Submitted:
17 October 2024
Posted:
18 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Method
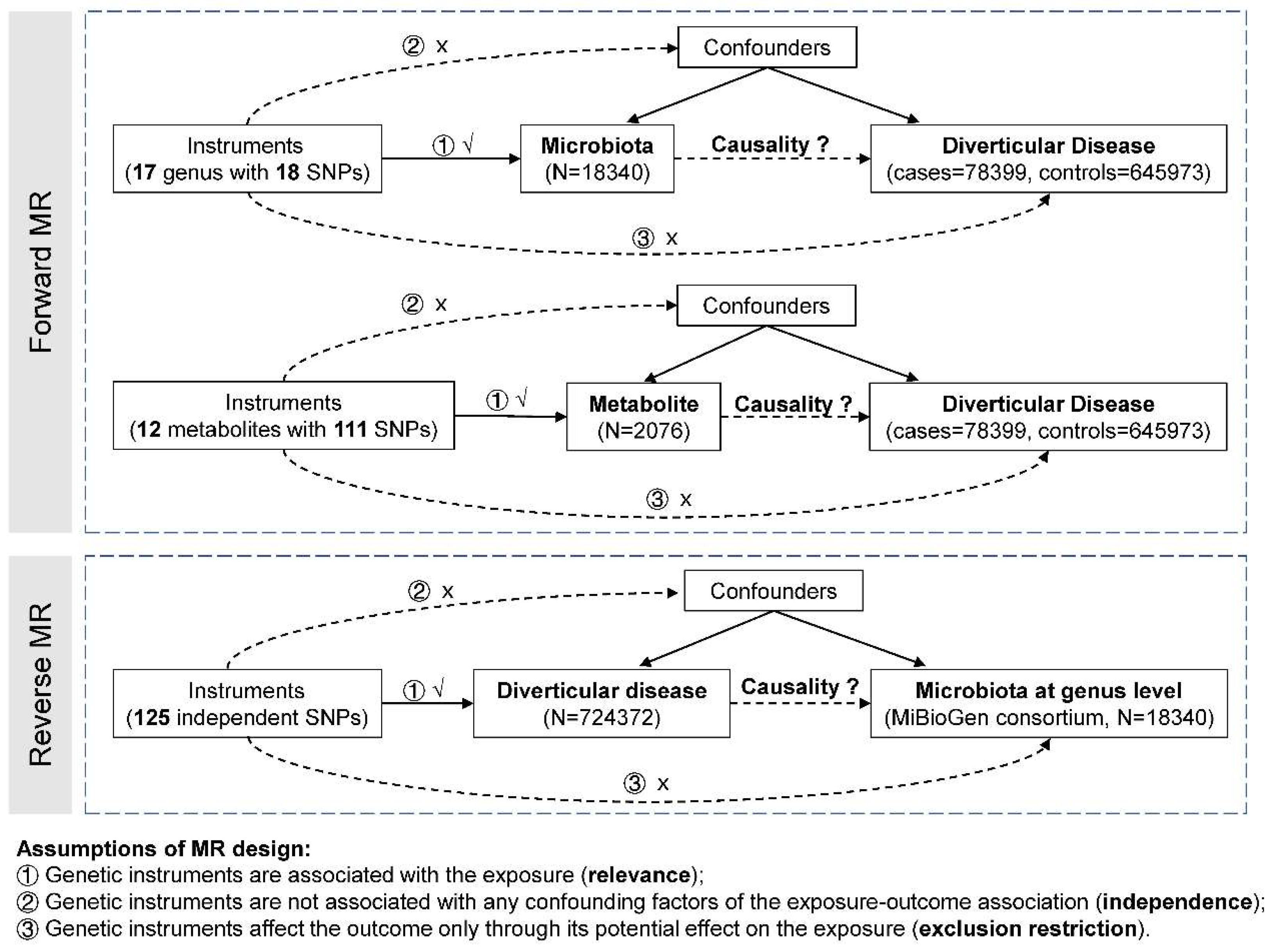
Study Design
Summary Statistics and Instrumental Variants Selection for Gut Microbiota
Instrumental Variants Selection for Metabolites
Summary Statistics and Instrumental Variants Selection for Diverticular Disease
Statistical Analysis
Results
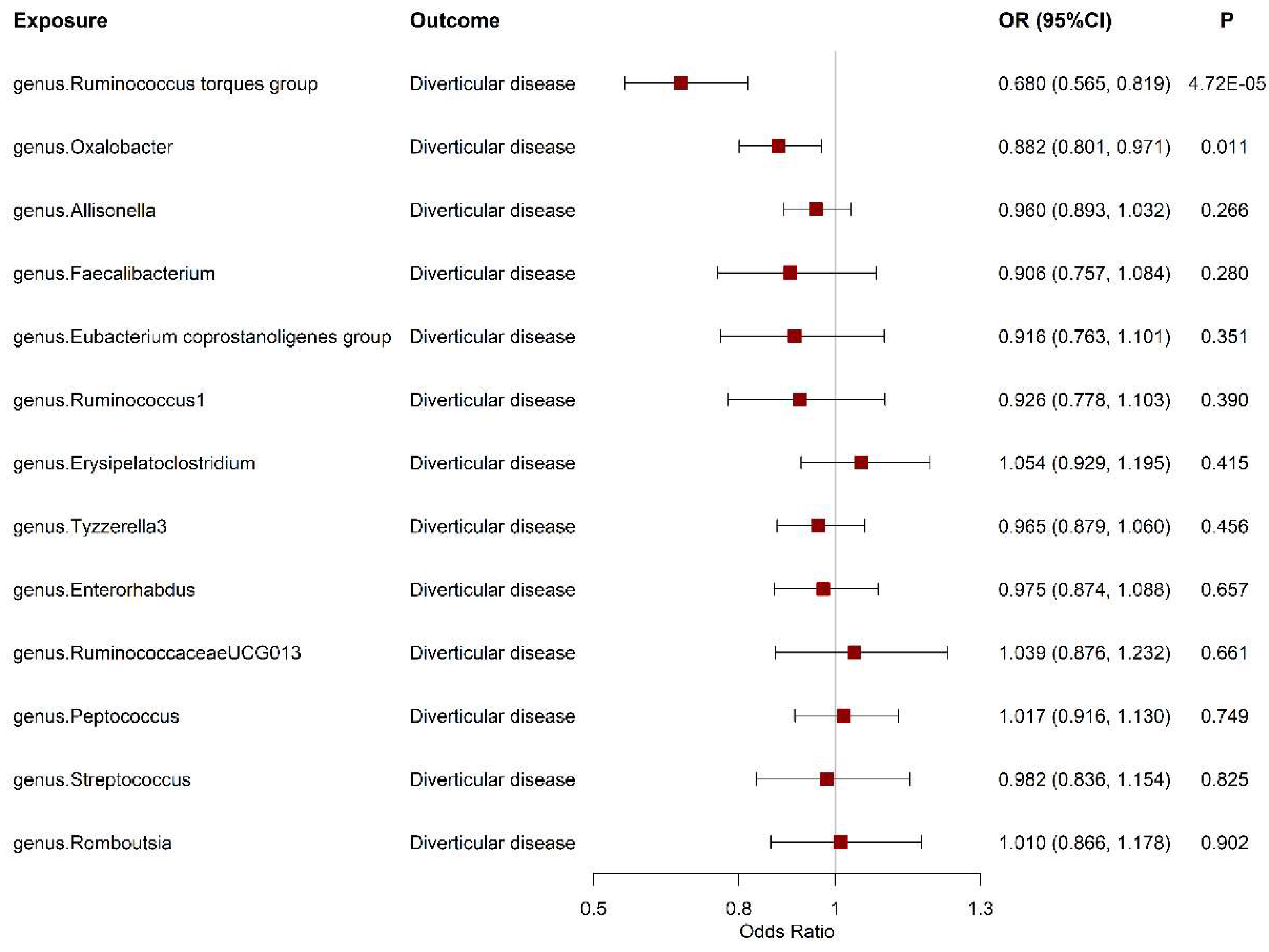
The Association between Gut Microbiota and Diverticular Disease Risk
The Association between Circulating Metabolite Level and Diverticular Disease Risk
The Effect of Diverticular Disease on Gut Microbiome
Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Consent for Publicatio
Availability of Data and Materials
Acknowledgments
Competing Interests
List of Abbreviations
References
- Fedirko V, Kopetz S, Daniel CR. Diverticular disease and cancer risk: More than a gut feeling. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2023;115(1):12-3. [CrossRef]
- Weizman AV, Nguyen GC. Diverticular disease: epidemiology and management. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011;25(7):385-9. [CrossRef]
- Etzioni DA, Mack TM, Beart RW, Jr., Kaiser AM. Diverticulitis in the United States: 1998-2005: changing patterns of disease and treatment. Ann Surg. 2009;249(2):210-7. [CrossRef]
- Sandler RS, Everhart JE, Donowitz M, Adams E, Cronin K, Goodman C, et al. The burden of selected digestive diseases in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2002;122(5):1500-11. [CrossRef]
- Tursi A, Scarpignato C, Strate LL, Lanas A, Kruis W, Lahat A, et al. Colonic diverticular disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020;6(1):20. [CrossRef]
- Barbara G, Scaioli E, Barbaro MR, Biagi E, Laghi L, Cremon C, et al. Gut microbiota, metabolome and immune signatures in patients with uncomplicated diverticular disease. Gut. 2017;66(7):1252-61. Epub 2016 Sep 12. [CrossRef]
- Lopetuso LR, Petito V, Graziani C, Schiavoni E, Paroni Sterbini F, Poscia A, et al. Gut Microbiota in Health, Diverticular Disease, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Time for Microbial Marker of Gastrointestinal Disorders. Dig Dis. 2018;36(1):56-65. Epub 2017 Jul 7. [CrossRef]
- Tursi A, Mastromarino P, Capobianco D, Elisei W, Miccheli A, Capuani G, et al. Assessment of Fecal Microbiota and Fecal Metabolome in Symptomatic Uncomplicated Diverticular Disease of the Colon. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;50(Suppl 1):S9-S12. doi: 0.1097/MCG.0000000000000626.
- Jones RB, Fodor AA, Peery AF, Tsilimigras MCB, Winglee K, McCoy A, et al. An Aberrant Microbiota is not Strongly Associated with Incidental Colonic Diverticulosis. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):4951. [CrossRef]
- Smith GD, Ebrahim S. ‘Mendelian randomization’: can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease? Int J Epidemiol. 2003;32(1):1-22. [CrossRef]
