Submitted:
14 October 2024
Posted:
16 October 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Traditional Paradigm
2.1. Pro-Oxidants and Antioxidants
2.2. Excitotoxicity and Neuroprotection
2.2.1. Excitotoxicity
2.2.2. Neuroprotection
3. Emerging Evidence
3.1. Pro-Oxidants or Antioxidants?
3.2. Receptor Agonists or Antagonists?
3.3. Immunomodulators
3.4. The Body-Brain Axes
3.4.1. The Gut-Brain Axis
3.4.2. The Muscle-Brain Axis
3.4.3. Other Axes
4. Paradigm Shift
4.1. Molecule-Molecule Interactions
4.2. Molecule-Neural Transmission Interactions
4.3. Molecule-Immune System Interactions
4.4. Connecting to Systems Biology
4.5. Zero-Order Responses, Resilience Measurement, and Intolerance, Among Others
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | anthranilic acid |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| AhR | aryl hydrocarbon receptor |
| AMPA | alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid |
| ALS | amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| BBB | blood-brain barrier |
| BPF | Bisphenol F |
| CA | cinnabarinic acid |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| GPR35 | G-protein-coupled receptor 35 |
| 3-HAA | 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid |
| HD | Huntington’s disease |
| 3-HK | 3-hydroxykynurenine |
| IAA | indole-3-acetic acid |
| IAld | indole-3-aldehyde |
| IAM | indole-3-acetamide |
| IDO | indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase |
| ILA | indole-3-lactic acid |
| INS | indoxyl sulfate |
| IPA | indole-3-propionic acid |
| IPyA | indole-3-pyruvic acid |
| KATs | kynurenine aminotransferases |
| KYN | kynurenine |
| KYNA | kynurenic acid |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| mGluRs | metabotropic glutamate receptors |
| MS | multiple sclerosis |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| PA | picolinic acid |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| QUIN | quinolinic acid |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| TDO | tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase |
| Tregs | regulatory T cells |
| Trp | tryptophan |
| XA | xanthurenic acid |
References
- Török, N.; Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Searching for peripheral biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases: the tryptophan-kynurenine metabolic pathway. International journal of molecular sciences 2020, 21, 9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, A.; Ikeda, Y.; Yoshikawa, S.; Taniguchi, K.; Sawamura, H.; Morikawa, S.; Nakashima, M.; Asai, T.; Matsuda, S. The tryptophan and kynurenine pathway involved in the development of immune-related diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A.-B. Tryptophan metabolism and disposition in cancer biology and immunotherapy. Bioscience Reports 2022, 42, BSR20221682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Chang, R.; Zou, J.; Tan, S.; Huang, Z. The role and mechanism of tryptophan–kynurenine metabolic pathway in depression. Reviews in the Neurosciences 2023, 34, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutakhail, A.; Boulet, L.; Khabil, S.; Nazari, Q.A.; Hamid, H.; Coudoré, F. Neuropathology of kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism. Current pharmacology reports 2020, 6, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hestad, K.; Alexander, J.; Rootwelt, H.; Aaseth, J.O. The role of tryptophan dysmetabolism and quinolinic acid in depressive and neurodegenerative diseases. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolšak, A.; Gobec, S.; Sova, M. Indoleamine and tryptophan 2, 3-dioxygenases as important future therapeutic targets. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2021, 221, 107746. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, M.; Tóth, F.; Polyák, H.; Szabó, Á.; Mándi, Y.; Vécsei, L. Immune influencers in action: metabolites and enzymes of the tryptophan-kynurenine metabolic pathway. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gáspár, R.; Halmi, D.; Demján, V.; Berkecz, R.; Pipicz, M.; Csont, T. Kynurenine pathway metabolites as potential clinical biomarkers in coronary artery disease. Frontiers in Immunology 2022, 12, 768560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebnord, E.W.; Strand, E.; Midttun, Ø.; Svingen, G.F.; Christensen, M.H.; Ueland, P.M.; Mellgren, G.; Njølstad, P.R.; Tell, G.S.; Nygård, O.K. The kynurenine: tryptophan ratio as a predictor of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus in individuals with coronary artery disease. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-J.; Ching, J.; Wee, H.N.; Liu, S.; Gurung, R.L.; Lee, J.; Zheng, H.; Lee, L.S.; Ang, K.; Shao, Y.M. Plasma tryptophan-kynurenine pathway metabolites and risk for progression to end-stage kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes care 2023, 46, 2223–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basson, C.; Serem, J.C.; Hlophe, Y.N.; Bipath, P. The tryptophan–kynurenine pathway in immunomodulation and cancer metastasis. Cancer Medicine 2023, 12, 18691–18701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, A.; Murray, P.J. Tryptophan and indole metabolism in immune regulation. Current opinion in immunology 2021, 70, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Kuzhiumparambil, U.; Bandodkar, A.; Bandodkar, S.; Dale, R.C.; Fu, S. Cerebrospinal fluid metabolites in tryptophan-kynurenine and nitric oxide pathways: biomarkers for acute neuroinflammation. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2021, 63, 552–559. [Google Scholar]
- Mithaiwala, M.N.; Santana-Coelho, D.; Porter, G.A.; O’connor, J.C. Neuroinflammation and the kynurenine pathway in CNS disease: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Cells 2021, 10, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.S.; Azzolini, M.; Ruas, J.L. The kynurenine connection: How exercise shifts muscle tryptophan metabolism and affects energy homeostasis, the immune system, and the brain. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Portuguez, R.; Sutphin, G.L. Kynurenine pathway, NAD+ synthesis, and mitochondrial function: Targeting tryptophan metabolism to promote longevity and healthspan. Experimental gerontology 2020, 132, 110841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebig, J. Über Kynurensäure, Justus Liebig’s Ann. Chem 1853, 86, 125–126. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, F.G.; Cole, S.W. A contribution to the chemistry of proteids: Part I. A preliminary study of a hitherto undescribed product of tryptic digestion. The Journal of physiology 1901, 27, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, Z.; Yoshimatsu, N. Über eine neue Substanz, die aus Tryptophan im Tierkörper gebildet wird. 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupa, A.; Kowalska, I. The kynurenine pathway—new linkage between innate and adaptive immunity in autoimmune endocrinopathies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 9879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarcz, R.; Stone, T.W. The kynurenine pathway and the brain: Challenges, controversies and promises. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitz, J. The kynurenine pathway: a finger in every pie. Molecular psychiatry 2020, 25, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, A.; Tankiewicz-Kwedlo, A.; Krupa, A.; Pawlak, D. Role of kynurenine pathway in oxidative stress during neurodegenerative disorders. Cells 2021, 10, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ala, M. The footprint of kynurenine pathway in every cancer: a new target for chemotherapy. European Journal of Pharmacology 2021, 896, 173921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, W.; McGuinness, A.J.; Rocks, T.; Ruusunen, A.; Cleminson, J.; Walker, A.J.; Gomes-da-Costa, S.; Lane, M.; Sanches, M.; Diaz, A.P. The kynurenine pathway in major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of 101 studies. Molecular psychiatry 2021, 26, 4158–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo-Huitrón, R.; Blanco-Ayala, T.; Ugalde-Muñiz, P.; Carrillo-Mora, P.; Pedraza-Chaverrí, J.; Silva-Adaya, D.; Maldonado, P.; Torres, I.; Pinzón, E.; Ortiz-Islas, E. On the antioxidant properties of kynurenic acid: free radical scavenging activity and inhibition of oxidative stress. Neurotoxicology and teratology 2011, 33, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostapiuk, A.; Urbanska, E.M. Kynurenic acid in neurodegenerative disorders—Unique neuroprotection or double-edged sword? CNS neuroscience & therapeutics 2022, 28, 19–35. [Google Scholar]
- Leipnitz, G.; Schumacher, C.; Dalcin, K.B.; Scussiato, K.; Solano, A.; Funchal, C.; Dutra-Filho, C.S.; Wyse, A.T.; Wannmacher, C.M.; Latini, A. In vitro evidence for an antioxidant role of 3-hydroxykynurenine and 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid in the brain. Neurochemistry international 2007, 50, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, S.; Nishiyama, N.; Saito, H.; Katsuki, H. Hydrogen peroxide-mediated neuronal cell death induced by an endogenous neurotoxin, 3-hydroxykynurenine. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1996, 93, 12553–12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leipnitz, G.; Schumacher, C.; Scussiato, K.; Dalcin, K.B.; Wannmacher, C.M.; Wyse, A.T.; Dutra-Filho, C.S.; Wajner, M.; Latini, A. Quinolinic acid reduces the antioxidant defenses in cerebral cortex of young rats. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience 2005, 23, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Cruz, V.P.-D.; Carrillo-Mora, P.; Santamaría, A. Quinolinic acid, an endogenous molecule combining excitotoxicity, oxidative stress and other toxic mechanisms. International Journal of Tryptophan Research 2012, 5, IJTR–S8158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Bohár, Z.; Vécsei, L. Are kynurenines accomplices or principal villains in dementia? Maintenance of kynurenine metabolism. Molecules 2020, 25, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Monitoring the redox status in multiple sclerosis. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birner, A.; Platzer, M.; Bengesser, S.A.; Dalkner, N.; Fellendorf, F.T.; Queissner, R.; Pilz, R.; Rauch, P.; Maget, A.; Hamm, C. Increased breakdown of kynurenine towards its neurotoxic branch in bipolar disorder. PloS one 2017, 12, e0172699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.W.; Darlington, L.G.; Badawy, A.A.-B.; Williams, R.O. The Complex World of Kynurenic Acid: Reflections on Biological Issues and Therapeutic Strategy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colín-González, A.L.; Maldonado, P.D.; Santamaría, A. 3-Hydroxykynurenine: an intriguing molecule exerting dual actions in the central nervous system. Neurotoxicology 2013, 34, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rózsa, E.; Robotka, H.; Vécsei, L.; Toldi, J. The Janus-face kynurenic acid. Journal of neural transmission 2008, 115, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-González, A.; Alvarez-Idaboy, J.R.; Galano, A. Dual antioxidant/pro-oxidant behavior of the tryptophan metabolite 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid: A theoretical investigation of reaction mechanisms and kinetics. New Journal of Chemistry 2017, 41, 3829–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, F.G. Feeding experiments illustrating the importance of accessory factors in normal dietaries. J Physiol 1912, 44, 425–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaessens, S.; Stroobant, V.; De Plaen, E.; Van den Eynde, B.J. Systemic tryptophan homeostasis. Frontiers in molecular biosciences 2022, 9, 897929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leathwood, P.D. Tryptophan availability and serotonin synthesis. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 1987, 46, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewska, M.; Zajac, K.; Zemelka, M.; Szczepanik, M. Influence of melatonin and its precursor L-tryptophan on Th1 dependent contact hypersensitivity. J. Physiol. Pharmacol 2007, 58, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Oxenkrug, G. Insulin resistance and dysregulation of tryptophan–kynurenine and kynurenine–nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide metabolic pathways. Molecular neurobiology 2013, 48, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Cetina Biefer, H.; Vasudevan, A.; Elkhal, A. Aspects of tryptophan and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in immunity: A new twist in an old tale. International Journal of Tryptophan Research 2017, 10, 1178646917713491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondanelli, G.; Volpi, C. The double life of serotonin metabolites: in the mood for joining neuronal and immune systems. Current Opinion in Immunology 2021, 70, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseghi, S.; Arjmandi-Rad, S.; Nasehi, M.; Zarrindast, M.-R. Cannabinoids and sleep-wake cycle: the potential role of serotonin. Behavioural Brain Research 2021, 412, 113440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacqué-Cazenave, J.; Bharatiya, R.; Barrière, G.; Delbecque, J.-P.; Bouguiyoud, N.; Di Giovanni, G.; Cattaert, D.; De Deurwaerdère, P. Serotonin in animal cognition and behavior. International journal of molecular sciences 2020, 21, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Deurwaerdère, P.; Di Giovanni, G. Serotonin in health and disease. 2020, 21, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Liu, W.; Guan, J.; Cui, J.; Shi, R.; Wang, L.