Submitted:
08 October 2024
Posted:
10 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
BPD is Associated with NDI: Clinical Evidence
Extracellular Vesicles in Neonatal Lung and Brain Injury
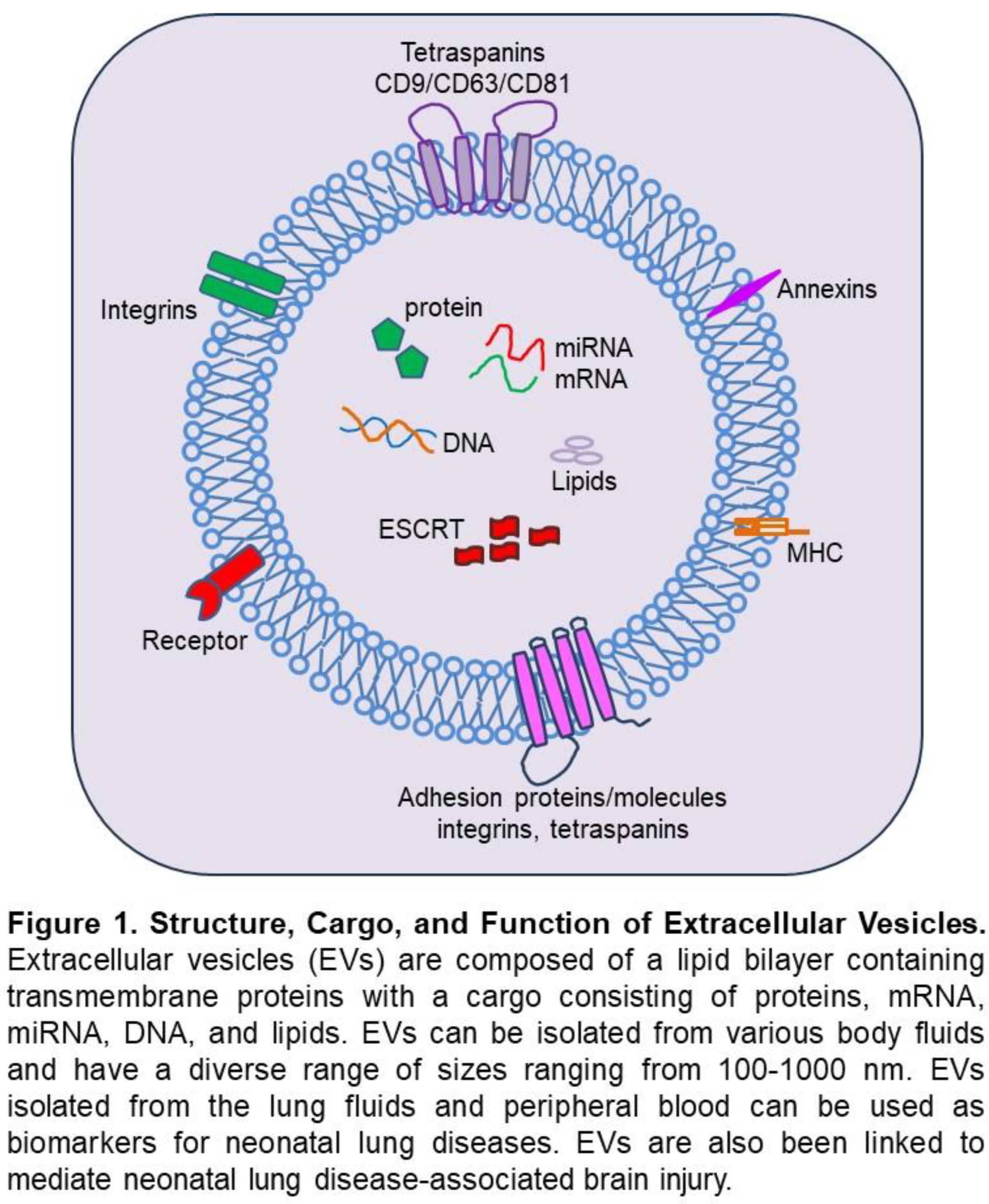
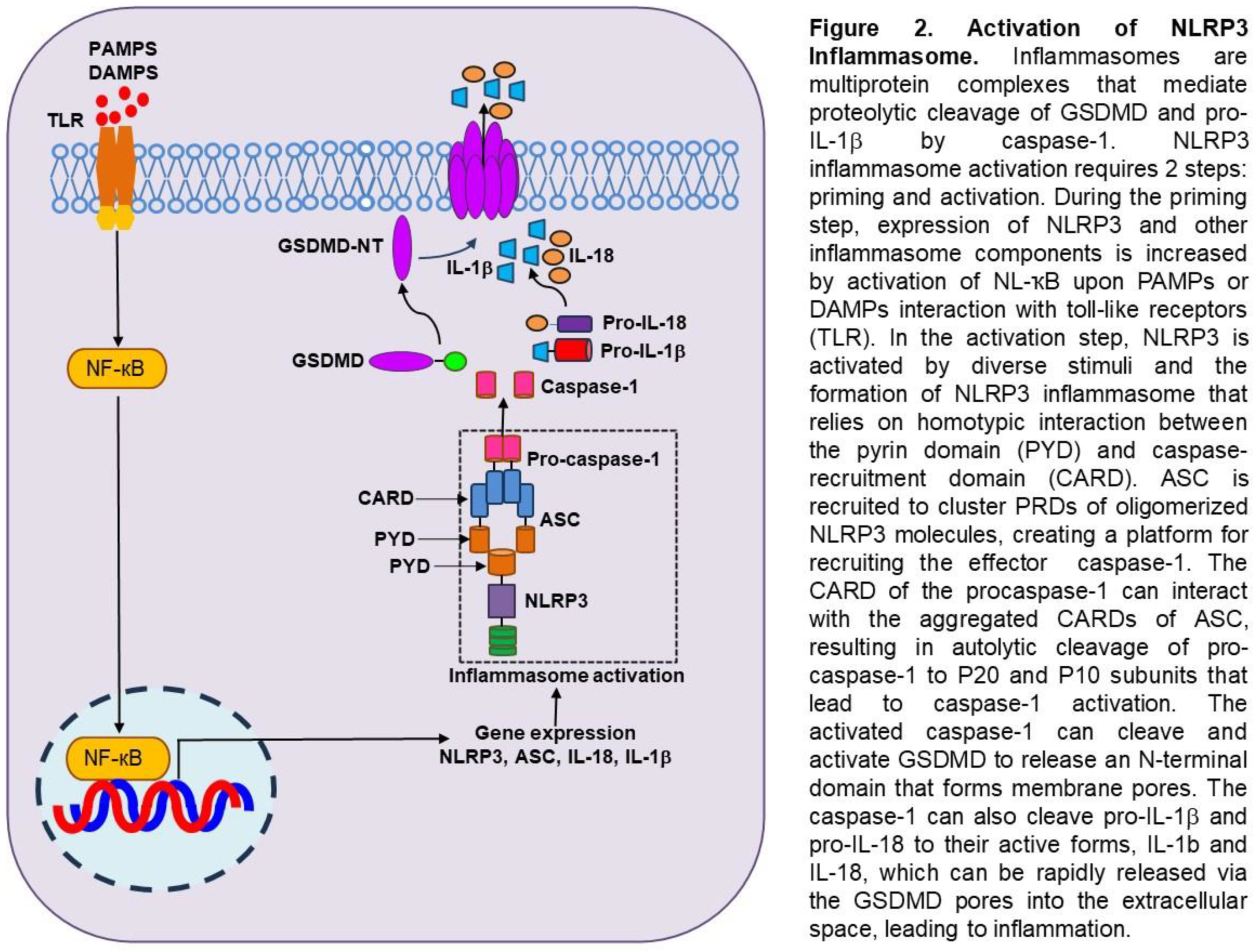
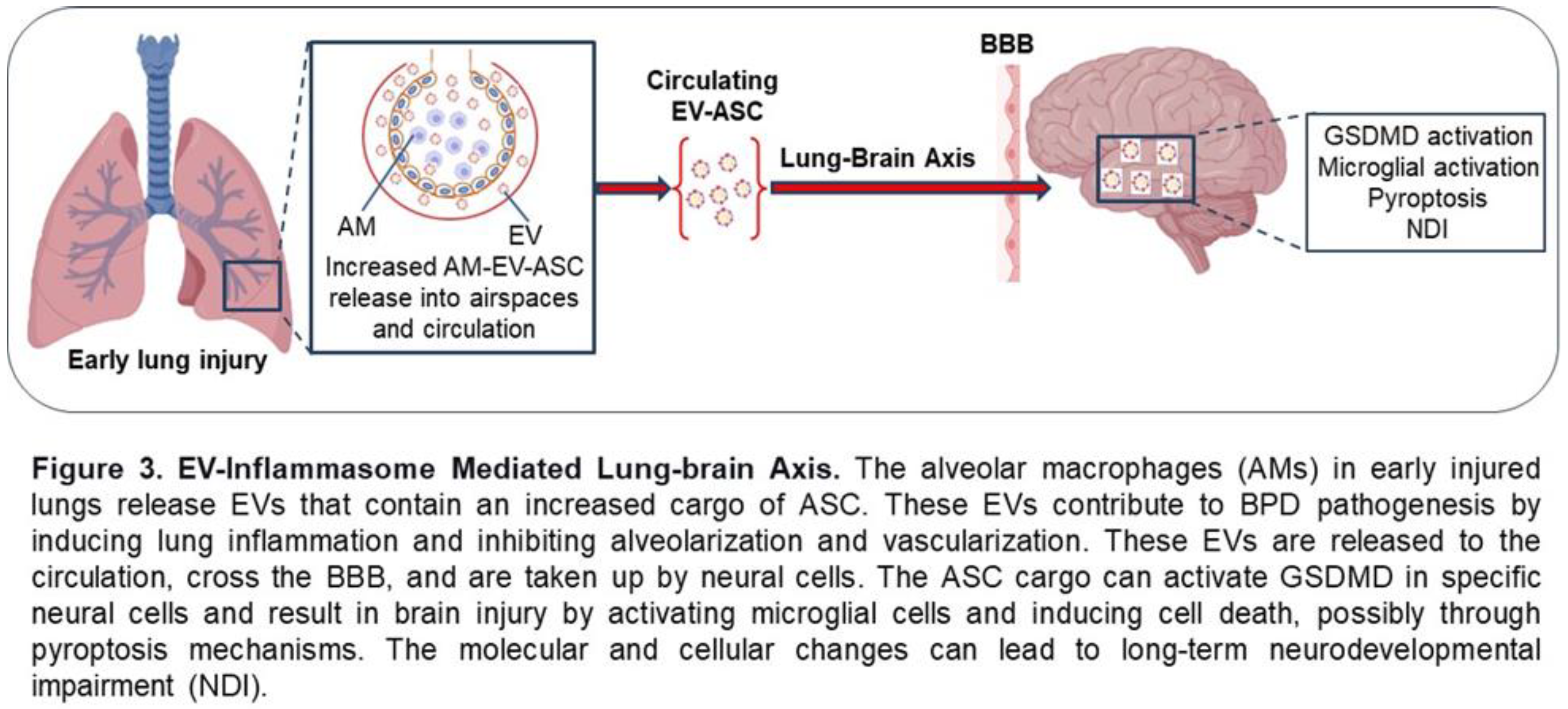
Perspective
Conclusion
References
- Cao, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, M. Global, Regional, and National Incidence and Mortality of Neonatal Preterm Birth, 1990-2019. JAMA Pediatr. 2022, 176, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobe, A.H.; Bancalari, E. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001, 163, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.J.; Jobe, A.H.; Bancalari, E. What is BPD today and in the next 50 years? Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2021, 321, L974–L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, J.J. Brain injury in premature infants: a complex amalgam of destructive and developmental disturbances. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faramarzi, R.; Darabi, A.; Emadzadeh, M.; Maamouri, G.; Rezvani, R. Predicting neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants: A comprehensive evaluation of neonatal and maternal risk factors. Early Hum Dev. 2023, 184, 105834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas SR, Jain SK, Murthy P, Joseph CJ, Soraisham A, Tang S, et al. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes of Preterm Infants Born <29 Weeks with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia-Associated Pulmonary Hypertension: A Multicenter Study. Am J Perinatol. 2023.
