Submitted:
28 October 2024
Posted:
29 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
0. Introduction
1. Composition and Working Principle of the Grooving Device
1.1. Subsection
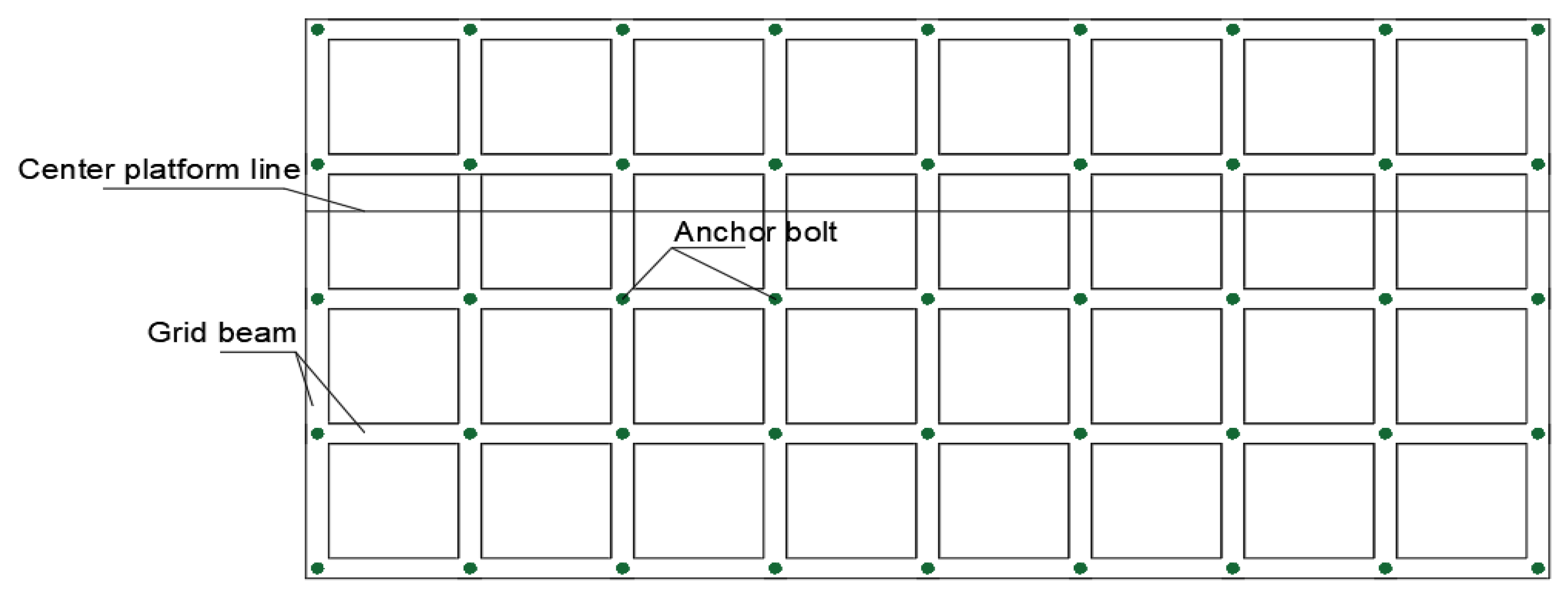
1.2. Overall Design of Slope Grooving System
