Submitted:
10 November 2024
Posted:
11 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
This paper investigates the competitiveness of compensation and benefits packages for healthcare professionals in Ghana to address the country’s shortage of skilled medical staff. By analyzing salary structures, incentives, and benefits compared to international standards, this study examines how remuneration impacts retention and migration rates. Findings indicate that low compensation and insufficient benefits are significant factors driving emigration and high turnover among healthcare workers. Additionally, the study discusses the relevance of Total Rewards Theory and best practices in compensation to enhance job satisfaction and retention. The results suggest policy recommendations to improve salary scales, working conditions, and career development opportunities, aiming to attract and retain qualified healthcare professionals within Ghana’s healthcare system.
Keywords:
I. Introduction
1.1. Background of the study
1.2. Key problem and research questions
- How competitive are the compensation and benefits packages offered to healthcare professionals in Ghana, and what are the factors contributing to their perceived inadequacy?
- What is the turnover rate of healthcare professionals in Ghana, and what are the factors contributing to the high turnover rate?
- What is the extent of the migration of healthcare professionals from Ghana, and what is the relationship between the perceived inadequacy of compensation and benefits packages and the migration of healthcare professionals?
2. Literature review
2.1. Theoretical framework
2.1.1. Total rewards theory:
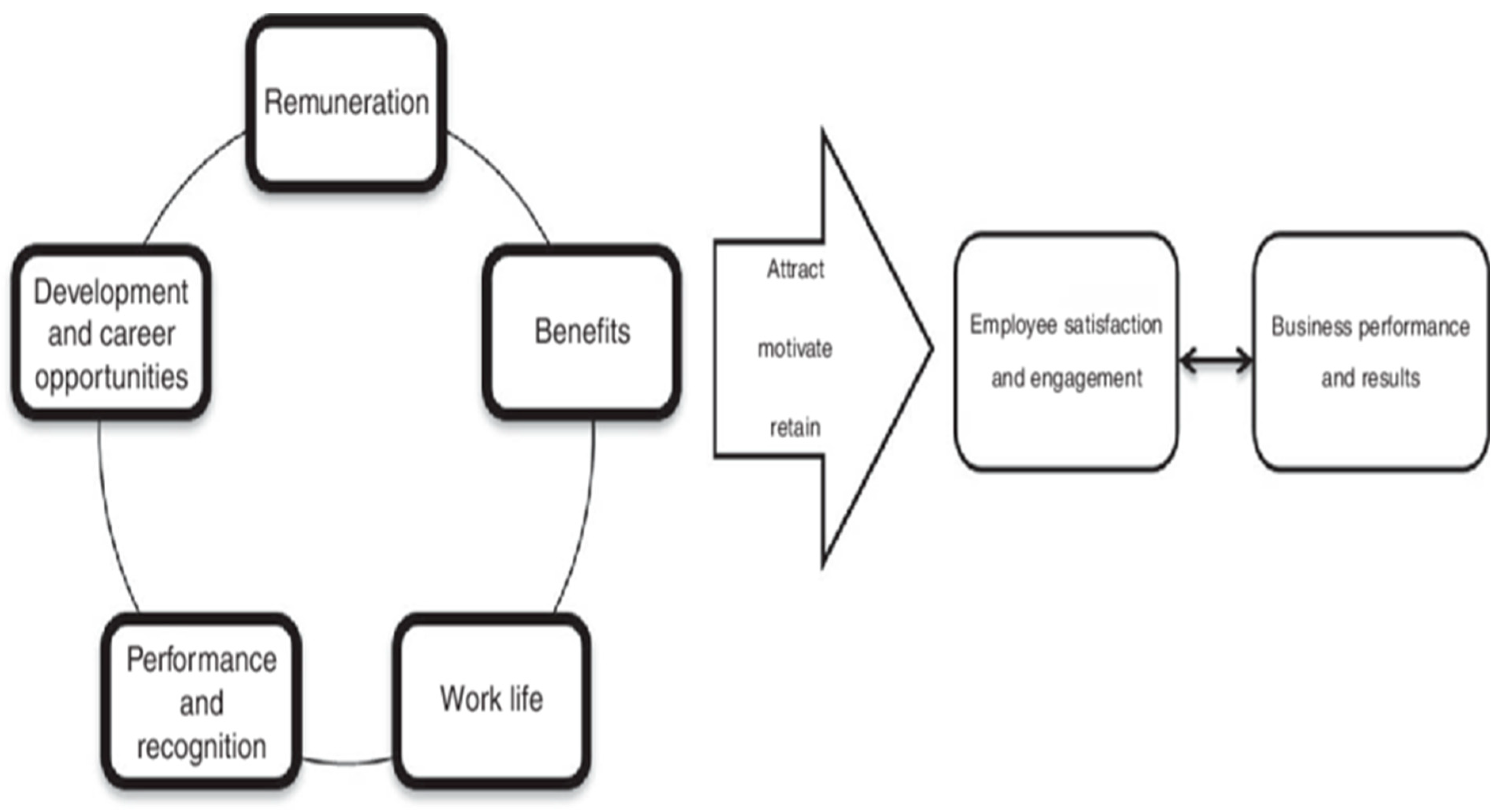
2.2. Employee retention
- The concept of offering a competitive compensation and benefits package is a crucial aspect of modern human resource management practices. It entails providing employees with a remuneration package that is commensurate with their skills, knowledge, and experience in a given field (Adzei & Atinga, 2012). This ensures a fair and equitable distribution of resources, which fosters employee satisfaction, loyalty, and commitment to organizational goals. As such, organizations that have robust compensation and benefits packages are better able to attract and retain talented employees, which contributes significantly to their overall success and competitiveness in the marketplace (Tsede & Kutin, 2013). The provision of competitively structured remuneration and benefits is an imperative aspect of attracting and retaining high-performing personnel. Empirical studies have indicated that remuneration packages that are in tandem with market standards play a vital role in determining employee retention rates (Cassar et al.; 2020). Offering performance-based monetary bonuses, incentives, and comprehensive healthcare benefits can potentially increase employee job satisfaction and mitigate the issue of employee turnover.
