Submitted:
11 October 2024
Posted:
11 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Virus
2.2. Purification of E Protein Using Immunoaffinity Column
2.3. NanoLC MS Analysis
2.4. Database Search and Data Processing
2.5. In Silico Glycosylation
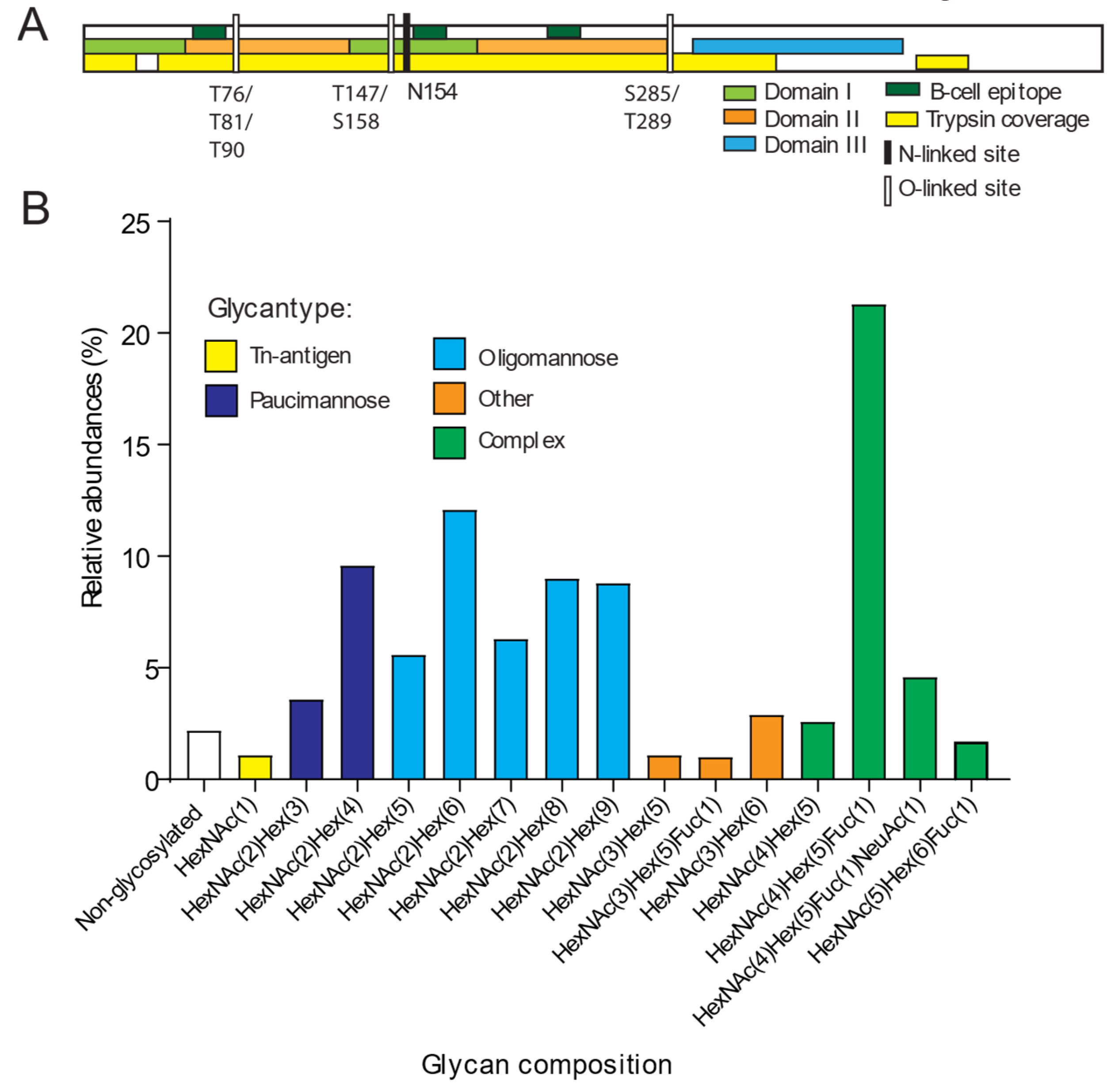
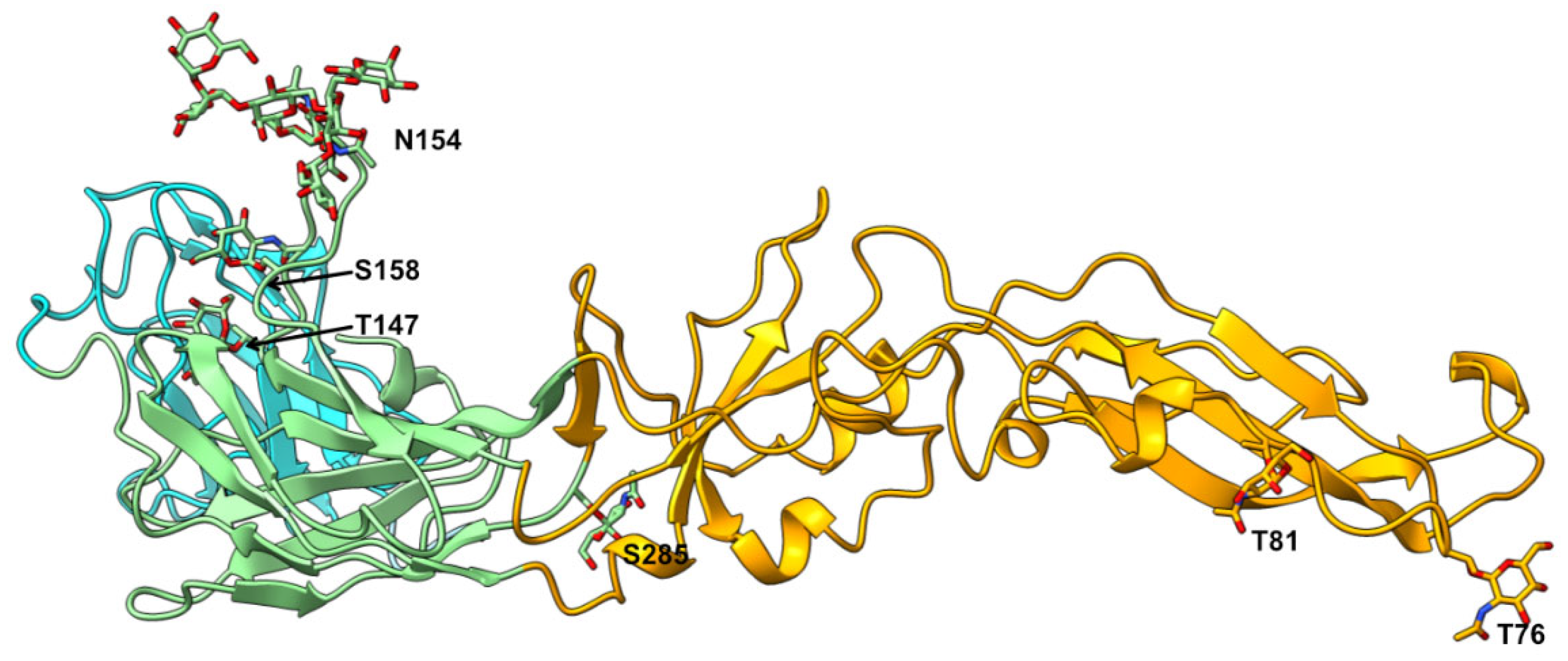
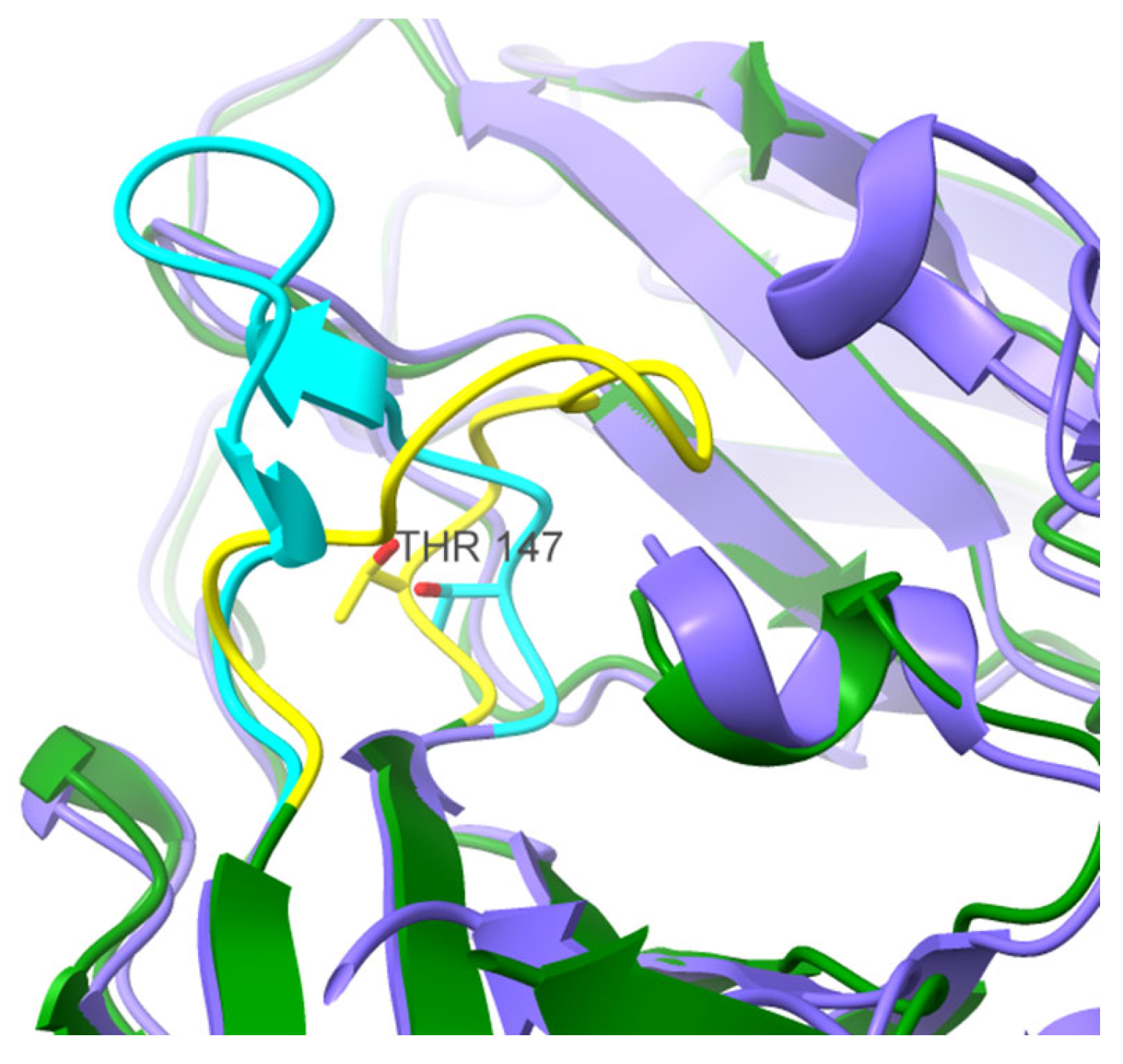
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruzek, D.; Avšič Županc, T.; Borde, J.; Chrdle, A.; Eyer, L.; Karganova, G.; Kholodilov, I.; Knap, N.; Kozlovskaya, L.; Matveev, A.; Miller, A.D.; Osolodkin, D.I.; Överby, A.K.; Tikunova, N.; Tkachev, S.; Zajkowska, J. Tick-borne encephalitis in Europe and Russia: Review of pathogenesis, clinical features, therapy, and vaccines. Antiviral Res 2019, 164, 23–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haglund, M.; Günther, G. Tick-borne encephalitis--pathogenesis, clinical course and long-term follow-up. Vaccine 2003, 21, S11–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasina, M.; Füzik, T.; Domanska, A.; Pulkkinen, L.I.A.; Šmerdová, L.; Formanová, P.P.; Straková, P.; Nováček, J.; Růžek, D.; Plevka, P.; Butcher, S.J. The structure of immature tick-borne encephalitis virus supports the collapse model of flavivirus maturation. Sci Adv 2024, 10, eadl1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubinski, M.; Beicht, J.; Gerlach, T.; Volz, A.; Sutter, G.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. , Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus: A Quest for Better Vaccines against a Virus on the Rise. Vaccines (Basel) 2020, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, K.E.; Rosdahl, A.; Insulander, M.; Vene, S.; Lindquist, L.; Gredmark-Russ, S.; Askling, H.H. Tick-borne Encephalitis Vaccine Failures: A 10-year Retrospective Study Supporting the Rationale for Adding an Extra Priming Dose in Individuals Starting at Age 50 Years. Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America 2020, 70, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotrič-Furlan, S.; Bogovič, P.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Jelovšek, M.; Lusa, L.; Strle, F. Tick-borne encephalitis in patients vaccinated against this disease. J Intern Med 2017, 282, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, T.J.; Hahn, C.S.; Galler, R.; Rice, C.M. FLAVIVIRUS GENOME ORGANIZATION, EXPRESSION, AND REPLICATION. Annual review of microbiology 1990, 44, 649–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulkkinen, L.I.A.; Barrass, S.V.; Domanska, A.; Överby, A.K.; Anastasina, M.; Butcher, S.J. Molecular Organisation of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus. Viruses 2022, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.H.; Klein, D.E.; Schmidt, A.G.; Peña, J.M.; Harrison, S.C. Sequential conformational rearrangements in flavivirus membrane fusion. eLife 2014, 3, e04389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaney, M.C.; Dellarole, M.; Duquerroy, S.; Medits, I.; Tsouchnikas, G.; Rouvinski, A.; England, P.; Stiasny, K.; Heinz, F.X.; Rey, F.A. Evolution and activation mechanism of the flavivirus class II membrane-fusion machinery. Nature communications 2022, 13, 3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.L.; Schalich, J.; Stiasny, K.; Mandl, C.W.; Heinz, F.X. Mutational evidence for an internal fusion peptide in flavivirus envelope protein E. Journal of virology 2001, 75, 4268–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jia, R.; Shen, H.; Wang, M.; Yin, Z.; Cheng, A. Structures and Functions of the Envelope Glycoprotein in Flavivirus Infections. Viruses 2017, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuivanen, S.; Hepojoki, J.; Vene, S.