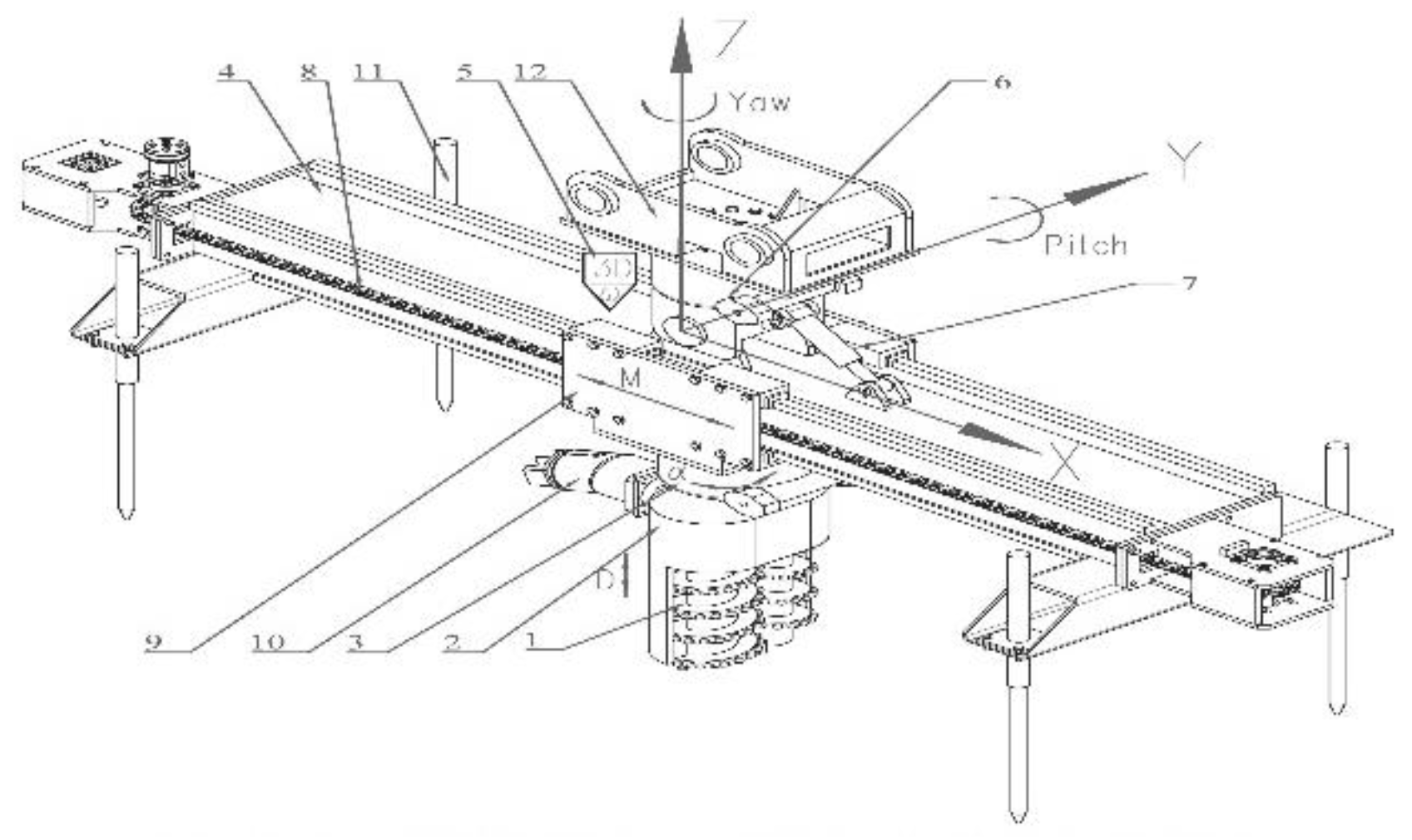
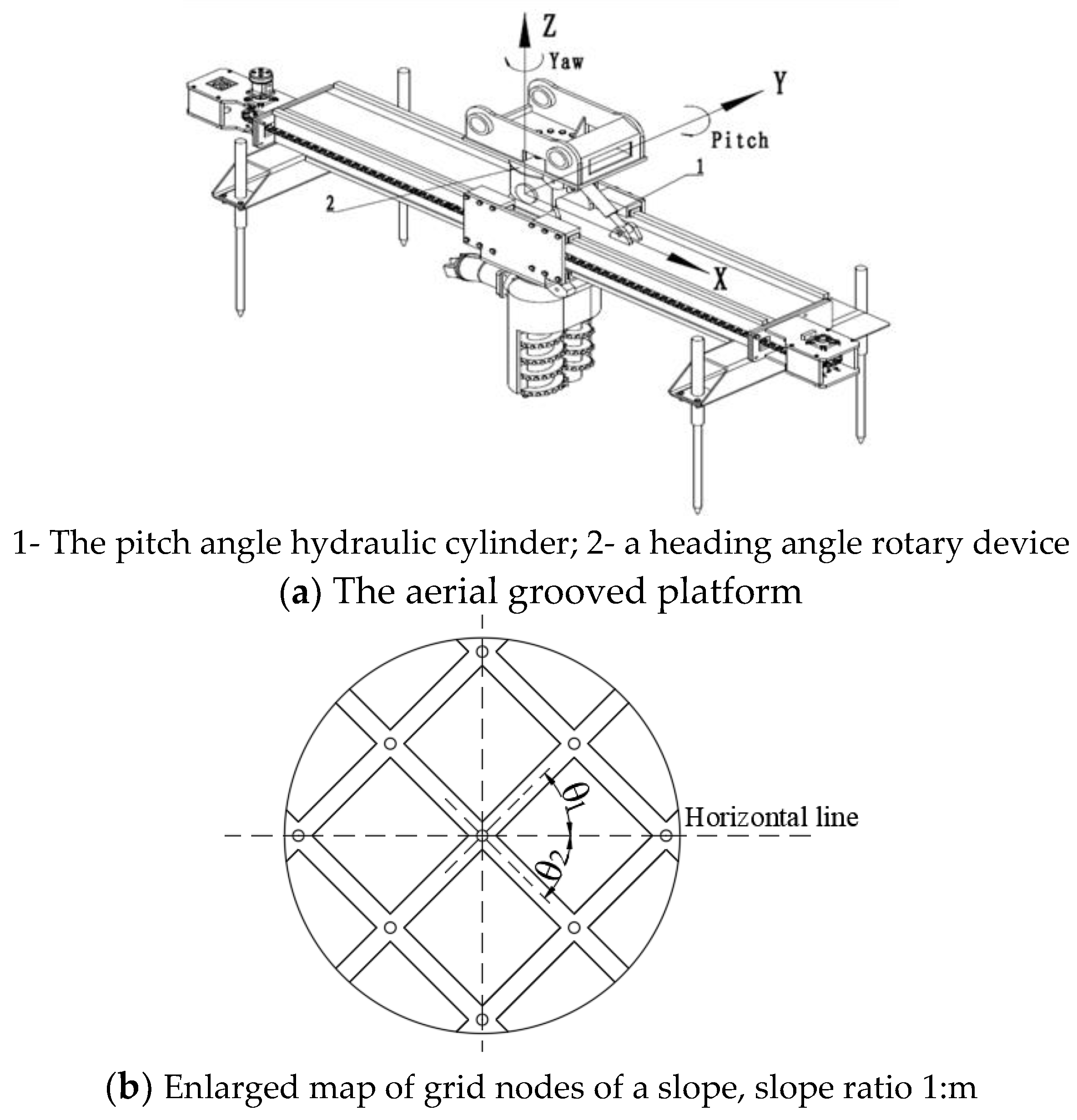
1.3. Design of the Spatial Positioning System
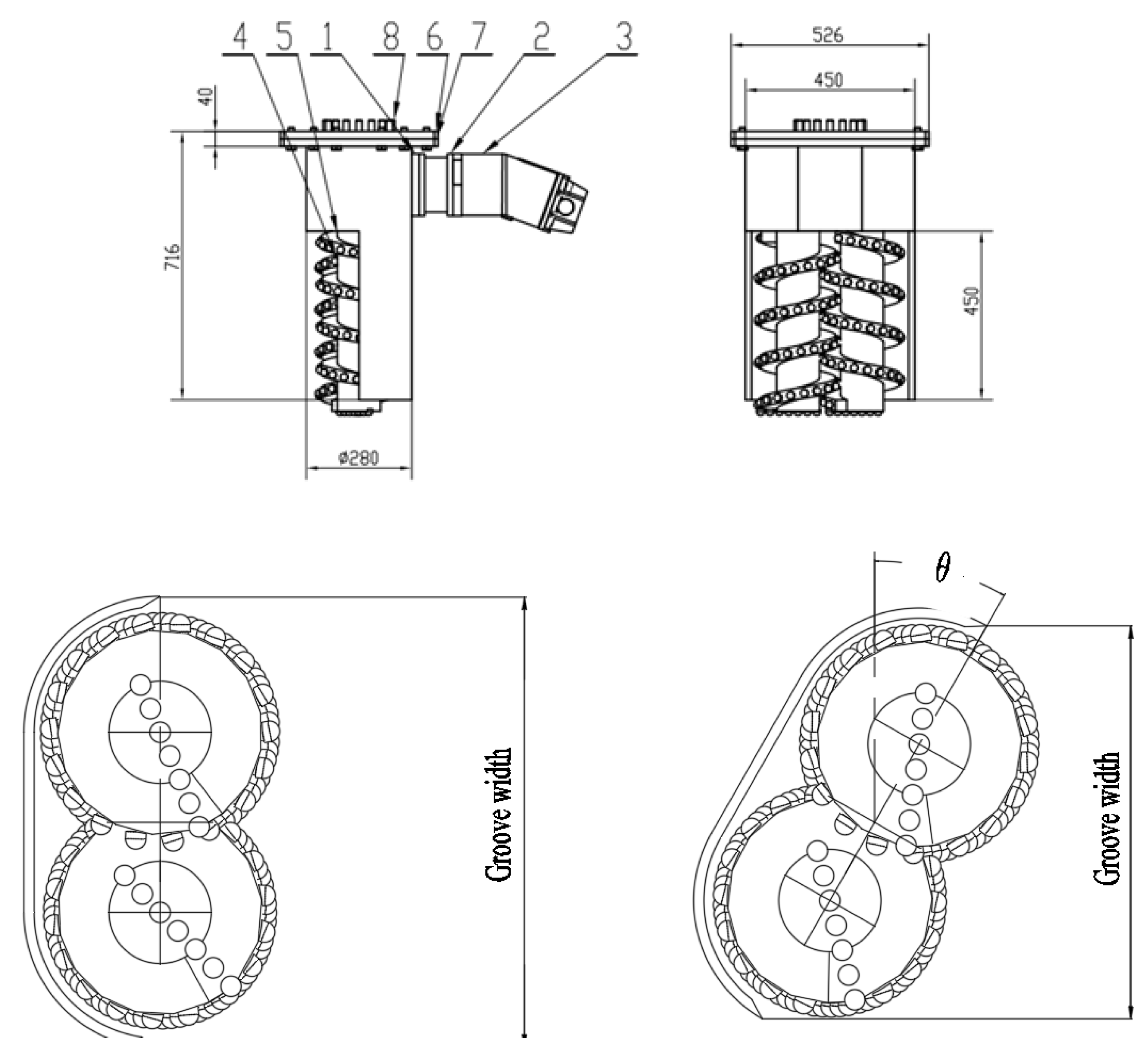
1.4. Groove Width and Depth Adjustment Mechanism
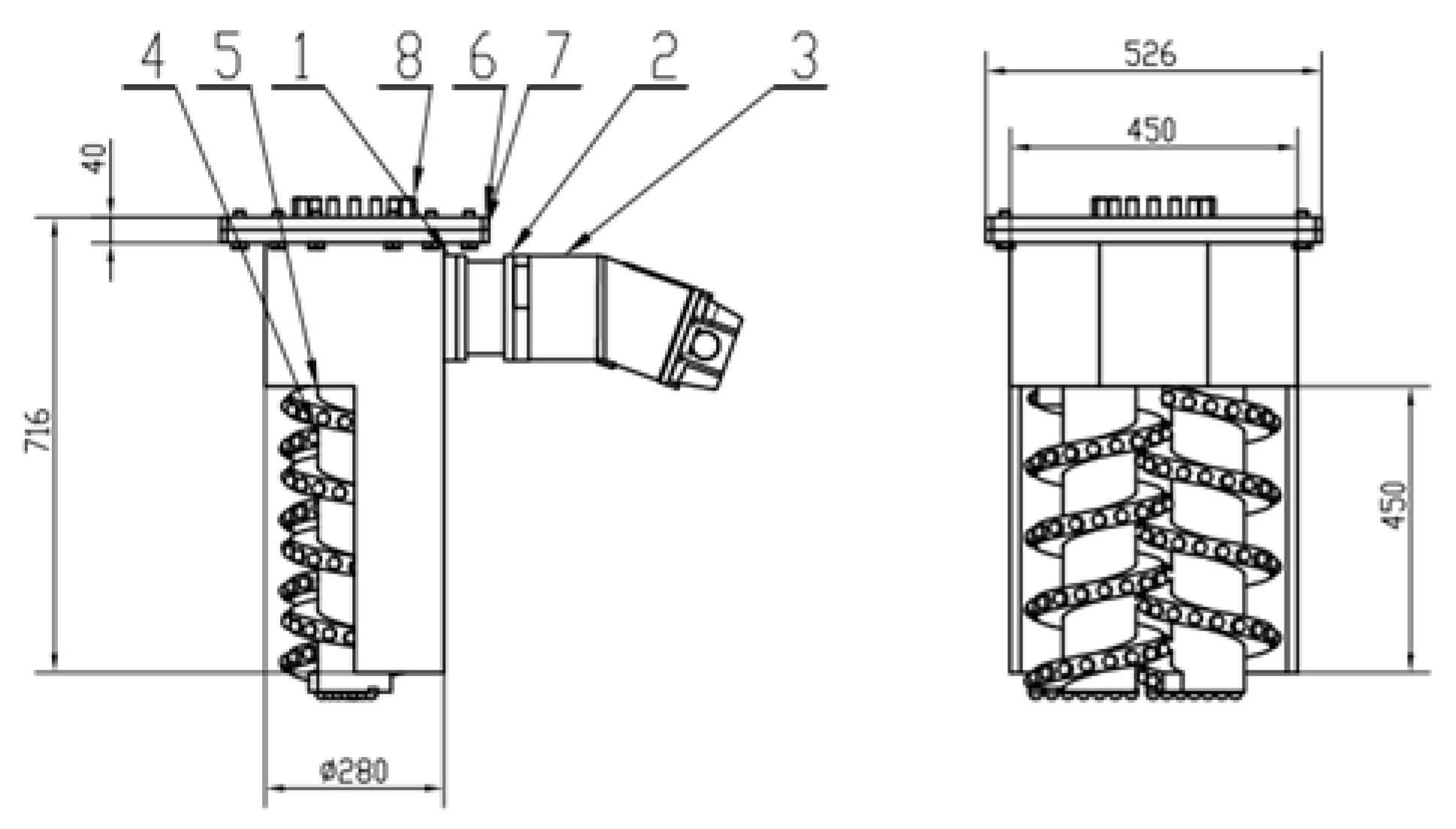