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y. Latest updates on the serotonergic system in depression and anxiety. Frontiers in Synaptic Neuroscience 2023, 15, 1124112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Li, G.; Zheng, Q.; Gu, X.; Shi, Q.; Su, Y.; Chu, Q.; Yuan, X.; Bao, Z.; Lu, J. Tryptophan metabolism in health and disease. Cell Metabolism 2023, 35, 1304–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, B.; Becker, K.; Fuchs, D.; Gostner, J.M. Kynurenine pathway metabolism and immune activation: Peripheral measurements in psychiatric and co-morbid conditions. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, E.; Welle, J.R.; Woolwine, B.J.; Goldsmith, D.R.; Baer, W.; Patel, T.; Felger, J.C.; Miller, A.H. Associations among peripheral and central kynurenine pathway metabolites and inflammation in depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, S.; Nadar, R.; Kim, S.; Liu, K.; Govindarajulu, M.; Cook, P.; Watts Alexander, C.S.; Dhanasekaran, M.; Moore, T. The influence of kynurenine metabolites on neurodegenerative pathologies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2024, 25, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giil, L.M.; Midttun, Ø.; Refsum, H.; Ulvik, A.; Advani, R.; Smith, A.D.; Ueland, P.M. Kynurenine pathway metabolites in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2017, 60, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Vakili, K.; Yaghoobpoor, S.; Tavasol, A.; Jazi, K.; Hajibeygi, R.; Shool, S.; Sodeifian, F.; Klegeris, A.; McElhinney, A. Dynamic changes in metabolites of the kynurenine pathway in Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease: A systematic Review and meta-analysis. Frontiers in Immunology 2022, 13, 997240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H.; Cheng, M.L.; Tang, H.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Wu, Y.R.; Chen, C.M. Alternations of Metabolic Profile and Kynurenine Metabolism in the Plasma of Parkinson’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol 2018, 55, 6319–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilman, P.L.; Wang, E.W.; Lewis, M.M.; Krzyzanowski, S.; Capan, C.D.; Burmeister, A.R.; Du, G.; Escobar Galvis, M.L.; Brundin, P.; Huang, X.; et al. Tryptophan Metabolites Are Associated With Symptoms and Nigral Pathology in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov Disord 2020, 35, 2028–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajsl, M.; Hlavackova, A.; Broulikova, K.; Sramek, M.; Maly, M.; Dyr, J.E.; Suttnar, J. Tryptophan Metabolism, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Neurovascular Disease. Metabolites 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hestad, K.; Alexander, J.; Rootwelt, H.; Aaseth, J.O. The Role of Tryptophan Dysmetabolism and Quinolinic Acid in Depressive and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomolecules 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, R.; Le, A.; Hong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, L.; Zang, W.; Jiang, C.; et al. Tryptophan Metabolism in Central Nervous System Diseases: Pathophysiology and Potential Therapeutic Strategies. Aging Dis 2023, 14, 858–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, A.; Tankiewicz-Kwedlo, A.; Krupa, A.; Pawlak, D. Role of Kynurenine Pathway in Oxidative Stress during Neurodegenerative Disorders. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Exploring the Etiological Links behind Neurodegenerative Diseases: Inflammatory Cytokines and Bioactive Kynurenines. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, C.L.; Guilarte, T.R. Cytotoxicity of 3-hydroxykynurenine in a neuronal hybrid cell line. Brain Res 1989, 495, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, S.; Nishiyama, N.; Saito, H.; Katsuki, H. Hydrogen peroxide-mediated neuronal cell death induced by an endogenous neurotoxin, 3-hydroxykynurenine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1996, 93, 12553–12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, S.; Nishiyama, N.; Saito, H.; Katsuki, H. 3-Hydroxykynurenine, an endogenous oxidative stress generator, causes neuronal cell death with apoptotic features and region selectivity. J Neurochem 1998, 70, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.R.; Stocker, R. Redox reactions related to indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and tryptophan metabolism along the kynurenine pathway. Redox Rep 1999, 4, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalho, S.M.; Sloan, L.A.; Araujo, A.C.; Laurindo, L.F.; Sloan, K.P. Vitamin D and Its Role on Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Cardiovascular Disease. In Lipophilic Vitamins in Health and Disease; Springer, 2024; pp. 291–311. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, T.; Matson, W.R.; Beal, M.F.; Myers, R.H.; Bird, E.D.; Milbury, P.; Saso, S. Kynurenine pathway abnormalities in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 1992, 42, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capucciati, A.; Galliano, M.; Bubacco, L.; Zecca, L.; Casella, L.; Monzani, E.; Nicolis, S. Neuronal Proteins as Targets of 3-Hydroxykynurenine: Implications in Neurodegenerative Diseases. ACS Chem Neurosci 2019, 10, 3731–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stípek, S.; Stastný, F.; Pláteník, J.; Crkovská, J.; Zima, T. The effect of quinolinate on rat brain lipid peroxidation is dependent on iron. Neurochem Int 1997, 30, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo-Huitrón, R.; Ugalde Muñiz, P.; Pineda, B.; Pedraza-Chaverrí, J.; Ríos, C.; Pérez-de la Cruz, V. Quinolinic acid: an endogenous neurotoxin with multiple targets. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013, 2013, 104024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behan, W.M.; McDonald, M.; Darlington, L.G.; Stone, T.W. Oxidative stress as a mechanism for quinolinic acid-induced hippocampal damage: protection by melatonin and deprenyl. Br J Pharmacol 1999, 128, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-De La Cruz, V.; Carrillo-Mora, P.; Santamaría, A. Quinolinic Acid, an endogenous molecule combining excitotoxicity, oxidative stress and other toxic mechanisms. Int J Tryptophan Res 2012, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemin, G.J. Quinolinic acid, the inescapable neurotoxin. Febs j 2012, 279, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.; Kumar, A. Improvement of mitochondrial function by paliperidone attenuates quinolinic acid-induced behavioural and neurochemical alterations in rats: implications in Huntington’s disease. Neurotox Res 2014, 26, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fão, L.; Rego, A.C. Mitochondrial and Redox-Based Therapeutic Strategies in Huntington’s Disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 2021, 34, 650–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Egidio, F.; Castelli, V.; Cimini, A.; d’Angelo, M. Cell Rearrangement and Oxidant/Antioxidant Imbalance in Huntington’s Disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez Ortega, D.; Ugalde Muñiz, P.E.; Blanco Ayala, T.; Vázquez Cervantes, G.I.; Lugo Huitrón, R.; Pineda, B.; González Esquivel, D.F.; Pérez de la Cruz, G.; Pedraza Chaverrí, J.; Sánchez Chapul, L. On the antioxidant properties of L-kynurenine: An efficient ROS scavenger and enhancer of rat brain antioxidant defense. Antioxidants 2021, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Singh, T.G.; Prabhakar, N.K.; Mannan, A. Kynurenine metabolism and alzheimer’s disease: the potential targets and approaches. Neurochemical Research 2022, 47, 1459–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubicova, L.; Chobot, V. Potential of kynurenine metabolites in drug development against neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regeneration Research 2021, 16, 308–309. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, C.; Hess, M.; Weimer, B.C. Microbial-derived tryptophan metabolites and their role in neurological disease: anthranilic acid and anthranilic acid derivatives. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, F.; Cseh, E.K.; Vécsei, L. Natural molecules and neuroprotection: kynurenic acid, pantethine and α-lipoic acid. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, Y.C.; Mendes, N.M.; Pereira de Lima, E.; Chehadi, A.C.; Lamas, C.B.; Haber, J.F.; dos Santos Bueno, M.; Araújo, A.C.; Catharin, V.C.S.; Detregiachi, C.R.P. Curcumin: A Golden Approach to Healthy Aging: A Systematic Review of the Evidence. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, S.; Peterhans, E.; Stocker, R. Antioxidant activities of some tryptophan metabolites: possible implication for inflammatory diseases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1990, 87, 2506–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, G.I.; Collins, C.A.; Stone, T.W.; Jacob, C. Electrochemical and in vitro evaluation of the redox-properties of kynurenine species. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2003, 300, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Németh, H.; Robotka, H.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Kynurenines in the central nervous system: recent developments. Central Nervous System Agents in Medicinal Chemistry (Formerly Current Medicinal Chemistry-Central Nervous System Agents) 2007, 7, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-De La Cruz, V.; Königsberg, M.; Santamaría, A. Kynurenine pathway and disease: an overview. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2007, 6, 398–410. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, T.; Forrest, C.; Mackay, G.; Stoy, N.; Darlington, L. Tryptophan, adenosine, neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. Metabolic brain disease 2007, 22, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guillemin, G.J. Kynurenine pathway metabolites in humans: disease and healthy states. International journal of tryptophan research 2009, 2, IJTR–S2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Du, J.; Lu, C.; Zhang, L.; Sun, S.; Wang, S.; Li, Y. Kynurenic acid inhibits macrophage pyroptosis by suppressing ROS production via activation of the NRF2 pathway. Molecular Medicine Reports 2023, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.S.; Schmitz, F.; Marques, E.P.; Siebert, C.; Wyse, A.T. Intrastriatal quinolinic acid administration impairs redox homeostasis and induces inflammatory changes: prevention by kynurenic acid. Neurotoxicity Research 2020, 38, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos, D.; Lőrinczi, B.; Szatmári, I.; Vécsei, L.; Tanaka, M. The Impact of C-3 Side Chain Modifications on Kynurenic Acid: A Behavioral Analysis of Its Analogs in the Motor Domain. International journal of molecular sciences 2024, 25, 3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, R. The Kynurenine Pathway in Gut Permeability and Inflammation. Inflammation 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydon, H. Anthranilic acid as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of tryptophan by Bact. typhosum. British Journal of Experimental Pathology 1948, 29, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Francisco-Marquez, M.; Fernández, M.A.; Galano, A. Anthranilic acid as a secondary antioxidant. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth, H.; Toldi, J.; Vecsei, L. Role of kynurenines in the central and peripherial nervous systems. Current neurovascular research 2005, 2, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mándi, Y.; Vécsei, L. The kynurenine system and immunoregulation. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2012, 119, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajda, C.; Majláth, Z.; Pukoli, D.; Vécsei, L. Kynurenines and Multiple Sclerosis: The Dialogue between the Immune System and the Central Nervous System. Int J Mol Sci 2015, 16, 18270–18282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Tuka, B.; Vécsei, L. Navigating the Neurobiology of Migraine: from pathways to potential therapies. 2024, 13, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, P. The ‘Yin’ and the ‘Yang’ of the kynurenine pathway: excitotoxicity and neuroprotection imbalance in stress-induced disorders. Behav Pharmacol 2019, 30, 163–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kincses, Z.T.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Kynurenines, neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s disease. J Cell Mol Med 2010, 14, 2045–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zádori, D.; Klivényi, P.; Szalárdy, L.; Fülöp, F.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Mitochondrial disturbances, excitotoxicity, neuroinflammation and kynurenines: novel therapeutic strategies for neurodegenerative disorders. J Neurol Sci 2012, 322, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamos, E.; Pardutz, A.; Klivenyi, P.; Toldi, J.; Vecsei, L. The role of kynurenines in disorders of the central nervous system: possibilities for neuroprotection. J Neurol Sci 2009, 283, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Yu, J.T.; Tan, L. The kynurenine pathway in neurodegenerative diseases: mechanistic and therapeutic considerations. J Neurol Sci 2012, 323, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas, K.; Szabó, E.; Vécsei, L. Mitochondria, Oxidative Stress and the Kynurenine System, with a Focus on Ageing and Neuroprotection. Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, R.; Forteza, M.J.; Ketelhuth, D.F.J. The interplay between cytokines and the Kynurenine pathway in inflammation and atherosclerosis. Cytokine 2019, 122, 154148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Quintana, F.J. Regulation of the Immune Response by the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor. Immunity 2018, 48, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, D.; Song, P.; Zou, M.H. Tryptophan-kynurenine pathway is dysregulated in inflammation, and immune activation. