Submitted:
21 October 2024
Posted:
24 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
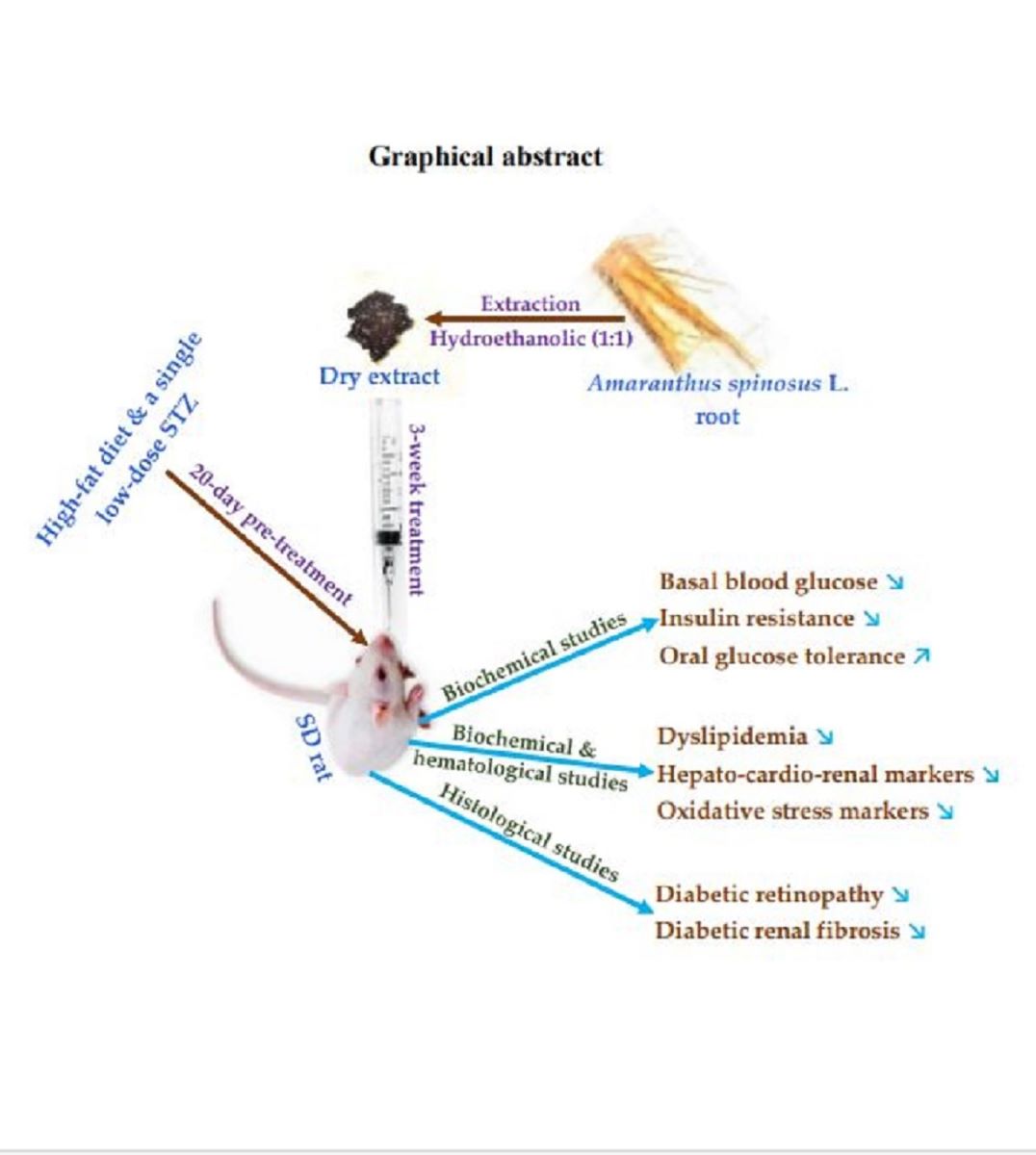
2. Results
2.1. Validated model
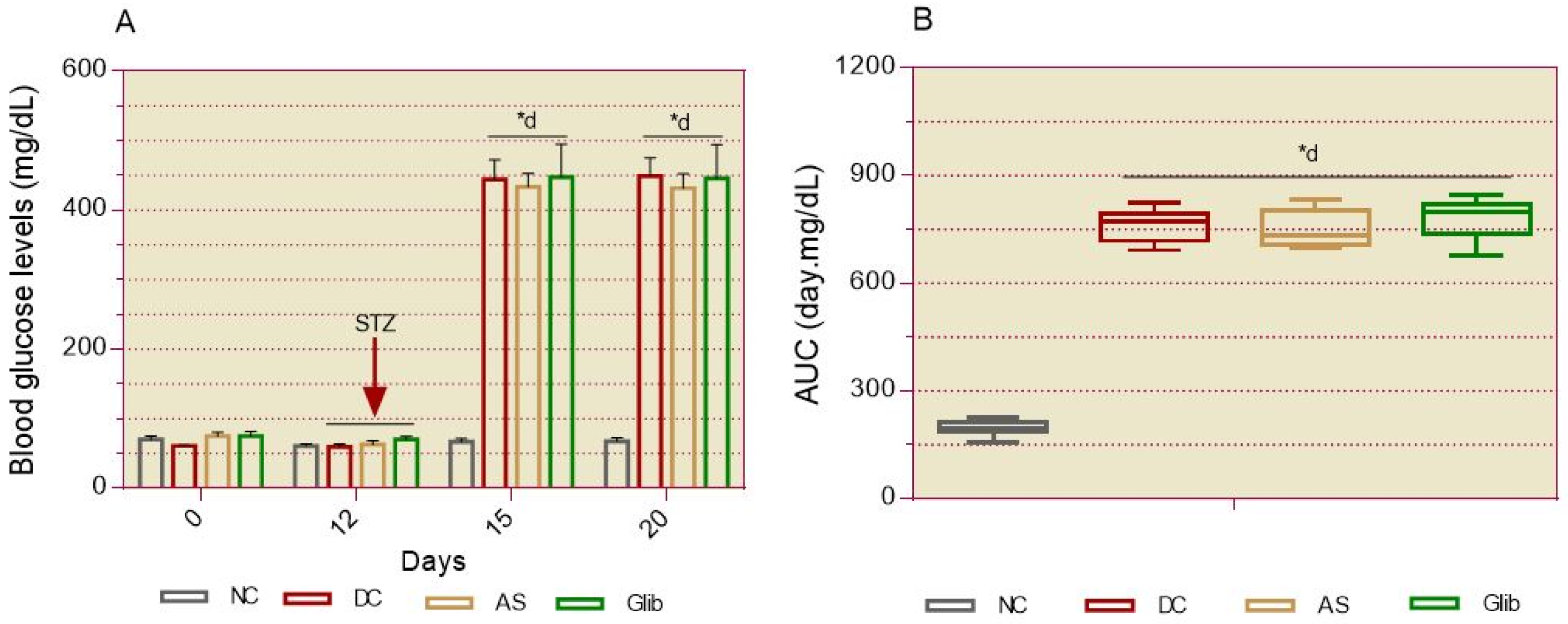
2.1.1. Basal Blood Glucose
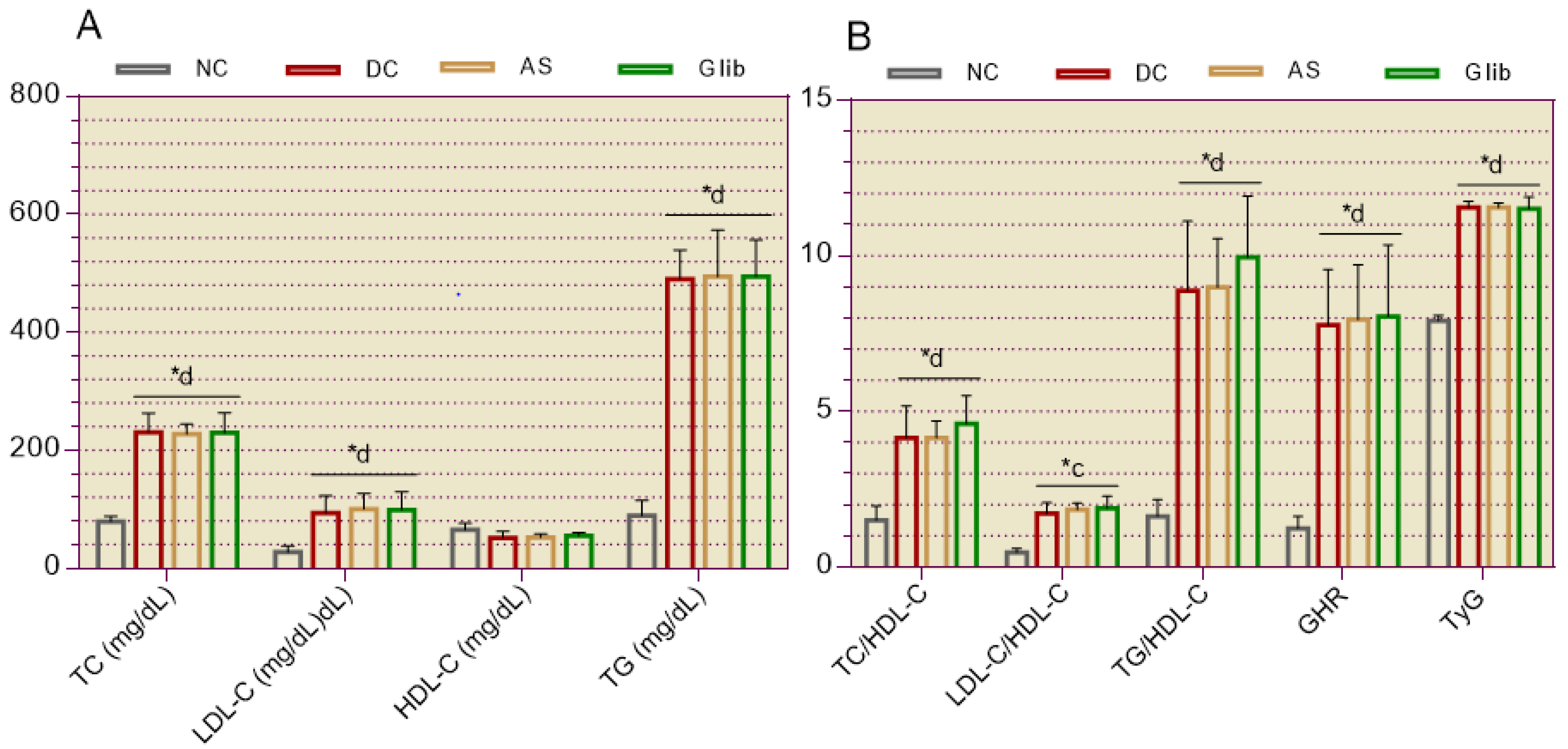
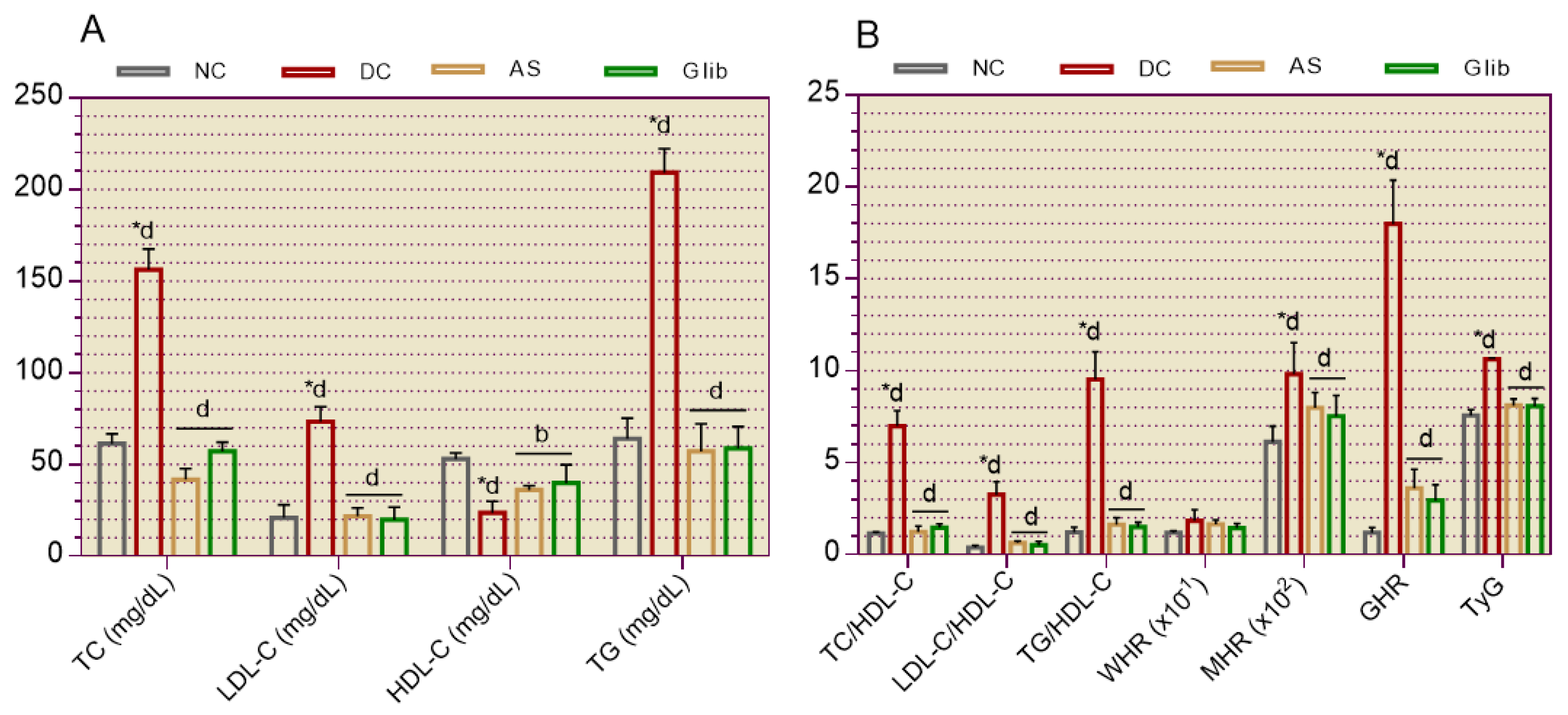
2.1.2. Serum Biochemical Markers for the Cardiovascular System
