Submitted:
26 October 2024
Posted:
28 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Motivation
1.2. Research Questions
1.3. Research Contribution
- This review presents a detailed analysis of the application of Lean Six Sigma within SMEs, emphasizing the unique challenges these enterprises face due to resource constraints and operational complexities. The study aggregates insights from various industries, highlighting how SMEs can adopt LSS methodologies to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and improve overall performance.
- By systematically analyzing existing literature, the research identifies the primary factors that contribute to the successful implementation of LSS in SMEs, such as leadership commitment, employee engagement, and the alignment of LSS initiatives with strategic business goals. It also discusses common barriers, including limited financial resources, lack of specialized skills, and resistance to change.
- The review identifies gaps in the current literature, particularly in the integration of digital technologies and Industry 4.0 solutions with LSS practices in the SME context. It encourages future research to explore the synergistic effects of combining LSS with advanced technologies to optimize outcomes in resource-constrained settings.
- The study offers practical guidance for SMEs seeking to implement LSS, providing best practices and strategies to overcome common challenges. It includes recommendations for adapting LSS tools and techniques to the specific needs and limitations of SMEs, ensuring more sustainable and impactful outcomes.
1.4. Research Novelty
2. Materials and Methods
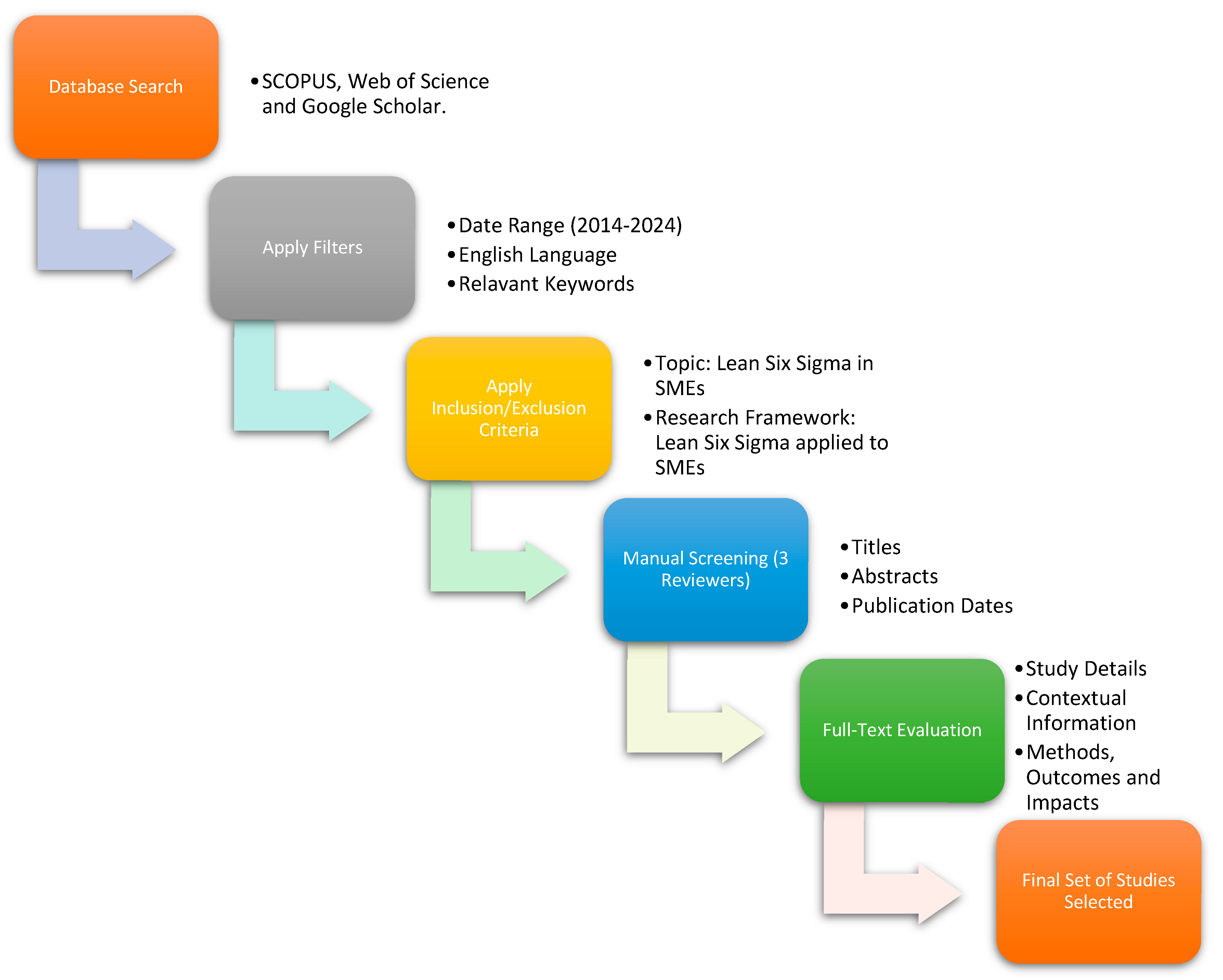
2.1. Eigibility Criteria
2.2. Information Sources
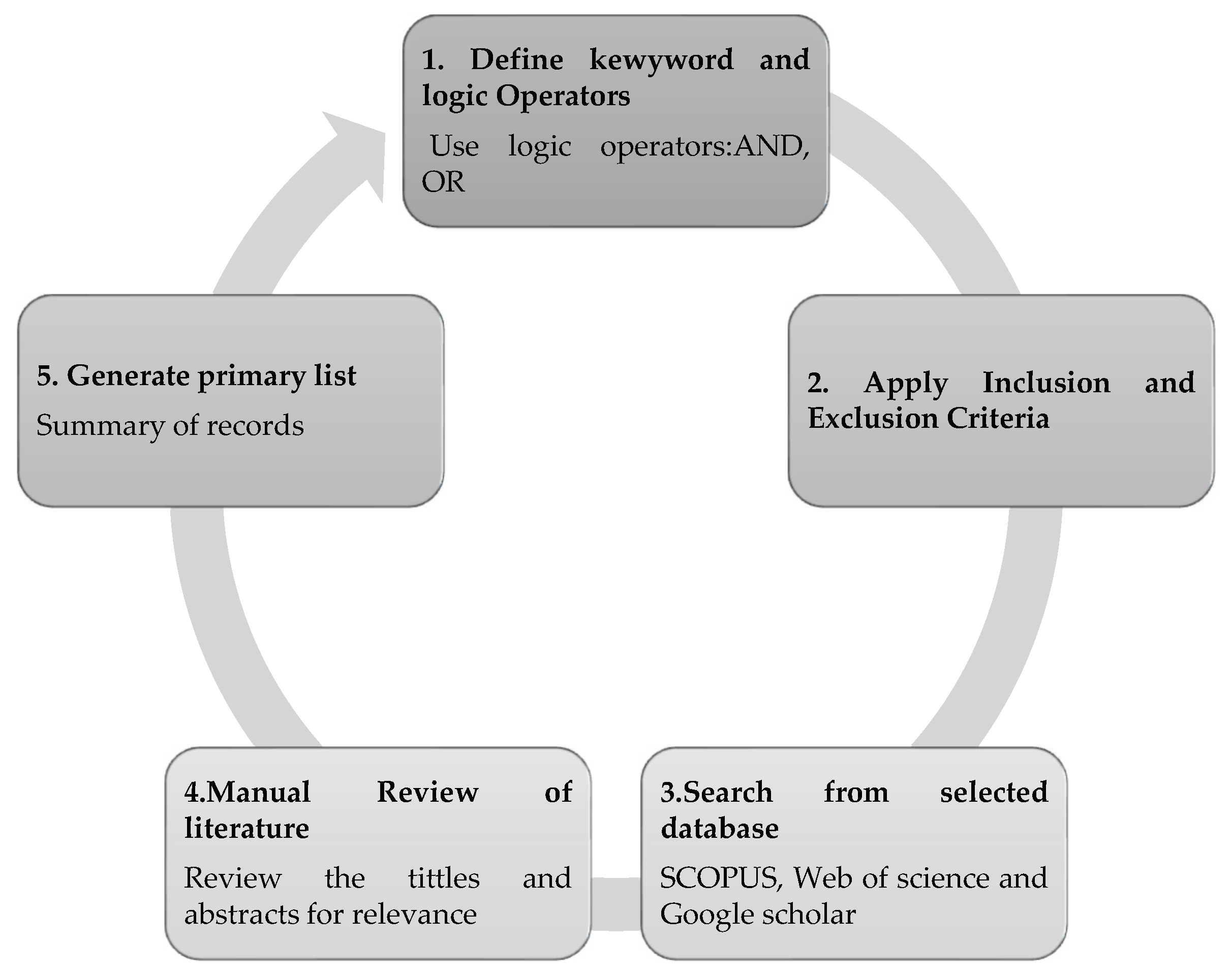
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Selection Process
2.5. Data Collection Process
2.6. Data Items
2.6.1. Data Items Collection Method
2.6.2. Data Items Variables
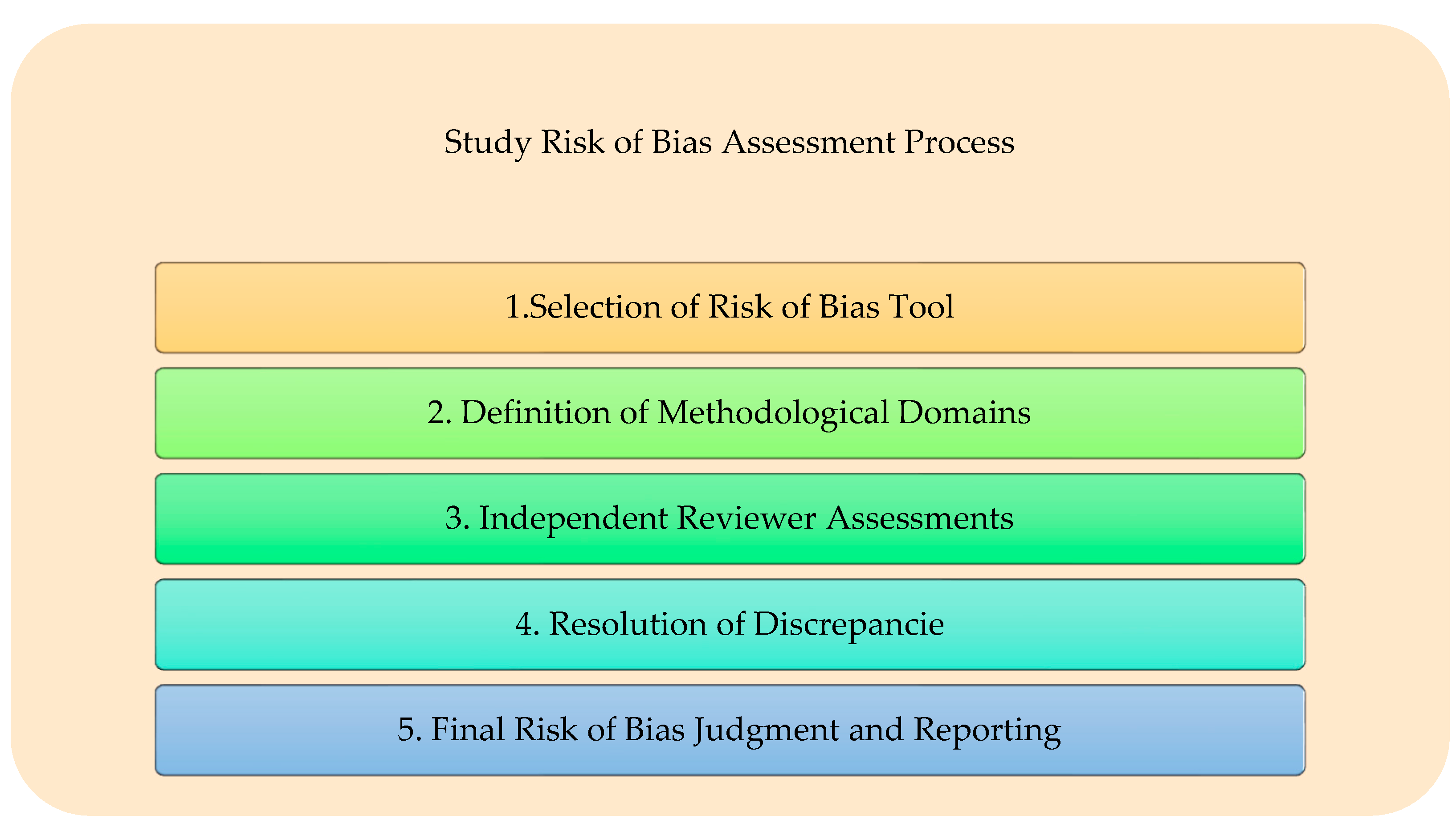
2.7. Study Risk of Bias Assessment
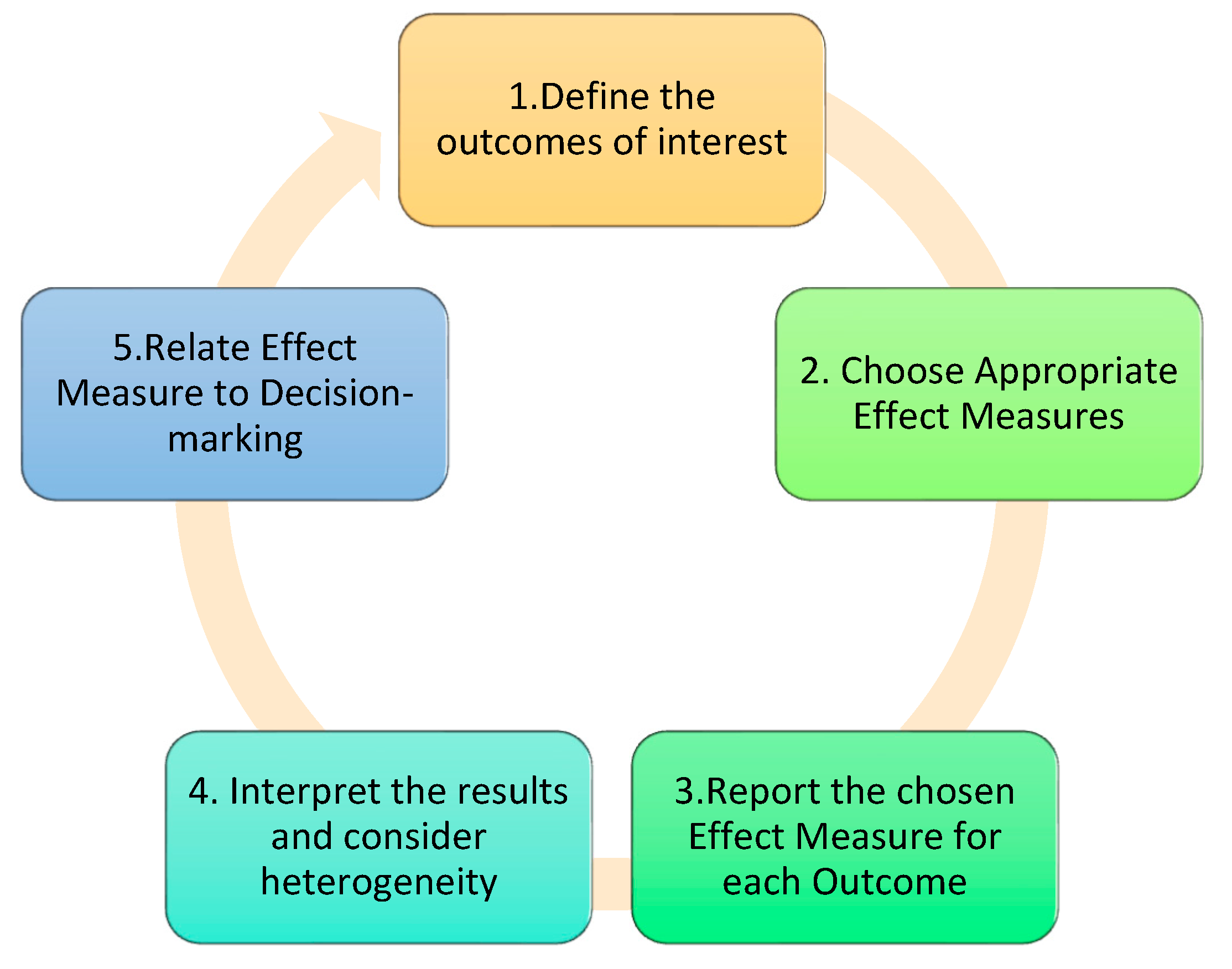
2.8. Effect Measures
2.9. Synthesis Method
2.9.1. Eligibility Criteria for Synthesis Grouping
2.9.2. Data Preparation and Transformation Methods
2.9.3. Data Presentation and Visualization Techniques
2.9.4. Methods for Data Synthesis and Meta-Analysis
2.9.5. Investigation of Heterogeneity Sources
2.9.6. Sensitivity Analyses
2.10. Reporting Bias Assessment
2.11. Certainity of Evidence
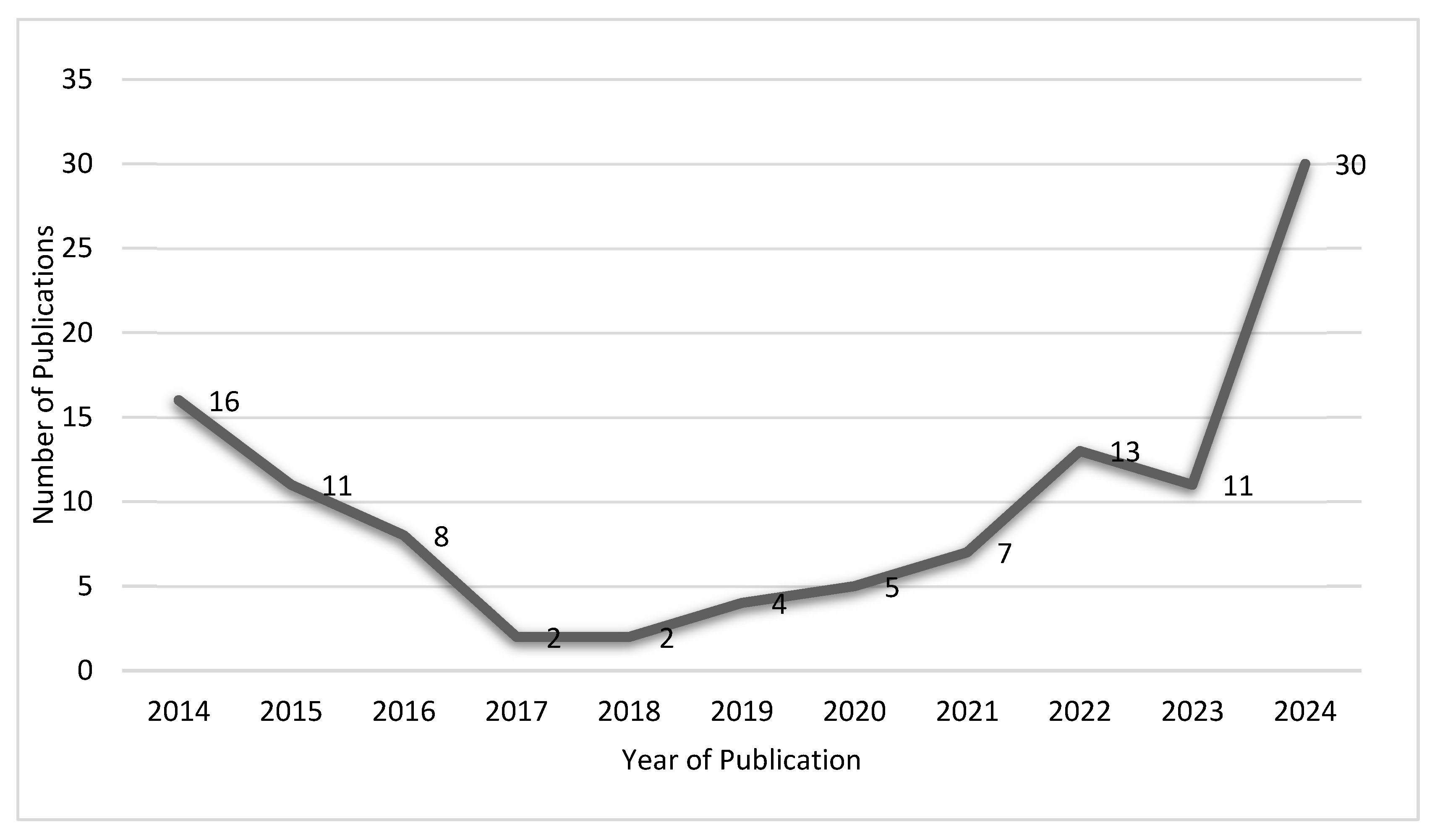
3. Results
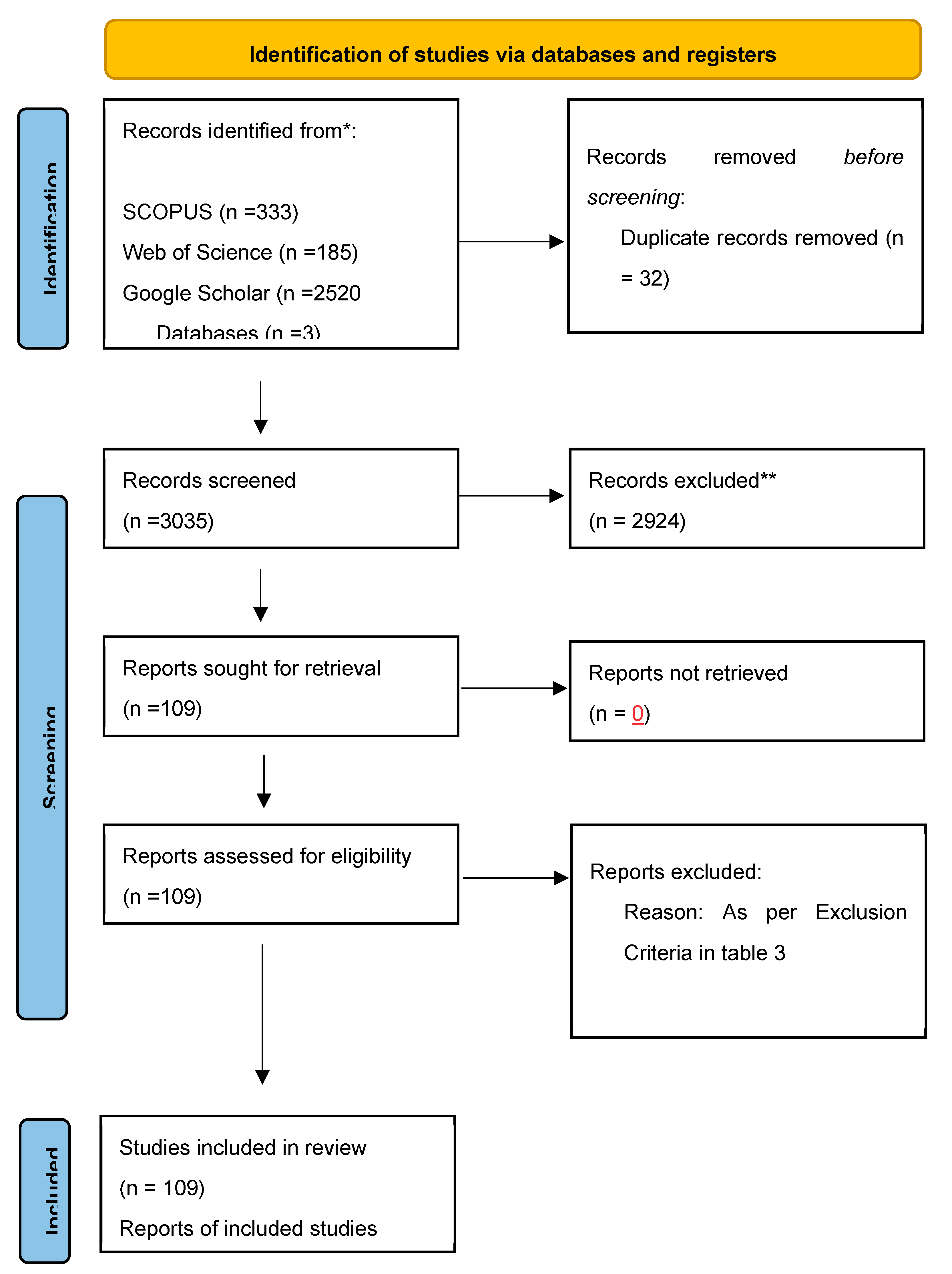
3.1. Study Selection
3.1.1. Results of the Search and Selection Process
3.1.2. Studies Which Met the Inclusion Criteria But Excluded
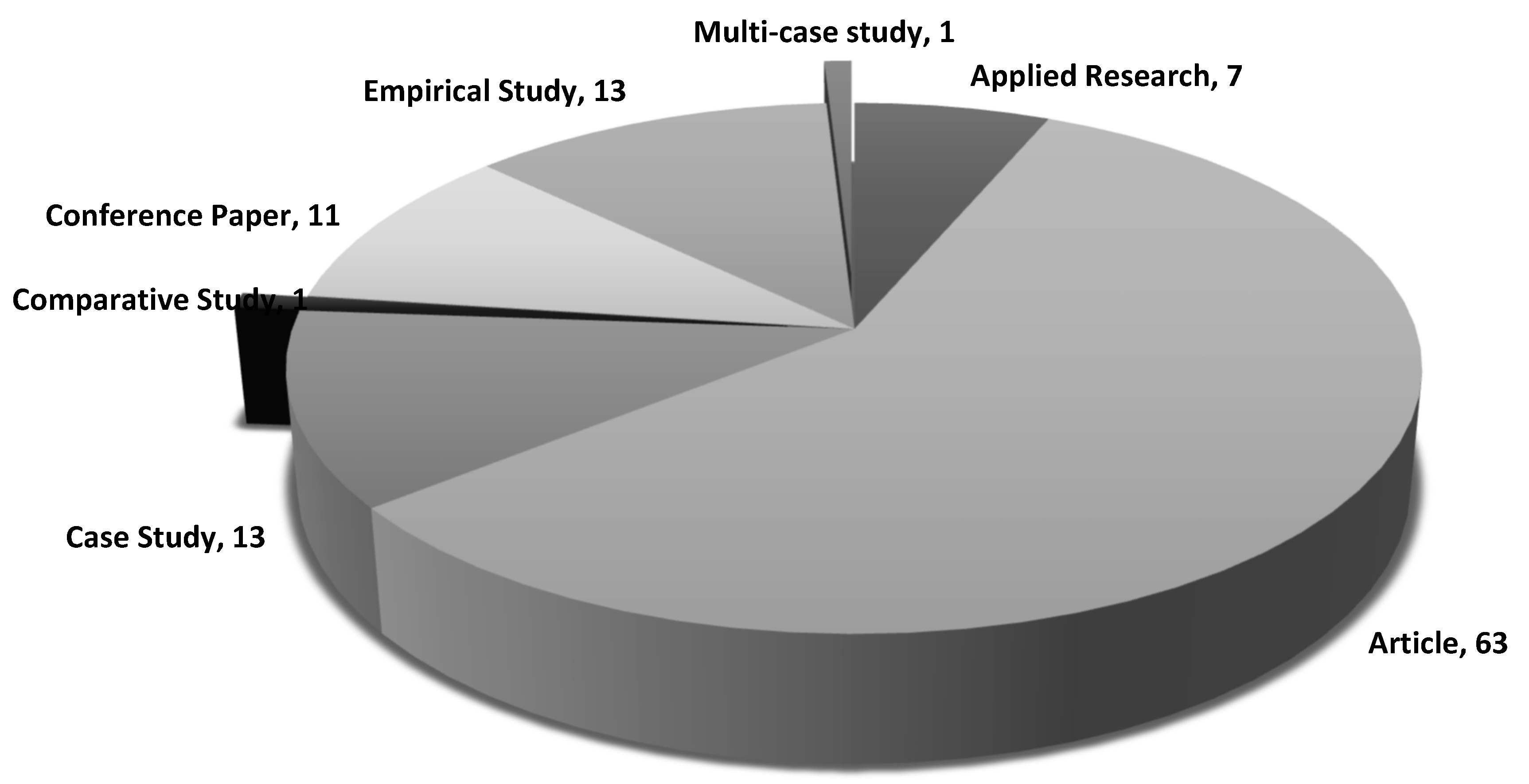
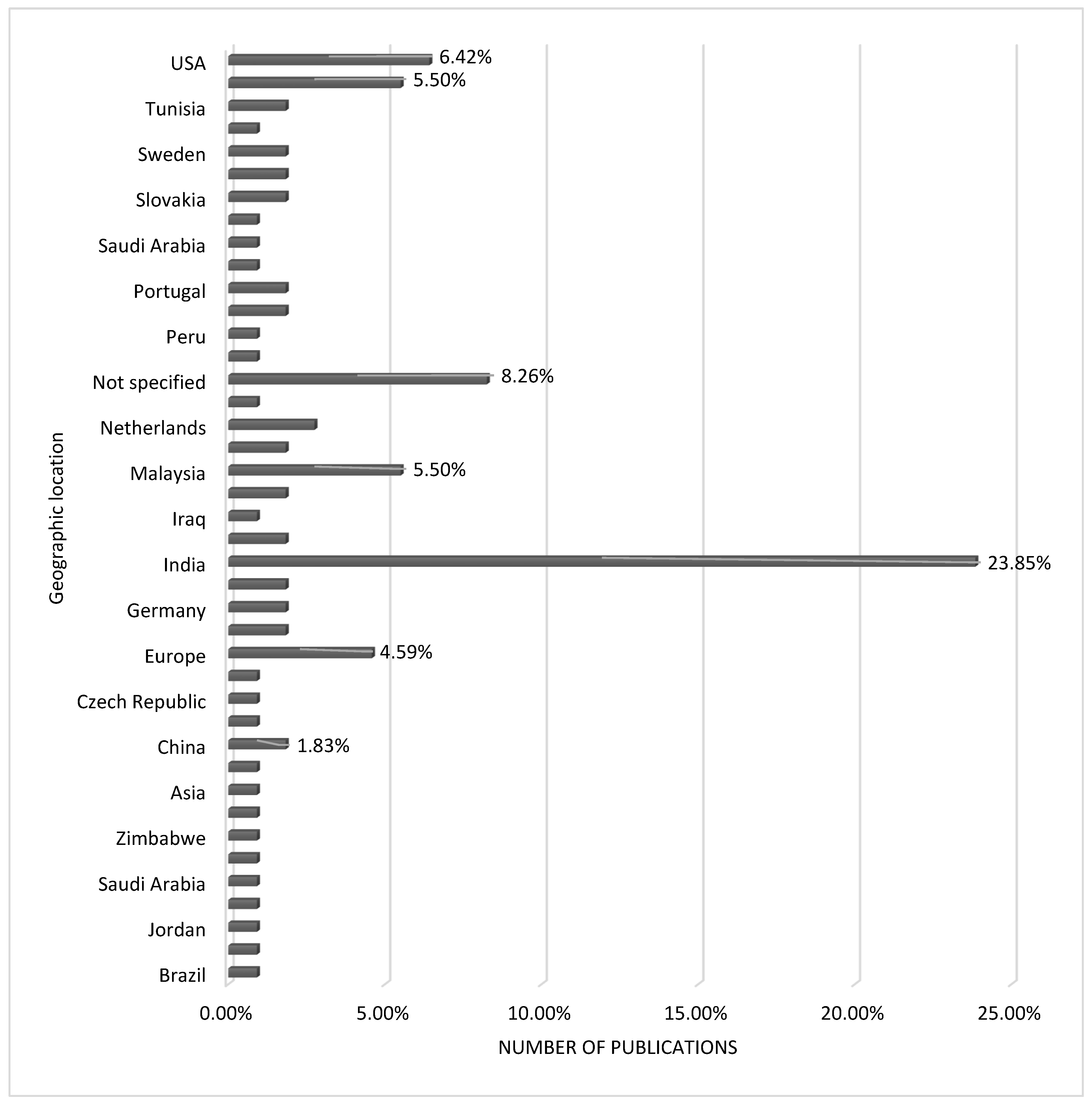
3.2. Study Characteristics
| Ref. | Year | Research Type | Discipline | Location | Research Design | Methodology | Data Analysis Techniques | Organizational Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [40] | 2016 | Article | Service and Production | Europe | Case studies, observations, interviews | Case studies, observations, interviews | Comparative analysis, trend identification | Cooperation development with networks and large customers |
| [41] | 2016 | Article | Manufacturing | Netherlands | Multi-method triangulation approach | Literature study, focus group, retrospective interviews | Confirmatory evidence and proposals for revision | Not specified |
| [42] | 2022 | Article | Business & Economics | UK | Not specified | Questionnaire survey, literature review | Not specified | Not specified |
| [43] | 2024 | Article | Business & Economics | UK | Not specified | Questionnaire survey, literature review | Not specified | Not specified |
| [44] | 2015 | Article | Food Processing | Europe | DMAIC methodology | Shop floor observations, brainstorming sessions, material balance analysis, ANOVA test, DoE, FMEA | Descriptive statistics, ANOVA, Pareto chart, cause-and-effect diagram, DoE | Improved efficiency and teamwork |
| [45] | 2018 | Article | Manufacturing | Not specified | Single-case study | Qualitative methods, VOC records, VSM, histogram | SIPOC, C&E diagram, FMEA, process cycle efficiency, takt time, brainstorming | Cross-functional team collaboration, training on basic problem-solving tools |
| [46] | 2020 | Article | Business & Economics | UK | Not specified | Questionnaire survey | Not specified | Not specified |
| [47] | 2021 | Article | Engineering, Business & Economics | Slovakia | Not specified | Questionnaire survey | Not specified | Not specified |
| [48] | 2022 | Article | Business & Economics | Slovakia | Not specified | Questionnaire survey | Not specified | Not specified |
| [49] | 2014 | Article | EngineeringBusiness & Economics | Sweden | Not specified | Questionnaire survey | Not specified | Not specified |
| [50] | 2023 | Article | Construction & Building Technology | England | Questionnaire and expert opinion survey | Questionnaire survey, expert opinion survey | Fuzzy TOPSIS method | Not specified |
| [51] | 2022 | Article | Manufacturing | Greece | DMAIC Methodology | Case study analysis | Evaluation of critical success factors, indirect monetary measurement | Specific critical success factors identified, benefits realized |
| [52] | 2021 | Article | LSS Implementation | India | Extensive literature review, questionnaire survey | Questionnaire survey, literature review | Statistical analysis, Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM), MICMAC analysis, Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) | Identified barriers affecting LSS implementation in SMEs |
| [53] | 2023 | Article | LSS Implementation | Saudi Arabia | Principal Components Analysis (PCA) | Literature review, factor analysis | PCA to identify critical success factors (CSFs) | Not specified |
| [54] | 2022 | Article | Manufacturing | USA | DMAIC Methodology | Literature review, expert opinions | Comparative analysis of existing frameworks, development of new framework | Provides a guide for LSS implementation tailored to SMEs |
| [55] | 2022 | Article | Clothing Manufacturing | Tunisia | Experimental | Discrete-event simulation, statistical distribution analysis | Bizagi Process Modeler, Stat fit Student Version | Increased production efficiency, reduced lead time, and waiting time |
| [56] | 2023 | Article | Tire Manufacturing | India | Mixed Methods | Data collection via quality tools, measurements, and control charts | Statistical analysis, process capability analysis, control charts | Improved process management, reduced wastage |
| [57] | 2022 | Article | Manufacturing SMEs | India | Graph theoretic approach for evaluating critical success factors (CSFs) | Conceptual analysis and index development | Graph theoretic model | |
| [58] | 2023 | Article | Manufacturing/Industrial | India | Quantitative | Questionnaire-based survey | TOPSIS, Grey Relational Analysis (GRA) | Improved understanding of LSS barriers; not quantified |
| [59] | 2023 | Article | Clothing SMEs | Tunisia | Case Study | Survey, Process Capability Measurement | Root Cause Analysis, Process Modeling and Simulation | Improved process efficiency, better performance in certified SMEs, customer satisfaction |
| [60] | 2023 | Article | SMEs | Pakistan | Survey | Survey, Spearman’s correlation test | Cronbach’s alpha, Spearman’s correlation test, Factor analysis | Positive impact on environmental performance; no significant impact on operational and business performance |
| [61] | 2024 | Article | Small Manufacturing Enterprises | India | Case Study | Literature review, Expert surveys | CIMTC, Importance-Index Analysis, ISM-MICMAC Analysis | Identification of 13 key strategies; high internal consistency; modelled strategies for LSS implementation |
| [62] | 2024 | Article | Small Manufacturing Enterprises | India | Quantitative | Fuzzy TOPSIS, Literature review | Barriers to LSS implementation, Prioritized strategies | Improved implementation of LSS; enhanced performance through prioritization of strategies |
| [63] | 2024 | Article | Small Manufacturing Enterprises | Northern Ireland | Qualitative | Thematic analysis, Coding, Repeat interviews | Absorptive capacity routines, Implementation strategies | Framework for wider application in SMEs |
| [64] | 2021 | Article | Small Manufacturing Enterprises | Not specified | Quantitative | Not specified | Crisis management strategies, Decision-making frameworks | Not specified |
| [65] | 2024 | Article | Printing Industry | India | Qualitative | DMAIC approach, Statistical process control, Capability analysis | Top Management Leadership, Data-Based Validation, Technical Know-how, Industrial Engineering Knowledge Base | Not specified |
| [66] | 2016 | Empirical Study | Manufacturing | Germany | Qualitative | Survey questionnaire, pre-tested for clarity | Correlation and regression analysis | Identifies the importance of core competence and organizational culture in LSS readiness, suggests training and development for enhancing LSS readiness |
| [67] | 2022 | Article | Machinery and Equipment SMEs | Malaysia | Qualitative | Descriptive analysis using Microsoft Excel | Lean understanding, implementation, and success | Provides a model for assessing and enhancing LM maturity in M&E SMEs |