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2015, 20, 1116–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jászberényi, M.; Thurzó, B.; Bagosi, Z.; Vécsei, L.; Tanaka, M. The Orexin/Hypocretin System, the Peptidergic Regulator of Vigilance, Orchestrates Adaptation to Stress. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemin, G.J.; Meininger, V.; Brew, B.J. Implications for the kynurenine pathway and quinolinic acid in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurodegener Dis 2005, 2, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddison, D.C.; Giorgini, F. The kynurenine pathway and neurodegenerative disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2015, 40, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A. Hypothesis kynurenic and quinolinic acids: The main players of the kynurenine pathway and opponents in inflammatory disease. Med Hypotheses 2018, 118, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, T.; Morrison, P.F.; Heyes, M.P.; Markey, S.P. Effects of systemic and central nervous system localized inflammation on the contributions of metabolic precursors to the L-kynurenine and quinolinic acid pools in brain. J Neurochem 2002, 82, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorobogatov, K.; De Picker, L.; Verkerk, R.; Coppens, V.; Leboyer, M.; Müller, N.; Morrens, M. Brain Versus Blood: A Systematic Review on the Concordance Between Peripheral and Central Kynurenine Pathway Measures in Psychiatric Disorders. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 716980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yu, S.; Long, Y.; Shi, A.; Deng, J.; Ma, Y.; Wen, J.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Tryptophan metabolism: Mechanism-oriented therapy for neurological and psychiatric disorders. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 985378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertollo, A.G.; Mingoti, M.E.D.; Ignácio, Z.M. Neurobiological mechanisms in the kynurenine pathway and major depressive disorder. Rev Neurosci 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.W.; Darlington, L.G.; Badawy, A.A.; Williams, R.O. The Complex World of Kynurenic Acid: Reflections on Biological Issues and Therapeutic Strategy. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, D.; Deshpande, V.K.; Shi, Y.; Lahiri, D.K.; Greig, N.H.; Rogers, J.T.; Huang, X. N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists and memantine treatment for Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia and Parkinson’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 2012, 9, 746–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, D.; Zanetti, F.; Mende, Y.; Nicotera, P. Neurodegenerative processes in Huntington’s disease. Cell Death Dis 2011, 2, e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsette, R.E. Neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis: the role of oxidative stress and excitotoxicity. J Neurol Sci 2008, 274, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltramino, C.A.; de Olmos, J.S.; Gallyas, F.; Heimer, L.; Záborszky, L. Silver staining as a tool for neurotoxic assessment. NIDA Res Monogr 1993, 136, 101–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, A.C.; Collins, J.F.; Schwarcz, R. On the excitotoxic properties of quinolinic acid, 2,3-piperidine dicarboxylic acids and structurally related compounds. Neuropharmacology 1983, 22, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, F.; Lombardi, G.; Carlà, V.; Moneti, G. The excitotoxin quinolinic acid is present and unevenly distributed in the rat brain. Brain Res 1984, 295, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruyn, R.P.; Stoof, J.C. The quinolinic acid hypothesis in Huntington’s chorea. J Neurol Sci 1990, 95, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, D.L.; Castillo, P.E. Synaptic plasticity of NMDA receptors: mechanisms and functional implications. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2012, 22, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Tsien, J.Z. Memory and the NMDA receptors. N Engl J Med 2009, 361, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyes, M.P.; Rubinow, D.; Lane, C.; Markey, S.P. Cerebrospinal fluid quinolinic acid concentrations are increased in acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol 1989, 26, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Araki, M.; Nagatsu, I.; Yoshida, M. Astroglial cell alteration caused by neurotoxins: immunohistochemical observations with antibodies to glial fibrillary acidic protein, laminin, and tyrosine hydroxylase. Exp Neurol 1989, 106, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksdotter-Nilsson, M.; Jonsson, G.; Dahl, D.; Björklund, H. Astroglial development in microencephalic rat brain after fetal methylazoxymethanol treatment. Int J Dev Neurosci 1986, 4, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordelon, Y.M.; Chesselet, M.F.; Nelson, D.; Welsh, F.; Erecińska, M. Energetic dysfunction in quinolinic acid-lesioned rat striatum. J Neurochem 1997, 69, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.A.; Grando, V.; Dutra Filho, C.S.; Wannmacher, C.M.; Wajner, M. Evidence that quinolinic acid severely impairs energy metabolism through activation of NMDA receptors in striatum from developing rats. J Neurochem 2006, 99, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.S.Y.; Francis, H.M.; Lim, C.K. Exploring the roles of tryptophan metabolism in MS beyond neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration: A paradigm shift to neuropsychiatric symptoms. Brain Behav Immun Health 2021, 12, 100201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.; Laurie, C.; Mosley, R.L.; Gendelman, H.E. Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders. Int Rev Neurobiol 2007, 82, 297–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Shi, Y.; Chen, W.; Jia, X.; Asakawa, T. Can kynurenine pathway be considered as a next-generation therapeutic target for Parkinson’s disease? An update information. Biosci Trends 2022, 16, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Tan, V.; Lovejoy, D.; Braidy, N.; Rowe, D.B.; Brew, B.J.; Guillemin, G.J. Involvement of quinolinic acid in the neuropathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 346–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, C.; Marchi, N.; Hossain, M.; Rasmussen, P.; Alexopoulos, A.V.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Yang, H.; Janigro, D. A pro-convulsive carbamazepine metabolite: quinolinic acid in drug resistant epileptic human brain. Neurobiol Dis 2012, 46, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidetti, P.; Schwarcz, R. 3-Hydroxykynurenine and quinolinate: pathogenic synergism in early grade Huntington’s disease? Adv Exp Med Biol 2003, 527, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.W. Endogenous neurotoxins from tryptophan. Toxicon 2001, 39, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerstiaens, A.; Huybrechts, J.; Kotanen, S.; Lebeau, I.; Meylaers, K.; De Loof, A.; Schoofs, L. Neurotoxic and neurobehavioral effects of kynurenines in adult insects. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003, 312, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, C.M.; Mackay, G.M.; Stoy, N.; Egerton, M.; Christofides, J.; Stone, T.W.; Darlington, L.G. Tryptophan loading induces oxidative stress. Free Radic Res 2004, 38, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Ocampo, J.; Ramírez-Ortega, D.; Cervantes, G.I.; Pineda, B.; Balderas, P.M.; González-Esquivel, D.; Sánchez-Chapul, L.; Lugo-Huitrón, R.; Silva-Adaya, D.; Ríos, C.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction related to cell damage induced by 3-hydroxykynurenine and 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid: Non-dependent-effect of early reactive oxygen species production. Neurotoxicology 2015, 50, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Szabó, Á.; Spekker, E.; Polyák, H.; Tóth, F.; Vécsei, L. Mitochondrial Impairment: A Common Motif in Neuropsychiatric Presentation? The Link to the Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic System. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Vakili, K.; Yaghoobpoor, S.; Tavasol, A.; Jazi, K.; Hajibeygi, R.; Shool, S.; Sodeifian, F.; Klegeris, A.; McElhinney, A.; et al. Dynamic changes in metabolites of the kynurenine pathway in Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease: A systematic Review and meta-analysis. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 997240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, P.J.; Grossman, C.J.; Hayes, A.G. Kynurenic acid antagonises responses to NMDA via an action at the strychnine-insensitive glycine receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 1988, 154, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. NMDA Receptor Function During Senescence: Implication on Cognitive Performance. Front Neurosci 2015, 9, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Li, X.H.; Zhuo, M. NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity in the anterior cingulate cortex. Neuropharmacology 2021, 197, 108749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, A.F.; Boegman, R.J.; Beninger, R.J.; Jhamandas, K. Protection against quinolinic acid-mediated excitotoxicity in nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons by endogenous kynurenic acid. Neuroscience 1997, 78, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Q.; Salituro, F.G.; Schwarcz, R. Enzyme-catalyzed production of the neuroprotective NMDA receptor antagonist 7-chlorokynurenic acid in the rat brain in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 1997, 319, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russi, P.; Alesiani, M.; Lombardi, G.; Davolio, P.; Pellicciari, R.; Moroni, F. Nicotinylalanine increases the formation of kynurenic acid in the brain and antagonizes convulsions. J Neurochem 1992, 59, 2076–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vécsei, L.; Beal, M.F. Comparative behavioral and pharmacological studies with centrally administered kynurenine and kynurenic acid in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 1991, 196, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, M.F.; Matson, W.R.; Swartz, K.J.; Gamache, P.H.; Bird, E.D. Kynurenine pathway measurements in Huntington’s disease striatum: evidence for reduced formation of kynurenic acid. J Neurochem 1990, 55, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, F. Tryptophan metabolism and brain function: focus on kynurenine and other indole metabolites. Eur J Pharmacol 1999, 375, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boegman, R.J.; Jhamandas, K.; Beninger, R.J. Neurotoxicity of tryptophan metabolites. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1990, 585, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarcz, R. Metabolism and function of brain kynurenines. Biochem Soc Trans 1993, 21, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Q.; Guidetti, P.; Goodman, J.H.; Varasi, M.; Ceresoli-Borroni, G.; Speciale, C.; Scharfman, H.E.; Schwarcz, R. Kynurenergic manipulations influence excitatory synaptic function and excitotoxic vulnerability in the rat hippocampus in vivo. Neuroscience 2000, 97, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemin, G.J.; Kerr, S.J.; Smythe, G.A.; Smith, D.G.; Kapoor, V.; Armati, P.J.; Croitoru, J.; Brew, B.J. Kynurenine pathway metabolism in human astrocytes: a paradox for neuronal protection. J Neurochem 2001, 78, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevandavakkam, M.A.; Schwarcz, R.; Muchowski, P.J.; Giorgini, F. Targeting kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (KMO): implications for therapy in Huntington’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2010, 9, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocki, T.; Wnuk, S.; Kloc, R.; Kocki, J.; Owe-Larsson, B.; Urbanska, E.M. New insight into the antidepressants action: modulation of kynurenine pathway by increasing the kynurenic acid/3-hydroxykynurenine ratio. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2012, 119, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Yang, S.; Lu, L.; Zong, M.; Fan, L.; Kang, C. Unlocking the potential of the 3-hydroxykynurenine/kynurenic acid ratio: a promising biomarker in adolescent major depressive disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liloia, D.; Zamfira, D.A.; Tanaka, M.; Manuello, J.; Crocetta, A.; Keller, R.; Cozzolino, M.; Duca, S.; Cauda, F.; Costa, T. Disentangling the role of gray matter volume and concentration in autism spectrum disorder: A meta-analytic investigation of 25 years of voxel-based morphometry research. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2024, 105791. [Google Scholar]
- Battaglia, S.; Avenanti, A.; Vécsei, L.; Tanaka, M. Neural correlates and molecular mechanisms of memory and learning. 2024, 25, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. A Decade of Dedication: Pioneering Perspectives on Neurological Diseases and Mental Illnesses. 2024, 12, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valotto Neto, L.J.; Reverete de Araujo, M.; Moretti Junior, R.C.; Mendes Machado, N.; Joshi, R.K.; dos Santos Buglio, D.; Barbalho Lamas, C.; Direito, R.; Fornari Laurindo, L.; Tanaka, M. Investigating the Neuroprotective and Cognitive-Enhancing Effects of Bacopa monnieri: A Systematic Review Focused on Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Apoptosis. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, S.; Avenanti, A.; Vécsei, L.; Tanaka, M. Neurodegeneration in cognitive impairment and mood disorders for experimental, clinical and translational neuropsychiatry. 2024, 12, 574. [Google Scholar]
