Submitted:
10 October 2024
Posted:
11 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
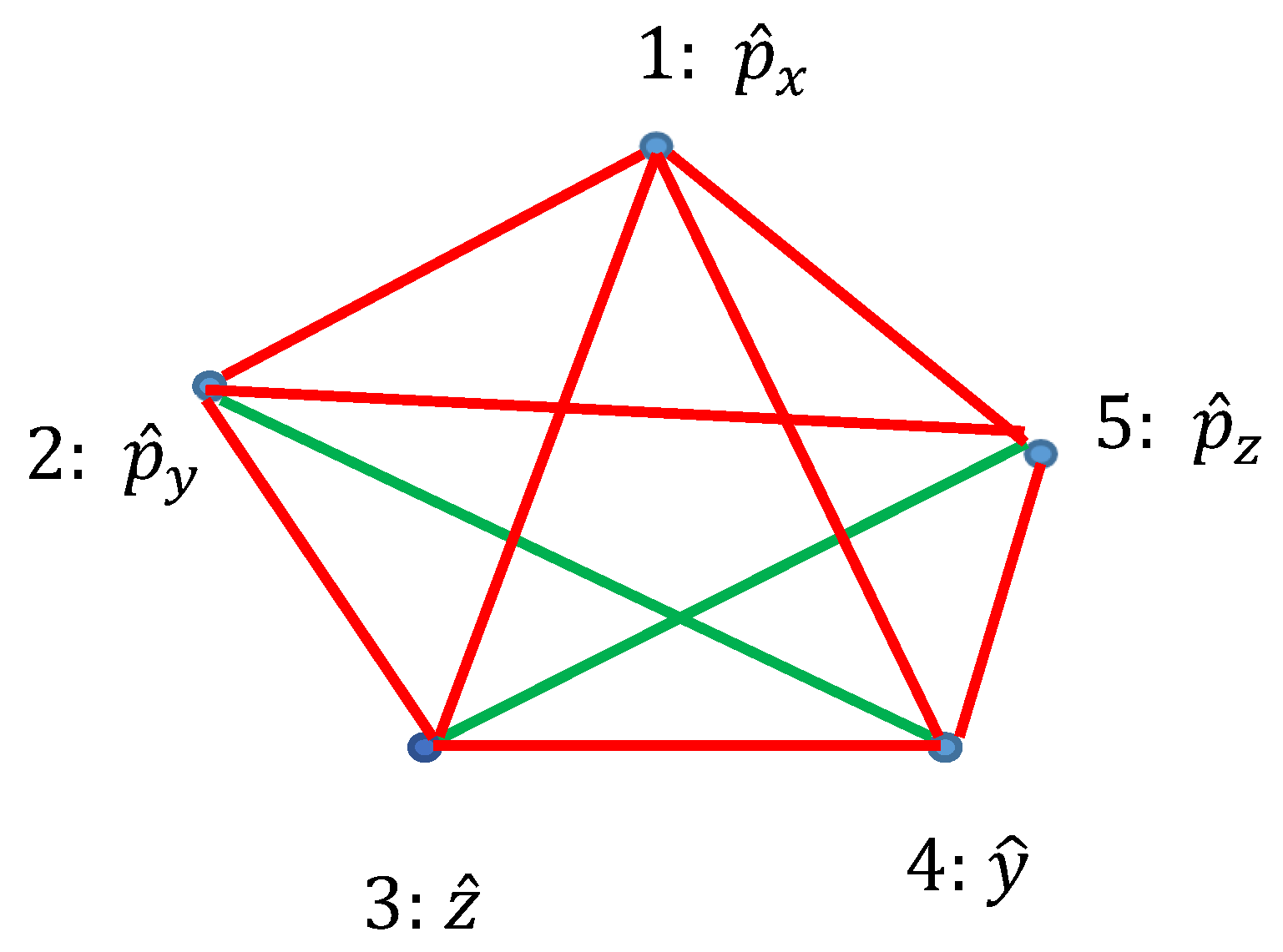
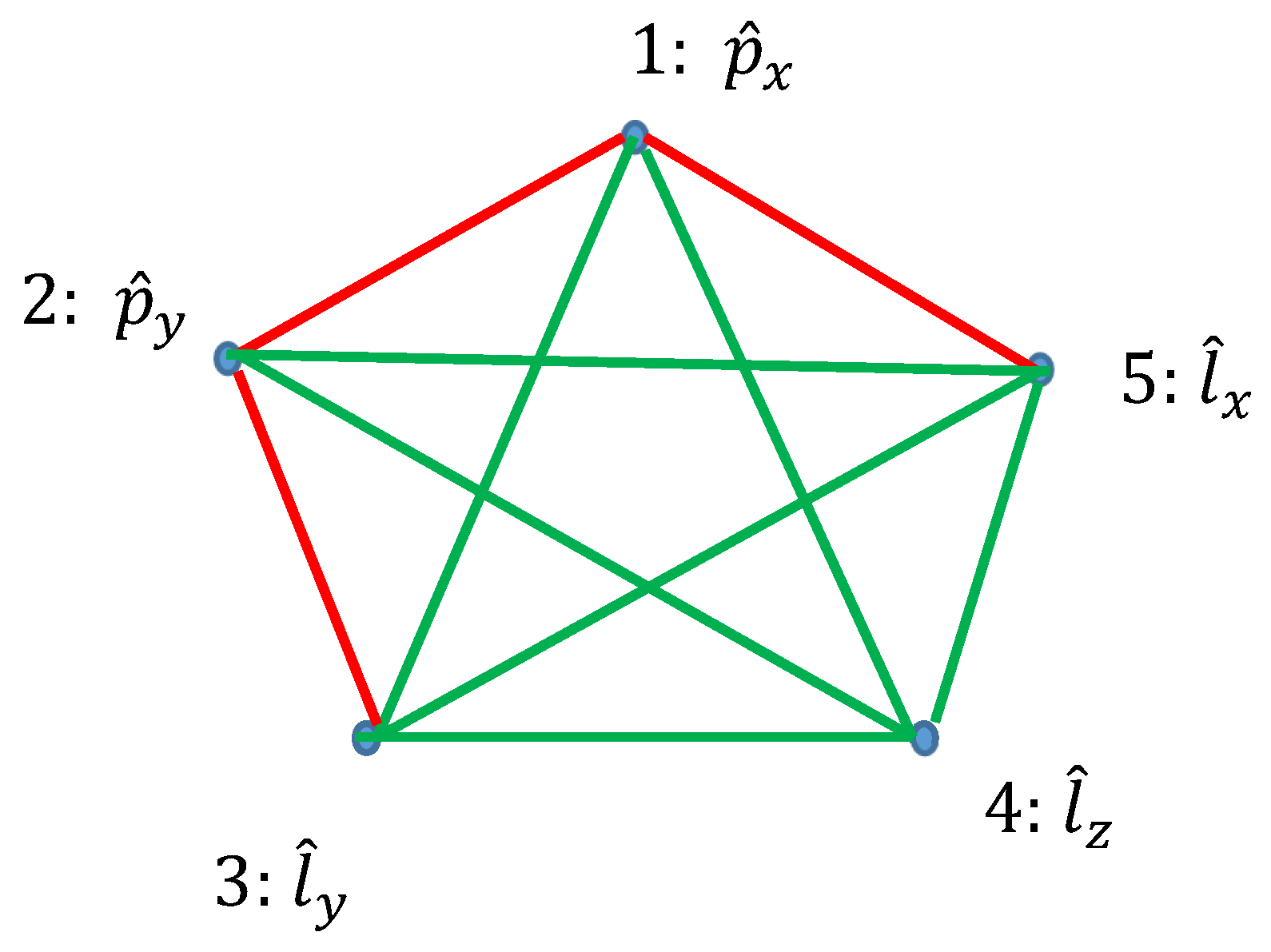
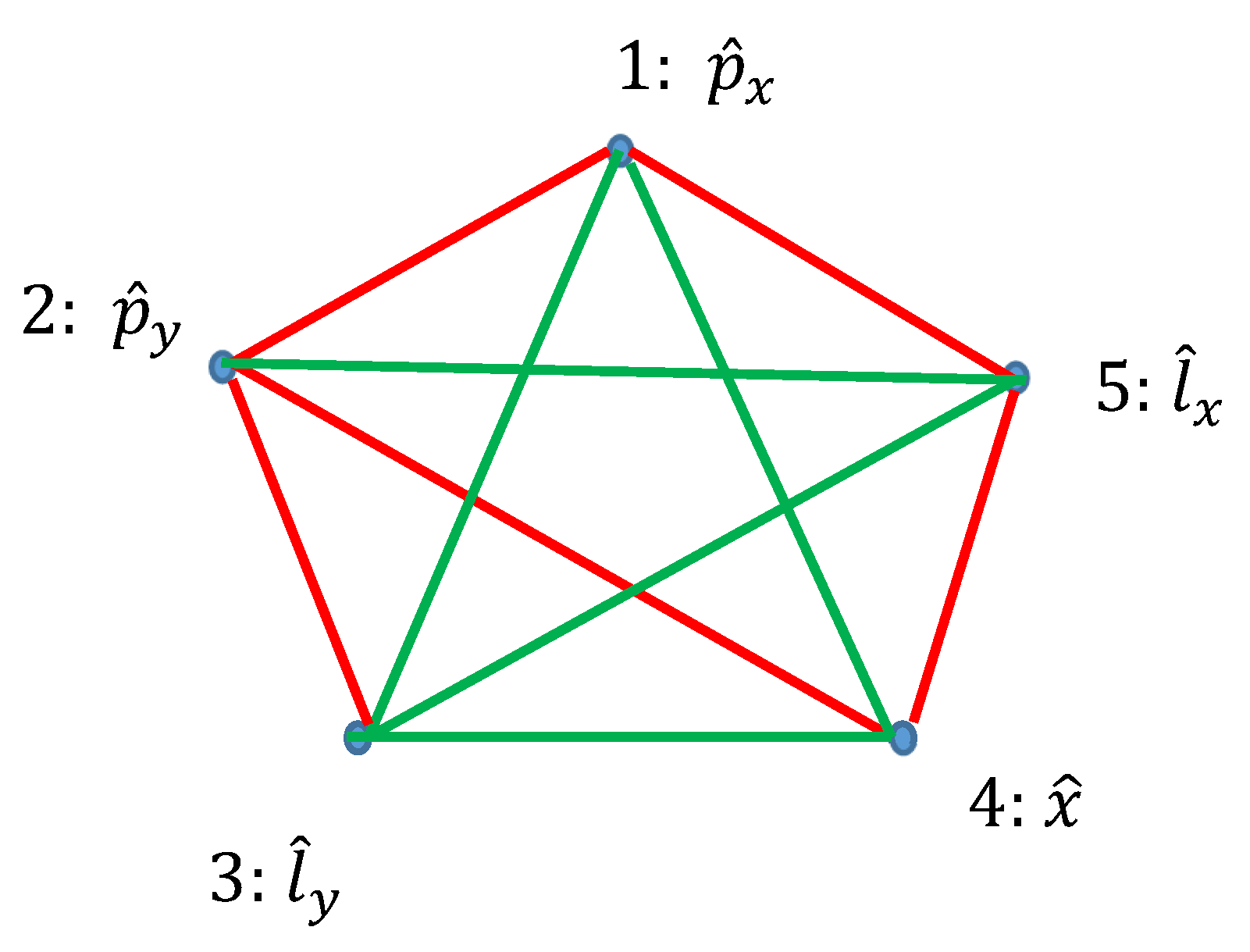
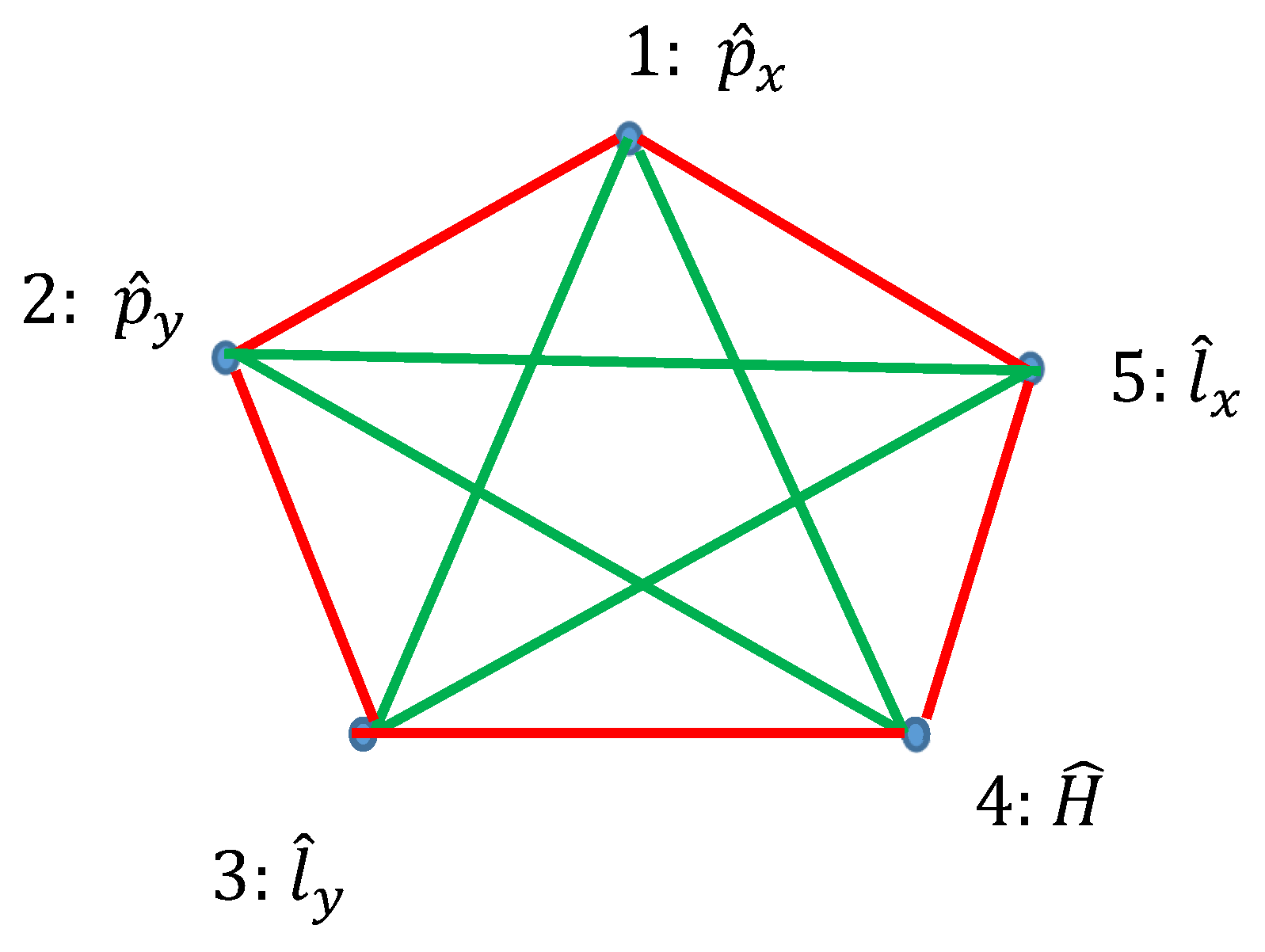
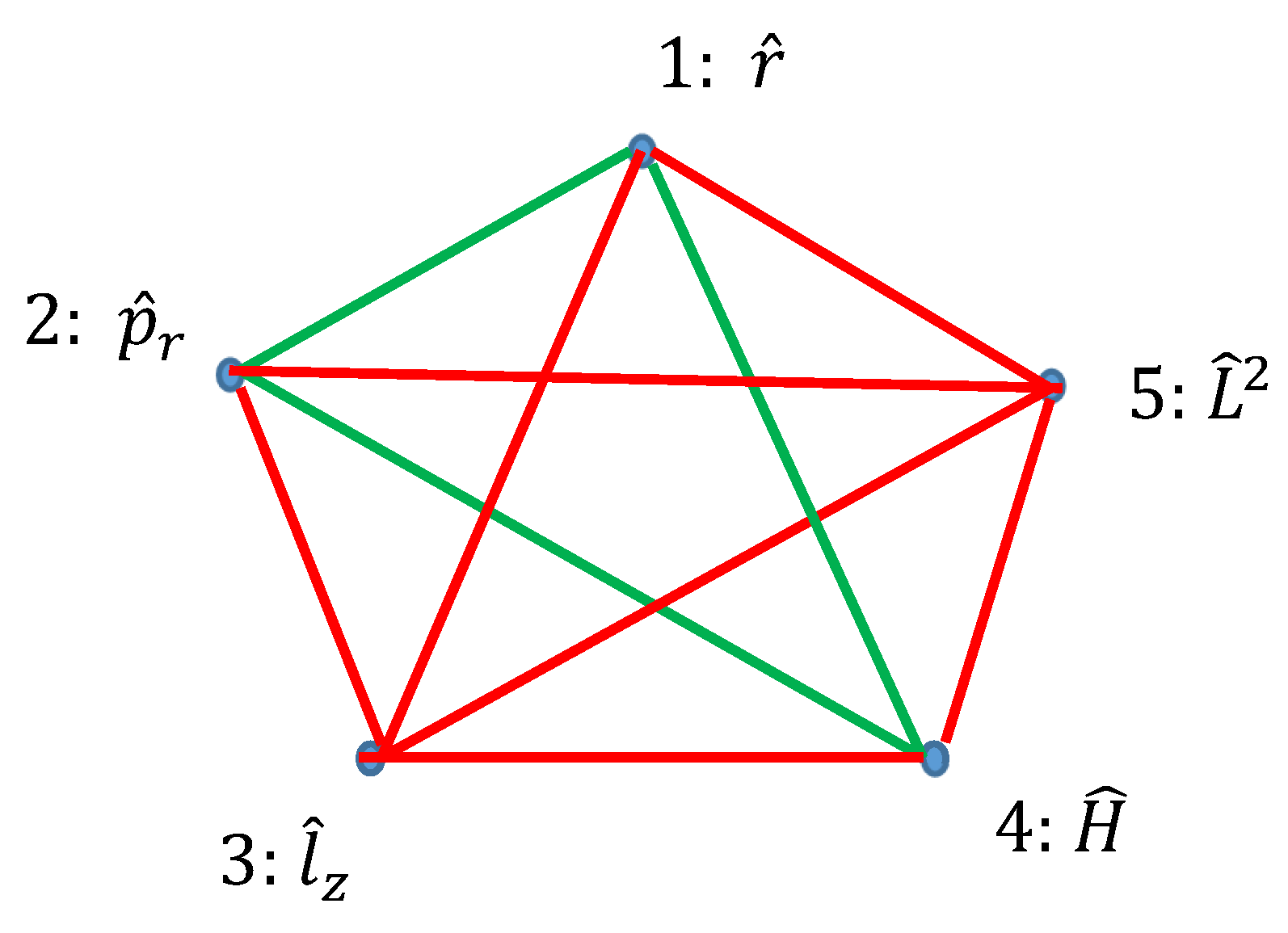
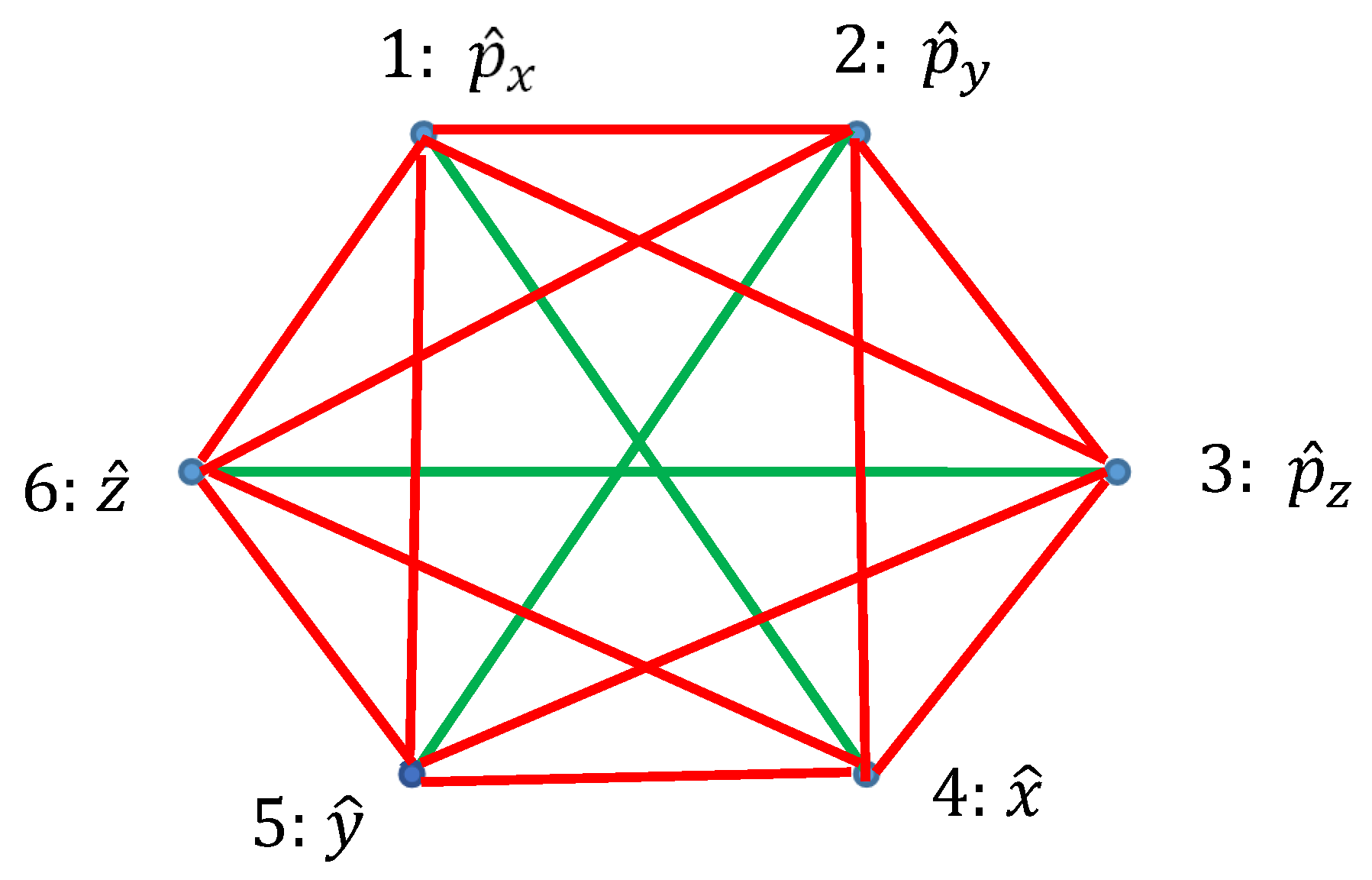
