Submitted:
07 October 2024
Posted:
08 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Challenges
1.2. Research Contribution
1.3. Summary of Existing Surveys
1.4. Structure of this Paper
| Key Ideas | Survey Scope | Cross-Layer Inspired? | Challenges | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPWANs like LoRaWAN in IoT: Challenges and Cross-Layer Optimization, Cognitive Radio, EE Multi-Channel Cross-Layer MAC Framework | 6G, LoRaWAN in IoT, CSMA Protocols, 6G Communication, EE in IoT Networks, CSMA Protocols | Yes | Protocol optimization, data rate, duty cycle, Massive connectivity Requirement, Energy Constraint | [4] |
| Cyber-physical systems: Testing platforms and vulnerability modelling, Combining Exposure Indicators and Predictive Analytics, Internal Assessment and Evaluation, H2020 ECHO Project Implementation, | Cyber-physical systems, Exposure Indicators and Predictive Analytics, Privacy-Preserving Evaluation, Cybersecurity Information Sharing | No | Data security, vulnerability modelling, Gaps Between Exposure Indicators and Predictive Analytics, Sensitive Information Protection, Trust and Transparency Among Stakeholders | [5] |
| Social Internet of Things (SIoT) Security, CPS in Industry, Hybrid Risk Identification Methodology, Four-Step Risk Identification Process, | SIoT security, Risk Identification in Industry, CPS Interactions, Risk Management Standards and Frameworks | Yes | Security, energy efficiency, graph-powered learning, Comprehensive Risk Identification, Complexity of CPS Interconnections, Redundancy of Risks | [6] |
| IoT Security Challenges and Solutions, Flying Ad Hoc Networks Challenges, Energy-Aware Routing Scheme, Path Selection Metrics, Performance Evaluation | IoT security challenges, Routing Algorithms in FANETs, Virtual Relay Tunnel (VRT) Concept, Comparison of Routing Schemes | No | Security vulnerabilities, cryptographic protocols, Dynamic Topology and High Mobility, Energy Restrictions, Efficient Path Selection | [7] |
| Smart City Concept, Smart City Security and Privacy: Suggested Solutions Using Blockchain and Encryption, Blockchain for Security | Adaptive cybersecurity, IoT and Cloud-based Security Issues, Data Privacy and Security Solutions, Smart City Data Management | No | Real-world network packet collection, machine learning, Resource Optimization vs. Security, Decentralized and Distributed Structure, Implementing Blockchain | [8] |
| Comprehensive Overview of IoT Security, Rapid Growth of IoT, IoT Security Concerns, Case Study on Camera-based IoT, Importance of Privacy and Stakeholder Roles | IoT security overview, IoT Overview and Security, Threat Analysis for Smart Camera Systems (SCS), IoT Security and Privacy | No | IoT development, security solutions, Complexity of IoT Security, Vulnerabilities in IoT Applications, Stakeholder Responsibility | [9] |
| NOMA-based-MIoT Communication System, 5G Technology in MIoT, NOMA-based Heterogeneous Communication System, Energy Efficiency (EE) Optimization, Iterative Approach for Optimization | MIoT Networks, MIoT communication, Energy Efficiency in MIoT, Optimization Techniques, Handling uncertain channel state Information | Yes | Energy efficiency, spectrum consumption, Complexity of Optimization, Inadequate Channel State Information, Balancing Constraints, Quality of Service | [10] |
| Energy-efficient Routing for Smart Dust Head Networks, Challenges with Movable Smart Dust Basestation, Flooding Approach, EE Routing Mechanism, Fuzzy Clustering and Optimization | Smart Dust energy-efficient routing, Movable BS Positioning, Routing Architectures, Optimization Techniques | No | Energy-efficient routing, network performance, High Power Usage, Network Stability, Efficient Routing | [11] |
| Cognitive Radio Technology for Energy-efficient IoT, IoT and Spectrum Demand, Cognitive Radio (CR) Technology, Efficient Communication Protocols, Cross-Layer Design Proposal | CR Technology for IoT, Cross-Layer Optimization, Simulation and Performance Evaluation | Yes | Spectrum optimization, Spectrum Utilization, Energy Efficiency, Network Adaptation | [12] |
1.5. Cross Layer Framework
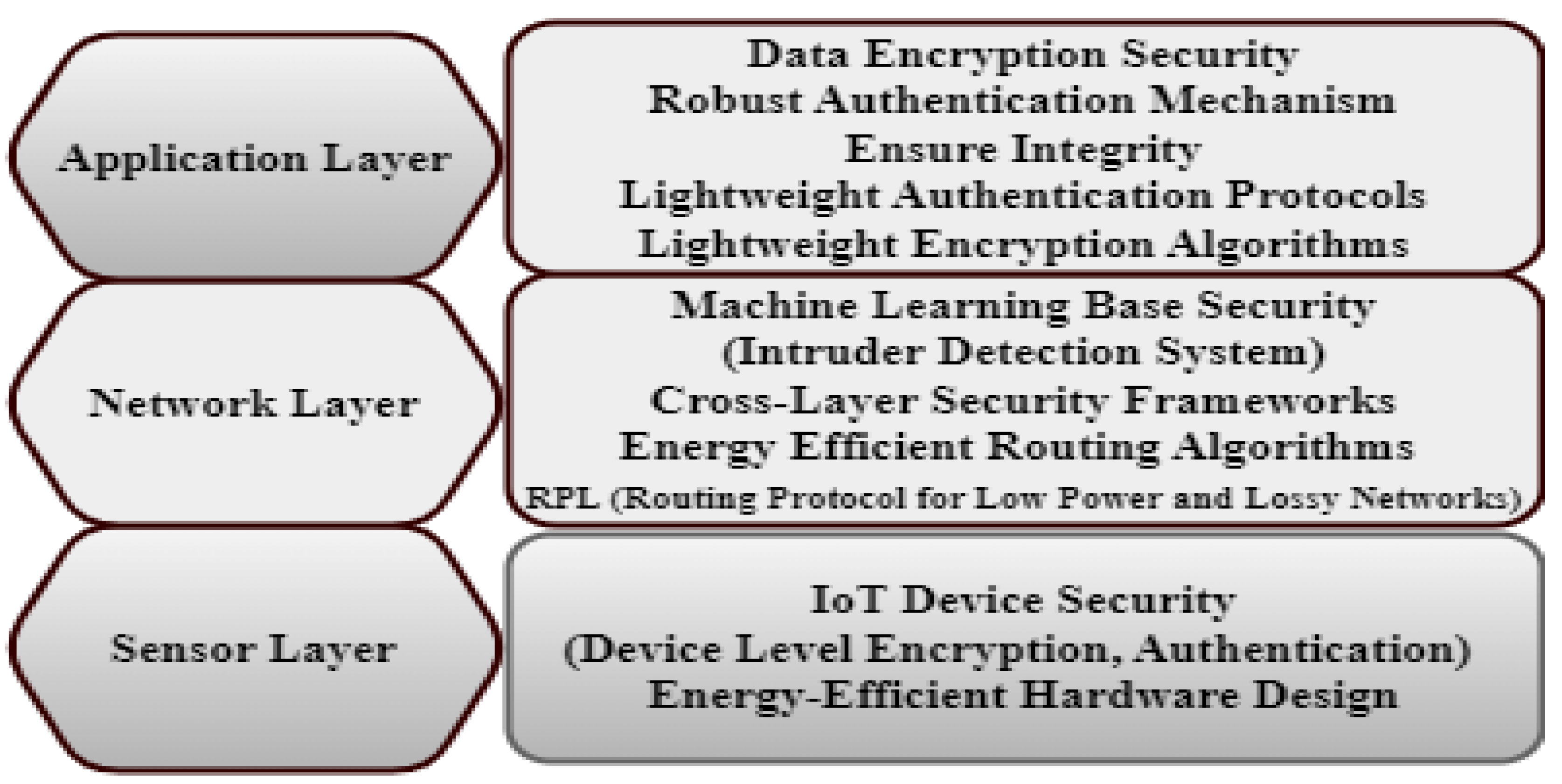
1.6. IoT Network Design
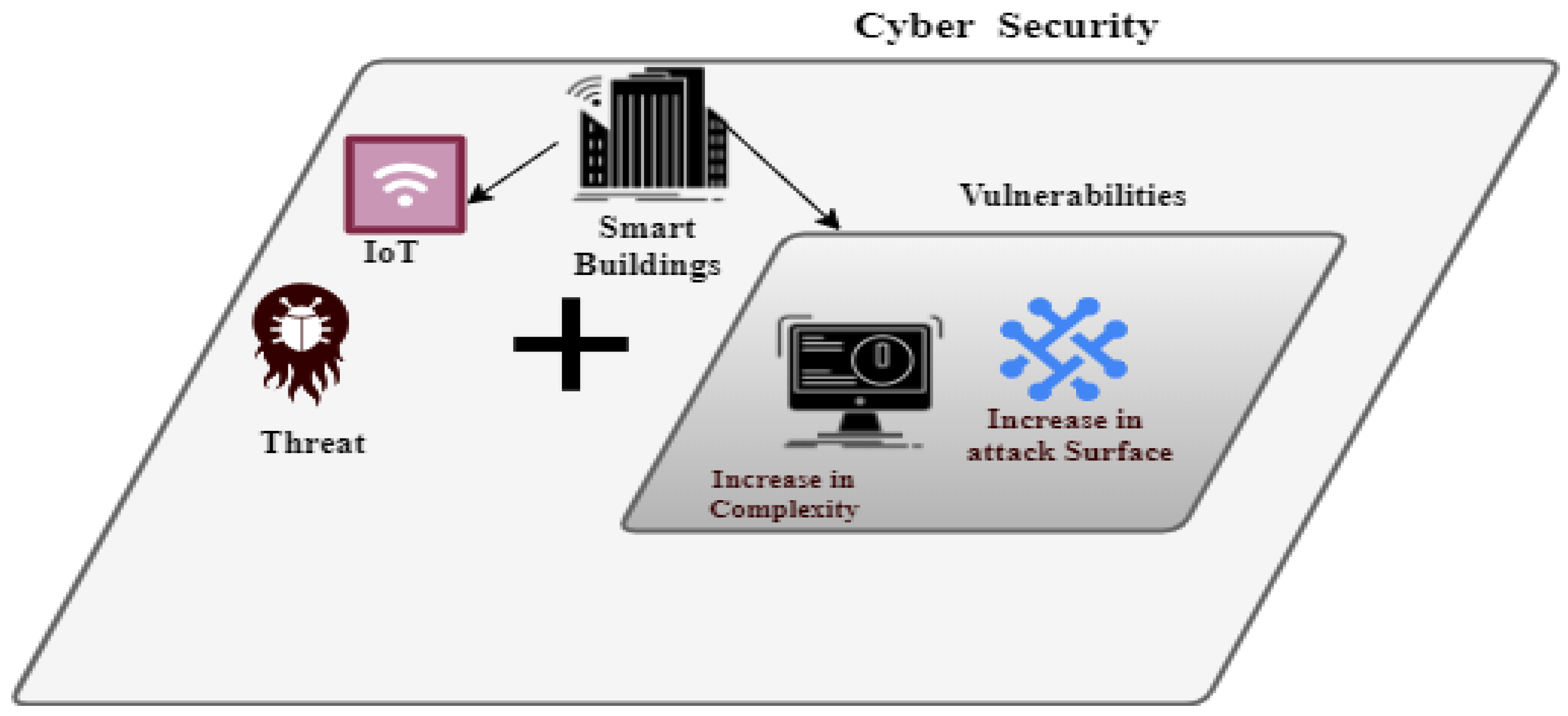
2. Energy Effectiveness and Security Measures of IoT Networks
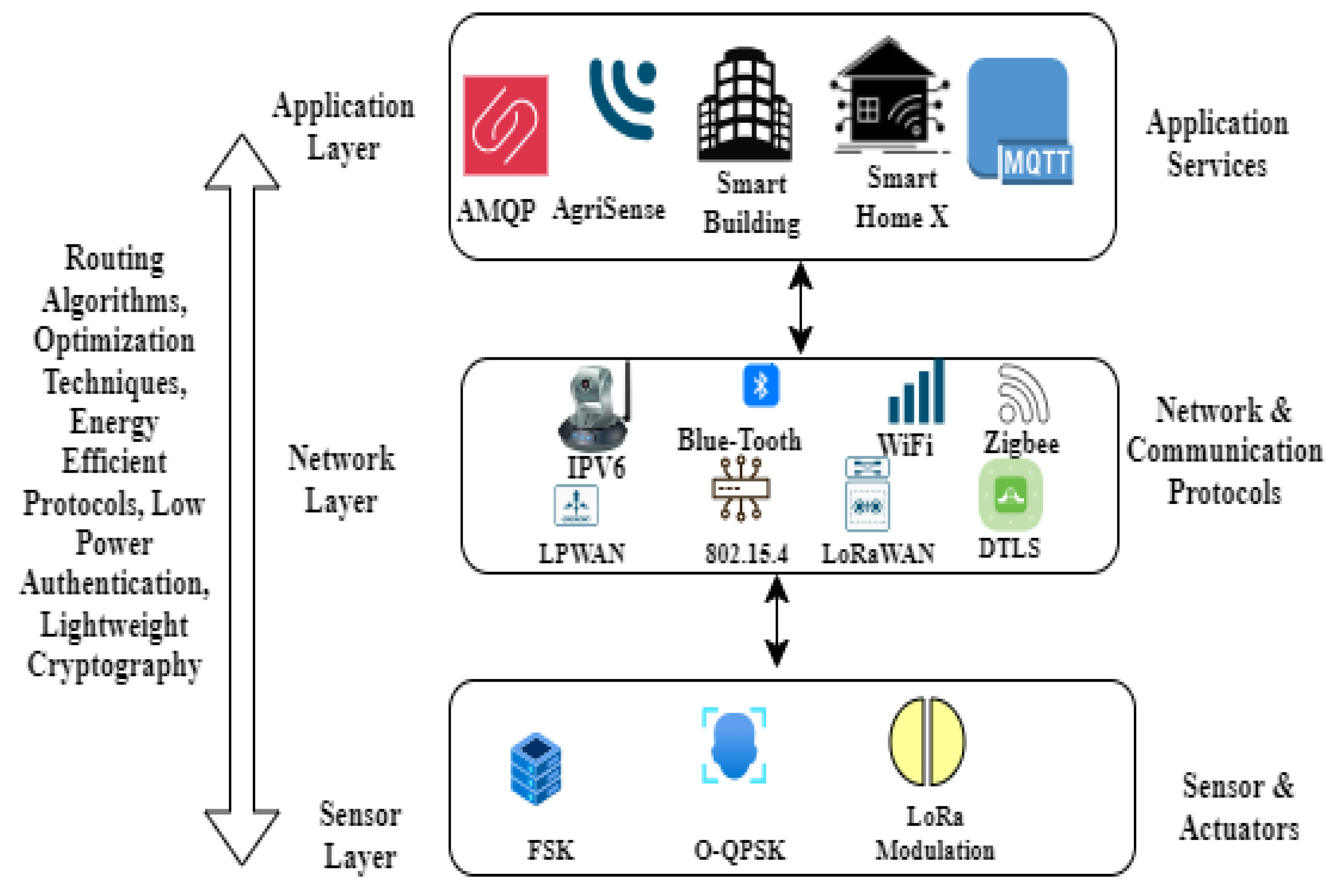
2.1. Cross-Layer Energy Efficient Framework
2.2. Cross Layer Security Measures
| Key Contributions | Performance Evaluation Methods | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enhanced LoRaWAN for IoT applications,Cross-Layer Optimization Overview, Classification of Techniques, Identification of Issues and Challenges, Performance Overview | State-of-the-Art Summary, Cross-Layer Optimisation of LoRaWAN, Overview of Challenges of LoRaWAN | Lack of empirical validation, Lack of Summary, Protocol Stack Restrictions, Optimization Gaps | [16] |
