Submitted:
18 October 2024
Posted:
24 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Evaluations
2.3. Catheterization
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Patient Data
3.2. QoR-15
3.2. Figures, Tables and Schemes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Limitations
Additional Note
Best Paper Presentation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Survey USG. The M7.8 and M7.5 Kahramanmaraş Earthquake Sequence struck near Nurdağı, Turkey (Türkiye) on February 6, 2023. 2023. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/news/featured-story/m78-and-m75-kahramanmaras-earthquake-sequence-near-nurdagi-turkey-turkiye.
- Waloejo CS, Sulistiawan SS, Semedi BP, Dzakiyah AZ, Stella MA, Ikhromi N, et al. The Anesthetic Techniques for Earthquake Victims in Indonesia. Open Access Emerg Med. 2022, 14, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long B, Liang SY, Gottlieb M. Crush injury and syndrome: A review for emergency clinicians. Am J Emerg Med. 2023, 69, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvi O, Azizoglu M, Temel G, Tulgar S, Chitneni A, Cinar EN, et al. Translation and Validation of the Turkish Version of the Quality of Postoperative Recovery Score QoR-15: A Multi-Centred Cohort Study. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2022, 50, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammack F, Shipton EA. The christchurch earthquake: crush injury, neuropathic pain, and posttraumatic stress disorder. Case Rep Med. 2013, 2013, 973234. [Google Scholar]
- Pang HN, Lim W, Chua WC, Seet B. Management of musculoskeletal injuries after the 2009 western Sumatra earthquake. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2011, 19, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cindy TSY, Shrestha R, Smriti Mahaju B, Amatya A. Anesthesiology in Times of Physical Disasters-Earthquakes and Typhoons. Anesthesiol Clin. 2021, 39, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehavi A, Meroz Y, Maryanovsky M, Merin O, Blumberg N, Bar-On E, et al. Role of regional anaesthesia in disaster medicine: field hospital experience after the 2015 Nepal Earthquake. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2016, 33(5), 312–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice MJ, Gwertzman A, Finley T, Morey TE. Anesthetic practice in Haiti after the 2010 earthquake. Anesth Analg. 