- Davey Smith G, Hemani G. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(R1):R89-98. Epub 2014 Jul 4. [CrossRef]
- Kurilshikov A, Medina-Gomez C, Bacigalupe R, Radjabzadeh D, Wang J, Demirkan A, et al. Large-scale association analyses identify host factors influencing human gut microbiome composition. Nat Genet. 2021;53(2):156-65. Epub 2021 Jan 18. [CrossRef]
- Clarke L, Zheng-Bradley X, Smith R, Kulesha E, Xiao C, Toneva I, et al. The 1000 Genomes Project: data management and community access. Nat Methods. 2012;9(5):459-62. [CrossRef]
- Rhee EP, Ho JE, Chen MH, Shen D, Cheng S, Larson MG, et al. A genome-wide association study of the human metabolome in a community-based cohort. Cell Metab. 2013;18(1):130-43. [CrossRef]
- Lander E, Kruglyak L. Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat Genet. 1995;11(3):241-7. [CrossRef]
- Sanna S, van Zuydam NR, Mahajan A, Kurilshikov A, Vich Vila A, Võsa U, et al. Causal relationships among the gut microbiome, short-chain fatty acids and metabolic diseases. Nat Genet. 2019;51(4):600-5. Epub 2019 Feb 18. [CrossRef]
- Gagnon E, Mitchell PL, Manikpurage HD, Abner E, Taba N, Esko T, et al. Impact of the gut microbiota and associated metabolites on cardiometabolic traits, chronic diseases and human longevity: a Mendelian randomization study. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):60. [CrossRef]
- Liu X, Tong X, Zou Y, Lin X, Zhao H, Tian L, et al. Mendelian randomization analyses support causal relationships between blood metabolites and the gut microbiome. Nat Genet. 2022;54(1):52-61. Epub 2022 Jan 3. [CrossRef]
- Wu Y, Goleva SB, Breidenbach LB, Kim M, MacGregor S, Gandal MJ, et al. 150 risk variants for diverticular disease of intestine prioritize cell types and enable polygenic prediction of disease susceptibility. Cell Genom. 2023;3(7):100326. eCollection 2023 Jul 12. [CrossRef]
- Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Burgess S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-25. Epub 2015 Jun 6. [CrossRef]
- Burgess S, Bowden J, Fall T, Ingelsson E, Thompson SG. Sensitivity Analyses for Robust Causal Inference from Mendelian Randomization Analyses with Multiple Genetic Variants. Epidemiology. 2017;28(1):30-42. [CrossRef]
- Verbanck M, Chen CY, Neale B, Do R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet. 2018;50(5):693-8. Epub 2018 Apr 23. [CrossRef]
- Mj O, Turner GA, A S, Frizelle FA, R P. Distinct changes in the colonic microbiome associated with acute diverticulitis. Colorectal Dis. 2022;24(12):1591-601. Epub 2022 Aug 11. [CrossRef]
- Hansen SG, Skov MN, Justesen US. Two cases of Ruminococcus gnavus bacteremia associated with diverticulitis. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51(4):1334-6. Epub 2013 Jan 30. [CrossRef]
