Submitted:
18 October 2024
Posted:
22 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material Interpolation Format and Mathematical Model for Structural Topology Optimization of the APTS Mechanical Support Structure Bracket
2.1. Material Interpolation Format of SIMP and Structural Analysis
2.2. Mathematical Model for Structural Topology Optimization of the APTS Mechanical Support Structure Bracket
3. Explicit Sensitivity Analysis of Objective Functions and Constraints
3.1. Sensitivity of Compliance to Design Variables
3.2. Sensitivity of Displacement Constraints with Respect to Design Variables
3.3. Sensitivity of Stress Constraints with Respect to Design Variables
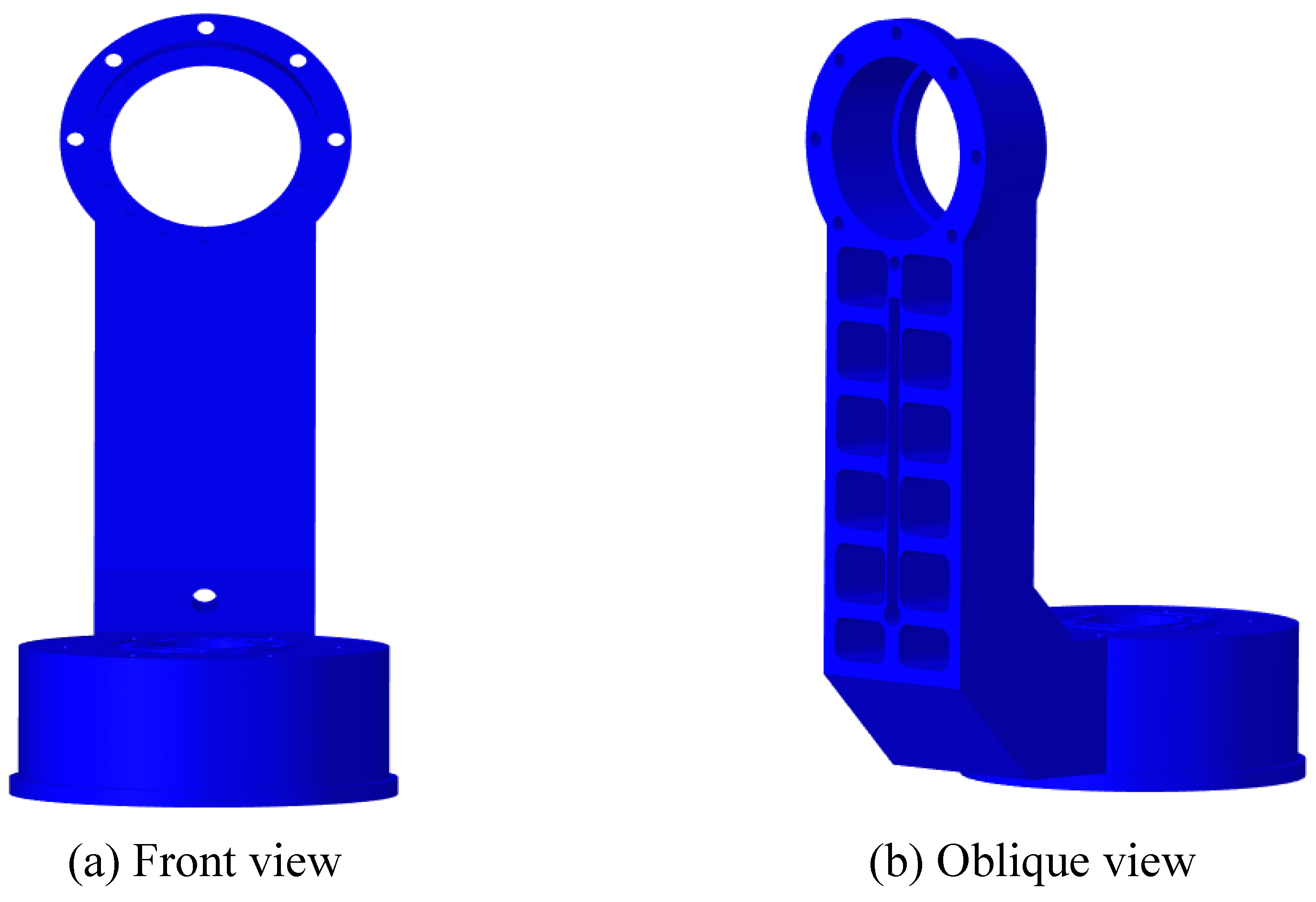
4. Structural Analysis of the APTS’ L-Shaped Bracket Structure
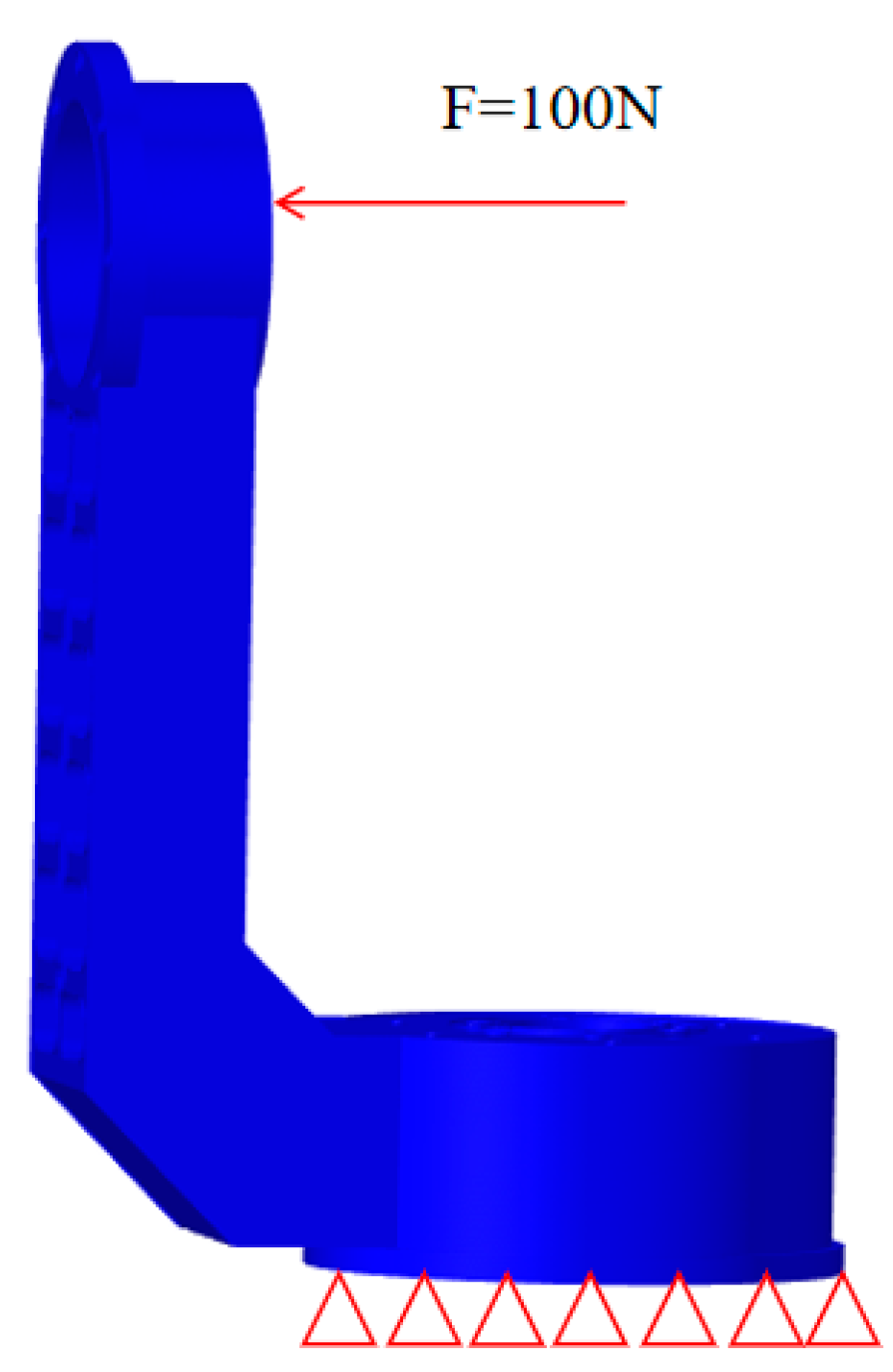