2010, 111, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missair A, Pretto EA, Visan A, Lobo L, Paula F, Castillo-Pedraza C, et al. A matter of life or limb? A review of traumatic injury patterns and anesthesia techniques for disaster relief after major earthquakes. Anesth Analg. 2013, 117, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilfeld, BM. Continuous peripheral nerve blocks: a review of the published evidence. Anesth Analg. 2011, 113, 904–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre LV, Cunha GP, Sousa P, Takeda A, Cunha Ferraro LH. [Peripheral nerve block and rebound pain: literature review]. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2019, 69, 587–593. [Google Scholar]
- Lavand'homme, P. Rebound pain after regional anesthesia in the ambulatory patient. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2018, 31, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li J, Karmakar MK, Li X, Kwok WH, Ngan Kee WD. Regional hemodynamic changes after an axillary brachial plexus block: a pulsed-wave Doppler ultrasound study. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2012, 37, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luebbert E, Rosenblatt MA. Postoperative Rebound Pain: Our Current Understanding About the Role of Regional Anesthesia and Multimodal Approaches in Prevention and Treatment. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2023, 27, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark PA, Myles PS, Burke JA. Development and psychometric evaluation of a postoperative quality of recovery score: the QoR-15. Anesthesiology. 2013, 118, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadsden J, Warlick A. Regional anesthesia for the trauma patient: improving patient outcomes. Local Reg Anesth. 2015, 8, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Shih BF, Huang FY, Shen SJ, Zheng CW, Lee CW, Yang MW, et al. An alternative to opioid-based intravenous patient controlled analgesia in severe burn patients undergoing full thickness split graft in upper limbs. J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2023, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Fatima H, Chaudhary O, Krumm S, Mufarrih SH, Mahmood F, Pannu A, et al. Enhanced Post-Operative Recovery with Continuous Peripheral Nerve Block After Lower Extremity Amputation. Ann Vasc Surg. 2021, 76, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam D, Pierson D, Salaria O, Wardhan R, Li J. Pain Control with Regional Anesthesia in Patients at Risk of Acute Compartment Syndrome: Review of the Literature and Editorial View. J Pain Res. 2023, 16, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi G, Gandhi K, Shah N, Gadsden J, Corman SL. Peripheral nerve blocks in the management of postoperative pain: challenges and opportunities. J Clin Anesth. 