Submitted:
14 October 2024
Posted:
15 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
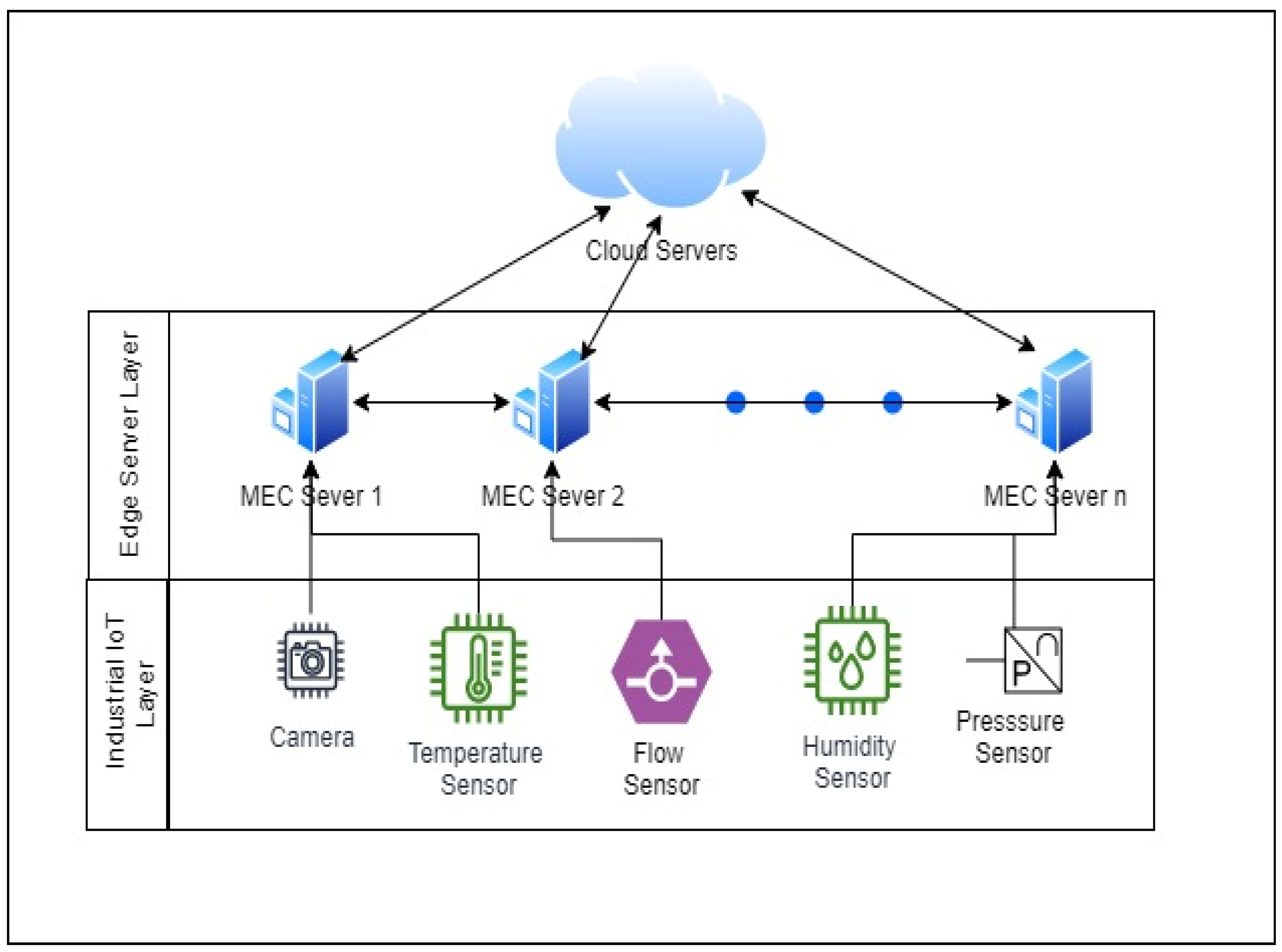
3. Problem Definition
4. Processing Delay Formulation
5. Energy Consumption Formulation
6. Calculation Model
7. Algorithm Implementation
Improved Particle Coding
- T as task count,
- N as edge server count,
- CFreqs = {CFreqs,1, CFreqs,2, CFreqs,3 … CFreqs,N} represents the edge server CPU frequency, and
- channel gain matrix Cg as
- Steps in Algorithm
- S1: Population Initialization
- S2: Fitness Value Calculation
- S3: Identify the Group’s Best Fitness Value
- S4: Update Particle Position and Velocity
- Wp is the inertia weight, a positive constant to balance the global search (Higher the value improves the exploration) and local search (lower the value improves the exploitation).