- Career development and growth opportunities are also other strategies likely to influence retention. Opportunities for professional growth and advancement are highly esteemed by employees. It has been proposed by Meyers et.; al. (2019) that in order to cultivate a sense of progression and involvement among employees, organizations should offer training schemes, mentoring projects, and strategies for professional growth. Providing consistent performance evaluations and opportunities for continual skill development has the potential to enhance job satisfaction and bolster employee retention rates (Okyere et al.; 2022).
- The establishment of a favorable working atmosphere that fosters a balance between professional and personal obligations, inclusivity, and a caring ethos is of utmost importance. The results of recent research indicate that employees who hold a positive perception of their work environment demonstrate increased tendencies to maintain their affiliations with their employing organizations (Ng and Feldman, 2015). Fostering transparent communication, acknowledging employee accomplishments, and advocating for a harmonious work-life equilibrium can significantly enhance healthy professional loyalty.
- The level of engagement exhibited by employees has a significant bearing on the degree of commitment they exhibit towards their respective organizations. According to Macey et.; al. (2019), incorporating employees into the decision-making process, soliciting their feedback, and acknowledging their contributions can lead to elevated levels of job satisfaction and retention. The implementation of employee recognition initiatives, such as peer-to-peer acknowledgment and the bestowment of employee of the month accolades, can effectively cultivate a culture of gratitude and commitment.
- Flexible work arrangements, namely the provision of remote work options or adaptable hours, have garnered significant attention in contemporary times. According to Allen et.; al. (2017), research indicates that the provision of flexible work arrangements exerts a favorable influence on the retention of employees. Organizations ought to investigate malleable work policies in order to adapt to the varied requirements of their workforce.
- The implementation of governmental and policy interventions is paramount in enhancing compensation and benefits schemes. The imperative for governance and policy reforms to be efficacious necessitates a concentrated effort toward the development of fair and equitable compensation structures, periodic evaluation of remuneration packages, and the provision of sufficient resources to address the challenges facing the healthcare sector (Agyemang et.; al, 2011). The imperative to bring about constructive transformation necessitates collaboration among the government, healthcare institutions, and professional organizations.