2016, 35, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerner P, Cozowicz C, Memtsoudis SG. Outcomes After Orthopedic Trauma Surgery - What is the Role of the Anesthesia Choice? Anesthesiol Clin. 2022, 40, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine AC, Teicher C, Aluisio AR, Wiskel T, Valles P, Trelles M, et al. Regional Anesthesia for Painful Injuries after Disasters (RAPID): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2016, 17, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vietor R, 3rd, Buckenmaier C, 3rd. Regional Anesthesia in the Field for Trauma Victims. Anesthesiol Clin. 2021, 39, 337–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James M, Bentley RA, Womack J, Goodman BA. Safety profile and outcome after ultrasound-guided suprainguinal fascia iliaca catheters for hip fracture: a single-centre propensity-matched historical cohort study. Can J Anaesth. 2022, 69, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendtsen TF, Pedersen EM, Moriggl B, Hebbard P, Ivanusic J, Borglum J, et al. Anatomical considerations for obturator nerve block with fascia iliaca compartment block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2021, 46, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucher JF, Barletta JF, Shirah GR, Prokuski LJ, Montanarella PD, Dzandu JK, et al. The safety of continuous fascia iliaca block in patients with hip fracture taking pre-injury anticoagulant and/or antiplatelet medications. Am J Surg. 2022, 224, 1473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleckner LL, Bina S, Kwon KH, McKnight G, Dragovich A, Buckenmaier CC, 3rd. Serum ropivacaine concentrations and systemic local anesthetic toxicity in trauma patients receiving long-term continuous peripheral nerve block catheters. Anesth Analg. 2010, 110, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleckner L, Solla C, Fileta BB, Howard R, Morales CE, Buckenmaier CC. Serum free ropivacaine concentrations among patients receiving continuous peripheral nerve block catheters: is it safe for long-term infusions? Anesth Analg. 