Ramsey theory enables re-shaping of the basic ideas of the quantum mechanics. Quantum observables, represented by linear Hermitian operators are seen as the vertices of the graph. Relation of commutation define coloring of the edges linking the vertices: if the operators commute, they are connected with the red link; if they do not commute they are connected with the green link. Thus, a bi-colored, complete, Ramsey graph emerges. According to the Ramsey theorem, complete, bi-colored graph built of six vertices, will inevitably contain at least one monochromatic triangle; in other words, the Ramsey number R(3,3)=6. In our interpretation, this triangle represents the triad of observables, which could or, alternatively, could not be established simultaneously in a given quantum system. The Ramsey approach to the quantum mechanics is illustrated with the numerous examples, including the motion of a particle in a centrally symmetrical field.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Observables, Operators and Graphs
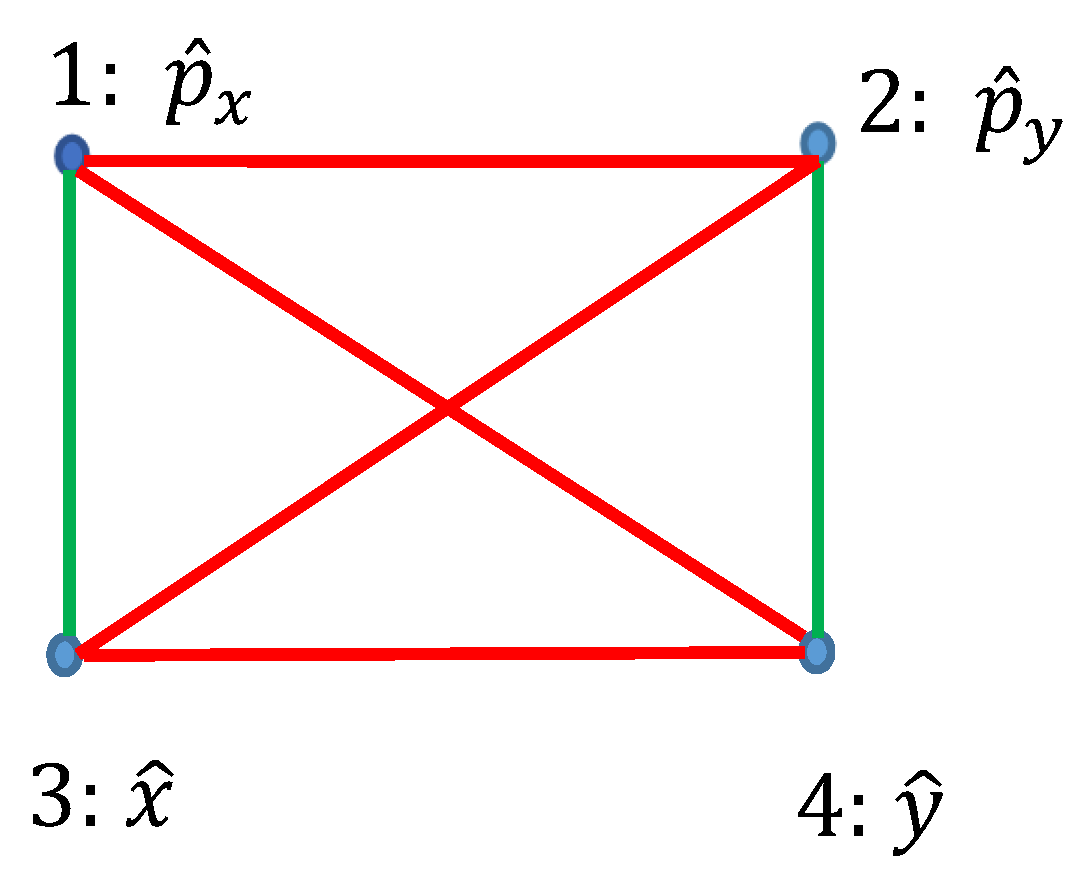
2.2. Graph Approach to the Observables: Converting Observables into Graph
2.3. Graphs Possessing Six Vertices Emerging from Quantum Observables and the Ramsey Theorem
3. Discussion
- i)
- Generalization of the reported approach for the systems of quantum particles.
- ii)
- Involving infinite Ramsey theory for the analysis of the problems of quantum mechanics and quantum electrodynamics.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramsey, F. P. On a Problem of Formal Logic. In: Gessel, I., Rota, GC. (eds) Classic Papers in Combinatorics. Modern Birkhäuser Classics. Birkhäuser Boston, 2009, pp. 264-286.