1.5. Excavation Cutter Disk System
1.6. Self-Stabilization System and Control System
2. Main Parameters of the Grooving Technology and Device
2.1. Principle and Technology of the Grooving Machine
2.2. Main Parameters of the Device
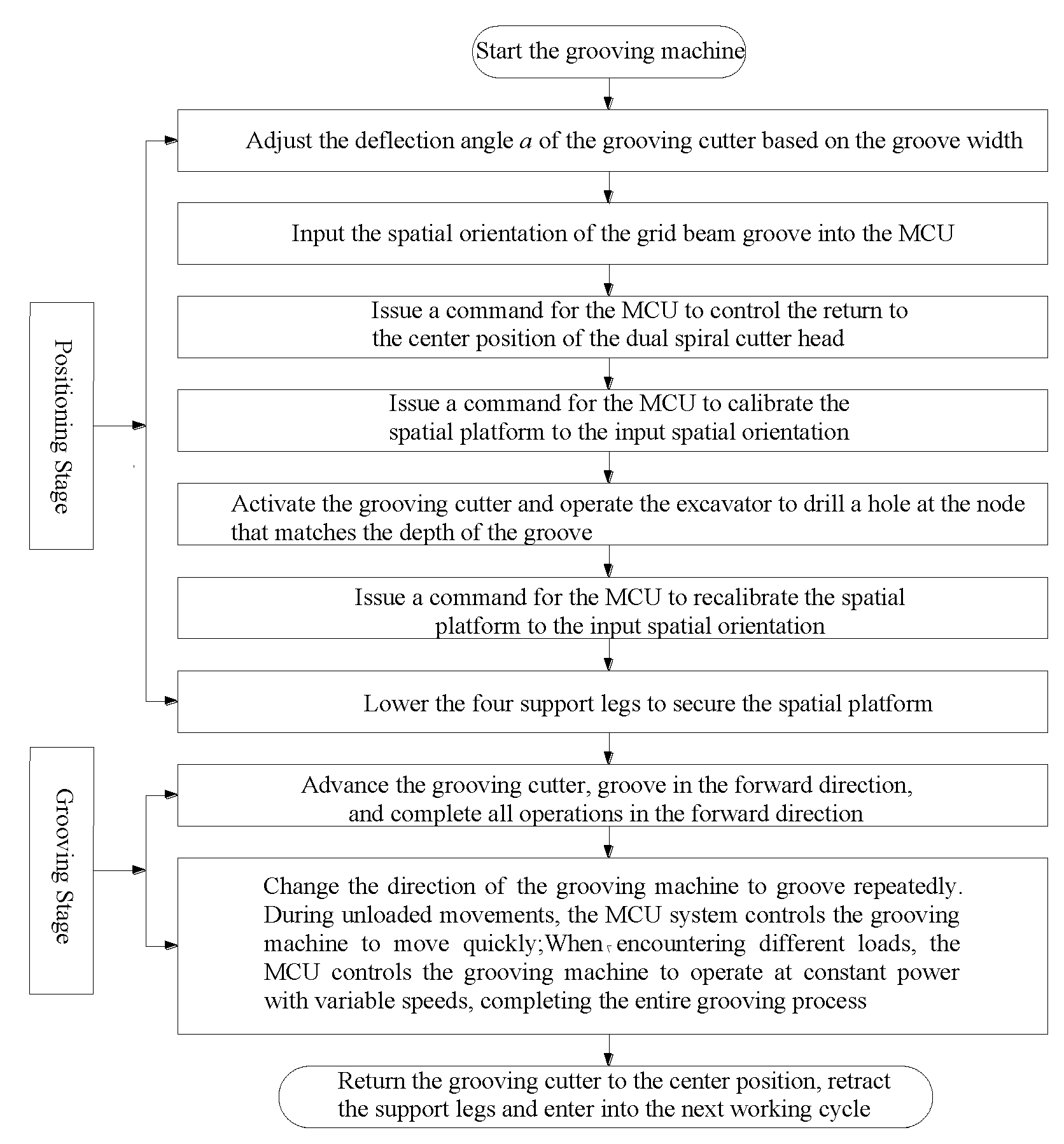