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O. Identification of linear human B-cell epitopes of tick-borne encephalitis virus. Virol J 2014, 11, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiermayr, S.; Stiasny, K.; Heinz, F.X. Impact of quaternary organization on the antigenic structure of the tick-borne encephalitis virus envelope glycoprotein E. Journal of virology 2009, 83, 8482–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarmer, J.; Zlatkovic, J.; Tsouchnikas, G.; Vratskikh, O.; Strauß, J.; Aberle, J.H.; Chmelik, V.; Kundi, M.; Stiasny, K.; Heinz, F.X. Variation of the specificity of the human antibody responses after tick-borne encephalitis virus infection and vaccination. Journal of virology 2014, 88, 13845–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, F.A.; Heinz, F.X.; Mandl, C.; Kunz, C.; Harrison, S.C. The envelope glycoprotein from tick-borne encephalitis virus at 2 A resolution. Nature 1995, 375, 291–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pletnev, A.G.; Bray, M.; Lai, C.J. Chimeric tick-borne encephalitis and dengue type 4 viruses: effects of mutations on neurovirulence in mice. Journal of virology 1993, 67, 4956–4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, B.E.E.; Koraka, P.; van den Doel, P.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Haagmans, B.L.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E. DC-SIGN enhances infection of cells with glycosylated West Nile virus in vitro and virus replication in human dendritic cells induces production of IFN-α and TNF-α. Virus research 2008, 135, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, A.; Yoshii, K.; Obara, M.; Ueki, T.; Mizutani, T.; Kariwa, H.; Takashima, I. Role of the N-linked glycans of the prM and E envelope proteins in tick-borne encephalitis virus particle secretion. Vaccine 2005, 23, 3043–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayce, A.C.; Alonzi, D.S.; Killingbeck, S.S.; Tyrrell, B.E.; Hill, M.L.; Caputo, A.T.; Iwaki, R.; Kinami, K.; Ide, D.; Kiappes, J.L.; Beatty, P.R.; Kato, A.; Harris, E.; Dwek, R.A.; Miller, J.L.; Zitzmann, N. Iminosugars Inhibit Dengue Virus Production via Inhibition of ER Alpha-Glucosidases—Not Glycolipid Processing Enzymes. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases 2016, 10, e0004524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, D.W.C.; Whiteman, M.C.; Zhang, S.; Huang, C.Y.H.; Schneider, B.S.; Smith, D.R.; Gromowski, G.D.; Higgs, S.; Kinney, R.M.; Barrett, A.D.T. Envelope protein glycosylation status influences mouse neuroinvasion phenotype of genetic lineage 1 West Nile virus strains. Journal of virology 2005, 79, 8339–8347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattová, E.; Straková, P.; Pokorná-Formanová, P.; Grubhoffer, L.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Zdráhal, Z.; Palus, M.; Ruzek, D. Comprehensive N-glycosylation mapping of envelope glycoprotein from tick-borne encephalitis virus grown in human and tick cells. Scientific reports 2020, 10, 13204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haglund, M.; Vene, S.; Forsgren, M.; Günther, G.; Johansson, B.; Niedrig, M.; Plyusnin, A.; Lindquist, L.; Lundkvist, A. Characterisation of Human Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus From Sweden. Journal of Medical Virology 2003, 71, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiśniewski, J.R.; Zougman, A.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nat Methods 2009, 6, 359–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, E.C.; Goddard, T.D.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Pearson, Z.J.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Tools for structure building and analysis. Protein Sci 2023, 32, e4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group, W. GLYCAM Web. http://glycam.org.