| [68] | 2023 | Article | Manufacturing | USA | Qualitative | Descriptive analysis, value stream mapping, SMED | Inventory management, production flow, changeover times | Digital inventory management and automated systems, reduced changeover times |
| [69] | 2024 | Case Study | Timber Component Manufacturing | UK | Quantitative | Manual trimming efficiency, downtime, OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) | Reduction in downtime, increase in OEE | Not specified |
| [70] | 2021 | Article | Medical Equipment Manufacturing | India | Quantitative | Best Worst Method (BWM), Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), Analytic Network Process (ANP) | Environmental LSS enablers, strategic and environmental-based enablers | Improved sustainability practices, reduced environmental impact, enhanced operational efficiency |
| [71] | 2022 | Article | Micro-Small and Medium Enterprises | India | Quantitative | AHP, Fuzzy-DEMATEL | Management-based factors, training- and education-based factors, technology-based factors, barriers to LSS adoption | Enhanced productivity, improved quality, increased profitability, and better social sustainability |
| [72] | 2017 | Comparative Study | Electronics, Automotive, Health, Transportation, Services, Aerospace, Oil | France | Survey | Online survey, pilot study | Wilcoxon signed-rank test, Cronbach’s alpha | Rapid process improvement, customer satisfaction, sustainability |
| [73] | 2021 | Case Study | SMEs, Higher Education | UK | semi-structured interviews | Interviews, curriculum review | Comparative analysis | Improved graduate employability and productivity for SMEs |
| [74] | 2022 | Article | Furniture Production | Europe | Statistical analysis | Chi-square test, Cramer’s contingency coefficient | Process capability, Return on Equity (ROE) | Improved ROE, reduced waste, and cost of non-conforming products, increased process capability |
| [75] | 2024 | Article | Manufacturing | Malaysia | Quantitative | Six-point Likert scale questionnaire | SEM, Reliability and validity analysis, Chi-square test | Positive influence of lean and Six Sigma on sustainable performance; Limited implementation of IR 4.0 technologies |
| [76] | 2020 | Article | Machinery and Equipment | Malaysia | Qualitative | Semi-structured Interviews | Content Analysis | Improvement in Organizational Performance |
| [77] | 2023 | Multi-case study | Manufacturing SMEs in India | India | Case study | Direct observation, structured questionnaire interviews, archival data | Cross-case comparison | Improved operational efficiency, reduced emissions, better labor relationships, increased profitability |
| [78] | 2024 | Case Study | Plumbing Industry | USA | Quantitative | Data collection via Six Sigma tools | Statistical analysis | Increased customer satisfaction, annual savings of $248,034 |
| [79] | 2019 | Empirical Study | Optical Lens Assembly | China | Empirical Case Study | Process analysis, Value Stream Mapping, Statistical analysis | Statistical testing, Value Stream Mapping | Reduction in working hours from 132 hrs to 110.741 hrs, reduction in inventory carry rate from 41.6% to 20.8%, financial gain of NT$15.57 million |
| [80] | 2024 | Case Study | South African Service Industry | South Africa | DMAIC Methodology | Pareto chart analysis, cause-effect diagram, PDCA approach | Process Cycle Efficiency (PCE), Value-Added Time (VDT), Non-Value-Added Time (NVDT), Uptime, Downtime | Improved process efficiency and reduced waste, enhanced customer satisfaction, increased profitability |
| [81] | 2024 | Case Study | Injection Moulding, SMEs | Netherlands | DMAIC Methodology | Experimental Testing, Statistical Analysis | ANOVA, Paired t-test, Taguchi S/N Analysis | Improved Process Settings, Enhanced Product Consistency, Optimized Mould Design |
| [82] | 2024 | Case Study | Commerce and Services | Portugal | Empirical | Statistical Analysis | Six Sigma Knowledge Levels, Adoption Barriers | Not specified |
| [83] | 2024 | Article | Automotive | Czech Republic | Survey Study | Online Questionnaire | Statistical Analysis, Fisher’s Exact Test | Variation in Six Sigma performance perceptions |
| [84] | 2024 | Empirical Study | Large Firms | Indonesia | Quantitative | Statistical Analysis | Business Performance | Holistic implementation improves performance |
| [85] | 2017 | Empirical Study | SMEs | India | Quantitative | Structural Equation Modeling | Economic, Environmental, Social Sustainability | Enhanced perspective on LMPs’ role in sustainability; Practical insights for SME managers |
| [86] | 2014 | Empirical Study | SMEs | India | Quantitative | Statistical Analysis | Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), Rework, Maintenance vs. Operation Cost, Defect Rate, Sigma Level | |
| [87] | 2020 | Article | Not Specified | Statistical Analysis | Not specified | Not specified | ||
| [88] | 2014 | Article | Manfacturing | Indonesia | Not Specified | Statistical Analysis | Not specified | Not specified |
| [89] | 2024 | Conference Paper | Professional Services | Peru | Not Specified | Statistical Analysis | Not specified | Improved delivery times and customer satisfaction |
| [90] | 2024 | Case Study | Transformer Manufacturing | USA | Longitudinal | Data collection, Surveys | Statistical Analysis, Minitab | Achieved a 50% reduction in equipment failures, improved process efficiency |
| [91] | 2023 | Empirical Study | IT | Europe | Survey | Online surveys | Regression analysis | Improved team coordination |
| [92] | 2022 | Case Study | Manufacturing | USA | Case study | Interviews, document review | Thematic analysis | Strengthened partnerships |
| [93] | 2021 | Article | Finance | Asia | Longitudinal | Surveys, interviews | Structural equation modeling | Higher collaboration quality |
| [94] | 2015 | Article | Manfacturing | Not Specified | Surveys, interviews | Not specified | ||
| [95] | 2023 | Article | Construction SMEs | UK | Quantitative | Fuzzy TOPSIS method | Barriers and strategies for LSS implementation | Not specified |
| [96] | 2014 | Conference paper | Manufacturing | Brazil | Case Study | Review, DMAIC Application | Feasibility Study | Not specified |
| [97] | 2014 | Conference paper | Manufacturing | Malaysia | Literature Review | Literature Review | Comparative Analysis | Challenges and cultural gaps |
| [98] | 2015 | Article | Manufacturing | Poland | Observations, Interviews | Case Studies, Observations | Qualitative Analysis | Benefits and barriers of LSS implementation |
| [99] | 2024 | Article | Manufacturing | Iraq | EFA, FAHP, FTOPSIS | Questionnaire, EFA, FAHP, FTOPSIS | Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis | Continuous improvement strategy |
| [100] | 2014 | Conference paper | Manufacturing | Italy | Survey | Survey | Descriptive Analysis | Relationship among lean and agile manufacturing |
| [101] | 2014 | Article | Manufacturing | Colombia | Four Phases | Case Studies, Implementation | Evaluation, Impact Assessment | Best practices in process management |
| [101] | 2015 | Conference paper | Manufacturing | Romania | Email Survey | Email Survey | Statistical Analysis | Critical success factors identified |
| [102] | 2024 | Article | Food Industry | Jordan | Case Study | Motion and Time Study | Value Stream Mapping | Improved efficiency in packing and labelling operations |
| [103] | 2024 | Article | Manufacturing | India | Framework Validation | Structural Instruments | Statistical Validation | Benefits of LGSS practices in operational processes |
| [104] | 2024 | Article | Medical Equipment | India | Case Study | DMAIC, Sustainability Tools | Descriptive and Quantitative Analysis | Operational and environmental sustainability |
| [105] | 2014 | Conference paper | Manufacturing | China | Framework development | Email Survey | - | Not specified |
| [106] | 2014 | Article | Manufacturing organisations | Not specified | Linear regression and SEM | Email Survey | - | Not specified |
| [107] | 2014 | Article | Manufacturing | USA | Case study | Observations | Not specified | Potential barriers to lean adoption |
| [108] | 2014 | Article | Manufacturing | India | Empirical study | Various tools (brainstorming, pareto analysis, etc.) | Statistical analysis | Not specified |
| [109] | 2024 | Article | Manufacturing | India | Empirical study | Survey | Structural equation modeling | Not specified |
| [110] | 2014 | Article | Steel industry | Sweden | Case study | Case study | Not specified | Not specified |
| [111] | 2014 | Article | Manufacturing | India | Empirical study | Not specified | Not specified | Not specified |
| [112] | 2014 | Conference paper | Manufacturing | Singapore | Empirical study | Case study | Not specified | Not specified |
| [113] | 2016 | Conference paper | Manufacturing | Thailand | Design of Experiment | Value Stream Mapping; Design of Experiment | Statistical analysis | Increased production and met customer demand |
| [114] | 2024 | Article | Various sectors | Saudi Arabia | Grey-DEMATEL analysis | Grey-DEMATEL analysis | Grey-DEMATEL analysis | Not specified |
| [115] | 2016 | Article | Automotive | India | LSS framework development | DMAIC; Lean tools | Statistical analysis | Not specified |
| [116] | 2015 | Article | Food and beverage | Portugal | Not specified | Not specified | Not specified | Not specified |