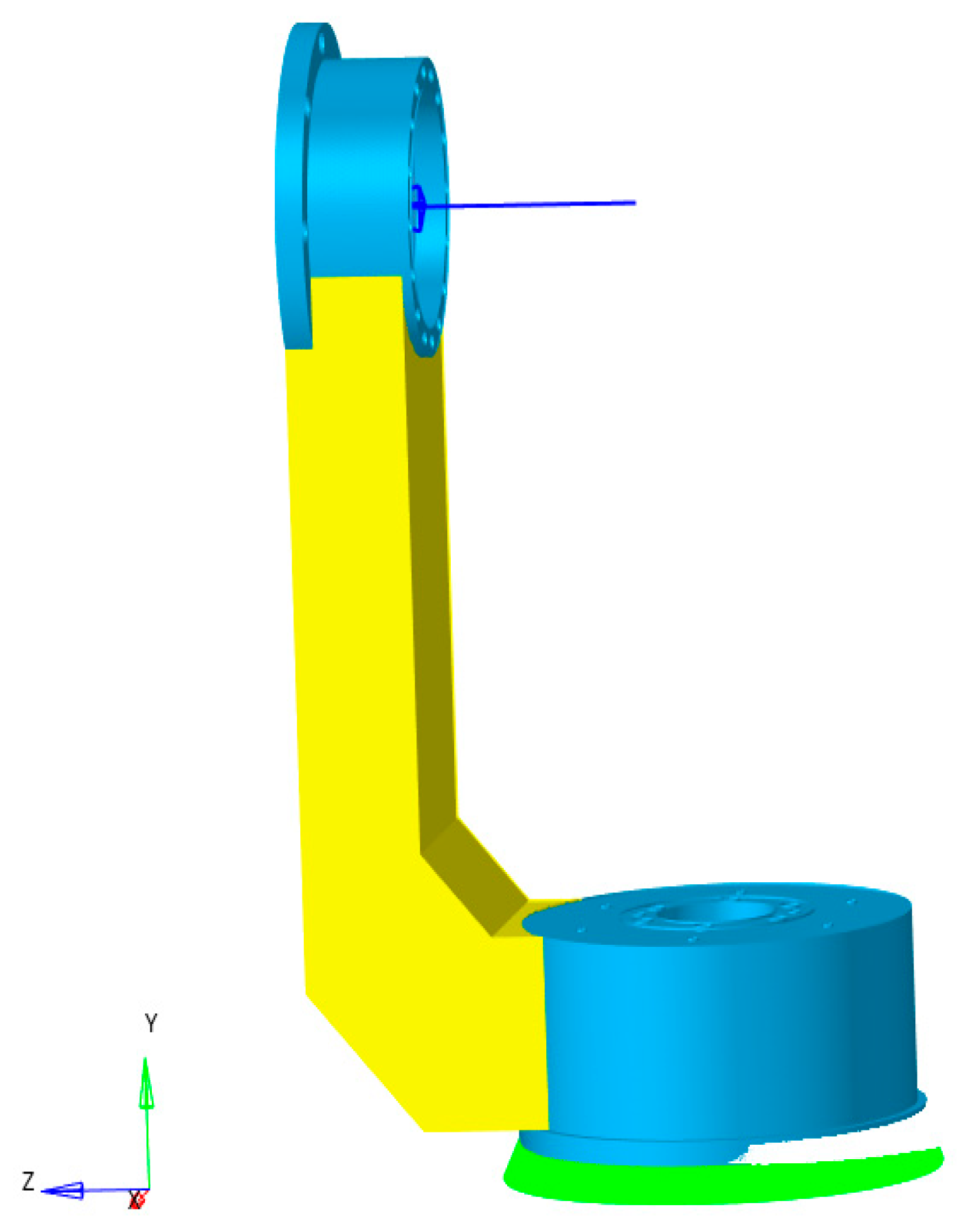
4.1. Loading and Boundary Conditions of the APTS’ Bracket Structure
4.2. Material Properties and Mesh Division of the APTS’ Bracket Structure
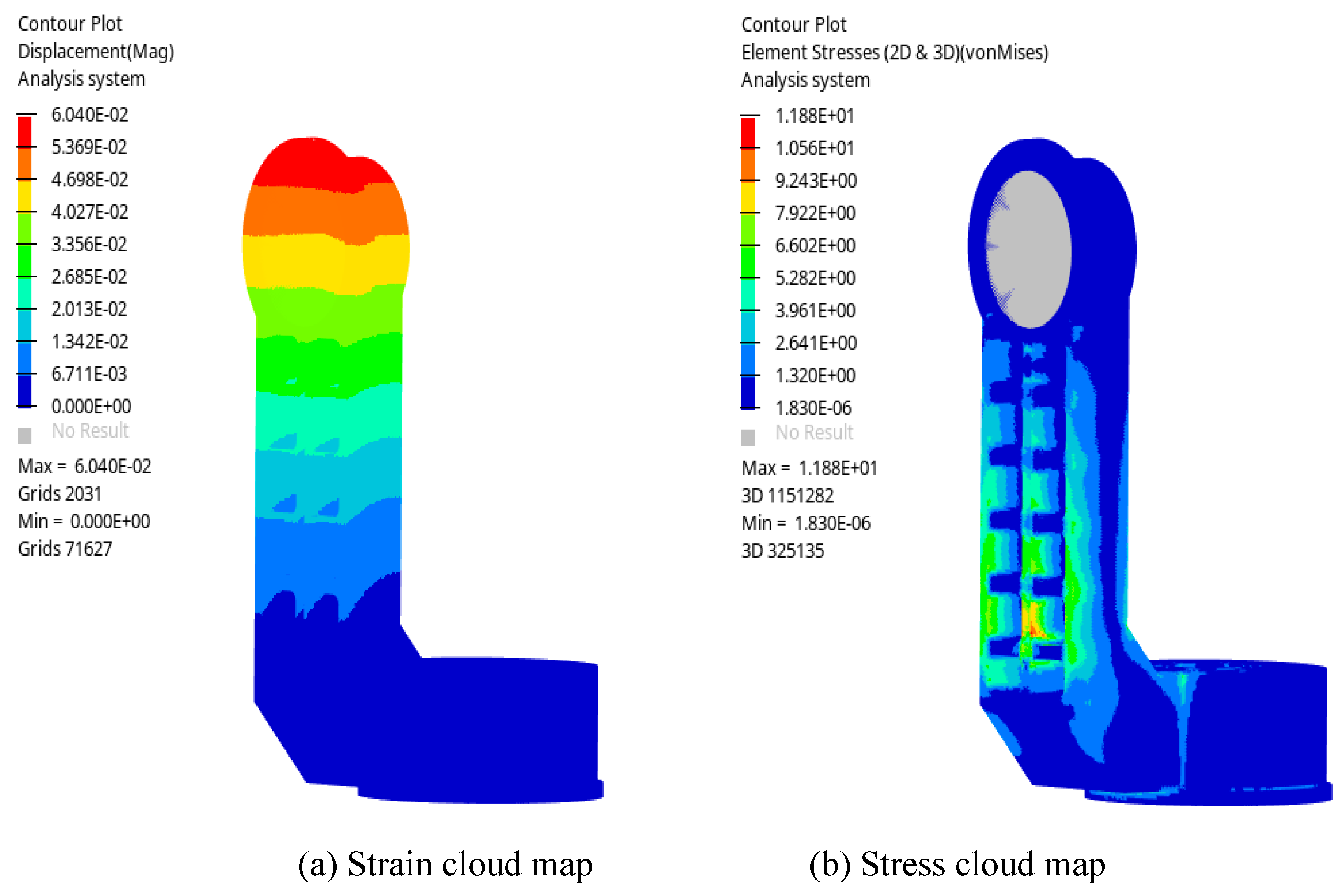
4.3. Static Analysis of the APTS’ Bracket Structure
5. Topology Design Optimization of the APTS’ Bracket Structure
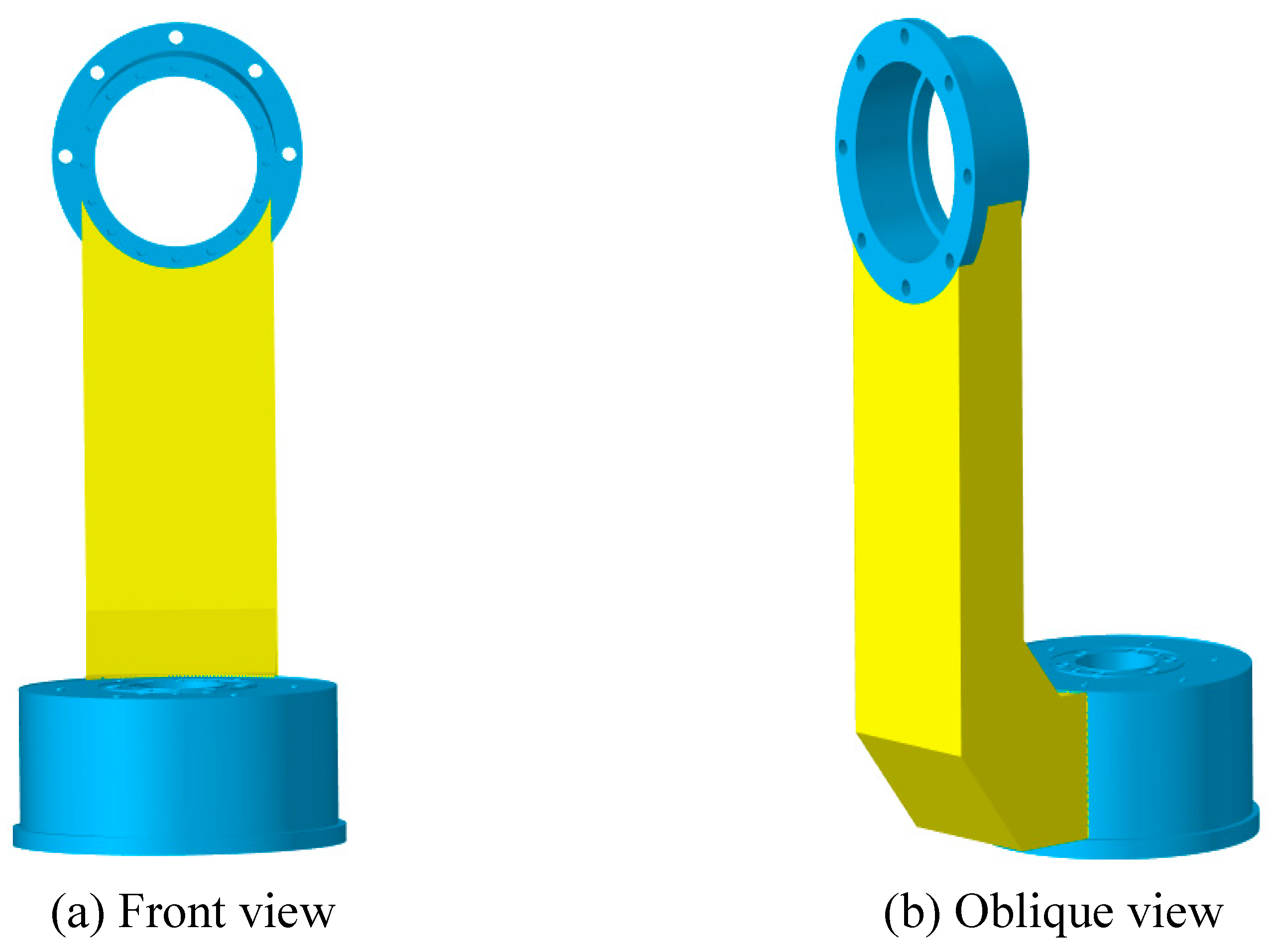