- Treluyer L, Nuytten A, Guellec I, Jarreau PH, Benhammou V, Cambonie G, et al. Neurodevelopment and healthcare utilisation at age 5-6 years in bronchopulmonary dysplasia: an EPIPAGE-2 cohort study. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2023, 109, 26–33.
- Bhattacharya S, Go D, Krenitsky DL, Huyck HL, Solleti SK, Lunger VA, et al. Genome-wide transcriptional profiling reveals connective tissue mast cell accumulation in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012, 186, 349–358.
- Oluwole I, Tan JBC, DeSouza S, Hutchinson M, Leigh RM, Cha M, et al. The association between bronchopulmonary dysplasia grade and risks of adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes among preterm infants born at less than 30 weeks of gestation. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023, 36, 2167074.
- Waitzman, N.J.; Jalali, A.; Grosse, S.D. Preterm birth lifetime costs in the United States in 2016: An update. Semin Perinatol. 2021, 45, 151390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavolti, A.M.; Bassler, D.; Arlettaz-Mieth, R.; Faldella, G.; Latal, B.; Natalucci, G. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia-impact of severity and timing of diagnosis on neurodevelopment of preterm infants: a retrospective cohort study. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2018, 2, e000165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithopoulos MA, Toussay X, Zhong S, Xu L, Mustafa SB, Ouellette J, et al. Neonatal hyperoxia in mice triggers long-term cognitive deficits via impairments in cerebrovascular function and neurogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2022, 132(22).
- Obst S, Herz J, Alejandre Alcazar MA, Endesfelder S, Mobius MA, Rudiger M, et al. Perinatal Hyperoxia and Developmental Consequences on the Lung-Brain Axis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022, 2022:5784146.
- Kim YE, Park WS, Sung DK, Ahn SY, Sung SI, Yoo HS, et al. Intratracheal transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells simultaneously attenuates both lung and brain injuries in hyperoxic newborn rats. Pediatr Res. 2016, 80, 415–424.
- Dapaah-Siakwan F, Zambrano R, Luo S, Duncan MR, Kerr N, Donda K, et al. Caspase-1 Inhibition Attenuates Hyperoxia-induced Lung and Brain Injury in Neonatal Mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019, 61, 341–354.
- Northway, W.H.; Jr Rosan, R.C.; Porter, D.Y. Pulmonary disease following respirator therapy of hyaline-membrane disease. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 1967, 276, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abman, S.H.; Bancalari, E.; Jobe, A. The Evolution of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia after 50 Years. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017, 195, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapcharoensap W, Gage SC, Kan P, Profit J, Shaw GM, Gould JB, et al. Hospital variation and risk factors for bronchopulmonary dysplasia in a population-based cohort. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, e143676.
