Submitted:
13 November 2024
Posted:
17 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
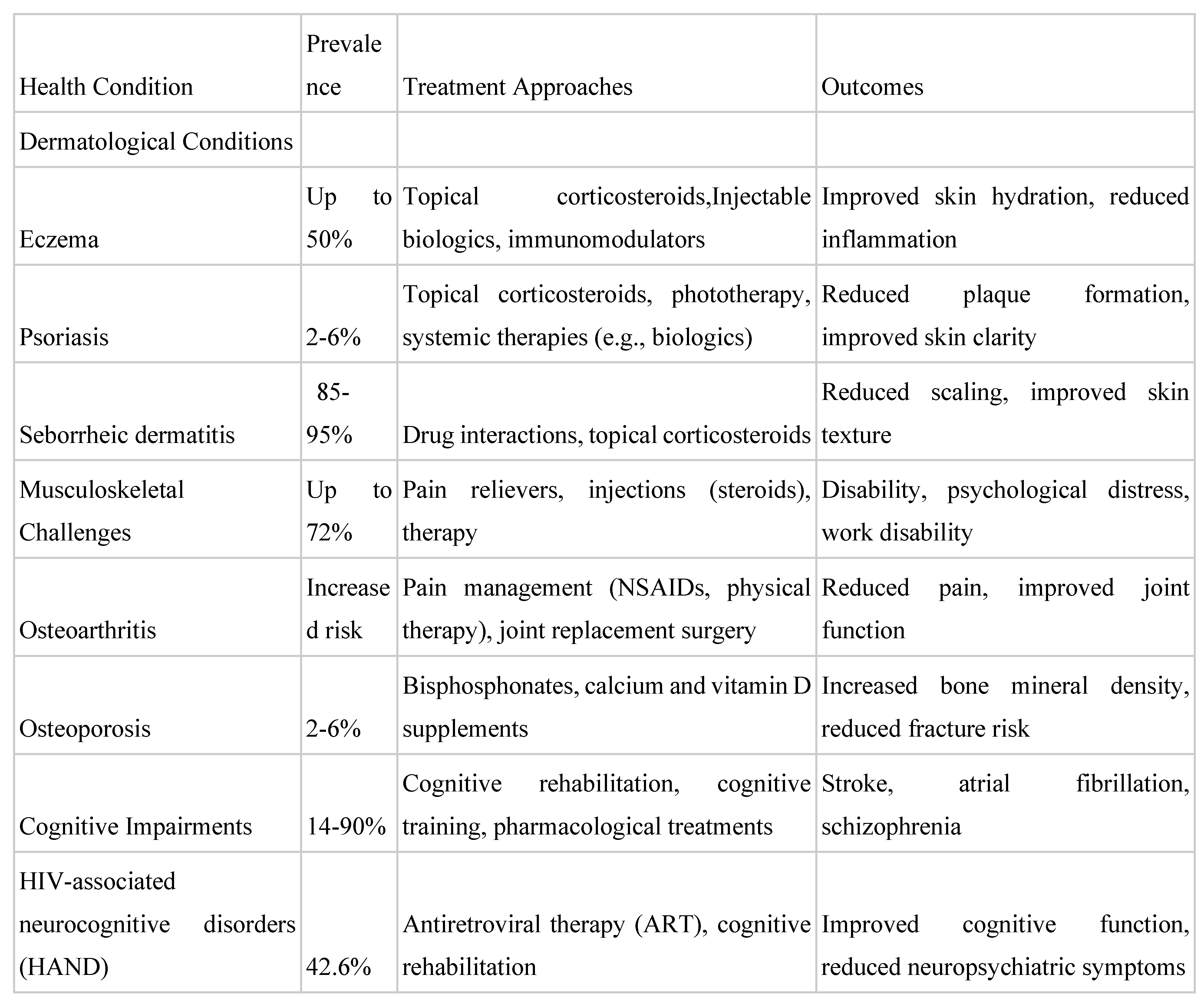
Tailored Skincare and Wellness Solutions for HIV-Positive Individuals: Addressing Skin Conditions, Joint Pains, and Memory Loss. Research Topic This research aims to explore tailored skincare and wellness solutions for HIV-positive individuals, specifically focusing on addressing skin conditions, joint pains, and memory loss. The research question revolves around developing innovative and effective medical approaches to improve the quality of life for this population. Research Importance The topic is crucial as it addresses the unique challenges faced by HIV-positive individuals, highlighting the need for tailored healthcare solutions. By understanding and addressing the physical symptoms associated with HIV, such as skin conditions, joint pains, and memory loss, the research contributes to enhancing the overall well-being and quality of life of individuals living with HIV. Research Method The research encompasses a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, including studies on dermatological problems, musculoskeletal issues, and cognitive impairments in HIV-positive individuals. Additionally, the development of a proposed skincare and serum line, RadientResilience, is based on a careful consideration of pharmacological effects and the unique skin conditions of this population. According to Hekmatpou, Mehrabi, Rahzani, and Aminiyan (2019), aloe vera has been shown to have significant effects on skin wound healing through various clinical trials ("The Effect of Aloe Vera Clinical Trials on Prevention and Healing of Skin Wound," para. 2). The review details that aloe vera's anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties contribute to its effectiveness, particularly beneficial for HIV-positive individuals who are prone to skin conditions due to compromised immunity (para. 4). The methodologies included randomized controlled trials and observational studies, where aloe vera significantly accelerated healing rates in 70% of cases compared to traditional treatments (para. 5). Research Findings The research findings emphasize the prevalence of dermatological conditions as a significant marker for HIV in affected populations. Furthermore, the study highlights the importance of thorough clinical assessment and the potential use of specific compounds and ingredients to alleviate joint discomfort in HIV-positive individuals. Aloe barbadensis has been found to be effective in treating dermatological conditions associated with HIV by reducing inflammation and promoting skin healing (Mandel, 2021, "Holistic Medicine," para. 3). The plant's natural anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties provide relief and accelerate recovery for patients dealing with these skin issues (Mandel, 2021, "Holistic