5.1. Preprocessing for the Geometric Model of the Support Structure
5.2. Boundary Conditions and Loading Application for the Support Structure
5.3. Manufacturing Constraints for the Topology Optimization of the Support Structure
6. Numerical Examples and Discussion of Results
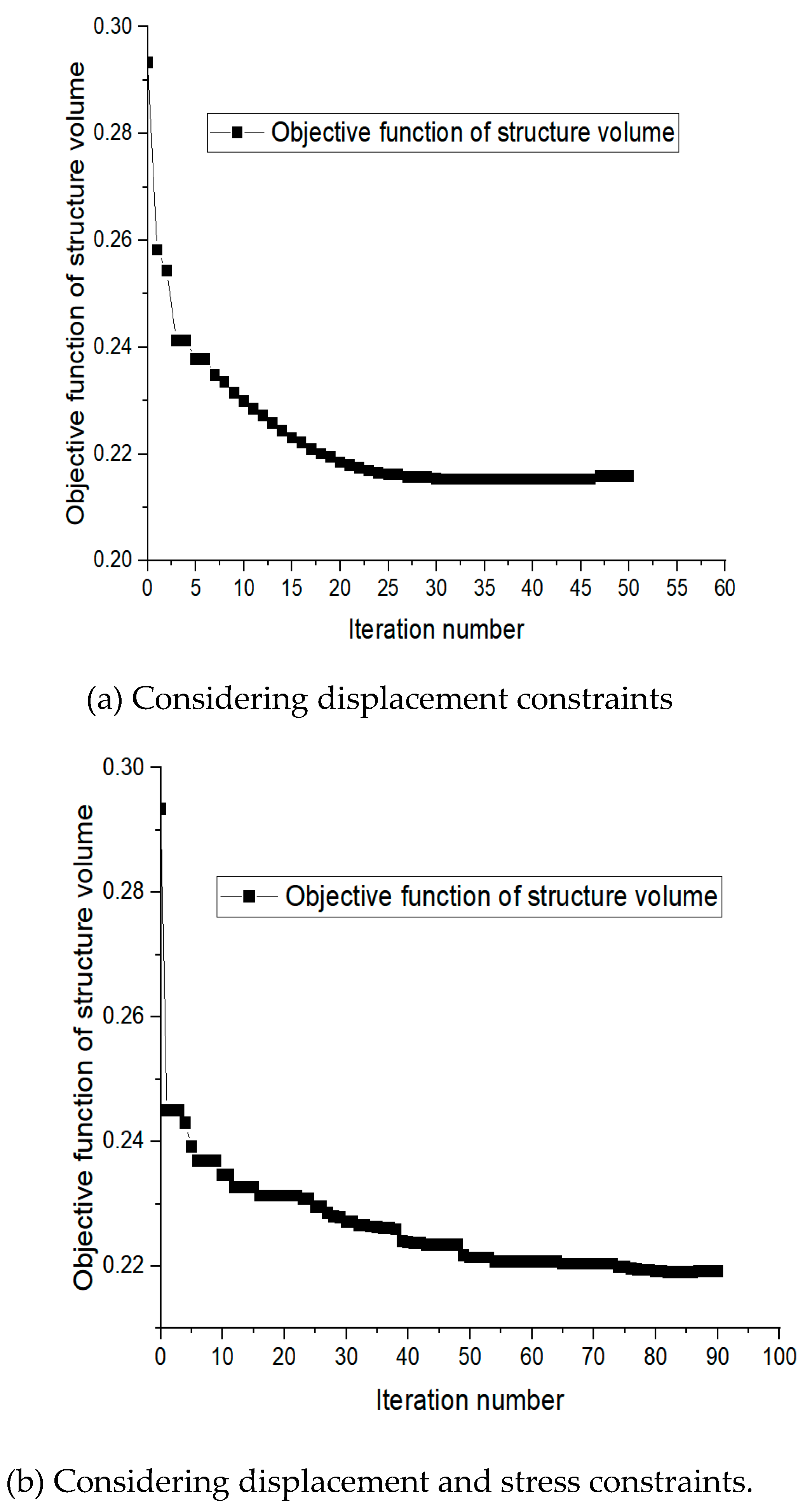
6.1. Topology Optimization Results Considering Displacement and Stress Constraints
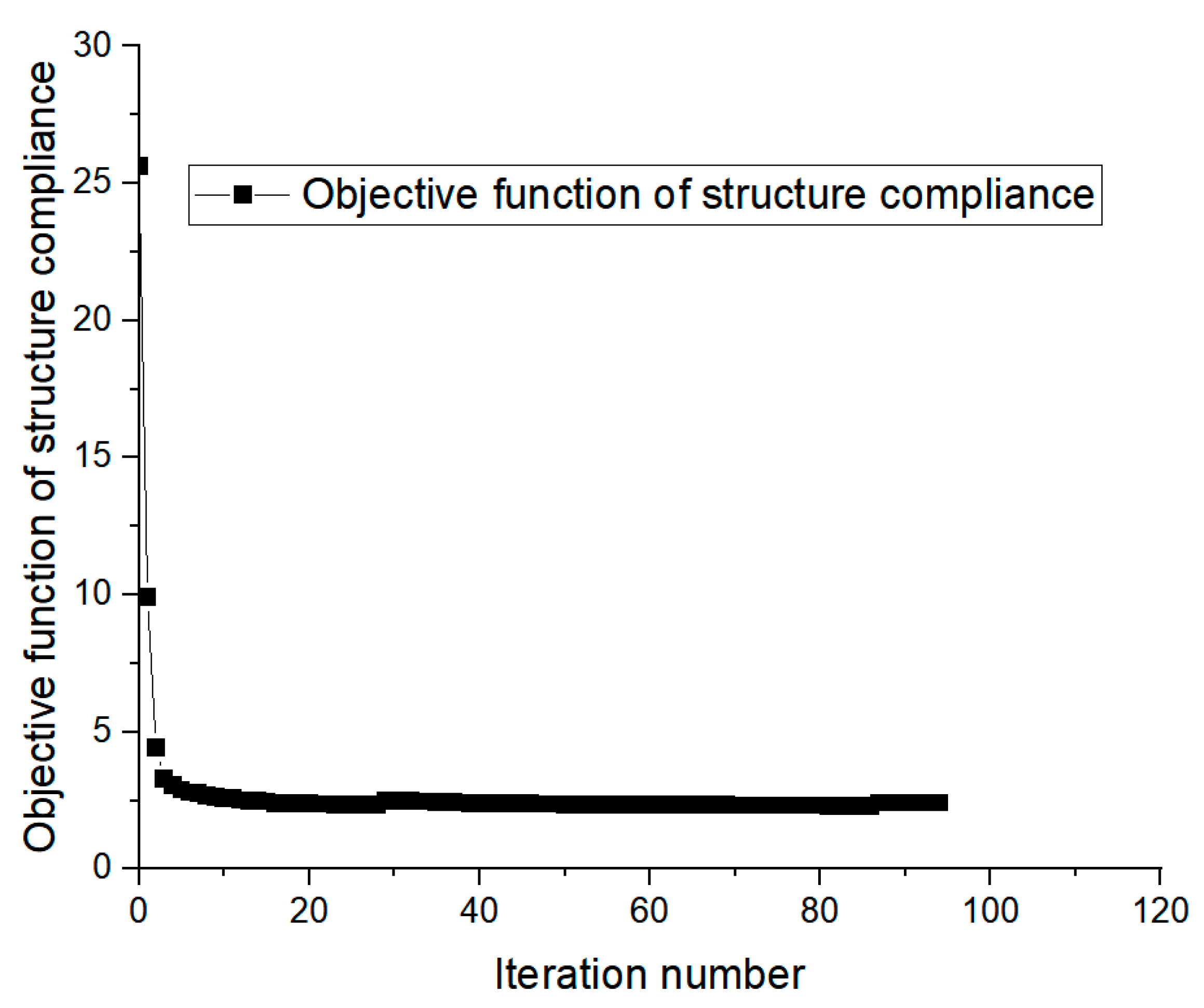