- Adams M, Bassler D, Bucher HU, Roth-Kleiner M, Berger TM, Braun J, et al. Variability of Very Low Birth Weight Infant Outcome and Practice in Swiss and US Neonatal Units. Pediatrics. 2018, 141(5).
- Bhunwal, S.; Mukhopadhyay, K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Dey, P.; Dhaliwal, L.K. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Preterm Neonates in a Level III Neonatal Unit in India. Indian Pediatr. 2018, 55, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose C, Van Marter LJ, Laughon M, O'Shea TM, Allred EN, Karna P, et al. Fetal growth restriction and chronic lung disease among infants born before the 28th week of gestation. Pediatrics. 2009, 124, e450–8.
- Isayama T, Lee SK, Yang J, Lee D, Daspal S, Dunn M, et al. Revisiting the Definition of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: Effect of Changing Panoply of Respiratory Support for Preterm Neonates. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 271–279.
- Lee, J.H.; Noh, O.K.; Chang, Y.S.; Korean Neonatal, N. Neonatal Outcomes of Very Low Birth Weight Infants in Korean Neonatal Network from 2013 to 2016. J Korean Med Sci. 2019, 34, e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin HJ, Du LZ, Ma XL, Shi LP, Pan JH, Tong XM, et al. Mortality and Morbidity of Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants in the Mainland of China: A Multi-center Study. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015, 128, 2743–2750.
- Su BH, Hsieh WS, Hsu CH, Chang JH, Lien R, Lin CH, et al. Neonatal outcomes of extremely preterm infants from taiwan: comparison with Canada, Japan, and the USA. Pediatr Neonatol. 2015, 56, 46–52.
- Higgins RD, Jobe AH, Koso-Thomas M, Bancalari E, Viscardi RM, Hartert TV, et al. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: Executive Summary of a Workshop. J Pediatr. 2018, 197:300-8.
- Jensen EA, Dysart K, Gantz MG, McDonald S, Bamat NA, Keszler M, et al. The Diagnosis of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Very Preterm Infants. An Evidence-based Approach. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019, 200, 751–759.
- Thebaud B, Goss KN, Laughon M, Whitsett JA, Abman SH, Steinhorn RH, et al. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019, 5, 78.
- Anderson, P.J.; Doyle, L.W. Neurodevelopmental outcome of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Perinatol. 2006, 30, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallini, F.; Arena, R.; Stella, G.; Frezza, S.; Maggio, L. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of premature infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Acta Biomed. 2014, 85, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Van Marter LJ, Kuban KC, Allred E, Bose C, Dammann O, O'Shea M, et al. Does bronchopulmonary dysplasia contribute to the occurrence of cerebral palsy among infants born before 28 weeks of gestation? Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2011, 96, F20–9.
- Vohr, B.R.; Wright, L.L.; Poole, W.K.; McDonald, S.A. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants <32 weeks' gestation between 1993 and 1998. Pediatrics. 2005, 116, 635–643. [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore, M.D.; Rivers, A.; Hack, M. Increased risk of cerebral palsy among very low-birthweight infants with chronic lung disease. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1990, 32, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintz SR, Kendrick DE, Stoll BJ, Vohr BR, Fanaroff AA, Donovan EF, et al. Neurodevelopmental and growth outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants after necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatrics. 2005, 115, 696–703.
- Arnaud C, Daubisse-Marliac L, White-Koning M, Pierrat V, Larroque B, Grandjean H, et al. Prevalence and associated factors of minor neuromotor dysfunctions at age 5 years in prematurely born children: the EPIPAGE Study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2007, 161, 1053–1061.
- Short EJ, Klein NK, Lewis BA, Fulton S, Eisengart S, Kercsmar C, et al. Cognitive and academic consequences of bronchopulmonary dysplasia and very low birth weight: 8-year-old outcomes. Pediatrics. 2003, 112, e359.
- Davis, N.M.; Ford, G.W.; Anderson, P.J.; Doyle, L.W.; Victorian Infant Collaborative Study, G. Developmental coordination disorder at 8 years of age in a regional cohort of extremely-low-birthweight or very preterm infants. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2007, 49, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallini F, Coppola M, De Rose DU, Maggio L, Arena R, Romano V, et al. Neurodevelopmental outcomes in very preterm infants: The role of severity of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Early Hum Dev. 2021, 152:105275.
- Schmidt B, Asztalos EV, Roberts RS, Robertson CM, Sauve RS, Whitfield MF, et al. Impact of bronchopulmonary dysplasia, brain injury, and severe retinopathy on the outcome of extremely low-birth-weight infants at 18 months: results from the trial of indomethacin prophylaxis in preterms. JAMA. 2003, 289, 1124–1129.
- Schmidt B, Anderson PJ, Doyle LW, Dewey D, Grunau RE, Asztalos EV, et al. Survival without disability to age 5 years after neonatal caffeine therapy for apnea of prematurity. JAMA. 2012, 307, 275–282.