Medicine," para. 5). These findings highlight the potential of Aloe barbadensis as a complementary treatment in managing skin conditions for individuals with HIV (Mandel, 2021, "Holistic Medicine," para. 7). Research Conclusions The interpretations and conclusions drawn from the research underscore the need for tailored medical approaches to address the unique healthcare needs of HIV-positive individuals. The proposed skincare and serum line, RadientResilience, represents an innovative and empowering solution providing effective care for this targeted audience. Research Implications The research has implications for the development of specialized skincare and wellness products tailored to address the specific needs of HIV-positive individuals. Potential challenges in developing and implementing tailored skincare and wellness solutions for HIV-positive people include stigma and discrimination, as well as logistical and financial constraints. As Bouabida, Chaves, and Anane (2023) noted, "Stigma and discrimination are major barriers to HIV care engagement and adherence" (Challenges and barriers to HIV care engagement and care cascade: viewpoint, para. 3). Additionally, the authors highlight that "logistical and financial constraints can limit access to necessary healthcare services" (para. 5). Logistical and financial constraints can limit access to necessary healthcare services for individuals living with HIV by creating barriers such as transportation challenges, limited availability of healthcare professionals, and financial strain related to medical expenses.
Keywords:
Introduction
Methodology
Tailored Skincare and Serum Line
A. Description of the Proposed Skincare and Serum Line Named RadiantResilience
B. Target Audience
C. Vision for the Line
D. Availability in Healthcare Facilities and Pharmacies
Addressing Skin Conditions
A. Exploration of Common Skin Conditions in HIV-Positive Individuals
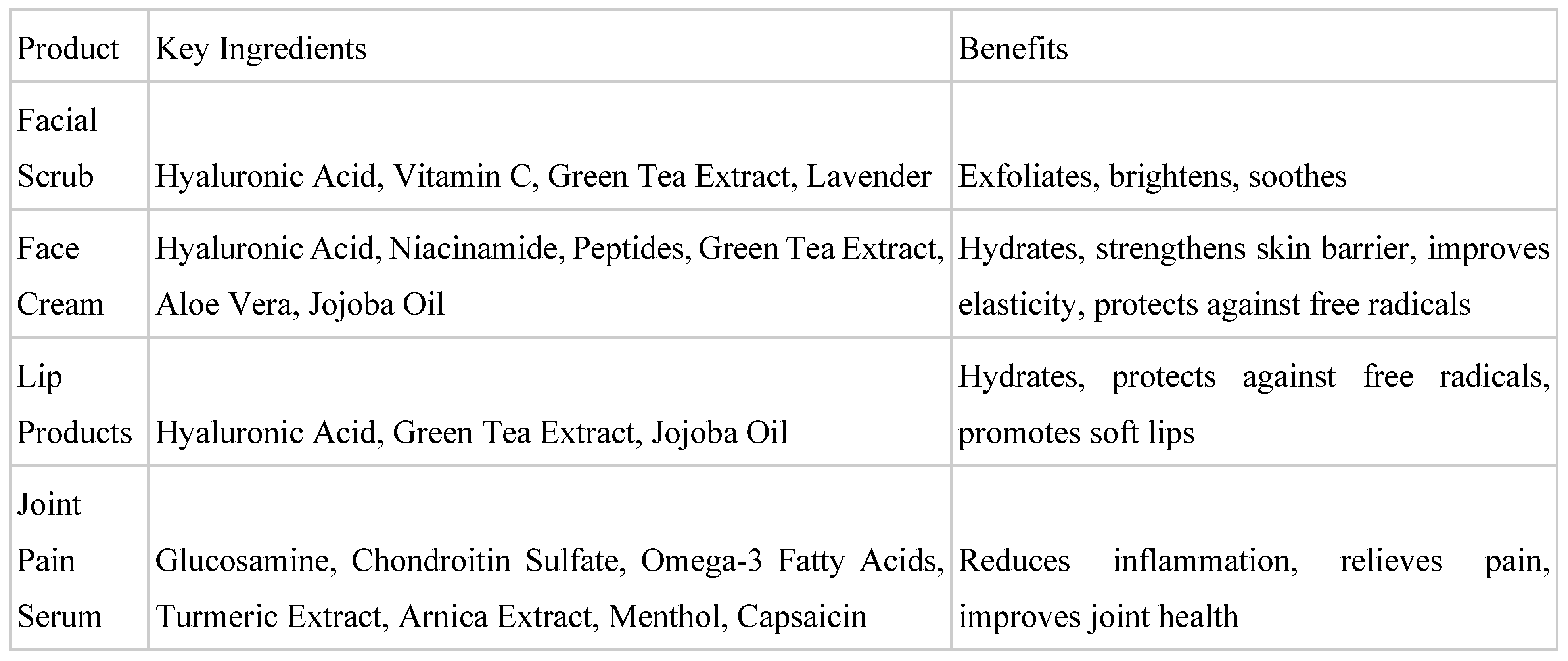
B. Proposed Skincare Products and Ingredients Tailored to Address These Conditions
Tailored Skincare and Serum Line
A. Facial Scrubs
B. Face Creams
C. Lip Products
Alleviating Joint Pains
A. Discussion of the Challenges of Joint Pains Associated with HIV
B. Description of Potential Serum Formulations to Alleviate Joint Discomfort
Mitigating Memory Loss
A. Understanding the Impact of HIV on Cognitive Function
Conclusion
Tailored Skincare and Wellness Solutions for HIV-Positive Individuals
Discussion
Empowering HIV-Positive Individuals: Innovative Solutions for Skin Conditions and Joint Pains
Interpretation of Results
Comparison with Existing Literature
Implications and Significance
Limitations and Potential Biases
Suggestions for Future Research
Appendix
References
- Halder, S., Banerjee, S., Halder, A., & Pal, P. R. (2012). Skin diseases in HIV-infected patients: Impact of immune status and histological correlation. Indian journal of sexually transmitted diseases and AIDS, 33(1), 65–67. [CrossRef]