- Kvasnovsky CL, Leong LEX, Choo JM, Abell GCJ, Papagrigoriadis S, Bruce KD, et al. Clinical and symptom scores are significantly correlated with fecal microbiota features in patients with symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease: a pilot study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;30(1):107-12. [CrossRef]
- Togo AH, Diop A, Bittar F, Maraninchi M, Valero R, Armstrong N, et al. Description of Mediterraneibacter massiliensis, gen. nov., sp. nov., a new genus isolated from the gut microbiota of an obese patient and reclassification of Ruminococcus faecis, Ruminococcus lactaris, Ruminococcus torques, Ruminococcus gnavus and Clostridium glycyrrhizinilyticum as Mediterraneibacter faecis comb. nov., Mediterraneibacter lactaris comb. nov., Mediterraneibacter torques comb. nov., Mediterraneibacter gnavus comb. nov. and Mediterraneibacter glycyrrhizinilyticus comb. nov. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2018;111(11):2107-28. Epub 2018 May 31. [CrossRef]
- Liu C, Finegold SM, Song Y, Lawson PA. Reclassification of Clostridium coccoides, Ruminococcus hansenii, Ruminococcus hydrogenotrophicus, Ruminococcus luti, Ruminococcus productus and Ruminococcus schinkii as Blautia coccoides gen. nov., comb. nov., Blautia hansenii comb. nov., Blautia hydrogenotrophica comb. nov., Blautia luti comb. nov., Blautia producta comb. nov., Blautia schinkii comb. nov. and description of Blautia wexlerae sp. nov., isolated from human faeces. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2008;58(Pt 8):1896-902. [CrossRef]
- Ze X, Duncan SH, Louis P, Flint HJ. Ruminococcus bromii is a keystone species for the degradation of resistant starch in the human colon. ISME J. 2012;6(8):1535-43. Epub Feb 16. [CrossRef]
- Kelly CJ, Zheng L, Campbell EL, Saeedi B, Scholz CC, Bayless AJ, et al. Crosstalk between Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Intestinal Epithelial HIF Augments Tissue Barrier Function. Cell Host Microbe. 2015;17(5):662-71. Epub Apr 9. [CrossRef]
- Kim MH, Kang SG, Park JH, Yanagisawa M, Kim CH. Short-chain fatty acids activate GPR41 and GPR43 on intestinal epithelial cells to promote inflammatory responses in mice. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(2):396-406.e1-10. Epub May 7. [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gallausiaux C, Marinelli L, Blottière HM, Larraufie P, Lapaque N. SCFA: mechanisms and functional importance in the gut. Proc Nutr Soc. 2021;80(1):37-49. Epub 2020 Apr 2. [CrossRef]
- Dawson KA, Allison MJ, Hartman PA. Isolation and some characteristics of anaerobic oxalate-degrading bacteria from the rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980;40(4):833-9. [CrossRef]