| Designed energy-efficient MAC solution for NB-IoT, Energy-Efficient MAC Layer Solution, Optimization Framework, Cross-Layer Approach, Probabilistic Sleep Scheduling | MINLP optimization; Lyapunov optimization, Distributed sleep scheduling, Simulation Results, High Traffic Load Testing | Reliance on simulation, Resource Constraints, Traffic Model Assumptions, Scalability | [17] |
| Integrated energy-efficient OF into RPL routing, Introduction of ELITE, New Routing Metric, Cross-Layer Integration, Path Selection Improvement | Energy-efficient cross-layer OF integration, RPL protocol, Comparison with Existing OFs, Simulation Results | Limited evaluation in diverse IoT environments, potential complexity in implementation, MAC Layer Dependency, Metric Specificity, Generalizability | [18] |
| Enhance HCN energy efficiency with NOMA, Focus on Energy Efficiency, Optimization Problem Formulation, Introduction of Quantum-inspired political optimizer(QPO) Algorithm | Hybrid resource allocation optimization, Simulation Results(Evaluation of the QPO algorithm’s performance) | Reliance on simulated comparisons, potential challenges in real-world deployment, Non-Convex Problem Complexity, Algorithm Specific | [19] |
| Optimized routing for energy efficiency in FANETs, Virtual relay tunnel based on a suggested energy-conscious routing strategy (ECRS), Incorporation of Multiple Metrics, Path Correlation Metric (enhance route selection) | Energy-aware routing with virtual relay tunnel, comparison against existing methods, Comparative Analysis, Simulation Studies | Limited real-world validation; potential trade-offs between efficiency and longevity, Specificity to FANETs, Complexity in Path Selection, Comparative Scope | [20] |
| Investigated energy management in edge computing, Energy-Efficient Secure Data Transmission, Multi-Scale Grasshopper Optimization, Robust Multi-Cascaded CNN (RMC-CNN), Dynamic Honey Pot Encryption Algorithm | Cross-layer energy optimization, Comparison with Existing Techniques, Encryption and Decryption Time Analysis, | Lack of empirical validation; potential complexity in cross-layer management, Specific Dataset Focus, Complexity of Encryption and Detection Mechanisms, Scalability and Real-Time Constraints | [21] |
| Developed energy-efficient MAC for CR-enabled 6G-IoT, Joint Adaptation of Physical and MAC Layer Parameters, Per-Bit Energy Efficiency Maximization | Multi-channel MAC design, Numerical Results | Reliance on simulations; potential challenges in real-world deployment, Specific to Non-Persistent CSMA, Simulation-Based Evaluation, Design Constraints in 6G-IoT, Design Constraints in 6G-IoT | [4] |
| Integrated energy-efficient protocols into IoT, Cross-Layer Energy Architecture Model, Focus on Green and Renewable Energy, Mathematical Modeling | Utilization of MQTT, CoAP, Zigbee, Wi-Fi for energy efficiency; support for various IoT applications, Mathematical Analysis, Power Savings Estimation, | Lack of empirical validation, Limited Exploration of Practical Implementation, Focus on Theoretical Framework, Scalability and Applicability | [22] |
| Investigated energy efficiency, Thorough Review of IoT for EE, Identification of Common Design Factors, Future Research Directions | Examination of hardware, software for energy management, use of historical data for forecasting, Review and Analysis, Identification of Patterns | Lack of real-world validation, Lack of Original Empirical Data, Application-Specific Variables, Focus on Heating Systems | [23] |
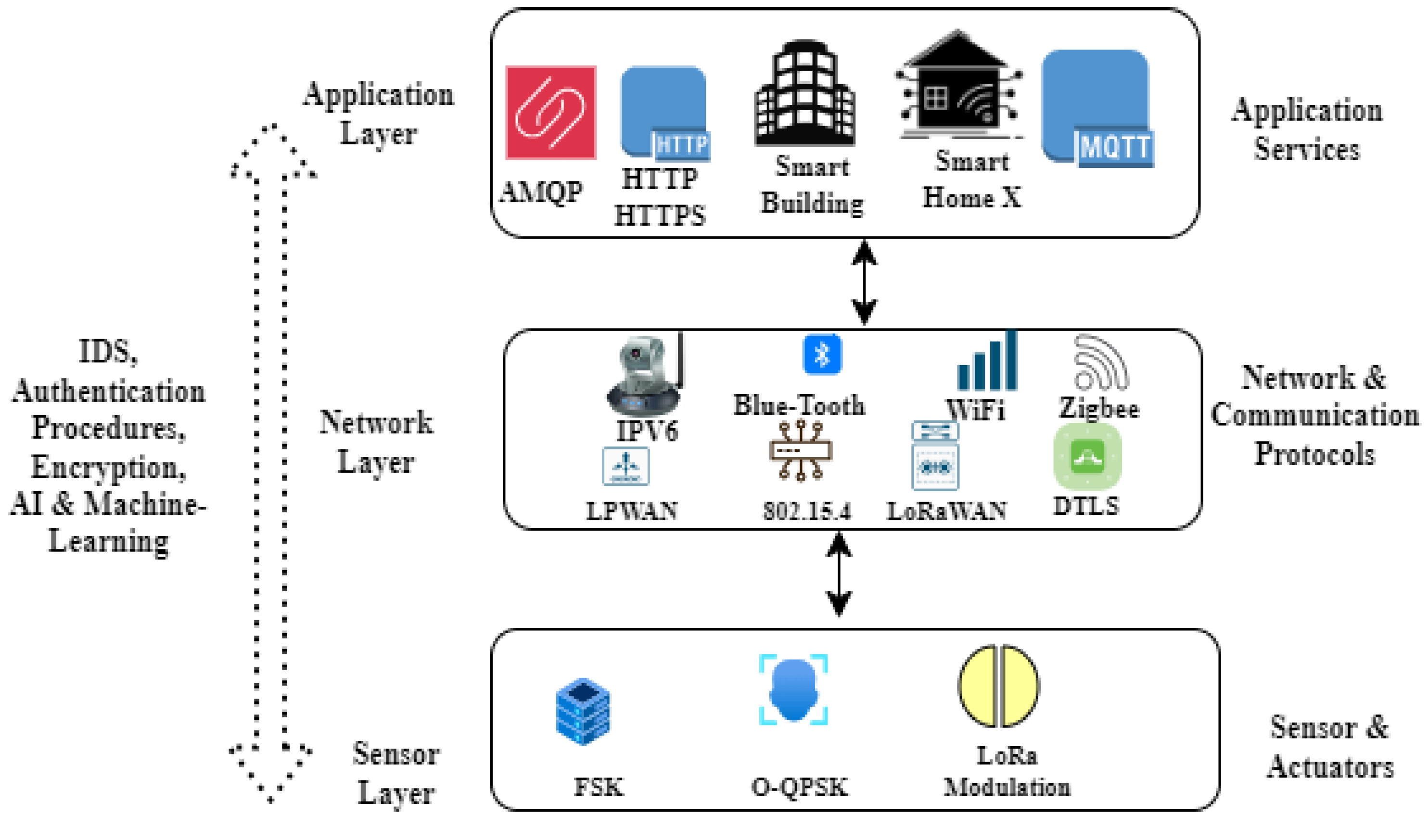
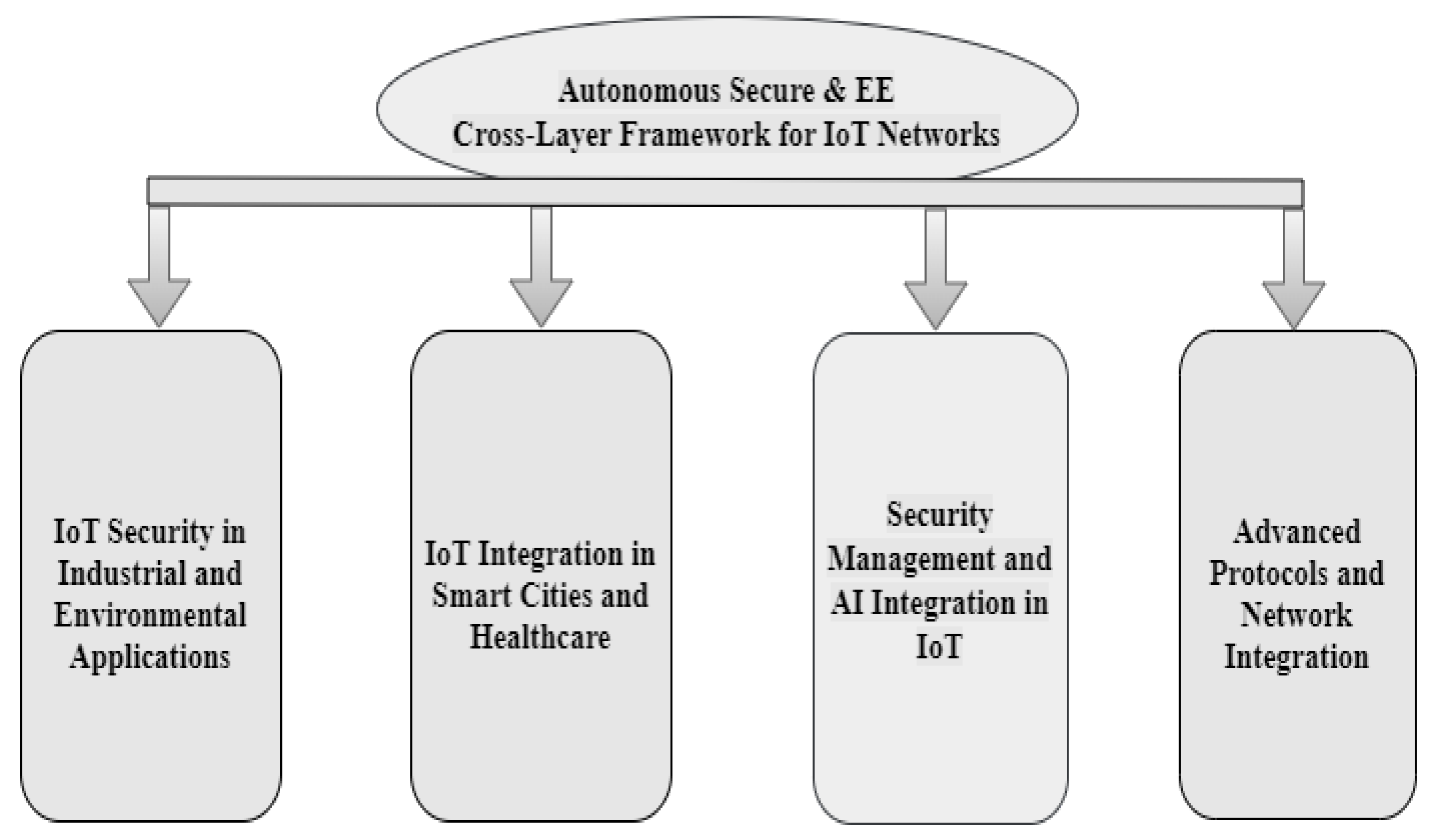
2.3. Autonomous Secure and Energy Efficient Cross-Layer Framework for IoT Networks
- (a)
- Security Management and AI Integration in IoT Utilizing agentless SIEM modules, such as the Wazuh module, enhances IoT network security by analysing device traffic and creating alerts for anomalies without requiring endpoint software. This approach successfully protects industrial control systems in Industry 4.0 settings, as demonstrated using the SWaT dataset [24]. The integration of IoT with AI enables continuous data collection and opens new commercial opportunities through intelligent decision-making. Businesses can leverage AI to analyse IoT data with minimal human intervention, enhancing competitiveness [25]. Implementing federated learning models combined with host and network intrusion detection systems within fog computing environments significantly enhances DDoS attack detection and mitigation. This decentralized approach enhances security and lowers the possibility of single points of failure, achieving 89.753% detection accuracy [26]. utilizing machine learning techniques to identify denial-of-service attacks, such as support vector machines, random forests, and K nearest neighbours in IoT networks demonstrates strong detection capabilities, particularly in Information-Centric Networks (ICNs) [27].