- Chartrand, G.; Zhang, P. New directions in Ramsey theory. Discrete Math. Lett. 2021, 6, 84–96. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, R. L.; Rothschild, B.L.; Spencer, J, H. Ramsey theory, 2nd ed., Wiley-Interscience Series in Discrete Mathematics and Optimization, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, A Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1990, pp. 10-110.
- Graham, R.; Butler, S. Rudiments of Ramsey Theory (2nd ed.). American Mathematical Society: Providence, Rhode Island, USA, 2015; pp. 7–46.
- Landman, B. M.; Robertson, A. Ramsey Theory on the Integers, Student Mathematical Library, vol. 24, Providence, RI: AMS, 2004.
- Li, Y.; Lin, Q. Elementary methods of the graph theory, Applied Mathematical Sciences. Springer, pp. 3-44, Cham, Switzerland, 2020.
- Di Nasso, M.; Goldbring, I.; Lupini M., Nonstandard Methods in Combinatorial Number Theory, Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 2239, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2019.
- Katz, M.; Reimann, J. Introduction to Ramsey Theory: Fast Functions, Infinity, and Metamathematics, Student Mathemati-cal Library Volume: 87; 2018; pp. 1-34.
- Erdős, P. , Gyárfás, A. A variant of the classical Ramsey problem. Combinatorica 1997, 17, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdős, P. Solved and unsolved problems in combinatorics and combinatorial number theory. Congressus Numerantium 1981, 32, 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- Conlon, J.; Fox, B. Sudakov, Recent developments in graph Ramsey theory. Surveys in Combinatorics, 2015, 424, 49–118. [Google Scholar]