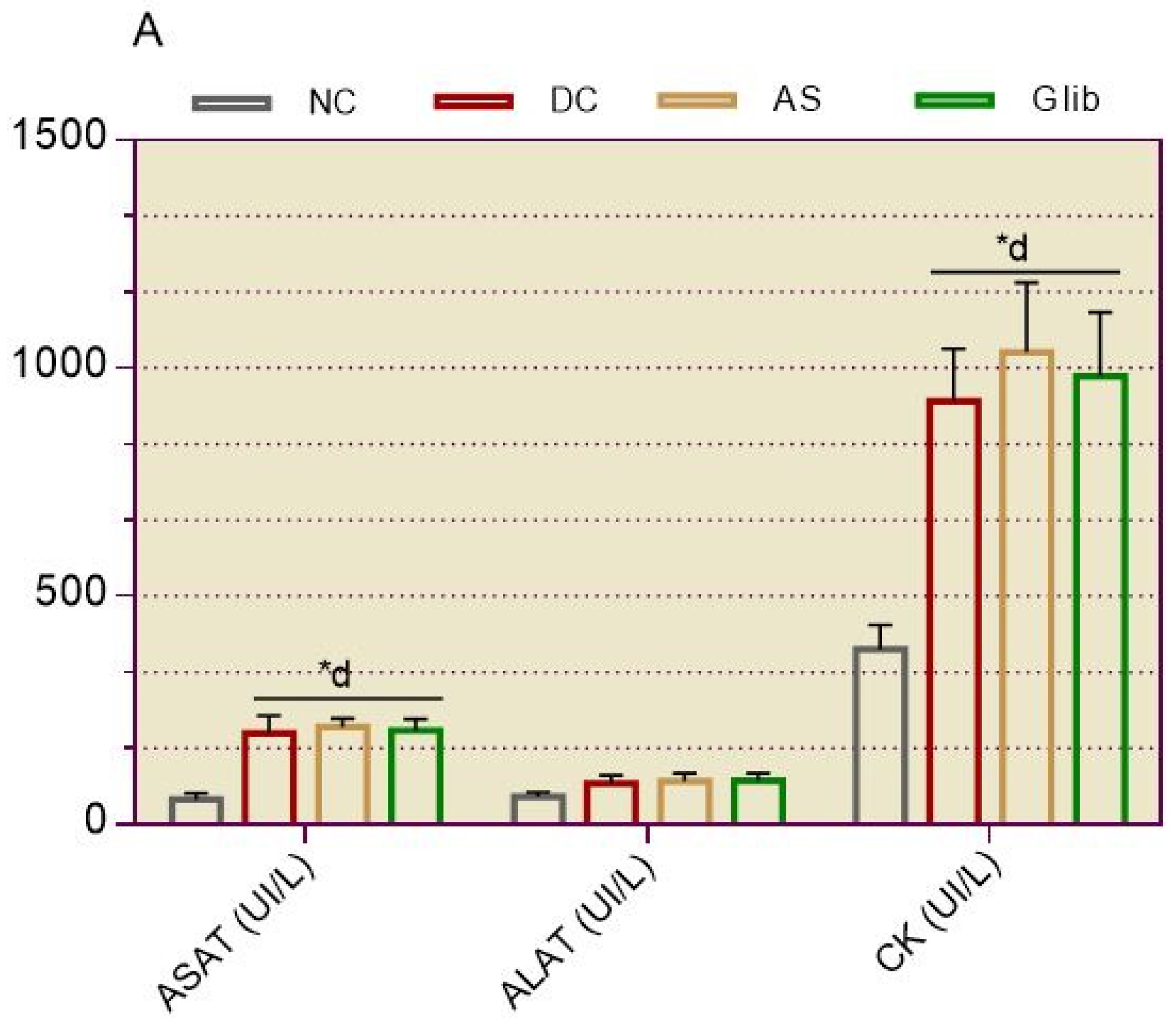
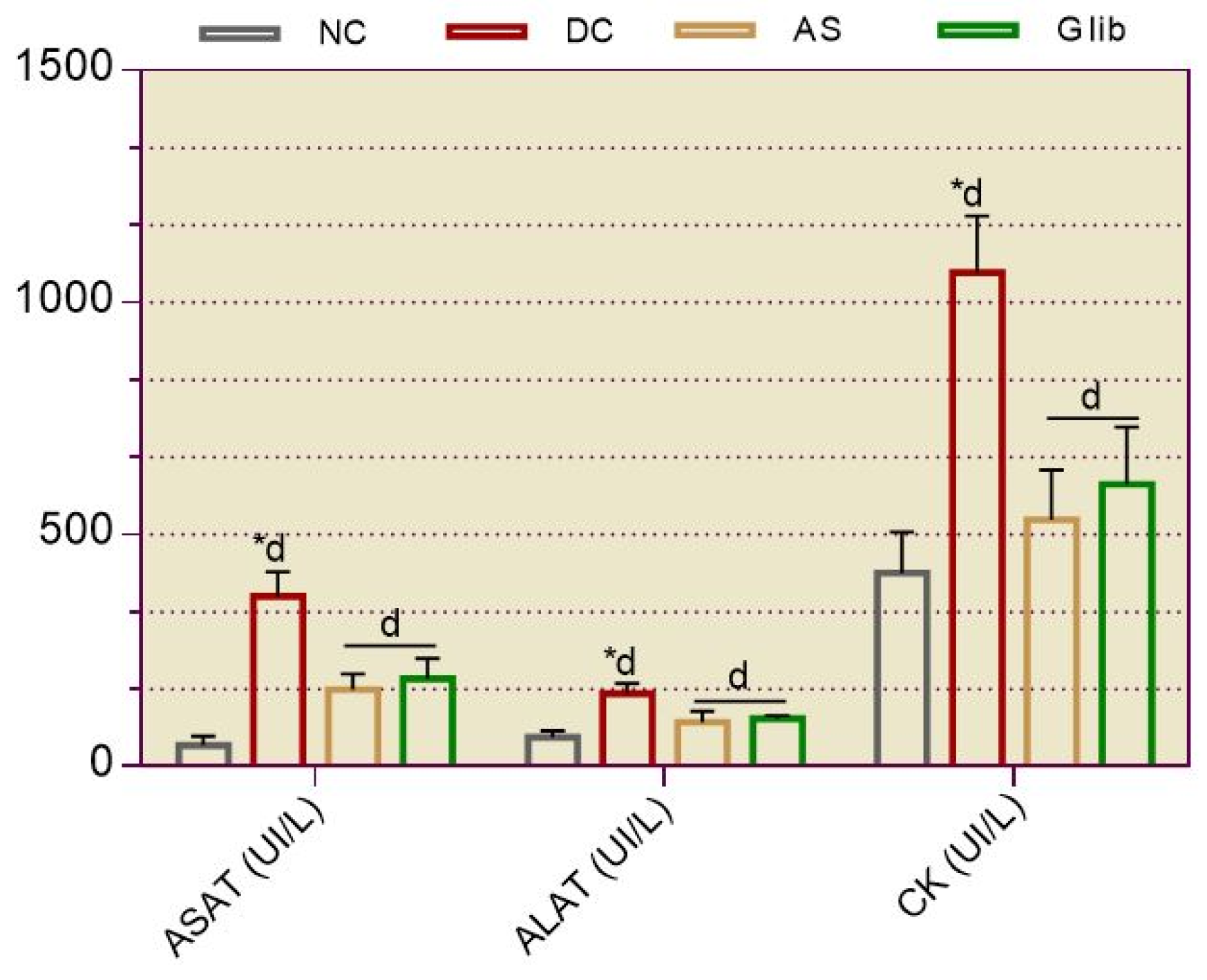
2.1.3. Serum Biochemical Markers for Hepatic and Cardiac
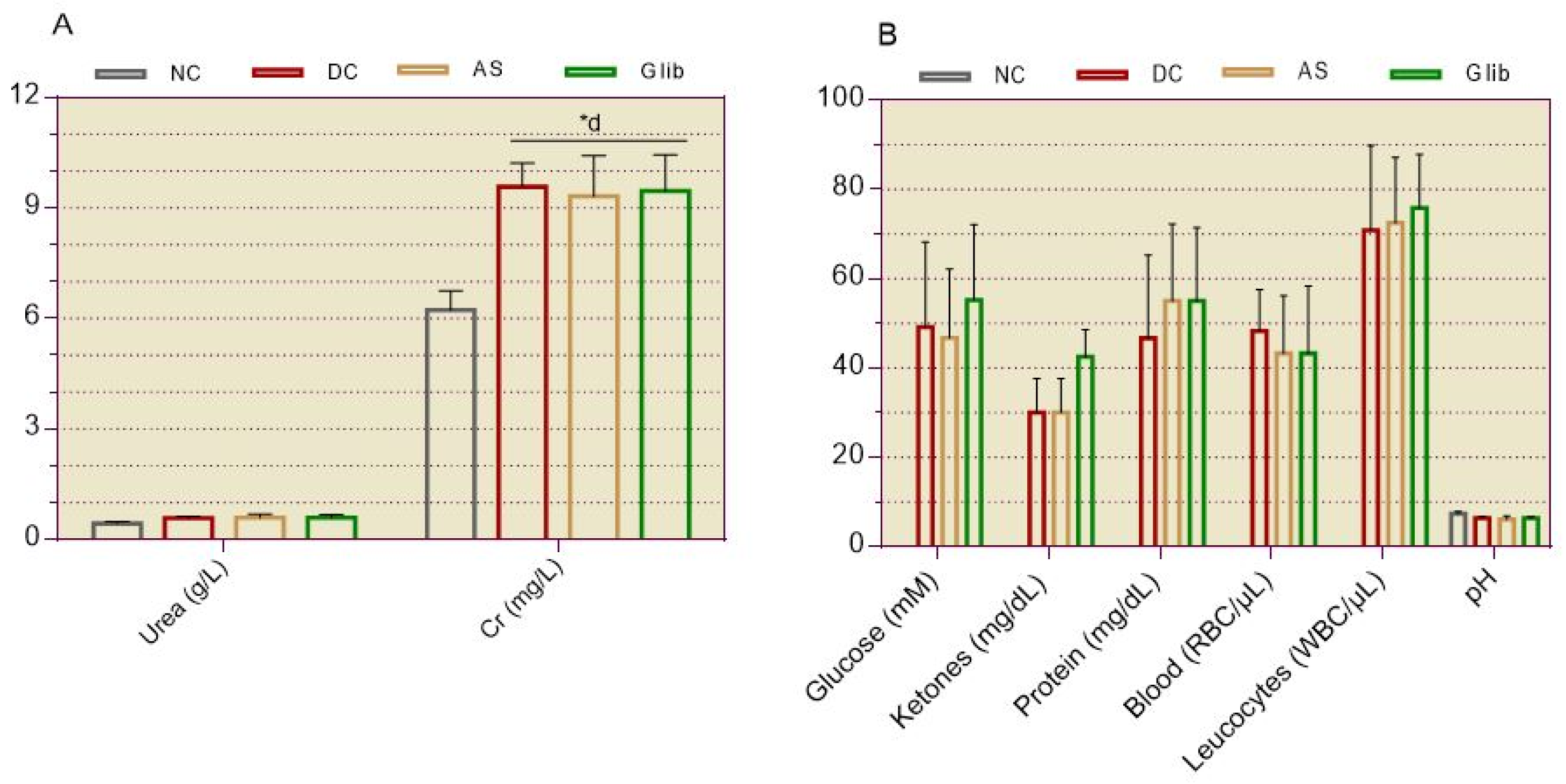
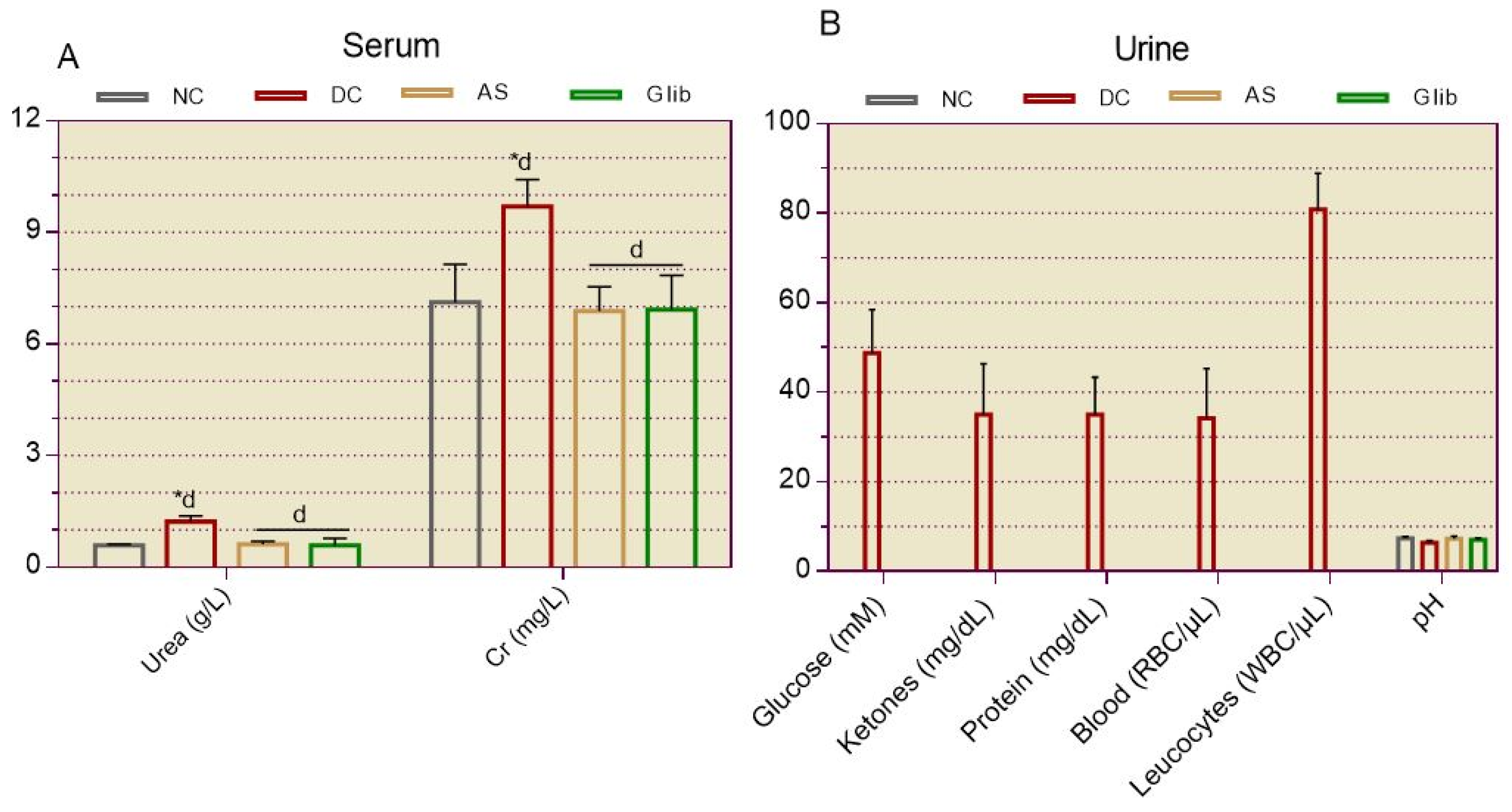
2.1.4. Serum and Urine Biochemical Markers for Renal
2.2. Treatment
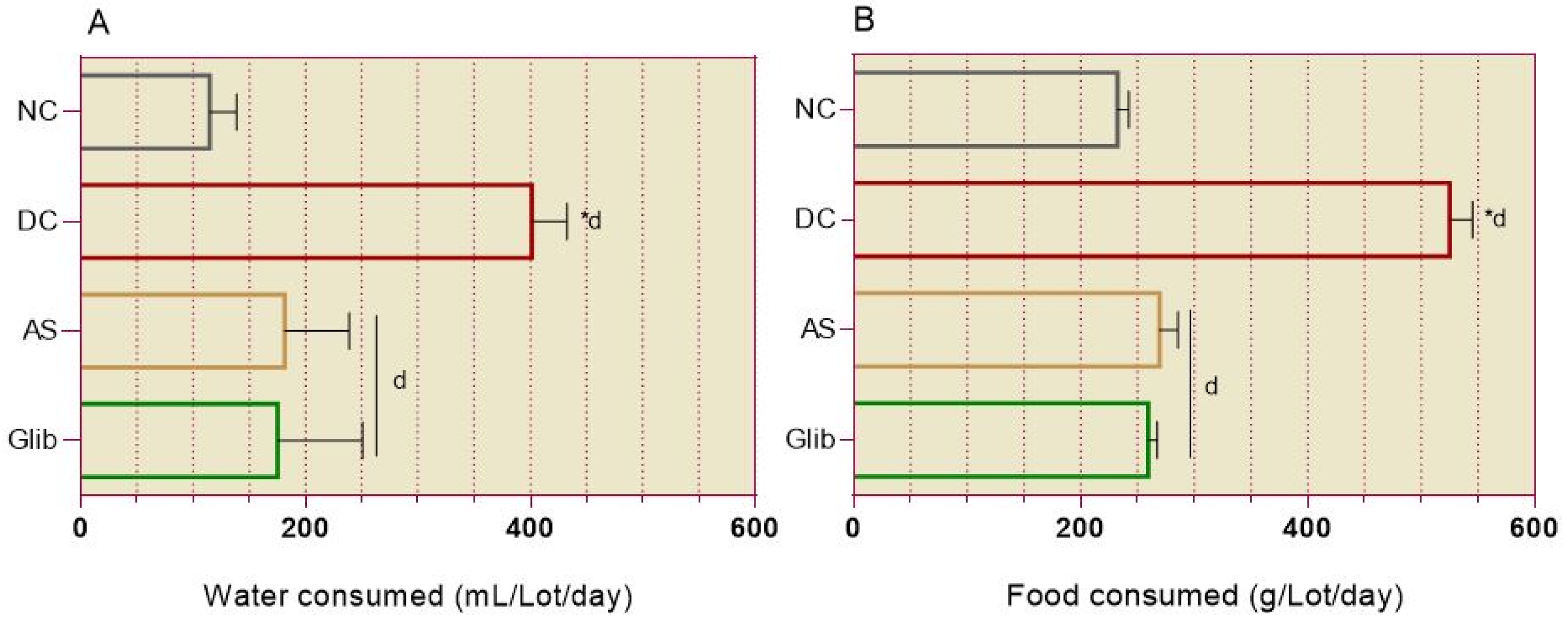
2.2.1. Diabetic Syndrome Markers