- (b)
- Advanced Protocols and Network Integration Utilizing PCC-RPL and SLF-RPL frameworks improves the security of the RPL protocol in IoT networks by reducing wormhole attacks. SLF-RPL shows better energy efficiency, lower packet loss, and higher attack detection rates compared to PCC-RPL [28]. Integrating Software-Defined Networking (SDN) with Recursive Internetwork Architecture (RINA) enhances IoT network security, flexibility, and scalability. This method facilitates seamless edge-to-cloud connectivity and network function data sharing while maintaining operational integrity [29]. Developing secure, lightweight authentication strategies for low-power IoT devices ensures data privacy and user authentication, which is crucial for applications like Industry 4.0, smart cities, and healthcare [30]. Utilizing learning automata and clustering, this protocol enhances network performance in UV networks by optimizing cluster node count, service class, and network topology.
- (c)
- IoT Integration in Smart Cities and Healthcare Exploring the impact of network softwarization in the industrial sector, this study emphasizes how AI and IoT will play a part in mobile networks in the future., identifying gaps and suggesting areas for further research [31]. The integration of IoT, smart cities, and 5G technology enhances urban living by improving sustainability, efficiency, and responsiveness to citizen demands, transforming urban landscapes [32]. Proposing a Semantic IoT Middleware (SIM) for the healthcare sector addresses data interoperability, heterogeneity, and security using blockchain and AI for optimization and security enhancement [33]. Addressing data security and privacy in E-healthcare applications, this study integrates blockchain with NuCypher encryption to enhance resource use, resilience, and traceability [34].
- (d)
- IoT Security in Industrial and Environmental Applications Integrating Raspberry Pi clusters with BME680 sensors in Kubernetes for environmental monitoring, coupled with OpenID Connect and HashiCorp Vault for dynamic secret management, reduces vulnerabilities and improves responsiveness in IoT installations by 40% and 30%, respectively [35]. The LEMARS model combines heuristic-driven techniques and Feistel architecture to provide a lightweight encryption solution for secure satellite photography, demonstrating higher attack resilience and quality metrics [36]. Systematizing existing research on enhancing IoT resilience, this study proposes a taxonomy and classification of resilience mechanisms to address practical concerns in building reliable systems [37]. Examining static, dynamic, symbolic, and hybrid analysis techniques for finding vulnerabilities in embedded firmware, this overview suggests taxonomies and evaluates these approaches for future research [38].
| Key Contributions | Limitations | Security Measures? | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-layer security and privacy were designed, Integration of IoT technologies with AI for security, Adoption of blockchain for decentralized coordination, Multidisciplinary approaches to ensure IoT security | Application layer security has not been explored, Resource constraints, Privacy concerns, Security issues, Lack of training data, Centralized architecture limitations | AI-based real-time data analysis, Blockchain for secure resource and data sharing, Addressing IoT and WSNs security threats dynamically | [39] |
| Presented various IoT framework tiers,Development of model to mitigate DDoS attacks in local networks, Utilization of Host Intrusion Detection Systems, Integration of Network Intrusion Detection System with federated learning | Think about tiered communication alone, Privacy concerns in decentralized IoT infrastructure, Potential for increased complexity in federated training/detection, Possible challenges in real-time and precise attack detection | Use of HIDS and NIDS for comprehensive attack identification, Federated learning data analysis/anomaly detection, Distributed architecture to prevent volumetric attack traffic, Near-real-time detection in fog Computing | [40] |
| Systematic literature review (SLR) on AI methods for IoT cybersecurity, investigation of machine learning and deep learning methods for IoT security, Finding popular techniques for high accuracy detection, such as random forests (RF) and support vector machines (SVM) | Framework for detecting intrusions at the network layer, Lacks a cross-layer strategy, Existing security and privacy challenges despite AI advancements, Need for intelligent architectural frameworks for better intrusion detection | Artificial intelligence (AI) techniques are utilized to secure Internet of Things devices. applying AI methods to identify cybersecurity threats, intelligent intrusion detection systems (IDS) with frameworks based on AI, Examination of AI techniques based on attack categories | [1] |