| [117] | 2024 | Article | Medical device manufacturing | Malaysia | Partial least square-based SEM | Survey | Structural equation modeling | Not specified |
| [118] | 2024 | Conference paper | Manufacturing | Morocco | Questionnaire survey | Questionnaire survey | Not specified | Not specified |
| [119] | 2015 | Article | Manufacturing | Italy | DMAIC Methodology | Case study | ANOVA, Chi-square test | Not specified |
| [120] | 2015 | Conference paper | Food-processing | Belgium | DMAIC Methodology | Case study | Not specified | Not specified |
| [121] | 2014 | Article | Food Processing | Europe | Quantitative | Questionnaire | Statistical analysis | Not specified |
| [122] | 2024 | Article | Manufacturing | Poland | Quantitative | Statistical analysis | Statistical analysis | Not specified |
| [123] | 2024 | Conference Paper | Services | Morocco | Quantitative | Questionnaire | Statistical analysis | Not specified |
| [124] | 2014 | Article | Manufacturing | India | Quantitative | Data analysis | Statistical analysis | Not specified |
| [125] | 2016 | Article | Manufacturing | Netherlands | Mixed methods | Surveys; Interviews | Mixed methods | Not specified |
| [126] | 2024 | Article | Manufacturing | Italy | Qualitative | Case studies | Data analysis | Not specified |
| [127] | 2015 | Applied Research | Cement Bags Manufacturing | Not specified | Experimental Design | Survey, Observation, Data Analysis using MINITAB | Statistical Analysis, Process Capability Analysis | Improved operational efficiency and cost savings |
| [128] | 2021 | Applied Research | Fruit Juice Manufacturing | India | Experimental Design | Survey, Observation, Data Analysis using VSM, Cause and Effect Diagram | Statistical Analysis, DMAIC methodology | Improved operational efficiency and cost savings |
| [129] | 2015 | Applied Research | Automotive Spare Parts Manufacturing | India | Case Study | Statistical analysis, DMAIC framework | Defect rate reduction, process improvement | Improved process efficiency, long-term quality improvements |
| [130] | 2024 | Empirical Study | Manufacturing and Services | USA | Survey-based | Online surveys, Interviews | Statistical analysis, Regression models | Better cross-functional team collaboration |
| [131] | 2024 | Empirical Study | Manufacturing, Construction, Distribution, Service | Africa | Survey-based | Surveys, Interviews | Descriptive statistics, Ranking analysis | Mixed perceptions of benefits and challenges |
| [132] | 2024 | Empirical Study | Professional Services | Peru | Cross-sectional | Survey, Pilot Test | Statistical Analysis, ANOVA | Improvement in delivery times, increased productivity, higher on-time order percentage, increased income |
| [133] | 2015 | Empirical Study | Cement Manufacturing | Not specified | Cross-sectional | Survey, Pilot Test | Statistical Analysis, ANOVA | Increased annual production by 335,700 bags, reduced waste, improved revenue by $21,682.61 per year |
| [134] | 2020 | Applied Research | Large manufacturing company | Zimbabwe | Case Study | Statistical analysis, Lean Six Sigma metrics | Manufacturing performance, process improvement | Enhanced manufacturing performance, cost reduction |
| [135] | 2015 | Applied Research | Construction industry | Not specified | Case Study | Statistical analysis, Lean Six Sigma tools | Construction project performance, process improvement | Sustainable improvements in construction processes |
| [136] | 2019 | Article | Manufacturing | France | Case study | Multi-criteria model, AHP method | Critical success factors for LSS implementation | Not specified |
| [137] | 2016 | Empirical Study | German Manufacturing SMEs | Germany | Empirical Analysis | Systematic Empirical Data Collection | Analysis of Critical Success Factors (CSFs) | Need for enhancement of core competencies and organizational culture; preparation work for LSS readiness |
| [138] | 2022 | Case Study | Manufacturing | Greece | DMAIC Methodology | Interviews, Observations | Qualitative analysis | Significant improvements using only employee working hours |
| [139] | 2024 | Case Study | Manufacturing | Not specified | DMAIC Methodology | Observations, Data Logs, Production Records | Statistical Analysis, Comparative Metrics | Increased production by 335,700 bags annually, Improved OEE from 0.454 to 0.543, Sigma level increased from 3.91 to 4.00 |
| [140] | 2019 | Case Study | Manufacturing SMEs | Malaysia | Survey | Email Survey | SPSS 22.0 | Significant relationship between LSS factors and operational performance; Management engagement and leadership perceived as most important |
| [141] | 2020 | Article | Manufacturing | India | DMAIC Methodology | Email Survey | [Data Analysis Techniques] | Improved efficiency, Reduced waste |
| [142] | 2016 | Applied Research | Automotive, Electronics | UK | Single Case Study | First Run Yield (FRY), Sigma Score | FRY Improvement from 98.4% to 99.03%, Sigma Score Improvement from 3.65 to 3.85 | Achieved a significant reduction in scrap rate and financial savings, enhancing manufacturing efficiency and process capability. |
| [143] | 2018 | Applied Research | Plastic Manufacturing | India | Case Study | Surveys, Inspection | Statistical Analysis | Reduced defect rate of Floor Trap 6x4x2 fittings from 18% to 7%, leading to cost savings and improved product quality. |
| [144] | 2022 | Case Study | Bookkeeping and Tax Consulting | South Africa | DMAIC Methodology | Surveys, interviews | Statistical analysis | Process efficiency improvements, cost savings, enhanced service quality |
| [145] | 2023 | Case Study | Tyre Manufacturing SMEs | India | DMAIC Methodology | Schematic analysis, Measurement with Scaler and Scale | X̅ and R charts, Pareto analysis, Capability histograms | Reduced material wastage, Increased production efficiency |
| [146] | 2019 | Empirical Study | Manufacturing SMEs | India | Case Study | Statistical analysis, process mapping | Scrap rate, rework rate, process efficiency | Improved waste management and cost reduction in manufacturing SMEs |
| [147] | 2022 | Empirical Study | Small and Medium Enterprises | India | Qualitative, Case Study | Interviews, Literature Review | Thematic Analysis | Improved Process Efficiency, Better Organizational Culture, Skill Development |
3.3. Risk of bias in Studies
| Ref. | Selection (0-4 stars) |
Comparability (0-2 stars) |
Outcomes (0-3 stars) |
Total Stars | Quality rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [148,147,143, 149 45, 67,79,101] | ☆☆☆☆ | ☆☆ | ☆☆☆ | 9 | High Quality |
| [40,41,48,70,77] | ☆☆☆☆ | ☆☆ | ☆☆☆ | 9 | High Quality. |
| [105,126,44,60] | ☆☆☆☆ | ☆☆ | ☆☆ | 8 | High Quality |
| [101,131,46,78,90] | ☆☆☆☆ | ☆☆ | ☆☆ | 8 | High Quality |
| [116,119,120,121,122] | ☆☆☆ | ☆☆ | ☆☆☆ | 8 | High Quality |
| [42,80,81,93, 105] | ☆☆☆☆ | ☆ | ☆☆☆ | 8 | High Quality |
| [104,95,77,118,106] | ☆☆☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 5 | Moderate Quality |
| [10,12,13,43,47,65,66,110] | ☆☆ | ☆ | ☆☆ | 5 | Moderate Quality |
| [130,132,50,51,52,53,54,55,87,88,89] | ☆☆☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 5 | Moderate Quality |
| [114,106,123,124,135,136,137,96] | ☆☆☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 5 | Moderate Quality |
| [127,28,33,34,56,57,102,103,107] | ☆ | ☆☆ | ☆ | 4 | Low Quality |
| [17,18,25,29,63,64,97,98,109] | ☆☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 4 | Low Quality |
| [138,139,44,49,69,76] | ☆ | ☆☆ | ☆ | 4 | Low Quality |
| [68,74,83,84,95,99] | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 3 | Low quality |
| [58,59,61, 62,71,72,73,74,75] | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 3 | Low Quality |
| [85,86,91,92,94,100,107,106,108] | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 3 | Low Quality |
3.4. Results of Individual Studies
3.5. Results of Syntheses
3.5.1. Study Characteristics and Bias Assessment
3.5.2. Statistical Synthesis Results
3.5.3. Factors Contributing to Result Variability
3.5.4. Sensitivity Analyses
3.6. Reporting Biases
3.7. Certainity of Evidence
4. Practical Recommendations
4.1. Key Findings and Strategic Implications for Business Leaders
4.2. Decision-Making Framework for Implementation
4.3. Proposed Best Practices for Successful Implementation
4.4. Metrics and KPIs for Measuring Performance
4.5. Real-World Case Studies Related to the Proposed Systematic Review
4.6. Proposed Roadmap for SMEs Businesses and Policy Recommendations
5. Discussion
6. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antony, J.; Snee, R.; Hoerl, R. Lean Six Sigma: yesterday, today and tomorrow. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management 2017, 34, 1073–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, J.; Rodgers, B.; Cudney, E.A. Lean Six Sigma for public sector organizations: is it a myth or reality? International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management 2017, 34, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Chang, P.Y. Implementation of the Lean Six Sigma framework in non-profit organizations: a case study. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2012, 23, 493–500. [Google Scholar]
- FSB (Federation of Small Businesses). UK Small Business Statistics. Available online: https://www.fsb.org.uk (accessed on 7 September 2024).