2014, 118, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrewes DG, Jenkins LM. The Role of the Amygdala and the Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex in Emotional Regulation: Implications for Post-traumatic Stress Disorder. Neuropsychol Rev. 2019, 29, 220–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrie, AM. Regional anesthesia and analgesia for trauma: an updated review. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2022, 35, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher RM, Polomano RC, Giordano NA, Farrar JT, Guo W, Taylor L, et al. Prospective cohort study examining the use of regional anesthesia for early pain management after combat-related extremity injury. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2019, 44, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu JR, Mir H, Wally MK, Seymour RB, Orthopaedic Trauma Association Musculoskeletal Pain Task F. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Pain Management in Acute Musculoskeletal Injury. J Orthop Trauma. 2019, 33, e158–e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnerup NB, Attal N, Haroutounian S, McNicol E, Baron R, Dworkin RH, et al. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilfeld BM, Khatibi B, Maheshwari K, Madison S, Ali Sakr Esa W, Mariano ER, et al. Patient-centered results from a multicenter study of continuous peripheral nerve blocks and postamputation phantom and residual limb pain: secondary outcomes from a randomized, clinical trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2023, 48, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont L, Khanal S, Thuring D, Junod JD, Hagon O. Anaesthesia in the wake of the Nepal earthquake: Experience and immediate lessons learnt. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2016, 33, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
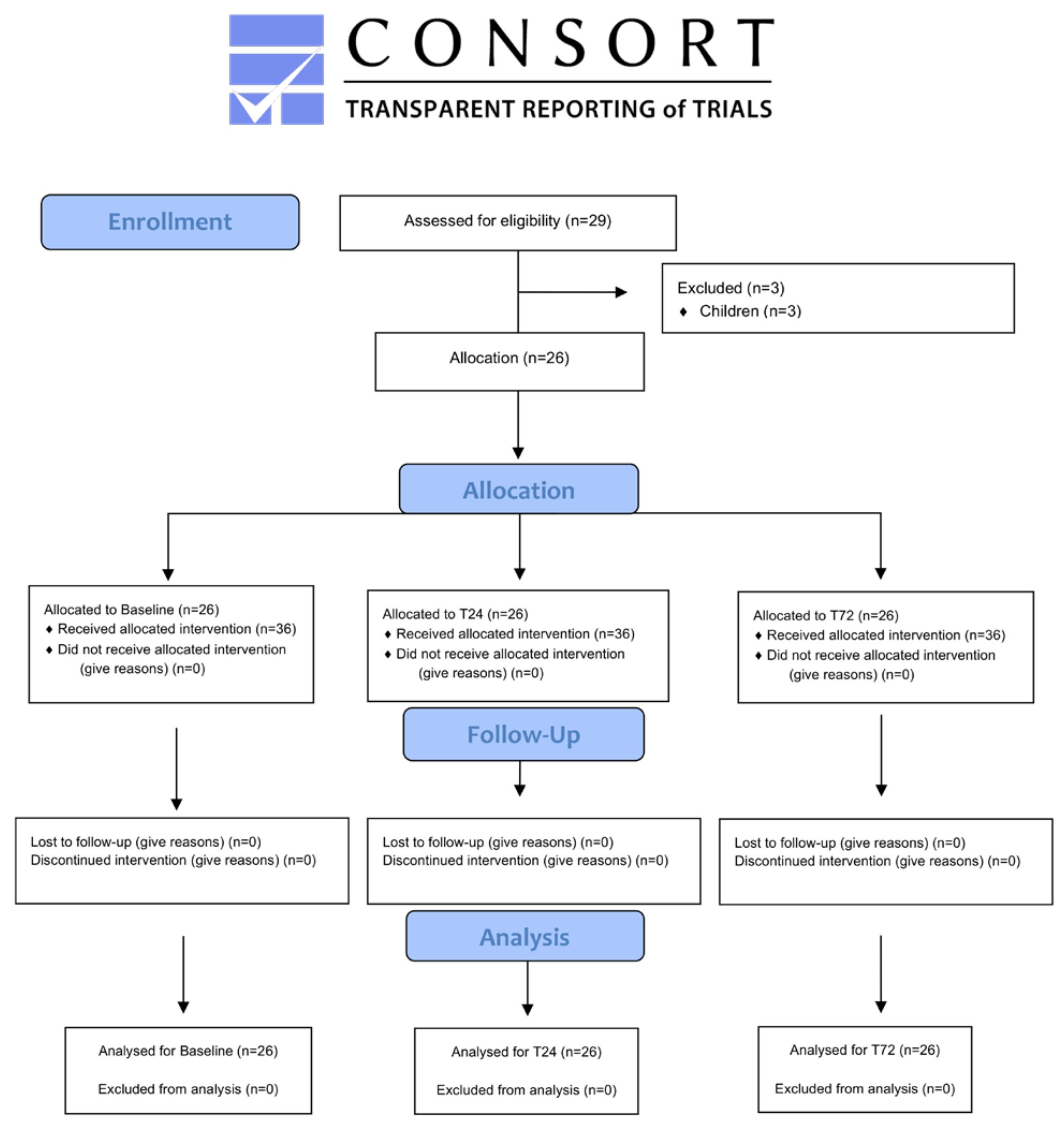
| n | Before Exclusion | n | After Exclusion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 29 | 32.72 ± 15.50 | 26 | 35.57 ± 13.69 |
| Gender (female/male) | 29 | 18/11 | 26 | 15/11 |
| Height (cm) | 29 | 150.34 ± 43.69 | 26 | 156.30 ± 42.17 |
| Weight (kg) | 29 | 68.89 ± 19,78 | 26 | 73.80 ± 13,92 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29 | 26.05 ± 3.79 | 26 | 25.95 ± 3.87 |
| ASA(I/II) | 29 | 24/5 | 26 | 21/5 |
| Duration of Catheters IQR (25%-75%) |
40 | 8 (4.00–12.75) | 36 | 8 (4.25–12.75) |
| Catheter side (Left/Right/Epidural) | 40 | 24/14/2 | 36 | 22/12/2 |