6.2. Topology Optimization Results for Minimizing Compliance Considering Volume Fraction Constraints
6.3. Topology Optimization Structure Smoothing for the Support Structure
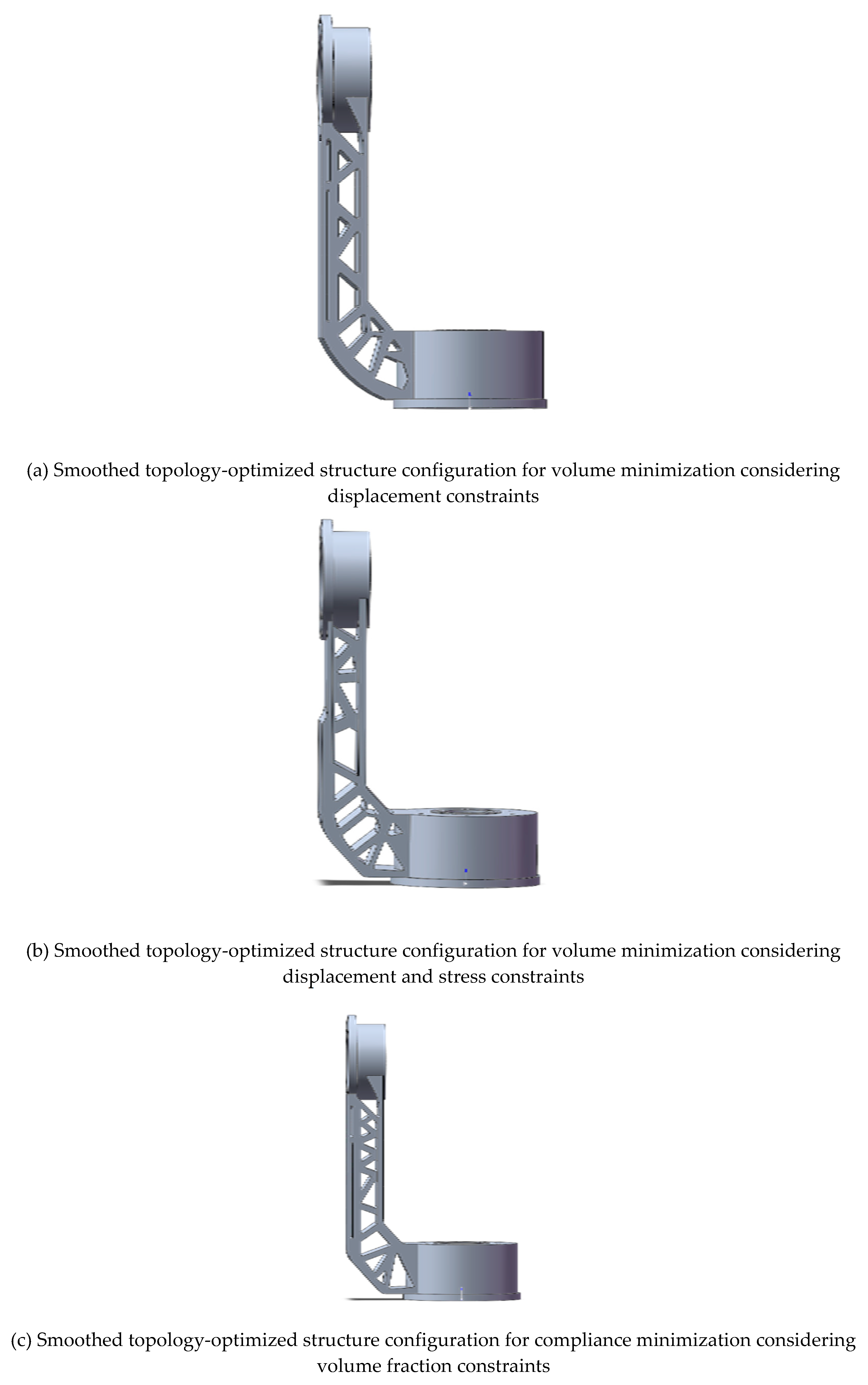
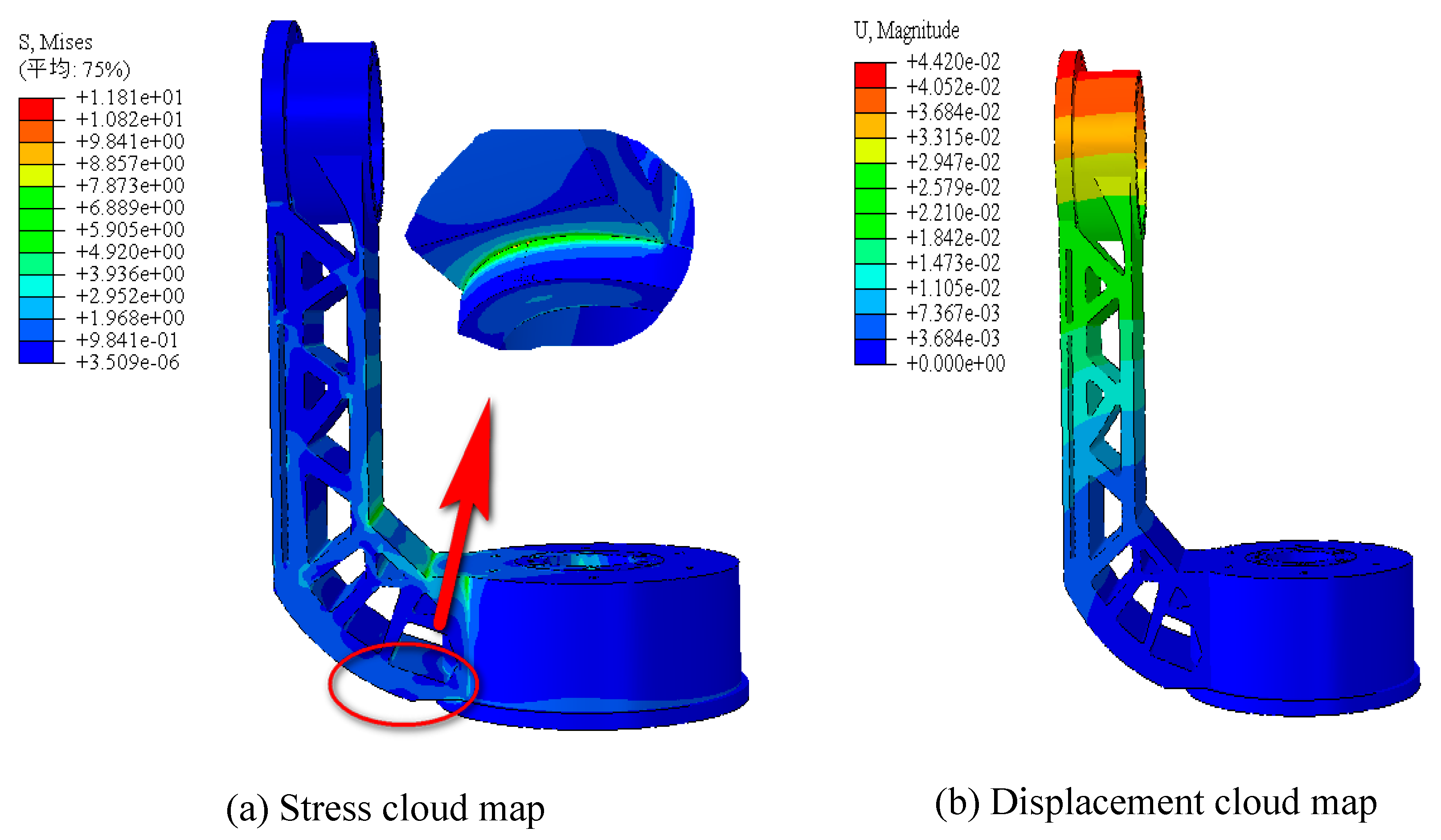
6.4. Verification of the strength and stiffness of the optimized structure
7. Conclusion
- Volume Minimization with Displacement Constraints:
- 2.