- Katz TA, Vliegenthart RJS, Aarnoudse-Moens CSH, Leemhuis AG, Beuger S, Blok GJ, et al. Severity of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Neurodevelopmental Outcome at 2 and 5 Years Corrected Age. J Pediatr. 2022, 243:40-6 e2.
- Reuner, G.; Fields, A.C.; Wittke, A.; Lopprich, M.; Pietz, J. Comparison of the developmental tests Bayley-III and Bayley-II in 7-month-old infants born preterm. Eur J Pediatr. 2013, 172, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.; Johnson, S.; Haider, S.; Hennessy, E.; Marlow, N. Relationship between test scores using the second and third editions of the Bayley Scales in extremely preterm children. J Pediatr. 2012, 160, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg AA, Lee NR, Vaver KN, Werner D, Fashaw L, Hale K, et al. School-age outcomes of newborns treated for persistent pulmonary hypertension. J Perinatol. 2010, 30, 127–134.
- Short EJ, Kirchner HL, Asaad GR, Fulton SE, Lewis BA, Klein N, et al. Developmental sequelae in preterm infants having a diagnosis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia: analysis using a severity-based classification system. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2007, 161, 1082–1087.
- Natarajan G, Pappas A, Shankaran S, Kendrick DE, Das A, Higgins RD, et al. Outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: impact of the physiologic definition. Early Hum Dev. 2012, 88, 509–515.
- Lewis BA, Singer LT, Fulton S, Salvator A, Short EJ, Klein N, et al. Speech and language outcomes of children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Commun Disord. 2002, 35, 393–406.
- Majnemer, A.; Riley, P.; Shevell, M.; Birnbaum, R.; Greenstone, H.; Coates, A.L. Severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia increases risk for later neurological and motor sequelae in preterm survivors. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2000, 42, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, H.G.; Klein, N.; Schatschneider, C.; Hack, M. Predictors of early school age outcomes in very low birth weight children. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 1998, 19, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, H.G.; Minich, N.; Bangert, B.; Filipek, P.A.; Hack, M. Long-term neuropsychological outcomes of very low birth weight: associations with early risks for periventricular brain insults. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2004, 10, 987–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annesi, C.A.; Levin, J.C.; Litt, J.S.; Sheils, C.A.; Hayden, L.P. Long-term respiratory and developmental outcomes in children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia and history of tracheostomy. J Perinatol. 2021, 41, 2645–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMauro, S.B. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2021, 56, 3509–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery, C.; Ostrowski, M.; Segura, E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009, 9, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyorgy B, Szabo TG, Pasztoi M, Pal Z, Misjak P, Aradi B, et al. Membrane vesicles, current state-of-the-art: emerging role of extracellular vesicles. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011, 68, 2667–2688.
- van der Pol E, Boing AN, Harrison P, Sturk A, Nieuwland, R. Classification, functions, and clinical relevance of extracellular vesicles. Pharmacol Rev. 2012, 64, 676–705.
- Buzas, E.I. The roles of extracellular vesicles in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023, 23, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018, 7, 1535750.
- Doyle, L.M.; Wang, M.Z. Overview of Extracellular Vesicles, Their Origin, Composition, Purpose, and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis. Cells. 2019, 8(7).
- De Lorenzis, E.; Rindone, A.; Di Donato, S.; Del Galdo, F. Circulating extracellular vesicles in the context of interstitial lung disease related to systemic sclerosis: A scoping literature review. Autoimmun Rev. 2023, 22, 103401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, C.; Huang, X.; Chen, S.; Li, Y. Role of Extracellular microRNAs in Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury. J Immunol Res. 2023, 2023:5509652.
- Tine M, Neri T, Biondini D, Bernardinello N, Casara A, Conti M, et al. Do Circulating Extracellular Vesicles Strictly Reflect Bronchoalveolar Lavage Extracellular Vesicles in COPD? Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24(3).
- Li Z, Wang X, Wang X, Yi X, Wong YK, Wu J, et al. Research progress on the role of extracellular vesicles in neurodegenerative diseases. Transl Neurodegener. 2023, 12, 43.
- Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, C.; Liu, K. A new diagnostic tool for brain disorders: extracellular vesicles derived from neuron, astrocyte, and oligodendrocyte. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023, 16:1194210.
- Kerr NA, de Rivero Vaccari JP, Abbassi S, Kaur H, Zambrano R, Wu S, et al. Traumatic Brain Injury-Induced Acute Lung Injury: Evidence for Activation and Inhibition of a Neural-Respiratory-Inflammasome Axis. J Neurotrauma. 2018, 35, 2067–2076.
- Schiller, E.A.; Cohen, K.; Lin, X.; El-Khawam, R.; Hanna, N. Extracellular Vesicle-microRNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers in Preterm Neonates. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24(3).
- Ransom, M.A.; Blatt, A.M.; Pua, H.H.; Sucre, J.M.S. The emerging role of extracellular vesicles in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2024, 326, L517–L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal CV, Olave N, Travers C, Rezonzew G, Dolma K, Simpson A, et al. Exosomal microRNA predicts and protects against severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely premature infants. JCI Insight. 2018, 3(5).