| At the most basic level of security, perception, the physical layer, and the wireless network layer were considered, Proposal of a global perspective security framework for PIoT, Focus on security issues in the perception layer of PIoT, Development of security policies and countermeasures for PIoT, Application of research results in real-world projects | Complexity of securing a large, complex cyber-physical network like PIoT, Potential challenges in implementing the proposed security framework across all layers, Complexity of securing a large, complex cyber-physical network like PIoT, Potential challenges in implementing the proposed security framework across all layers | The deployment of the autonomous safety system. security audits, residual information protection, intrusion prevention, and data backup, systems, Security framework spanning from perception layer to application layer, Specific security policies and countermeasures for addressing PIoT security issues | [2] |
| Discussion of existing vulnerabilities and attacks in the IoT ecosystem, Testing secure framework for IoT applications, Framework evaluates IoT applications from the initial phase | Complexity of securing IoT applications,Potential challenges in implementing comprehensive monitoring and security testing. | Monitoring and security testing framework and evaluate IoT applications, Focus on addressing security issues from the early stages of IoT application development | [3] |
| Examination of communication standards (ITU-T), Discussion of 4-levels of IoT security gateways, Overview of testing methods for IoT devices | Potential complexity in securing diverse communication standards, Challenges in applying uniform security measures across different levels | Identification of 4-levels of security in IoT systems, Application of security testing methods to evaluate IoT components and systems | [41] |
| Review of IoT threats, security requirements, challenges, Proposal of a novel paradigm combining IoT architecture with SDN, Discussion on SDN-based IoT deployment models | Challenges in unifying all IoT stakeholders on a single platform, Potential hurdles in implementing SDN-based security solutions across diverse IoT environments | Introduction of SDN-based IoT security solutions, Comprehensive overview of software-defined security (SDSec), Emphasis on network-based security solutions for the IoT paradigm | [42] |
| Analysis of IoT’s impact across various domains, Discussion of Service Oriented Architecture model, Divided into application network and perception layers, Examination of IoT security attacks during COVID-19 | Numerous privacy concerns in rapidly developing IoT environments, Increased security attacks on IoT devices, especially during the COVID-19 | Security and privacy challenges in IoT based on SOA layers, Identification of different technologies used for communication in each IoT layer, Overview of attacks targeting specific SOA layers and IoT devices | [15] |
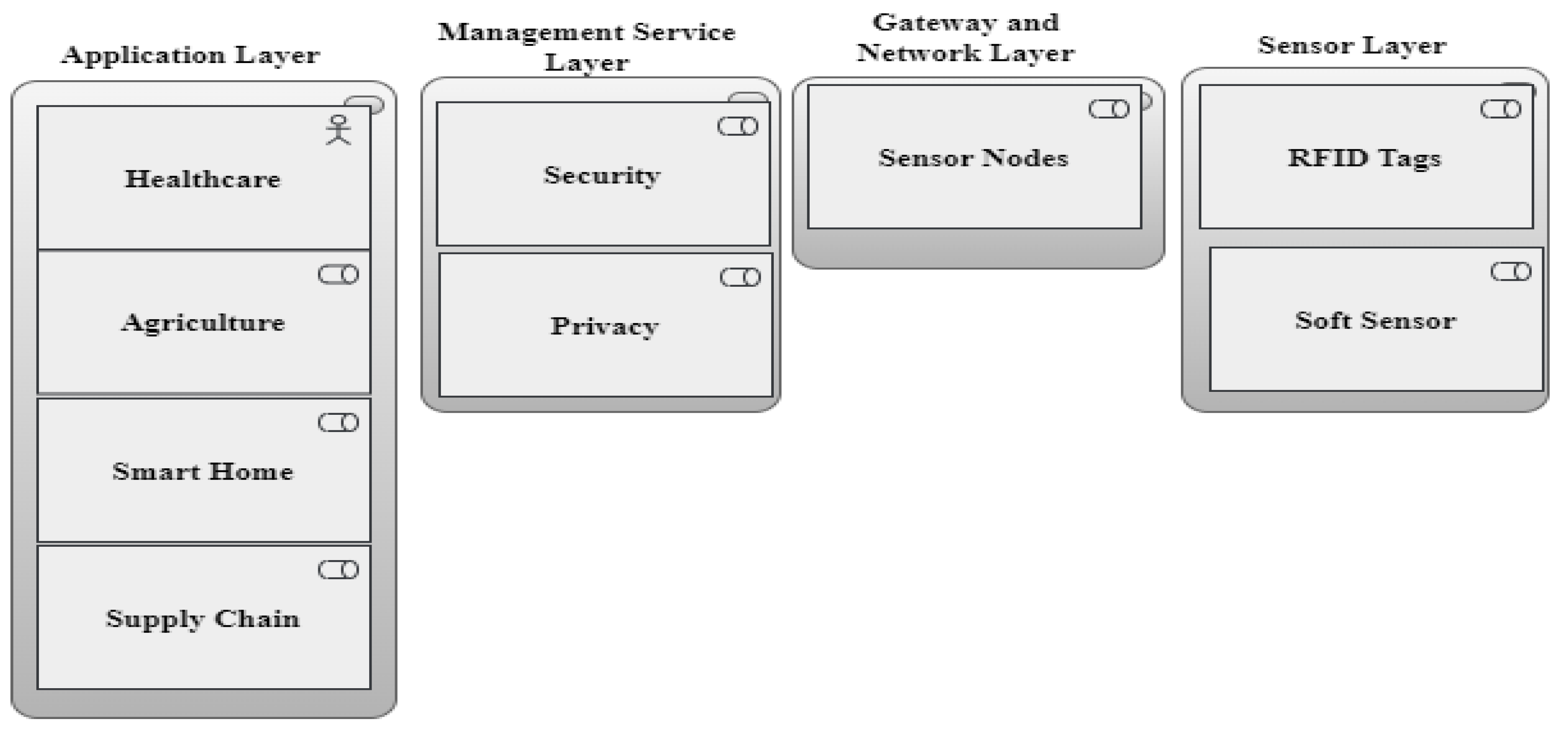
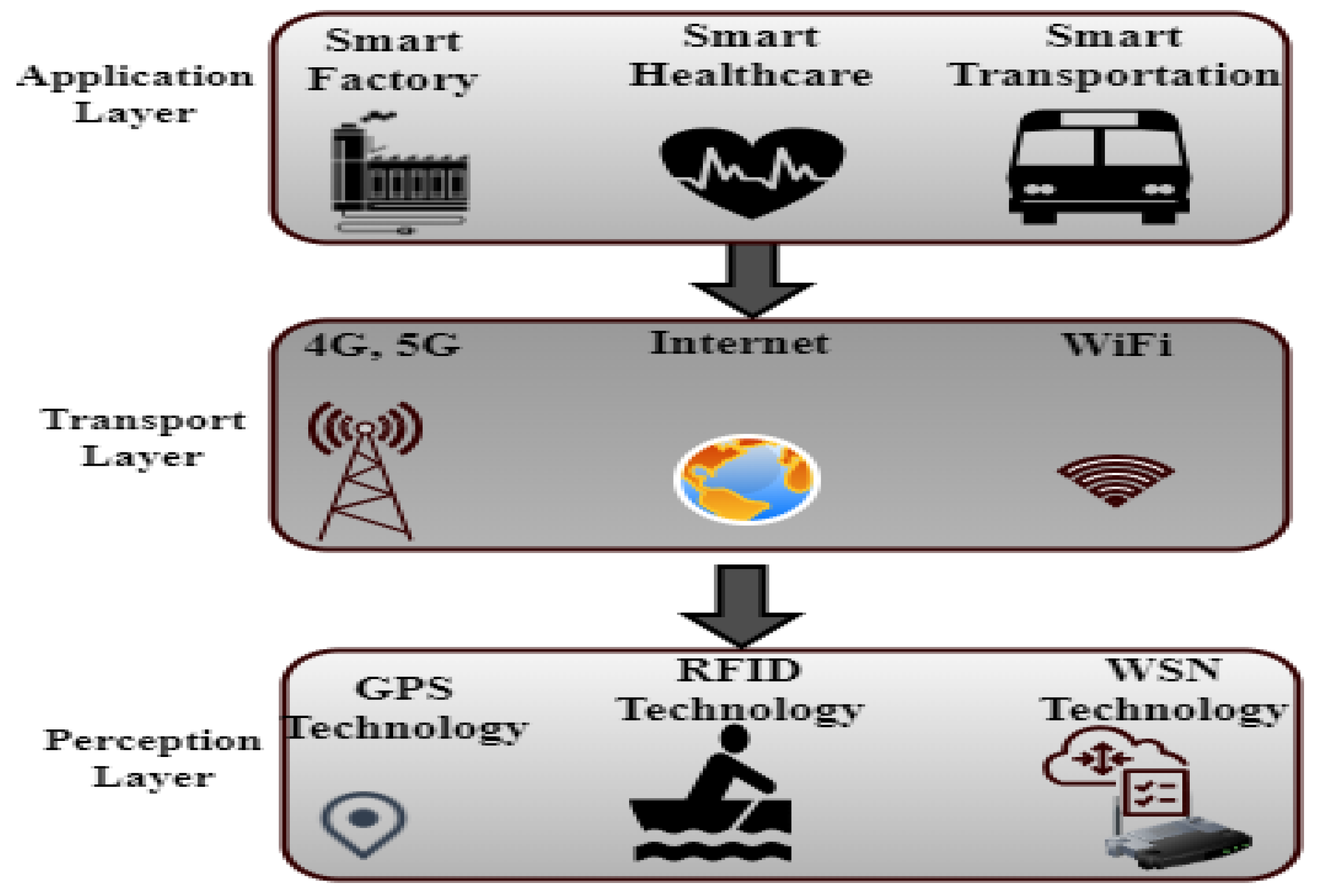
2.4. IoT Layered Architecture
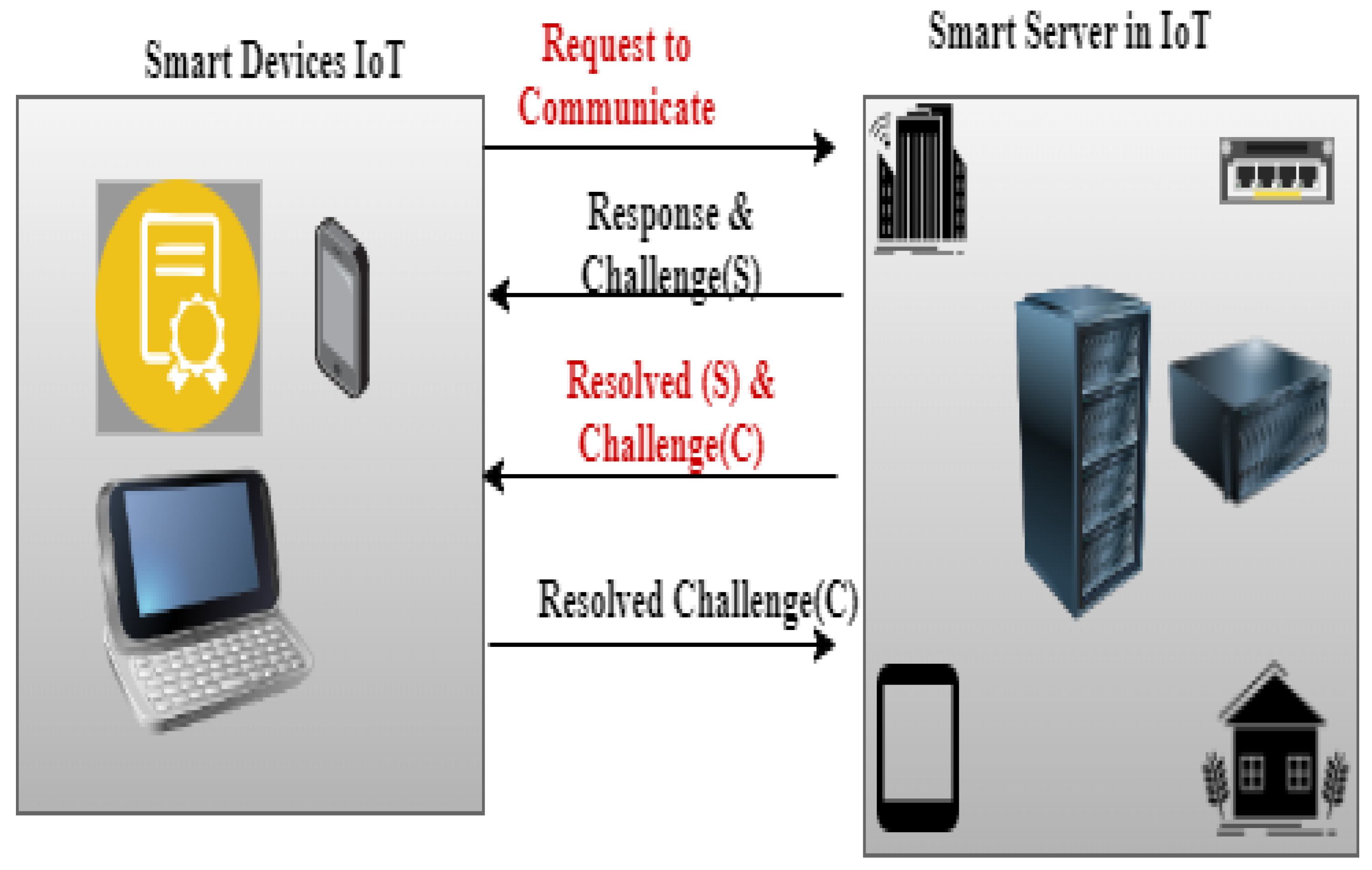
2.5. Quality Standards and Trustworthiness
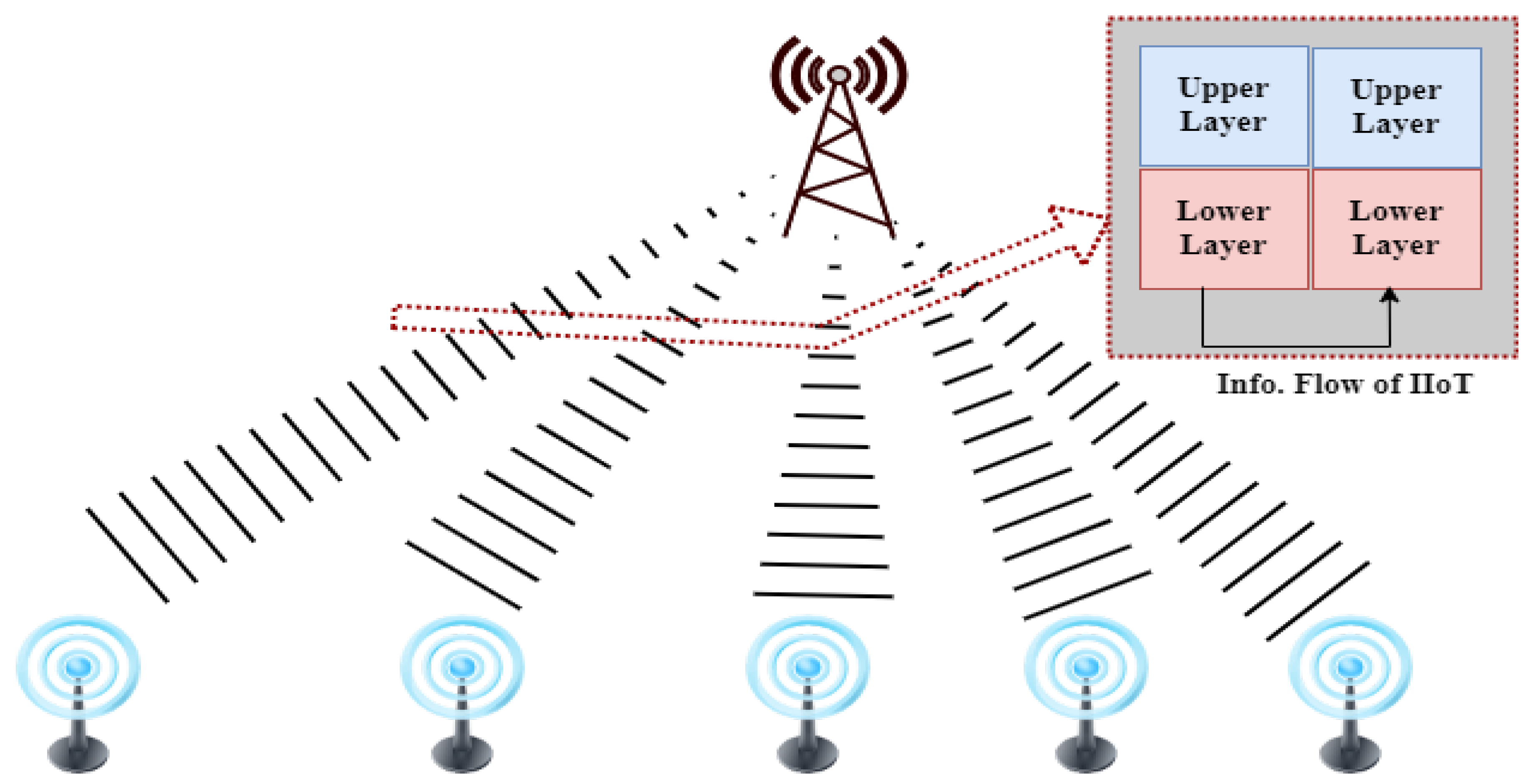
2.6. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
2.7. MAC-Routing
2.8. Energy Efficiency Cross Layer Design
| Survey Scope | IoT Security | Security-Measure Implemented | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoT Security Research,Focuses on the deployment of IoT technology in industrial automation, Next Generation Cyber Security Architecture (NCSA) for the Industrial IoT | NCSA Implementation, Automated Cyber-Defense | Vulnerabilities, attacks, cross-layer security, Real-time Protection, Identity Token Mechanism | Limited consideration of interaction of cyber-physical devices,Specific Focus on IIoT, No Detailed Performance Evaluation, Potential Integration Challenges | [77] |
| In-depth analysis of the IIoT ecosystem focusing on security and digital forensics, Overview of the state-of-the-art in IIoT security and digital forensics, Highlighting key achievements, Challenges | Examination of the structural and dynamic complexity of IIoT, Exploration of vulnerabilities introduced by the continuous integration of IIoT | Analysis of cutting-edge security mechanisms deployed in IIoT ecosystems to protect processes,Survey of digital forensics literature related to IIoT, Focusing on techniques and tools to mitigate security breaches | NCSA proposed for real-time threat detection,Complexity and Integration, Evolving Threat Landscape, Need for Future Research | [69] |