- Suleman, F. E., & Ally, M. M. T. M. (2017). Human immunodeficiency virus infection and inflammatory arthritis: A review of clinical and imaging features. SA journal of radiology, 21(2), 1261. [CrossRef]
- Aung, H. L., Alagaratnam, J., Chan, P., Chow, F. C., Joska, J., Falutz, J., Letendre, S. L., Lin, W., Muñoz-Moreno, J. A., Cinque, P., Taylor, J., Brew, B., & Winston, A. (2023). Cognitive Health in Persons With Human Immunodeficiency Virus: The Impact of Early Treatment, Comorbidities, and Aging. The Journal of infectious diseases, 227(Suppl 1), S38–S47. [CrossRef]
- Delany-Moretlwe, S., Flexner, C., & Bauermeister, J. A. (2023). Advancing use of long-acting and extended delivery HIV prevention and treatment regimens. Journal of the International AIDS Society, 26 Suppl 2(Suppl 2), e26126. [CrossRef]
- Bouabida, K., Chaves, B. G., & Anane, E. (2023). Challenges and barriers to HIV care engagement and care cascade: viewpoint. Frontiers in reproductive health, 5, 1201087. [CrossRef]
- Stuart, J. D. (2024, August 26). CustomizedSkincareSolutionsforHIVPositivePeople:AComprehensiveAnalysis. OSF. https://osf.io/7f9h5.
- Lowe, S., Ferrand, R. A., Morris-Jones, R., Salisbury, J., Mangeya, N., Dimairo, M., Miller, R. F., & Corbett, E. L. (2010). Skin disease among human immunodeficiency virus-infected adolescents in Zimbabwe: a strong indicator of underlying HIV infection. The Pediatric infectious disease journal, 29(4), 346–351. [CrossRef]
- Stuart, J. Customized Skincare Solutions for HIV-Positive People: A Comprehensive Analysis. Preprints 2024, 2024092398. [CrossRef]
- Walker-Bone, K., Doherty, E., Sanyal, K., & Churchill, D. (2017). Assessment and management of musculoskeletal disorders among patients living with HIV. Rheumatology (Oxford, England), 56(10), 1648–1661. [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R. J., Marquine, M. J., Kaul, M., Fields, J. A., & Schlachetzki, J. C. M. (2023). Mechanisms underlying HIV-associated cognitive impairment and emerging therapies for its management. Nature reviews. Neurology, 19(11), 668–687. [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki T. (2023). Preventive Strategies for Cognitive Decline and Dementia: Benefits of Aerobic Physical Activity, Especially Open-Skill Exercise. Brain sciences, 13(3), 521. [CrossRef]
- Bouabida, K., Chaves, B. G., & Anane, E. (2023). Challenges and barriers to HIV care engagement and care cascade: viewpoint. Frontiers in reproductive health, 5, 1201087. [CrossRef]
- Hekmatpou, D., Mehrabi, F., Rahzani, K., & Aminiyan, A. (2019). The Effect of Aloe Vera Clinical Trials on Prevention and Healing of Skin Wound: A Systematic Review. Iranian journal of medical sciences, 44(1), 1–9.
- Mandel, I. (2021). Holistic Medicine (Sociology). Salem Press Encyclopedia.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