- Ransom MA, Bunn KE, Negretti NM, Jetter CS, Bressman ZJ, Sucre JMS, et al. Developmental trajectory of extracellular vesicle characteristics from the lungs of preterm infants. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2023, 324, L385–L92.
- Go H, Maeda H, Miyazaki K, Maeda R, Kume Y, Namba F, et al. Extracellular vesicle miRNA-21 is a potential biomarker for predicting chronic lung disease in premature infants. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020, 318, L845–L51.
- Ali A, Zambrano R, Duncan MR, Chen S, Luo S, Yuan H, et al. Hyperoxia-activated circulating extracellular vesicles induce lung and brain injury in neonatal rats. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 8791.
- Zhou Y, Liu Y, Xu G, Liu L, Li H, Li Y, et al. Human breast milk-derived exosomes through inhibiting AT II cell apoptosis to prevent bronchopulmonary dysplasia in rat lung. J Cell Mol Med. 2022, 26, 4169–4182.
- Bellio MA, Young KC, Milberg J, Santos I, Abdullah Z, Stewart D, et al. Amniotic fluid-derived extracellular vesicles: characterization and therapeutic efficacy in an experimental model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Cytotherapy. 2021, 23, 1097–1107.
- Vechetti IJ, Norrbom J, Alkner B, Hjalmarsson E, Palmcrantz A, Ponten E, et al. Extracellular vesicle characteristics and microRNA content in cerebral palsy and typically developed individuals at rest and in response to aerobic exercise. Front Physiol. 2022, 13:1072040.
- Zhong XQ, Yan Q, Chen ZG, Jia CH, Li XH, Liang ZY, et al. Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Exosomes From Very Preterm Infants With Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Impaired Endothelial Angiogenesis: Roles of Exosomal MicroRNAs. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021, 9:637248.
- Genschmer KR, Russell DW, Lal C, Szul T, Bratcher PE, Noerager BD, et al. Activated PMN Exosomes: Pathogenic Entities Causing Matrix Destruction and Disease in the Lung. Cell. 2019, 176(1-2):113-26 e15.
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Yin, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L. CircRNA, lncRNA, and mRNA profiles of umbilical cord blood exosomes from preterm newborns showing bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Eur J Pediatr. 2022, 181, 3345–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada I, Gabrielli M, Turola E, Iorio A, D'Arrigo G, Parolisi R, et al. Glia-to-neuron transfer of miRNAs via extracellular vesicles: a new mechanism underlying inflammation-induced synaptic alterations. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 135, 529–550.
- Bakhti, M.; Winter, C.; Simons, M. Inhibition of myelin membrane sheath formation by oligodendrocyte-derived exosome-like vesicles. J Biol Chem. 2011, 286, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fevrier B, Vilette D, Archer F, Loew D, Faigle W, Vidal M, et al. Cells release prions in association with exosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004, 101, 9683–9688.
- Fitzner D, Schnaars M, van Rossum D, Krishnamoorthy G, Dibaj P, Bakhti M, et al. Selective transfer of exosomes from oligodendrocytes to microglia by macropinocytosis. J Cell Sci. 2011, 124(Pt 3):447-58.
- Fruhbeis C, Frohlich D, Kuo WP, Amphornrat J, Thilemann S, Saab AS, et al. Neurotransmitter-triggered transfer of exosomes mediates oligodendrocyte-neuron communication. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001604.
- Lewis, S. Glia: Transporting cargo from A to B. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013, 14, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Schiapparelli, L.; Cline, H.T. Exosomes function in cell-cell communication during brain circuit development. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, B.M.; Hill, A.F. Extracellular vesicles--Their role in the packaging and spread of misfolded proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015, 40:89-96.
- Budnik, V.; Ruiz-Canada, C.; Wendler, F. Extracellular vesicles round off communication in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016, 17, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson AG, Gray E, Heman-Ackah SM, Mager I, Talbot K, Andaloussi SE, et al. Extracellular vesicles in neurodegenerative disease - pathogenesis to biomarkers. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016, 12, 346–357.
- Zhang L, Graf I, Kuang Y, Zheng X, Haupt M, Majid A, et al. Neural Progenitor Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Enhance Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity by NF-kappaB (Nuclear Factor-kappaB)-Dependent Regulation of ABCB1 (ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter B1) in Stroke Mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021, 41, 1127–1145.
- Spaull R, McPherson B, Gialeli A, Clayton A, Uney J, Heep A, et al. Exosomes populate the cerebrospinal fluid of preterm infants with post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2019, 73:59-65.
- Gall, A.R.; Amoah, S.; Kitase, Y.; Jantzie, L.L. Placental mediated mechanisms of perinatal brain injury: Evolving inflammation and exosomes. Exp Neurol. 2022, 347:113914.
- Leon J, Acurio J, Bergman L, Lopez J, Karin Wikstrom A, Torres-Vergara P, et al. Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier by Extracellular Vesicles From Preeclampsia Plasma and Hypoxic Placentae: Attenuation by Magnesium Sulfate. Hypertension. 2021, 78, 1423–1433.