| Complication type (NV/D/inf/none) | 40 | 1/6/4/29 | 36 | 1/6/4/25 |
| Catheter type (Catheter of the patients) | ||||
| SiFICBc | 16 | Case 7-10-11-13-14-16-18(2x)-22-23-25-26-27-28-29 | 15 | Excluded: Case 9 |
| SCPBc | 8 | Case 2-4-12-15-19-24 | 6 | Excluded: Case 6-21 |
| ISPBc | 2 | Case 1-4 | 2 | - |
| PBc | 5 | Case 3-5-7-8 | 4 | Excluded: Case 9 |
| ACBc | 1 | Case 5 | 1 | - |
| EpiDc | 2 | Case 13-14 | 2 | - |
| PBc + SiFICBc | 2 | Case 20 | 2 | - |
| SCPBc + SiFICBc | 2 | Case 17 | 2 | - |
| Bilateral SiFICBc | 2 | Case 14 | 2 | - |
| Infusion rate (mg/kg/day) | ||||
| ISPBc | 2 | 0.65 ± 0.17 | 2 | 0.65 ± 0.17 |
| SCPBc | 10 | 0.58 ± 0.12 | 8 | 0.59 ± 0.13 |
| PBc | 6 | 0.67 ± 0.14 | 5 | 0.71 ± 0.13 |
| ACBc | 1 | 0.80 ± 0.00 | 1 | 0.80 ± 0.00 |
| SiFICBc | 19 | 1.44 ± 0.41 | 18 | 1.47 ± 0.41 |
| EpiDc | 2 | 0.50 ± 0.00 | 2 | 0.50 ± 0.00 |
| Total | 40 | 1.01 ± 0.51 | 36 | 1.05 ± 0.52 |
| Position | Coverage | Procedure | Infusion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supraclavicular Brachial Plexus Catheterization (SCPBc) | Supine In-plane Linear probe (8-12 mHz) |
Elbow Below elbow |
View of first rib, brachial plexus and subclavian artery No-fly zone below the lower cordon |
0.1% bupivacaine 0.5 mg/kg/24h 1 mL bolus 30 minutes lock-out |
| Interscalene Brachial Plexus Catheterization (ISPBc) |
Supine In-plane Linear probe (8-12 mHz) |
Above elbow Shoulder joint |
In the anterior and middle scalene muscles between the upper and middle brachial trunk | 0.1% bupivacaine 0.5 mg/kg/24h 1 mL bolus 30 minutes lock-out |
| Popliteal Block Catheterization (PBc) |
Lateral dekubitis (L/R) In-plane Linear probe (8-12 mHz) |
Foot Ankle Below knee |
Above the popliteal artery between the posterior tibial and common peroneal nerves | 0.1% bupivacaine 0.5 mg/kg/24h 1 mL bolus 30 minutes lock-out |
| Adductor Channel Block Catheterization (ACBc) | Supine In plane Linear probe (8-12 mHz) |
Below knee Knee |
Below the sartorius muscle Lateral to the femoral artery At the entrance to the adductor canal |
0.1% bupivacaine 0.5 mg/kg/24h 1 mL bolus 30 minutes lock-out |
| Suprainguinal Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block Catheterization (SiFICBc) |
Supine In-plane Linear probe (8-12 mHz) |
Knee Above knee Wide tissue defects |
Below the deep circumflex artery The internal abdominal aponeurosis with the sartorius aponeurosis Between the iliacus muscle and the iliac fascia |
0.1% bupivacaine 1 mg/kg/24h 2 mL bolus 30 minutes lock-out |