- Struwe, W.B.; Chertova, E.; Allen, J.D.; Seabright, G.E.; Watanabe, Y.; Harvey, D.J.; Medina-Ramirez, M.; Roser, J.D.; Smith, R.; Westcott, D.; Keele, B.F.; Bess, J.W., Jr.; Sanders, R.W.; Lifson, J.D.; Moore, J.P.; Crispin, M. Site-Specific Glycosylation of Virion-Derived HIV-1 Env Is Mimicked by a Soluble Trimeric Immunogen. Cell Rep 2018, 24, 1958–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitsuhara, Y.; Toyoda, T.; Itai, T.; Yamaguchi, H. Chaperone-Like Functions of High-Mannose Type and Complex-Type N-Glycans and Their Molecular Basis1. The Journal of Biochemistry 2002, 132, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In Essentials of Glycobiology, Varki, A.; Cummings, R.D.; Esko, J.D.; Stanley, P.; Hart, G.W.; Aebi, M.; Darvill, A.G.; Kinoshita, T.; Packer, N.H.; Prestegard, J.H.; Schnaar, R.L.; Seeberger, P.H., Eds. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. Copyright 2015-2017 by The Consortium of Glycobiology Editors, La Jolla, California. All rights reserved.: Cold Spring Harbor (NY), 2015.
- Rey, F.A.; Stiasny, K.; Heinz, F.X. Flavivirus structural heterogeneity: implications for cell entry. Current opinion in virology 2017, 24, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Al-Shareffi, E.; Haltiwanger, R.S. Biological functions of fucose in mammals. Glycobiology 2017, 27, 601–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, S.; Shimomura, M.; Kamada, Y.; Maeda, H.; Sobajima, T.; Hikita, H.; Iijima, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Misaki, R.; Fujiyama, K.; Nagamori, S.; Kanai, Y.; Takehara, T.; Ueda, K.; Kuroda, S. i.; Miyoshi, E. Core-fucosylation plays a pivotal role in hepatitis B pseudo virus infection: a possible implication for HBV glycotherapy. Glycobiology 2016, 26, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norden, R.; Samuelsson, E.; Nystrom, K. NFkappaB-mediated activation of the cellular FUT3, 5 and 6 gene cluster by herpes simplex virus type 1. Glycobiology 2017, 27, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyström, K.; Nordén, R.; Muylaert, I.; Elias, P.; Larson, G.; Olofsson, S. Induction of sialyl-Lex expression by herpes simplex virus type 1 is dependent on viral immediate early RNA-activated transcription of host fucosyltransferase genes. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 847–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyström, K.; Grahn, A.; Lindh, M.; Brytting, M.; Mandel, U.; Larson, G.; Olofsson, S. Virus-induced transcriptional activation of host FUT genes associated with neo-expression of Ley in cytomegalovirus-infected and sialyl-Lex in varicella-zoster virus-infected diploid human cells. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 355–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Chastain, A.; Moir, S.; Ford, J.; Trandem, K.; Martinelli, E.; Cicala, C.; Crocker, P.; Arthos, J.; Sun, P.D. Siglecs facilitate HIV-1 infection of macrophages through adhesion with viral sialic acids. PloS one 2011, 6, e24559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahantarig, A.; Růzek, D.; Vancová, M.; Janowitz, A.; St'astná, H.; Tesarová, M.; Grubhoffer, L. Tick-borne encephalitis virus infection of cultured mouse macrophages. Intervirology 2009, 52, 283–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kost, T.A.; Condreay, J.P.; Jarvis, D.L. Baculovirus as versatile vectors for protein expression in insect and mammalian cells. Nature biotechnology 2005, 23, 567–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, Y.; Förster, S.; Gielen, G.H.; Loke, I.; Thaysen-Andersen, M.; Laurini, C.; Wehrand, K.; Pietsch, T.; Diestel, S. Paucimannosidic glycoepitopes inhibit tumorigenic processes in glioblastoma multiforme. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 4449–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pont, L.; Kuzyk, V.; Benavente, F.; Sanz-Nebot, V.; Mayboroda, O.A.; Wuhrer, M.; Lageveen-Kammeijer, G.S.M. Site-Specific N-Linked Glycosylation Analysis of Human Carcinoembryonic Antigen by Sheathless Capillary Electrophoresis-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J Proteome Res 2021, 20, 1666–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordén, R.; Nilsson, J.; Samuelsson, E.; Risinger, C.; Sihlbom, C.; Blixt, O.; Larson, G.; Olofsson, S.; Bergstrom, T. Recombinant Glycoprotein E of Varicella Zoster Virus Contains Glycan-Peptide Motifs That Modulate B Cell Epitopes into Discrete Immunological Signatures. International journal of molecular sciences 2019, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsson, E.; Mirgorodskaya, E.; Nyström, K.; Bäckström, M.; Liljeqvist, J.; Nordén, R. Sialic Acid and Fucose Residues on the SARS-CoV-2 Receptor-Binding Domain Modulate IgG Antibody Reactivity. ACS Infect Dis 2022, 8, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saksida, A.; Jakopin, N.; Jelovšek, M.; Knap, N.; Fajs, L.; Lusa, L.; Lotrič-Furlan, S.; Bogovič, P.; Arnež, M.; Strle, F.; Avšič-Županc, T. Virus RNA Load in Patients with Tick-Borne Encephalitis, Slovenia. Emerg Infect Dis 2018, 24, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S. Computational analysis of perturbations in the post-fusion Dengue virus envelope protein highlights known epitopes and conserved residues in the Zika virus. F1000Res 2016, 5, 1150–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roby, J.A.; Setoh, Y.X.; Hall, R.A.; Khromykh, A.A. Post-translational regulation and modifications of flavivirus structural proteins. The Journal of general virology 2015, 96, 1551–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, S.S.; Fan, Y.C.; Crill, W.D.; Chang, R.Y.; Chang, G.J. Mutation analysis of the cross-reactive epitopes of Japanese encephalitis virus envelope glycoprotein. The Journal of general virology 2012, 93, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, F.A.; Stiasny, K.; Vaney, M.C.; Dellarole, M.; Heinz, F.X. The bright and the dark side of human antibody responses to flaviviruses: lessons for vaccine design. EMBO Rep 2018, 19, 206–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, S.; Blixt, O.; Bergstrom, T.; Frank, M.; Wandall, H.H. Viral O-GalNAc peptide epitopes: a novel potential target in viral envelope glycoproteins. Rev. Med. Virol. 2016, 26, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clo, E.; Kracun, S.K.; Nudelman, A.S.; Jensen, K.J.; Liljeqvist, J.A.; Olofsson, S.; Bergstrom, T.; Blixt, O. Characterization of the viral O-glycopeptidome: a novel tool of relevance for vaccine design and serodiagnosis. Journal of virology 2012, 86, 6268–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeletti, D.; Gibbs, J.S.; Angel, M.; Kosik, I.; Hickman, H.D.; Frank, G.M.; Das, S.R.; Wheatley, A.K.; Prabhakaran, M.; Leggat, D.J.; McDermott, A.B.; Yewdell, J.W. Defining B cell immunodominance to viruses. Nature immunology 2017, 18, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, F.Y.; Li, X.; Tsuji, M.; Kasper, D.L. A mechanism for glycoconjugate vaccine activation of the adaptive immune system and its implications for vaccine design. Nature medicine 2011, 17, 1602–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