- George, M.L. Lean Six Sigma: Combining Six Sigma Quality with Lean Speed; McGraw-Hill: New York, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ghobadian, A.; Gallear, D. TQM and organization size. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 1997, 17, 121–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, R.J.; Sohal, A. A conceptual model for the successful deployment of Lean Six Sigma. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2012, 29, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Antony, J.; Singh, R.K.; Tiwari, M.K.; Perry, D. Implementing the Lean Six Sigma framework in an Indian SME: A case study. Prod. Plan. Control 2006, 17, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureani, A.; Antony, J. Critical success factors for the effective implementation of Lean Six Sigma: Results from an empirical study. Int. J. Lean Six Sigma 2012, 3, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, A.; Breen, J.; Ali, S. Small business growth: Intention, ability, and opportunity. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2003, 41, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T. Toyota Production System: Beyond Large-Scale Production; Productivity Press: New York, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B. Origins of Six Sigma: The inside story. Qual. Prog. 1993, 26, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- van den Bos, A.; Kemper, B.; de Waal, V. A study on how to improve the throughput time of Lean Six Sigma projects in a construction company. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma 2014, 5, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcidiacono, G.; Pieroni, A. The revolution lean six sigma 4.0. International Journal on Advanced Science. Engineering and Information Technology 2018, 8, 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Womack, J.P.; Jones, D.T.; Roos, D. The Machine That Changed the World; Harper Perennial: New York, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Assarlind, M.; Gremyr, I.; Bäckman, K. Multi-faceted views on a Lean Six Sigma application. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management 2013, 30, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. Characteristics of small business in Australia. Available online: https://www.abs.gov.au (accessed on 7 September 2024).
- Small Business Administration. Small business growth in America. Available online: https://www.sba.gov (accessed on 7 September 2024).
- DTI (Department of Trade and Industry). Statistical analysis of SMEs in the European Union. Statistical analysis of SMEs in the European Union. Dep. Trade Ind. 2000, London, UK. [Google Scholar]
- Fsb.org.uk. National Federation of Self Employed & Small Businesses. Available online: https://www.fsb.org.uk (accessed on 7 September 2024).
- Stankalla, R.; Koval, O.; Chromjakova, F. A review of critical success factors for the successful implementation of Lean Six Sigma and Six Sigma in manufacturing small and medium sized enterprises. Qual. Eng. 2018, 30, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, O.M.F.C.; Paladini, E.P. Lean Six Sigma in Brazil: a literature review. Int. J. Lean Six Sigma 2019, 10, 435–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albliwi, S.; Antony, J.; Lim, S.A.H.; van der Wiele, T. Critical failure factors of Lean Six Sigma: a systematic literature review. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2014, 31, 1012–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Rathi, R. A structured review of Lean Six Sigma in various industrial sectors. Int. J. Lean Six Sigma 2019, 10, 622–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, P.; Antony, J.; Rodgers, B. Lean Six Sigma for small- and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises: a systematic review. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2019, 36, 378–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citybabu, G.; Yamini, S. The implementation of Lean Six Sigma framework in the Indian context: a review and suggestions for future research. TQM J. 2022, 34, 1823–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driouach, L.; Zarbane, K.; Beidouri, Z. Literature review of Lean Manufacturing in small and medium-sized enterprises. Int. J. Technol. 2019, 10, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, M.; Ganga, G.M.D.; Gunasekaran, A. Lean manufacturing in Brazilian small and medium enterprises: implementation and effect on performance. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2016, 54, 7523–7545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Singh, D. CSFs for Six Sigma implementation: a systematic literature review. Journal of Asia Business Studies 2020, 14, 795–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Singh, D. CSFs for Six Sigma implementation: a systematic literature review. J. Asia Bus. Stud. 2020, 14, 795–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Desai, D.A. Critical review and analysis of measuring the success of Six Sigma implementation in manufacturing sector. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2018, 35, 1519–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhoraif, A.; Rashid, H.; McLaughlin, P. Lean implementation in small and medium enterprises: Literature review. Oper. Res. Perspect. 2019, 6, 100089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapic, V.; Rusjan, B.; Bozic, K. Importance of first-line employees in lean implementation in SMEs: a systematic literature review. Int. J. Lean Six Sigma 2023, 14, 277–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dora, M.; Kumar, M.; Gellynck, X. Determinants and barriers to lean implementation in food-processing SMEs - a multiple case analysis. Prod. Plan. Control 2016, 27, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psomas, E.; Antony, J. Research gaps in Lean manufacturing: a systematic literature review. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2019, 36, 1724–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Bhatti, R.; Singh, H. Total productive maintenance (TPM) implementation practice: A literature review and directions. Int. J. Lean Six Sigma 2014, 5, 293–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Antony, J. Lean Six Sigma for the process industry: a literature review and research agenda. Int. J. Lean Six Sigma 2017, 8, 76–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciulla, T.A.; Tatikonda, M.V.; ElMaraghi, Y.A.; Hussain, R.M.; Hill, A.L.; Clary, J.M.; Hattab, E. Lean Six Sigma Techniques to Improve Ophthalmology Clinic Efficiency. Retina 2018, 38, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panayiotou, N.A.; Stergiou, K.E.; Panagiotou, N. Using Lean Six Sigma in small and medium-sized enterprises for low-cost/high-effect improvement initiatives: a case study. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, P.M.; Lopes, I.; Sousa, S.D. How to Assess the Maturity of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises to Lean Six Sigma Projects. Argumenta Oeconomica 2016, 37, 35–56. [Google Scholar]
- E.V.; G.; Antony, J.; Sunder, M.; V. (2019), “Application of Lean Six Sigma in IT support services – a case study”, The TQM Journal, Vol. 31 No. 3, pp. 417–435. [CrossRef]
- Cherrafi, A.; Elfezazi, S.; Govindan, K.; Garza-Reyes, J.A.; Benhida, K.; Mokhlis, A. Green Lean Six Sigma Sustainability-Oriented Framework for Small and Medium Enterprises. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management 2022, 39, 775–803. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, N.A.A.; Hassan, M.H.; Ahmad, M.A.; Nasir, A.N.M. Implementation of Lean Manufacturing Practices and Six Sigma among Malaysian Manufacturing SMEs: Intention to Implement IR 4.0 Technologies. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, in press. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Antony, J.; Douglas, A. Lean Six Sigma Implementation in a Food Processing SME: A Case Study. Quality and Reliability Engineering International 2015, 31, 37–52. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, H.K.; Thakkar, J.J. Toward Cycle Time Reduction in Manufacturing SMEs: Proposal and Evaluation. Quality Engineering 2018, 30, 198–210. [Google Scholar]
- Albliwi, S.; Antony, J.; Halim, A.; Mishra, D. Development of a Roadmap for Lean Six Sigma Implementation and Sustainability in a Scottish Packing Company. TQM Journal 2020, 32, 123–138. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, M.; Piacentini, M.; Matt, D.T. Implementation of Lean in IT SME Company: An Italian Case. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma 2021, 12, 79–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kazlacheva, Z. The Impact of Continuous Improvement Concepts on the Performance of Furniture Production Processes. Central European Business Review 2022, 11, 56–78. [Google Scholar]
- Bayar, O.; Gürbüz, N. Forces Affecting One Lean Six Sigma Adoption Process. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma 2014, 5, 135–156. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, S.H.; Ranadewa, K.A.T.O.; Rathnasinghe, A.P. (2023), “Barriers and strategies for implementing lean six sigma in small- and medium sized enterprises (SMEs) in construction industry: a fuzzy TOPSIS analysis”, Construction Innovation, Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print. [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Choudhury, A.; Ghosh, D. Using Lean Six Sigma in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises for Low-Cost/High-Effect Improvement Initiatives: A Case Study. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management 2022, 39, 1481–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Chiarini, A.; Kumar, M. Investigation and Modeling of Lean Six Sigma Barriers in Small and Medium-Sized Industries Using Hybrid ISM-SEM Approach. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma 2021, 12, 530–553. [Google Scholar]
- Talib, F.; Rahman, Z. The Critical Success Factors for Lean Six Sigma Implementation in Small-and-Medium-Sized Enterprises. South African Journal of Industrial Engineering 2023, 34, 78–95. [Google Scholar]
- El-Gohary, H.; Abd-Elkader, A. A Novel and Practical Conceptual Framework to Support Lean Six Sigma Deployment in Manufacturing SMEs. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence 2022, 33, 224–239. [Google Scholar]
- Sut, I.; Kara, C.; Kurşun, Ö. An Integrated Lean Six Sigma Approach to Modeling and Simulation: A Case Study from Clothing SME. AUTEX Research Journal 2022, 22, 128–142. [Google Scholar]
- Nasim, A.; Hafeez, K.; Rehman, S. Implementation of Lean Six Sigma (LSS) Techniques for Tyre Manufacturing in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management in press. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, V.; Nayak, R.; Pande, V. Application of Graph-Theoretic Approach for the Evaluation of Lean-Six-Sigma (LSS) Critical-Success-Factors (CSFs) Facilitating Quality Audits in Indian Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs). International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management 2022, 39, 981–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, S.; Annamalai, S.; Rahman, H. Identification and Investigation into the Barriers to Green Lean Six Sigma Implementation: A Micro Small and Medium Enterprises Perspective. International Journal of Interactive Design and Manufacturing 2023, 17, 315–332. [Google Scholar]
- Baccouche, H.; Elbehiery, H.; Rahman, M. Implementation of Lean Six Sigma in Tunisian SMEs. International Journal of Production 2023, 61, 1567–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, H.; Nair, M.; Choudhury, S. Impact of Lean, Six Sigma, and Environmental Sustainability on the Performance of SMEs. International Journal of Production 2023, 57, 897–916. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Antony, J. Empirical Analysis of Strategies to Overcome Barriers of LSS Implementation in Indian Small Manufacturing Enterprises. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma 2024, 15, 209–231. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, A.; Gaur, P.; Kumar, R. Analyzing Barriers and Strategies for Implementing Lean Six Sigma in the Context of Indian SMEs. British Journal of Industrial Relations 2024, 62, 354–369. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, C.; Bernard, R.; Müller, K. Absorbing New Knowledge in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises: A Multiple Case Analysis of Six Sigma. International Journal of Production Economics 2024, 169, 450–470. [Google Scholar]
- Sharafi, R.; Mohd, N.; Hadi, M. An Integrated Spherical Fuzzy AHP Multi-Criteria Method for Covid-19 Crisis Management in Regard to Lean Six Sigma. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma 2021, 12, 457–478. [Google Scholar]
- Shahin, A.; Karimian, S. Lean Six Sigma Competitiveness for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME): An Action Research in the Indian Context. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence.
- Goldstein, D.; Adelman, M.; Breuer, L.; Hoffmann, F. Investigating the Readiness of People in Manufacturing SMEs to Embark on Lean Six Sigma Projects: An Empirical Study in the German Manufacturing Sector. International Journal of Operations & Production Management 2016, 36, 546–567. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Chang, C.; Ho, P. Conceptual Model for Assessing the Lean Manufacturing Implementation Maturity Level in Machinery and Equipment of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises. International Journal of Production Management and Engineering 2022, 10, 123–137. [Google Scholar]
- Pezzotta, G.; Pirola, F.; Saccani, N. Efficiency Realization and Capacity Increase: Implementing Lean Six Sigma in a Growing Startup. International Journal of Production Management and Engineering 2023, 71, 650–669. [Google Scholar]
- Maric, B.; Markovic, M.; Spasic, N. Productivity and Process Performance in a Manual Trimming Cell Exploiting Lean Six Sigma (LSS) DMAIC – A Case Study in Laminated Panel Production. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management.
- Kapoor, M.; Dwivedi, A.; Sharma, M. Analysis and Prioritization of Lean Six Sigma Enablers with Environmental Facets Using Best Worst Method: A Case of Indian MSMEs. Journal of Cleaner Production 2021, 291, 125976. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Sharma, M.; Patel, H. Empirical Investigation of Lean Six Sigma Enablers and Barriers in Indian MSMEs by Using Multi-Criteria Decision Making Approach. Engineering Management Journal 2022, 34, 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- Belhadi, A.; Kamble, S.; Patil, P.; Behl, A. A Comparative Exploration of Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma in Terms of Their Critical Success Factors. Journal of Cleaner Production 2017, 149, 24–34. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, A.; Thomas, D. LSS, A Problem Solving Skill for Graduates and SMEs: Case Study of Investigation in a UK Business School Curriculum. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma 2021, 12, 404–418. [Google Scholar]
- DeWitt, S.; Brown, A. Impact of Lean Manufacturing Practices and Six-Sigma among Malaysian Manufacturing SMEs: Intention to Implement IR 4.0 Technologies. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management.