- Pbest is the particle’s personal best position.
- Gbest is the swam’s global best position.
- is the ith particle velocity.
- is the ith particle position.
- l1 and l2 are cognitive and social learning factors.
- U1 and U2 are random numbers
- n is max iteration count.
- i is current iteration
- l_max as 2.5 and l_min as 1.5
- S5: Genetic Algorithm (GA) Operations
- Selection: Select a collection of particles based on their fitness (e.g., tournament selection or roulette wheel selection).
- Crossover: Do crossover on selected collection of particles to produce new offsprings.
- Mutation: Do mutation to the crossover offsprings to maintain diversity.
- Merge Population: Combine the original particle population with the new mutated offsprings, by replacing least performing particles.
- Evaluation: Evaluate the fitness of the new population.
- Update Best Positions: Update the particle’s personal and global best position values if better solutions are found.
- S6: Termination
| Algorithm: IPSOGA |
|
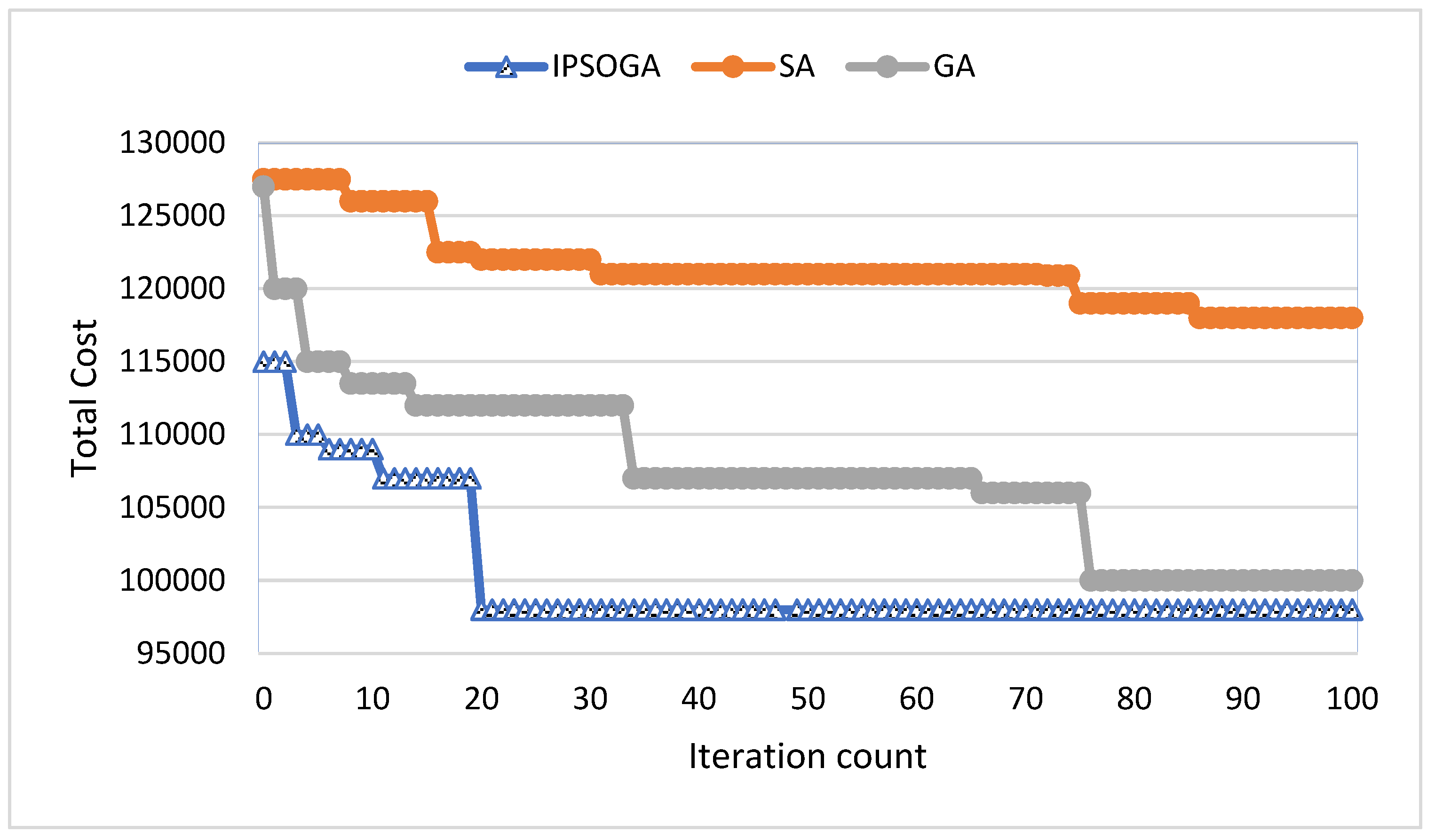
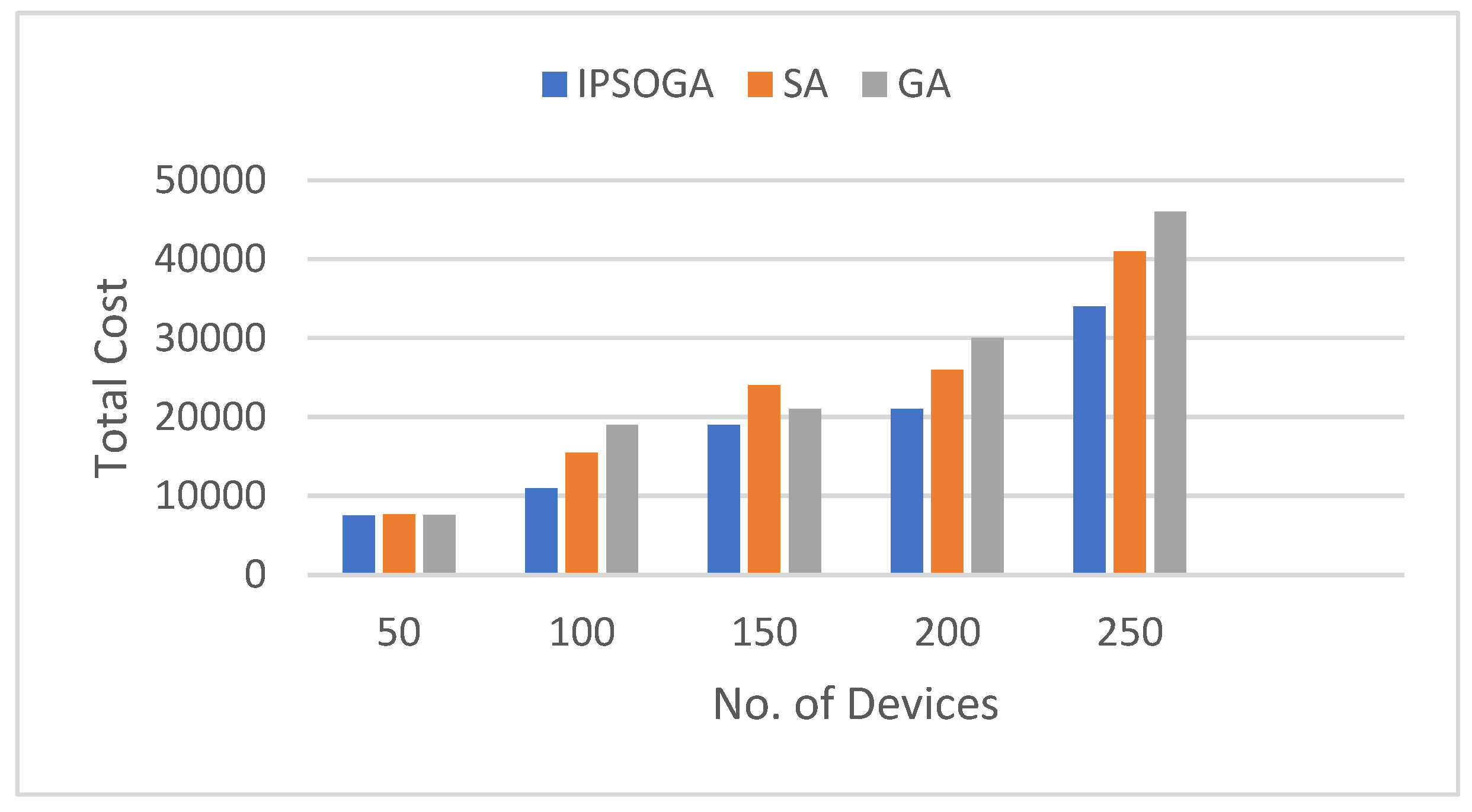
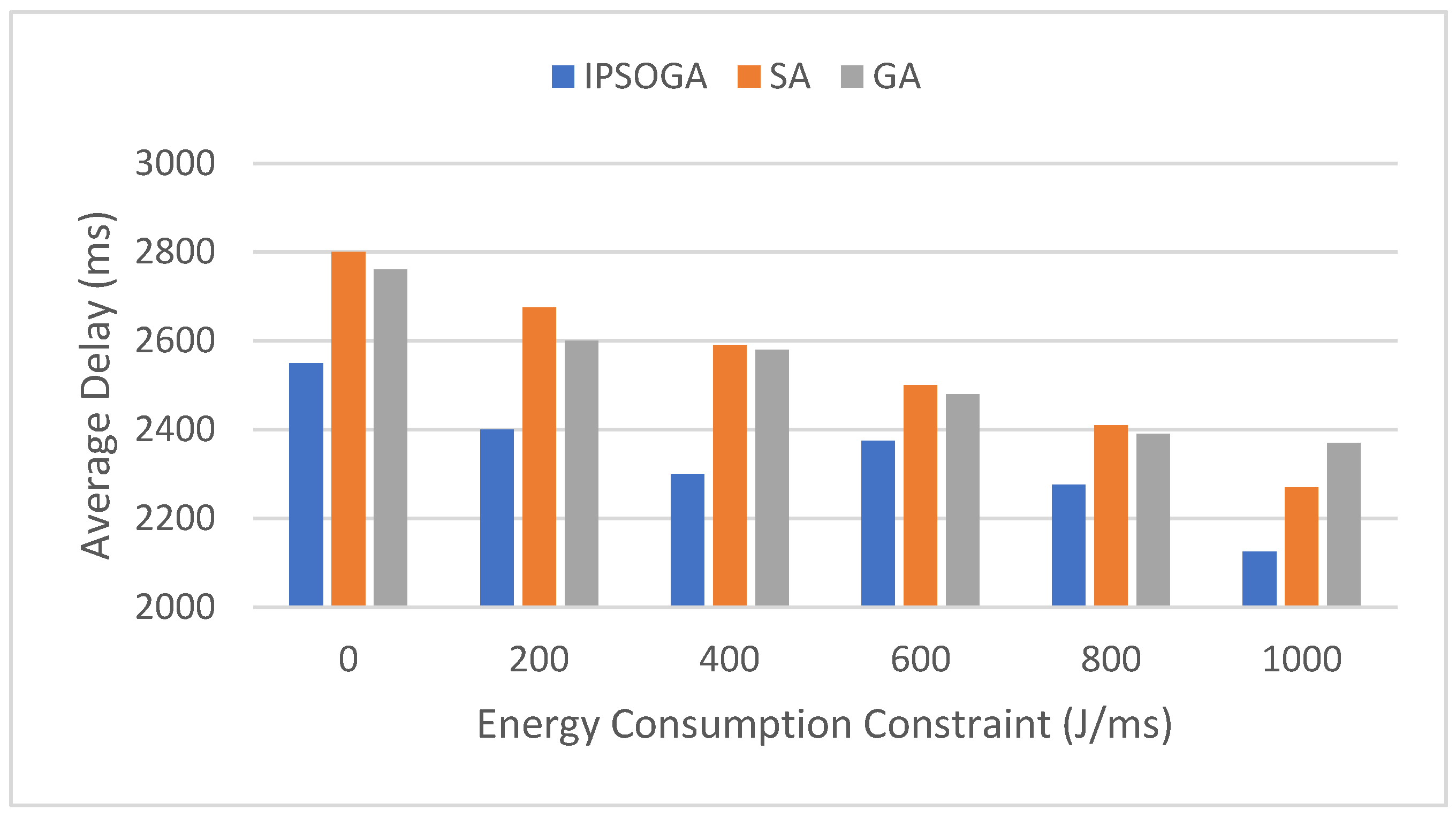
8. Results Analysis and Discussion
Experiment Settings
Baseline Algorithms
(1) Genetic Algorithm (GA)
(2) Simulated Annealing Algorithm (SA)
- Initialization: Temperature (T) initialization and solution state (S) initialization.