| Cyber-physical system risk identification, Analysis of risk identification in Industry (CPS), Examination of methodologies for identifying risks across physical, Interconnection layers in CPS | Focus on the security vulnerabilities and cyber-attacks associated with interconnected devices and equipment in Industry CPS | Proposed a new hybrid methodology for risk identification in Industry, Integrating existing frameworks and standards such as ISO 31000, PMBOK, HAZOP, and NIST, Developed a four-step process that includes identifying risks from various sources | Lack of consideration for interaction of cyber-physical devices, Incompleteness of Existing Methodologies | [6] |
| Threat detection in industrial networks, Exploration of a framework combining using AI tools, Focus on threat detection within real industrial IoT sensor networks | Addresses the challenge of detecting threats IIoT networks while maintaining privacy and security | Big data architecture, predictive analytics | Limited to real industrial network, AI-based predictive analytics, Securely sharing results, Application of the framework as part of the H2020 ECHO project | [5] |
| Cross-layer authentication framework, Focuses on addressing security challenges in IIoT of 5G technology, Explores the security implications of bypassing upper authentication protocols and supporting small data transmission during initial access in IIoT systems | Highlights the vulnerabilities in IIoT due to the use of 5G, Emphasizes the need for secure cross-layer authentication frameworks to address these vulnerabilities | Device authentication vulnerabilities, 5G technology, Proposes a secure cross-layer authentication framework, Utilizes a quantum walk-based privacy-preserving, Derives the space of one-time keys for encryption | Proposal addresses security vulnerabilities, Complexity, Scalability, Performance Overhead | [58] |
| Adaptive Cybersecurity system, Cybersecurity for networked devices using virtual environment services | Addresses increased risks due to widespread device connectivity | Real-world network packet collection, Machine learning, Honeynet architecture, Adaptive Cybersecurity (AC) system | Performance improvements needed, dataset expansion planned, Data dependency, Scalability challenges | [61] |
3. Key Strategies and Trends
3.1. Key Strategies
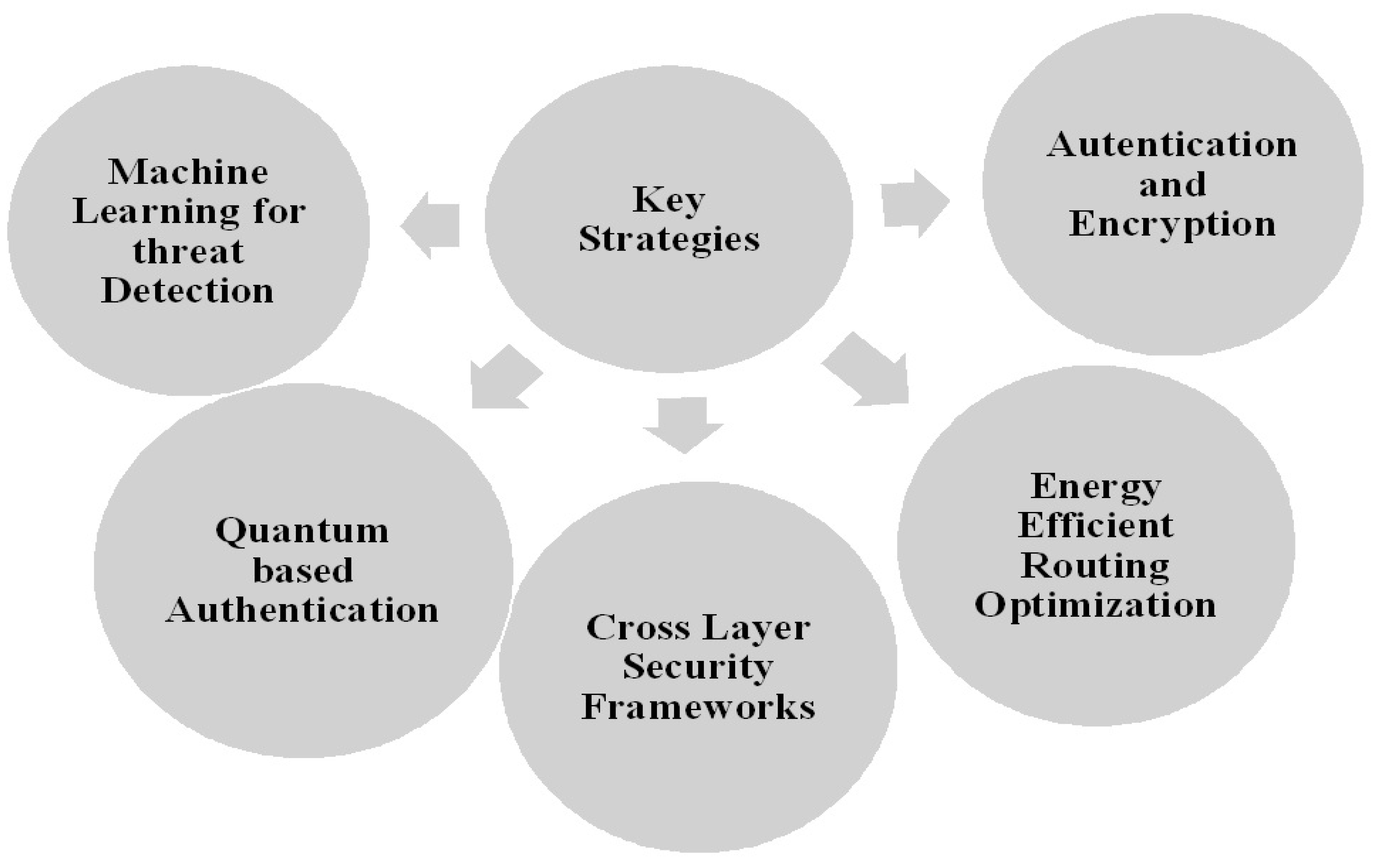
- (a)
- Authentication and Encryption: As the number of IoT devices continues to grow rapidly, ensuring robust authentication and encryption mechanisms becomes imperative to protect sensitive data and maintain privacy [9,62]. Authentication mechanisms such as cryptographic protocols and identity management systems help verify the identities of devices and users, while encryption techniques such as symmetric and asymmetric encryption ensure secure communication channels. Additionally, blockchain technology is being explored to provide tamper-proof and decentralized solutions for data integrity and transaction security in IoT environments.
- (b)
- Machine Learning for Threat Detection: With the increasing sophistication of cyber threats targeting IoT systems, machine learning algorithms are being leveraged for threat detection and prevention [61]. These algorithms analyze vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices to identify patterns indicative of malicious activities or anomalies. By continuously learning from new data, machine learning models can adapt and improve their accuracy in detecting and mitigating security threats, thereby enhancing the resilience of IoT networks.
- (c)
- Cross-Layer Security Frameworks: Cyber-physical systems (CPS) present unique security challenges due to their interconnected nature and reliance -on both physical and digital components [6]. To address these challenges, hybrid security frameworks integrating established risk management methodologies such as ISO standards with domain-specific risk models are being developed. These frameworks facilitate comprehensive risk identification and management across multiple layers of CPS architectures, from the physical layer to the application layer. By considering interactions between different layers, organizations can better assess and mitigate security vulnerabilities in their IoT deployments.
- (d)
- Quantum-based Authentication: With the advent of Industry IoT (IIoT) and the proliferation of 5G technology, traditional authentication mechanisms face new challenges related to device authentication vulnerabilities [58]. To address these challenges, cross-layer authentication frameworks based on quantum walk on circles are proposed. These frameworks utilize quantum principles to ensure secure device identification and authentication, thereby mitigating the risks associated with compromised authentication credentials and unauthorized access to IIoT networks.