2.3. Best practices in Compensation and benefits packages for healthcare professionals.
- Competitive Base Salary and Performance-based Incentives: A crucial component in the recruitment and retention of healthcare professionals is the provision of a competitive base salary. In order to guarantee competitiveness, the benchmarking of regional or national salary data is recommended, as asserted by Kohl et.; al. (2019). Furthermore, providing performance-based incentives that are linked to tangible objectives has the potential to inspire healthcare professionals to attain exceptional outcomes (Harrison et al.; 2018).
- Comprehensive Benefits Package: A comprehensive benefits package is a crucial requirement for effectively providing support for the physical and financial well-being of healthcare professionals. The provision of comprehensive benefits packages comprising health insurance coverage, retirement plans, disability insurance, and life insurance has been highlighted as a crucial component in the recent study by Kohl et.; al. (2019). Providing an array of advantages to staff members serves as an indication of dedication to promoting the comprehensive well-being of the workforce.
- Professional Development and Continuing Education: The provision of opportunities for professional growth and ongoing education is fundamental in both attracting and retaining healthcare practitioners. Aiding healthcare professionals in attending conferences, workshops, and courses serves as a means of keeping up to date with contemporary advancements in their respective fields, and cultivates an atmosphere of perpetual learning (Harrison et al.; 2018).
- Flexible Work Arrangements: Healthcare practitioners routinely encounter rigorous work schedules and extended time commitments. According to Kohl et.; al. (2019), the provision of adaptable work options, such as part-time or remote work, can contribute to the enhancement of work-life equilibrium and the augmentation of job contentment. The implementation of flexible scheduling and shift patterns may serve as a viable solution to counteract the problem of staffing shortages whilst also enhancing employee retention.
- Recognition and Rewards: Recognizing and appreciating the efforts of healthcare professionals is an essential element for their job satisfaction and motivation. In order to foster a culture of appreciation, recognition programs such as employee of the month awards or other public acknowledgments can be implemented, which can have a positive impact on morale. According to Harrison et al. (2018), such programs can enhance the recognition of employees' contributions and reinforce a sense of belonging to the organization. Furthermore, non-monetary rewards such as personalized thank-you notes or public appreciation events can also be effective in boosting the morale of healthcare professionals.
- Wellness Programs and Employee Assistance: Healthcare institutions ought to prioritize the wellness of their employees through the provision of wellness programs and employee assistance services. Kohl et al. (2019) assert that various interventions, such as access to fitness facilities, well-being workshops, psychological assistance, and therapeutic interventions, may be implemented as part of an organization's efforts to promote employee health and wellness. The promotion of employee well-being has been found to be positively associated with increased levels of job satisfaction and correspondingly diminished turnover rates within organizational settings.
- Clear Career Development Pathways: Healthcare practitioners are frequently driven by the chance to advance and progress in their careers. It is essential that organizations create well-defined pathways for career development that include mentorship programs, tuition reimbursement, and possibilities for leadership roles as suggested by Harrison et al. (2018). By providing opportunities for professional growth, organizations can not only bolster retention rates but also attract ambitious individuals seeking to advance in their careers. Thus, it is critical for healthcare organizations to invest in their workforce by establishing career development pathways that foster a sense of growth and advancement.
- Open Communication and Feedback: Establishing effective communication channels and providing regular feedback mechanisms are crucial in enhancing the satisfaction and engagement of healthcare professionals. Kohl et.; al. (2019) suggests that performance evaluations, seeking input on organizational decisions, and creating avenues for employee suggestions and concerns can significantly contribute to a positive work environment.
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Design and Approach
- Data Collection:
- 2.