- Iteration: Generate a new solution S′, then calculate the increment ΔE=C(S′)−C(S), where C(S) is the cost function.
- If ΔE<0, then S′ is accepted as the new current solution.
- If ΔE≥0,S′ is accepted as the new current solution with a probability of exp(−ΔE/T).
- Termination: If the termination condition is met, the current solution is output as the optimal solution, and the program terminates.
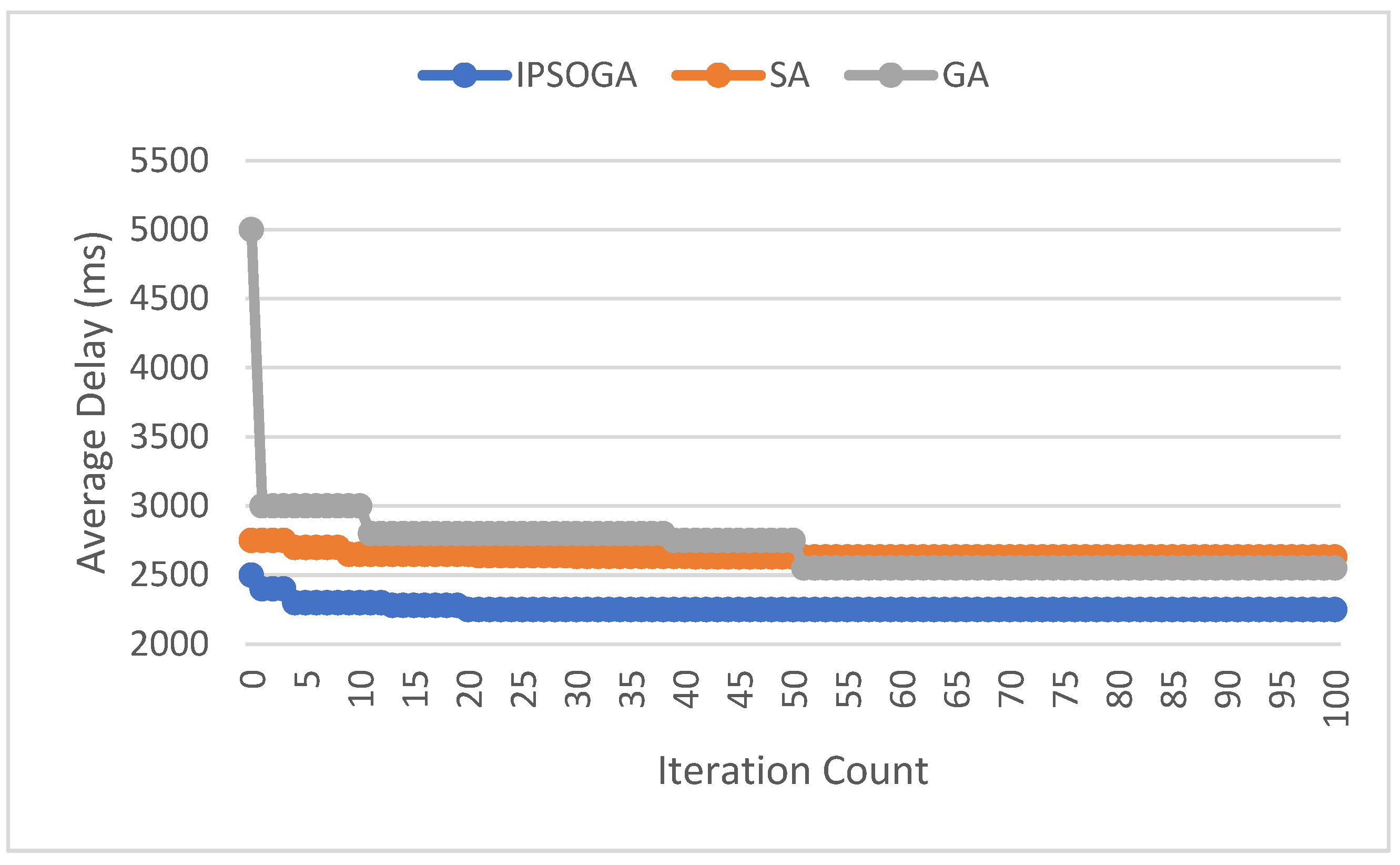
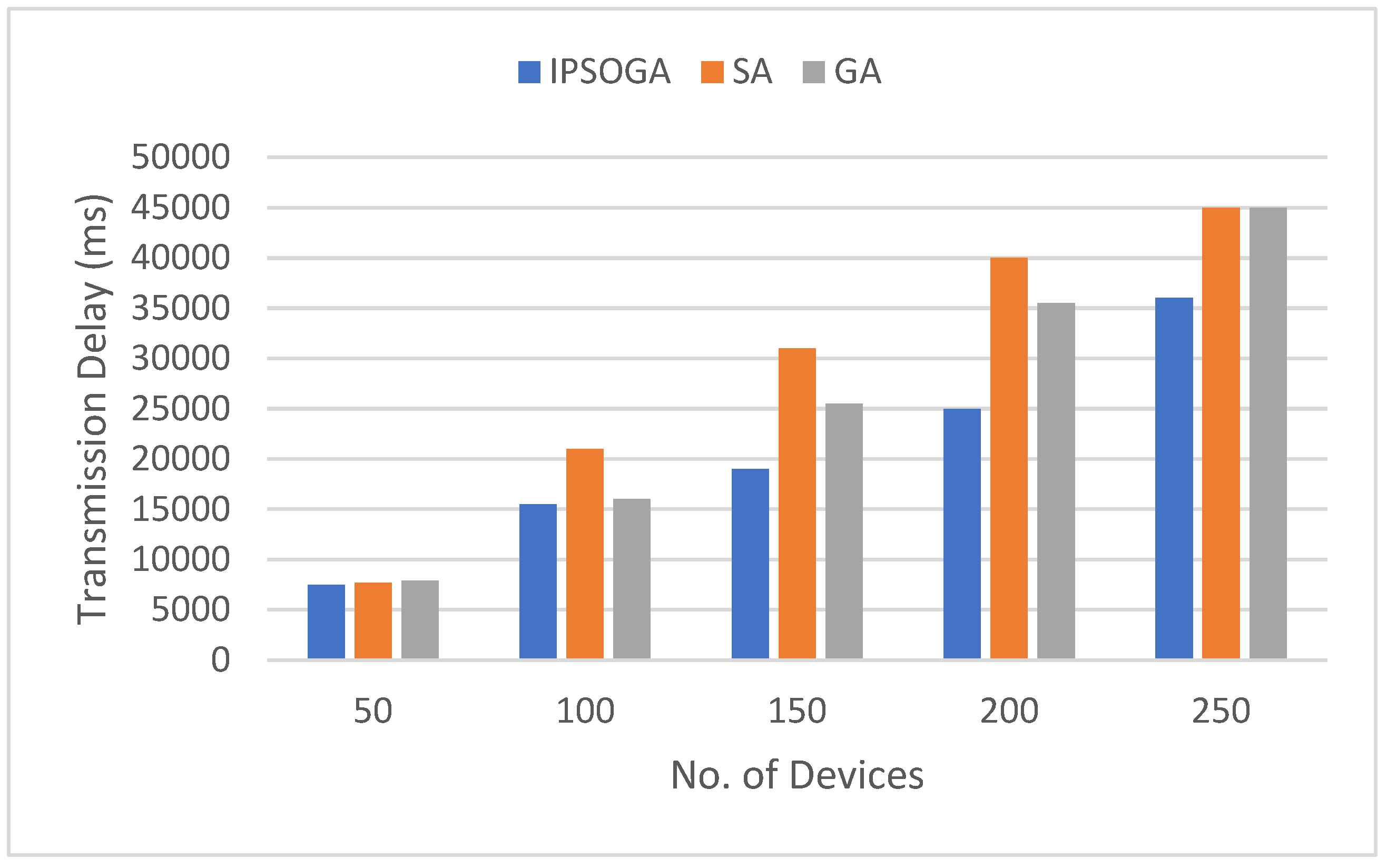
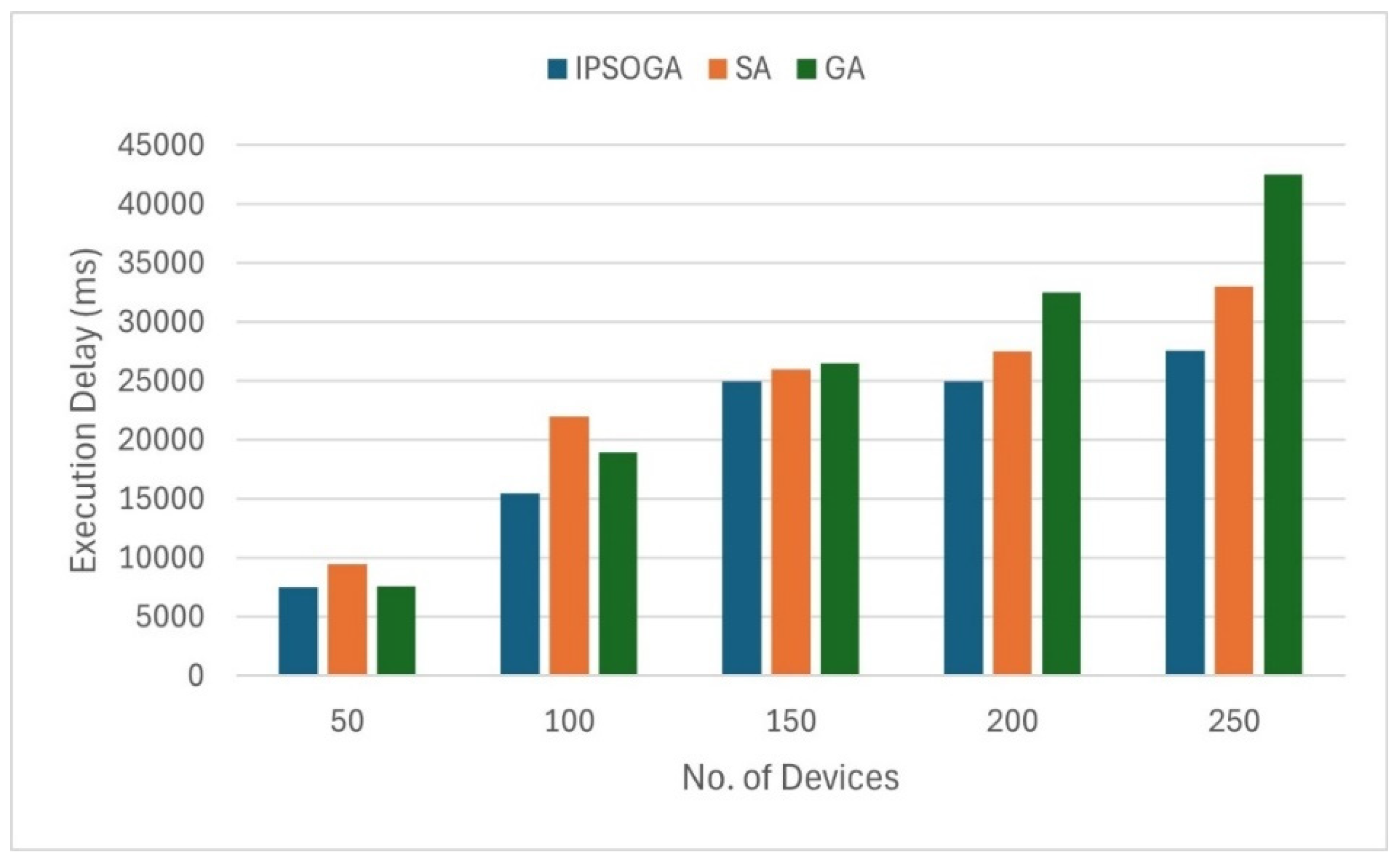
9. Results Analysis
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
Authors Biography
References
- T. Qiu, J. Chi, X. Zhou, Z. Ning, M. Atiquzzaman and D. O. Wu, “Edge Computing in Industrial Internet of Things: Architecture, Advances and Challenges,” in IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 2462-2488, Fourthquarter 2020. [CrossRef]
- F. Spinelli and V. Mancuso, “Toward Enabled Industrial Verticals in 5G: A Survey on MEC-Based Approaches to Provisioning and Flexibility,” in IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 596-630, Firstquarter 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Chi, T. Qiu, F. Xiao and X. Zhou, “ATOM: Adaptive Task Offloading With Two-Stage Hybrid Matching in MEC-Enabled Industrial IoT,” in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 23, no. 5, pp. 4861-4877, May 2024. [CrossRef]
- L. Lyu et al., “Adaptive Edge Sensing for Industrial IoT Systems: Estimation Task Offloading and Sensor Scheduling,” in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 391-402, 1 Jan.1, 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. K. Kasi et al., “Heuristic Edge Server Placement in Industrial Internet of Things and Cellular Networks,” in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 8, no. 13, pp. 10308-10317, 1 July1, 2021. [CrossRef]
- X. Dai et al., “Task Co-Offloading for D2D-Assisted Mobile Edge Computing in Industrial Internet of Things,” in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 480-490, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- X. Deng, J. Yin, P. Guan, N. N. Xiong, L. Zhang and S. Mumtaz, “Intelligent Delay-Aware Partial Computing Task Offloading for Multiuser Industrial Internet of Things Through Edge Computing,” in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 2954-2966, 15 Feb.15, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Mahmood et al., “Industrial IoT in 5G-and-Beyond Networks: Vision, Architecture, and Design Trends,” in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 18, no. 6, pp. 4122-4137, June 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. -H. Chao, J. -H. Wu, Y. Chiang and H. -Y. Wei, “5G Edge Computing Experiments with Intelligent Resource Allocation for Multi-Application Video Analytics,” 2021 30th Wireless and Optical Communications Conference (WOCC), Taipei, Taiwan, 2021, pp. 80-84. [CrossRef]
- T. Tan and G. Cao, “Deep Learning Video Analytics Through Edge Computing and Neural Processing Units on Mobile Devices,” in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 1433-1448, 1 March 2023. [CrossRef]
- Vijayaram, B., Vasudevan, V. Wireless edge device intelligent task offloading in mobile edge computing using hyper-heuristics. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2022, 126 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Yung-Ting Chuang, Yuan-Tsang Hung, A real-time and ACO-based offloading algorithm in edge computing, Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, Volume 179, 2023, 104703, ISSN 0743-7315. [CrossRef]