- Liu M, Zhang Y, Wu J, Gao M, Zhu Z, Chen H. Causal relationship between kidney stones and gut microbiota contributes to the gut-kidney axis: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Microbiol. 2023;14:1204311. eCollection 2023. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Zhang X, Chen D, Lu J, Gong Q, Fang J, et al. Causal associations between gut microbiome and cardiovascular disease: A Mendelian randomization study. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:971376. eCollection 2022. [CrossRef]
- Cao J, Wang N, Luo Y, Ma C, Chen Z, Chenzhao C, et al. A cause-effect relationship between Graves’ disease and the gut microbiome contributes to the thyroid-gut axis: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol. 2023;14:977587. eCollection 2023. [CrossRef]
- Liu B, Ye D, Yang H, Song J, Sun X, Mao Y, et al. Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analysis Investigates Causal Associations Between Gut Microbial Genera and Inflammatory Bowel Disease, and Specificity Causal Associations in Ulcerative Colitis or Crohn’s Disease. Front Immunol. 2022;13:921546. eCollection 2022. [CrossRef]
| Exposure or Outcome | Participants Included in Analysis | Adjustments | Number of genetic instruments | PubMed ID and/ or URL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gut microbiota taxa | 18340 European-descent individuals | Age and any necessary study-specific covariates | 18 SNPs for 17 gut microbiota taxa | 33462485 https://mibiogen.gcc.rug.nl/ |
| Gut microbial metabolites | 2076 European-descent individuals | Age, sex | 111 SNPs for 12 gut microbial metabolites | 23823483 |
| Diverticular disease | 78399 cases and 645973 controls of European ancestry | sex, age, and genetic principal components | 125 | 37492107 |
| Exposure | Outcome | Method | Nsnp | OR | LCI | UCI | pval | P_heterogeneity | P_intercept |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Betaine | DD | MR Egger | 12 | 1.01 | 0.98 | 1.04 | 0.389 | 0.436 | |
| Weighted median | 12 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.03 | 0.310 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 12 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 0.692 | 0.721 | |||
| Simple mode | 12 | 1.01 | 0.98 | 1.04 | 0.521 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 12 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.03 | 0.375 | ||||
| Choline | DD | MR Egger | 6 | 0.97 | 0.86 | 1.11 | 0.697 | 0.447 | |
| Weighted median | 6 | 1.01 | 0.97 | 1.04 | 0.655 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 6 | 1.03 | 0.99 | 1.06 | 0.185 | 0.058 | |||
| Simple mode | 6 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 1.04 | 0.902 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 6 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 1.04 | 0.897 | ||||
| Serotonin | DD | MR Egger | 7 | 1.02 | 0.86 | 1.20 | 0.840 | 0.870 | |
| Weighted median | 7 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 1.04 | 0.829 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 7 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.03 | 0.779 | 0.604 | |||