- Balogh, L.; Tanaka, M.; Török, N.; Vécsei, L.; Taguchi, S. Crosstalk between existential phenomenological psychotherapy and neurological sciences in mood and anxiety disorders. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Battaglia, S.; Giménez-Llort, L.; Chen, C.; Hepsomali, P.; Avenanti, A.; Vécsei, L. Innovation at the intersection: emerging translational research in neurology and psychiatry. 2024, 13, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhász, L.; Szolnoki, B.Z.; Nászai, A.; Szabó, Á.; Rutai, A.; Tallósy, S.P.; Toldi, J.; Tanaka, M.; Ono, E.; Vécsei, L. Electron transport disturbances in kynurenine aminotransferase knockout mice. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics 2024, 1865, 149389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, N.R.; Jamie, J.F.; Davies, M.J.; Truscott, R.J. Protein-bound kynurenine is a photosensitizer of oxidative damage. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2004, 37, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratek-Gerej, E.; Ziembowicz, A.; Godlewski, J.; Salinska, E. The mechanism of the neuroprotective effect of kynurenic acid in the experimental model of neonatal hypoxia–ischemia: The link to oxidative stress. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Haneda, M.; Yoshino, M. Prooxidant action of xanthurenic acid and quinoline compounds: role of transition metals in the generation of reactive oxygen species and enhanced formation of 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine in DNA. Biometals 2006, 19, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Ito, M.; Yoshino, M. Xanthurenic acid inhibits metal ion-induced lipid peroxidation and protects NADP-isocitrate dehydrogenase from oxidative inactivation. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 2001, 47, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malina, H.Z.; Hess, O.M. Xanthurenic acid translocates proapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins into mitochondria and impairs mitochondrial function. BMC Cell Biol 2004, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Wu, L.; Dong, S.; Zhu, X.; Fan, Z.; Kou, J.; Liu, F.; Yu, B.; Li, F. Inhibition of KMO Ameliorates Myocardial Ischemia Injury via Maintaining Mitochondrial Fusion and Fission Balance. Int J Biol Sci 2023, 19, 3077–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Esquivel, D.; Ramírez-Ortega, D.; Pineda, B.; Castro, N.; Ríos, C.; Pérez de la Cruz, V. Kynurenine pathway metabolites and enzymes involved in redox reactions. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korlimbinis, A.; Hains, P.G.; Truscott, R.J.; Aquilina, J.A. 3-Hydroxykynurenine oxidizes alpha-crystallin: potential role in cataractogenesis. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 1852–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leipnitz, G.; Schumacher, C.; Dalcin, K.B.; Scussiato, K.; Solano, A.; Funchal, C.; Dutra-Filho, C.S.; Wyse, A.T.; Wannmacher, C.M.; Latini, A.; et al. In vitro evidence for an antioxidant role of 3-hydroxykynurenine and 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid in the brain. Neurochem Int 2007, 50, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eryavuz Onmaz, D.; Tezcan, D.; Abusoglu, S.; Sak, F.; Humeyra Yerlikaya, F.; Yilmaz, S.; Abusoglu, G.; Kazim Korez, M.; Unlu, A. Impaired kynurenine metabolism in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Biochem 2023, 114, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Hu, C.; Luo, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, L. Pu-erh tea increases the metabolite Cinnabarinic acid to improve circadian rhythm disorder-induced obesity. Food Chem 2022, 394, 133500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollner, H. Effects of cinnabarinic acid on mitochondrial respiration. Biochem Pharmacol 1976, 25, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamura, Y.; Uesugi, K.; Naito, J.; Ishiguro, I. Cinnabarinic acid was formed in damaged mitochondria and its effect on mitochondrial respiration. Adv Exp Med Biol 1999, 467, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramatsu, R.; Hara, T.; Akimoto, H.; Takikawa, O.; Kawabe, T.; Isobe, K.; Nagase, F. Cinnabarinic acid generated from 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid strongly induces apoptosis in thymocytes through the generation of reactive oxygen species and the induction of caspase. J Cell Biochem 2008, 103, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, F.; Candido, K.D.; Knezevic, N.N. The Role of the Kynurenine Signaling Pathway in Different Chronic Pain Conditions and Potential Use of Therapeutic Agents. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezrich, J.D.; Fechner, J.H.; Zhang, X.; Johnson, B.P.; Burlingham, W.J.; Bradfield, C.A. An interaction between kynurenine and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor can generate regulatory T cells. J Immunol 2010, 185, 3190–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, H.; Chang, H.W.; Tseng, H.C.; Hsu, S.C.; Yang, S.J.; Hung, C.H.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, S.K. A tryptophan metabolite, kynurenine, promotes mast cell activation through aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Allergy 2014, 69, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, H.; Parker, E.; Hamrick, M.W. Kynurenine signaling through the aryl hydrocarbon receptor: Implications for aging and healthspan. Exp Gerontol 2020, 130, 110797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.W. Kynurenic acid antagonists and kynurenine pathway inhibitors. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2001, 10, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuboly, G.; Tar, L.; Bohar, Z.; Safrany-Fark, A.; Petrovszki, Z.; Kekesi, G.; Vecsei, L.; Pardutz, A.; Horvath, G. The inimitable kynurenic acid: the roles of different ionotropic receptors in the action of kynurenic acid at a spinal level. Brain Res Bull 2015, 112, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.W. Does kynurenic acid act on nicotinic receptors? An assessment of the evidence. J Neurochem 2020, 152, 627–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Dietrich, D.; Gräsel, I.; Reuter, G.; Seifert, G.; Steinhäuser, C. 6-Hydroxykynurenic acid and kynurenic acid differently antagonise AMPA and NMDA receptors in hippocampal neurones. J Neurochem 2001, 77, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, C.; Weeks, A.M.; Staley, K.J.; Partin, K.M. Kynurenic acid has a dual action on AMPA receptor responses. Neurosci Lett 2006, 402, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, C.M.; Moffitt, J.A.; Hay, M.; Hasser, E.M. Glutamate in the nucleus of the solitary tract activates both ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors. Am J Physiol 1998, 275, R1858–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deora, G.S.; Kantham, S.; Chan, S.; Dighe, S.N.; Veliyath, S.K.; McColl, G.; Parat, M.O.; McGeary, R.P.; Ross, B.P. Multifunctional Analogs of Kynurenic Acid for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: Synthesis, Pharmacology, and Molecular Modeling Studies. ACS Chem Neurosci 2017, 8, 2667–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Wang, X.L.; Feng, S.T.; Chen, N.H.; Wang, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y. Novel rapid-acting glutamatergic modulators: Targeting the synaptic plasticity in depression. Pharmacol Res 2021, 171, 105761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNatale, B.C.; Murray, I.A.; Schroeder, J.C.; Flaveny, C.A.; Lahoti, T.S.; Laurenzana, E.M.; Omiecinski, C.J.; Perdew, G.H. Kynurenic acid is a potent endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand that synergistically induces interleukin-6 in the presence of inflammatory signaling. Toxicol Sci 2010, 115, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, F.; Cozzi, A.; Sili, M.; Mannaioni, G. Kynurenic acid: a metabolite with multiple actions and multiple targets in brain and periphery. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2012, 119, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lara, L.; Pérez-Severiano, F.; González-Esquivel, D.; Elizondo, G.; Segovia, J. Absence of aryl hydrocarbon receptors increases endogenous kynurenic acid levels and protects mouse brain against excitotoxic insult and oxidative stress. J Neurosci Res 2015, 93, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés Malagón, E.M.; López Ornelas, A.; Olvera Gómez, I.; Bonilla Delgado, J. The Kynurenine Pathway, Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor, and Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sci 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, S.A.; Copeland, C.S.; Uebele, V.N.; Thomson, F.J.; Salt, T.E. Modulation of hippocampal synaptic transmission by the kynurenine pathway member xanthurenic acid and other VGLUT inhibitors. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, C.S.; Neale, S.A.; Salt, T.E. Actions of Xanthurenic acid, a putative endogenous Group II metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist, on sensory transmission in the thalamus. Neuropharmacology 2013, 66, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Dey, A.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V.; Swati, K.; Ojha, S.; Prakash, A.; Kumar, D.; Ambasta, R.K.; Jha, N.K.; Jha, S.K.; et al. Glutamatergic neurotransmission: A potential pharmacotherapeutic target for the treatment of cognitive disorders. Ageing Res Rev 2023, 85, 101838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, F.; Lionetto, L.; Curto, M.; Iacovelli, L.; Copeland, C.S.; Neale, S.A.; Bruno, V.; Battaglia, G.; Salt, T.E.; Nicoletti, F. Cinnabarinic acid and xanthurenic acid: Two kynurenine metabolites that interact with metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Ma, N.; He, T.; Johnston, L.J.; Ma, X. Tryptophan (Trp) modulates gut homeostasis via aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2020, 60, 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Cui, C. The therapeutic potential of diet on immune-related diseases: based on the regulation on tryptophan metabolism. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2022, 62, 8793–8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosio, L.F.; Insfran, C.; Volpini, X.; Acosta Rodriguez, E.; Serra, H.M.; Quintana, F.J.; Cervi, L.; Motrán, C.C. Role of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) in the Regulation of Immunity and Immunopathology During Trypanosoma cruzi Infection. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.K.; Kwon, B. Immune regulation through tryptophan metabolism. Exp Mol Med 2023, 55, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Perdew, G.H. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor as a mediator of host-microbiota interplay. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1859812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, F.; Lionetto, L.; Molinaro, G.; Bertrand, H.O.; Acher, F.; Ngomba, R.T.; Notartomaso, S.; Curini, M.; Rosati, O.; Scarselli, P.; et al. Cinnabarinic acid, an endogenous metabolite of the kynurenine pathway, activates type 4 metabotropic glutamate receptors. Mol Pharmacol 2012, 81, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, M.M.; Mold, J.E.; Kanwar, B.; Huang, Y.; Louie, A.; Pollastri, M.P.; Wang, C.; Patel, G.; Franks, D.G.; Schlezinger, J.; et al. Identification of cinnabarinic acid as a novel endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand that drives IL-22 production. PLoS One 2014, 9, e87877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, S.-H.; Ma, Z.-X.; Feltenberger, J.B.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Scarlett, C.; Lin, Z.; Satyshur, K.A.; Cortopassi, M.; Jefcoate, C.R. Trace derivatives of kynurenine potently activate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR). Journal of Biological Chemistry 2018, 293, 1994–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezrich, J.D.; Fechner, J.H.; Zhang, X.; Johnson, B.P.; Burlingham, W.J.; Bradfield, C.A. An interaction between kynurenine and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor can generate regulatory T cells. The Journal of Immunology 2010, 185, 3190–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, I.Y.; Moyer, B.J.; Ringelberg, C.S.; Wilkins, O.M.; Pooler, D.B.; Ness, D.B.; Coker, S.; Tosteson, T.D.; Lewis, L.D.; Chamberlin, M.D. Kynurenine-Induced Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Signaling in Mice Causes Body Mass Gain, Liver Steatosis, and Hyperglycemia. Obesity 2021, 29, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, J.H.; Di Meglio, P.; Hirota, K.; Ahlfors, H.; Stockinger, B. Differential influences of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor on Th17 mediated responses in vitro and in vivo. PloS one 2013, 8, e79819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchiy, V.; Martin, C.R.; Mayer, E.A. The gut–brain axis and the microbiome: mechanisms and clinical implications. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2019, 17, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.R.; Mayer, E.A. Gut-brain axis and behavior. Intestinal microbiome: functional aspects in health and disease 2017, 88, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Gershon, M.D.; Margolis, K.G. The gut, its microbiome, and the brain: connections and communications. The Journal of clinical investigation 2021, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Inslicht, S.S.; Bhargava, A. Gut-Brain Axis: Role of Microbiome, Metabolomics, Hormones, and Stress in Mental Health Disorders. Cells 2024, 13, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undieh, U.A.U. Dysfunction of the Gut Microbiome-Brain Axis in Neurodegenerative Disease: Role of Indole and Its Metabolites; Drexel University: 2023.