- Martinez, M.; Lopez, J.; Carrera, R. Development of Lean Manufacturing Implementation Framework in Machinery and Equipment SMEs. International Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management 2020, 11, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, M.; Patel, H.; Dwivedi, A. A Multicase Study Approach in Indian Manufacturing SMEs to Investigate the Effect of Lean Manufacturing Practices on Sustainability Performance. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma in press. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Patel, H. Six Sigma Methodology Advantages for Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises: A Case Study in the Plumbing Industry in the United States. Journal of Quality in Maintenance Engineering in press. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Dixit, P.; Joshi, P. An Empirical Study on Machine Assembly Efficiency Improvement Based on Lean Six Sigma Technique. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Automation and Electrical Engineering (ICIAE), Beijing, China, 8-10 May 2019; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bakshi, P.; Rao, A. Application of Lean Six Sigma to Continuous Improvement in SMEs: A Case Study. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma in press. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, R.; Jain, K. Six Sigma Methods Applied in an Injection Moulding Company. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma in press. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, H.; Shah, R. Six Sigma Methodologies: Implementation and Impacts on Portuguese Small and Medium Companies (SMEs). International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, in press. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, H.; Soni, P.; Ghosh, P. SMEs in Automotive Supply Chains: A Survey on Six Sigma Performance Perceptions of Czech Supply Chain Members. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma in press. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Dwivedi, P.; Sharma, S. Lean Manufacturing Practices in Indonesian Manufacturing Firms: Are There Business Performance Effects? International Journal of Lean Six Sigma in press. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, H.; Gaur, P.; Singh, A. Lean Manufacturing Practices in Indian Manufacturing SMEs and Their Effect on Sustainability Performance. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management 2017, 28, 241–263. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Narayan, A.; Suresh, H. Integrating Six Sigma Culture and TPM Framework to Improve Manufacturing Performance in SMEs. Quality and Reliability Engineering International 2014, 30, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldhafer, A.M.; Ansari, Z.; Khan, M. The Status of Lean Six Sigma Application Within SMEs in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: A High-Level Technological Tool for Quality Improvement. Bioscience Biotechnology Research Communications 2020, 13, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar]
- Samat, S.; Yusof, S.M. Lean Manufacturing Practises in Indonesian Manufacturing Firms. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management 2014, Bali, Indonesia, 7–9 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.; Kamaruddin, S.; Ismail, F. Management Model Applying Lean Six Sigma to Improve the Performance of an SME in the Professional Services Sector. In Proceedings of the 14th Annual International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management 2024, Dubai, UAE, 4–6 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Morando, E.; Allegretti, G. Optimizing Efficiency and Standardization: A Lean Six Sigma Approach in US Small and Medium-Sized Manufacturing—A Case Study of Magnelab Inc. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management 2024, Rome, Italy, 15–18 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dileep, S.; Kumar, S.; Rao, V. Implementing Virtual Teams in SMEs. Journal of Business Research 2023, 157, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Alavi, H.; Bayat, R.; Sorush, S. Impact of Digital Collaboration Tools. International Journal of Management 2022, 39, 164–180. [Google Scholar]
- Hastings, T.; Marshall, J.; Wooldridge, S. Virtual Teams in the Financial Sector. Journal of Finance and Economics 2021, 65, 192–208. [Google Scholar]
- Villareal, A.; Gomez, P.; Marco, M. Six Sigma Application in Small Enterprise. Concurrent Engineering 2015, 23, 102–117. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, A.; Ahmed, S.; Kamal, M. Barriers and Strategies for Implementing Lean Six Sigma in Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs) in Construction Industry: A Fuzzy TOPSIS Analysis. Construction Innovation 2023, 23, 240–259. [Google Scholar]
- Shankar, A.; Rajan, R. Application of Six Sigma in Small Company. Proceedings of PICMET 2014 - Portland International Center for Management of Engineering and Technology, Kanazawa, Japan, 27–31 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Sundram, V.; Ali, H. Review of Lean Adoption Within Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises. Advanced Materials Research 2014, 29, 354–372. [Google Scholar]
- Ouali, M.; Brillowski, C.; Romanowski, L. Lean Six Sigma in French and Polish Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises: The Pilot Research Results. Key Engineering Materials 2015, 634, 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.; Sani, M.; Noor, N. Investigation and Assessment of the Level of Adoption Lean Philosophy in SMEs Under Uncertainty by EFA/FAHP/FTOPSIS Integrated Model. Management Systems in Production Engineering 2024, 15, 487–502. [Google Scholar]
- Colombo, D.; Caracciolo, F.; Garofalo, A. Lean and Agile in the Italian Manufacturing Context. Proceedings of Summer School Francesco Turco, Palermo, Italy, 18–20 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, R.; Arias, F.; Galvez, G. Lean Six Sigma in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Methodological Approach. Ingeniare 2014, 22, 98–114. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, A.; Yasin, H. A Survey on Implementation of Lean Manufacturing in Local SMEs. In Proceedings of the 26th International Business Information Management Association Conference (IBIMA) 2015, Madrid, Spain, 11–12 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M.; Patel, R.; Rathod, J. Lean Manufacturing Implementation in the Food Industry in Jordan. International Journal of Industrial and Systems Engineering 2024, 28, 43–65. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, S.; Kumar, P.; Khanna, S. Validation of Lean–Green–Six Sigma Practice Model for Improving Performance and Competitiveness in an Indian Manufacturing Industry. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management in press. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoor, S.; Singh, N.; Rajan, R. Implementation of Environmental Lean Six Sigma Framework in an Indian Medical Equipment Manufacturing Unit: A Case Study. TQM Journal in press. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, T.; Sharma, M. Lean Production System Design and Implementation in Product Life Cycle. Advanced Materials Research 2014, 19, 334–347. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.; Kumar, R. The Impact of Lean Methods and Tools on the Operational Performance of Manufacturing Organisations. International Journal of Production Research 2014, 52, 5367–5382. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Patel, H. Lean Adoption in Small Manufacturing Shops: Attributes and Challenges. Journal of Technology, Management, and Applied Engineering 2014, 30, 122–135. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Sharma, M. Integrating Six Sigma Culture and TPM Framework to Improve Manufacturing Performance in SMEs. Quality and Reliability Engineering International 2014, 30, 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, P.; Sharma, M. How Does Green Lean Practices Affect Environmental Performance? Evidence from Manufacturing Industries in India. Measuring Business Excellence 2024, 23, 47–61. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekar, A.; Sundaram, K. Six Sigma in Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises: A Black Belt Project in the Swedish Steel Industry. International Journal of Six Sigma and Competitive Advantage 2014, 9, 128–146. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.; Sharma, M. Six Sigma Implementation by Indian Manufacturing SMEs - An Empirical Study. Academy of Strategic Management Journal 2014, 13, 78–96. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, S.; Kumar, P. Lean Implementation in Small and Medium Enterprises - A Singapore Context. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management, Singapore, 9–12 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.; Karim, S. Application of Lean Manufacturing Concepts to Reduce Manufacturing Lead Times within the Meatball Production Process. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Amman, Jordan, 25–28 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, A.; Khodadadi, S.; Rezaei, S. Roadblocks in Integrating Lean Six Sigma and Industry 4.0 in Small and Medium Enterprises. Systems 2024, 12, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Sharma, M. Deploying Lean Six Sigma Framework in an Automotive Component Manufacturing Organization. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma 2016, 7, 397–418. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, P.; Hossain, A. Application of Lean Manufacturing Tools in the Food and Beverage Industries. Journal of Technology Management and Innovation 2015, 10, 176–190. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaram, A.; Narayanan, P. The Moderating Role of Lean Six Sigma Practices on Quality Management Practices and Quality Performance in Medical Device Manufacturing Industry. TQM Journal in press. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, H.; Sharma, M. The Implementation of Lean Manufacturing Tools in Morocco: A Study on Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference on Innovative Research in Applied Science, Engineering and Technology (IRASET), Rabat, Morocco, 8–10 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, R.; Gupta, S. Improvement of OEE Performance Using a Lean Six Sigma Approach: An Italian Manufacturing Case Study. International Journal of Productivity and Quality Management 2015, 16, 229–248. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, R.; Mandal, A. Lean Six Sigma Implementation in a Food Processing SME: A Case Study. Quality and Reliability Engineering International 2015, 31, 137–150. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Singh, R. Application of Lean Practices in Small and Medium-Sized Food Enterprises. British Food Journal 2014, 116, 372–394. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, S.; Gupta, R. The Impact of Selected Lean Manufacturing Tools on the Level of Delays in the Production Process: A Case Study. Management Systems in Production Engineering 2024, 15, 278–293. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, H.; Sharma, M. Analysis of the Level of Implementation of the Lean Six Sigma Approach in Moroccan Services. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference on Innovative Research in Applied Science, Engineering and Technology (IRASET), Rabat, Morocco, 8–10 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, A.; Kumar, S. Implementing Lean Sigma in an Indian Rotary Switches Manufacturing Organisation. Production Planning and Control 2014, 25, 1476–1488. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Verma, V. Implementation of Continuous Improvement Based on Lean Six Sigma in Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises. Total Quality Management and Business Excellence 2016, 27, 1416–1443. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, S.; Malik, H. Data Science Supporting Lean Production: Evidence from Manufacturing Companies. Systems 2024, 12, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, R.; Usmani, S. An Application of Lean Six Sigma (LSS) in Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): Cement Bags Industry. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research 2015, 6, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, H.; Sharma, M. Profit Enhancement for Small, Medium Scale Enterprises Using Lean Six Sigma. Materials Today: Proceedings 2021, 12, 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, H.; Kumar, V. Minimization of Rejection Rate Using Lean Six Sigma Tool in Medium Scale Manufacturing Industry. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research 2015, 6, 102–112. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.; Sharma, S. The Effect of Business Improvement Methods on Innovation in Small and Medium Enterprises. Journal of Business Research 2024, 96, 214–230. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, H.; Jamal, P. Benefits and Challenges of Lean Implementation. Journal of Small Business Management 2024, 48, 64–83. [Google Scholar]
- Thakkar, J.J.; Jaiswal, K. A Management Model Based on Lean Six Sigma for SMEs in the Professional Services Sector. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Dubai, UAE, 4–6 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.S. Association between technological innovation and firm performance in small and medium-sized enterprises: The moderating effect of environmental factors. International Journal of Innovation Science 2019, 11, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Kumar, P. Dimensions of Innovation and Their Effects on the Performance of Small and Medium Enterprises: The Moderating Role of Firm’s Age and Size. International Journal of Operations & Production Management 2020, 40, 254–276. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, K.; Patel, H. Lean Six Sigma in the Construction Industry: A Case Study. Construction Management and Economics 2015, 33, 522–540. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Shah, M. A New Framework to Support Lean Six Sigma Deployment in SMEs. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma 2019, 10, 876–900. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Patel, R. Investigating the Readiness of People in Manufacturing SMEs to Embark on Lean Six Sigma Projects. International Journal of Operations & Production Management 2016, 36, 124–141. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, M.; Kumar, V. Using Lean Six Sigma in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises for Low-Cost/High-Effect Improvement Initiatives: A Case Study. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management 2022, 39, 1163–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Patel, H. Improvement of Cement Bag Production Processes Through Lean Six Sigma: Reducing Waste and Enhancing Efficiency. International Journal of Industrial Engineering 2024, 30, 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Rathi, V.; Kumar, P. Critical Success Factors of Lean Six Sigma and Its Relation on Operational Performance of SMEs Manufacturing Companies: A Survey Result. International Journal of Supply Chain Management 2019, 8, 891–905. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, K.; Sharma, P. A Conceptual Examination of Lean, Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma Models for Managing Waste in Manufacturing SMEs. World Journal of Science, Technology and Sustainable Development 2020, 17, 36–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Gupta, P. Reducing the Scrap Rate in an Electronic Manufacturing SME Through Lean Six Sigma Methodology. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma 2016, 7, 459–476. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, S.; Sharma, V. Quality Improvement in Plastic Injection Molding Industry: Applying Lean Six Sigma to SME in Kuwait. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Kuwait, 21–23 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, V.; Shah, N. Application of Lean Six Sigma to a Small Enterprise in the Gauteng Province: A Case Study. African Journal of Business Management 2022, 16, 191–202. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, M.; Sharma, A. Implementation of Lean Six Sigma (LSS) Techniques for Tyre Manufacturing in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management in press. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, Z.; Yadav, R. Developing a Lean Six Sigma Conceptual Model and Its Implementation: A Case Study. Industrial Engineering Journal 2019, 62, 543–562. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanujan, R.; Verma, P. A Study on Six-Sigma Practice and Implementation in Small and Medium Enterprises (SME). aWEshkar 2022, 21, 51–69. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaleb, A.A.; El-Sharief, M.A.; El-Sebaie, M.G. Implementation of lean six sigma (LSS) techniques in small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to enhance productivity. IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering 2017, 14, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiu, S.; Ngobeni, M.; Mathabela, L.; Thango, B. Applications and Competitive Advantages of Data Mining and Business Intelligence in SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024090940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhize, A.; Mokhothu, K.; Tshikhotho, M.; Thango, B. Evaluating the Impact of Cloud Computing on SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024090882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kgakatsi, M.; Galeboe, O.; Molelekwa, K.; Thango, B. The Impact of Big Data on SME Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024090985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molete, O.B.; Mokhele, S.E.; Ntombela, S.D.; Thango, B.A. The Impact of IT Strategic Planning Process on SME Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothapo, M.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. Tracking and Measuring Social Media Activity: Key Metrics for SME Strategic Success – A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngcobo, K.; Bhengu, S.; Mudau, A.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. Enterprise Data Management: Types, Sources, and Real-Time Applications to Enhance Business Performance - A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohlala, T.T.; Mehlwana, L.L.; Nekhavhambe, U.P.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. Strategic Innovation in HRIS and AI for Enhancing Workforce Productivity in SMEs: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabalala, K.; Boyana, S.; Kolisi, L.; Thango, B.A.; Matshaka, L. Digital Technologies and Channels for Competitive Advantage in SMEs: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndzabukelwako, Z.; Mereko, O.; Sambo, T.V.; Thango, B. The Impact of Porter’s Five Forces Model on SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maswanganyi, N.G.; Fumani, N.M.; Khoza, J.K.; Thango, B.A.; Matshaka, L. Evaluating the Impact of Database and Data Warehouse Technologies on Organizational Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumede, T.T.; Chiworeka, J.M.; Magoda, A.S.; Thango, B. Building Effective Social Media Strategies for Business: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myataza, A.; Mafunga, M.; Mkhulisi, N.S.; Thango, B.A. A Systematic Review of ERP, CRM, and HRM Systems for SMEs: Managerial and Employee Support. Preprints 2024, 2024100384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudau, M.C.; Moshapo, L.W.; Monyela, T.M.; Thango, B.A. The Role of Manufacturing Operations in SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanyi, M.; Xaba, S.; Mlotshwa, N.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. The Role of Data Networks and APIs in Enhancing Operational Efficiency in SME: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skosana, S.; Mlambo, S.; Madiope, T.; Thango, B. Evaluating Wireless Network Technologies (3G, 4G, 5G) and Their Infrastructure: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024101331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtjilibe, T.; Rameetse, E.; Mgwenya, N.; Thango, B. Exploring the Challenges and Opportunities of Social Media for Organizational Engagement in SMEs: A Comprehensive Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024101438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nethanani, R.; Matlombe, L.; Vuko, S.; Thango, B. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems and their Impact on SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024101538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraba, J.; Mamogobo, M.; Thango, B. The Balanced Scorecard Methodology: Performance Metrics and Strategy Execution in SMEs: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024101598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankge, F.; Pogiso, K.; Ndaba, Z.; Thango, B. A Systematic Review of Success Factors and Failure Reasons in Enterprise Systems for Executive, Managerial, and Operational Support. Preprints 2024, 2024101670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebaea, R.; Roshe, Y.; Ntontela, S.; Thango, B.A. The Role of Data Governance in Ensuring System Success and Long-Term IT Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024101841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechele, G.; Rabedzwa, G.; Nongayo, S.; Thango, B. Systematic Review on SEO and Digital Marketing Strategies for Enhancing Retail SMEs’ Performance. Preprints 2024, 2024101715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sithole, S.; Grahn, T.; Pillay, D.; Thango, B. Aligning IT and Business Strategies: Achievements and Challenges – A Systematic Literature Review. Preprints 2024, 2024102056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivhada, U.; Zulu, P.; Sambo, H.; Thango, B. Performance Improvements from Virtual Collaboration and Communication Technologies in SMEs: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024101971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


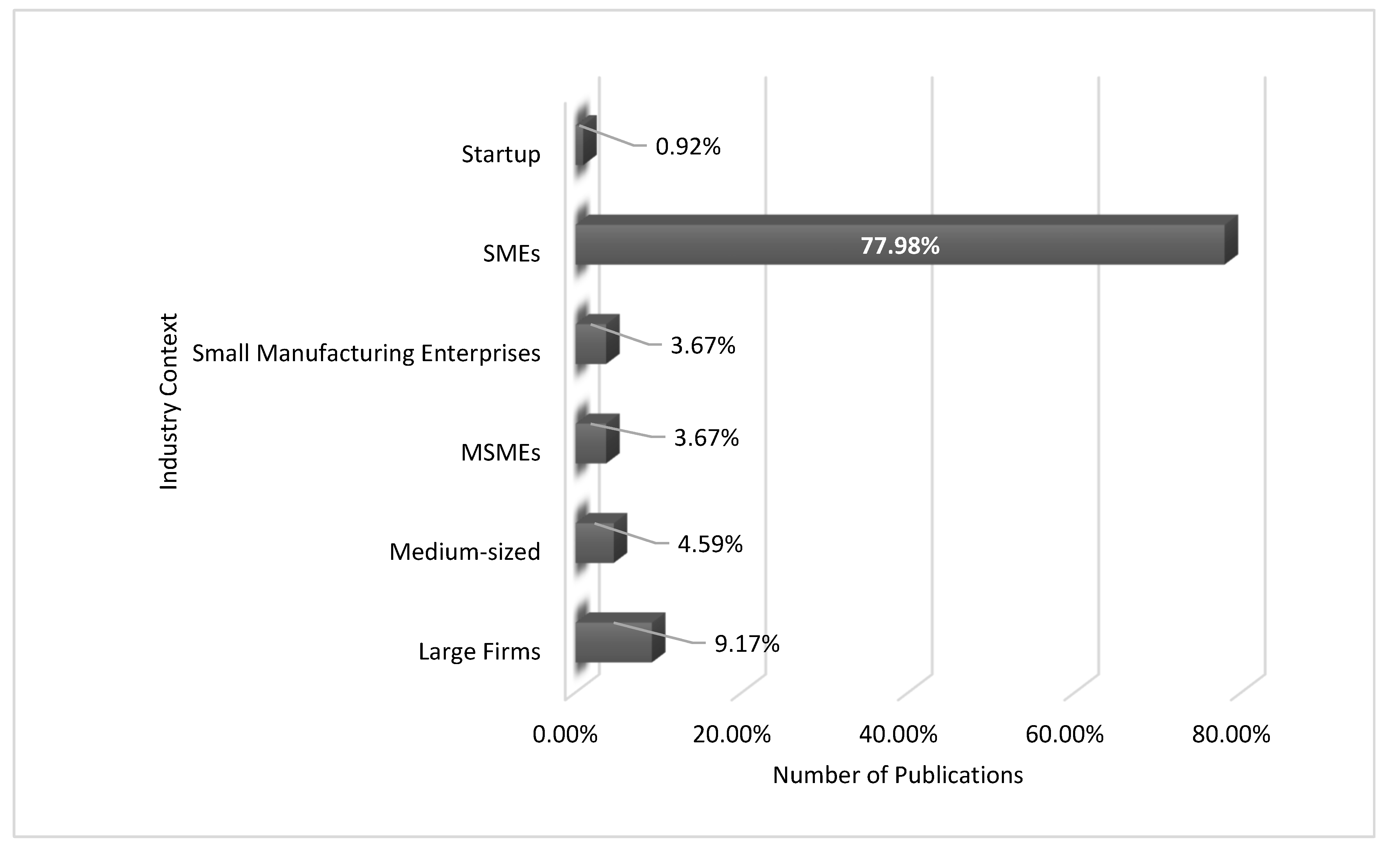
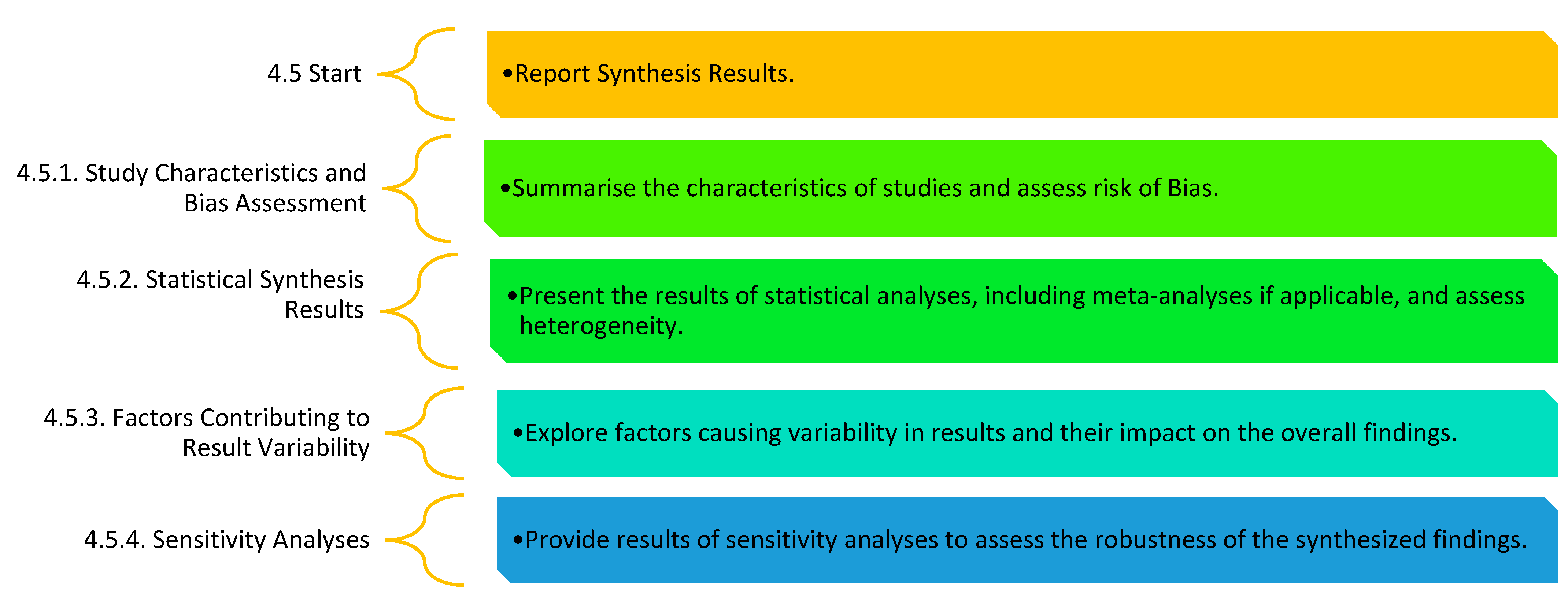
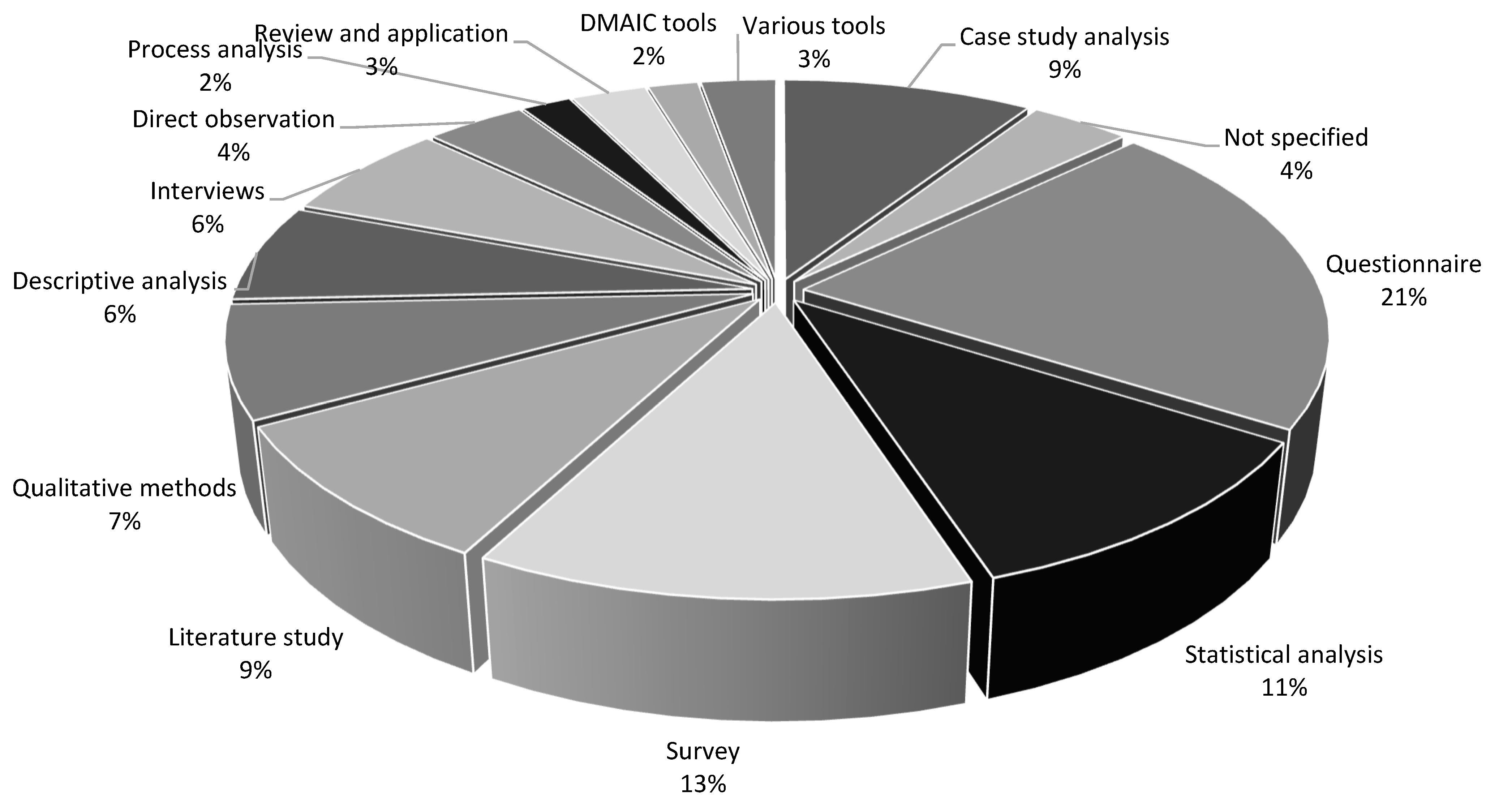
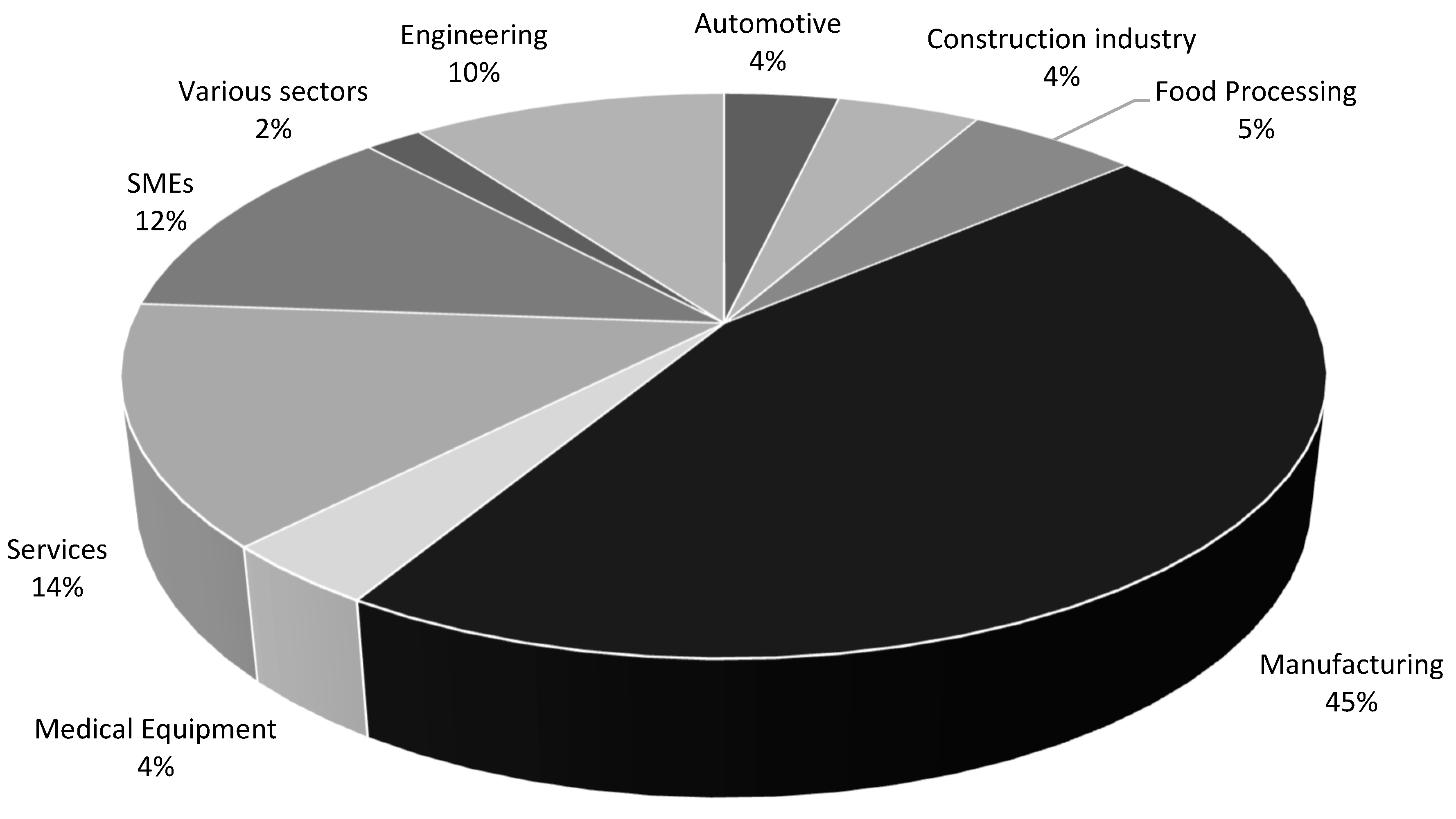
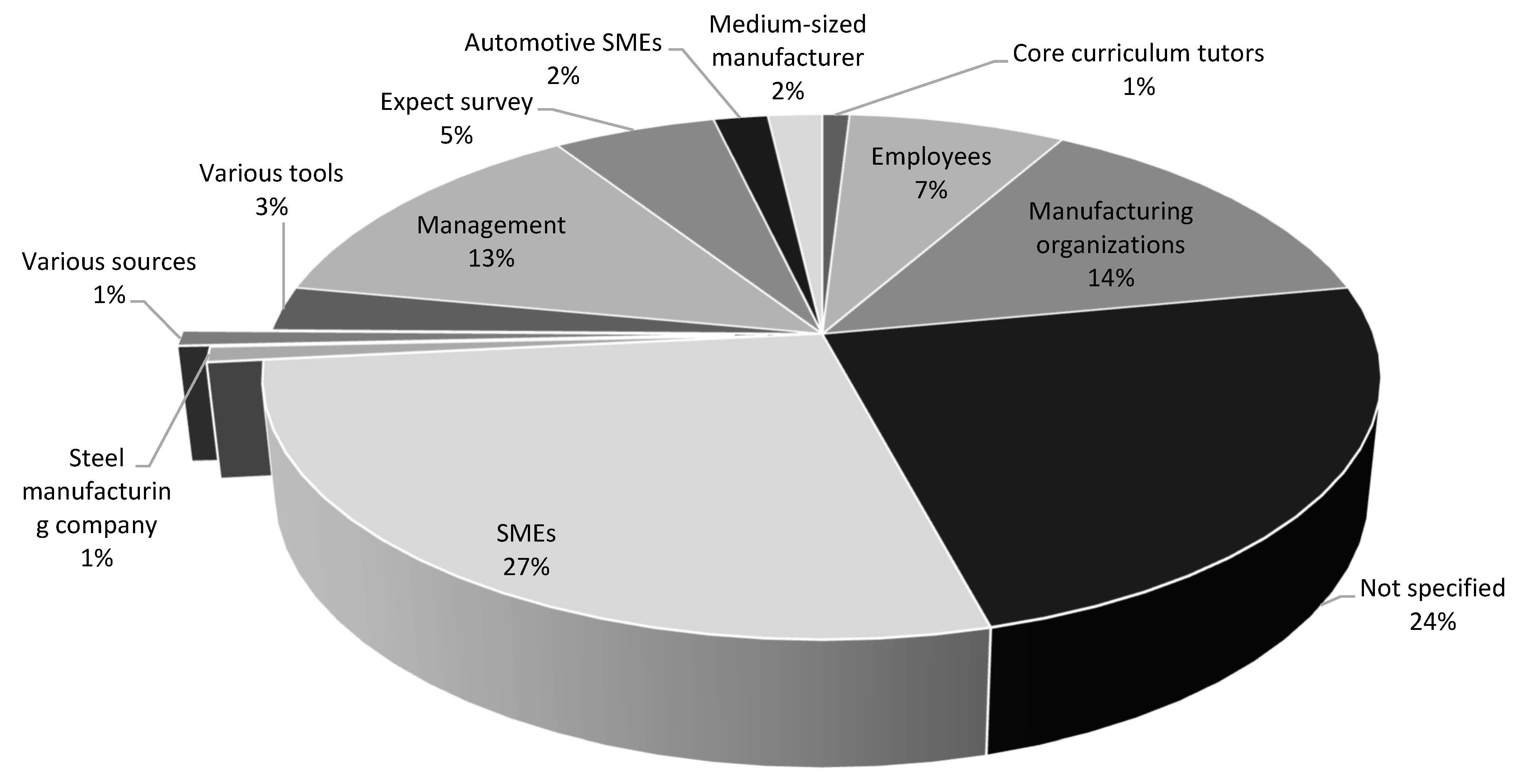
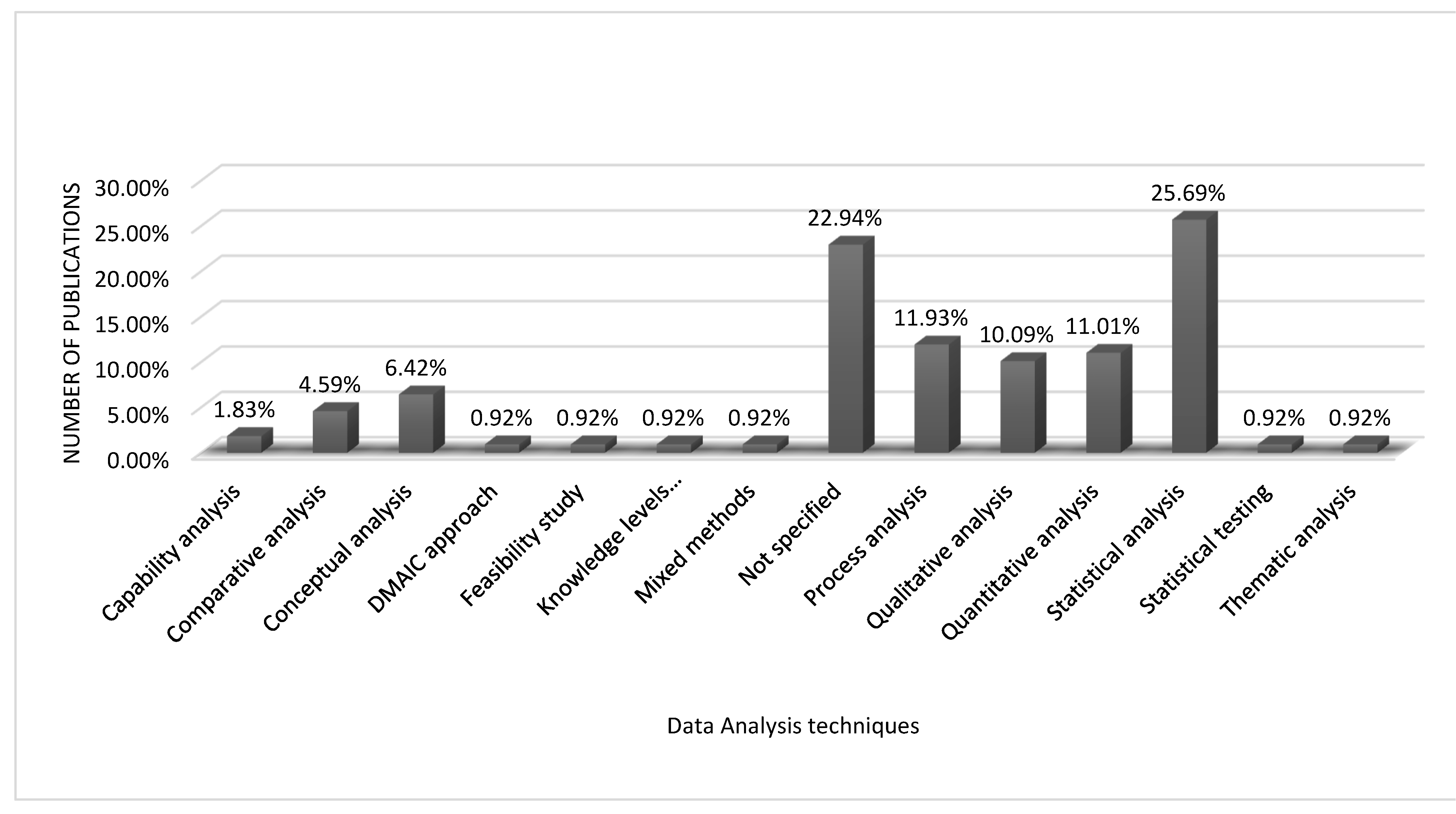
| Ref. | Cites | Year | Contributions | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [21] | 356 | 2014 | Explores the critical failure factors for Lean Six Sigma in various sectors, based on a systematic literature review of 56 papers published between 1995 and 2013. | Identifies 34 common failure factors; provides insights across different sectors and organizational sizes. | Discusses many gaps and limitations that need further research. |
| [22] | 69 | 2014 | Reviews literature on Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) implementation practices in manufacturing organizations, with a focus on SMEs in India, and identifies gaps in current research and practices. | Highlights the importance of TPM for productivity and competitive advantage; suggests directions for future research. | Focuses primarily on Indian SMEs; may not be generalizable to other contexts. |
| [23] | 136 | 2016 | Explores lean manufacturing in food-processing SMEs, identifying barriers to adoption and challenges specific to the food industry, based on a multiple-case-study research approach. | Offers insights into contextual factors and barriers specific to the food-processing industry; helps practitioners anticipate obstacles. | Focuses exclusively on food-processing SMEs; may not be generalizable to other sectors. |
| [24] | 128 | 2016 | Investigates Lean Manufacturing (LM) practices in Brazilian SMEs, analyzing the implementation and its impact on performance using structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). | Provides insights into fragmented LM practices and their impact on performance; highlights specific areas for improvement. | Limited to Brazilian SMEs; fragmented approach to LM implementation. |
| [25] | 25 | 2018 | Reviews the implementation of Six Sigma in various manufacturing industries, examining its success using different performance indicators, based on a critical review of 112 research articles. | Offers insight into the implementation and measurement of Six Sigma in manufacturing; identifies gaps in research. | Does not cover service industries; limited to specific performance indicators. |
| [26] | 40 | 2018 | Examines critical success factors for Lean Six Sigma and Six Sigma implementation in small and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises, comparing them with larger corporations. | Identifies key success factors for both SMEs and large organizations. | Implementation challenges in SMEs due to resource limitations. |
| [27] | 26 | 2019 | Investigates Lean Six Sigma in the Brazilian context, focusing on its characteristics and opportunities for future research, based on a review of 104 scientific publications. | Highlights critical success factors, particularly top management support; provides practical applications in large Brazilian industries. | Limited to Brazilian studies; lacks a standard framework for LSS. |
| [28] | 121 | 2019 | Reviews benefits and challenges of Lean Six Sigma implementation across various sectors from 2000 to 2018, including manufacturing, health care, human resource, financial, and education. | Offers a comprehensive review of LSS implementation across multiple sectors; identifies research gaps. | May not fully capture recent developments beyond 2018. |
| [29] | 55 | 2019 | Explores common themes and research gaps in Lean Six Sigma related to small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) within manufacturing organizations, using a systematic review methodology. | Identifies research gaps and provides insights for improving LSS implementation in SMEs. | Limited to peer-reviewed English papers; excludes conference and white papers. |
| [30] | 11 | 2019 | Examines the impact of Lean Manufacturing (LM) on performance in manufacturing SMEs and introduces a new lean implementation framework for very small businesses (VSBs). | Highlights recent progress in LM among SMEs; proposes a framework for VSBs. | Limited to manufacturing SMEs; may not apply to other sectors. |
| [31] | 92 | 2019 | Reviews Lean implementation (LI) in SMEs, identifying main challenges and critical success factors through a systematic review methodology of 403 papers. | Provides a comprehensive view of Lean implementation challenges and CSFs in SMEs. | Focuses on SMEs only; may not address Lean implementation in large organizations. |
| [32] | 52 | 2019 | Identifies research gaps in Lean manufacturing (LM) literature from a systematic review of 120 articles published between 2005 and 2016, and groups these gaps into meaningful themes. | Provides a detailed analysis of LM research gaps and groups them into logical themes. | May not cover the latest research developments post-2016. |
| [33] | 8 | 2020 | Identifies and explores critical success factors (CSFs) for Six Sigma through an extensive literature review of 64 research articles, proposing a categorized list of vital CSFs. | Provides a categorized list of CSFs; useful for increasing the success rates of Six Sigma programs. | Focuses on SMEs only; does not consider failure experiences of larger industries. |
| [34] | 25 | 2021 | Compares the effect of Lean Manufacturing (LM) implementation in manufacturing sectors of developing and developed countries, based on a review of 63 studies published between 2015 and March 2020. | Provides comparative insights into LM practices across different economies; highlights difficulties faced by SMEs. | Limited to manufacturing sectors; no reported negative impacts of LM. |
| [35] | 12 | 2022 | Reviews Lean Six Sigma literature in the Indian context from 2010 to 2021, focusing on various perspectives such as author profiles, types of firms, methodologies used, and key findings. | Provides a comprehensive classification and framework for future research in LSS within India. | Limited to studies published in the Indian context; may not address global trends. |
| [36] | 3 | 2023 | Identifies enablers and barriers to Lean implementation among first-line employees (FLEs) in SMEs, highlighting future research avenues for improving understanding of lean methodology implementation. | Provides insights into FLEs’ roles and factors affecting lean implementation; offers a framework for future research. | Limited citations; focused on FLEs’ roles in lean implementation. |
| [37] | 0 | 2024 | Examines human-related lean practices (HRLP) in the context of lean manufacturing (LM) implementation in SMEs, based on a review of 193 publications between 2013 and 2023. | Provides a thorough analysis of HRLPs important for lean success; helps in guiding lean implementation in SMEs. | Limited to publications in English; may not cover all HRLPs or regional variations. |
| Proposed systematic review | Provides a comprehensive consolidation of existing research on the implementation of Lean Six Sigma in SMEs, identifies configurations, performance metrics, and common challenges. Proposes regression models for financial metrics associated with LSS components. | Offers a holistic analysis of Lean Six Sigma applications, bridging gaps in performance metrics across different industry contexts; highlights research gaps for future exploration. | - | ||
| Q | Research Questions |
|---|---|
| Q1 | What are the key success factors and barriers to the implementation of Lean Six Sigma in SMEs across various industries and geographical contexts? |
| Q2 | To what extent does the adoption of Lean Six Sigma influence employee engagement, satisfaction, and skill development in small and medium-sized enterprises? |
| Q3 | What are the most common challenges faced by SMEs in integrating Lean Six Sigma into existing workflows, and how can these be mitigated? |
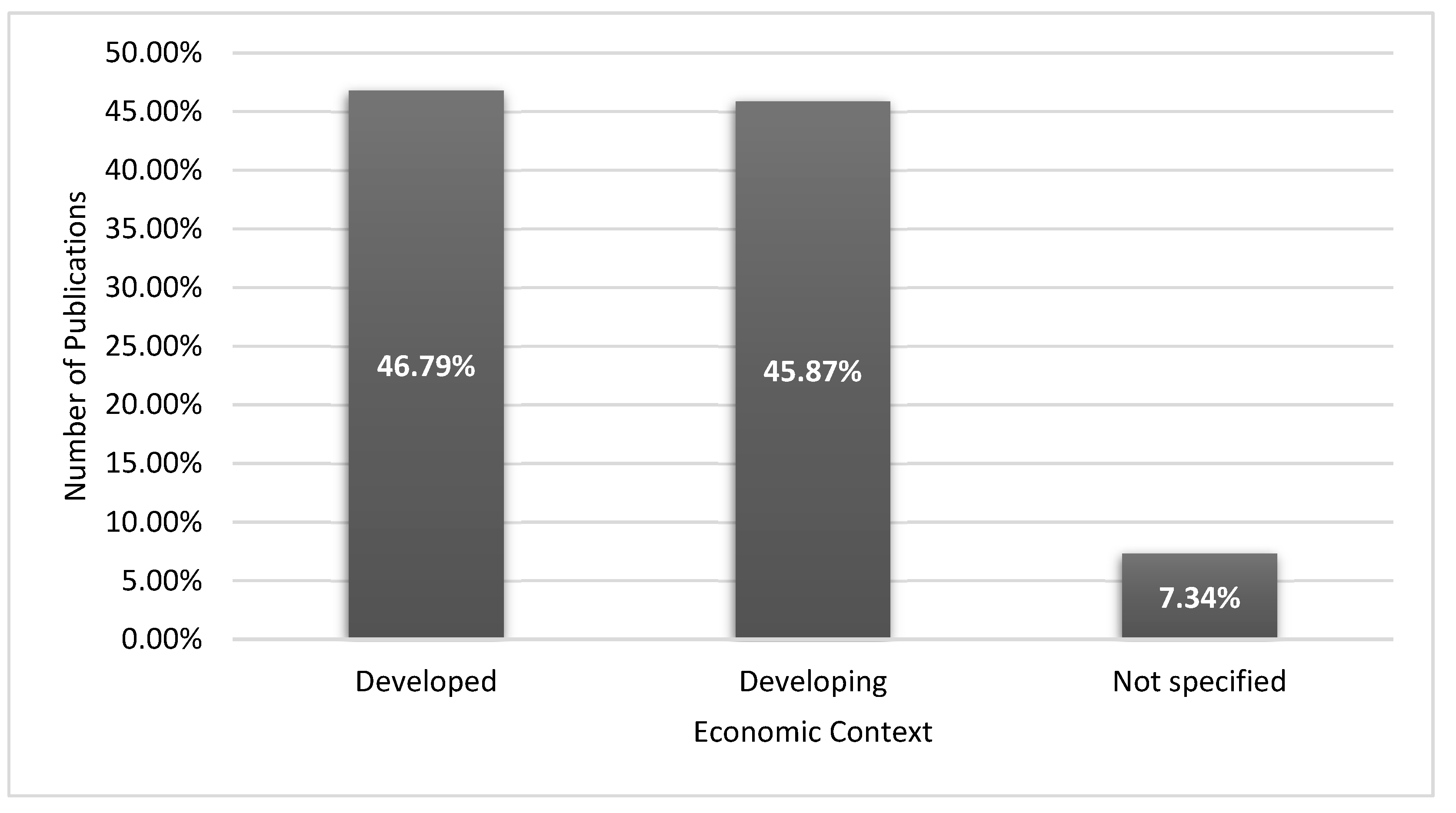
| Q4 | How do the outcomes of Lean Six Sigma implementation vary between manufacturing SMEs in developed versus developing countries? |
| Q5 | What financial metrics or performance indicators are most influenced by Lean Six Sigma practices in SMEs, and how can regression models predict their impact? |
| Criteria | Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Topic | Publications examining the application of Lean Six Sigma in SMEs, with empirical evidence or case studies. | Publications lacking focus on Lean Six Sigma applications in SMEs. |
| Research Framework | Articles incorporating a research framework where Lean Six Sigma is methodologically applied to SMEs. | Articles without a framework on Lean Six Sigma applications in SMEs. |
| Language | Papers written in English to ensure accessibility and standardized interpretation. | Papers in languages other than English. |
| Period | Publications between 2014 and 2024 to capture contemporary and relevant insights. | Publications outside the 2014–2024 timeframe. |
| Database | Access Platform | Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria Applied | Purpose of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
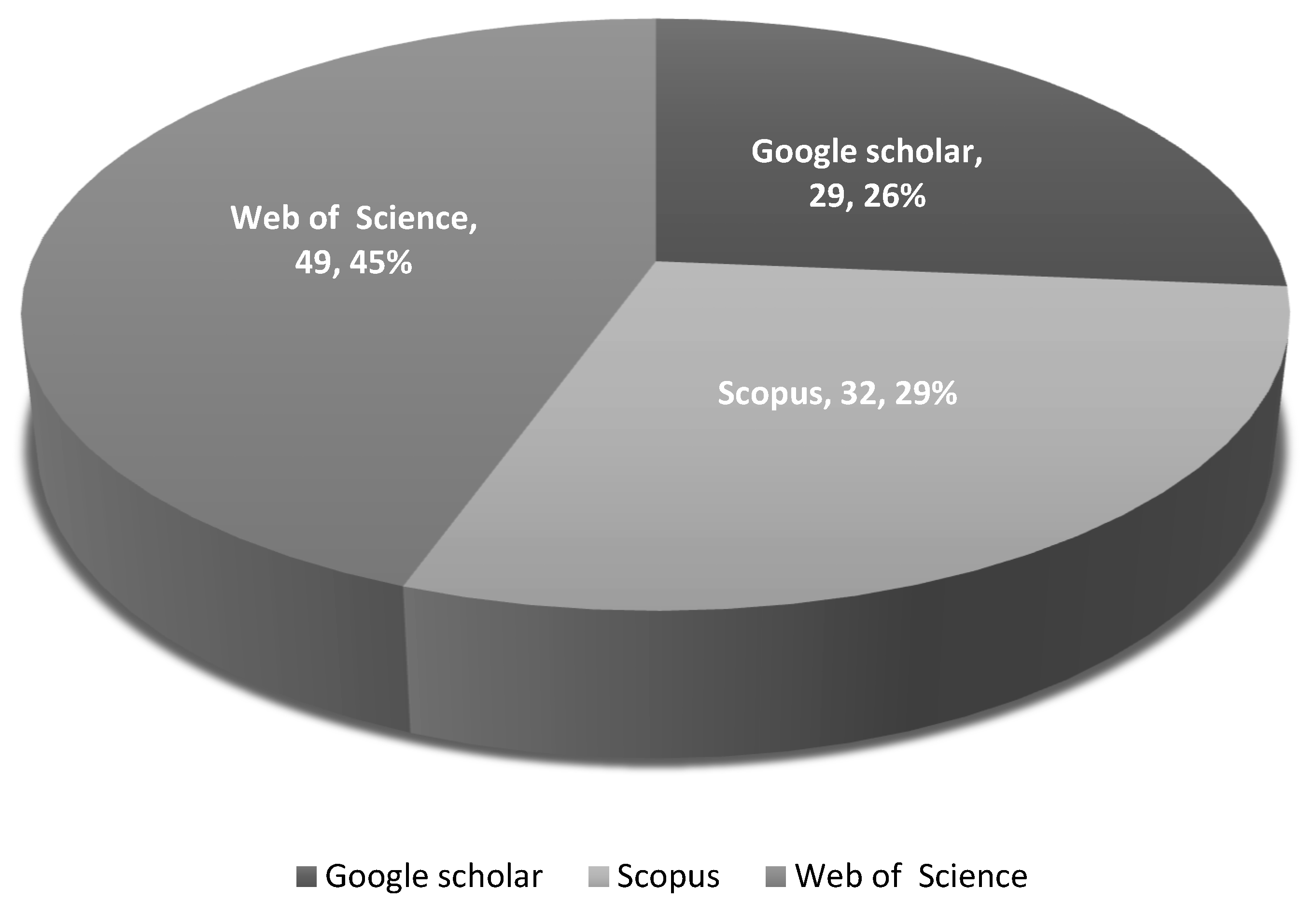
| Google Scholar | Browser | Yes | Ensures broad coverage across multidisciplinary sources. |
| Scopus | OpenAthens (UJ Online Library) | Yes | Accesses high-quality, peer-reviewed journal articles. |
| Web of Science | OpenAthens (UJ Online Library) | Yes | Provides publications with strong research impact and citations. |
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
| Research Title | The title of each study was included in the review |
| Year of Publication | The year when the study was published |
| Online database | The database where the study was sourced (Google Scholar, SCOPUS, Web of Science |
| Journal Name | The Publisher in which the articles was published |
| Research Type | The type of publication (e.g., Article, Journal, Case study, Applied Research, Empirical study, etc.) |
| Number of Citations | The number of times the study has been cited by other researchers |
| Financial Information | Any financial performance information that was mentioned in the study. |
| Innovation Performance | Innovations or improvements reported as an outcome of the research. |
| Organizational Outcomes | Impacts on organizational processes, efficiency, teamwork, etc. |
| Employee Outcome | Effects on employee skills, confidence, or overall performance. |
| Customer Outcome | Impacts on customer satisfaction, complaints, or behavior |
| long term Impacts | Long-term effects of the research, such as sustainability or competitive advantage |
| Category | Data Extracted |
|---|---|
| Study Details | Research Title, Year of Publication, Online Database, Journal Name, Research Type, Number of Citations, Google Scholar Ranking |