- Shuai Liu, Chunli Guo, Fadi Al-Turjman, Khan Muhammad, Victor Hugo C. de Albuquerque, Reliability of response region: A novel mechanism in visual tracking by edge computing for IIoT environments, Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Volume 138, 2020, 106537, ISSN 0888-3270. [CrossRef]
- Bao-Shan Sun, Hao Huang, Zheng-Yi Chai, Ying-Jie Zhao, Hong-Shen Kang, Multi-objective optimization algorithm for multi-workflow computation offloading in resource-limited IIoT, Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, Volume 89, 2024, 101646, ISSN 2210-6502. [CrossRef]
- Xiaojuan Zhu, Tianhao Zhang, Jinwei Zhang, Bao Zhao, Shunxiang Zhang, Cai Wu, Deep reinforcement learning-based edge computing offloading algorithm for software-defined IoT, Computer Networks, Volume 235, 2023, 110006, ISSN 1389-1286. [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| N (Edge Server) | 10 |
| M (Device Count) | 50 |
| Di | 5−50 Mbit |
| Fi | 500−1500 Cycles/bit |
| Fu,i | 1 GHz−5 GHz |
| Fs,j | 5 GHz−10 GHz |
| W | 2 MHz |
| Pi | 50−600 mW |
| Cgi,j | 2 × 10−6−2 × 10−5 |
| W∗ N0 | 1 × 10−8 W |
| 1100J | |
| g | 10−3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