- (e)
- Energy-Efficient Routing and Optimization Energy efficiency is a critical concern in IoT deployments, particularly in resource-constrained environments [7,17,18,21]. Strategies such as energy-efficient routing schemes and cross-layer optimization techniques aim to minimize energy consumption while maximizing network performance and reliability. These approaches leverage techniques such as virtual relay tunnels, mixed-integer nonlinear programming (MINLP), and optimized transmission modes to optimize energy usage at both the MAC and physical layers of IoT networks. Additionally, the integration of renewable energy sources with IoT architectures further enhances energy efficiency and sustainability, reducing reliance on traditional power sources and minimizing environmental impact.
3.2. Emerging Trends
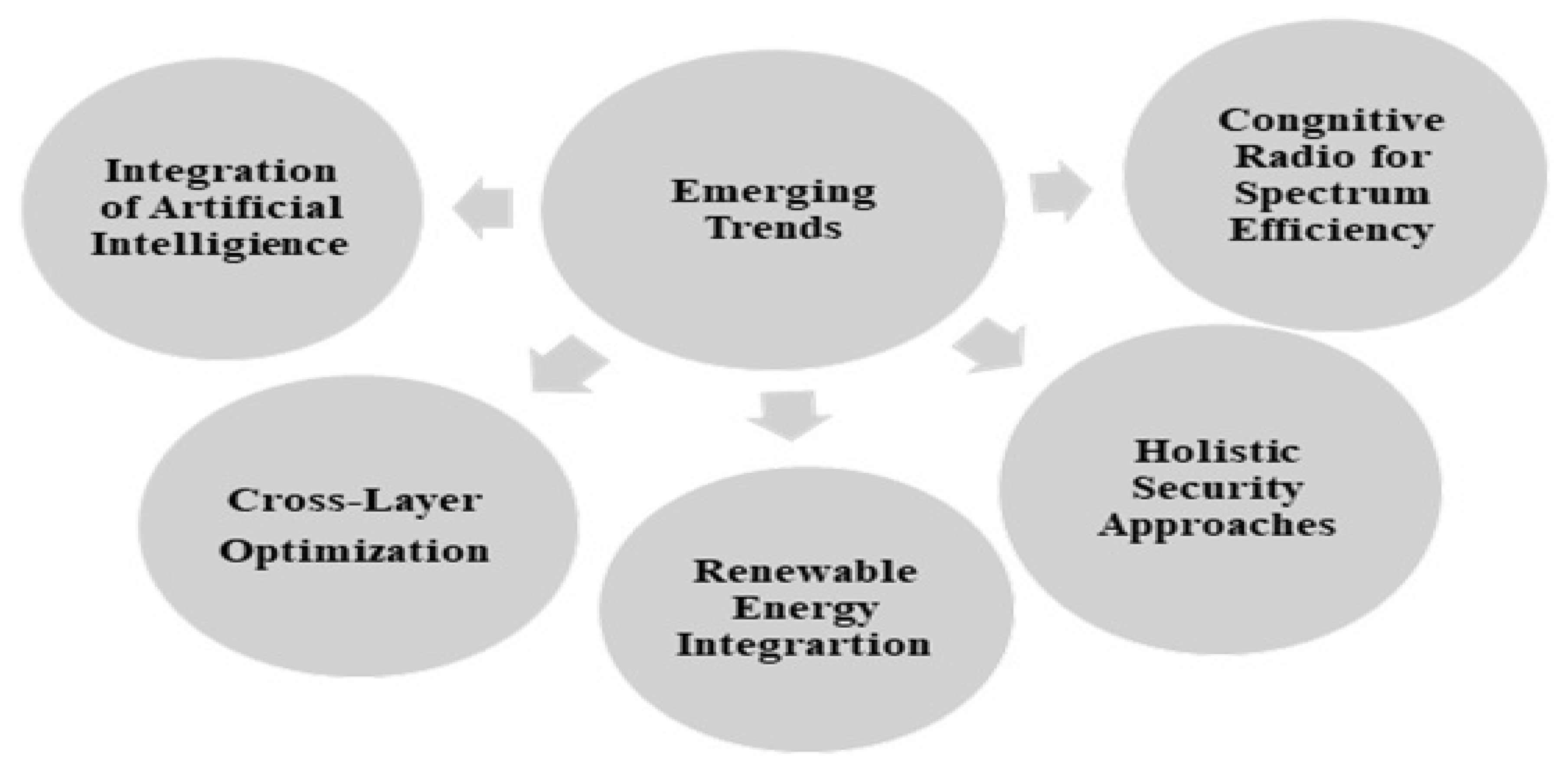
- (a)
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms is emerging as a trend to enhance IoT security and efficiency [61,87]. These technologies enable predictive analytics for threat detection and optimization of energy consumption in IoT systems. By analyzing large datasets generated by IoT devices, AI algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies indicative of security threats, enabling proactive mitigation strategies. Additionally, AI-based solutions facilitate the integration of variable renewable energy sources into power systems, improving forecasting accuracy and grid management.
- (b)
- Cognitive Radio for Spectrum Efficiency: With the advent of 6G IoT networks, cognitive radio (CR) technology is proposed to optimize spectrum usage and energy efficiency [4]. Multi-channel MAC frameworks tailored for CR-enabled networks aim to improve IoT network performance and connectivity by dynamically allocating spectrum resources based on network conditions and user requirements. These frameworks enhance spectrum efficiency while minimizing interference and energy consumption, thereby enabling reliable and scalable communication in dense IoT deployments.
- (c)
- Renewable Energy Integration The integration of renewable energy sources with IoT architectures is gaining traction for enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability [87]. Deep learning applications facilitate the integration of variable renewable energy sources into power systems, improving forecasting accuracy and grid management. By leveraging AI-based solutions, organizations can optimize energy usage and minimize reliance on traditional power sources, thereby reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
- (d)
- Holistic Security Approaches: As IoT ecosystems become increasingly complex, holistic security approaches are being advocated to mitigate evolving cyber threats [9] [62]. These approaches encompass robust authentication mechanisms, encryption protocols, and proactive threat detection strategies to safeguard against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security risks. By adopting comprehensive security measures, organizations can ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their IoT deployments, thereby enhancing trust and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- (e)
- Cross-Layer Optimization: Cross-layer optimization techniques are being explored to improve energy efficiency and performance in IoT networks [21]. By jointly optimizing parameters across different protocol layers, such as the physical and MAC layers, organizations can minimize energy consumption while meeting the diverse requirements of IoT applications. These approaches enable dynamic adaptation to changing network conditions and user demands, enhancing reliability and scalability in IoT deployments. These findings highlight the necessity of comprehensive approaches to cyber-physical systems and IoT security, including improved cybersecurity architectures, all-encompassing security measures, and creative solutions that make use of cutting-edge technology like machine learning and quantum cryptography (See Table 5 for Key strategies and Trends).
| Main Contributions | Trends | Application Area | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Big Data Architecture, Predictive Analytics, Threat detection, Obscuring sensitive data, Evaluation framework | Enhances trust among stakeholders, Closes security gaps | Industrial networks | [5] |
| Cross-layer Optimization, LoRaWAN, Flexibility across protocol layers, Energy-efficient | Optimizes protocol, Enhances performance | IoT applications, LPWANs | [16] |
| Hybrid Methodology, Risk Identification, ISO 31000, PMBOK, HAZOP, NIST strategies | Reduces risk redundancy, Comprehensive analysis | Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) | [6] |
| Social IoT (SIoT), Cross-layer Security, Data trustworthiness, Graph-powered learning strategies | Enhances network navigability, Balance energy efficiency | SIoT ecosystems | [14] |
| Lightweight Encryption, Key Management, Random key encryption, Information-theoretic security | Efficient and secure, Suitable for resource-limited IoT | IoT, Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) | [52] |
| Cross-layer Intrusion Detection, Ensemble Learning, IoT-Sentry, Cooja IoT simulator analysis | High detection accuracy, Minimal overhead | Standardized IoT networks | [53] |
| IoT Authentication Strategies, Categorization by hierarchy, centralization, distribution | Comprehensive review, Encourages further research | IoT authentication | [55] |
| Lightweight Mutual Authentication, Smart city applications, Performance optimization | Balances security and efficiency, Outperforms existing protocols | Smart cities, Traffic and water management | [57] |
| Cross-layer Authentication, Quantum Walk, Device identifier encoding, Privacy-preserving protocol | High security and privacy, Low latency | IIoT, 5G networks | [58] |
| Honeynet Architecture, Machine Learning, Real-world attack detection, Web-based IDS-AC | Effective attack warnings, User self-update | Industrial networks, Cybersecurity | [61] |
| Survey of IoT Security Research, Vulnerabilities, Mitigation strategies, Future directions | Comprehensive overview, Guides future research | IoT development, Security solutions | [62] |
| ESPINA Protocol, IoT network technologies in delay, Improved security with keys-renewal strategy, Reduces computational cost | Energy optimization, 6G wireless connectivity, Superior to current protocols, Effective for 6G standards,6G wireless communications, Energy-efficient and secure protocols | Healthcare IoT, Embedded systems, Security-sensitive applications | [73] |
| CLCSR Protocol, Attack detection, Secure clustering, Lightweight cryptography | Enhances network performance, Privacy preservation | E-healthcare, Smart cities | [74] |
| Hierarchical Authentication, Key Agreement, Physically unclonable functions, Elliptic curve cryptography | Efficient and secure, Resistant to common attacks | Industry 4.0, IoT environments | [76] |
4. Open Research Problems and Challenges
4.1. Open Research Issues
- DDOS: It is still very difficult to create strong security measures to keep malware infiltrations, DDoS attacks, and privilege escalation out of IoT networks. For greater application and efficacy, existing solutions such as the agentless Wazuh SIEM module offer a good foundation, but they still require improvement [24].
- Routing Protocols:It is crucial to create safe routing protocols for Internet of Things networks in order to thwart assaults like denial-of-service and wormhole attacks. Additional optimization is required for attack detection and energy efficiency in frameworks such as parental change control routing protocol for low power and lossy and subjective logical framework routing protocol for low power and lossy network [28].
- Blockchain Technology: It is a viable way to improve IoT security and data integrity, particularly in the agricultural and healthcare industries [33].
- Semantic IoT Middleware: It’s crucial to create energy-efficient Internet of Things architectures that can handle a lot of devices without using a lot of power. Measures in this direction include the Semantic IoT Middleware and the hierarchical ensemble TinyML [94].
- Robustness and Resilience:It is essential to increase the robustness and resilience of IoT systems to withstand different kinds of cyberattacks and operational failures. More work needs to be done on taxonomies and classifications of resilience mechanisms [72].
4.2. Open Research Challenges
- Host intruder Detection(HIDS): HIDS system and network intruder detection system integration with federated learning to build decentralized, robust security solutions in fog computing environments [26].
- Integration of IoT & AI:Ensuring the smooth integration of IoT and AI to manage analytics and real-time data processing. Addressing security and privacy concerns with data while keeping performance high [32].
- RPL Protocol:Improving the RPL protocol in order to reduce packet loss, increase attack detection rates, and boost energy efficiency [28]. Customizing secure routing protocols to different Internet of Things contexts ensures scalability and compatibility.
- Blockchain Solution:Putting into practice blockchain solutions that are lightweight and don’t put an undue strain on IoT device resources [100]. Ensuring blockchain’s compatibility with current IoT platforms to enable smooth integration.
- Data Governance:Strong frameworks for data governance that strike a compromise between the requirement for data accessibility and privacy [68].
- Encryption & Authentication: Efficient encryption and secure authentication systems that work with low-power Internet of Things devices [81].