| Simple mode | 7 | 1.01 | 0.96 | 1.07 | 0.700 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 7 | 1.01 | 0.96 | 1.06 | 0.744 | ||||
| Propionic acid | DD | Inverse variance weighted | 2 | 1.01 | 0.98 | 1.05 | 0.443 | 0.425 | NA |
| Carnitine | DD | MR Egger | 11 | 1.03 | 0.99 | 1.06 | 0.168 | 0.270 | |
| Weighted median | 11 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 0.598 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 11 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 0.285 | 0.862 | |||
| Simple mode | 11 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 1.03 | 0.779 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 11 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.03 | 0.849 | ||||
| Indole 3 propionate | DD | MR Egger | 12 | 0.99 | 0.92 | 1.07 | 0.826 | 0.803 | |
| Weighted median | 12 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 1.02 | 0.787 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 12 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.02 | 0.919 | 0.366 | |||
| Simple mode | 12 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 1.03 | 0.574 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 12 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 1.03 | 0.641 | ||||
| Ribose 5-P and Ribulose 5-P | DD | MR Egger | 7 | 0.97 | 0.91 | 1.03 | 0.313 | 0.619 | |
| Weighted median | 7 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 1.02 | 0.506 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 7 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 1.01 | 0.136 | 0.154 | |||
| Simple mode | 7 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 1.02 | 0.629 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 7 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 1.02 | 0.552 | ||||
| Taurine | DD | MR Egger | 8 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.01 | 0.401 | 0.110 | |
| Weighted median | 8 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 0.559 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 8 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 0.358 | 0.370 | |||
| Simple mode | 8 | 1.02 | 0.98 | 1.06 | 0.291 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 8 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 0.708 | ||||
| Carnosine | DD | MR Egger | 13 | 1.02 | 0.99 | 1.06 | 0.218 | 0.154 | |
| Weighted median | 13 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.01 | 0.227 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 13 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.01 | 0.753 | 0.084 | |||
| Simple mode | 13 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 1.02 | 0.607 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 13 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 1.01 | 0.386 | ||||