- Volume Minimization with Displacement and Stress Constraints:
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bendsøe MP. Topology design of structures, materials and mechanisms—status and perspectives.IFIP Conference on System Modeling and Optimization. Boston, MA: Springer US, 1999; 1-17.
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, W.; Beckers, P.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Z. Simultaneous design of components layout and supporting structures using coupled shape and topology optimization technique. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2008, 36, 29–41, . [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fan, J.; Long, K.; Xu, B.; Zhu, J.; Yan, J. Concurrent multi-material and multi-scale design optimization of fiber-reinforced composite material and structures for minimum structural compliance. Compos. Struct. 2023, 311, . [CrossRef]
- Ho TH, Milner SD, Davis CC. Pointing, acquisition, and tracking system with omnivision.Free-Space Laser Communications V. SPIE, 2005; 5892: 420-431.
- Kaushal H, Jain VK, Kar S, Kaushal H, Jain VK, Kar S. Acquisition, tracking, and pointing. Free Space Optical Communication, 2017; 119-137.
- Cheng KT, Olhoff N. An investigation concerning optimal design of solid elastic plates. International Journal of Solids and Structures 1981; 17(3): 305-323.
- Bendsøe, M.P.; Kikuchi, N. Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1988, 71, 197–224, . [CrossRef]
- Xie YM, Steven GP. Optimal design of multiple load case structures using an evolutionaryprocedure. Engineering computations, 1994; 11(4): 295-302.
- Allaire, G.; Jouve, F.; Toader, A.-M. Structural optimization using sensitivity analysis and a level-set method. J. Comput. Phys. 2004, 194, 363–393, . [CrossRef]
- Díaaz, A.R.; Kikuchi, N. Solutions to shape and topology eigenvalue optimization problems using a homogenization method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1992, 35, 1487–1502, . [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Kikuchi, N. A homogenization method for shape and topology optimization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1991, 93, 291–318, . [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. Minimum length scale control in structural topology optimization based on the Moving Morphable Components (MMC) approach. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2016, 311, 327–355, . [CrossRef]