- Młynarska, E.; Gadzinowska, J.; Tokarek, J.; Forycka, J.; Szuman, A.; Franczyk, B.; Rysz, J. The role of the microbiome-brain-gut axis in the pathogenesis of depressive disorder. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, K.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Mayer, E.A. The microbiota-gut-brain axis: from motility to mood. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, L.; Mastandrea, I.; Melekhova, A.; Elinav, E. Mechanisms by which microbiome-derived metabolites exert their impacts on neurodegeneration. Cell Chemical Biology 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spivak, I.; Fluhr, L.; Elinav, E. Local and systemic effects of microbiome-derived metabolites. EMBO reports 2022, 23, e55664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, H.; Thaiss, C.A.; Levy, M.; Elinav, E. The cross talk between microbiota and the immune system: metabolites take center stage. Current opinion in immunology 2014, 30, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusufu, I.; Ding, K.; Smith, K.; Wankhade, U.D.; Sahay, B.; Patterson, G.T.; Pacholczyk, R.; Adusumilli, S.; Hamrick, M.W.; Hill, W.D. A tryptophan-deficient diet induces gut microbiota dysbiosis and increases systemic inflammation in aged mice. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22, 5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Li, D.; Shi, Y.; Li, Q.; Guo, X.; Dong, K.; Chen, Q.; Lou, X.; Li, Z.; Li, P. Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota and kynurenine (Kyn) pathway activity as potential biomarkers in patients with major depressive disorder. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuco, A.; Urits, I.; Hasoon, J.; Chun, R.; Gerald, B.; Wang, J.K.; Kassem, H.; Ngo, A.L.; Abd-Elsayed, A.; Simopoulos, T. Current perspectives on gut microbiome dysbiosis and depression. Advances in therapy 2020, 37, 1328–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, Z.; Wu, H.; Wu, F.; Miao, Z.; Shi, H.; Huang, F.; Wu, X. TGR5 deficiency-induced anxiety and depression-like behaviors: The role of gut microbiota dysbiosis. Journal of Affective Disorders 2024, 344, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intili, G.; Paladino, L.; Rappa, F.; Alberti, G.; Plicato, A.; Calabrò, F.; Fucarino, A.; Cappello, F.; Bucchieri, F.; Tomasello, G. From Dysbiosis to neurodegenerative diseases through different communication pathways: An overview. Biology 2023, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.J.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Clarke, G. Kynurenine pathway metabolism and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, S.M.; Clarke, G.; Borre, Y.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J. Serotonin, tryptophan metabolism and the brain-gut-microbiome axis. Behavioural brain research 2015, 277, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delzenne, N.M.; Cani, P.D.; Everard, A.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Bindels, L.B. Gut microorganisms as promising targets for the management of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 2206–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, S.; Schwarz, M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Stärkel, P.; de Timary, P. Alterations of kynurenine pathway in alcohol use disorder and abstinence: a link with gut microbiota, peripheral inflammation and psychological symptoms. Translational Psychiatry 2021, 11, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercik, P.; Collins, S.M. The effects of inflammation, infection and antibiotics on the microbiota-gut-brain axis. microbial endocrinology: the microbiota-gut-brain axis in health and disease 2014, 279–289. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Xu, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Bai, M.; Peng, C.; Li, T.; Yin, Y. Impact of the gut microbiota on intestinal immunity mediated by tryptophan metabolism. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 2018, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubková, B.; Valko-Rokytovská, M.; Čižmárová, B.; Zábavníková, M.; Mareková, M.; Birková, A. Tryptophan: Its metabolism along the kynurenine, serotonin, and indole pathway in malignant melanoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 9160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herderich, M.; Gutsche, B. Tryptophan-derived bioactive compounds in food. Food Reviews International 1997, 13, 103–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A.-B. Tryptophan metabolism in alcoholism. Nutrition research reviews 2002, 15, 123–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Otagiri, M.; Maruyama, T. New Insight Into the Redox Properties of Uremic Solute Indoxyl Sulfate as a Pro-and Anti-Oxidant. Therapeutic Apheresis and Dialysis 2011, 15, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapa, S.F.; Prisco, F.; Popolo, A.; Iovane, V.; Autore, G.; Di Iorio, B.R.; Dal Piaz, F.; Paciello, O.; Nishijima, F.; Marzocco, S. Pro-Inflammatory Effects of Indoxyl Sulfate in Mice: Impairment of Intestinal Homeostasis and Immune Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.-Q.; Wang, Y.-N.; Feng, H.-Y.; Guo, Z.-Y.; Li, X.; Nie, X.-L.; Zhao, Y.-Y. Host/microbiota interactions-derived tryptophan metabolites modulate oxidative stress and inflammation via aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2022, 184, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwan, P.; Stepniak, J.; Karbownik-Lewinska, M. Cumulative protective effect of melatonin and indole-3-propionic acid against KIO3—induced lipid peroxidation in porcine thyroid. Toxics 2021, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.-L.; Chen, X.-W.; Wang, Y.-F.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, W.-J.; Zhou, B.-W.; Ci, P.-F.; Liu, K.-X. Microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites indole-3-lactic acid is associated with intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury via positive regulation of YAP and Nrf2. Journal of Translational Medicine 2023, 21, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Cui, C. The therapeutic potential of diet on immune-related diseases: based on the regulation on tryptophan metabolism. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 2022, 62, 8793–8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J. Diverse roles of microbial indole compounds in eukaryotic systems. Biological Reviews 2021, 96, 2522–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zgarbová, E.; Vrzal, R. Skatole: A thin red line between its benefits and toxicity. Biochimie 2023, 208, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennoune, N.; Andriamihaja, M.; Blachier, F. Production of indole and indole-related compounds by the intestinal microbiota and consequences for the host: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, H.; Yu, X.; Ye, Z. Biosynthetic pathways and functions of indole-3-acetic acid in microorganisms. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatova, O.; Shestopalov, A. Tryptophan Metabolism: A New Look at the Role of Tryptophan Derivatives in the Human Body. Biology Bulletin Reviews 2023, 13, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Li, B.; Xie, T.; Xu, C.; Ren, X.; Jiang, F.; Lei, T.; Zhou, P. Indole-3-aldehyde alleviates chondrocytes inflammation through the AhR-NF-κB signalling pathway. International Immunopharmacology 2022, 113, 109314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelante, T.; Puccetti, M.; Giovagnoli, S.; Romani, L. Regulation of host physiology and immunity by microbial indole-3-aldehyde. Current Opinion in Immunology 2021, 70, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Y.; Guo, X.; Ren, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, W.; Yu, K. Indole-3-aldehyde Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Gut Barrier Disruption by Increasing Intestinal Stem Cell Expansion. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2024, 72, 18930–18941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumavath, R.N.; Barh, D.; Azevedo, V.; Kumar, A.P. Potential pharmacological applications of enzymes associated with bacterial metabolism of aromatic compounds. Journal of Microbiology and Antimicrobials 2017, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, T.; Pei, Z.; Fang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W.; Lu, W. Uncovering the specificity and predictability of tryptophan metabolism in lactic acid bacteria with genomics and metabolomics. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 2023, 13, 1154346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopelski, P.; Mogilnicka, I. Biological effects of indole-3-propionic acid, a gut microbiota-derived metabolite, and its precursor tryptophan in mammals’ health and disease. International journal of molecular sciences 2022, 23, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrikx, T.; Schnabl, B. Indoles: metabolites produced by intestinal bacteria capable of controlling liver disease manifestation. Journal of Internal Medicine 2019, 286, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arosio, B.; Calvani, R.; Ferri, E.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Carandina, A.; Campanelli, F.; Ghiglieri, V.; Marzetti, E.; Picca, A. Sarcopenia and Cognitive decline in older adults: targeting the muscle–brain Axis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, E.P.; Tanaka, M.; Lamas, C.B.; Quesada, K.; Detregiachi, C.R.P.; Araújo, A.C.; Guiguer, E.L.; Catharin, V.M.C.S.; de Castro, M.V.M.; Junior, E.B. Vascular Impairment, Muscle Atrophy, and Cognitive Decline: Critical Age-Related Conditions. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, B.K. Physical activity and muscle–brain crosstalk. Nature Reviews Endocrinology 2019, 15, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, T.; Turska, M.; Kocki, T.; Zawadka, M.; Zieliński, G.; Turski, W.A.; Gawda, P. Effect of 4-week physical exercises on tryptophan, kynurenine and kynurenic acid content in human sweat. Scientific reports 2021, 11, 11092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugué, P.-A.; Li, S.; Marinis, S.; Hodge, A. Combined association of diet and physical activity with plasma concentrations of markers of the kynurenine pathway. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 2023, 82, E201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.; Harijanto, C.; Vogrin, S.; Guillemin, G.; Duque, G. Does exercise influence kynurenine/tryptophan metabolism and psychological outcomes in persons with age-related diseases? A systematic review. International Journal of Tryptophan Research 2021, 14, 1178646921991119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervenka, I.; Agudelo, L.Z.; Ruas, J.L. Kynurenines: Tryptophan’s metabolites in exercise, inflammation, and mental health. Science 2017, 357, eaaf9794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente-Silva, P.; Ruas, J.L. Tryptophan-kynurenine metabolites in exercise and mental health. Hormones, metabolism and the benefits of exercise 2017, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Valente-Silva, P.; Cervenka, I.; Ferreira, D.M.; Correia, J.C.; Edman, S.; Horwath, O.; Heng, B.; Chow, S.; Jacobs, K.R.; Guillemin, G.J. Effects of tryptophan supplementation and exercise on the fate of kynurenine metabolites in mice and humans. Metabolites 2021, 11, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agudelo, L.Z.; Femenía, T.; Orhan, F.; Porsmyr-Palmertz, M.; Goiny, M.; Martinez-Redondo, V.; Correia, J.C.; Izadi, M.; Bhat, M.; Schuppe-Koistinen, I. Skeletal muscle PGC-1α1 modulates kynurenine metabolism and mediates resilience to stress-induced depression. Cell 2014, 159, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, P.; Farzi, A.; Hassan, A.M.; Zenz, G.; Jačan, A.; Reichmann, F. Visceral inflammation and immune activation stress the brain. Frontiers in immunology 2017, 8, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, L.; Fan, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Wu, W.; Tao, J.; Huan, F. Bisphenol F exposure induces depression-like changes: Roles of the kynurenine metabolic pathway along the “liver-brain” axis. Environmental Pollution 2024, 346, 123356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchetti, J.; Fumagalli, F.; Olivari, D.; Affatato, R.; Fracasso, C.; De Giorgio, D.; Perego, C.; Motta, F.; Passoni, A.; Staszewsky, L. Brain kynurenine pathway and functional outcome of rats resuscitated from cardiac arrest. Journal of the American Heart Association 2021, 10, e021071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.Y.; van Praag, H. On the run for hippocampal plasticity. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine 2018, 8, a029736. [Google Scholar]
- Kindler, J.; Lim, C.K.; Weickert, C.S.; Boerrigter, D.; Galletly, C.; Liu, D.; Jacobs, K.R.; Balzan, R.; Bruggemann, J.; O’Donnell, M. Dysregulation of kynurenine metabolism is related to proinflammatory cytokines, attention, and prefrontal cortex volume in schizophrenia. Molecular psychiatry 2020, 25, 2860–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheibani, M.; Shayan, M.; Khalilzadeh, M.; Soltani, Z.E.; Jafari-Sabet, M.; Ghasemi, M.; Dehpour, A.R. Kynurenine pathway and its role in neurologic, psychiatric, and inflammatory bowel diseases. Molecular Biology Reports 2023, 50, 10409–10425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, R.M.; Shayesteh, S.; Ala, M.; Yousefi-Manesh, H.; Rashidian, A.; Hashemian, S.M.; Sorouri, M.; Dehpour, A.R. Dapsone ameliorates colitis through TLR4/NF-kB pathway in TNBS induced colitis model in rat. Archives of medical research 2021, 52, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlokovic, B.V. Neurovascular pathways to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and other disorders. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2011, 12, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, A.; Kalaska, B.; Pawlak, D. Kynurenine pathway in chronic kidney disease: what’s old, what’s new, and what’s next? International Journal of Tryptophan Research 2020, 13, 1178646920954882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, H.N.; Liu, J.-J.; Ching, J.; Kovalik, J.-P.; Lim, S.C. The kynurenine pathway in acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease. American Journal of Nephrology 2021, 52, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tankiewicz, A.; Pawlak, D.; Topczewska-Bruns, J.; Buczko, W. Kidney and liver kynurenine pathway enzymes in chronic renal failure. In Developments in Tryptophan and Serotonin Metabolism; Springer: 2003; pp. 409-414.