5. Conclusion
References
- Abdullahi, M.; Baashar, Y.; Alhussian, H.; Alwadain, A.; Aziz, N.; Capretz, L.F.; Abdulkadir, S.J. Detecting Cybersecurity Attacks in Internet of Things Using Artificial Intelligence Methods: A Systematic Literature Review, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zou, W.; Chen, X.; Yang, C.; Cao, J. The security for power internet of things: Framework, policies, and countermeasures. Proceedings - 2014 International Conference on Cyber-Enabled Distributed Computing and Knowledge Discovery, CyberC 2014. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2014, pp. 139–142. [CrossRef]
- SǎLndescu, C.; Grigorescu, O.; Rughiniş, R.; Deaconescu, R.; Cǎlin, M. Why IoT security is failing. the Need of a Test Driven Security Approach. Proceedings - 17th RoEduNet IEEE International Conference: Networking in Education and Research, RoEduNet 2018, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Bani Irshaid, M.; Bany Salameh, H.; Jararweh, Y. Intelligent multichannel cross-layer framework for enhanced energy-efficiency in 6G-IoT wireless networks. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments 2023, 57, 103211. [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, B. Combining exposure indicators and predictive analytics for threats detection in real industrial IoT sensor networks 2020. pp. 423–428.
- Santos, M.F.O.; Melo, W.S.; Machado, R. Cyber-Physical Risks identification on Industry 4.0: A Methodology Proposal. 2022 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 and IoT, MetroInd 4.0 and IoT 2022 - Proceedings 2022, pp. 300–305. [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Ali, S.; Mohammed, A.H.; Lansky, J.; Mildeova, S.; Yousefpoor, M.S.; Yousefpoor, E.; Hassan Ahmed, O.; Rahmani, A.M.; Mehmood, A. An energy-aware routing scheme based on a virtual relay tunnel in flying ad hoc networks. Alexandria Engineering Journal 2024. [CrossRef]
- Karaturk, E. Security Concepts in Smart Cities 2020.
- Elkhouly, S.M.E.; Ahmed, Y.; Yehia, E.A. The Cyber Security Vulnerabilities in the Internet of Things : A Case Study. Cf 2020, 18, 97–111.
- Arumugam, K.; Rajesha, N.; Prasad, M.; Shanmugasundaram, N.; Rao, D.S.; Suneela, B. Spectrum Sensing Framework and Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation for Cognition Enhancement Network. 2023 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics, ICCCI 2023 2023, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, D.; Rajanna, G.S. Energy aware data harvesting strategy based on optimal node selection for extended network lifecycle in smart dust. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems 2023, 44, 939–949. [CrossRef]
- Salameh, H.A.; Bani Irshaid, M.; Al Ajlouni, A.; Aloqaily, M. Energy-efficient cross-layer spectrum sharing in CR green IoT networks. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking 2021, 5, 1091–1100. [CrossRef]
- Ambika, K.; Malliga, S. Secure hyper intelligence in routing protocol with low-power (RPL) Networks in IoT. Advances in Engineering Software 2022, 173, 103247. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Huo, Y. Cross-layer secure transmission schemes for social internet of things: Overview, opportunities and challenges. Neurocomputing 2022, 500, 703–711. [CrossRef]
- Debnath, D.; Chettri, S.K.; Dutta, A.K. Security and Privacy Issues in Internet of Things. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems 2022, 314, 65–74. [CrossRef]
- Chaguile, C.C.; Alipio, M.; Bures, M. A Classification of Cross-Layer Optimization Approaches in LoRaWAN for Internet of Things. International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks, ICUFN 2023, 2023-July, 259–264. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, D.; Acharya, T.; Chakravarty, S. Energy efficient data gathering in IoT networks with heterogeneous traffic for remote area surveillance applications: A cross layer approach. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking 2021, 5, 1165–1178. [CrossRef]
- Safaei, B.; Monazzah, A.M.H.; Ejlali, A. ELITE: An Elaborated Cross-Layer RPL Objective Function to Achieve Energy Efficiency in Internet-of-Things Devices. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8, 1169–1182. [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Gao, H.; Guo, L.; Li, H. Energy-efficient joint resource allocation for heterogeneous cellular networks with wireless backhauls. AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications 2024, 176, 155170. [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Ali, S.; Hussein, A.; Lansky, J. An energy-aware routing scheme based on a virtual relay tunnel in flying ad hoc networks. Alexandria Engineering Journal 2024. [CrossRef]
- Uddin, R.S.; Manifa, N.Z.; Chakma, L.; Islam, M.M. Cross-Layer Architecture for Energy Optimization of Edge Computing. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, LNICST 2023, 491 LNICST, 687–701. [CrossRef]
- Sakthidasan Sankaran, K.; Kim, B.H. Deep learning based energy efficient optimal RMC-CNN model for secured data transmission and anomaly detection in industrial IOT. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments 2023, 56, 102983. [CrossRef]
- Yaici, W.; Krishnamurthy, K.; Entchev, E.; Longo, M. Survey of Internet of Things (IoT) Infrastructures for Building Energy Systems. GIoTS 2020 - Global Internet of Things Summit, Proceedings 2020. [CrossRef]
- Zahid, H.; Hina, S.; Hayat, M.F.; Shah, G.A. Agentless Approach for Security Information and Event Management in Industrial IoT. Electronics (Switzerland) 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Nguyen, T.N. AI Models for Blockchain-Based Intelligent Networks in IoT Systems; Vol. 6, 2023. [CrossRef]
- de Caldas Filho, F.L.; Soares, S.C.M.; Oroski, E.; de Oliveira Albuquerque, R.; da Mata, R.Z.A.; de Mendonça, F.L.L.; de Sousa Júnior, R.T. Botnet Detection and Mitigation Model for IoT Networks Using Federated Learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 1–35. [CrossRef]
- Bukhowah, R.; Aljughaiman, A.; Rahman, M.M. Detection of DoS Attacks for IoT in Information-Centric Networks Using Machine Learning: Opportunities, Challenges, and Future Research Directions. Electronics (Switzerland) 2024, 13. [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.; Sajid, A.; Kiren, T.; Khan, I.U.; Dewi, C.; Cauteruccio, F.; Christanto, H.J. A Subjective Logical Framework-Based Trust Model for Wormhole Attack Detection and Mitigation in Low-Power and Lossy (RPL) IoT-Networks. Information (Switzerland) 2023, 14. [CrossRef]
- Sarabia-Jácome, D.; Giménez-Antón, S.; Liatifis, A.; Grasa, E.; Catalán, M.; Pliatsios, D. Progressive Adoption of RINA in IoT Networks: Enhancing Scalability and Network Management via SDN Integration. Applied Sciences (Switzerland) 2024, 14. [CrossRef]
- Saurabh.; Sharma, C.; Khan, S.; Mahajan, S.; Alsagri, H.S.; Almjally, A.; Alabduallah, B.I.; Ansari, A.A. Lightweight Security for IoT. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems 2023, 45, 5423–5439. [CrossRef]
- Rojas, E.; Carrascal, D.; Lopez-Pajares, D.; Alvarez-Horcajo, J.; Carral, J.A.; Arco, J.M.; Martinez-Yelmo, I. A Survey on AI-Empowered Softwarized Industrial IoT Networks. Electronics (Switzerland) 2024, 13. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Tanwar, S.; Jadeja, R.; Singh, S.; Polkowski, Z. Secure and intelligent IoT-enabled smart cities; Vol. i, 2024; pp. 1–453. [CrossRef]
- Elkhodr, M.; Khan, S.; Gide, E. A Novel Semantic IoT Middleware for Secure Data Management: Blockchain and AI-Driven Context Awareness. Future Internet 2024, 16, 1–31. [CrossRef]
- Almagrabi, A.O. Challenges and vulnerability evaluation of smart cities in IoT device based on cybersecurity mechanism. Expert Systems 2023, 40, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Donca, I.C.; Stan, O.P.; Misaros, M.; Stan, A.; Miclea, L. Comprehensive Security for IoT Devices with Kubernetes and Raspberry Pi Cluster. Electronics (Switzerland) 2024, 13, 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Madhu, D.; Vasuhi, S. Lightweight Encryption Assisted Man-in-The-Middle Attack-Resilient Steganography Model for Secure Satellite Imagery Services: LEMARS. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems 2023, 45, 2847–2869. [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.; Eichhammer, P.; Reiser, H.P.; Domaschka, J.; Hauck, F.J.; Habiger, G. A Survey on Resilience in the IoT: Taxonomy, Classification, and Discussion of Resilience Mechanisms. ACM Computing Surveys 2022, 54. [CrossRef]
- Magara, T.; Zhou, Y. Internet of Things (IoT) of Smart Homes: Privacy and Security. Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering 2024, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Mohaisen, A.; Chen, S. XLF: A cross-layer framework to secure the internet of things (IoT). Proceedings - International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems 2019, 2019-July, 1830–1839. [CrossRef]
- Tandon, A.; Srivastava, P. Location based secure energy efficient cross layer routing protocols for IOT enabling technologies. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering 2019, 8, 368–374.
- Lazarev, A. MODERN METHODS OF TESTING AND INFORMATION SECURITY PROBLEMS IN IoT. Bulletin of TUIT: Management and Communication Technologies 2021. [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, W.; Abbas, H.; Daneshmand, M.; Rauf, B.; Bangash, Y.A. An In-Depth Analysis of IoT Security Requirements, Challenges, and Their Countermeasures via Software-Defined Security. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2020, 7, 10250–10276. [CrossRef]
- Ozalp, A.N.; Albayrak, Z.; Cakmak, M.; Ozdogan, E. Layer-based examination of cyber-attacks in IoT. HORA 2022 - 4th International Congress on Human-Computer Interaction, Optimization and Robotic Applications, Proceedings 2022. [CrossRef]
- Zeadally, S.; Das, A.K.; Sklavos, N. Cryptographic technologies and protocol standards for Internet of Things. Internet of Things (Netherlands) 2021, 14, 100075. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Dhiman, G.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, A.; Tselykh, A. An IoT and Blockchain-based approach for the smart water management system in agriculture. Expert Systems 2023, 40, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Arulselvan, G.; Rajaram, A. Hybrid trust-based secure routing protocol for detection of routing attacks in environment monitoring over MANETs. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems 2023, 45, 6575–6590. [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.; Patel, R.; Varma, S. A novel of congestion control architecture using edge computing and trustworthy blockchain system. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems 2023, 44, 6303–6326. [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, A.; Butt, M.A.; Ali, H.; Usman, M.; Halabi, O.; Al-Fuqaha, A.; Abbasi, Q.H.; Imran, M.A.; Qadir, J. Secure and Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence-extended Reality (AI-XR) for Metaverses. ACM Computing Surveys 2024, 56, 1–38, [2210.13289]. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Chang, C.; Ma, Y.; Yang, C.; Yuan, L. Secure multi-path routing for Internet of Things based on trust evaluation. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering 2024, 21, 3335–3363. [CrossRef]
- Becherer, M.; Hussain, O.K.; Zhang, Y.; Den Hartog, F.; Chang, E. On Trust Recommendations in the Social Internet of Things - A Survey. ACM Computing Surveys 2024, 56. [CrossRef]
- Qasem, A.; Shirani, P.; Debbabi, M.; Wang, L.; Lebel, B.; Agba, B.L. Automatic Vulnerability Detection in Embedded Devices and Firmware: Survey and Layered Taxonomies. ACM Computing Surveys 2021, 54. [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.W.; Yang, E.H.; Wang, J. Lightweight security protocols for the Internet of Things. IEEE International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, PIMRC 2017, 2017-Octob, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Kamaldeep.; Malik, M.; Dutta, M.; Granjal, J. IoT-Sentry: A Cross-Layer-Based Intrusion Detection System in Standardized Internet of Things. IEEE Sensors Journal 2021, 21, 28066–28076. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Niu, J.; Bhuiyan, M.Z.A.; Wu, F.; Karuppiah, M.; Kumari, S. A robust ECC-Based provable secure authentication protocol with privacy preserving for industrial internet of things. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2018, 14, 3599–3609. [CrossRef]
- Saadeh, M.; Sleit, A.; Qatawneh, M.; Almobaideen, W. Authentication techniques for the internet of things: A survey. Proceedings - 2016 Cybersecurity and Cyberforensics Conference, CCC 2016 2016, pp. 28–34. [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Mohapatra, P. BF-IoT: Securing the IoT networks via fingerprinting-based device authentication. Proceedings - 15th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems, MASS 2018 2018, pp. 254–262. [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Liu, D. for IoT and Its Applications 2017. 2, 359–370.