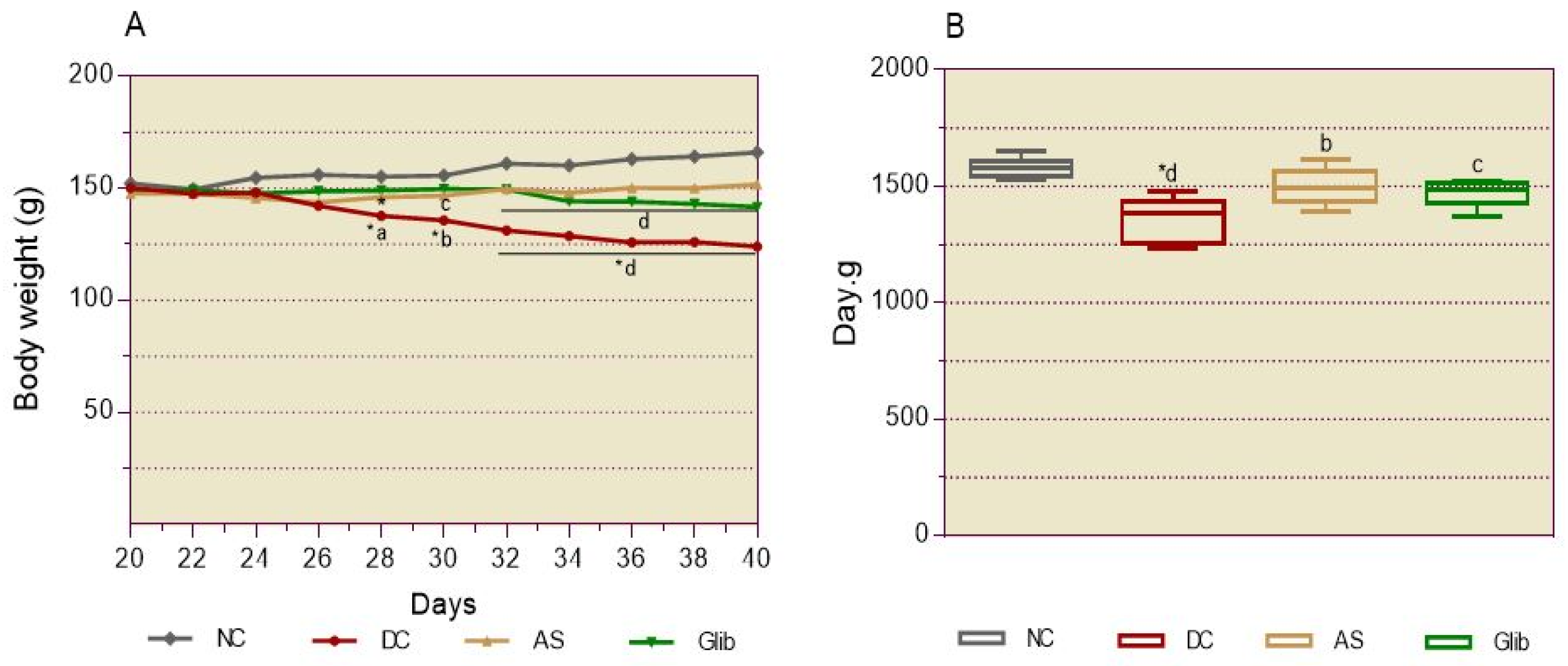
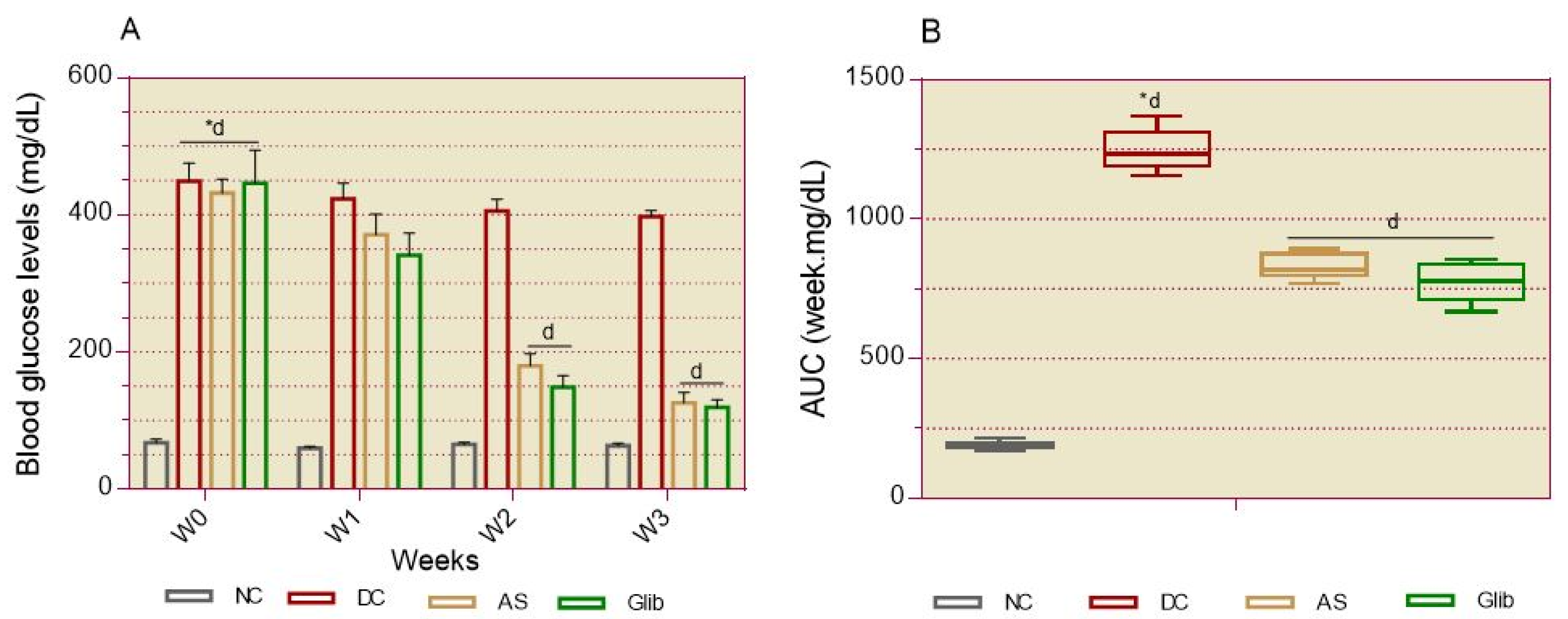
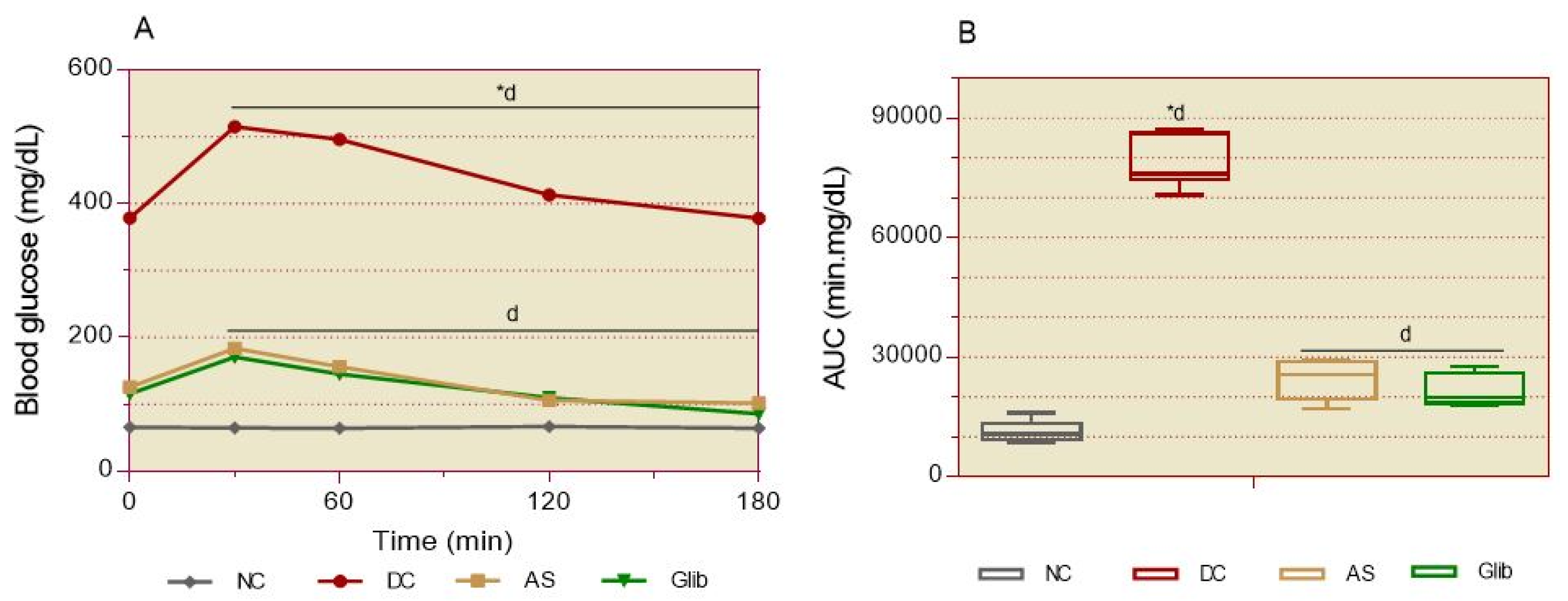
2.2.2. Basal Blood Glucose
2.2.3. Oral Glucose Intolerance
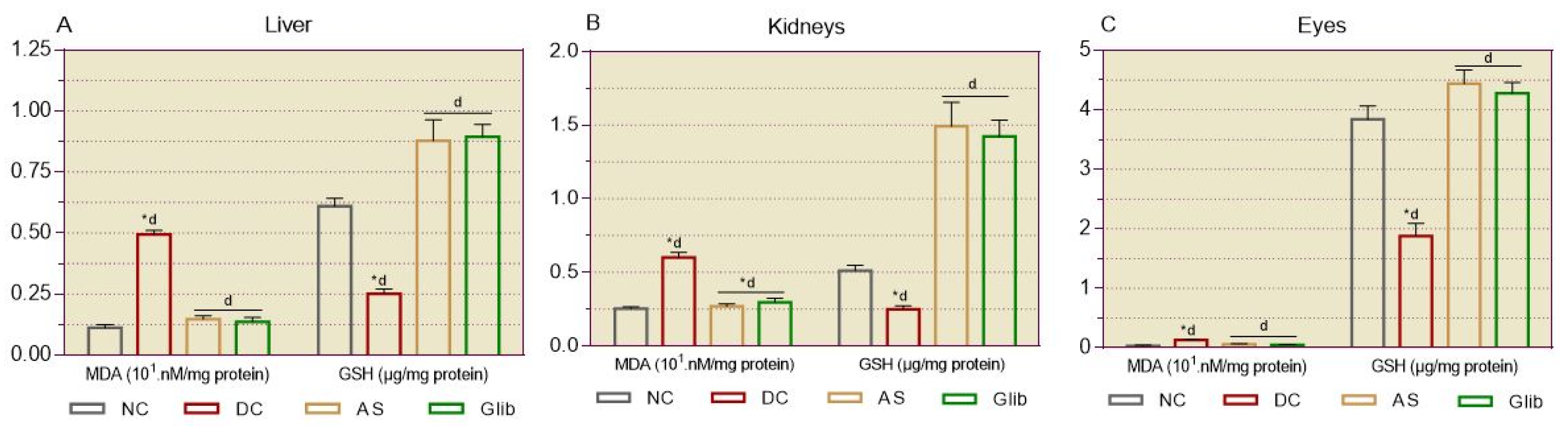
2.2.4. Markers of Oxidative Stress in Tissues
2.2.5. Cardiovascular System Markers
2.2.6. Serum Biochemical Markers for Hepatic and Cardiac