| Contextual Information | Industry or Sector, SME Characteristics, Geographic Location, Economic Context |
| Methods of Information | Type of Study, Research Design, Sample Size, Sample Characteristics, Data Collection Methods, Data Analysis Techniques, Methodologies, Types of Virtual Collaboration (Synchronous, Asynchronous, Hybrid) |
| Outcomes and Impacts | Operational Performance, Financial Information, Innovation Performance, Collaboration Outcomes, Employee Outcomes, Customer Outcomes, Long-term Impacts |
| Criteria | Method Used |
|---|---|
| Handling Missing Information | Studies lacking essential information were excluded from the review. For studies providing data in ranges (e.g., survey responses between 90–120 participants), midpoint estimates were used to standardize the figures. |
| Data Conversions | Fractions and percentages were converted to decimals using Microsoft Excel, ensuring uniformity and facilitating direct comparisons across all data points. |
| Steps | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Data Collection | Collect raw data from reviewed studies. |
| 2. Data Preparation | Address missing information and perform data conversions. |
| 3. Tabulation Methods | Structure tables to include study contributions, benefits, challenges, and impacts; order tables by publication year and citation count. |
| 4. Graphical Methods | Create pie charts, graphs, and flow charts to visually represent study selection and outcome distribution. |
| 5. Presentation of Results | Combine tabular and graphical methods to offer a comprehensive and transparent view of findings. |
| 6. Review and Finalize | Review for completeness and accuracy; prepare results for inclusion in the review. |
| Outcome | Effect Measure | Thresholds/Ranges | Number of studies | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operational Performance | Continuous (Mean Difference, MD) | Trivial Effect: MD < 5%Small Effect: MD = 5%–10%Moderate Effect: MD = 10%–20%Large Effect: MD > 20% | 109 | Improvements in operational performance indicators such as cycle time, defect rates, and throughput are common. A reduction of less than 5% is considered trivial, while anything over 20% is seen as a major improvement. |
| Financial Performance | Continuous (Mean Difference, MD) | Trivial Effect: MD < 2%Small Effect: MD = 2%–5%Moderate Effect: MD = 5%–10%Large Effect: MD > 10% | 109 | Financial metrics are more sensitive, with small percentage changes representing significant monetary impact, particularly for SMEs. Effects are measured by cost savings, ROI, and revenue growth with more conservative thresholds. |
| Quality Performance | Continuous (Mean Difference, MD)Binary (Risk Ratio, RR) | (Continuous)Trivial Effect: MD < 5%Small Effect: MD = 5%–10% Moderate Effect: MD = 10%–15% Large Effect: MD > 15%RR (Binary):No/Trivial Effect: RR = 1.0Small Effect: RR = 0.9–0.95Moderate Effect: RR = 0.8–0.9Large Effect: RR < 0.8 | 67 | Quality improvements are essential in manufacturing. MD is used for ratios or percentages such as First Pass Yield (FPY), while RR assesses the probability of achieving desired quality levels. Industry-standard thresholds are applied |
| Bias Type | Challenges | Assessment method | Number of studies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Publication type | Only studies with positive results may be published. | Compare the variety of industries and sectors in the studies. Check for missing sectors to identify | 109 |
| Selecting Reporting | Negative findings may be excluded, skewing results toward positive outcomes | Compare the Lean Six Sigma tools used in the study to the outcomes reported. If only a subset of tools is reported, it indicates selective reporting. | 32. |
| Time lag bias | Positive results may be published faster than negative ones | Review the publication dates to see if older studies omit negative results. | 46. |
| Language bias | Articles in non-English languages are not included | Check the country of origin of the studies. An overrepresentation of English-speaking countries could indicate language bias. | 109 |
| Outcome Reporting Bias | Only high-magnitude outcomes are reported. | Examine the reported results to determine if only favorable outcomes are included. | 50 |
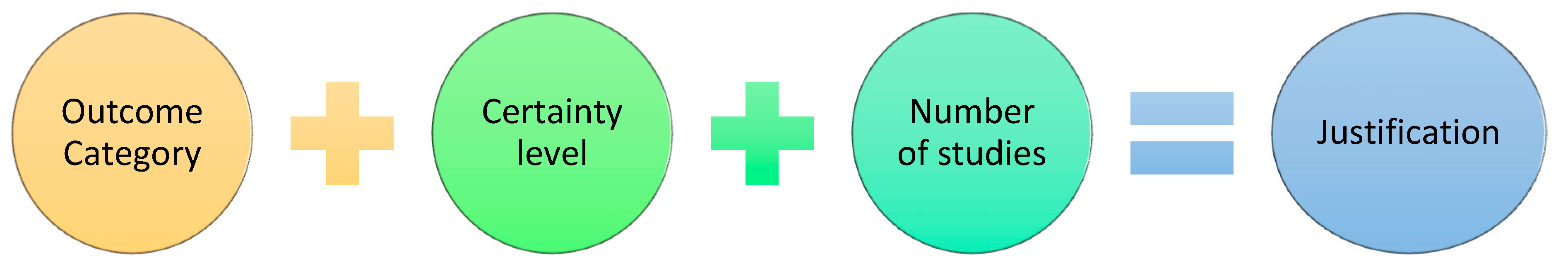
| Outcome Category | Certainty level | Number of studies | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Information | High | 33 | The financial outcomes were consistently reported across a significant number of studies. |
| Innovation Performance | High | 34 | Innovation performance was reported in many studies, with consistent findings. |
| Organizational Outcomes | High | 87 | Many studies provided detailed and consistent data on organizational outcomes. |
| Employee Outcome | High | 47 | Employee-related outcomes were well-reported across the dataset, with consistent results. |
| Customer Outcomes | High | 30 | Customer outcomes were documented in a sufficient number of studies, showing consistent patterns. |
| Long term impacts | High | 59 | Long-term impacts were widely covered in the studies, with robust and consistent evidence |
| Industry | Key Finding | Strategic Implications for Business Leaders | Opportunities | Challenges | Relevance to Proposed Systematic Review | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | LSS significantly reduces cycle times and defects (77.98%). | Implement LSS to streamline production processes and enhance product quality. | Optimize production processes, improve competitiveness. | Overcoming resistance to change, resource constraints. | Demonstrates the broad applicability of LSS in improving manufacturing performance. | Process efficiency, quality enhancement. | Increased operational efficiency, customer satisfaction. |
| Food Processing | Achieved quality improvements in First Pass Yield (67%). | Utilize LSS to improve product quality and reduce waste. | Waste reduction, enhanced product consistency. | Limited resources for training and technology. | Highlights LSS’s role in quality control across different manufacturing sectors. | Quality control, waste reduction. | Enhanced product quality, cost savings. |
| Automotive | LSS helps minimize production costs through process optimization (63.58%). | Focus on cost-effective process improvements to maximize profitability. | Lower production costs, increased financial returns. | Integrating LSS with existing processes. | Demonstrates the financial benefits of LSS in cost-intensive industries. | Cost reduction, profitability improvement. | Increased cost efficiency, higher ROI. |
| Medical Equipment | LSS reduces cycle times and enhances compliance with quality standards (45%). | Implement LSS to improve compliance and regulatory adherence. | Meet industry standards, reduce regulatory risks. | Adapting LSS to stringent compliance requirements. | Shows LSS’s adaptability in high-regulation industries. | Compliance, regulatory adherence. | Improved compliance, operational reliability. |
| Construction | Improved operational efficiency and customer satisfaction (50%). | Use LSS to optimize project management and streamline workflows. | Increase project delivery speed, boost client satisfaction. | Coordinating LSS training across teams. | Demonstrates the versatility of LSS beyond traditional manufacturing. | Project management, workflow optimization. | Enhanced project efficiency, customer loyalty. |
| Textiles | Enhanced process flow and defect reduction (60%). | Leverage LSS to optimize supply chain and production processes. | Improved supply chain integration, higher product quality. | Difficulty in implementing process changes. | Highlights LSS’s role in supply chain and quality management. | Supply chain management, quality improvement. | Higher product quality, reduced defects. |
| Pharmaceuticals | LSS adoption boosts operational consistency and reduces waste (55%). | Focus on minimizing waste to ensure cost-effective production. | Reduce waste, improve operational consistency. | High compliance standards and training costs. | Shows LSS’s potential for driving consistency in highly regulated industries. | Waste reduction, operational consistency. | Reduced production costs, regulatory compliance. |
| Industry | Step | Framework Focus | Key Features | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome | Ties to Proposed Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Step 1: Needs Analysis | Assess operational inefficiencies. | Identify areas for cycle time and defect reduction. | Process efficiency, quality enhancement. | Improved operational performance. | Reinforces focus on reducing cycle time and defects. |
| Step 2: Select Platform | Choose appropriate LSS tools. | Select tools such as DMAIC, 5S, or Kaizen. | Process improvement, waste reduction. | Optimal tool selection for targeted improvements. | Ensures tool suitability for specific process needs. | |
| Step 3: Pilot Testing | Conduct small-scale process changes. | Test LSS methodologies in a controlled environment. | Risk management, process validation. | Verified improvements before full-scale adoption. | Confirms pilot’s effectiveness in real-world settings. | |
| Step 4: Full Integration | Implement LSS across all processes. | Standardize successful pilot outcomes. | Comprehensive process optimization. | Consistent quality and reduced operational costs. | Demonstrates systematic approach to full integration. | |
| Step 5: Optimization | Refine processes based on feedback. | Monitor performance and adjust LSS practices. | Continuous improvement, data-driven decisions. | Sustained improvements and long-term efficiency. | Validates ongoing refinement for continual gains. | |
| Food Processing | Step 1: Needs Analysis | Evaluate waste and quality issues. | Focus on identifying sources of waste and defects. | Quality control, cost reduction. | Enhanced product consistency and lower waste. | Highlights LSS’s role in quality and waste management. |
| Step 2: Select Platform | Choose LSS techniques for production. | Tools like SPC and FMEA for quality improvement. | Quality enhancement, risk minimization. | Suitable tools for addressing food safety standards. | Aligns tool selection with industry-specific needs. | |
| Step 3: Pilot Testing | Apply LSS to specific production lines. | Implement on a limited scale to assess feasibility. | Safety standards, operational testing. | Measured impact on quality and safety compliance. | Demonstrates practical application in food processing. | |
| Step 4: Full Integration | Roll out LSS practices plant-wide. | Standardize improvements across all facilities. | Consistency, quality assurance. | Uniform quality and safety standards met. | Ensures scalability of LSS in large-scale operations. | |
| Step 5: Optimization | Monitor results and refine processes. | Continuously evaluate and improve LSS practices. | Continuous improvement, compliance. | Sustained product quality and cost reduction. | Reinforces ongoing process optimization practices. | |
| Automotive | Step 1: Needs Analysis | Assess production cost drivers. | Identify high-cost processes and areas for savings. | Cost efficiency, profitability improvement. | Reduced production costs and increased margins. | Demonstrates LSS’s financial benefits in cost-intensive sectors. |
| Step 2: Select Platform | Choose LSS tools targeting cost reduction. | Tools like VSM and Kaizen for process flow analysis. | Process efficiency, waste minimization. | Cost-effective solutions for optimizing production. | Ensures the alignment of tools with cost-saving goals. | |
| Step 3: Pilot Testing | Implement LSS in key departments. | Test methods in areas like assembly or quality control. | Risk management, process validation. | Verified improvements in targeted departments. | Confirms approach in reducing production costs. | |
| Step 4: Full Integration | Extend LSS practices to all departments. | Integrate successful methods organization-wide. | Comprehensive optimization, cost reduction. | Uniform reduction in production costs. | Demonstrates holistic LSS application across the industry. | |
| Step 5: Optimization | Continuous review of cost performance. | Refine processes based on cost analysis feedback. | Continuous improvement, financial sustainability. | Long-term cost efficiency and higher profitability. | Supports ongoing financial performance optimization. | |
| Medical Equipment | Step 1: Needs Analysis | Identify compliance and quality gaps. | Focus on areas with regulatory requirements. | Compliance, quality standards. | Improved adherence to regulatory guidelines. | Emphasizes LSS’s adaptability to compliance-heavy sectors. |
| Step 2: Select Platform | Select LSS tools for quality management. | Tools like 5S and Six Sigma for defect reduction. | Quality control, compliance improvement. | Suitable tools for meeting industry standards. | Aligns tools with regulatory compliance needs. | |
| Step 3: Pilot Testing | Test LSS in quality-sensitive areas. | Conduct trials in production and inspection stages. | Compliance validation, risk assessment. | Validated compliance with quality standards. | Demonstrates LSS’s role in improving regulatory adherence. | |
| Step 4: Full Integration | Standardize LSS practices organization-wide. | Implement across all quality-sensitive processes. | Comprehensive compliance, operational reliability. | Consistent adherence to quality standards. | Reinforces broad LSS implementation across regulated areas. | |
| Step 5: Optimization | Monitor compliance and quality metrics. | Continuously evaluate and refine LSS practices. | Continuous improvement, regulatory compliance. | Long-term adherence to regulatory standards. | Supports sustained compliance with ongoing process refinement. | |
| Construction | Step 1: Needs Analysis | Evaluate project management inefficiencies. | Identify delays and cost overruns in projects. | Project management, efficiency improvement. | Optimized project workflows and reduced delays. | Shows LSS’s versatility in project management contexts. |
| Step 2: Select Platform | Choose LSS tools suitable for project workflows. | Tools like Gantt charts and critical path analysis. | Workflow optimization, time management. | Effective tools for managing complex projects. | Aligns tool selection with construction project needs. | |
| Step 3: Pilot Testing | Apply LSS to small-scale projects. | Implement on selected projects to assess viability. | Risk management, feasibility testing. | Verified improvements in project management. | Confirms LSS’s impact on construction project efficiency. | |
| Step 4: Full Integration | Scale LSS practices to larger projects. | Implement across multiple sites or project phases. | Standardization, efficiency enhancement. | Uniform efficiency across all project phases. | Demonstrates scalability of LSS in large-scale projects. | |
| Step 5: Optimization | Continuously monitor project metrics. | Adjust LSS practices based on project performance. | Continuous improvement, project success. | Sustained project efficiency and client satisfaction. | Reinforces ongoing refinement for better project outcomes. |
| Industry | Best Practice | SME Type | Operational Challenge | Strategic Drivers | Expected Impact | Ties to Systematic Review Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Employee Training on LSS Tools | Medium-sized Manufacturers | Resistance to adopting new methodologies | Workforce empowerment, process optimization | Increased employee engagement and skill development | Highlights need for training to reduce resistance to change. |
| Data-Driven Decision Making | Small Manufacturers | Limited data collection capabilities | Data accuracy, performance monitoring | Improved decision-making and process control | Reinforces importance of using data in LSS for accurate improvements. | |
| Regular Process Audits | Small and Medium Enterprises | Inconsistent process standards | Continuous improvement, quality assurance | Enhanced process standardization and quality control | Emphasizes need for regular monitoring and audits to maintain quality. | |