3. Technology of Construction Operation
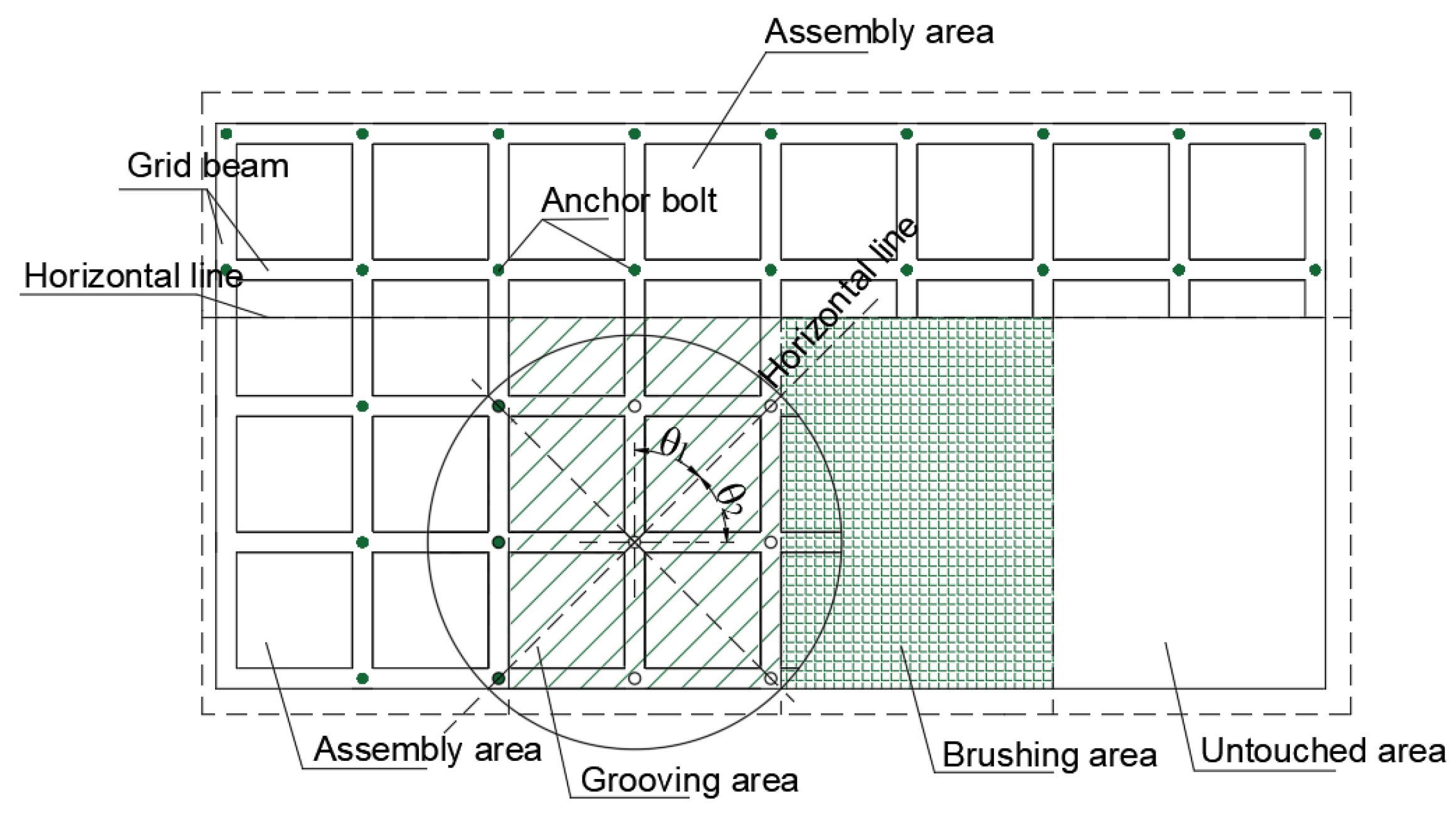
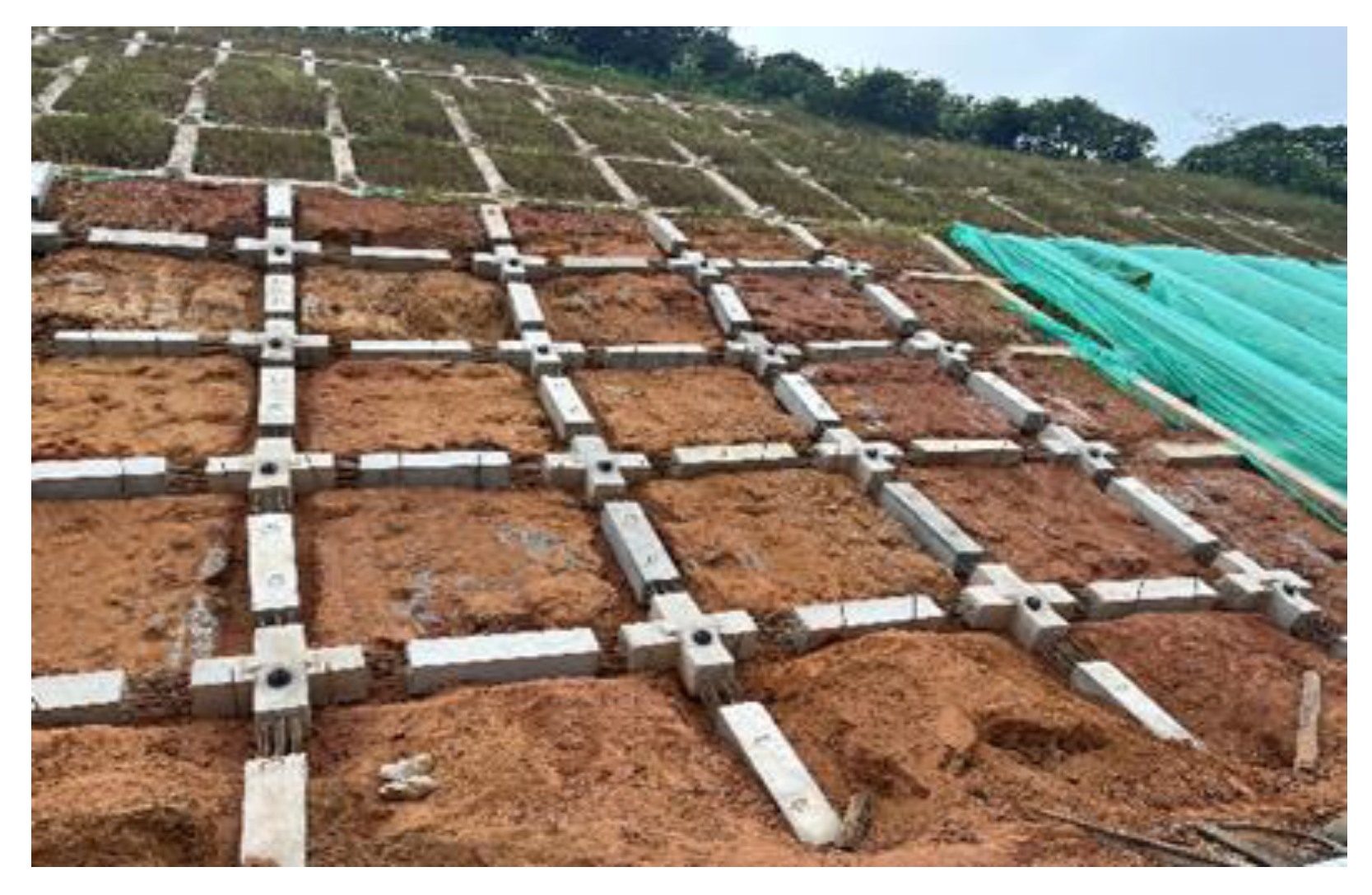
4. Application Examples
4.1. Field Test
4.2. Test Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- This paper presents a new technical approach that shifts the grooving of slope grid beams from manual construction to mechanized construction. The mechanized grooving device consists of interlocking double spiral cutting heads, groove width and depth adjustment mechanisms, a cutter working platform, a platform azimuth adjuster, a cutter sliding mechanism, a hydraulic motor, a hydraulic power system, and a platform anchoring mechanism. This device can perform grooving operations on slopes with different angles and varying degrees of weathered rock, accurately carving foundation grooves for slope protection grid beams to specified depths and widths, ensuring flat groove bottoms, consistent groove widths, straight axis, and facilitating the installation of prefabricated grid beams or significantly improving the quality of cast-in-place grid beams.