- Gorji, H.; Yang, J.W.; Hannan, M.; He, J.; Miller, L.M.; Mathew, A.V.; Seliger, S.L.; Tamura, M.; Mehta, R.; Kotanko, P. Kynurenine Metabolism and Neurocognition in CKD: CRIC Study: TH-PO1066. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2023, 34, 390–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, D.; Pawlak, K.; Malyszko, J.; Mysliwiec, M.; Buczko, W. Accumulation of toxic products degradation of kynurenine in hemodialyzed patients. International Urology and Nephrology 2001, 33, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, W.A. The blood–brain barrier as an endocrine tissue. Nature Reviews Endocrinology 2019, 15, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, B.; Babaeizad, A.; Banihashemian, S.Z.; Feyzabadi, Z.K.; Dadashpour, M.; Pahlevan, D.; Ghaffari, H.; Eslami, M. Gastrointestinal tract, microbiota and multiple sclerosis (MS) and the link between gut microbiota and CNS. Current microbiology 2023, 80, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, J.M.; Redus, L.; O’Connor, J.C. Kynurenine metabolic balance is disrupted in the hippocampus following peripheral lipopolysaccharide challenge. Journal of Neuroinflammation 2016, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcocer-Cuarón, C.; Rivera, A.L.; Castaño, V.M. Hierarchical structure of biological systems: a bioengineering approach. Bioengineered 2014, 5, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bick, C.; Gross, E.; Harrington, H.A.; Schaub, M.T. What are higher-order networks? SIAM Review 2023, 65, 686–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Wang, J.; Perc, M.; Wang, Z. Reputation and reciprocity. Physics of life reviews 2023, 46, 8–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurock, M.; Stark, S.M.; Klein, M.T. Molecular simulation of kinetic interactions in complex mixtures. In Computer-aided design of catalysts; CRC Press: 2020; pp. 55-88.
- Sánchez, W.N.; Robeson, L.; Carrasco, V.; Figueroa, N.L.; Burgos-Bravo, F.; Wilson, C.A.; Casanova-Morales, N. Determination of protein–protein interactions at the single-molecule level using optical tweezers. Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics 2022, 55, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liao, W.; Tong, Z.; Yuan, F.; Mao, L.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y. The concentration-, pH-and temperature-responsive self-assembly of undenatured type II collagen: Kinetics, thermodynamics, nanostructure and molecular mechanism. Food Hydrocolloids 2023, 137, 108424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohi, Y.; Kimura, S.; Haji, A. Modulation of glutamatergic transmission by presynaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate mechanisms in second-order neurons of the rat nucleus tractus solitarius. Neuroscience Letters 2015, 587, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, A.J. An historical perspective: the second order neuron in the pain pathway. Frontiers in Pain Research 2022, 3, 845211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, D.; Bushey, D.; Li, F.; Hibbard, K.L.; Sammons, M.; Funke, J.; Litwin-Kumar, A.; Hige, T.; Aso, Y. Hierarchical architecture of dopaminergic circuits enables second-order conditioning in Drosophila. Elife 2023, 12, e79042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, N.; Torabi-Parizi, P.; Gottschalk, R.A.; Germain, R.N.; Dutta, B. Network representations of immune system complexity. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Systems Biology and Medicine 2015, 7, 13–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Tan, J.; Liu, Z. Impact of higher-order interactions and individual emotional heterogeneity on information-disease coupled dynamics in multiplex networks. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 2023, 177, 114186. [Google Scholar]
- Treur, J. On Structure, Dynamics, and Adaptivity for Biological and Mental Processes: a Higher-Order Adaptive Dynamical System Modeling Perspective. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society, 2024.
- Nijhout, H.F.; Best, J.A.; Reed, M.C. Systems biology of robustness and homeostatic mechanisms. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Systems Biology and Medicine 2019, 11, e1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.A.; Ferrucci, L.; Fülöp, T.; Gravel, D.; Hao, N.; Kriete, A.; Levine, M.E.; Lipsitz, L.A.; Olde Rikkert, M.G.; Rutenberg, A. A complex systems approach to aging biology. Nature Aging 2022, 2, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, D.; Almpanis, A.; Noel, A.; Deng, Y.; Schober, R. A survey of molecular communication in cell biology: Establishing a new hierarchy for interdisciplinary applications. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2021, 23, 1494–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Karafyllis, I.; Krstic, M. Nonlinear stabilization under sampled and delayed measurements, and with inputs subject to delay and zero-order hold. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 2011, 57, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laracuente, M.-L.; Marina, H.Y.; McHugh, K.J. Zero-order drug delivery: State of the art and future prospects. Journal of Controlled Release 2020, 327, 834–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Hüttinger, E.; Christodoulides, P.; Miyauchi, K.; Irvine, A.D.; Okada-Hatakeyama, M.; Kubo, M.; Tanaka, R.J. Mathematical modeling of atopic dermatitis reveals “double-switch” mechanisms underlying 4 common disease phenotypes. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2017, 139, 1861–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, A.; Vijayasree, V.; Das, S.; Sivamani, Y.; Elayaperumal, S. Overview of drugs and drug targets. In Biochemical and Molecular Pharmacology in Drug Discovery; Elsevier: 2024; pp. 45-69.
- Fischer, E. Einfluss der Configuration auf die Wirkung der Enzyme. Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft 1894, 27, 2985–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, F. Emil Fischer’s Lock-and-Key Hypothesis after 100 years-Towards a Supracellular Chemistry’. Perspectives in supramolecular chemistry: The lock-and-key principle 1994, 1, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Brunori, M. Allostery turns 50: Is the vintage yet attractive? Protein Science: a Publication of the Protein Society 2011, 20, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.V. The possible effects of the aggregation of the molecules of hemoglobin on its dissociation curves. j. physiol. 1910, 40, iv. [Google Scholar]
- Cattoni, D.I.; Chara, O.; Kaufman, S.B.; González Flecha, F.L. Cooperativity in binding processes: New insights from phenomenological modeling. PloS one 2015, 10, e0146043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, D.A.; Stoddart, L.A.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Hill, S.J. Binding kinetics of ligands acting at GPCRs. Molecular and cellular endocrinology 2019, 485, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummino, P.J.; Copeland, R.A. Residence time of receptor− ligand complexes and its effect on biological function. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 5481–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peletier, L.A. An Extended Model Including Target Turnover, Ligand–Target Complex Kinetics, and Binding Properties to Describe Drug–Receptor Interactions. Computational Methods for Estimating the Kinetic Parameters of Biological Systems 2021, 19–46. [Google Scholar]
- Borisov, D.; Veselovsky, A. Ligand–receptor binding kinetics in drug design. Biochemistry (Moscow), Supplement Series B: Biomedical Chemistry 2020, 14, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, B. A guide to enzyme kinetics in early drug discovery. The FEBS Journal 2023, 290, 2292–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, Q.H. The reaction of oxygen with hemoglobin and the kinetic basis of the effect of salt on binding of oxygen. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1970, 245, 3285–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, Q.H. Kinetics of oxygen binding to hemoglobin A. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 5191–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, R.L.; Antonini, E.; Brunori, M.; Wyman, J.; Rossi-Fanelli, A. Observations on the kinetics of the reaction of hemoglobin with oxygen. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1967, 242, 4841–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomaya, A.Y.; Pan, Y. Biomolecular networks: methods and applications in systems biology; John Wiley & Sons: 2009.
- Lü, J.; Wang, P. Modeling and analysis of bio-molecular networks; Springer: 2020.
- Hampel, H.; Nisticò, R.; Seyfried, N.T.; Levey, A.I.; Modeste, E.; Lemercier, P.; Baldacci, F.; Toschi, N.; Garaci, F.; Perry, G. Omics sciences for systems biology in Alzheimer’s disease: State-of-the-art of the evidence. Ageing Research Reviews 2021, 69, 101346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azer, K.; Kaddi, C.D.; Barrett, J.S.; Bai, J.P.; McQuade, S.T.; Merrill, N.J.; Piccoli, B.; Neves-Zaph, S.; Marchetti, L.; Lombardo, R. History and future perspectives on the discipline of quantitative systems pharmacology modeling and its applications. Frontiers in physiology 2021, 12, 637999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ji, J.; Song, F.; Hu, J. Intercellular receptor-ligand binding: effect of protein-membrane interaction. Journal of Molecular Biology 2023, 435, 167787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markin, C.; Mokhtari, D.; Sunden, F.; Appel, M.; Akiva, E.; Longwell, S.; Sabatti, C.; Herschlag, D.; Fordyce, P. Revealing enzyme functional architecture via high-throughput microfluidic enzyme kinetics. Science 2021, 373, eabf8761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loisios-Konstantinidis, I.; Mavroudis, P.D.; Macheras, P. Dynamical aspects of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic & quantitative systems pharmacology models. Approaching Complex Diseases: Network-Based Pharmacology and Systems Approach in Bio-Medicine 2020, 35–61. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, M. A textbook of physiology, book three: The central nervous system and its instruments. 1897.
- Bennett, M.R. The early history of the synapse: from Plato to Sherrington. Brain research bulletin 1999, 50, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, G.M.; Erulkar, S.D. Centenary of the synapse: from Sherrington to the molecular biology of the synapse and beyond. Trends in neurosciences 1997, 20, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loewi, O. Über humorale übertragbarkeit der Herznervenwirkung. Pflügers Archiv European Journal of Physiology 1921, 189, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.; García, A.G. One hundred years from Otto Loewi experiment, a dream that revolutionized our view of neurotransmission. Pflügers Archiv-European Journal of Physiology 2021, 473, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudor, K.I.; Matovinovic, M.; Tudor, D.M.; Bosnic, A. ON THE OCCASION OF THE CELEBRATION OF THE CENTENNIAL ANNIVERSARY OF THE DISCOVERY OF THE FIRST NEURO-TRANSMITTER, ACETYLCHOLINE (ALIAS “VAGUSSTOFF”) BY OTTO LOEWI.