| Food Processing | Cross-Functional Team Collaboration | Medium-sized Food Processors | Coordination challenges across departments | Teamwork, operational efficiency | Improved communication and streamlined processes | Shows the benefit of teamwork in overcoming cross-departmental challenges. |
| Implementation of 5S | Small Food Processors | Inefficient workspace organization | Workplace organization, waste reduction | More organized workspaces and reduced waste levels | Aligns with systematic review findings on the importance of workspace organization. | |
| Quality Management Systems (QMS) | Small and Medium Enterprises | Difficulty maintaining consistent product quality | Quality control, compliance | Enhanced product consistency and compliance | Supports need for quality management to achieve consistent results. | |
| Automotive | Lean Awareness Programs | Small Automotive Suppliers | Lack of awareness about LSS principles | Knowledge dissemination, workforce engagement | Increased awareness and involvement in LSS initiatives | Reinforces the importance of awareness programs for successful adoption. |
| Use of Value Stream Mapping (VSM) | Medium-sized Automotive Firms | Identifying non-value-adding activities | Process optimization, cost reduction | Improved identification and elimination of waste | Demonstrates VSM’s effectiveness in optimizing production processes. | |
| Supplier Quality Development | Small and Medium Enterprises | Variability in supplier quality | Supplier collaboration, quality enhancement | Improved supplier quality and reduced variability | Ties to findings on the importance of supplier development programs. | |
| Medical Equipment | Standardization of Procedures | Medium-sized Firms | Variability in compliance requirements | Compliance, operational consistency | Consistent adherence to regulatory standards | Aligns with findings on the importance of standardizing processes in regulated industries. |
| Adoption of Statistical Process Control (SPC) | Small Medical Device Companies | Maintaining quality during scale-up | Quality assurance, process monitoring | Improved quality control during production increases | Supports systematic review recommendations for quality monitoring tools. | |
| Involvement of Regulatory Experts | Small and Medium Enterprises | Navigating complex regulatory requirements | Compliance management, risk mitigation | Enhanced ability to meet regulatory requirements | Emphasizes the role of regulatory expertise in compliance-heavy industries. | |
| Construction | Use of Gantt Charts for Project Management | Small Construction Firms | Managing project timelines and delays | Time management, project efficiency | Better management of schedules and project delivery | Demonstrates the benefit of project management tools in construction. |
| On-Site LSS Workshops | Medium-sized Construction Firms | Resistance to adopting LSS methods | Employee engagement, hands-on training | Increased adoption of LSS methods among employees | Reinforces systematic review findings on overcoming resistance through training. | |
| Integration of Digital Tools | Small and Medium Enterprises | Difficulty tracking project metrics | Digital transformation, data analytics | Enhanced tracking of project performance and outcomes | Shows importance of digital tools for monitoring progress and results. | |
| Textiles | Kaizen Events for Continuous Improvement | Small Textile Firms | High variability in production processes | Process consistency, quality improvement | Reduced variability and improved process stability | Ties to systematic review findings on Kaizen’s impact on continuous improvement. |
| Implementation of Just-in-Time (JIT) | Medium-sized Textile Companies | Excess inventory and production inefficiencies | Inventory management, cost efficiency | Reduced inventory costs and increased efficiency | Aligns with systematic review on the benefits of JIT in reducing inventory waste. | |
| Training Programs for Quality Control | Small and Medium Enterprises | Difficulty maintaining quality standards | Workforce skills development, quality management | Enhanced quality control capabilities among staff | Supports need for quality training in achieving consistent quality outcomes. | |
| Pharmaceuticals | Risk-Based Approach to Compliance | Small Pharmaceutical Firms | High regulatory compliance costs | Compliance, cost management | Reduced compliance costs through targeted risk management | Reinforces systematic review on the need for risk-based approaches in regulated sectors. |
| Use of Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) | Medium-sized Pharmaceutical Firms | Managing potential failure points in processes | Risk mitigation, process safety | Improved identification and control of failure risks | Supports findings on the use of FMEA for risk management in pharmaceuticals. | |
| Supplier Quality Agreements | Small and Medium Enterprises | Ensuring consistent quality from suppliers | Supplier collaboration, quality assurance | Enhanced quality consistency in the supply chain | Aligns with systematic review findings on the role of supplier agreements for quality. |
| Industry | Key Metrics/KPIs | Measurement Focus | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome | Ties to Systematic Review Findings | Priority (1 = Highest, 2 = Medium, 3 = Low) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Cycle Time | Process Efficiency | Operational performance, time management | Reduced production times and increased throughput | Supports focus on reducing cycle times for efficiency | 1 |
| Defect Rate | Quality Improvement | Product quality, defect reduction | Lower defect rates and improved product quality | Emphasizes importance of tracking defects to ensure quality | 1 | |
| Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) | Machine Utilization | Asset management, equipment reliability | Higher equipment availability and utilization | Aligns with systematic review on equipment utilization | 2 | |
| Food Processing | Waste Reduction Percentage | Resource Optimization | Cost efficiency, waste management | Lower raw material waste and reduced operational costs | Supports findings on waste reduction as a cost-saving measure | 1 |
| First Pass Yield (FPY) | Quality Control | Process quality, production consistency | Improved product consistency and reduced rework | Ties to systematic review on the importance of FPY in quality control | 1 | |
| Compliance Rate | Regulatory Adherence | Food safety, regulatory compliance | Higher adherence to food safety standards | Reinforces need for compliance metrics in food processing | 2 | |
| Automotive | Production Cost per Unit | Cost Management | Cost efficiency, profitability improvement | Reduced production costs and higher profit margins | Demonstrates importance of cost tracking for financial success | 1 |
| Customer Satisfaction Score | Customer Experience | Customer retention, product quality | Higher customer satisfaction and loyalty | Supports systematic review findings on customer satisfaction | 1 | |
| On-Time Delivery Rate | Supply Chain Efficiency | Delivery performance, logistics management | Improved delivery times and supply chain reliability | Aligns with systematic review focus on supply chain KPIs | 2 | |
| Medical Equipment | Regulatory Compliance Score | Compliance Adherence | Quality standards, risk management | Improved regulatory compliance and reduced risk | Emphasizes the importance of compliance in regulated industries | 1 |
| Process Capability Index (Cpk) | Process Stability | Quality control, process optimization | Enhanced process stability and product consistency | Aligns with findings on the use of Cpk for quality measurement | 2 | |
| Return on Assets (ROA) | Financial Performance | Asset utilization, investment efficiency | Improved financial returns on assets | Demonstrates financial benefits of LSS in asset-heavy industries | 3 | |
| Construction | Project Completion Time | Time Management | Project efficiency, on-time delivery | Reduced project delays and improved scheduling | Demonstrates relevance of time-based metrics in construction | 1 |
| Cost Variance | Budget Management | Cost control, financial planning | Improved budget adherence and reduced cost overruns | Supports findings on financial metrics in project-based industries | 1 | |
| Safety Incident Rate | Workplace Safety | Employee safety, risk management | Reduced workplace accidents and safety violations | Aligns with systematic review on safety improvements | 2 | |
| Textiles | Inventory Turnover | Inventory Management | Cost efficiency, inventory reduction | Faster inventory turnover and lower carrying costs | Supports systematic review on inventory-related metrics | 1 |
| Product Quality Index | Quality Improvement | Quality assurance, product consistency | Improved product quality and reduced returns | Reinforces importance of quality metrics in manufacturing | 1 | |
| Energy Consumption per Unit | Resource Efficiency | Sustainability, cost management | Lower energy costs and reduced environmental impact | Aligns with findings on the role of sustainability metrics | 3 | |
| Pharmaceuticals | Batch Yield Percentage | Production Efficiency | Quality control, process consistency | Higher yield rates and reduced production waste | Supports systematic review on yield improvement in manufacturing | 1 |
| Adverse Event Reporting Rate | Compliance Adherence | Regulatory requirements, risk management | Reduced adverse events and improved compliance | Aligns with findings on compliance tracking in pharmaceuticals | 1 | |
| Supplier Reliability Score | Supply Chain Management | Supplier quality, delivery performance | Improved supplier performance and reduced variability | Reinforces findings on supplier quality metrics | 2 |
| Industry | Case Study | Implementation | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | Apple - Lean Supply Chain Optimization | Applied Lean principles to its global supply chain, focusing on reducing waste and optimizing inventory. | Achieved faster production cycles, reduced inventory costs and improved supplier collaboration. |
| Technology | Microsoft - Six Sigma for Energy Efficiency | Applied Six Sigma to optimize data center energy consumption, reducing variability in processes. | Achieved a reduction in energy usage across global data centers and increased operational efficiency. |
| Semiconductors | Nvidia - Lean Manufacturing Initiative | Used Kaizen and Lean methods to reduce waste and enhance productivity in semiconductor manufacturing. | Improved production throughput and reduced defects in manufacturing processes . |
| E-commerce | Amazon - DMAIC for Delivery Optimization | Implemented DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology to optimize delivery logistics. | Achieved an improvement in logistics efficiency and significantly reduced delivery times in the supply chain. |
| Technology | Alphabet (Google) - Process Improvement | Utilized Lean Six Sigma techniques to improve server performance and reduce data processing times. | Enhanced server efficiency, resulting in a reduction in processing times for key services. |
| Oil & Gas | Saudi Aramco - Lean Six Sigma in Operations | Applied LSS to streamline oil refinery processes and reduce downtime. | Reduced operational costs and improved production uptime in refinery operations. |
| Social Media | Meta Platforms - Lean Product Development | Applied Lean principles to accelerate product development cycles and optimize project management. | Reduced time-to-market for new features and improved team collaboration. |
| Diversified Investments | Berkshire Hathaway - Process Efficiency | Implemented process improvement strategies in manufacturing subsidiaries to enhance operational productivity. | Achieved increased efficiency in multiple subsidiaries, resulting in improvement in manufacturing output. |
| Semiconductors | TSMC - Lean in Semiconductor Manufacturing | Used Lean tools such as 5S and Value Stream Mapping to optimize wafer production processes. | Improved yield rates and reduced production cycle times. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Eli Lilly - Lean Six Sigma in R&D | Integrated Lean Six Sigma into drug development processes to accelerate timelines and reduce inefficiencies. | Reduced R&D cycle time leading to faster approval and market launch of new drugs. |
| Industry | Roadmap Focus | Policy Framework | Strategic Link | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome | Estimated Time & When to Undertake | Champion(s) | Ties to Proposed Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | Data-driven quality management | Industry 4.0 Digitalization | Enhances data utilization for process optimization | Continuous improvement, innovation | Improved product quality, faster development cycles | 6-12 months, start immediately | CTO, Data Analytics Team | Highlights the role of LSS in tech industry |
| Manufacturing | Waste reduction and lean operations | Lean Manufacturing Standards (ISO 9001) | Links to sustainable production practices | Resource optimization, cost efficiency | Reduced operational costs, increased productivity | 12-18 months, initiate quarterly reviews | Plant Manager, Operations Team | Reinforces systematic waste reduction |
| Pharmaceuticals | Accelerating R&D and regulatory compliance | Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations | Aligns with regulatory standards for faster approvals | Compliance, innovation | Shortened R&D timelines, faster time-to-market | 18-24 months, start with pilot projects | R&D Director, Compliance Manager | Reduces bottlenecks in pharmaceutical R&D |
| Oil & Gas | Energy efficiency and process optimization | Environmental Protection and Sustainability Policies | Aligns with environmental regulations | Cost savings, environmental compliance | Reduced energy consumption, enhanced operational efficiency | 6-12 months, phase-wise implementation | Operations Manager, Sustainability Officer | Improves compliance and operational efficiency |
| E-commerce | Enhancing logistics and supply chain management | E-commerce and Digital Logistics Regulations | Supports digital transformation in logistics | Supply chain efficiency, customer satisfaction | Faster delivery times, lower logistics costs | 12 months, continuous improvement cycles | Logistics Manager, Supply Chain Coordinator | Ties to logistical efficiency improvements |
| Semiconductors | Quality control and production optimization | Semiconductor Manufacturing International Standards | Meets industry requirements for quality assurance | Product quality, defect reduction | Lower defect rates, higher yield | 6-9 months, implement in phases | Quality Assurance Manager, Production Lead | Emphasizes quality improvements in semiconductor manufacturing |
| Social Media | Streamlining product development and feature rollouts | Digital Product Development Policies | Promotes agile methodologies for faster iterations | User engagement, product innovation | Shorter time-to-market for new features | 6-12 months, iterative cycles | Product Development Manager, Agile Teams | Supports continuous product development |
| Diversified Investments | Enhancing operational efficiency across portfolio companies | Corporate Governance and Operational Policies | Ensures consistent process improvement across subsidiaries | Risk management, resource utilization | Increased subsidiary profitability, operational consistency | 24-36 months, start with high-impact subsidiaries | Portfolio Manager, Operational Excellence Team | Integrates LSS across diversified operations |
| Oil & Gas | Safety and compliance in upstream operations | Occupational Safety and Health Standards (OSHA) | Addresses safety regulations for high-risk operations | Employee safety, regulatory compliance | Fewer incidents, improved compliance rates | 12-18 months, phased safety enhancements | HSE Manager, Safety Compliance Team | Improves safety management in oil & gas operations |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