2.2.7. Serum and Urine Biochemical Markers for Kidneys
2.2.7. Blood Cells Profile
2.2.8. Anatomopathological Studies
2.2.8.1. Gross Observations
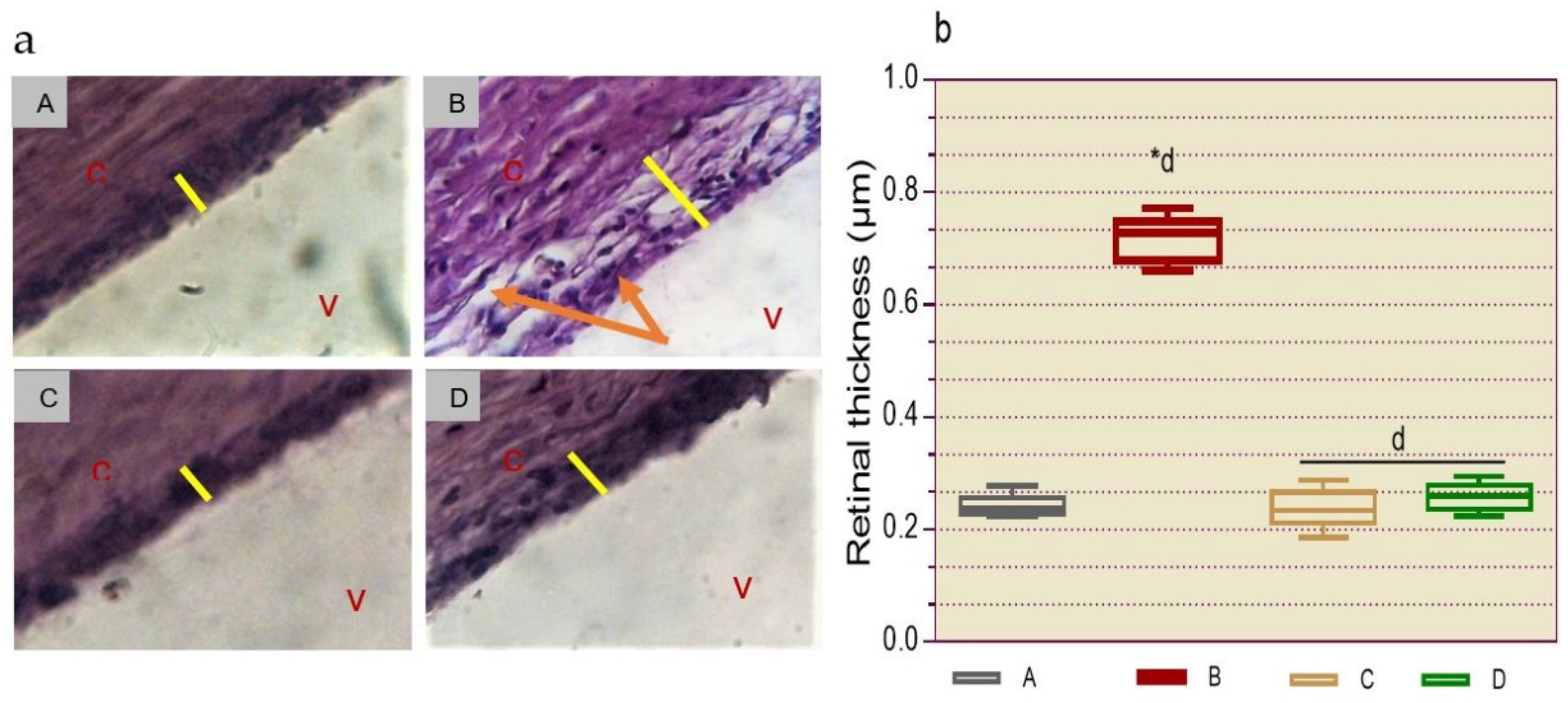
2.2.8.2. Histological Determination of Retinopathy
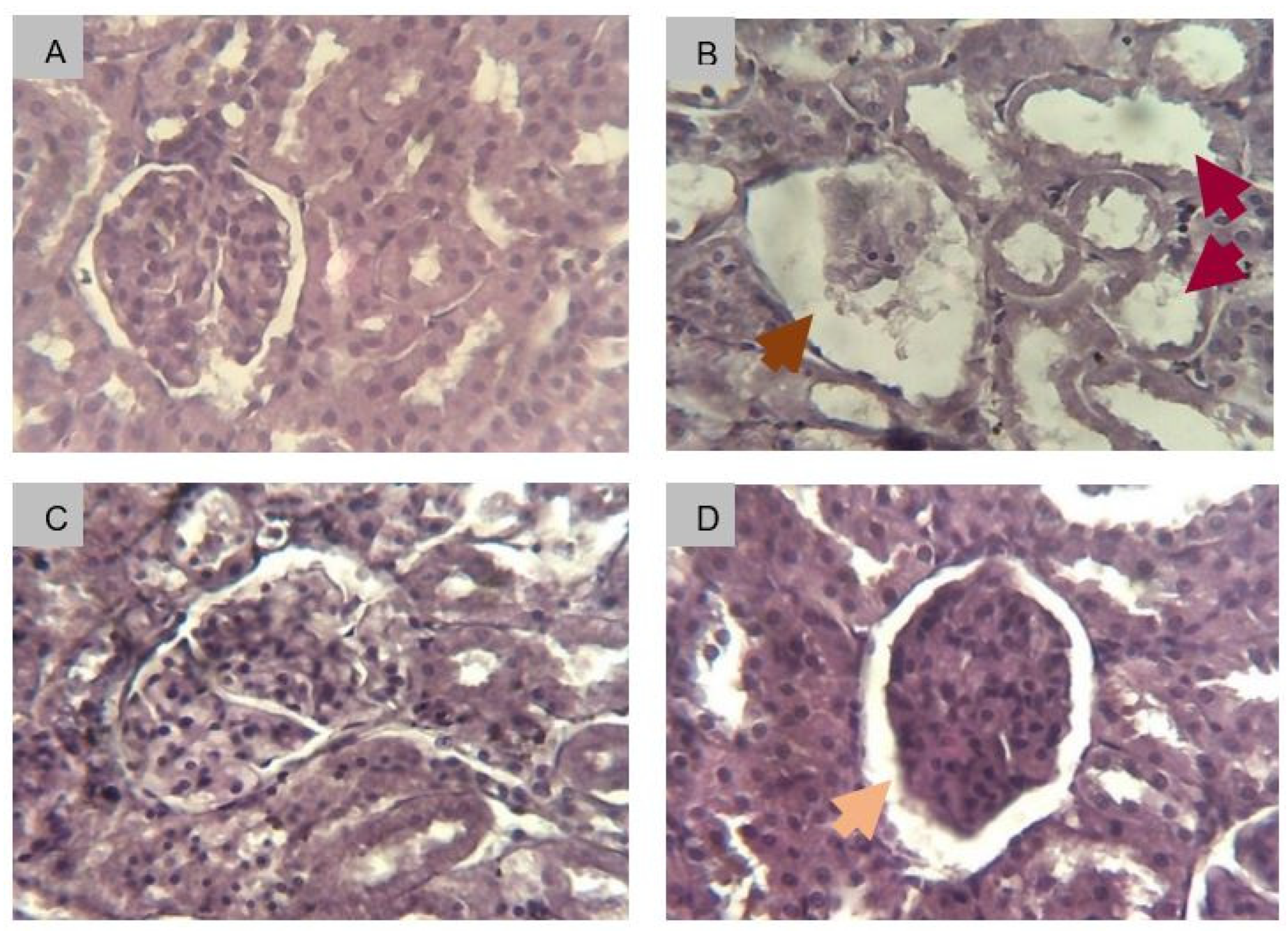
2.2.8.3. Histological Determination of Renal Fibrosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.1.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.1.2. Plant Material
4.1.3. Animals
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Extract Preparation
4.2.2. Study Design
4.2.3. Validation of the Animal Model
4.2.4. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of the Extract
4.3. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47 (Suppl. 1), S20–S42. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, W.S.; Eshaq, R.S.; Lee, M.; Kaur, G.; Harris, N.R. Retinal Physiology and Circulation: Effect of Diabetes. Compr. Physiol. 2020, 10, 933–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Diabetes Federation (IDF). IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation 2021. https://www.diabetesatlas.org.