- Ince, R.A.; Montani, F.; Arabzadeh, E.; Diamond, M.E.; Panzeri, S. On the presence of high-order interactions among somatosensory neurons and their effect on information transmission. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series; 2009; p. 012013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Dudko, O.K. A theory of synaptic transmission. Elife 2021, 10, e73585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destexhe, A.; Mainen, Z.; Sejnowski, T. An E cient Method for Computing Synaptic Conductances Based on a Kinetic Model of Receptor Binding. Neural computation 1994, 6, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, C.A.; Krishnakumar, S.S.; Timofeeva, Y.; Volynski, K.E. The release of inhibition model reproduces kinetics and plasticity of neurotransmitter release in central synapses. Communications Biology 2023, 6, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.S.; Li, S.; Cepeda, C.; Cromwell, H.C.; Altemus, K.L. Neuromodulatory actions of dopamine on synaptically-evoked neostriatal responses in slices. Synapse 1996, 24, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevathan, J.K.; Yousefi, A.; Park, H.O.; Bartoletta, J.J.; Ludwig, K.A.; Lee, K.H.; Lujan, J.L. Computational modeling of neurotransmitter release evoked by electrical stimulation: nonlinear approaches to predicting stimulation-evoked dopamine release. ACS chemical neuroscience 2017, 8, 394–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeholzer, A.; Deger, M.; Gerstner, W. Stability of working memory in continuous attractor networks under the control of short-term plasticity. PLoS computational biology 2019, 15, e1006928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tompa, P.; Töth-Boconádi, R.; Friedrich, P. Frequency decoding of fast calcium oscillations by calpain. Cell Calcium 2001, 29, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schild, J.; Clark, J.; Canavier, C.; Kunze, D.; Andresen, M. Afferent synaptic drive of rat medial nucleus tractus solitarius neurons: dynamic simulation of graded vesicular mobilization, release, and non-NMDA receptor kinetics. Journal of neurophysiology 1995, 74, 1529–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FallahBagheri, N.; Akan, O.B. A Molecular Communication Perspective of Alzheimer’s Disease: Impact of Amyloid Beta Oligomers on Glutamate Diffusion in the Synaptic Cleft. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.03396, 2024; arXiv:2409.03396 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bosl, W.J. Systems biology by the rules: hybrid intelligent systems for pathway modeling and discovery. BMC systems biology 2007, 1, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singel, D.J.; Stamler, J.S. Chemical physiology of blood flow regulation by red blood cells: the role of nitric oxide and S-nitrosohemoglobin. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2005, 67, 99–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, T.; Tanji, H.; Kato, H.; Mizugaki, M.; Itoyama, Y. Alterations of second messenger systems in the rat brain after 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the medial forebrain bundle. European journal of pharmaceutical sciences 1999, 8, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frade, J.G.L.d.O. Real-time change of nitric oxide in rat hippocampal slices and astrocytic glutathione release via glutamate-dependent pathways. 2008.
- Gosak, M.; Markovič, R.; Dolenšek, J.; Rupnik, M.S.; Marhl, M.; Stožer, A.; Perc, M. Network science of biological systems at different scales: A review. Physics of life reviews 2018, 24, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, C.; Colangelo, A.M.; Virtuoso, A.; Alberghina, L.; Papa, M. Neurons, glia, extracellular matrix and neurovascular unit: a systems biology approach to the complexity of synaptic plasticity in health and disease. International journal of molecular sciences 2020, 21, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkin, A.L.; Huxley, A.F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. The Journal of physiology 1952, 117, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkin, A.L.; Huxley, A.F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. Bulletin of mathematical biology 1990, 52, 25–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickle, J. Hodgkin’s and Huxley’s own assessments of their “quantitative description” of nerve membrane current. History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences 2023, 45, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behring, E.v. Ueber das zustandekommen der diphtherie-immunität und der tetanus-immunität bei thieren. Drucke 19. Jh. 1890. [Google Scholar]
- Winau, F.; Winau, R. Emil von Behring and serum therapy. Microbes and infection 2002, 4, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahaie, Y.M.; Watier, H. From the Gorgon’s blood to Behring’s Blutserumtherapie: A long path towards serum therapy. Immunological Reviews 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Ru, B.; Yang, Y.; Vu, T.; Paul, R.; Mirza, A.; Altan-Bonnet, G.; Liu, L.; Ruppin, E. Systematic investigation of cytokine signaling activity at the tissue and single-cell levels. Nature methods 2021, 18, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-R.; Byeon, Y.; Kim, D.; Park, S.-G. Recent insights of T cell receptor-mediated signaling pathways for T cell activation and development. Experimental & molecular medicine 2020, 52, 750–761. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Wei, Q.; Brzostek, J.; Gascoigne, N.R. Signaling from T cell receptors (TCRs) and chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) on T cells. Cellular & Molecular Immunology 2020, 17, 600–612. [Google Scholar]
- Toraño, A.; Moreno, I.; Infantes, J.A.; Domínguez, M. An Overview of ELISA-Based Initial Velocity Methods to Measure the Immunoreactive Fraction, Association Rate, And Equilibrium Constants of Monoclonal Antibodies. Asian Journal of Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2022, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, S.N.; McConnell, H.M. A first-order reaction controls the binding of antigenic peptides to major histocompatibility complex class II molecules. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1991, 88, 8164–8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimánek, V.; Pecen, L.; Řezáčková, H.; Topolčan, O.; Fajfrlík, K.; Sedláček, D.; Šín, R.; Bludovská, M.; Pazdiora, P.; Slouka, D. Long-Term Monitoring of the Antibody Response to a SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, R. Macrophage handling of soluble immune complexes. immunology today 1980, 1, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klasse, P. Neutralization of virus infectivity by antibodies: old problems in new perspectives. Advances in biology 2014, 2014, 157895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elveborg, S.; Monteil, V.M.; Mirazimi, A. Methods of inactivation of highly pathogenic viruses for molecular, serology or vaccine development purposes. Pathogens 2022, 11, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Balakrishnan, V.; Buzzard, G.; Geahlen, R.; Harrison, M.; Rundell, A. Modeling and analysis of early events in T-lymphocyte antigen-activated intracellular-signaling pathways. Journal of computational and applied mathematics 2005, 184, 320–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.H.; Silver, R. Neuroimmune signaling: cytokines and the central nervous system. In Neuroscience in the 21st century: from basic to clinical; Springer: 2022; pp. 883-922.
- Carreño, L.J.; Bueno, S.M.; Bull, P.; Nathenson, S.G.; Kalergis, A.M. The half-life of the T-cell receptor/peptide–major histocompatibility complex interaction can modulate T-cell activation in response to bacterial challenge. Immunology 2007, 121, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perley, J.P.; Mikolajczak, J.; Buzzard, G.T.; Harrison, M.L.; Rundell, A.E. Resolving early signaling events in T-cell activation leading to IL-2 and FOXP3 transcription. Processes 2014, 2, 867–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slansky, J.E.; Nakayama, M. Peptide mimotopes alter T cell function in cancer and autoimmunity. In Proceedings of the Seminars in immunology; 2020; p. 101395. [Google Scholar]
- Glover, R.E.; Koshkin, V.; Dunford, H.B.; Mason, R.P. The reaction rates of NO with horseradish peroxidase compounds I and II. Nitric Oxide 1999, 3, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Fordsmann, J.C.; Jensen, S.H.; Gesslein, B.; Lønstrup, M.; Hald, B.O.; Zambach, S.A.; Brodin, B.; Lauritzen, M.J. Stimulation-induced increases in cerebral blood flow and local capillary vasoconstriction depend on conducted vascular responses. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2018, 115, E5796–E5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, W.; Shan, H.; Dai, H.; Chen, L. Identifying function modules from protein–protein interaction networks based on Szemerédi’s Regularity Lemma. International Journal of Biomathematics 2024, 2350104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Jiang, S.-C.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Fu, Y.-F.; Hu, J.; Li, Z.-L. Quantification of cytokine storms during virus infections. Frontiers in Immunology 2021, 12, 659419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocquet-Garçon, A. Impact of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein on the Innate Immune System: A Review. Cureus 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Kishimoto, T. Interplay between interleukin-6 signaling and the vascular endothelium in cytokine storms. Experimental & molecular medicine 2021, 53, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Kwong, A.C.; Ordovas-Montanes, J. Deconstructing inflammatory memory across tissue setpoints using cell circuit motifs. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, N. Synthetic Biology Approaches to Understand and Engineer Immune Cells; University of California, San Francisco: 2023.
- Bocharov, G. Understanding complex regulatory systems: integrating molecular biology and systems analysis. Transfusion Medicine and Hemotherapy 2005, 32, 304–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaitly, T.; Gupta, S.K.; Wolkenhauer, O.; Schuler, G.; Vera, J. Envisioning the Application of Systems Biology in Cancer Immunology. Cancer Immunology: A Translational Medicine Context 2020, 599–624. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Fu, F.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L. Interlocked feedback loops balance the adaptive immune response. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering 2022, 19, 4084–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, M.; Mustafa, S. Systems biology–the transformative approach to integrate sciences across disciplines: Systems Biology: Integrating Biological Sciences. Physical Sciences Reviews 2023, 8, 2523–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, H. Looking beyond the details: a rise in system-oriented approaches in genetics and molecular biology. Current genetics 2002, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, H. Nobel Turing Challenge: creating the engine for scientific discovery. NPJ systems biology and applications 2021, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelling, J. Mathematical models in microbial systems biology. Current opinion in microbiology 2004, 7, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingalls, B.P. Mathematical modeling in systems biology: an introduction; MIT press: 2013.
- Banerjee, S. Mathematical modeling: models, analysis and applications; Chapman and Hall/CRC: 2021.
- Ricardo, H.J. A modern introduction to differential equations; Academic Press: 2020.
- Nakada, T.; Mager, D.E. Systems model identifies baseline cytokine concentrations as potential predictors of rheumatoid arthritis inflammatory response to biologics. British Journal of Pharmacology 2022, 179, 4063–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Sohail, A.; Nutini, A.; Arif, R.; Tavares, J.M.R. Computational model to explore the endocrine response to trastuzumab action in HER-2/neu positive breast cancer. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences 2022, 29, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, A.; Schütte, C.; Sigrist, S.J.; Winkelmann, S. Variance of filtered signals: Characterization for linear reaction networks and application to neurotransmission dynamics. Mathematical Biosciences 2022, 343, 108760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Xie, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, A.; Chen, L.; Stromberg, A.; Arnold, S.M.; Liu, C.; Wang, C. A Probabilistic Approach to Estimate the Temporal Order of Pathway Mutations Accounting for Intra-Tumor Heterogeneity. Cancers 2024, 16, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, G.; Reali, F.; Priami, C.; Marchetti, L. Stochastic simulation algorithms for computational systems biology: Exact, approximate, and hybrid methods. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Systems Biology and Medicine 2019, 11, e1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, D.; Day, P.J. Systems medicine: the application of systems biology approaches for modern medical research and drug development. Molecular Biology International 2015, 2015, 698169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer, O.S.; O’Malley, M.A. Evolutionary systems biology: what it is and why it matters. BioEssays 2013, 35, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Samad, H. Biological feedback control—Respect the loops. Cell Systems 2021, 12, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinquin, O.; Demongeot, J. Roles of positive and negative feedback in biological systems. Comptes rendus. Biologies 2002, 325, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paludan, S.R.; Pradeu, T.; Masters, S.L.; Mogensen, T.H. Constitutive immune mechanisms: mediators of host defence and immune regulation. Nature Reviews Immunology 2021, 21, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganath, V.A.; Maity, I. Artificial Homeostasis Systems Based on Feedback Reaction Networks: Design Principles and Future Promises. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2024, 63, e202318134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz de Arruda, G.; Aleta, A.; Moreno, Y. Contagion dynamics on higher-order networks. Nature Reviews Physics 2024, 6, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khammash, M.H. Perfect adaptation in biology. Cell Systems 2021, 12, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angarita-Rodríguez, A.; González-Giraldo, Y.; Rubio-Mesa, J.J.; Aristizábal, A.F.; Pinzón, A.; González, J. Control Theory and Systems Biology: Potential Applications in Neurodegeneration and Search for Therapeutic Targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 25, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filo, M.; Chang, C.-H.; Khammash, M. Biomolecular feedback controllers: from theory to applications. Current Opinion in Biotechnology 2023, 79, 102882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graw, S.; Chappell, K.; Washam, C.L.; Gies, A.; Bird, J.; Robeson, M.S.; Byrum, S.D. Multi-omics data integration considerations and study design for biological systems and disease. Molecular omics 2021, 17, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, G.T.; Kim, K.-P.; Kim, K. How to interpret and integrate multi-omics data at systems level. Animal cells and systems 2020, 24, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jendoubi, T. Approaches to integrating metabolomics and multi-omics data: a primer. Metabolites 2021, 11, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehlen, W. Wirkungsstärke intravenös verabreichter Arzneimittel als Zeitfunktion: Ein Beitrag zur mathematischen Behandlung pharmakologischer Probleme. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archiv für experimentelle Pathologie und Pharmakologie 1933, 171, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladtke, E. History of pharmacokinetics. In Pharmacokinetics: Mathematical and Statistical Approaches to Metabolism and Distribution of Chemicals and Drugs; Springer: 1988; pp. 1-9.
