests with Multi-Dimensional Test Parameters. AIAA AVIATION 2022 Forum. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- Schwaiger, F.; Schmiechen, K.; Holzapfel, F. Tico – a Toolbox to Author and Execute Large Parametrizable Test Suites in MATLAB. AIAA SCITECH 2023 Forum. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- Silva, J. R. , Silva, J. M., & Vaquero, T. S. (2020). Formal Knowledge Engineering for Planning: Pre and Post-Design Analysis. In M. Vallati & D. Kitchin (Eds.), Knowledge Engineering Tools and Techniques for AI Planning (pp. 47–65). Springer International Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, A.S. Managing Artifacts and Binaries in Continuous Integration / Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Pipelines. Int. J. Sci. Res. (IJSR) 2022, 11, 2003–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonika; Pal, V. ; Chauhan, N.; Kumar, H. A review of the software testing tools. Int. J. Sci. Res. Arch. 2024, 12, 2387–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, A. (2023). selenium: Low-Level Browser Automation Interface (p. 0.1.4) [Dataset]. [CrossRef]
- Thummalapenta, S.; Sinha, S.; Singhania, N.; Chandra, S. Automating test automation. 2012 34th International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE 2012). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, SwitzerlandDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 881–891.
- Turner, J.; Bowen, J. Automating Test Scripts for Android UI Testing. 10th International Conference on Software Engineering. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- Uittenhove, K.; Jeanneret, S.; Vergauwe, E. From Lab-Testing to Web-Testing in Cognitive Research: Who You Test is More Important than how You Test. J. Cogn. 2023, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Merode, H. Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD); Springer Nature: Dordrecht, GX, Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Van Merode, H. (2023b). Pipeline Development. In H. Van Merode, Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) (pp. 207–284). Apress. [CrossRef]
- Van Merode, H. (2023c). Use case. Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD),. In H. Van Merode, Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) (pp. 359–406). Apress. [CrossRef]
- Wechner, M.A.; Marb, M.M.; Holzapfel, F. A Strategy for Efficient and Automated Validation and Verification of Maneuverability Requirements. AIAA AVIATION 2023 Forum. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- White, J.T. Modular Open Architecture UAS Test Platform System of Systems. AIAA AVIATION 2023 Forum. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- Yadav, V.; Botchway, R.K.; Senkerik, R.; Oplatkova, Z.K. Robotic Automation of Software Testing From a Machine Learning Viewpoint. MENDEL 2021, 27, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Jiang, B. L: Software System Testing; Taylor & Francis, 2023.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