- Xu, D.; Yu, K.; Ritcey, J.A. Cross-Layer Device Authentication With Quantum Encryption for 5G Enabled IIoT in Industry 4.0. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2022, 18, 6368–6378. [CrossRef]
- Pamarthi, S.; Narmadha, R. Literature review on network security in Wireless Mobile Ad-hoc Network for IoT applications: network attacks and detection mechanisms. International Journal of Intelligent Unmanned Systems 2022, 10, 482–506. [CrossRef]
- Salman, O.; Abdallah, S.; Elhajj, I.H.; Chehab, A.; Kayssi, A. Identity-based authentication scheme for the Internet of Things. Proceedings - IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications 2016, 2016-Augus, 1109–1111. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.V.; Nguyen, H.T.; Le, T.Q.; Truong, Q.N.M. Abnormal network packets identification using header information collected from Honeywall architecture. Journal of Information and Telecommunication 2023, 7, 437–461. [CrossRef]
- Fei, W.; Ohno, H.; Sampalli, S. A Systematic Review of IoT Security: Research Potential, Challenges, and Future Directions. ACM Computing Surveys 2024, 56, 1–40. [CrossRef]
- Baccari, S.; Hadded, M.; Touali, H.; Muhlethaler, P. A Secure Trust-aware Cross-layer Routing Protocol for Vehicular Ad hoc Networks. Journal of Cyber Security and Mobility 2021, 10, 377–402. [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Bourouis, S.; Kamruzzaman, M.M.; Hadjouni, M.; Shaikh, Z.A.; Laghari, A.A.; Elmannai, H.; Dhahbi, S. Data Security in Healthcare Industrial Internet of Things With Blockchain. IEEE Sensors Journal 2023, 23, 25144–25151. [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.Z.; Hanapi, Z.M. Efficient Secure Routing Mechanisms for the Low-Powered IoT Network: A Literature Review. Electronics (Switzerland) 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Alhusayni, A.; Thayananthan, V.; Albeshri, A.; Alghamdi, S. Decentralized Multi-Layered Architecture to Strengthen the Security in the Internet of Things Environment Using Blockchain Technology. Electronics (Switzerland) 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Alvi, A.N.; Ali, B.; Saleh, M.S.; Alkhathami, M.; Alsadie, D.; Alghamdi, B. Secure Computing for Fog-Enabled Industrial IoT. Sensors 2024, 24, 1–21. [CrossRef]
- Bulut, C.; Wu, P.F. More than two decades of research on IoT in agriculture: a systematic literature review. Internet Research 2023. [CrossRef]
- Kebande, V.R.; Awad, A.I. Industrial Internet of Things Ecosystems Security and Digital Forensics: Achievements, Open Challenges, and Future Directions. ACM Computing Surveys 2024, 56. [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, F.; Davis, J.G. Service Computing for Industry 4.0: State of the Art, Challenges, and Research Opportunities. ACM Computing Surveys 2022, 54. [CrossRef]
- Nechibvute, A.; Mafukidze, H.D. Integration of SCADA and Industrial IoT: Opportunities and Challenges. IETE Technical Review (Institution of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineers, India) 2024, 41, 312–325. [CrossRef]
- Federici, F.; Martintoni, D.; Senni, V. A Zero-Trust Architecture for Remote Access in Industrial IoT Infrastructures. Electronics (Switzerland) 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Bomgni, A.B.; Mdemaya, G.B.; Ali, H.M.; Zanfack, D.G.; Zohim, E.G. ESPINA: efficient and secured protocol for emerging IoT network applications. Cluster Computing 2023, 26, 85–98. [CrossRef]
- Kore, A.; Patil, S. Cross layered cryptography based secure routing for IoT-enabled smart healthcare system. Wireless Networks 2022, 28, 287–301. [CrossRef]
- Kalyani, G.; Chaudhari, S. Cross Layer Security MAC Aware Routing Protocol for IoT Networks. Wireless Personal Communications 2022, 123, 935–957. [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Kaur, K.; Kaddoum, G.; Choo, K.K.R. Toward Secure and Provable Authentication for Internet of Things: Realizing Industry 4.0. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2020, 7, 4598–4606. [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumaran, C.; Muthusenthil, B.; Manickavasagam, B. A reliable next generation cyber security architecture for industrial internet of things environment. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering 2020, 10, 387–395. [CrossRef]
- Qadri, Y.A.; Nauman, A.; Zikria, Y.B.; Vasilakos, A.V.; Kim, S.W. The Future of Healthcare Internet of Things: A Survey of Emerging Technologies. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials 2020, 22, 1121–1167. [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; He, B.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Enhanced Clustering MAC Protocol Based on Learning Automata for UV Networks. Photonics 2024, 11. [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Verma, R.K. A Taxonomy and Survey on Grid-Based Routing Protocols Designed for Wireless Sensor Networks. ACM Computing Surveys 2024, 56, 1–41. [CrossRef]
- Al-Otaibi, S.; Khan, R.; Ali, H.; Khan, A.A.; Saeed, A.; Ali, J. A Hybrid and Lightweight Device-to-Server Authentication Technique for the Internet of Things. Computers, Materials and Continua 2024, 78, 3805–3823. [CrossRef]
- Akbar, M.S.; Hussain, Z.; Sheng, M.; Shankaran, R. Wireless Body Area Sensor Networks: Survey of MAC and Routing Protocols for Patient Monitoring under IEEE 802.15.4 and IEEE 802.15.6. Sensors 2022, 22. [CrossRef]
- Soundararajan, R.; Maheswar, R.; Muthuramalingam, A.; Hossain, E.; Lloret, J. Interleaved Honeypot-Framing Model with Secure MAC Policies for Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2022, 22. [CrossRef]
- Subramanyam, R.; Jancy, Y.A.; Nagabushanam, P. Cooperative optimization techniques in distributed MAC protocols – a survey. International Journal of Pervasive Computing and Communications 2024, 20, 285–307. [CrossRef]
- De Vincenzi, M.; Costantino, G.; Matteucci, I.; Fenzl, F.; Plappert, C.; Rieke, R.; Zelle, D. A Systematic Review on Security Attacks and Countermeasures in Automotive Ethernet. ACM Computing Surveys 2024, 56. [CrossRef]
- Erskine, S.K.; Chi, H.; Elleithy, A. SDAA: Secure Data Aggregation and Authentication Using Multiple Sinks in Cluster-Based Underwater Vehicular Wireless Sensor Network. Sensors 2023, 23. [CrossRef]
- Klaiber, J.; Van Dinther, C. Deep Learning for Variable Renewable Energy: A Systematic Review. ACM Computing Surveys 2023, 56. [CrossRef]
- Velayudhan, N.K.; S, A.; Devidas, A.R.; Ramesh, M.V. Delay and Energy Efficient Offloading Strategies for an IoT Integrated Water Distribution System in Smart Cities. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 179–207. [CrossRef]
- Maheswar, R.; Kathirvelu, M.; Mohanasundaram, K. Energy Efficiency in Wireless Networks. Energies 2024, 17, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Nathiya, N.; Rajan, C.; Geetha, K. An energy-efficient cluster routing for internet of things-enabled wireless sensor network using mapdiminution-based training-discovering optimization algorithm. Sadhana - Academy Proceedings in Engineering Sciences 2024, 49. [CrossRef]
- Esmali Nojehdeh, M.; Altun, M. Energy-Efficient Hardware Implementation of Fully Connected Artificial Neural Networks Using Approximate Arithmetic Blocks. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing 2023, 42, 5428–5452. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Jain, S.; Maik, V. Energy Efficient Clustering and Optimized LOADng Protocol for IoT. Intelligent Automation and Soft Computing 2022, 34, 357–370. [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, F.; Rui, X. An energy-aware approach for resources allocating in the internet of things using a forest optimization algorithm. Circuit World 2023, 49, 269–280. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Iborra, R.; Zoubir, A.; Hamdouchi, A.; Idri, A.; Skarmeta, A. Intelligent and Efficient IoT Through the Cooperation of TinyML and Edge Computing. Informatica (Netherlands) 2023, 34, 147–168. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.U.; Cao, W.; Tang, Z.; Ullah, A.; Pan, W. Energy-Efficient De-Duplication Mechanism for Healthcare Data Aggregation in IoT. Future Internet 2024, 16, 1–21. [CrossRef]
- Komala, C.R.; Velmurugan, V.; Maheswari, K.; Deena, S.; Kavitha, M.; Rajaram, A. Multi-UAV computing enabling efficient clustering-based IoT for energy reduction and data transmission. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems 2023, 45, 1717–1730. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.S.; Kurnaz, S.; Hamdi, M.M.; Khaleel, A.M.; Khaleel, A.M.; Seno, M.E. Study for Buildings with IoT System for Energy Management. ISMSIT 2022 - 6th International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies, Proceedings 2022, pp. 53–57. [CrossRef]
- Panchal, M.; Upadhyay, R.; Vyavahare, P.D. Cross-Layer based Energy Efficient Reliable Data Transmission System for IoT Networks. Proceedings - 2022 IEEE 11th International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies, CSNT 2022 2022, pp. 527–532. [CrossRef]
- Singhal, S.; Tripathi, S. Data-driven Secure Authentication for Smart Grid IoT Networks. Proceedings of CONECCT 2023 - 9th International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies 2023, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Bapatla, A.K.; Puthal, D.; Mohanty, S.P.; Yanambaka, V.P.; Kougianos, E. EasyChain: an IoT-friendly blockchain for robust and energy-efficient authentication. Frontiers in Blockchain 2023, 6, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, M.; Pankajavalli, P.B. Energy - Efficient routing and scheduling using clustering in geographic routing protocol. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems 2023, 44, 951–961. [CrossRef]
- Sugumaran, V.R.; Rajaram, A. Lightweight blockchain-assisted intrusion detection system in energy efficient MANETs. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems 2023, 45, 4261–4276. [CrossRef]
- Goyal, H.; Kodali, K.; Saha, S. LiPI: Lightweight Privacy-Preserving Data Aggregation in IoT 2022. [2207.12197]. [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, G.; Iqbal, F.; Altaf, A.; Rasheed, A. Techniques for Resource-Efficient, Lightweight Cryptography in IoT Devices for Smart Environment. Proceedings - 2023 6th International Conference of Women in Data Science at Prince Sultan University, WiDS-PSU 2023 2023, pp. 223–228. [CrossRef]
- Kousalya, R.; Sathish Kumar, G.A. A Survey of Light-Weight Cryptographic Algorithm for Information Security and Hardware Efficiency in Resource Constrained Devices. Proceedings - International Conference on Vision Towards Emerging Trends in Communication and Networking, ViTECoN 2019 2019. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