- Selection of Countries:
Data Analysis
4.1. Ghana
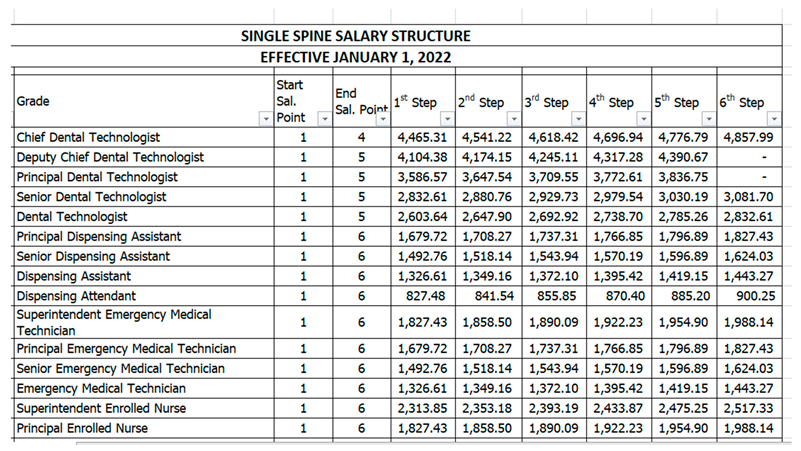
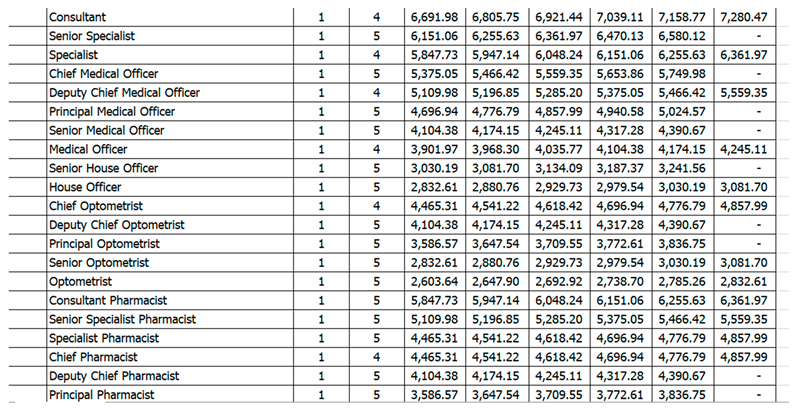
4.2. United Kingdom
4.3. United States
5. Discussion and Conclusion
- Salary disparities: The data about remuneration reveals that healthcare practitioners in Ghana tend to receive less substantial pay in comparison to their colleagues in the United Kingdom and the United States. The statistics indicate that doctors, nurses, and pharmacists in Ghana have an inferior annual average salary as compared to their peers in the aforementioned countries. Such disparities in compensation may have an impact on the quality of healthcare delivery in Ghana.
- Retaining Talent: Retaining talent in an organization is of paramount importance, and a crucial way to achieve this is by offering competitive compensation and benefits packages. However, it is worth noting that remuneration is not the only determining factor for talent retention, and other elements such as job satisfaction, career advancement prospects, work-life balance, and the quality of healthcare services provided are equally significant. Therefore, it is imperative that organizations take a holistic approach toward talent retention and ensure that all of these determinants are optimized to create a conducive work environment for employees. Only then can an organization achieve optimal performance, employee satisfaction, and retention.
- Challenges in Talent Retention: The retention of highly skilled healthcare professionals in Ghana may be impeded due to comparatively lower salaries. This may give rise to the possibility of healthcare professionals seeking opportunities abroad, where they may have access to better resources and infrastructure and potentially earn higher salaries. As such, the challenge of retaining healthcare professionals in Ghana may have implications for the country's healthcare system and access to quality healthcare services.
- Improving Competitiveness: In order to bolster the competitive edge of compensation and benefits packages in Ghana, it may behoove decision-makers to contemplate augmenting the salary scales, granting incentives for specialized skills and experience, and enhancing the working conditions and resources. Furthermore, it could be expedient to allocate resources toward professional development programs and providing prospects for career progression, which can further buttress talent retention. Taken together, these measures could potentially create a more enticing and compelling work environment that would attract and retain the best and brightest talent in the marketplace.