| TMAO | DD | MR Egger | 8 | 0.97 | 0.90 | 1.04 | 0.435 | 0.471 | |
| Weighted median | 8 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 1.02 | 0.384 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 8 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.02 | 0.727 | 0.742 | |||
| Simple mode | 8 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 1.03 | 0.562 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 8 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 1.02 | 0.521 | ||||
| Niacinamide | DD | Inverse variance weighted | 2 | 1.01 | 0.97 | 1.05 | 0.682 | 0.300 | NA |
| Pantothenic acid | DD | MR Egger | 10 | 1.04 | 0.97 | 1.11 | 0.276 | 0.120 | |
| Weighted median | 10 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.102 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 10 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.098 | 0.324 | |||
| Simple mode | 10 | 0.97 | 0.92 | 1.01 | 0.158 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 10 | 0.97 | 0.93 | 1.01 | 0.211 |
| Exposure | Outcome | Method | nsnp | beta | se | pval | P_heterogeneity | P_intercept |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DD | Allisonella | MR Egger | 77 | 0.237 | 0.183 | 0.200 | 0.214 | |
| Weighted median | 77 | 0.025 | 0.106 | 0.815 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 77 | 0.023 | 0.067 | 0.733 | 0.556 | |||
| Simple mode | 77 | 0.096 | 0.220 | 0.665 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 77 | 0.012 | 0.159 | 0.942 | ||||
| DD | Enterorhabdus | MR Egger | 93 | -0.039 | 0.112 | 0.731 | 0.747 | |
| Weighted median | 93 | -0.033 | 0.064 | 0.605 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 93 | -0.005 | 0.041 | 0.902 | 0.410 | |||
| Simple mode | 93 | -0.037 | 0.130 | 0.776 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 93 | -0.030 | 0.094 | 0.751 | ||||
| DD | Erysipelatoclostridium | MR Egger | 93 | -0.055 | 0.118 | 0.645 | 0.615 | |
| Weighted median | 93 | 0.009 | 0.057 | 0.872 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 93 | 0.001 | 0.043 | 0.987 | 0.002 | |||
| Simple mode | 93 | 0.120 | 0.148 | 0.422 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 93 | 0.084 | 0.106 | 0.430 | ||||
| DD | Eubacteriumcoprostanoligenesgroup | MR Egger | 94 | -0.051 | 0.072 | 0.477 | 0.775 | |
| Weighted median | 94 | -0.055 | 0.041 | 0.184 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 94 | -0.032 | 0.026 | 0.224 | 0.577 | |||
| Simple mode | 94 | -0.050 | 0.091 | 0.581 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 94 | -0.061 | 0.068 | 0.370 | ||||
| DD | Faecalibacterium | MR Egger | 94 | -0.025 | 0.071 | 0.719 | 0.937 | |
| Weighted median | 94 | -0.024 | 0.041 | 0.565 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 94 | -0.020 | 0.026 | 0.435 | 0.697 | |||