- Dickens AM, Tovar YRLB, Yoo SW, Trout AL, Bae M, Kanmogne M, et al. Astrocyte-shed extracellular vesicles regulate the peripheral leukocyte response to inflammatory brain lesions. Sci Signal. 2017, 10(473).
- Bianco F, Perrotta C, Novellino L, Francolini M, Riganti L, Menna E, et al. Acid sphingomyelinase activity triggers microparticle release from glial cells. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 1043–1054.
- Lombardi M, Parolisi R, Scaroni F, Bonfanti E, Gualerzi A, Gabrielli M, et al. Detrimental and protective action of microglial extracellular vesicles on myelin lesions: astrocyte involvement in remyelination failure. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 987–1012.
- Wies Mancini, V.S.B.; Mattera, V.S.; Pasquini, J.M.; Pasquini, L.A.; Correale, J.D. Microglia-derived extracellular vesicles in homeostasis and demyelination/remyelination processes. J Neurochem. 2024, 168, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drago F, Lombardi M, Prada I, Gabrielli M, Joshi P, Cojoc D, et al. ATP Modifies the Proteome of Extracellular Vesicles Released by Microglia and Influences Their Action on Astrocytes. Front Pharmacol. 2017, 8:910.
- Meng, Q.; Yang, P.; Lu, Y. MicroRNA-410 serves as a candidate biomarker in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy newborns and provides neuroprotection in oxygen-glucose deprivation-injured PC12 and SH-SY5Y cells. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y, Huang H, et al. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature. 2015, 526, 660–665.
- Li, Z.; Ji, S.; Jiang, M.L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.J. The Regulation and Modification of GSDMD Signaling in Diseases. Front Immunol. 2022, 13:893912.
- Gaidt, M.M.; Hornung, V. The NLRP3 Inflammasome Renders Cell Death Pro-inflammatory. J Mol Biol. 2018, 430, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasomes. Cell. 2010, 140, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broz, P.; Dixit, V.M. Inflammasomes: mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016, 16, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wu, H. Structural Mechanisms of NLRP3 Inflammasome Assembly and Activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2023, 41:301-16.
- Liao J, Kapadia VS, Brown LS, Cheong N, Longoria C, Mija D, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome is critically involved in the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Nat Commun. 2015, 6:8977.
- Chen, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhong, D.; Li, C.; Du, L. Caffeine prevents hyperoxia-induced lung injury in neonatal mice through NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-kappaB pathway. Respir Res. 2020, 21, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ran, X.; He, Y.; Ai, Q.; Shi, Y. Acetate Downregulates the Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasomes and Attenuates Lung Injury in Neonatal Mice With Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Front Pediatr. 2020, 8:595157.
- Wang M, Zhang F, Ning X, Wu C, Zhou Y, Gou Z, et al. Regulating NLRP3 Inflammasome-Induced Pyroptosis via Nrf2: TBHQ Limits Hyperoxia-Induced Lung Injury in a Mouse Model of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Inflammation. 2023, 46, 2386–2401.
- Hummler JK, Dapaah-Siakwan F, Vaidya R, Zambrano R, Luo S, Chen S, et al. Inhibition of Rac1 Signaling Downregulates Inflammasome Activation and Attenuates Lung Injury in Neonatal Rats Exposed to Hyperoxia. Neonatology. 2017, 111, 280–288.
- Vaidya R, Zambrano R, Hummler JK, Luo S, Duncan MR, Young K, et al. Recombinant CCN1 prevents hyperoxia-induced lung injury in neonatal rats. Pediatr Res. 2017, 82, 863–871.
- Qing, C.; Ziyun, L.; Xuefei, Y.; Xinyi, Z.; Xindong, X.; Jianhua, F. Protective Effects of 18beta-Glycyrrhetinic Acid on Neonatal Rats with Hyperoxia Exposure. Inflammation. 2022, 45, 1224–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang X, Huo R, Liang Z, Xu C, Chen T, Lin J, et al. Simvastatin Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Ameliorates Lung Injury in Hyperoxia-Induced Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia via the KLF2-Mediated Mechanism. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022, 2022:8336070.
- Sonny S, Yuan H, Chen S, Duncan MR, Chen P, Benny M, et al. GSDMD deficiency ameliorates hyperoxia-induced BPD and ROP in neonatal mice. Sci Rep. 2023, 13, 143.
- Chen D, Dixon BJ, Doycheva DM, Li B, Zhang Y, Hu Q, et al. IRE1alpha inhibition decreased TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation through miR-17-5p after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in rats. J Neuroinflammation. 2018, 15, 32.
- Serdar M, Kempe K, Rizazad M, Herz J, Bendix I, Felderhoff-Muser U, et al. Early Pro-inflammatory Microglia Activation After Inflammation-Sensitized Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Neonatal Rats. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13:237.
- Lv Y, Sun B, Lu XX, Liu YL, Li M, Xu LX, et al. The role of microglia mediated pyroptosis in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020, 521, 933–938.
- Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Lu, R.; Ge, M.; Zhang, L. MicroRNA-374a-5p inhibits neuroinflammation in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy via regulating NLRP3 inflammasome targeted Smad6. Life Sci. 2020, 252:117664.
- Zhang C, Guan Q, Shi H, Cao L, Liu J, Gao Z, et al. A novel RIP1/RIP3 dual inhibitor promoted OPC survival and myelination in a rat neonatal white matter injury model with hOPC graft. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021, 12, 462.
- Yang, L.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N.; Xue, X.; Fu, J. Caffeine treatment started before injury reduces hypoxic-ischemic white-matter damage in neonatal rats by regulating phenotypic microglia polarization. Pediatr Res. 2022, 92, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng Y, Zhu T, Chen B, Fang Y, Wu Y, Feng X, et al. Diallyl disulfide attenuates pyroptosis via NLRP3/Caspase-1/IL-1beta signaling pathway to exert a protective effect on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023, 124(Pt B):111030.
- Challa NVD, Chen S, Yuan H, Duncan MR, Moreno WJ, Bramlett H, et al. GSDMD gene knockout alleviates hyperoxia-induced hippocampal brain injury in neonatal mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2023, 20, 205.
- Chavez L, Meguro J, Chen S, de Paiva VN, Zambrano R, Eterno JM, et al. Circulating extracellular vesicles activate the pyroptosis pathway in the brain following ventilation-induced lung injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2021, 18, 310.
- Starke N, Challa NVD, Yuan H, Chen S, Duncan MR, Cabrera Ranaldi ED, et al. Extracellular Vesicle ASC: A Novel Mediator for Lung-Brain Axis in Preterm Brain Injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2024.
- Fox, J.E.; Austin, C.D.; Reynolds, C.C.; Steffen, P.K. Evidence that agonist-induced activation of calpain causes the shedding of procoagulant-containing microvesicles from the membrane of aggregating platelets. J Biol Chem. 1991, 266, 13289–13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.J.; Shin, Y.; Chung, S.; Hwang, D.W.; Lee, D.S. Convective exosome-tracing microfluidics for analysis of cell-non-autonomous neurogenesis. Biomaterials. 2017, 112:82-94.
- Li, B.; Antonyak, M.A.; Zhang, J.; Cerione, R.A. RhoA triggers a specific signaling pathway that generates transforming microvesicles in cancer cells. Oncogene. 2012, 31, 4740–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavian N, Marut W, Servettaz A, Nicco C, Chereau C, Lemarechal H, et al. Pantethine Prevents Murine Systemic Sclerosis Through the Inhibition of Microparticle Shedding. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1881–1890.
- Menck K, Sonmezer C, Worst TS, Schulz M, Dihazi GH, Streit F, et al. Neutral sphingomyelinases control extracellular vesicles budding from the plasma membrane. J Extracell Vesicles. 2017, 6, 1378056.
- Stratton, D.; Moore, C.; Zheng, L.; Lange, S.; Inal, J. Prostate cancer cells stimulated by calcium-mediated activation of protein kinase C undergo a refractory period before re-releasing calcium-bearing microvesicles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015, 460, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yu, D.; Williams, K.J.; Liu, M.L. Tobacco smoke induces the generation of procoagulant microvesicles from human monocytes/macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010, 30, 1818–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Kim, S.J. Clopidogrel effectively suppresses endothelial microparticle generation induced by indoxyl sulfate via inhibition of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Blood Purif. 2011, 32, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, M.; O'Driscoll, L. Inhibiting extracellular vesicles formation and release: a review of EV inhibitors. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020, 9, 1703244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarini A, Gui L, Viviani C, Armato U, Dal Pra, I. NLRP3 Inflammasome's Activation in Acute and Chronic Brain Diseases-An Update on Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives with Respect to Other Inflammasomes. Biomedicines. 2023, 11(4).
- Wang HQ, Song KY, Feng JZ, Huang SY, Guo XM, Zhang L, et al. Caffeine Inhibits Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome via Autophagy to Attenuate Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J Mol Neurosci. 2022, 72, 97–112.
- Xu J, Pickard JM, Nunez, G. FDA-approved disulfiram inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome by regulating NLRP3 palmitoylation. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114609.
- McBride C, Trzoss L, Povero D, Lazic M, Ambrus-Aikelin G, Santini A, et al. Overcoming Preclinical Safety Obstacles to Discover (S)-N-((1,2,3,5,6,7-Hexahydro-s-indacen-4-yl)carbamoyl)-6-(methylamino)-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrazolo [5,1-b][1,3]oxazine-3-sulfonamide (GDC-2394): A Potent and Selective NLRP3 Inhibitor. J Med Chem. 2022, 65, 14721–14739.
- Van Gorp, H.; Van Opdenbosch, N.; Lamkanfi, M. Inflammasome-Dependent Cytokines at the Crossroads of Health and Autoinflammatory Disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019, 11(1).
- Canna SW, Girard C, Malle L, de Jesus A, Romberg N, Kelsen J, et al. Life-threatening NLRC4-associated hyperinflammation successfully treated with IL-18 inhibition. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017, 139, 1698–1701.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