- Ting, D.S.W.; Cheung, G.C.M.; Wong, T.Y. Diabetic retinopathy: global prevalence, major risk factors, screening practices and public health challenges: a review. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016, 44, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Jamali, M.C.; Habib, A.; Hussain, M.S.; Akhtar, M.; Najmi, A.K. Diabetic kidney disease: An overview of prevalence, risk factors, and biomarkers. Clin Epidemiol Glob Health 2021, 9, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, N.; Curtis, A.J.; Heritier, S.; Gadowski, A.M.; Pavkov, M.E.; Kenealy, T.; Owens, D.R.; Thomas, R.L.; Song, S.; Wong, J.; Chan, J.C.; Luk, A.O.; Penno, G.; Ji, L.; Mohan, V.; Amutha, A.; Romero-Aroca, P.; Gasevic, D.; Magliano, D.J.; Teede, H.J.; et al. Impact of age at type 2 diabetes mellitus diagnosis on mortality and vascular complications: systematic review and meta-analyses. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioana, M.; Deng, J.; Nadarajah, A.; Hou, M.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, S.S.J.; Rivas, A.; Toor, P.P.; Banfield, L.; Thabane, L.; Chaudhary, V.; Samaan, M.C. Global Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy in Pediatric Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e231887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, S.; Nawroth, P.P.; Herzig, S.; Ekim Üstünel, B. Emerging targets in type 2 dia-betes and diabetic complications. Adv Sci. 2021, 8, 2100275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meir, J.; Huang, L.; Mahmood, S.; Whiteson, H.; Cohen, S.; Aronow, W.S. The vascular complications of diabetes: a review of their management, pathogenesis, and prevention. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 19, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, B.K.; Ali, N.A.A0; Setzer, W.N. A Survey of Chemical Compositions and Biological Activities of Yemeni Aromatic Medicinal Plants. Medicines 2015, 2, 67–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szopa, A.; Ekiert, R.; Ekiert, H. Current knowledge of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. (Chinese magnolia vine) as a medicinal plant species: a review on the bioactive components, pharmacological properties, analytical and biotechnological studies. Phytochem Rev 2017, 16, 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, F.; Sedaghat, S.; Moradi, O.; Arab Salmanabadi, S. Review on green nano-biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biological activities: With an emphasis on medicinal plants. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2021, 51, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iamonico, D. Taxonomic revision of the genus Amaranthus (Amaranthaceae) in Italy. Phytotaxa 2015, 199, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavarva, J.H.; Narasimhacharya, A.V. Systematic study to evaluate anti-diabetic potential of Amaranthus spinosus on type-1 and type-2 diabetes. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2013, 59, OL1818–OL1825. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mondal, A.; Guria, T.; Maity, T.K. A new ester of fatty acid from a methanol extract of the whole plant of Amaranthus spinosus and its α-glucosidase inhibitory activity. Pharm Biol. 2015, 53, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoswa, W.N.; Mokgalaboni, K. Comprehensive Overview of the Effects of Amaranthus and Abelmoschus esculentus on Markers of Oxidative Stress in Diabetes Mellitus. Life (Basel). 2023, 13, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, M.R.U.; Zihad, S.M.N.K.; Ghosh, P.; Sifat, N.; Rouf, R.; Al Shajib, G.M.; Alam, M.A.; Shilpi, J.A.; Uddin, S.J. Amaranthus spinosus Attenuated Obesity-Induced Metabolic Disorders in High-Carbohydrate-High-Fat Diet-Fed Obese Rats. Front nutr.. 2021, 8, 653918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchou, K.; Lawson-Evi, P.; Metowogo, K.; Eklu-Gadegbeku, K.; Aklikokou, K.; Gbeassor, M. Hypoglycemic effect and antioxidant potential of Pterocarpus erinaceus Poir. stem bark and Amaranthus spinosus L. roots extracts. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 12, 340–350. [Google Scholar]
- Atchou, K.; Lawson-Evi, P.; Eklu-Gadegbeku, K. In vitro study of protective effect of Pterocarpus erinaceus Poir. stem bark and Amaranthus spinosus L. root extracts on cataractogenesis and glomerulopathy. Bull. Natl Res Cent 2021, 45, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Al Qarni, A.; Hawwari, A.; Alghanem, A.F.; Ahmed, G. Metabolic Syndrome, Dyslipidemia and Regulation of Lipoprotein Metabolism. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2018, 14, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, A.G.; Andersson, D.P.; Dahlman, I.; Rydén, M.; Arner, P. Adipose Insulin Resistance Associates With Dyslipidemia Independent of Liver Resistance and Involves Early Hormone Signaling. Arterioscler., Thromb., Vasc. Biol. 2023, 43, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirillo, A.; Casula, M.; Olmastroni, E.; Norata, G.D.; Catapano, A.L. Global epidemiology of dyslipidaemias. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Duan, F.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Wan, N. TG/HDL-C Ratio for Predicting Insulin Resistance in Obese Children from Beijing, China. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 2023, 24, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghikia, A.; Landmesser, U. Lipoproteins and Cardiovascular Redox Signaling: Role in Atherosclerosis and Coronary Disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, F.; Martín, M.; Verona, J.; Gilligan, L.; Verona, M.F.; Botta, E.; Tetzlaff, W.; Lozano Chiappe, E.; Boero, L.; Brites, F. Increased Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein and Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2 Activities in Children and Adolescents Presenting High Triglyceride/High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) Ratio. “Indian J. Pediatr. 2021, 88, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soumya, R.S.; Raj, K.B.; Abraham, A. Passiflora edulis (var. Flavicarpa) Juice Supplementation Mitigates Isoproterenol-induced Myocardial Infarction in Rats. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 2021, 76, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minato-Inokawa, S.; Tsuboi-Kaji, A.; Honda, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Kitaoka, K.; Kurata, M.; Wu, B.; Kazumi, T.; Fukuo, K. Associations of alanine aminotransferase/aspartate aminotransferase with insulin resistance and β-cell function in women. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.A.; Deja, S.; Satapati, S.; Fu, X.; Burgess, S.C.; Browning, J.D. Impaired ketogenesis and increased acetyl-CoA oxidation promote hyperglycemia in human fatty liver. JCI insight 2019, 5, e127737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Xu, B.T.; Wan, S.R.; Ma, X.M.; Long, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Z.Z. The role of oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagoo, M.K.; Gnudi, L. Diabetic Nephropathy: An Overview. Methods Mol Biol 2020, 2067, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S.; Trehan, S.; Chawla, A.; Jaggi, S.; Chawla, R.; Kumar, V.; Singh, D. Relationship between diabetic retinopathy microalbuminuria and other modifiable risk factors. Prim. Care Diabetes 2021, 15, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thipsawat, S. Early detection of diabetic nephropathy in patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review of the literature. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res. 2021, 18, 14791641211058856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, R.J.; Rabin-Court, A.; Song, J.D.; Cardone, R.L.; Wang, Y.; Kibbey, R.G.; Shulman, G.I. Dehydration and insulinopenia are necessary and sufficient for euglycemic ketoacidosis in SGLT2 inhibitor-treated rats. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shum, M.; Segawa, M.; Gharakhanian, R.; Viñuela, A.; Wortham, M.; Baghdasarian, S.; Wolf, D.M.; Sereda, S.B.; Nocito, L.; Stiles, L.; Zhou, Z.; Gutierrez, V.; Sander, M.; Shirihai, O.S.; Liesa, M. Deletion of ABCB10 in beta-cells protects from high-fat diet induced insulin resistance. Mol. Metab. 2022, 55, 101403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson-Evi, P.; Motto, A.E.; Atchou, K.; Tona, K.; Eklu-Gadegbeku, K.; Aklikokou, K. Insulinomimetic activity assessment of antidiabetic plants used in togolese pharmacopoeia, in ovo and ex vivo study. Int J Biol Sci. 2021, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Gautier, J.F.; Chon, S. Assessment of Insulin Secretion and Insulin Resistance in Human. Diabetes Metab J 2021, 45, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caturano, A.; D’Angelo, M.; Mormone, A.; Russo, V.; Mollica, M.P.; Salvatore, T.; Galiero, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Vetrano, E.; Marfella, R.; Monda, M.; Giordano, A.; Sasso, F.C. Oxidative Stress in Type 2 Diabetes: Impacts from Pathogenesis to Lifestyle Modifications. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 6651–6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Tao, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L. The Utility of Exosomes in Diagnosis and Therapy of Diabetes Mellitus and Associated Complications. Front. endocrinol. 2021, 12, 756581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, W.; Du, X.; Luo, Z.; Hu, J.; Peng, S. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: pathogenetic mechanisms and treatment. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1265372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Q.; He, J.; Li, Y. Immune responses in diabetic nephropathy: Pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic target. Front. immunol. 2022, 13, 958790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ria, P.; De Pascalis, A.; Zito, A.; Barbarini, S.; Napoli, M.; Gigante, A.; Sorice, G.P. Diet and Proteinuria: State of Art. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibelalde, A.; Amenabar Alonso, A.; Pinar-Sueiro, S.; Bilbao-Garay, I.; Juaristi Eizmendi, L.; Sampedro, A. Albuminuria as a biomarker of severity in diabetic retinopathy and in the response to intravitreal treatment in diabetic macular edema. Int. Ophthalmol. 2023, 43, 2049–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, S.; Chougule, A.; Mohanty, S. Correlation of Albuminuria and Diabetic Retinopathy in Type-II Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Cureus 2022, 14, e21927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Gong, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xie, R. The link between diabetic retinal and renal microvasculopathy is associated with dyslipidemia and upregulated circulating level of cytokines. Front. Public Health 2023, 10, 1040319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, M.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, Y.; Song, Y.; Cai, Q. Peripheral white blood cell subtypes and the development/progression of diabetic macular edema in type 2 diabetic patients: a comparative study. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2022, 11, 2887–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, E.; Han, B.; Zhang, Q.; Rao, W.; Wang, Z.; Chang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, C.; Li, C.; Wu, D. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent the progression of early diabetic nephropathy through inhibiting inflammation and fibrosis. Stem Cell Res Ther 2020, 11, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohandes, S.; Doke, T.; Hu, H.; Mukhi, D.; Dhillon, P.; Susztak, K. Molecular pathways that drive diabetic kidney disease. J Clin Invest. 2023, 133, e165654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampe, D.; Schridde, L.; Korsten, P.; Ströbel, P.; Zeisberg, M.; Hakroush, S.; Tampe, B. Different Patterns of Kidney Fibrosis Are Indicative of Injury to Distinct Renal Compartments. Cells 2021, 10, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchou, K.; Lawson-Evi, P.; Diallo, A.; Eklu-Gadegbeku, K. Toxicological evaluation of the dried hydroethanolic extract of Amaranthus spinosus L. roots in Artemia salina larvae and Sprague Dawley rats. Clin. phytosci. 2021, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchou, K.; Lawson-Evi, P.; Eklu-Gadegbeku, K. Improvement of microvascular complications in STZ-diabetic rats treated with Pterocarpus erinaceus Poir. extract. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2023, 35, 101541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, B.L. Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Models in Mice and Rats. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, A.T.; Wolfe, D. Tissue processing and hematoxylin and eosin staining. Methods Mol Biol. 2014, 1180, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patlolla, A.K.; Barnes, C.; Yedjou, C.; Velma, V.R.; Tchounwou, P.B. 2009 Oxidative stress, DNA damage, and antioxidant enzyme activity induced by hexavalent chromium in Sprague-Dawley rats. J. Environ. Toxicol. 2021, 24, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 82, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | NC | DC | AS | Glib |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red blood cells | ||||
| RBC (106/µL) | 6.543 ± 0.109 | 5.807 ± 0.175 | 6.507 ± 0.139 | 6.202 ± 0.160 |
| HGB (g/dL) | 14.100 ± 0.191 | 13.217 ± 0.358 | 14.300 ± 0.211 | 13.467 ± 0.184 |
| HCT (%) | 37.433 ± 0.493 | 35.100 ± 0.334 | 39.317 ± 0.248 | 35.683 ± 0.363 |
| MCV (fl) | 57.017 ± 0.594 | 57.333 ± 0.285 | 57.265 ± 0.162 | 58.863 ± 0.397 |
| MCH (pg) | 21.500 ± 0.279 | 21.100 ± 0.231 | 21.195 ± 0.108 | 22.567 ± 0.213 |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 37.650 ± 0.437 | 36.583 ± 0.207 | 36.835 ± 0.176 | 38.213 ± 0.398 |
| White blood cells | ||||
| WBC (103/µL) | 6.383 ± 0.190 | 3.417 ± 0.145*d | 6.173 ± 0.281d | 5.550 ± 0.118d |
| Neutrophils (103/µL) | 2.568 ± 0.142 | 1.286± 0.087*b | 2.474 ± 0.096c | 2.165 ± 0.063c |
| Eosinophils (103/µL) | 0.170 ± 0.030 | 0.073 ± 0.013*a | 0.173 ± 0.017a | 0.153 ± 0.019a |
| Basophils (103/µL) | 0.010 ± 0.001 | 0.009 ± 0.001 | 0.011 ± 0.001 | 0.008 ± 0.001 |
| Lymphocytes (103/µL) | 3.234 ± 0.137 | 1.798 ± 0.083*c | 3.191 ± 0.126c | 2.909 ± 0.090c |
| Monocytes (103/µL) | 0.402 ± 0.018 | 0.251 ± 0.032*a | 0.326 ± 0.027 | 0.315 ± 0.031 |
| Platelets | ||||
| Platelets (106/µL) | 0.609 ± 0.025 | 0.295 ± 0.027*c | 0.570 ± 0.029b | 0.613 ± 0.024b |
| Organs (mg) | NC | DC | AS | Glib |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eyes | 0.230 ± 0.012 | 0.352 ± 0.026 | 0.222 ± 0.014 | 0.243 ± 0.012 |
| Kidneys | 0.907 ± 0.066 | 1.110 ± 0.095 | 0.988 ± 0.044 | 1.020 ± 0.064 |
| Liver | 5.132 ± 0.136 | 6.448 ± 0.207*d | 5.362 ± 0.140d | 5.473 ± 0.153d |
| Heart | 0.667 ± 0.046 | 0.655 ± 0.043 | 0.627 ± 0.062 | 0.650 ± 0.044 |
| Lungs | 0.950 ± 0.049 | 1.133 ± 0.037 | 1.107 ± 0.021 | 1.013 ± 0.060 |
| Brain | 1.560 ± 0.063 | 1.622 ± 0.032 | 1.473 ± 0.045 | 1.402 ± 0.119 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