| Simple mode | 94 | 0.007 | 0.094 | 0.937 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 94 | -0.008 | 0.066 | 0.904 | ||||
| DD | Oxalobacter | MR Egger | 92 | -0.023 | 0.143 | 0.870 | 0.728 | |
| Weighted median | 92 | 0.016 | 0.082 | 0.846 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 92 | 0.023 | 0.052 | 0.658 | 0.407 | |||
| Simple mode | 92 | -0.019 | 0.201 | 0.923 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 92 | 0.056 | 0.161 | 0.727 | ||||
| DD | Peptococcus | MR Egger | 93 | -0.028 | 0.127 | 0.827 | 0.944 | |
| Weighted median | 93 | 0.031 | 0.073 | 0.672 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 93 | -0.019 | 0.046 | 0.674 | 0.913 | |||
| Simple mode | 93 | 0.018 | 0.162 | 0.911 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 93 | 0.025 | 0.126 | 0.841 | ||||
| DD | Romboutsia | MR Egger | 94 | -0.134 | 0.085 | 0.119 | 0.247 | |
| Weighted median | 94 | -0.031 | 0.046 | 0.506 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 94 | -0.042 | 0.031 | 0.185 | 0.159 | |||
| Simple mode | 94 | 0.011 | 0.100 | 0.915 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 94 | 0.001 | 0.079 | 0.991 | ||||
| DD | RuminococcaceaeUCG013 | MR Egger | 94 | -0.054 | 0.073 | 0.466 | 0.531 | |
| Weighted median | 94 | -0.007 | 0.042 | 0.872 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 94 | -0.011 | 0.027 | 0.689 | 0.602 | |||
| Simple mode | 94 | -0.013 | 0.090 | 0.889 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 94 | -0.013 | 0.063 | 0.842 | ||||
| DD | Ruminococcus1 | MR Egger | 94 | -0.040 | 0.074 | 0.593 | 0.512 | |
| Weighted median | 94 | 0.029 | 0.042 | 0.480 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 94 | 0.006 | 0.027 | 0.836 | 0.677 | |||
| Simple mode | 94 | 0.027 | 0.091 | 0.769 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 94 | 0.044 | 0.073 | 0.548 | ||||
| DD | Ruminococcustorquesgroup | MR Egger | 94 | -0.014 | 0.071 | 0.839 | 0.860 | |
| Weighted median | 94 | -0.015 | 0.039 | 0.711 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 94 | -0.003 | 0.026 | 0.917 | 0.625 | |||
| Simple mode | 94 | -0.049 | 0.081 | 0.546 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 94 | 0.009 | 0.064 | 0.883 | ||||
| DD | Streptococcus | MR Egger | 94 | -0.016 | 0.074 | 0.834 | 0.771 | |
| Weighted median | 94 | -0.005 | 0.044 | 0.907 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 94 | -0.036 | 0.027 | 0.190 | 0.612 | |||
| Simple mode | 94 | -0.011 | 0.103 | 0.917 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 94 | -0.020 | 0.064 | 0.758 | ||||
| DD | Tyzzerella3 | MR Egger | 93 | 0.315 | 0.138 | 0.025 | 0.056 | |
| Weighted median | 93 | 0.050 | 0.077 | 0.516 | ||||
| Inverse variance weighted | 93 | 0.067 | 0.051 | 0.190 | 0.146 | |||
| Simple mode | 93 | 0.113 | 0.172 | 0.514 | ||||
| Weighted mode | 93 | 0.098 | 0.119 | 0.410 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