- Rozvany G. The SIMP method in topology optimization-theoretical background, advantages and new applications.8th Symposium on Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization. 2000; 4738.
- Zuo, W.; Saitou, K. Multi-material topology optimization using ordered SIMP interpolation. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2016, 55, 477–491, . [CrossRef]
- Norato J, Haber R, Tortorelli D, Bendsøe MP. A geometry projection method for shape optimization. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2004; 60(14): 2289-2312.
- Guo, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, J. Explicit structural topology optimization based on moving morphable components (MMC) with curved skeletons. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2016, 310, 711–748, . [CrossRef]
- Hoang, V.-N.; Jang, G.-W. Topology optimization using moving morphable bars for versatile thickness control. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 317, 153–173, . [CrossRef]
- Coniglio, S.; Morlier, J.; Gogu, C.; Amargier, R. Generalized Geometry Projection: A Unified Approach for Geometric Feature Based Topology Optimization. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2019, 27, 1573–1610, . [CrossRef]
- París, J.; Martínez, S.; Navarrina, F.; Colominas, I.; Casteleiro, M. Topology optimization of aeronautical structures with stress constraints: general methodology and applications. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G: J. Aerosp. Eng. 2011, 226, 589–600, . [CrossRef]
- López, C.; Baldomir, A.; Hernández, S. Deterministic versus reliability-based topology optimization of aeronautical structures. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2015, 53, 907–921, . [CrossRef]