- (2)
- The mechanized grooving device developed in this paper achieves an excavation speed of approximately 9.6 m³/h per unit, which is significantly higher than the traditional manual excavation speed of 2 m³/d per person. This advancement can greatly save labor and accelerate construction speed.
- (3)
- Field tests have shown that the grooving speed of this device on soil and weathered rock slopes is approximately 1.5 m/min and 0.5 m/min, respectively. Compared to traditional manual construction methods, this significantly improves construction efficiency and quality, with satisfactory results that have important guiding significance for practical engineering.
References
- HanDongdong, Men Yuming, WangPeng. Model test on the influence of stiffness and spacing of lattice beam on the force of bolt lattice beam [J].
- Han Dongdong, Men Yuming, Hu Zhaojiang. Experimental study on anti-slip mechanism and force of lattice bolt of soil landslide[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020,41(04):1189-1194+1202.
- Tu Ming. Development of automatic grooving machine for wooden sleepers for railway bridges[J]. Shanghai Railway Science and Technology, 2018(04):46-48.
- Liu Taiping. Research on the application of prestressed anchor cable technology in high slope protection[J]. China Residential Facilities, 2018(03):108-109.
- Li Rong, Huang Chunliang. Application of bolt lattice beam in high slope support engineering[J].Highway & Automobile Transport, 2017(03):102-104+161.
- Hou Xiaoqiang, Tian Shutao, Yao Zhengxue. Study on reinforcement mechanism and optimization design of high slope of frame prestressed bolt[J].Highway Engineering, 2015, 40(04):81-84+121.
- Han Dongdong, Men Yuming, Hu Zhaojiang. Experimental study on model of lattice prestressed bolt for landslide prevention and control[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(08):1375-1380.
- Wang Juanjuan, Deng Juntao, Men Yuming. Model test of bolt lattice beam and calculation of internal force of lattice beam[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2015, 42(02):64-68+76.
- Hao Jianbin, Li Jinhe, Cheng Tao, Men Yuming,Wang Banqiao. Study on vibration table model study of bolt lattice support slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(02):293-304.
- Zheng Ye, Fan Xiufeng, Shen Mengxing. Application of prestressed bolt lattice beam in the reinforcement of a highway slope[J]. Geotechnical Foundation,2014,28(01):1-1.
- Xiang Zuquan, Li Wanbai. Analysis and discussion on protection and reinforcement treatment technology of highway rock slope[J]. Urban Road, Bridge and Flood Control, 2012(05):50-52+57+7.
- Chen Daoyuan. Application of bolting lattice beam in soil slope support engineering[J]. Sichuan Building Materials, 2008(03):224-225+228.
- Lai Caidong. Application of bolting lattice technology in landslide prevention and control engineering[J]. Highway, 2008(03):37-38.
- CECS 22-2005, Technical regulations for geotechnical bolts (cables)[S].
- GB 50330-2002, Technical code for construction slope engineering[S].
- Li Jiaxin, Fang Hao, Cheng Yongliang, Lei Baodong, Guo Hong, Zheng Nan. Review of reinforcement mechanism and method of sandstone and soil[J]. Sichuan Architecture,2022,42(02):194-200.
- Cao Yican, Chen Peichong, Xu Guangbo. Research on slope protection structure design technology of prefabricated anchor sorghum beam[J]. China Survey & Design, 2020(05):94-97.



| Parameters | Values |
| Overall dimension | 3764mm×1150mm×2052mm |
| Power | 50kW |
| Milling Width | 27-40cm |
| Milling Depth | 0-40cm |
| Single-Pass Grooving Length | 0-2m |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