- Gaitan, F.; Clark, L. Ramsey Numbers and Adiabatic Quantum Computing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 010501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Z.; Chudak, F.; Macready, W. G.; Clark, L.; Gaitan, F. Experimental Determination of Ramsey Numbers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 130505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wouters, J.; Giotis, A.; Kang, R.; Schuricht, D.; Fritz, L. Lower bounds for Ramsey numbers as a statistical physics problem. J. Stat. Mech. 2022, 2022, 0332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messiah, A. Quantum Mechanics, Dover Books on Physics, Dover Publications, Mineola, NY, 2014.
- Landau L. D.; Lifshitz, E. M. Quantum mechanics. Non-Relativistic Theory, Volume 3 of Course of Theoretical Physics, 3rd Ed., Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1965.
- Zettili, N. Quantum Mechanics. Concepts and Applications. 2nd Ed., John Wiley & Sons Ltd., The Atrium, Southern Gate, Chichester, West Sussex, PO19 8SQ, United Kingdom, 2009.
- Bohm, D. Quantum Theory, Dover Publications, New York, NY, USA, 1989.
- Choudum, S. A.; Ponnusamy, B. Ramsey numbers for transitive tournaments. Discrete Mathematics 1999, 206, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvalb, N.; Frenkel, M.; Shoval, Sh.; Bormashenko, Ed. Dynamic Ramsey Theory of Mechanical Systems Forming a Complete Graph and Vibrations of Cyclic Compounds. Dynamics 2023, 3, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, M.; Shoval, Sh.; Bormashenko, Ed. Fermat Principle, Ramsey Theory and Metamaterials. Materials 2023, 16, 7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bormashenko, E. Universe as a Graph (Ramsey Approach to Analysis of Physical Systems). World Jour. of Physics 2023, 1, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
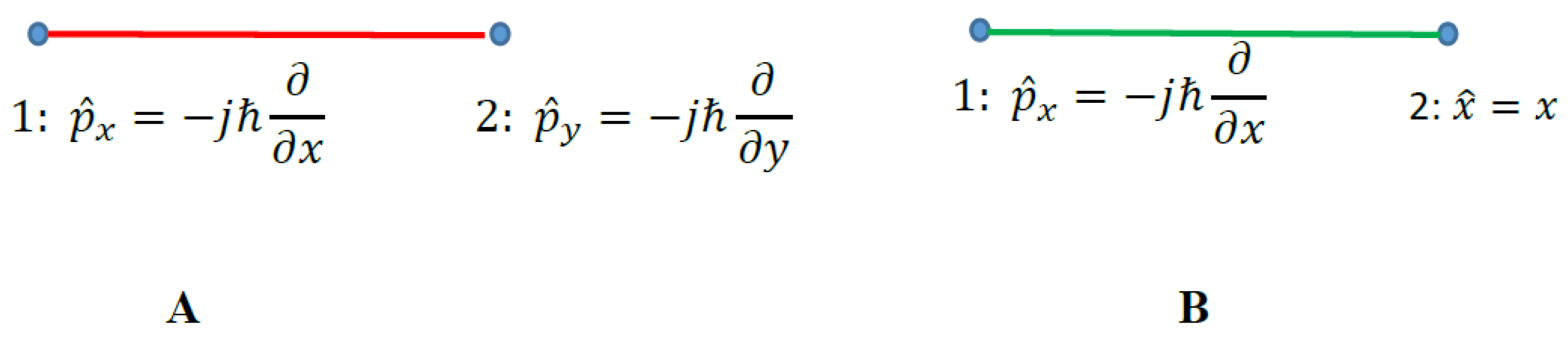
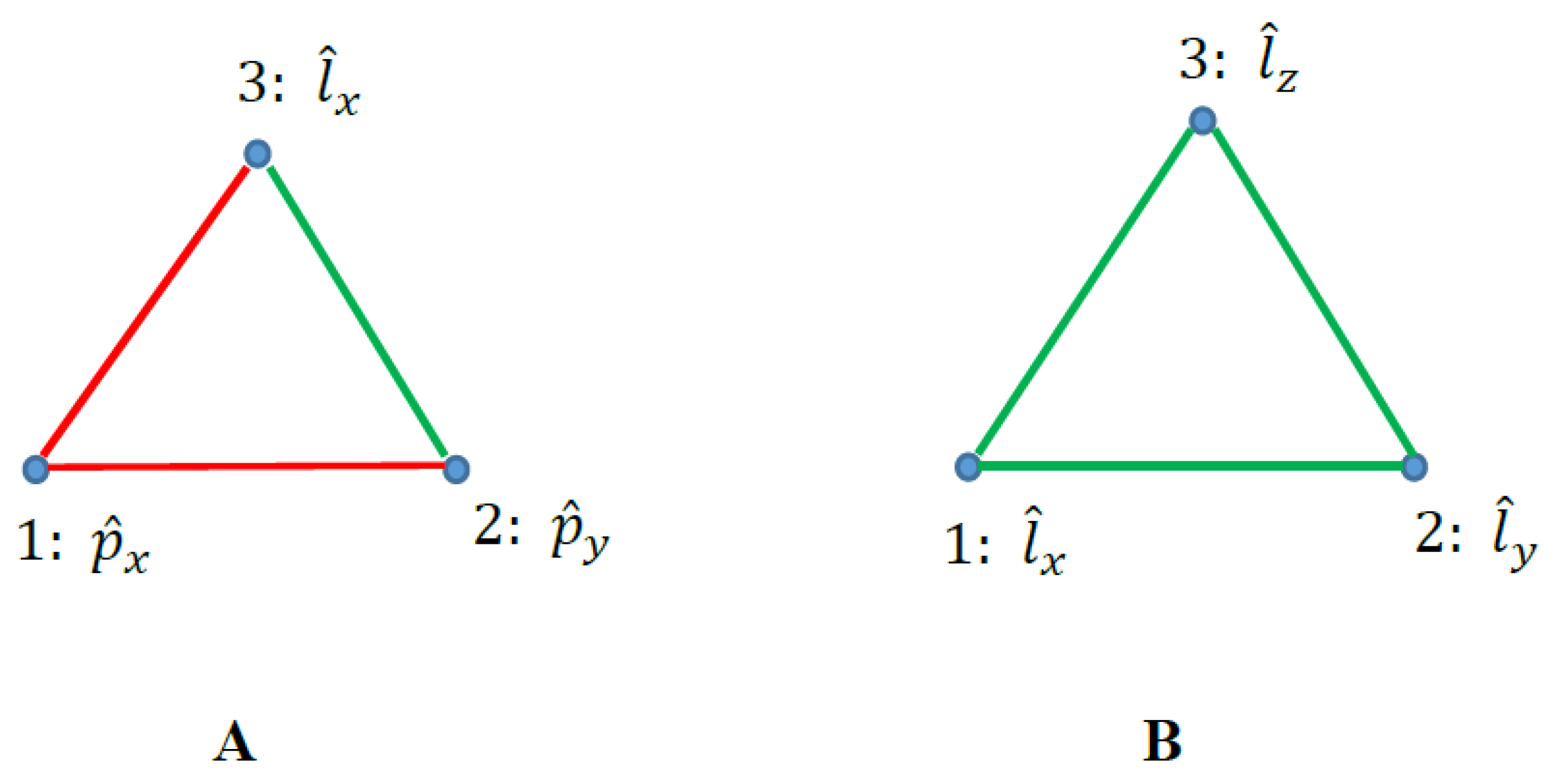

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