- Comprehensive Approach: Retaining skilled healthcare workers in Ghana is a complex task that involves addressing various factors beyond financial incentives. A comprehensive approach is required that encompasses professional development opportunities, a conducive work environment, and overall job satisfaction. By fostering a supportive and fulfilling work environment, healthcare facilities in Ghana can succeed in both attracting and retaining talented healthcare professionals.
6. Recommendations
- Salary increase: To address the issue of healthcare professionals leaving Ghana for opportunities abroad, it is imperative to conduct a comprehensive review of their salaries and consider increasing them to align with global standards. This measure could serve as a powerful incentive to attract and retain skilled professionals who might otherwise seek employment opportunities elsewhere. By enhancing the competitiveness of their remuneration packages, Ghana can strengthen its healthcare workforce and improve the quality of care delivered to its citizens.
- Performance-Based Incentives: The introduction of performance-based incentive programs which provide compensation to healthcare professionals for their outstanding work, accomplishments, and quality of outcomes is a possible strategy to encourage and retain top-performing individuals. By doing so, healthcare organizations can foster a culture of excellence in patient care. This method motivates employees to strive for excellence and continually improve their job performance, resulting in higher levels of patient satisfaction and better health outcomes.
- Professional Development Opportunities: Investing in continuous professional development programs and training initiatives is crucial for organizations in the healthcare industry. The provision of such opportunities can enable healthcare professionals to improve their knowledge and skills, which in turn can lead to greater job satisfaction and bolster the appeal of the compensation package. By prioritizing ongoing professional development, healthcare organizations can also demonstrate a commitment to their employees and position themselves as leaders in the industry.
- Career Advancement Pathways: Establishing unambiguous career advancement pathways for healthcare professionals, which encompasses prospects for promotion, leadership development, and specialization, can significantly enhance job satisfaction and encourage professionals to remain within the Ghanaian healthcare system. Clearly outlined paths for progression within the healthcare sector can also serve as incentives for professionals to strive for excellence and attain higher levels of education and training, which in turn can lead to improved patient outcomes. Moreover, robust career advancement opportunities can bolster the capacity of the healthcare system to attract and retain top talent, which is essential for the provision of high-quality care. As such, Ghanaian policymakers must prioritize the development of effective frameworks for career advancement and progression within the healthcare sector.
- Improved Working Conditions: Improving the operational circumstances in medical establishments, encompassing personnel levels, equipment, and infrastructure, is an imperative measure to undertake. An optimistic and encouraging occupational milieu is of paramount importance for the preservation of skilled labor. Mitigating factors such as workload, balancing work and personal life, and furnishing indispensable resources can significantly augment job contentment. Therefore, the administration must take adequate measures to enhance the working conditions of healthcare facilities for the betterment of society.
- Comprehensive Benefits Package: Healthcare organizations should provide a comprehensive benefits package that extends beyond mere monetary compensation. This package may encompass various employee benefits such as health insurance coverage, retirement plans, paid leave, and other similar benefits. The provision of such benefits enhances the overall well-being and job security of healthcare professionals. By prioritizing the provision of these benefits, healthcare organizations can attract and retain top talent in the industry.
- Recognition and Appreciation: Instituting initiatives aimed at acknowledging and lauding the endeavors and inputs of healthcare practitioners is a crucial undertaking. Such measures may encompass consistent recognition of achievements, hosting of events to appreciate employees, and avenues for peer acknowledgment. The sense of being esteemed and valued can have a marked effect on both job satisfaction and retention rates. Therefore, it is imperative that healthcare organizations prioritize the implementation of programs aimed at recognizing and appreciating the efforts of their professionals.
- Collaboration and Engagement: Encouraging a collaborative and team-oriented culture, along with ensuring employee engagement, is crucial for enhancing the efficacy of healthcare professionals. It is imperative to foster an environment where healthcare professionals can actively participate in decision-making processes and have a say in shaping policies and practices. Such an approach can not only strengthen their commitment to their profession but also instill a sense of ownership, thereby augmenting their overall job satisfaction and retention. Creating effective communication channels and gathering feedback are essential elements that can further reinforce these efforts.