| Epidural Catheterization (EpiDc) | Sitting Tuffier’s line With landmark |
Pelvic Lower abdomen Lower extremity |
L3-L4 L4-L5 |
4 mcg Fentanyl + 0.1% bupivacaine (mL) 0.5 mg/kg/24h (bupivacaine) 1 mL bolus 30 minutes lock-out |
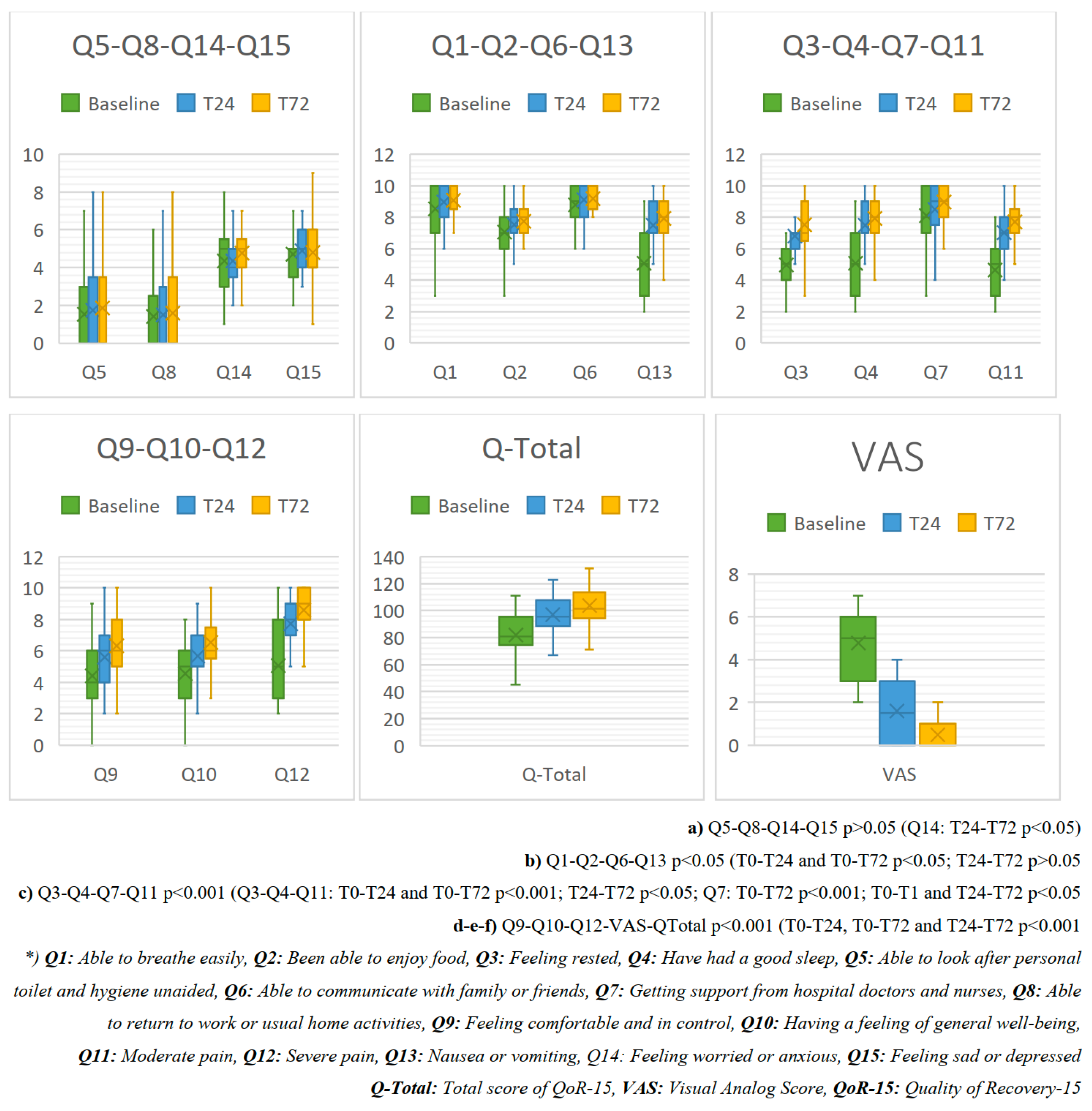
| Baseline | T24 | T72 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Section A How did you feel during the last 24 hours? Between 0 and 10 (0: never (bad) and 10: always (excellent) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Never ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Always 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | ||||
| Q1: Able to breathe easily | 8.52 ± 1.85 | 8.97 ± 1.26 | 9.06 ± 1.49 | 0.006 a,c |
| Q2: Been able to enjoy food | 7.03 ± 1.59 | 7.52 ± 1.37 | 7.73 ± 1.23 | 0.006 a,c |
| Q3: Feeling rested | 4.94 ± 1.54 | 6.79 ± 1.24 | 7.52 ± 1.62 | 0.000 a,b,c |
| Q4: Have had a good sleep | 5.06 ± 2.19 | 7.48 ± 1.50 | 7.91 ± 1.60 | 0.000 a,b,c |
| Q5: Able to look after personal toilet and hygiene unaided | 1.55 ± 2.64 | 1.76 ± 2.81 | 1.81 ± 1.95 | 0.061 |
| Q6: Able to communicate with family or friends | 8.79 ± 1.57 | 9.09 ± 1.18 | 9.18 ± 1.13 | 0.001 a,c |
| Q7: Getting support from hospital doctors and nurses | 8.09 ± 1.89 | 8.48 ± 1.48 | 8.94 ± 1.17 | 0.000 a,b,c |
| Q8: Able to return to work or usual home activities | 1.42 ± 2.27 | 1.52 ± 2.19 | 1.61 ± 2.39 | 0.424 |
| Q9: Feeling comfortable and in control | 4.42 ± 1.93 | 5.61 ± 1.93 | 6.33 ± 1.91 | 0.000 a,b,c |
| Q10: Having a feeling of general well-being | 4.55 ± 1.85 | 5.67 ± 1.49 | 6.55 ± 1.80 | 0.000 a,b,c |
|
Section B In the last 24 hours, have you experienced any of the following? Between 10 and 0, 10: never (excellent) and 0: always (bad) 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Never ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Always 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 | ||||
| Q11: Moderate pain | 4.64 ± 1.71 | 7.00 ± 1.58 | 7.00 ± 1.33 | 0.000 a,b,c |
| Q12: Severe pain | 5.06 ± 2.60 | 7.73 ± 2.48 | 8.61 ± 1.22 | 0.000 a,b,c |
| Q13: Nausea or vomiting | 7.33 ± 2.66 | 8.42 ± 1.54 | 8.55 ± 1.69 | 0.003 a,c |
| Q14: Feeling worried or anxious | 4.21 ± 1.78 | 4.36 ± 1.36 | 4.76 ± 1.69 | 0.435b |
| Q15: Feeling sad or depressed |
4.70 ± 1.44 | 4.88 ± 1.51 | 4.79 ± 1.76 | 0.695 |
| Total | 80.45 ± 17.76 | 95.27 ± 15.16 | 101.06 ± 15. 52 | 0.000 a,b,c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