- Berrocal, L.; Fernández, R.; González, S.; Periñán, A.; Tudela, S.; Vilanova, J.; Rubio, L.; Márquez, J.M.M.; Guerrero, J.; Lasagni, F. Topology optimization and additive manufacturing for aerospace components. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 4, 83–95, . [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, O. Topology optimization: a tool for the tailoring of structures and materials. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A: Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2000, 358, 211–227, . [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, C.; Zhou, L.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, W. A review of topology optimization for additive manufacturing: Status and challenges. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2020, 34, 91–110, . [CrossRef]
- Meng L, Zhang W, Quan D, Shi G, Tang L, Hou Y, Gao T. From topology optimization design to additive manufacturing: Today’s success and tomorrow’s roadmap[J]. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2020; 27: 805-830.
- Sigmund O, Maute K. Topology optimization approaches: A comparative review. Structural and multidisciplinary optimization, 2013; 48(6): 1031-1055.
- A Eschenauer, H.; Olhoff, N. Topology optimization of continuum structures: A review*. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2001, 54, 331–390, . [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Sigmund, O.; Groen, J.P. Topology optimization of multi-scale structures: a review. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2021, 63, 1455–1480, . [CrossRef]
- Bendsøe, M.P.; Sigmund, O. Material interpolation schemes in topology optimization. Arch. Appl. Mech. 1999, 69, 635–654, . [CrossRef]
- Stolpe, M.; Svanberg, K. An alternative interpolation scheme for minimum compliance topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2001, 22, 116–124, . [CrossRef]

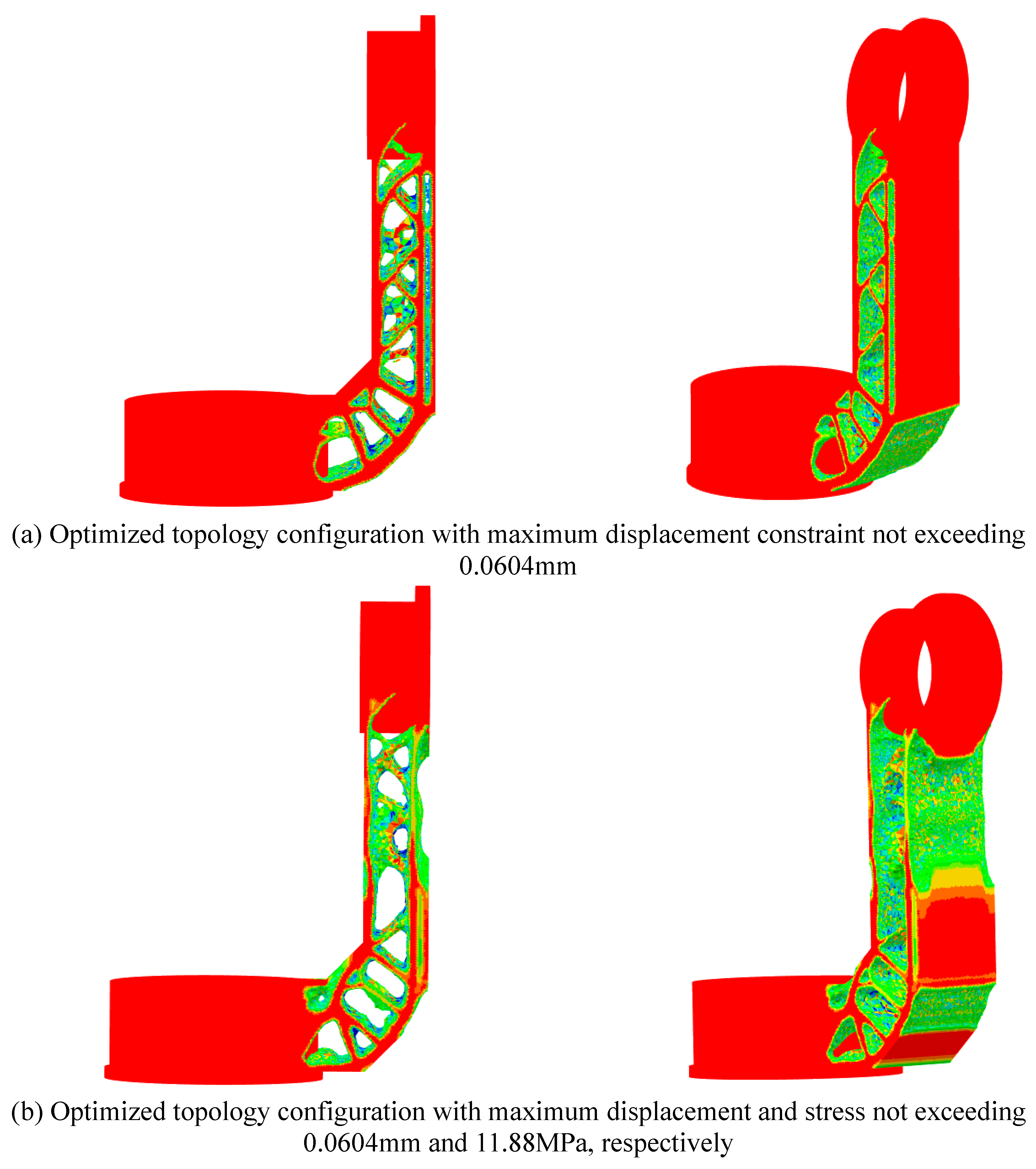
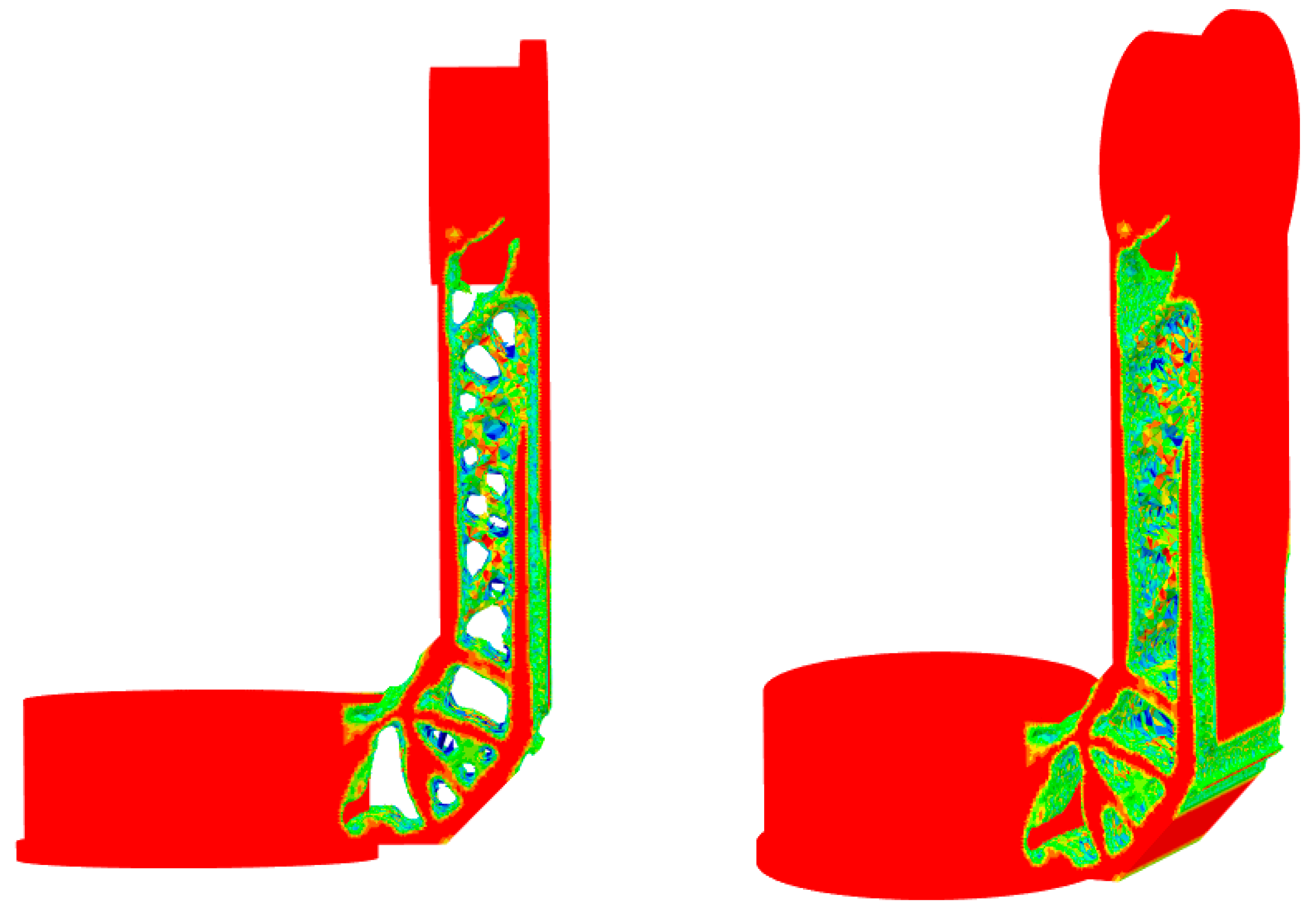
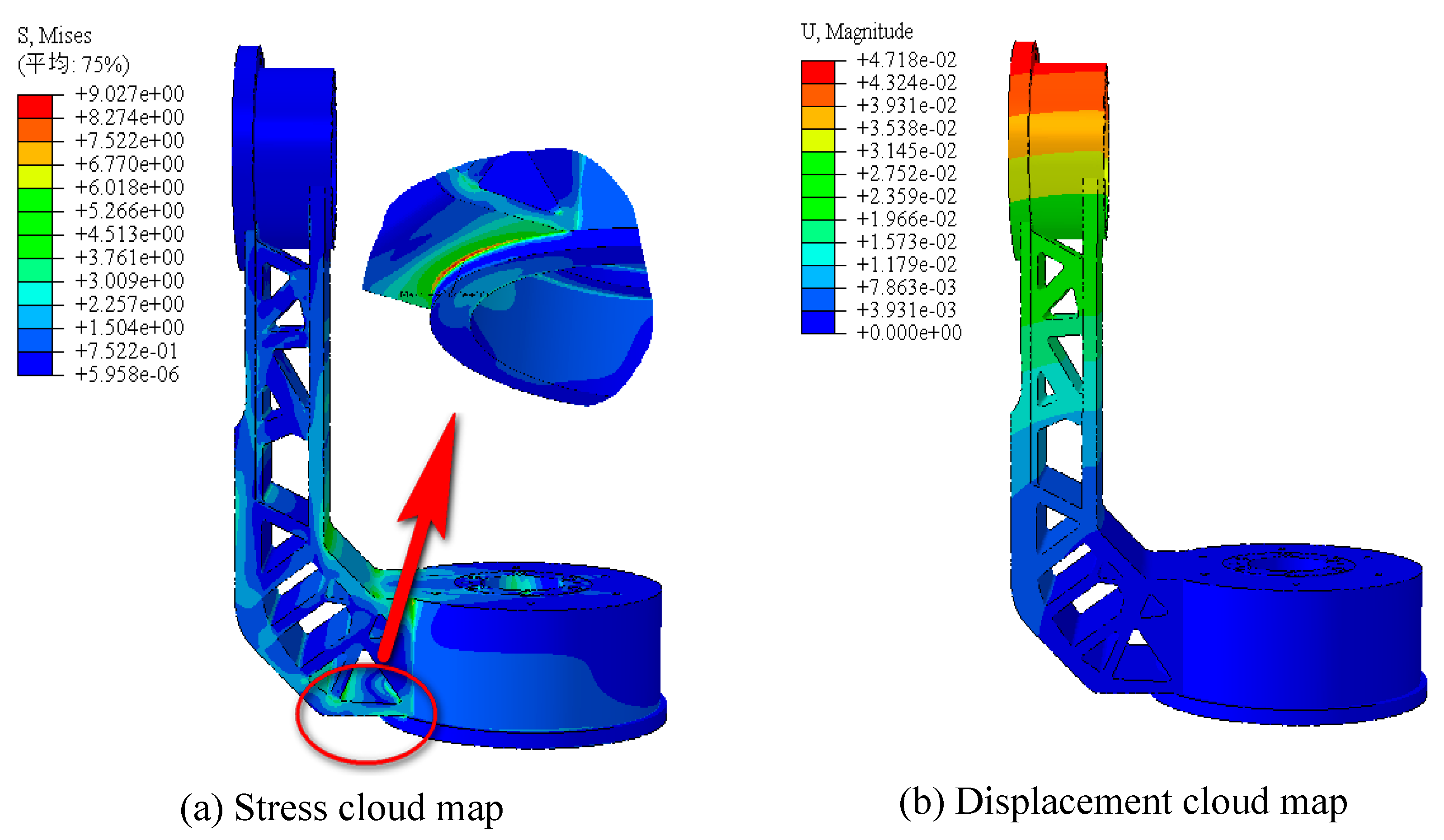
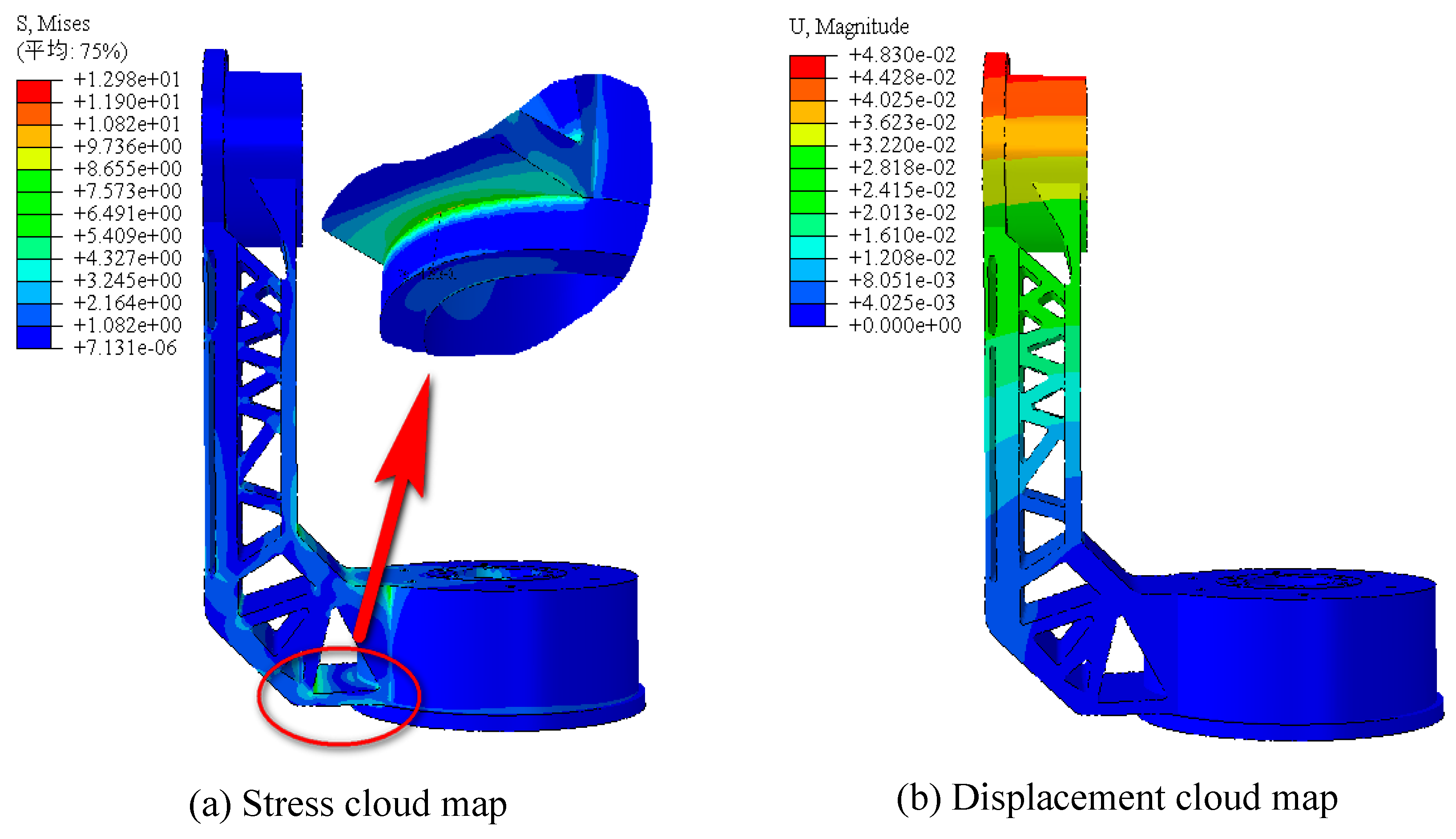
| Objective function | Maximum displacement/mm | Maximum von Mises stress/MPa | Weight/kg |
| Minimize volume (with displacement constraints) | 0.04420 | 11.81 | 0.648 |
| Minimize volume (with displacement and stress constraints) | 0.04718 | 9.027 | 0.635 |
| Minimize compliance | 0.04830 | 12.98 | 0.655 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