- Talevi, A.; Ruiz, M.E. Zero-Order Drug Release. In The ADME Encyclopedia: A Comprehensive Guide on Biopharmacy and Pharmacokinetics; Springer: 2021; pp. 1-6.
- Widmark, E. The theoretical basis and practical application of medical-legal determination of alcohol. Berlin: Urban und Schwarzenberg 1932, 1–140. [Google Scholar]
- Himeoka, Y.; Furusawa, C. Perturbation-response analysis of in silico metabolic dynamics in nonlinear regime: Hard-coded responsiveness in the cofactors and network sparsity. eLife 2024, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Filo, M.; Kumar, S.; Khammash, M. A hierarchy of biomolecular proportional-integral-derivative feedback controllers for robust perfect adaptation and dynamic performance. Nature communications 2022, 13, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, D.; Song, P.; Zou, M.-H. Tryptophan-kynurenine pathway is dysregulated in inflammation, and immune activation. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2015, 20, 1116–1143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hajsl, M.; Hlavackova, A.; Broulikova, K.; Sramek, M.; Maly, M.; Dyr, J.E.; Suttnar, J. Tryptophan metabolism, inflammation, and oxidative stress in patients with neurovascular disease. Metabolites 2020, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; F Carvalho, A.; Anderson, G.; Galecki, P.; Maes, M. The many neuroprogressive actions of tryptophan catabolites (TRYCATs) that may be associated with the pathophysiology of neuro-immune disorders. Current pharmaceutical design 2016, 22, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, W.J.; Klaassen, T.; Schmitt, J.A. Tryptophan, mood, and cognitive function. Brain, behavior, and immunity 2002, 16, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almulla, A.F.; Supasitthumrong, T.; Amrapala, A.; Tunvirachaisakul, C.; Jaleel, A.-K.K.A.; Oxenkrug, G.; Al-Hakeim, H.K.; Maes, M. The tryptophan catabolite or kynurenine pathway in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2022, 88, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, D.; Iyer, M.; Narayanasamy, A.; Siva, K.; Vellingiri, B. Kynurenine pathway in Parkinson’s disease—An update. Eneurologicalsci 2020, 21, 100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Yu, J.-T.; Tan, L. The kynurenine pathway in neurodegenerative diseases: mechanistic and therapeutic considerations. Journal of the neurological sciences 2012, 323, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohár, Z.; Toldi, J.; Fülöp, F.; Vécsei, L. Changing the face of kynurenines and neurotoxicity: therapeutic considerations. International journal of molecular sciences 2015, 16, 9772–9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuravlev, A.V.; Zakharov, G.A.; Shchegolev, B.F.; Savvateeva-Popova, E.V. Antioxidant properties of kynurenines: density functional theory calculations. PLOS Computational Biology 2016, 12, e1005213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. From Lab to Life: Exploring Cutting-Edge Models for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Szabó, Á.; Vécsei, L.; Giménez-Llort, L. Emerging translational research in neurological and psychiatric diseases: From in vitro to in vivo models. 2023, 24, 15739. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, M.; Szabó, Á.; Körtési, T.; Szok, D.; Tajti, J.; Vécsei, L. From CGRP to PACAP, VIP, and beyond: unraveling the next chapters in migraine treatment. Cells 2023, 12, 2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Chen, C. Towards a mechanistic understanding of depression, anxiety, and their comorbidity: Perspectives from cognitive neuroscience. 2023, 17, 1268156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoz, B.M. Brain-on-a-Chip: Characterizing the next generation of advanced in vitro platforms for modeling the central nervous system. APL bioengineering 2021, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofazzal Jahromi, M.A.; Abdoli, A.; Rahmanian, M.; Bardania, H.; Bayandori, M.; Moosavi Basri, S.M.; Kalbasi, A.; Aref, A.R.; Karimi, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Microfluidic brain-on-a-chip: perspectives for mimicking neural system disorders. Molecular neurobiology 2019, 56, 8489–8512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brofiga, M.; Massobrio, P. Brain-on-a-chip: Dream or reality? Frontiers in Neuroscience 2022, 16, 837623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanyam, M.; Goyal, J. Translational biomarkers: from discovery and development to clinical practice. Drug Discovery Today: Technologies 2016, 21, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.; Jodrell, D.I.; Tuveson, D.A. Predictive in vivo animal models and translation to clinical trials. Drug discovery today 2012, 17, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serelli-Lee, V.; Ito, K.; Koibuchi, A.; Tanigawa, T.; Ueno, T.; Matsushima, N.; Imai, Y. A State-of-the-Art Roadmap for Biomarker-Driven Drug Development in the Era of Personalized Therapies. Journal of Personalized Medicine 2022, 12, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, T.W. Does kynurenic acid act on nicotinic receptors? An assessment of the evidence. Journal of neurochemistry 2020, 152, 627–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-S.; Ogbechi, J.; Clanchy, F.I.; Williams, R.O.; Stone, T.W. IDO and kynurenine metabolites in peripheral and CNS disorders. Frontiers in Immunology 2020, 11, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
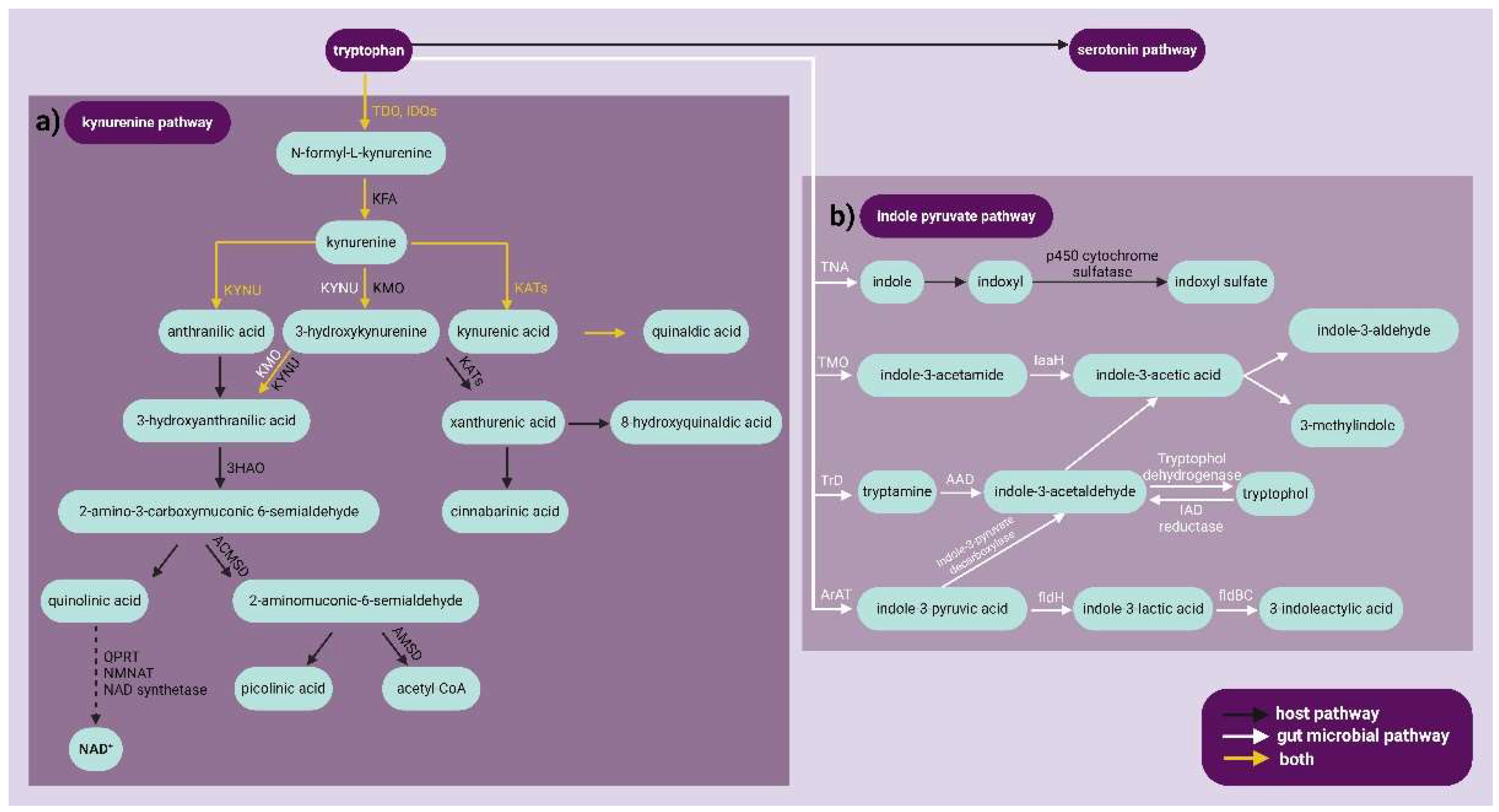
| Metabolites | Pro-oxidant | Antioxidant | NMDA receptor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agonist | Antagonist | |||
| Kynurenine | - | - | - | - |
| Kynurenic acid | - | + | - | + |
| Anthranilic acid | - | + | - | - |
| 3-Hydroxykynurenine | + | - | - | - |
| Xanthurenic acid | - | - | - | - |
| 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid | + | + | - | - |
| Quinolinic acid | + | - | + | - |
| Picolinic acid | - | + | - | - |
| Metabolites | Pro-oxidant | Antioxidant | NMDA receptor | AhR agonist | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agonist | Antagonist | ||||
| Kynurenine | + | + | - | - | + |
| Kynurenic acid | - | + | + | + | + |
| Anthranilic acid | - | + | - | - | + |
| 3-Hydroxykynurenine | + | + | - | - | + |
| Xanthurenic acid | + | + | - | - | + |
| Cinnabarinic acid | - | - | + | ||
| 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid | + | + | - | - | - |
| Quinolinic acid | + | - | + | - | - |
| Picolinic acid | - | + | - | - | - |
| Indoxyl sulfate | + | - | - | - | - |
| Indole-3-propionic acid | - | + | - | - | - |
| Indole-3-lactic acid | - | + | - | - | - |
| Indole-3-acetaldehyde | - | - | - | - | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