- Research and Data-Driven Approach: It is of paramount importance to maintain constant and thorough vigilance over healthcare labor market tendencies, both at a local and global scale. To this end, it is necessary to carry out regular surveys and research aimed at gathering feedback from healthcare experts in relation to their compensation and benefits preferences. The insights gleaned from this data can then be applied to the development of effective and adaptable compensation and benefits strategies. It is through such proactive measures that the healthcare industry can remain competitive and attract the best talent available.
Appendix
- Salary structure of Ghana Health professionals: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1aGmcLfRkMPU8FHlmA58X2S51kgObpRo2/edit#gid=1964483126
- Average salary of Healthcare professional for other OECD countries: https://www.qunomedical.com/en/research/healthcare-salary-index
References
- Adzei, F.A.; Atinga, R.A. Motivation and retention of health workers in Ghana’s district hospitals: Addressing the critical issues. Journal of Health, Organisation and Management 2012, 26, 467–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agyeman, M.O.; Agyemang, S.A.; Opoku, S.T. Job satisfaction and turnover Intention among healthcare professionals in Ghana: The role of compensation and benefits. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Asante, A.D.; Nketiah-Amponsah, E.; Andoh-Arthur, J. Migration of health professionals in Ghana: tracking compensation issues for better management. BMC health services research 2013, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ingelsrud, M.H. Hospital mergers in Norway: Employee health and turnover to three destinations. Nordic Journal of Working Life Studies 2017, 7, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.S.; et al. (2018). Employee Rewards: The Role of Purpose, Autonomy, and Rewards in Employee Motivation. Working Paper Series, Harvard Business School.
- Lawler, E.E. The Importance of Total Rewards and Why It Matters. WorldatWork Journal 2019, 28, 6–15. [Google Scholar]
- Meyers, M.C.; van Woerkom, M.; Bakker, A.B. The added value of the positive: A literature review of positive psychology interventions in organizations. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology 2019, 22, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.W.; Feldman, D.C. (2015). Ethical climates and employee commitment: Testing the mediating role of social exchange relationships.
- Okyere, E.; Ward, P.R.; Marfoh, K.; Mwanri, L. Incentives management among health workers in primary health-care facilities: addressing important issues in rural Ghana. Journal of Health Organization and Management 2022, 36, 712–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oruh, E.S.; Mordi, C.; Ajonbadi, A.; Mojeed-Sanni, B.; Nwagbara, U.; Rahman, M. Investigating the relationship between managerialist employment relations and employee turnover intention: The case of Nigeria. Employee Relations 2020, 42, 52–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchetti, L.T. (2022). Total Rewards or Totally Not What the People Want? Examining the Preferred Total Rewards of Those At Home Vs. in the Workplace.
- Rubel, M.R.B.; Hung Kee, D.M.; Rimi, N.N. High-performance work practices and medical professionals’ work outcomes: the mediating effect of perceived organizational support. Journal of Advances in Management Research 2020, 18, 368–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijdens, K.; de Vries, D.H.; Steinmetz, S. Health workforce remuneration: Comparing wage levels, ranking, and dispersion of 16 occupational groups in 20 countries. Human Resources for Health 2013, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsede, O.A.; Kutin, E. Total Reward Concept: A Key Motivational Tool For Corporate Ghana. Business and Economic Research 2013, 3, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winarno, A.; Prasetio, A.P.; Luturlean, B.S.; Wardhani, S.K. The link between perceived human resource practices, perceived organisational support and employee engagement: A mediation model for turnover intention. SA Journal of Human Resource Management 2022, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WorldatWork. (2019). Total Rewards: A Comprehensive Guide. WorldatWork Press.
- World Health Organization (2016). Health workforce migration in the WHO African Region: an overview and country perspectives. Geneva: World Health Organization.
- Zimmerman, R.D.; Swider, B.W.; Boswell, W.R. Synthesizing content models of employee turnover. Human Resource Management 2019, 58, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




